genetics
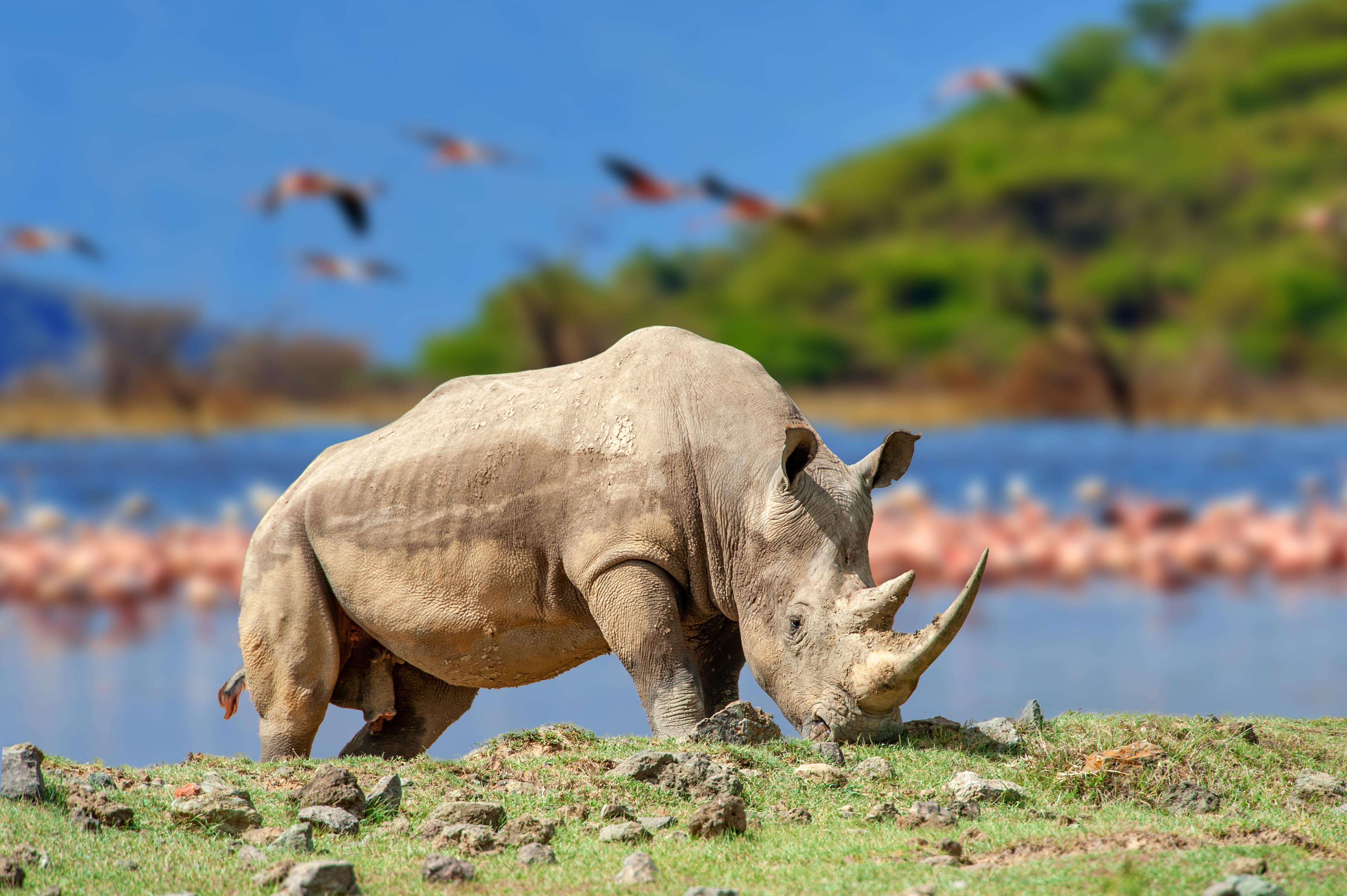
A recent study sheds light on the evolutionary history of rhinoceroses and their remarkably low levels of genetic diversity.
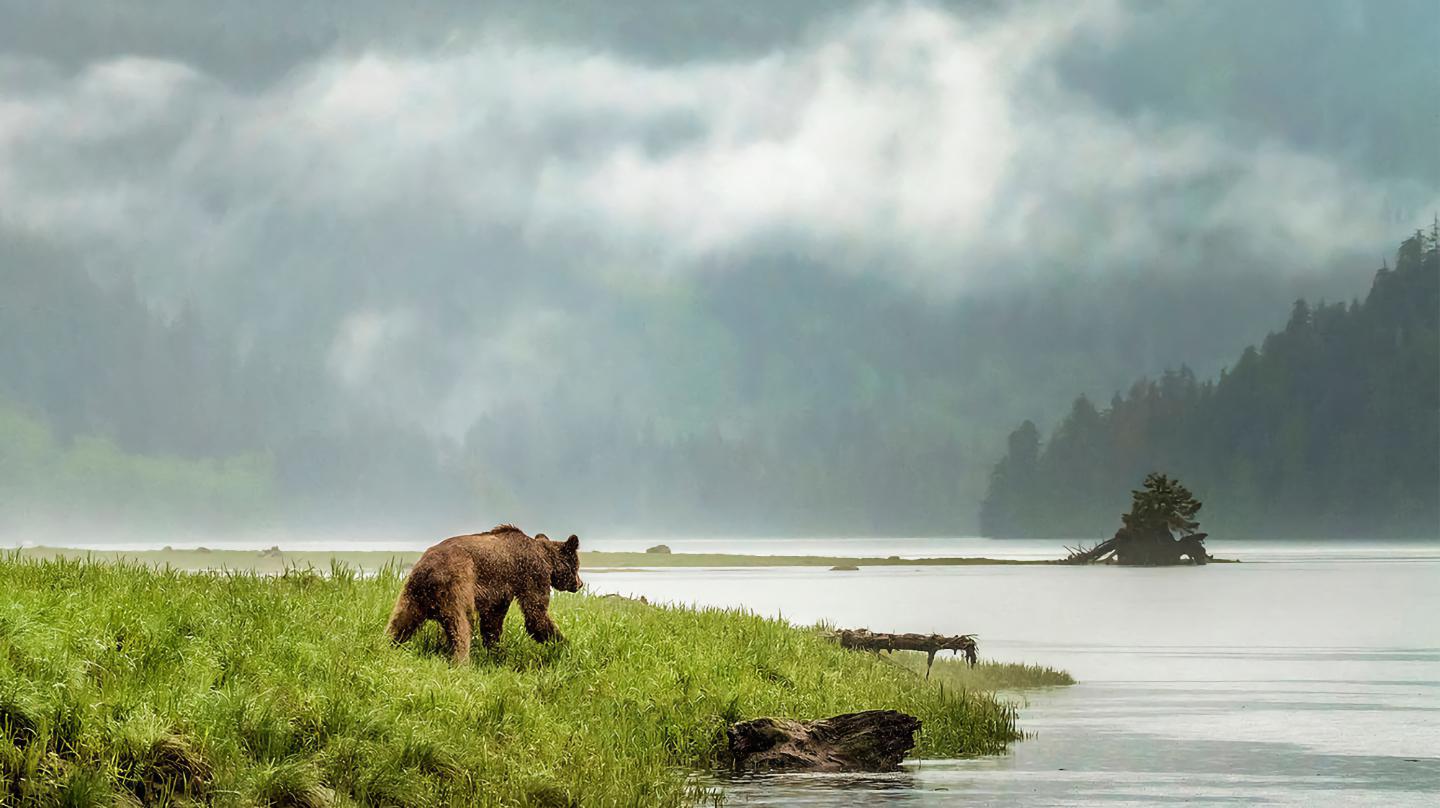
A genetic study of British Columbia grizzly bears finds a weird link to local human languages.
