Space & Astrophysics
A new government report describes 144 sightings of unidentified aerial phenomena.
Using image analysis tools developed for astronomy, researchers are predicting cancer therapy responses.
Jupiter’s mysterious auroral events are caused by vibrating waves of plasma.
A new artificial intelligence method removes the effect of gravity on cosmic images, showing the real shapes of distant galaxies.
Tiny fluctuations in old Kepler data reveals four runaway planets that are reminiscent of Earth.
Astronomers find a third type of supernova and explain a mystery from 1054 AD.
A new study proposes that Hawking radiation could be used to find dark matter in places like primordial black holes.
The Younger Dryas impact hypothesis argues that a comet strike caused major changes to climate and human cultures on Earth about 13,000 years ago.
Ernst Chladni proved that sound can be seen, and developed a technique of visualizing vibrations on a metal plate.
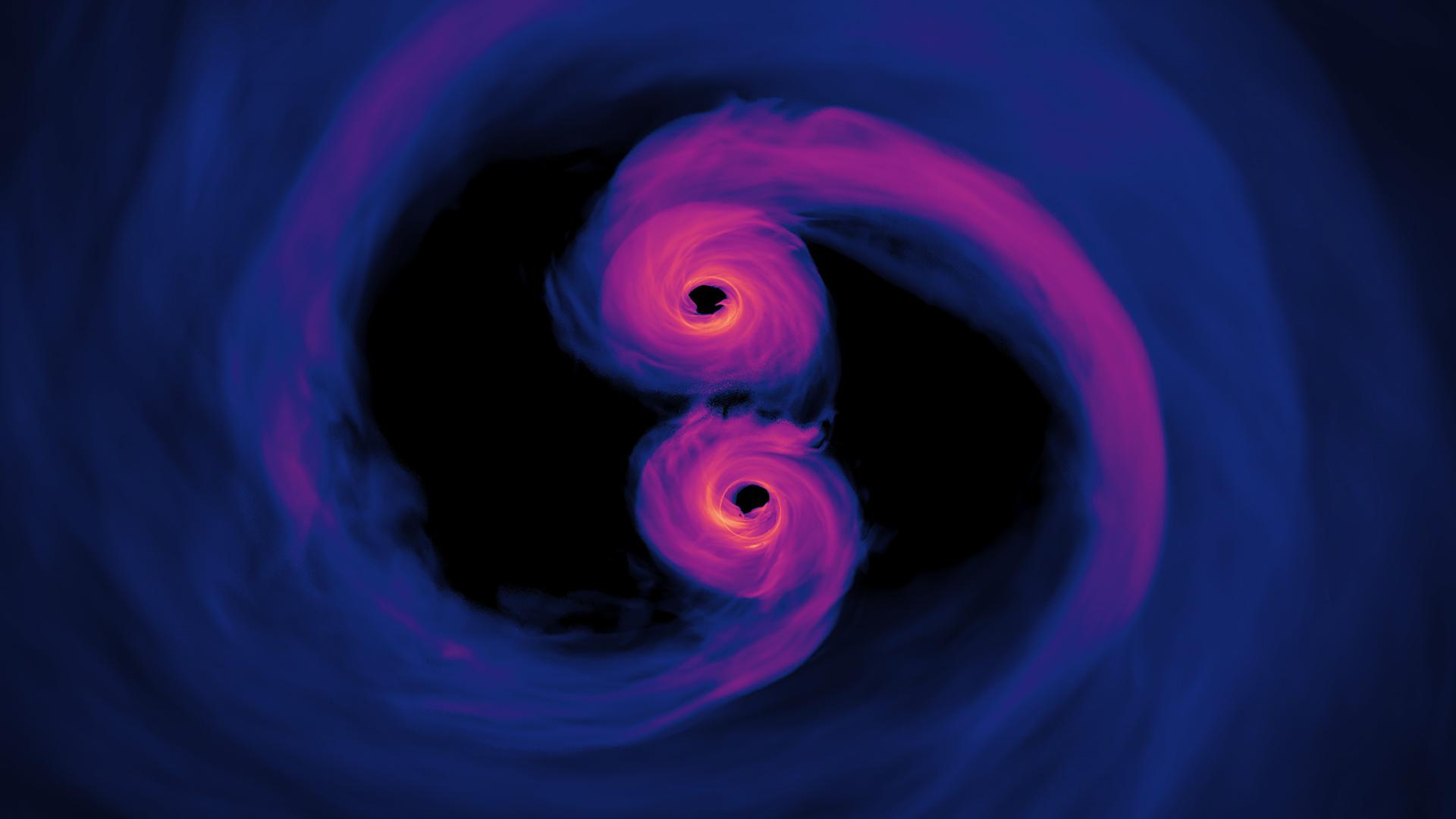
An analysis of the gravitational wave data from black hole mergers show that the event horizon area, and entropy, always increases.
