Mike Colagrossi
Mike Colagrossi is a writer and founder of Colagrossi Media, an email marketing agency.
An ad man at heart with a love for a witful turn of phrase, his eclectic writing expertise ranges from the domain of science and tech to digital marketing.
From Atlantis to Thule, these mythical locales have captivated people's imaginations for centuries.
They have more casual sex, too.
A Stanford new study delves into whether passions are fixed or developed.
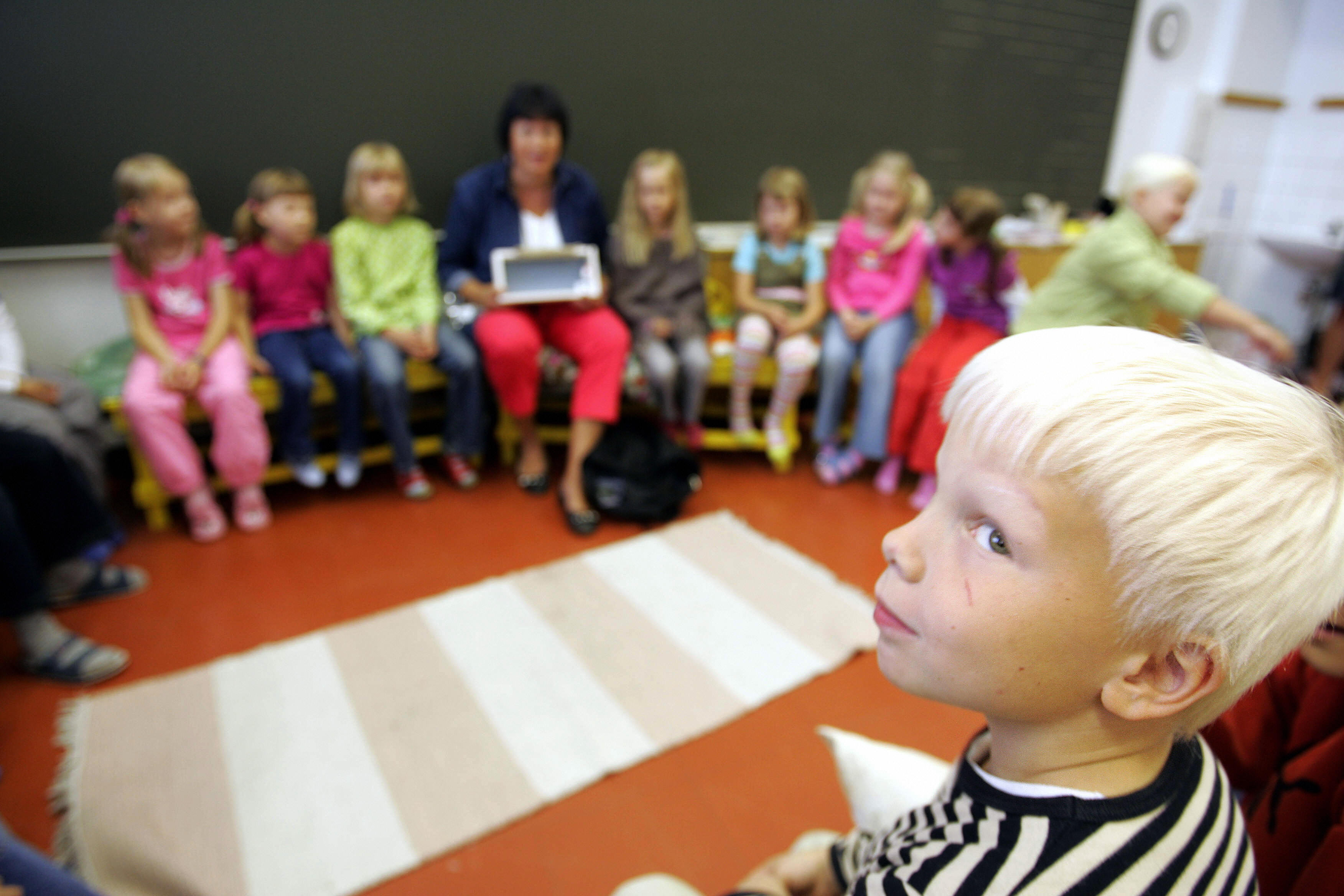
No standardized tests, no private schools, no stress. Finland's education system is consistently ranked best in the world. Why isn't America copying it?