Scientists discover surviving viruses in 15,000-year-old glacier ice on the Tibetan Plateau in China.
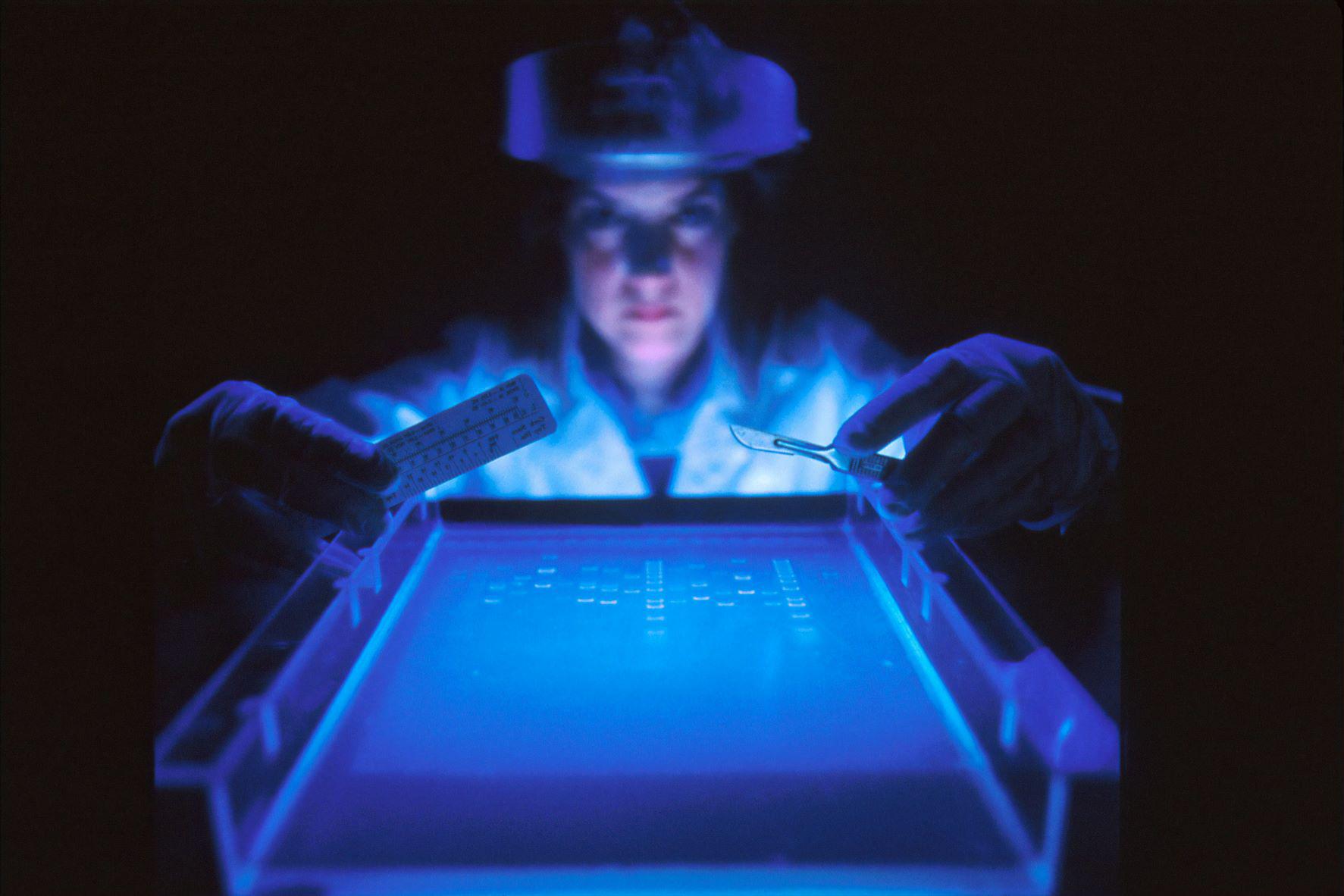
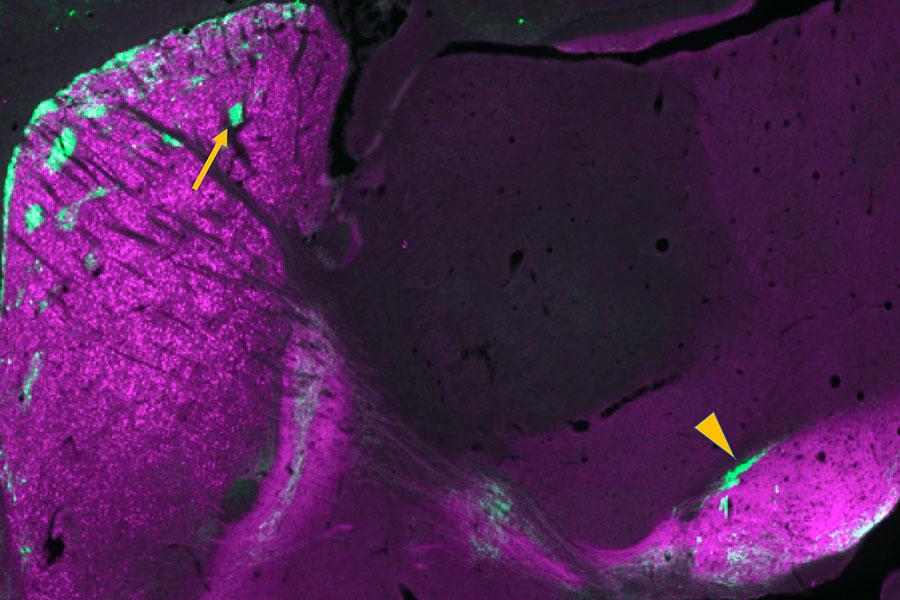
Brain cells snap strands of DNA in many more places and cell types than researchers previously thought.