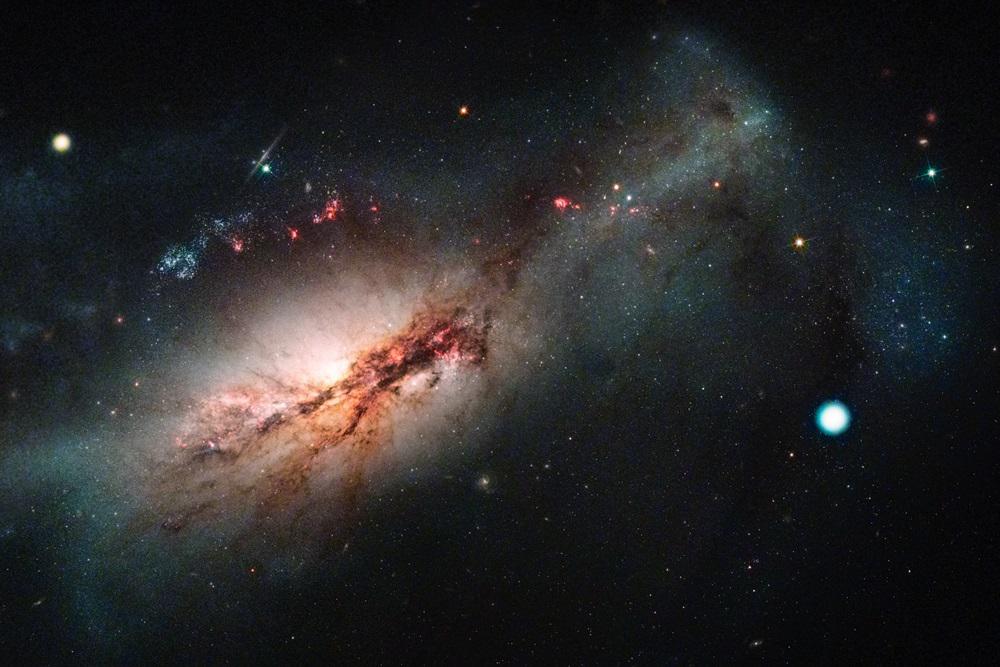
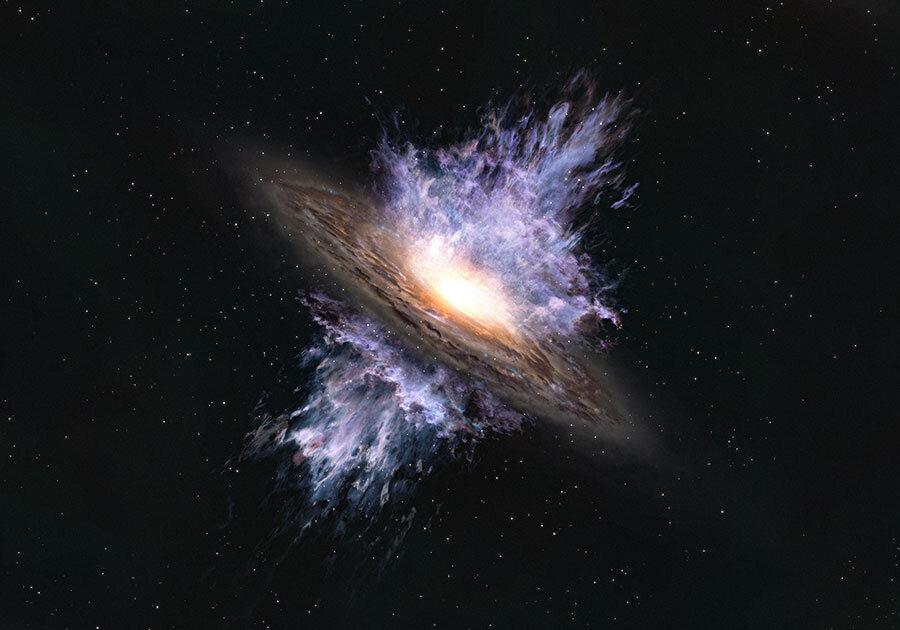
Researchers discovered a galactic wind from a supermassive black hole that sheds light on the evolution of galaxies.