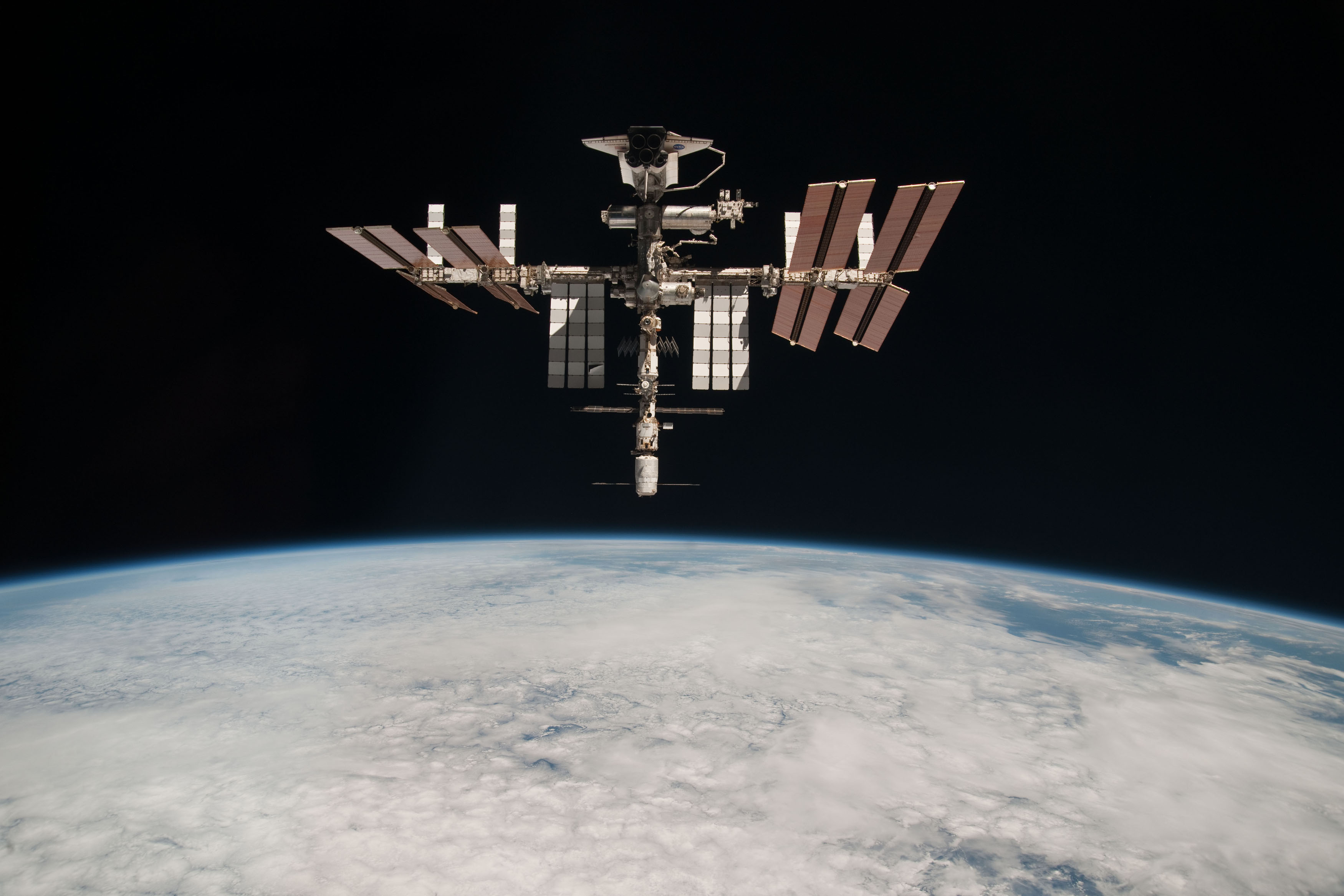
As one of the biggest manmade structures in the sky and at a cost of over $100b, it's the place where the space age dream is still alive.
We aren't lunarly exclusive. Earth has a few minimoons whizzing around us, including one that comes back into our orbit every 20 years or so.
