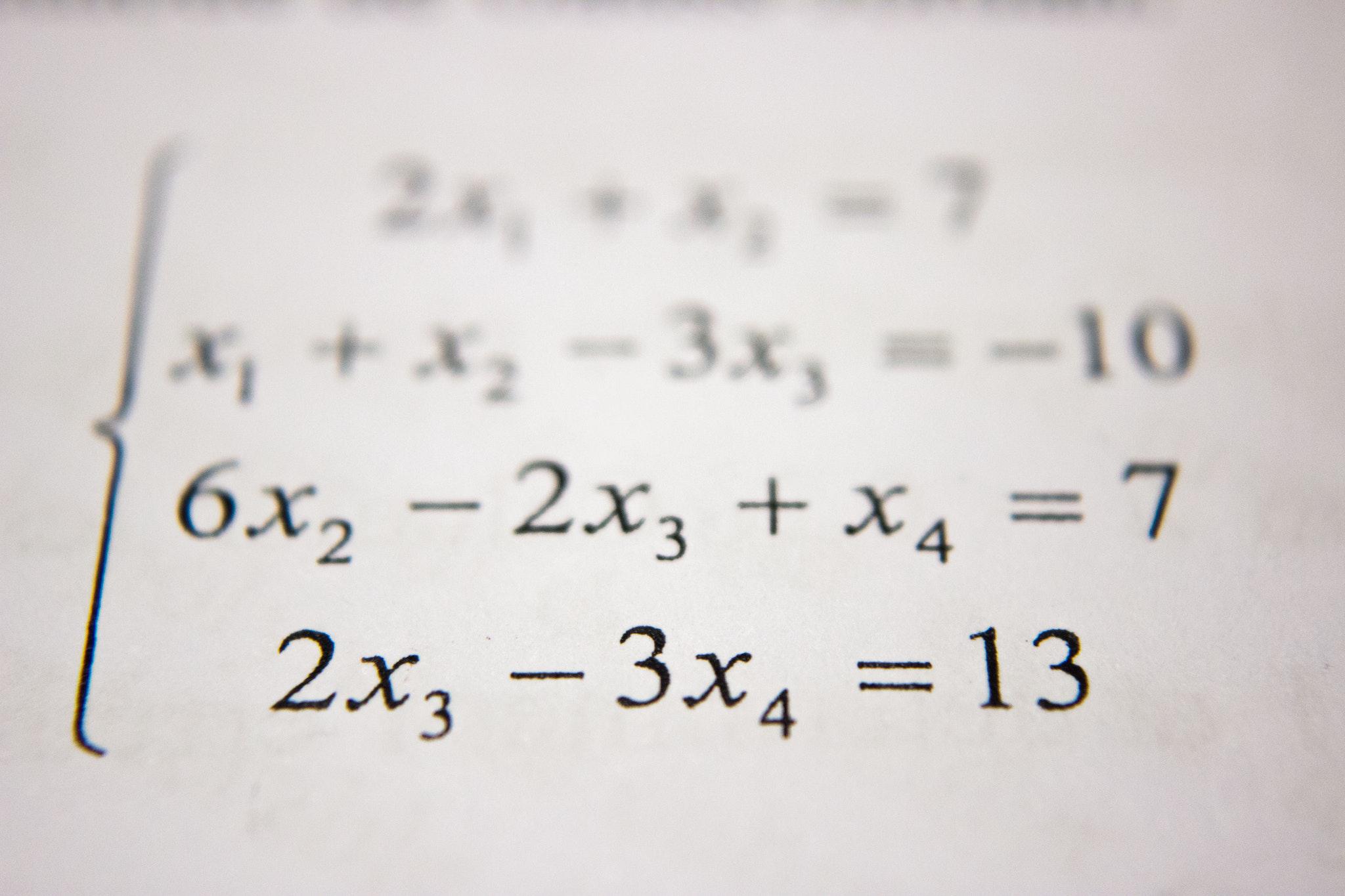Hard Science
All Stories
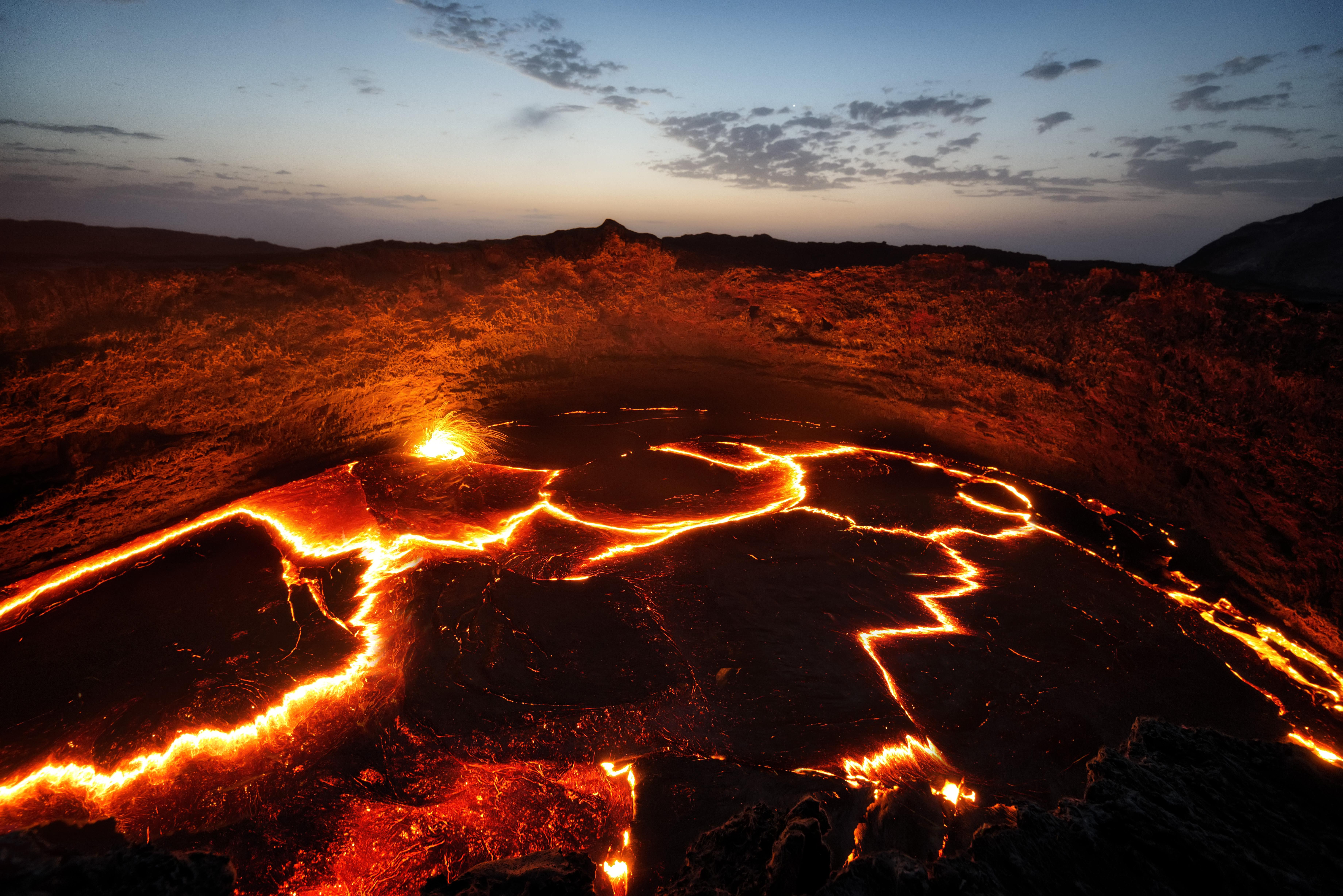
Scientists look to erupted sea glass — lava that erupted in the ocean and was instantly chilled by the surrounding water — to take Earth’s temperature.
We spend much of our early years learning arithmetic and algebra. What’s the use?