In 1933, the skull of a 50-year-old male of the Homo longi species was found in China, puzzling researchers.
Many thousands of different genetic variants are responsible for complex behavior.
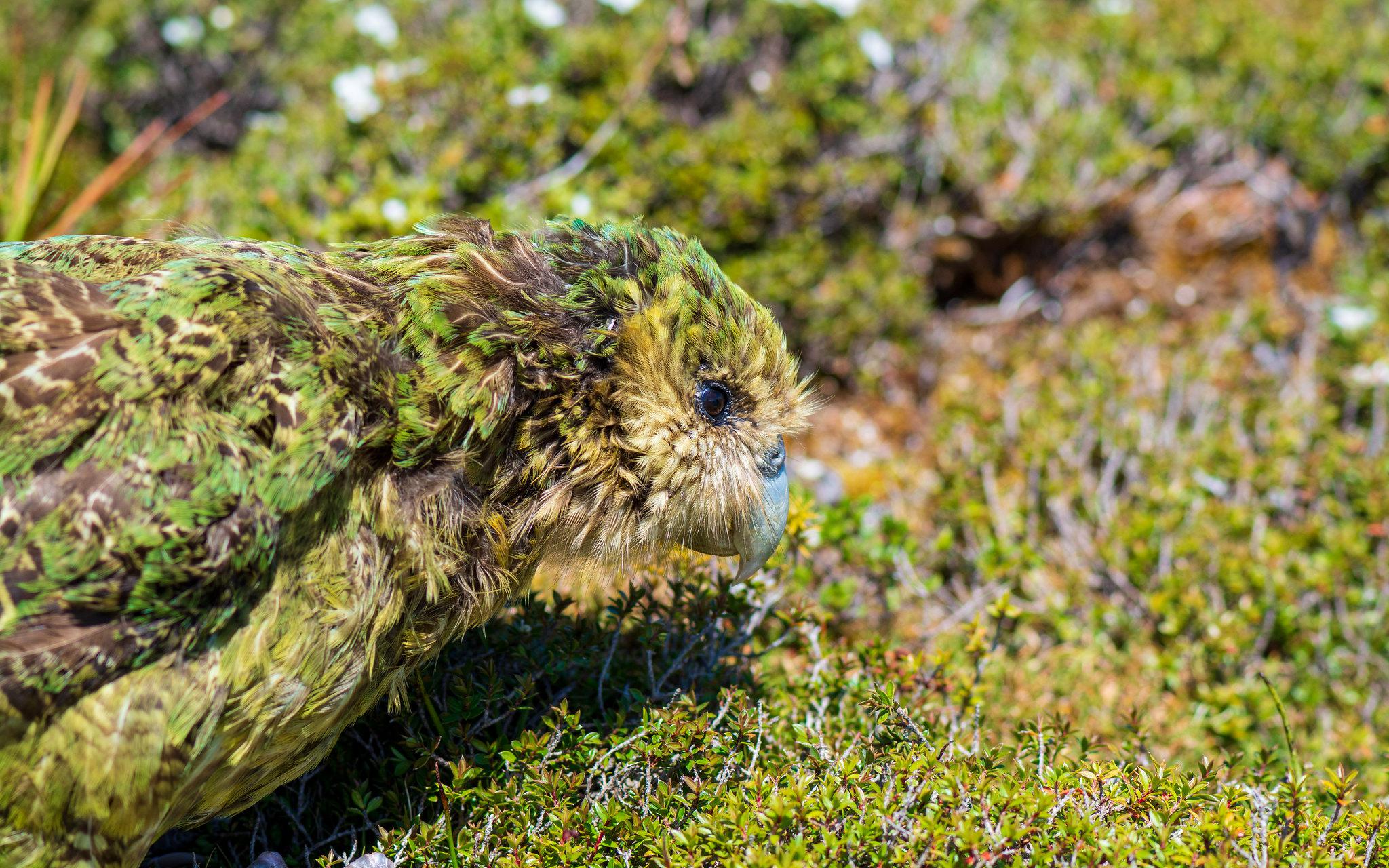
The Vertebrate Genomes Project may spell good news for the kakapo and the vaquita.
“The question is which are okay, which are not okay.”
▸
14 min
—
with
Want to live 100+ years? You may need unusually good DNA repair.