Every star we can see, including our sun, was born in one of these violent clouds.
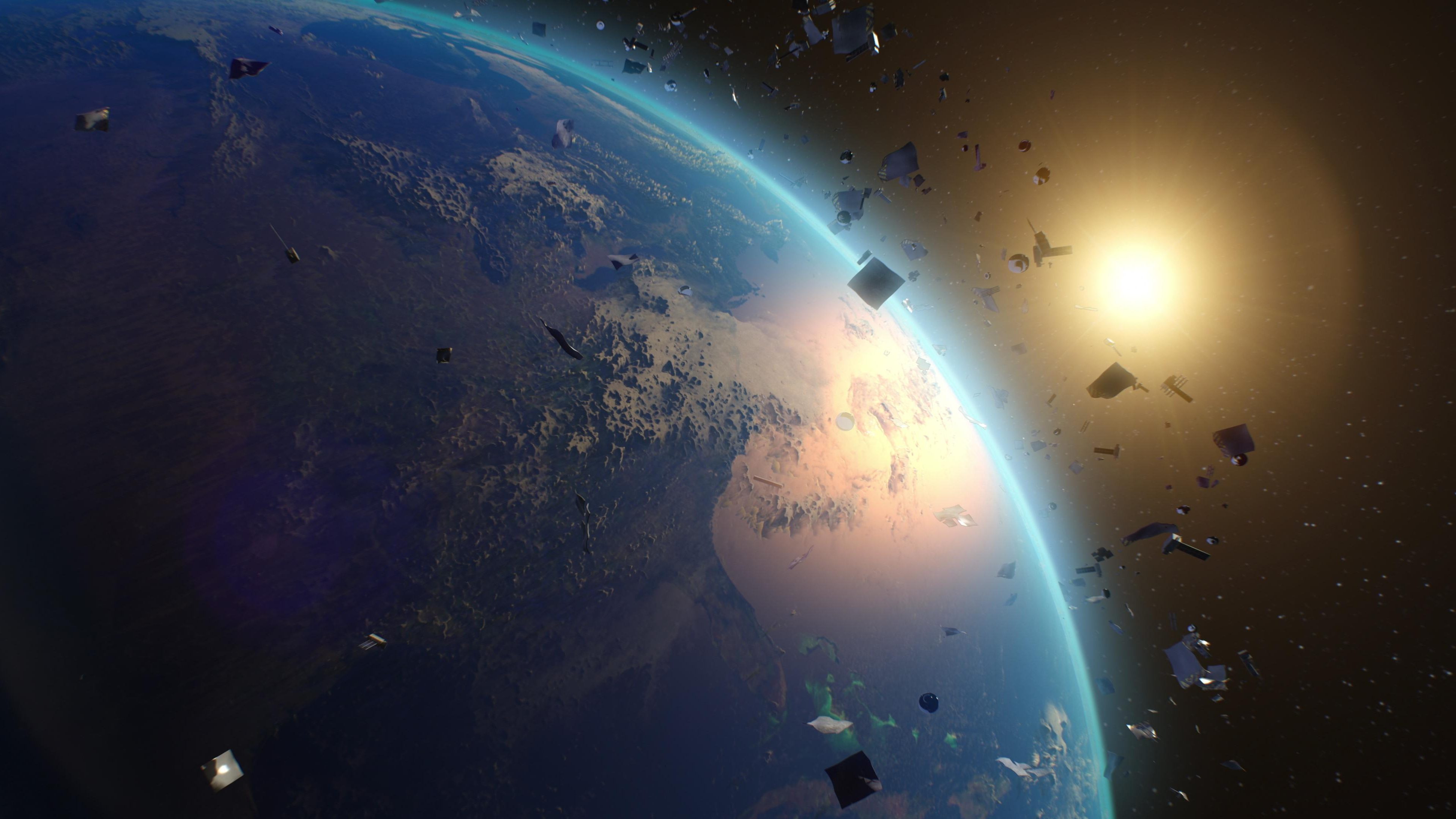
Tiny specks of space debris can move faster than bullets and cause way more damage. Cleaning it up is imperative.