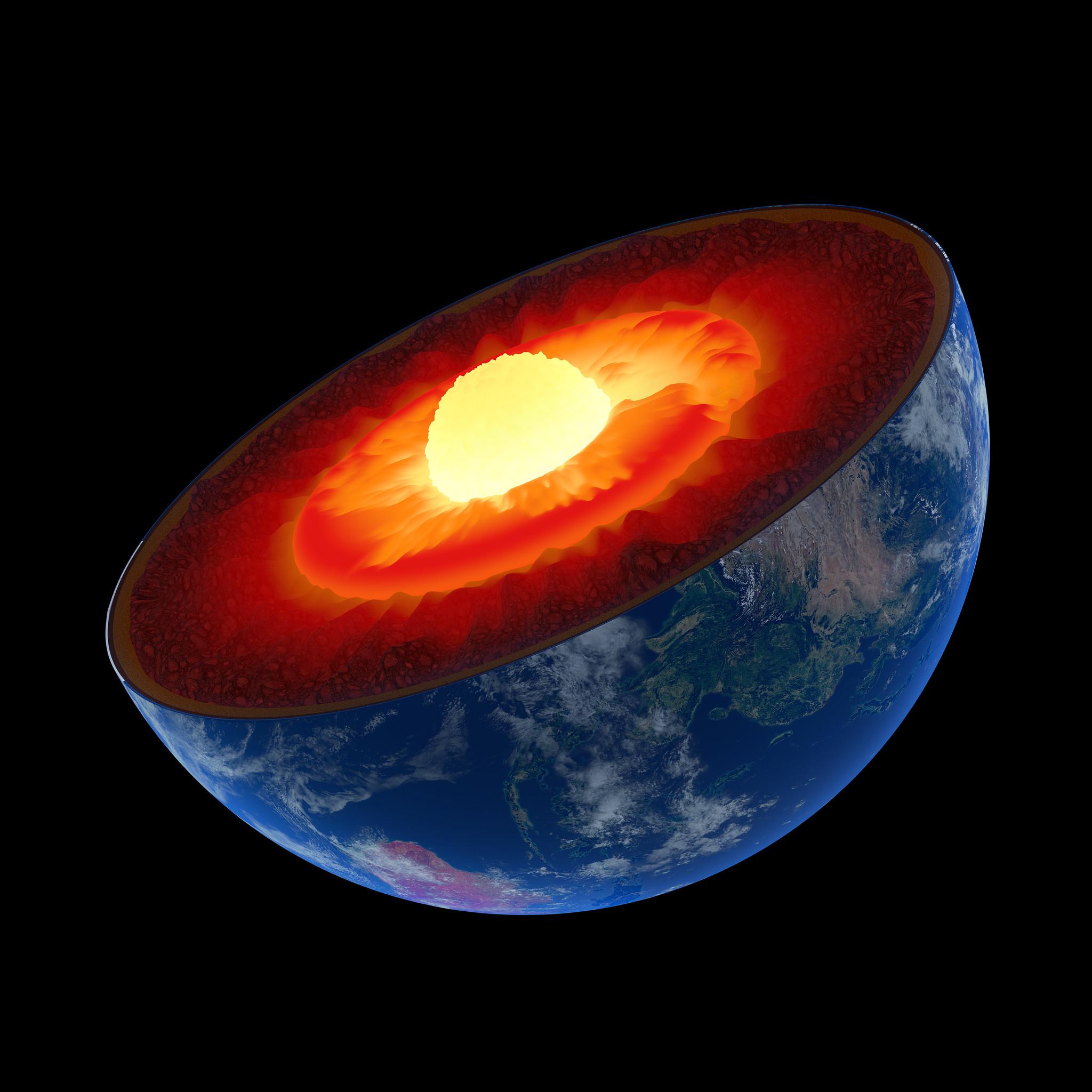
The eastern inner core located beneath Indonesia’s Banda Sea is growing faster than the western side beneath Brazil.