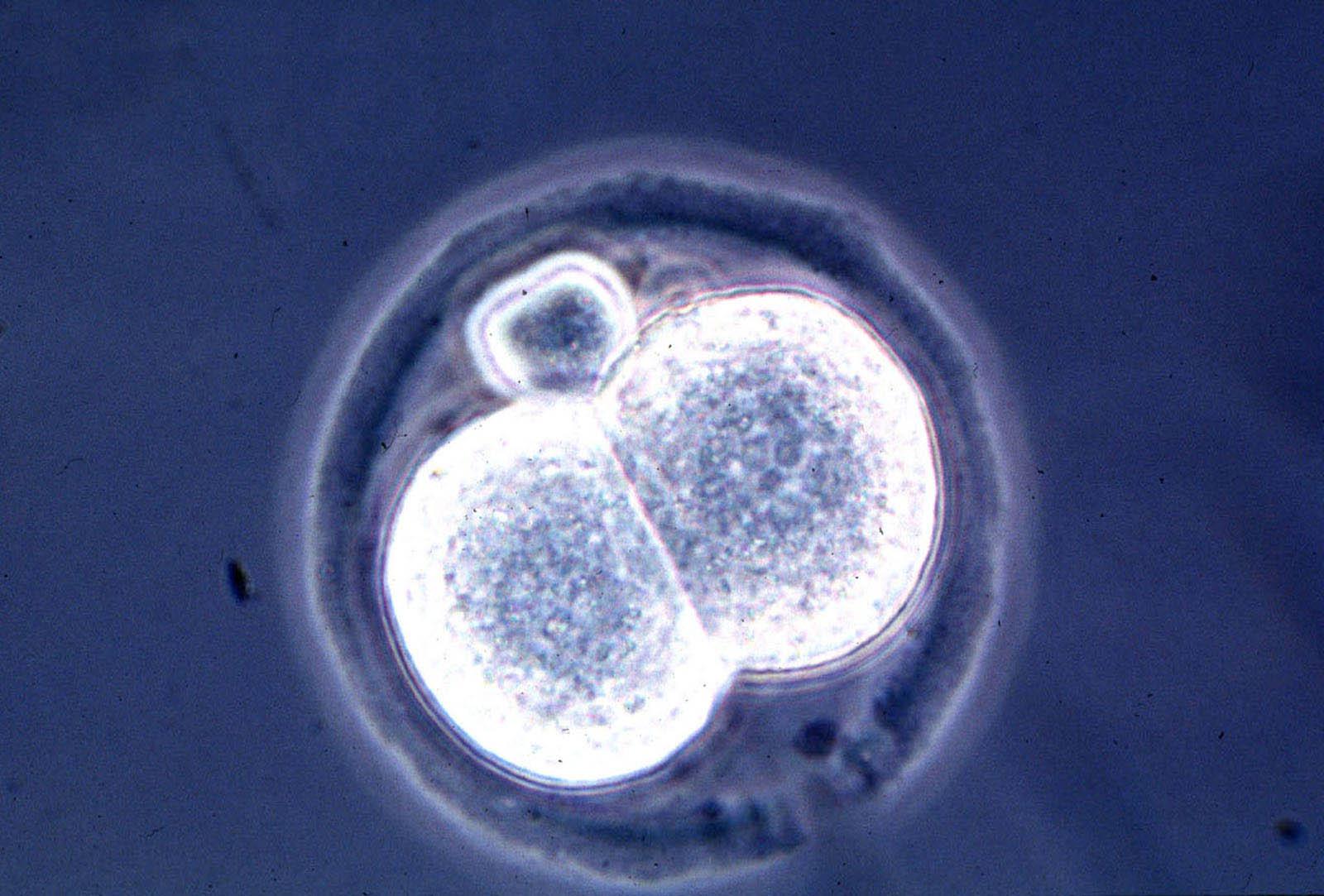
This spring, a U.S. and Chinese team announced that it had successfully grown, for the first time, embryos that included both human and monkey cells.
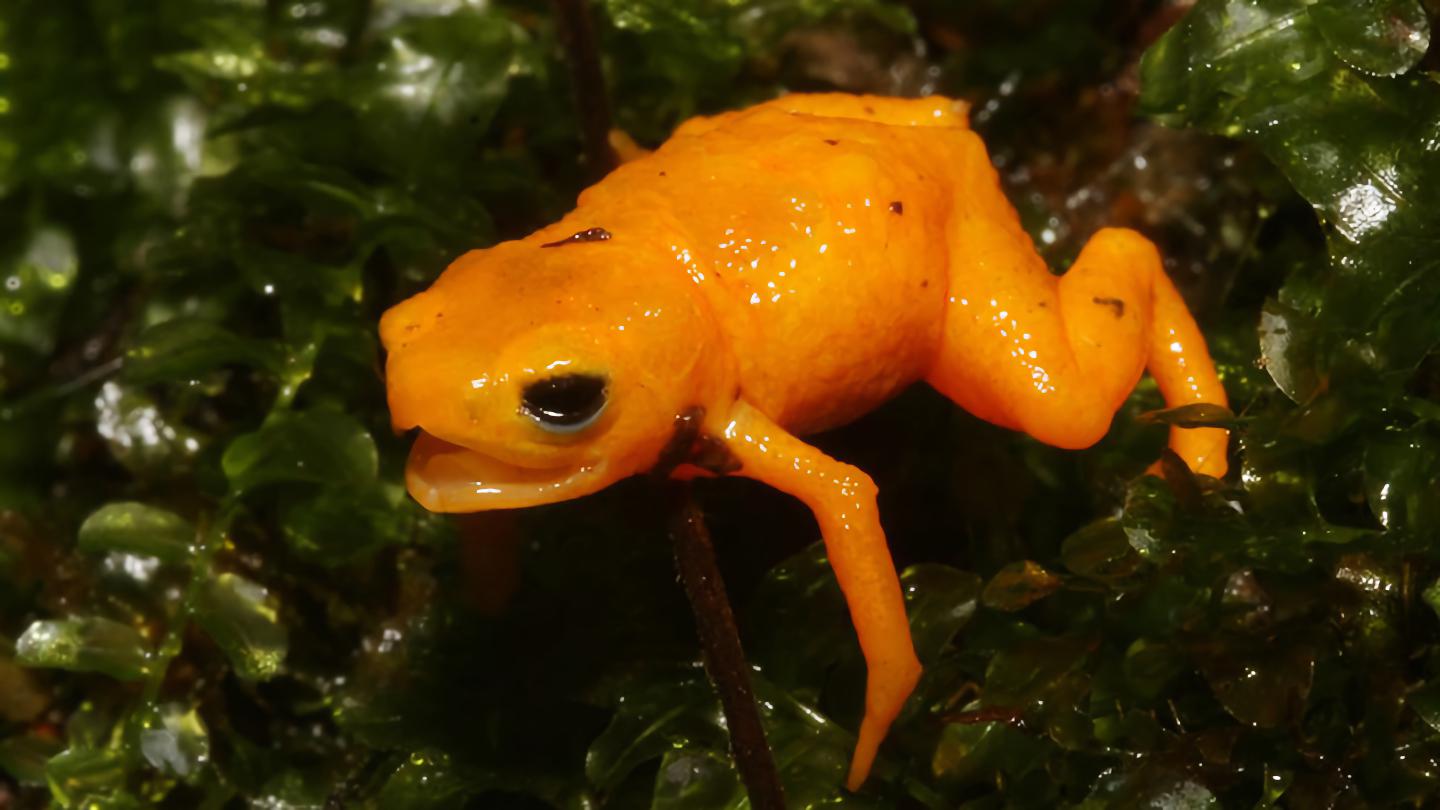
Roughly the size of a thumbnail, this newly discovered toadlet has some anatomical surprises.