▸
6 min
—
with
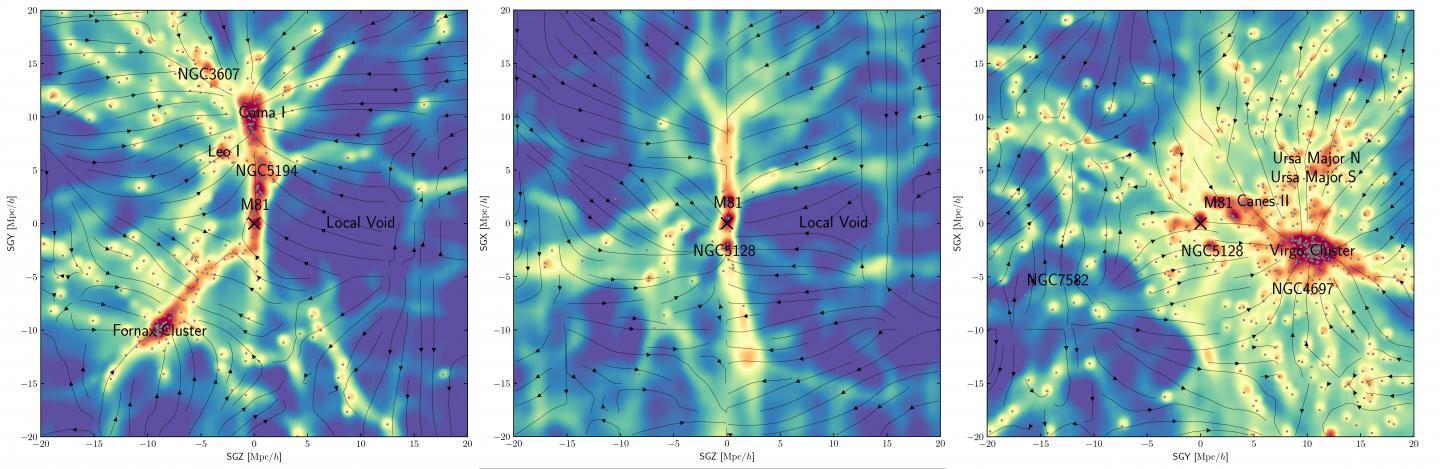
Astronomers possibly solve the mystery of how the enormous Oort cloud, with over 100 billion comet-like objects, was formed.
Can one equation unite all of physics?
▸
6 min
—
with
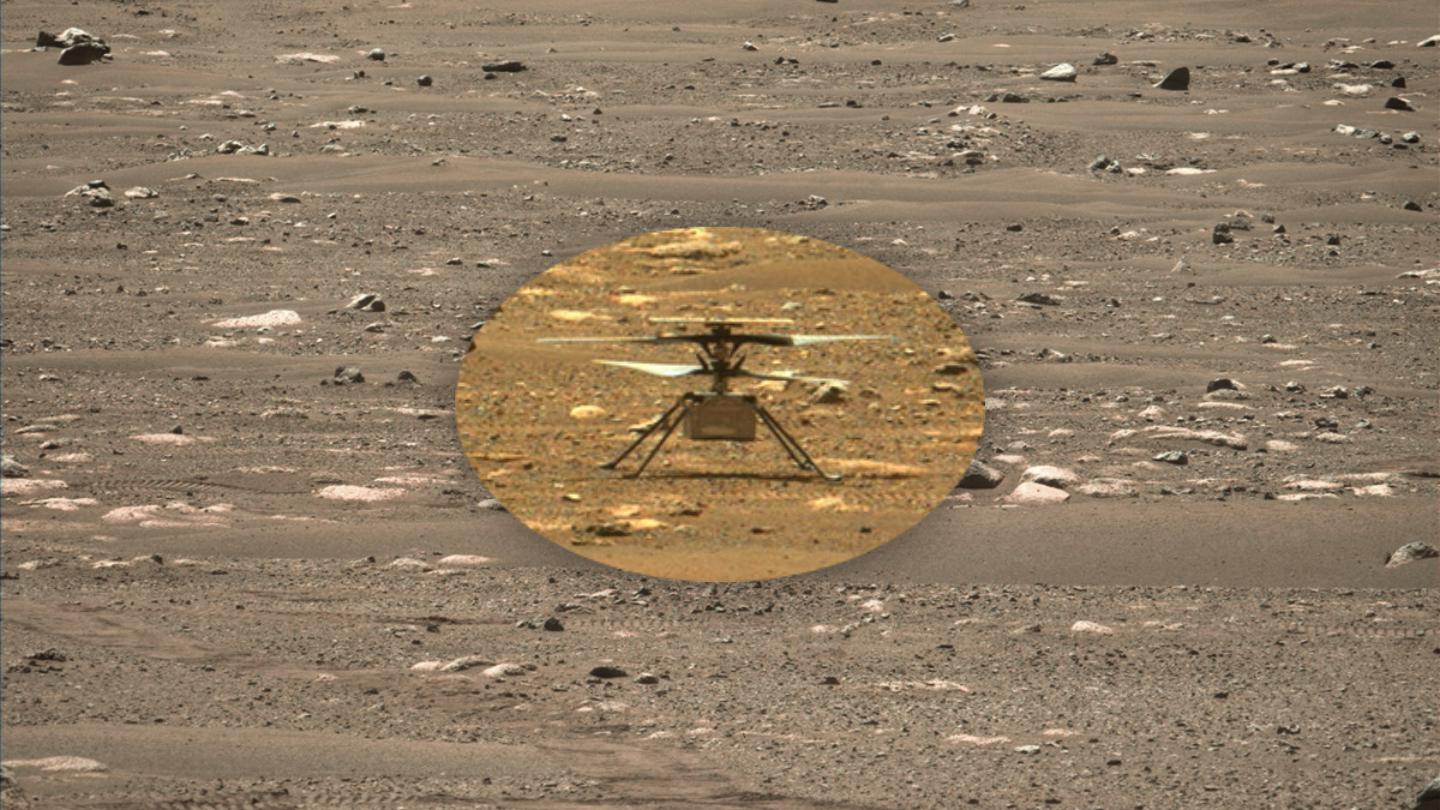