What inspired the Mona Lisa, China's Terracotta Warriors, and more?
Tesla CEO Elon Musk has shocked investors and now draws the ire of the SEC after clumsily announcing that he intended to take the company private.
The ultimate fate of the universe is a mind-bogglingly thing to think about. So what’s the final outcome for it all?
Why is only 10% of the population left-handed? There are a few new scientific clues pointing to the answer.
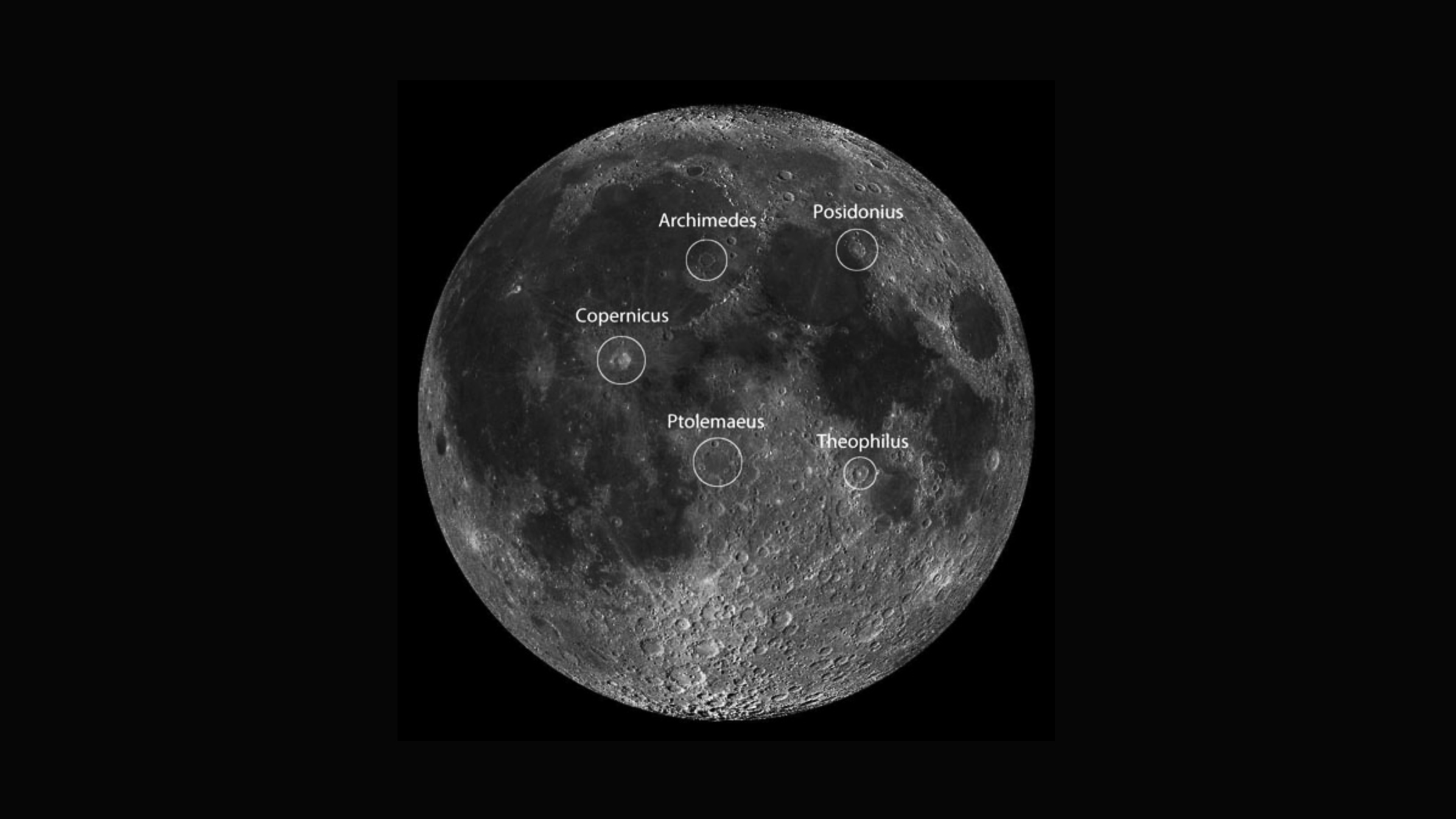
You've probably seen it hanging around. But how did it get there? And can we live there?