For every good idea in evolution, there is an unintended consequence. Disease is often one of them.
A lab identifies which genes are linked to abnormal repetitive behaviors found in addiction and schizophrenia.
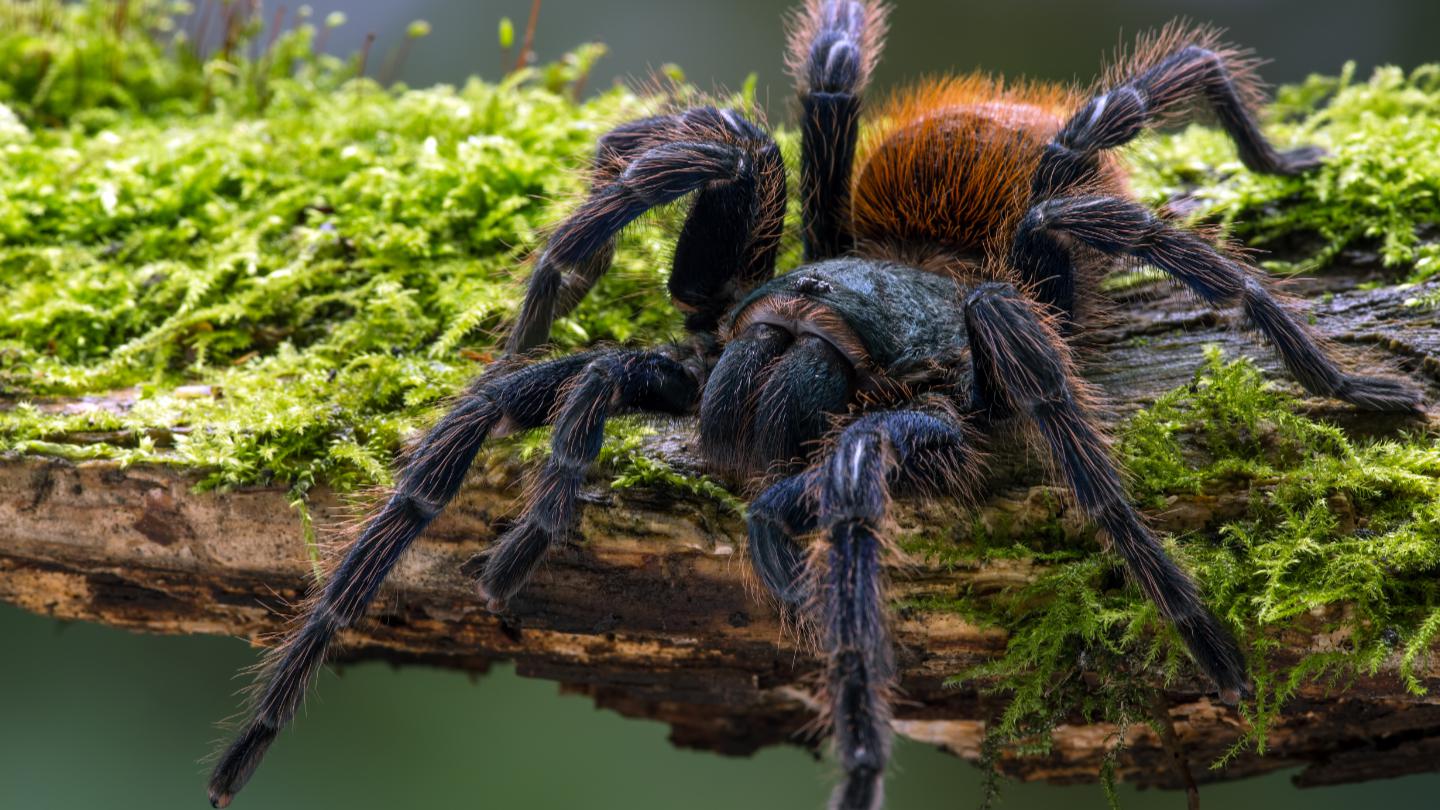
A study from Carnegie Mellon University tracks the travels of tarantulas since the Cretaceous period.
The potential of CRISPR technology is incredible, but the threats are too serious to ignore.
▸
14 min
—
with
New research reveals that the face can affect the shape of the brain through a complex “cross-talk” between the two structures.
The new treatment targets the underlying genetic cause of the disease.