The helicopter’s sixth mission almost went down in disaster.
Determining if the universe is infinite pushes the limits of our knowledge.
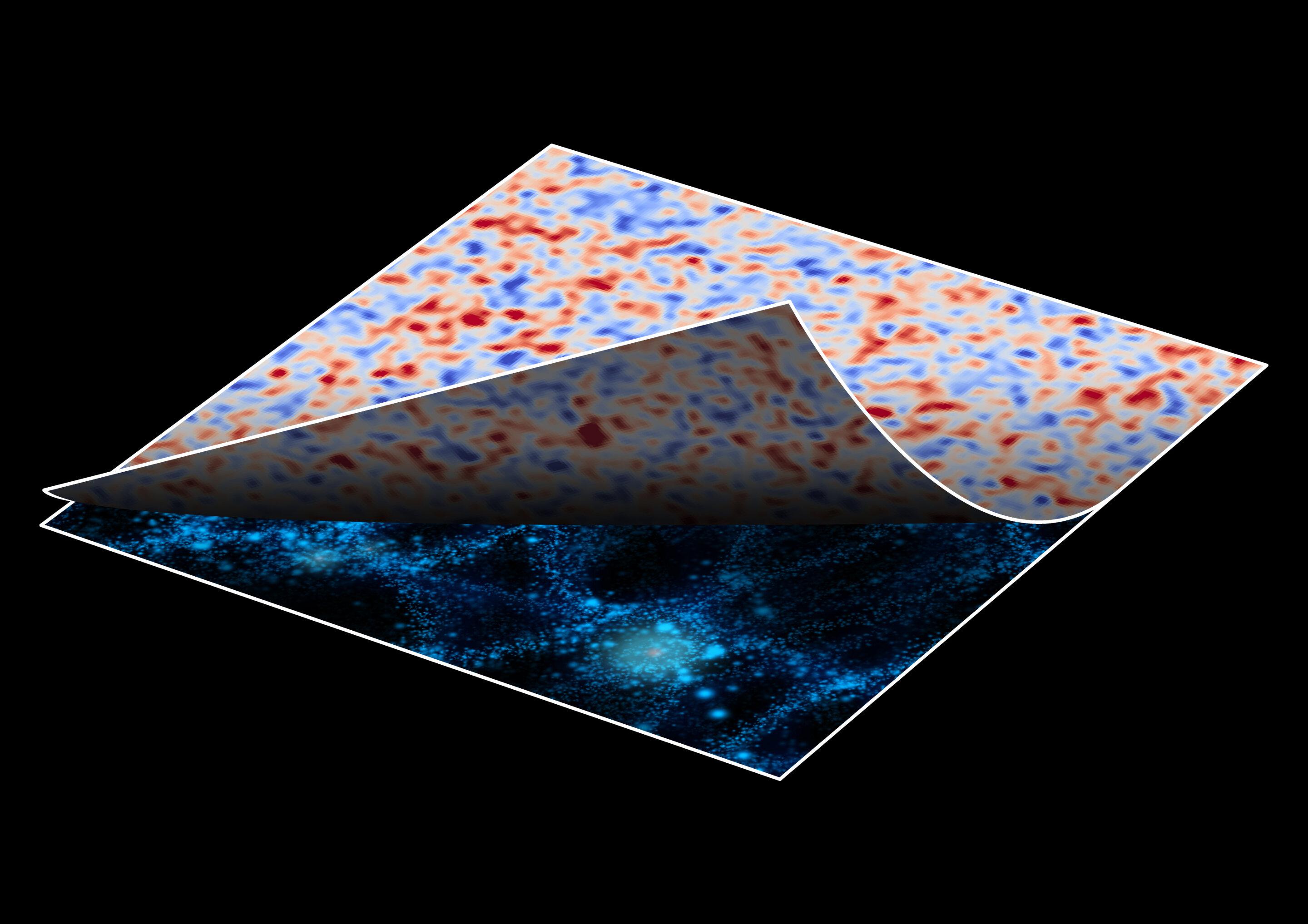
A new AI-generated map of dark matter shows previously undiscovered filamentary structures connecting galaxies.