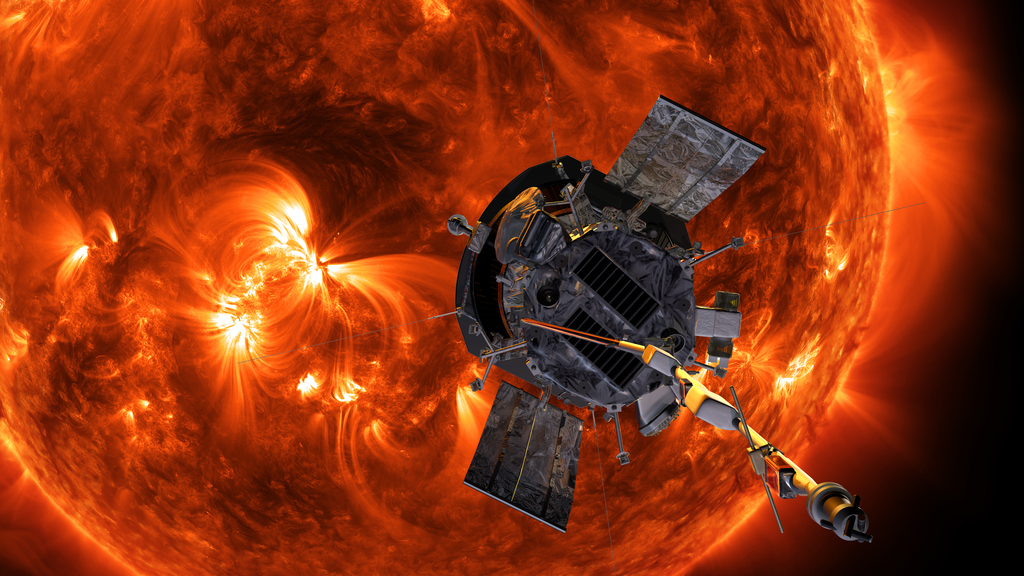
The probe, no larger than a car, will be the closest a man-made object has ever gotten to the sun. We will be able to study and see it like we’ve never seen it before.
Is Nessie real or just a tourism ploy? There might be more to this (in)famous monster than you think...
Only the pyramids stand today. What did the other 6 look like?
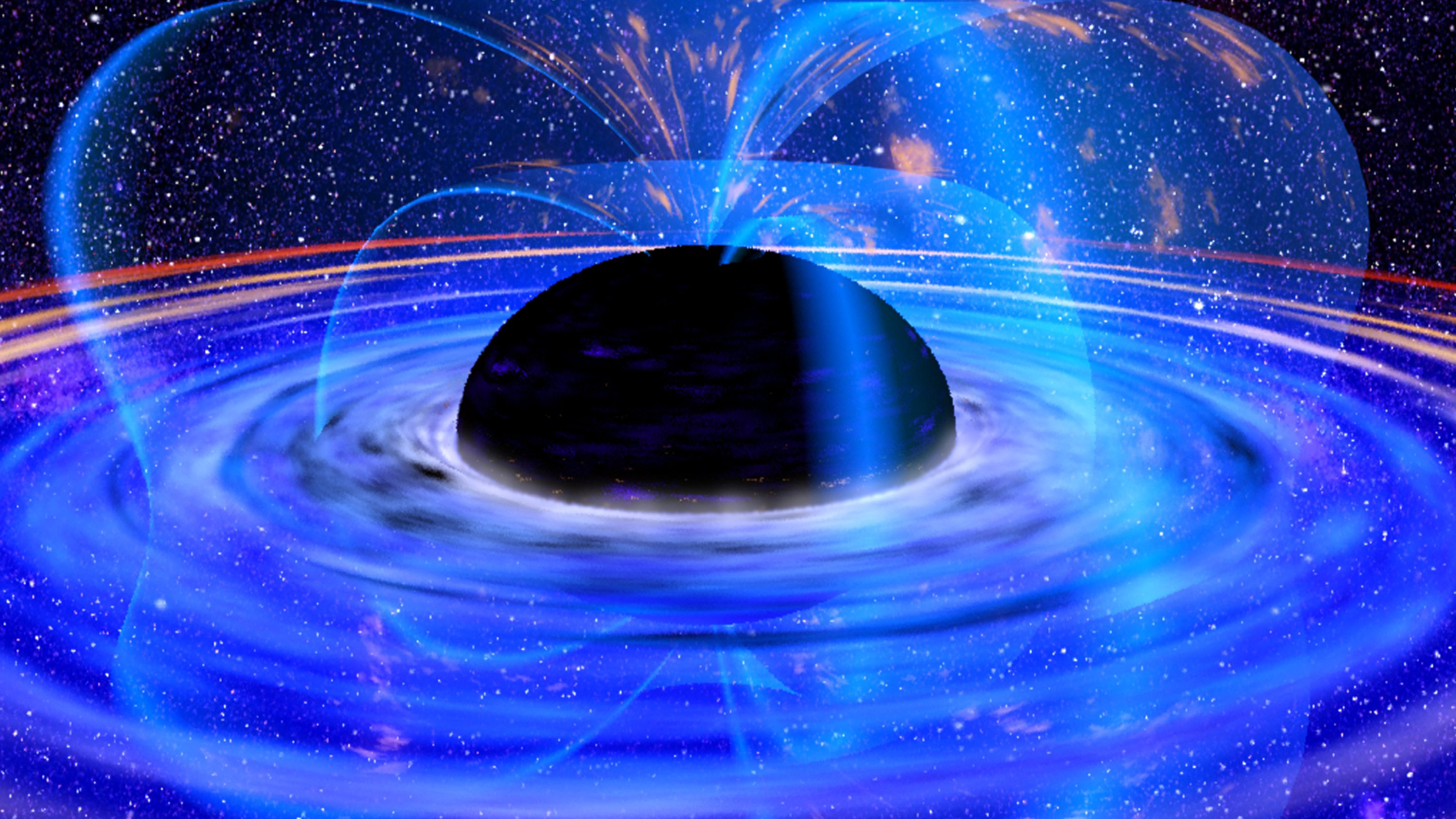
Everything you wanted to know about black holes, supernova, and quasars but were afraid to ask.