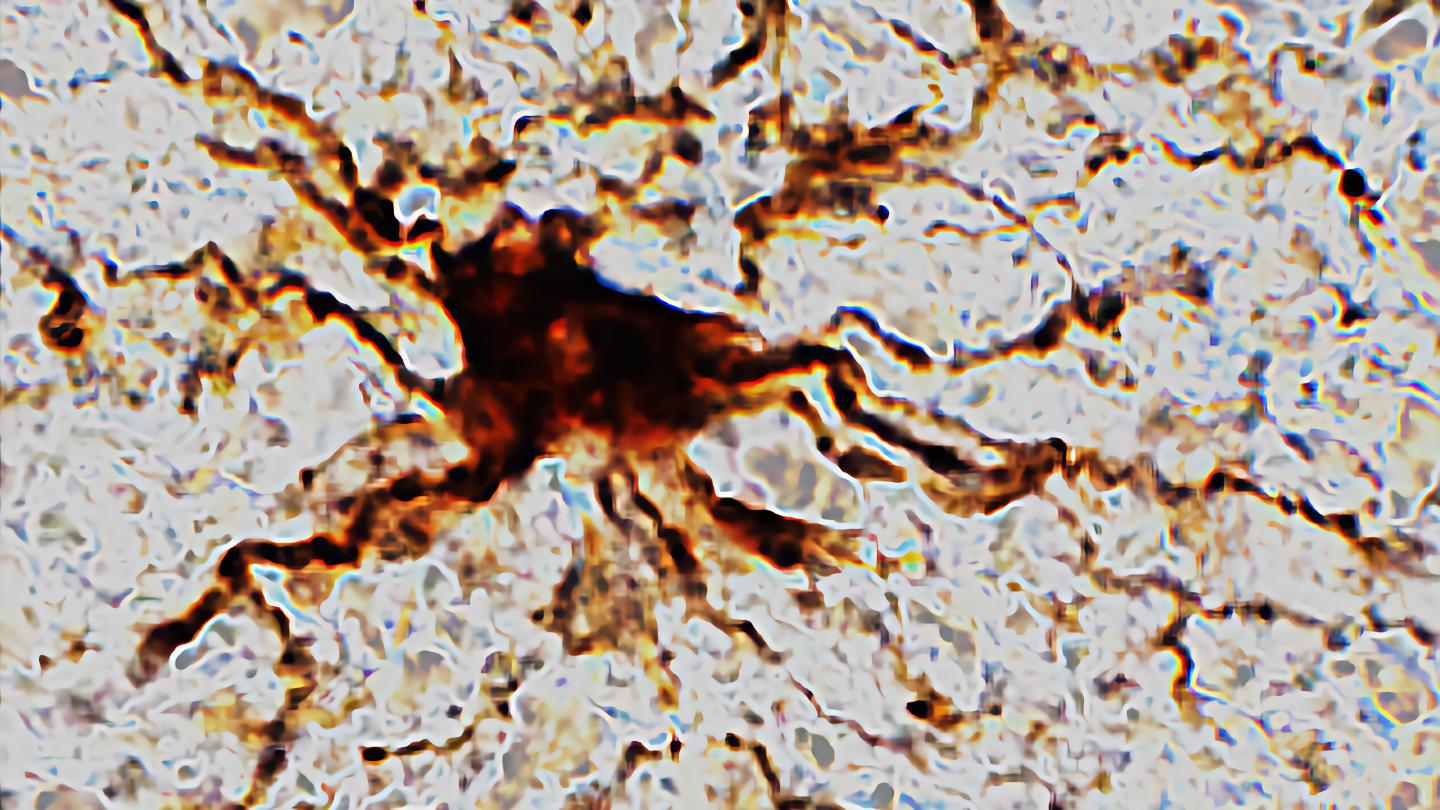
Researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago find that death triggers increased activity in certain brain cells.
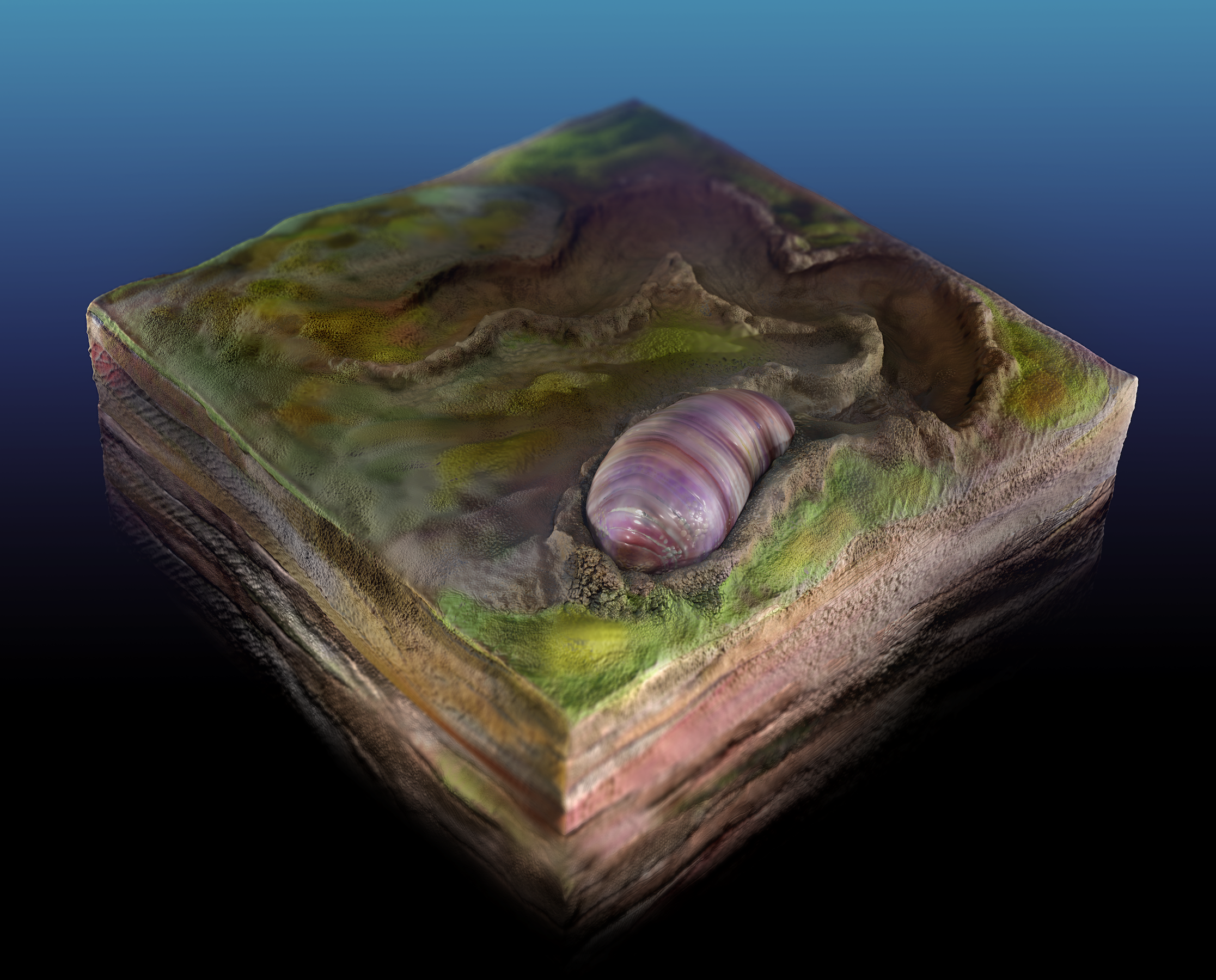
555-million-year-old oceanic creatures share genes with today’s humans, finds a new study.
“Large-scale indiscriminate killing is a horror that is not just a feature of the modern and historic periods, but was also a significant process in pre-state societies,” the researchers wrote.
What makes some people more likely to shiver than others?
After 20 months, scientists find lab-dish brain cells matured at a similar rate to those of an actual infant.