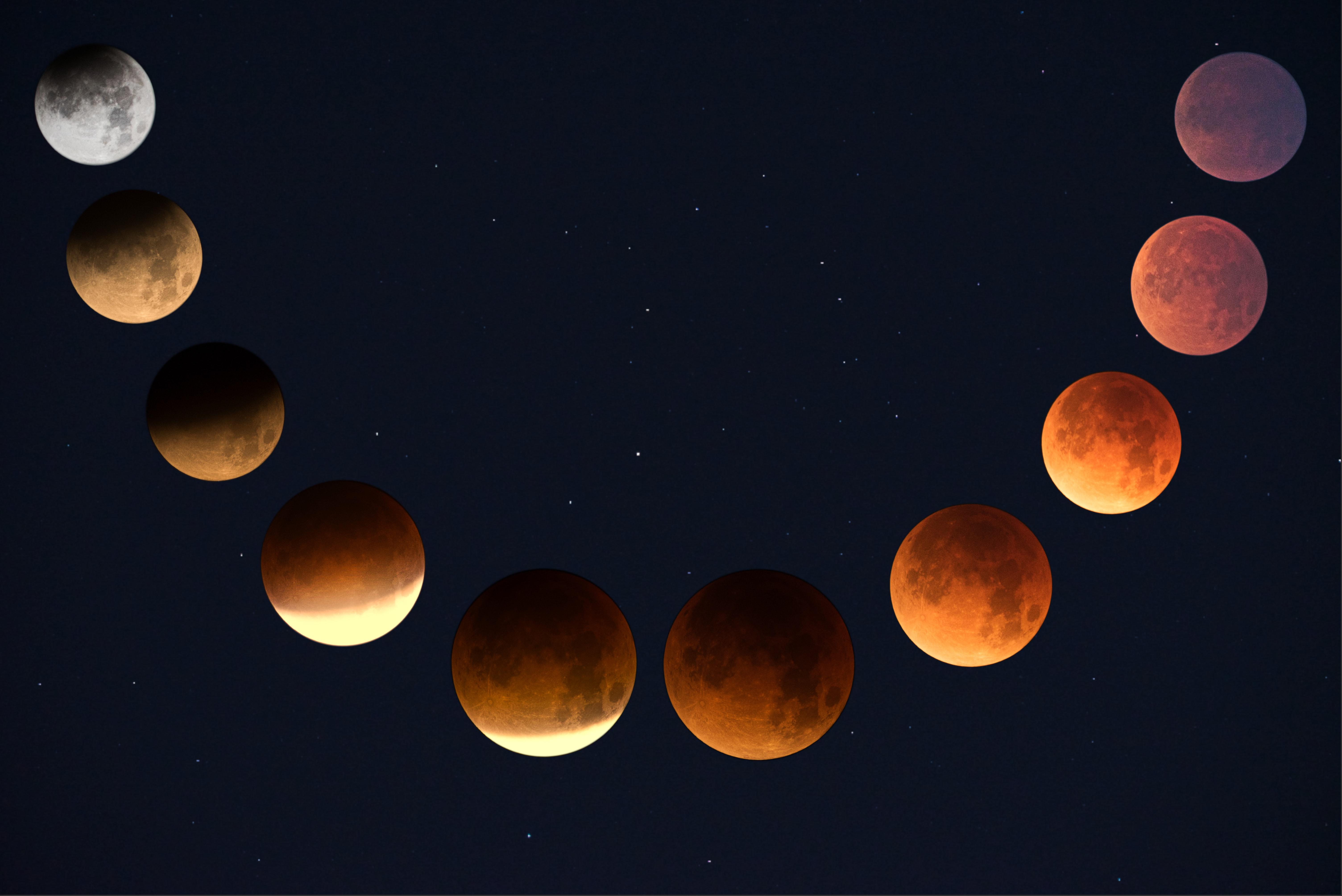
The eclipse season is starting with a bang.