The Medici family had a long and powerful influence in European history for hundreds of years. They were well known for their banking prowess and are synonymous as an unparalleled patron of the arts during the Italian Renaissance.
Bright pink? Lava? Liquid planets that could hold water? Some far-out planets are truly... out of this world.
The fear of robots taking over our economy is unfounded. After all, this kind of disruption happens a lot more often, in the historical sense, than you might think.
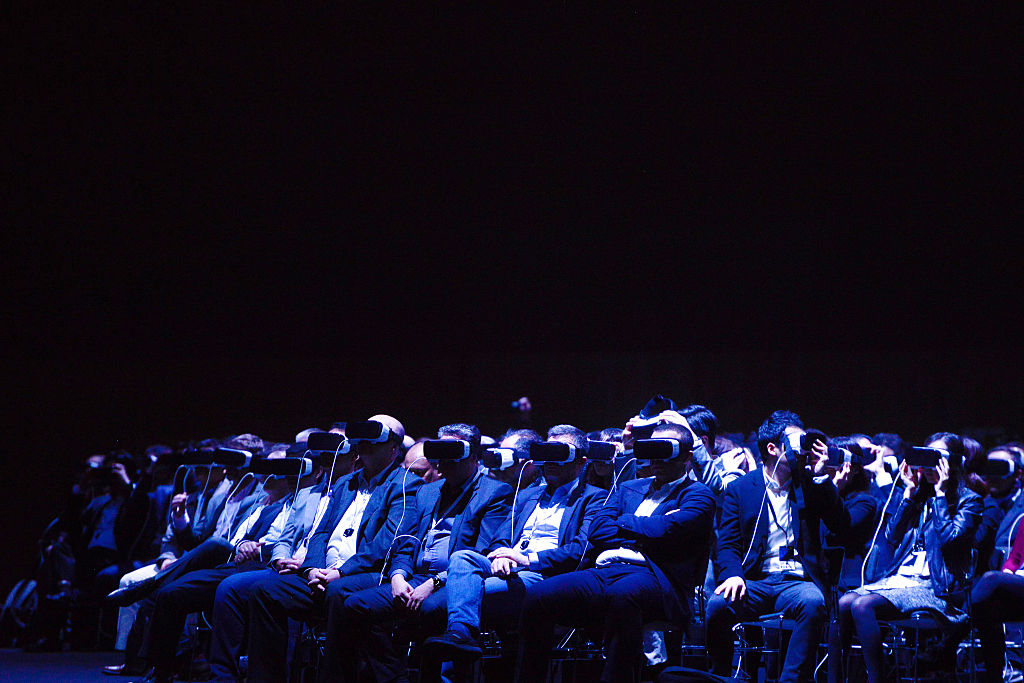
A primer on the amazing possibilities of mixed reality, augmented reality, and virtual reality technology.