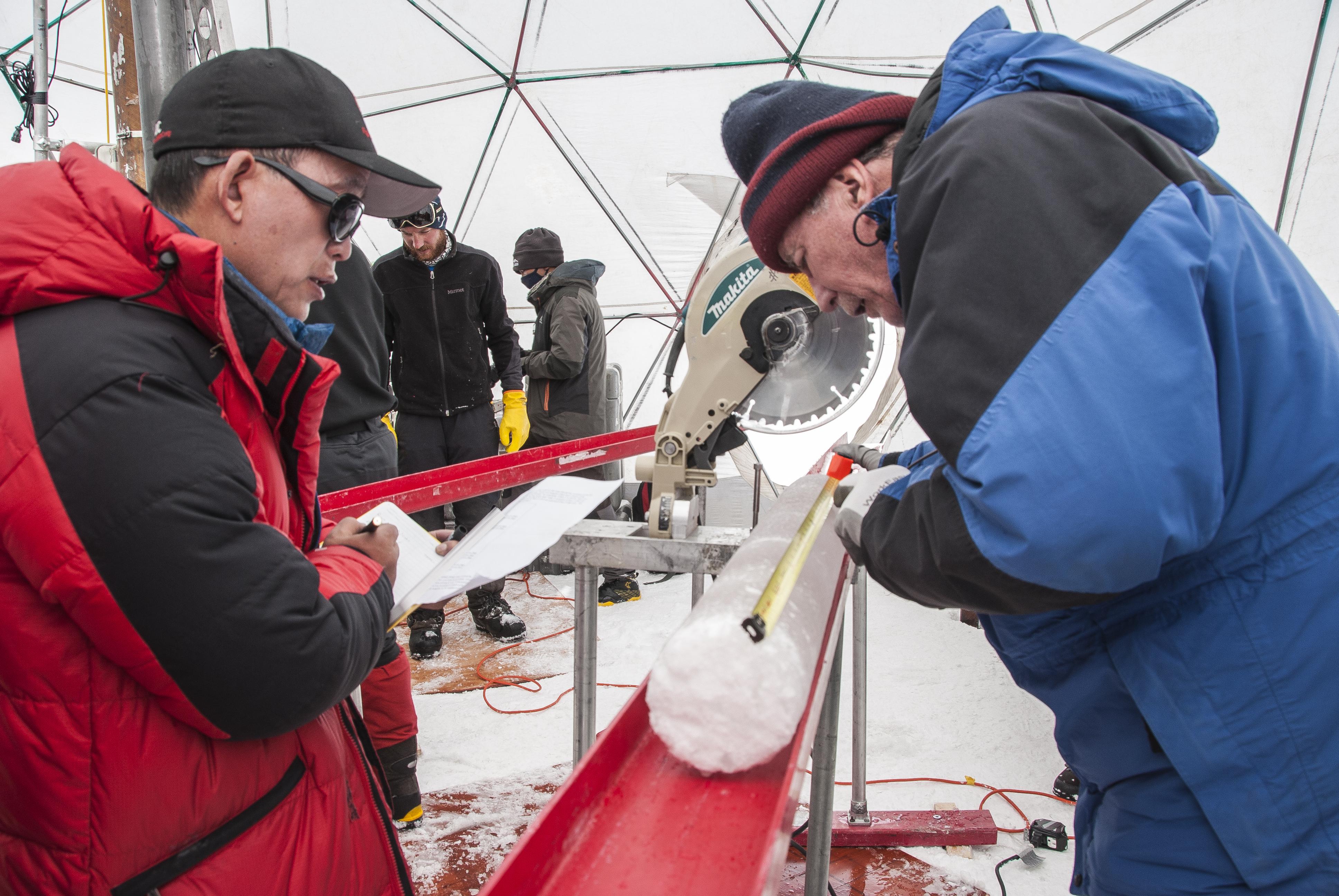
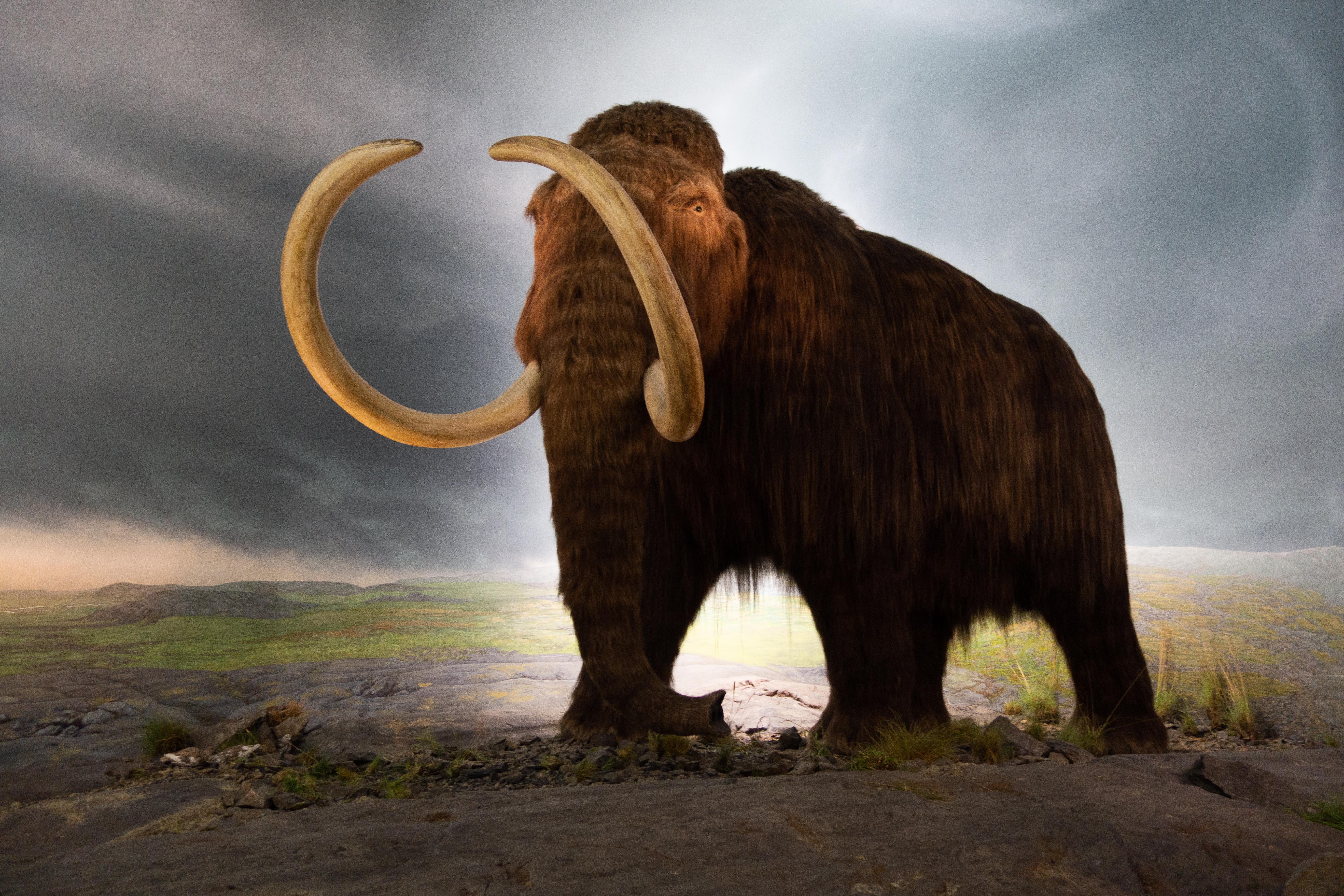
One million year old mammoth DNA more than doubles the previous record and suggests that even older genomes could be found.