It’s time to rethink how satellites and other objects are made and eventually destroyed.
▸
5 min
—
with
Since 1957, the world’s space agencies have been polluting the space above us with countless pieces of junk, threatening our technological infrastructure and ability to venture deeper into space.
A new paper reveals that the Voyager 1 spacecraft detected a constant hum coming from outside our Solar System.
Even with six months’ notice, we can’t stop an incoming asteroid.
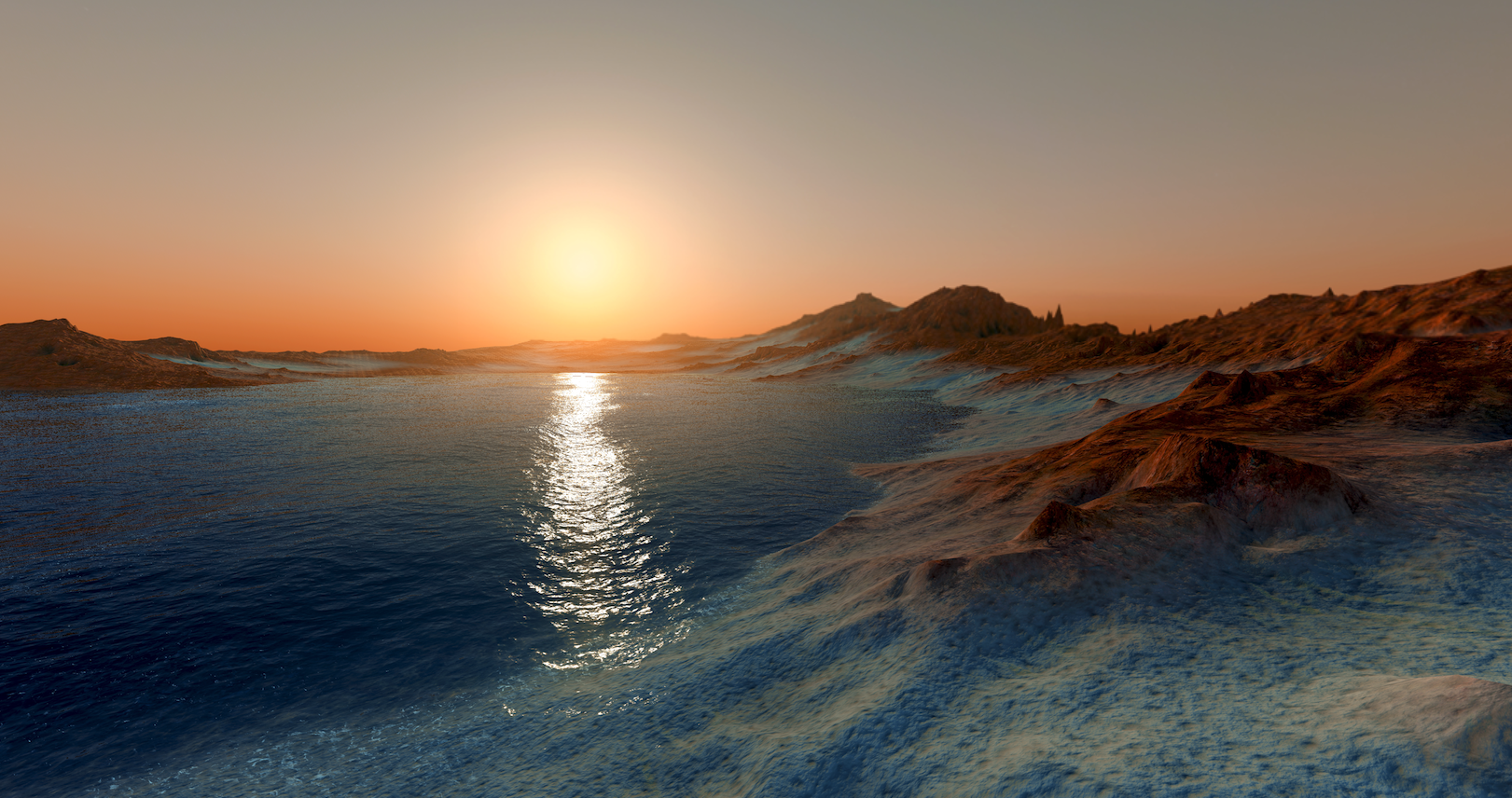
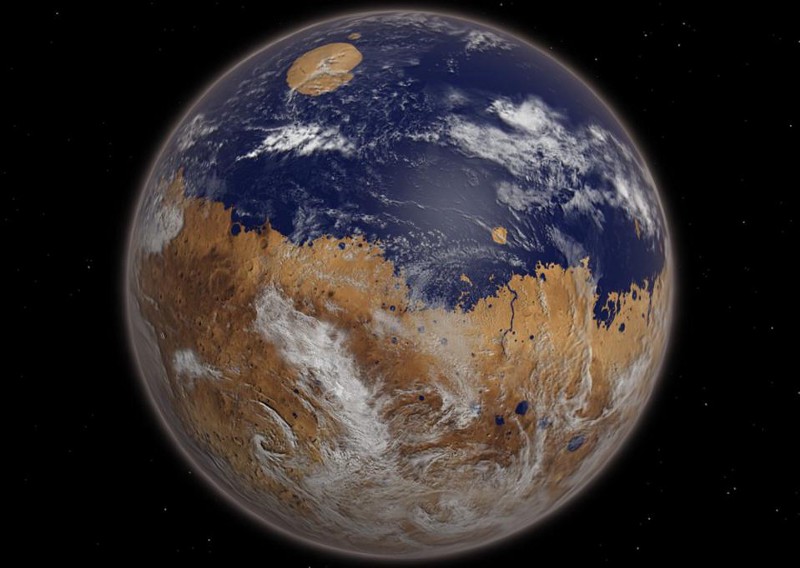
Scientists have long puzzled over how Mars, a cold and dry planet, was once warm enough to support liquid water.