There’s no escaping its vast power and utility for the human enterprise. Stories, great tales, and songs have all been written about the all-mighty dollar. Here's 10 documentaries that we think you'll enjoy.
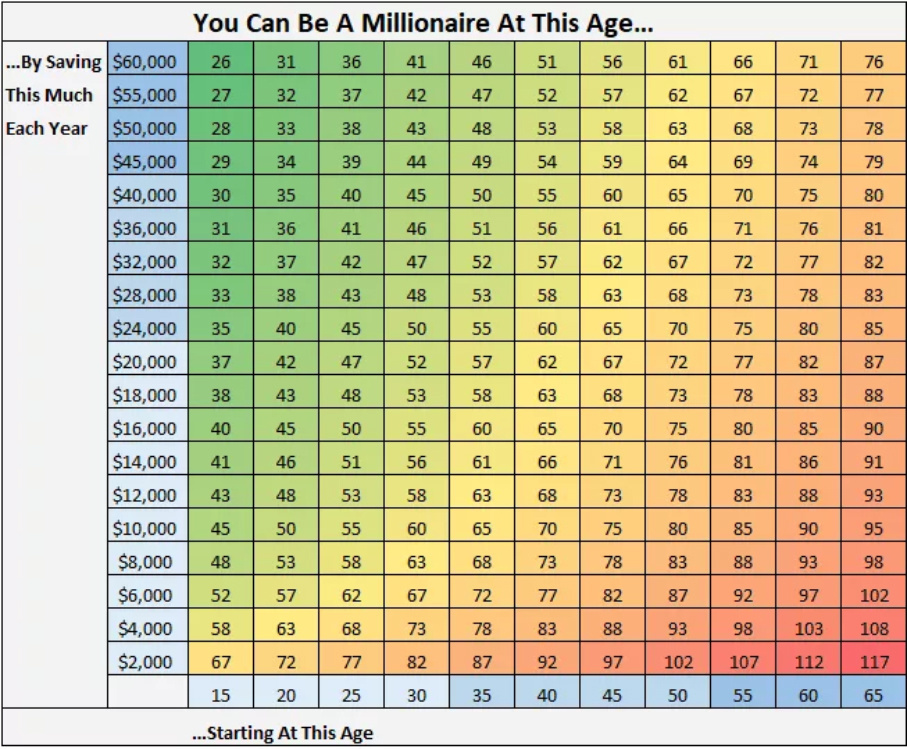
Becoming a millionaire is not out of grasp for the ordinary person. Here are tried and tested methods for wealth creation to get your plan in action.
We don’t have to stop inquiring or wondering about the far-flung vistas of reality, we just need to do it with some good old-fashioned logic.
Gender studies are leaving the college halls and heading into the lab. Increasingly, there have been more rigorous studies into how transgender people neurologically relate to the sex they identify with rather than their biological sex.
There's a lot of confusion as to what AI, machine learning, and robotics do. Sometimes, they can all be used together.
It's the dawn of a new age. AI, VR, and robotics are creating the future that science-fiction writers have dreamed about.
Can artificial intelligence rival the animal kingdom? We compare the intelligence of four animals to current A.I. capabilities.
For many years the concept of virtual worlds and far flung digital realities was the stuff of speculative fiction and philosophy. But it may soon take over the world.
Here are some of the best books on the rich history, rabid speculations and intriguing fictionalized world of artificial intelligence.
The NFL is known predominantly for its players’ display of athletic prowess. But you’d be surprised to know that many of these same players are incredibly smart. Here are some of the smartest NFL players ever to have graced the league.