Imagine poisoning your rival and yourself and giving only yourself the antidote.
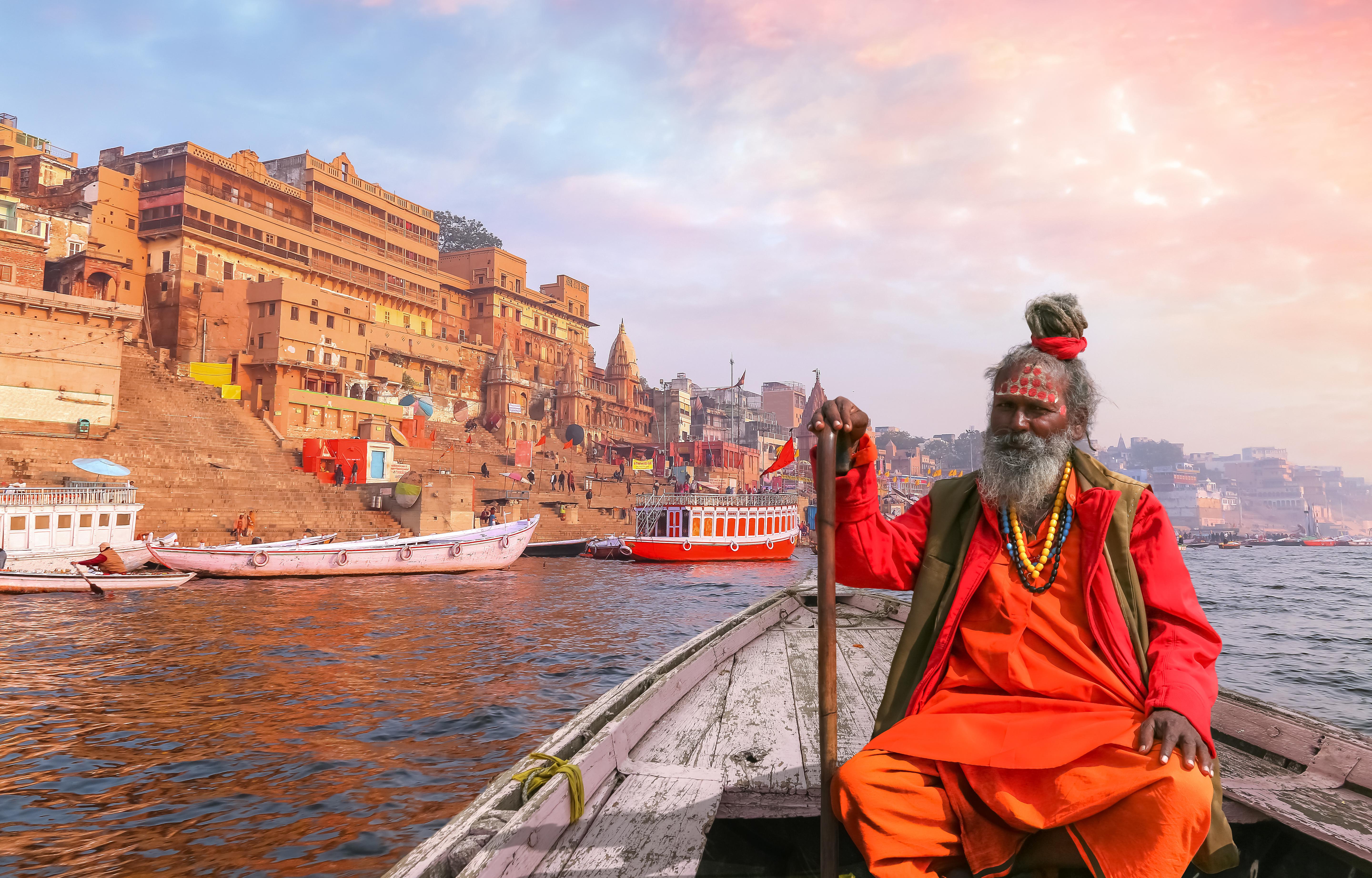
The study found that people who spoke the same language tended to be more closely related despite living far apart.
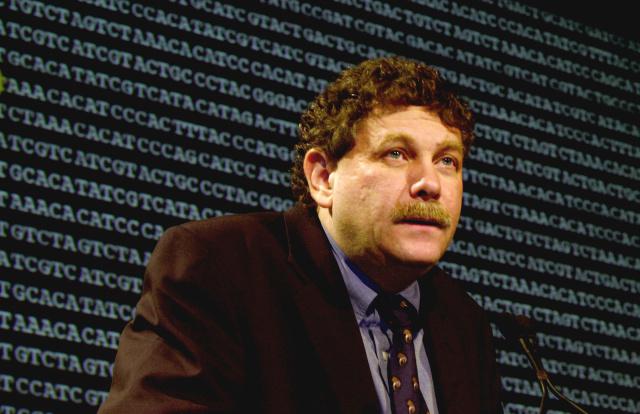
Dr. Eric Lander is a pioneer in genomics. What role will he play in the new administration?
How would the ability to genetically customize children change society? Sci-fi author Eugene Clark explores the future on our horizon in Volume I of the “Genetic Pressure” series.