While Mars is known as a frozen, red planet today, it has all the evidence we could ask for of a watery past, lasting for approximately the first 1.5 billion […]
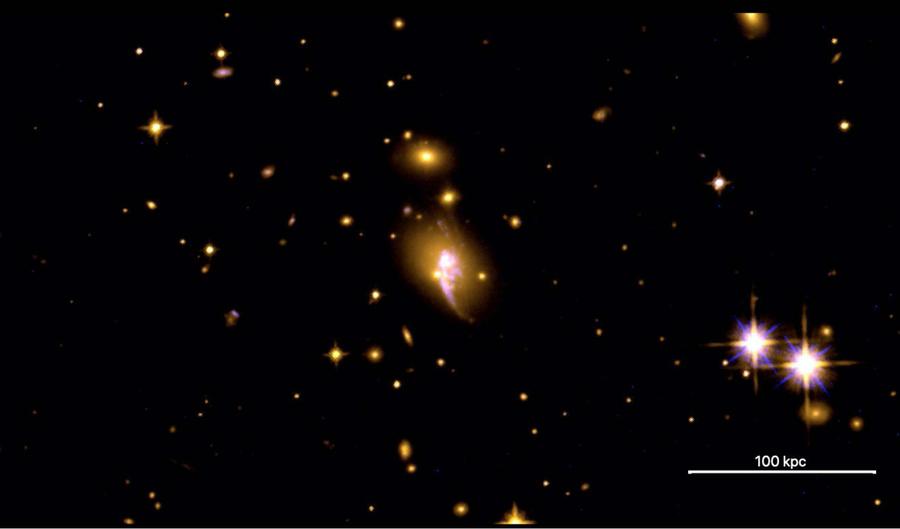
The research suggests that roughly 1 percent of galaxy clusters look atypical and can be easily misidentified.
Oxygen is thought to be a biomarker for extraterrestrial life, but there are at least three different ways that a lifeless planet can produce it.
A study looks at how to use nuclear detonations to prevent asteroids from hitting Earth.
The EmDrive turns out to be the “um…” drive after all, as a new study dubs any previous encouraging EmDrive results “false positives.”