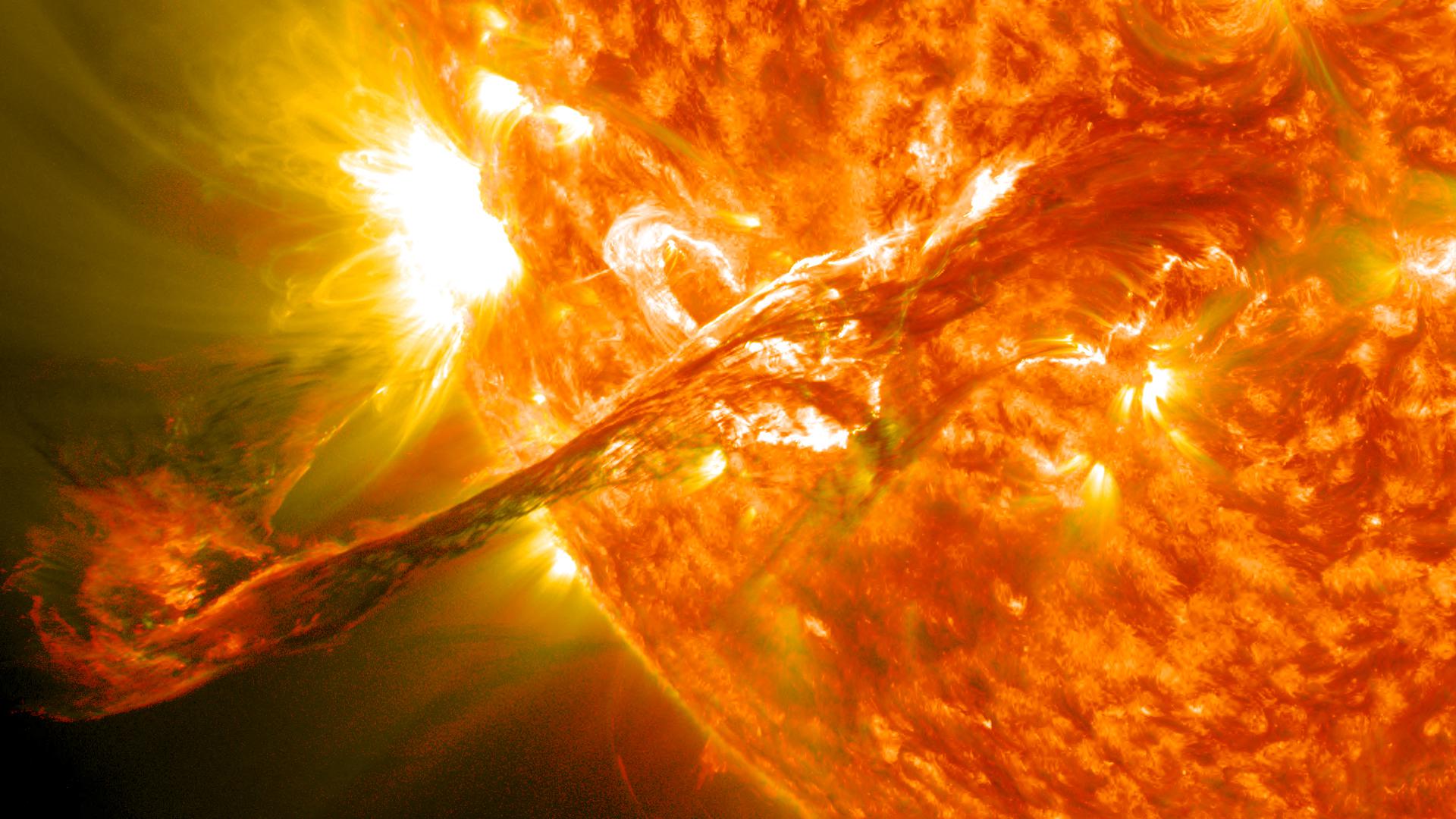
While we can see many solar storms coming, some are “stealthy.” A new study shows how to detect them.
Scientists do not know what is causing the overabundance of the gas.
A new government report describes 144 sightings of unidentified aerial phenomena.
Strange underwater icicles form in the Earth’s coldest regions and freeze living organisms in place.
A theoretical physicist returns to Penrose and Hameroff’s theory of “quantum consciousness.”
Using image analysis tools developed for astronomy, researchers are predicting cancer therapy responses.
Trees store carbon dioxide, have a cooling effect in cities, and reduce flood risks.
Jupiter’s mysterious auroral events are caused by vibrating waves of plasma.
A new artificial intelligence method removes the effect of gravity on cosmic images, showing the real shapes of distant galaxies.
Tiny fluctuations in old Kepler data reveals four runaway planets that are reminiscent of Earth.
If the laws of physics are symmetrical as we think they are, then the Big Bang should have created matter and antimatter in the same amount.
Astronomers find a third type of supernova and explain a mystery from 1054 AD.
A new study proposes that Hawking radiation could be used to find dark matter in places like primordial black holes.
The Younger Dryas impact hypothesis argues that a comet strike caused major changes to climate and human cultures on Earth about 13,000 years ago.
Ernst Chladni proved that sound can be seen, and developed a technique of visualizing vibrations on a metal plate.
The Taupo volcano was responsible for one of the most violent eruptions on record.
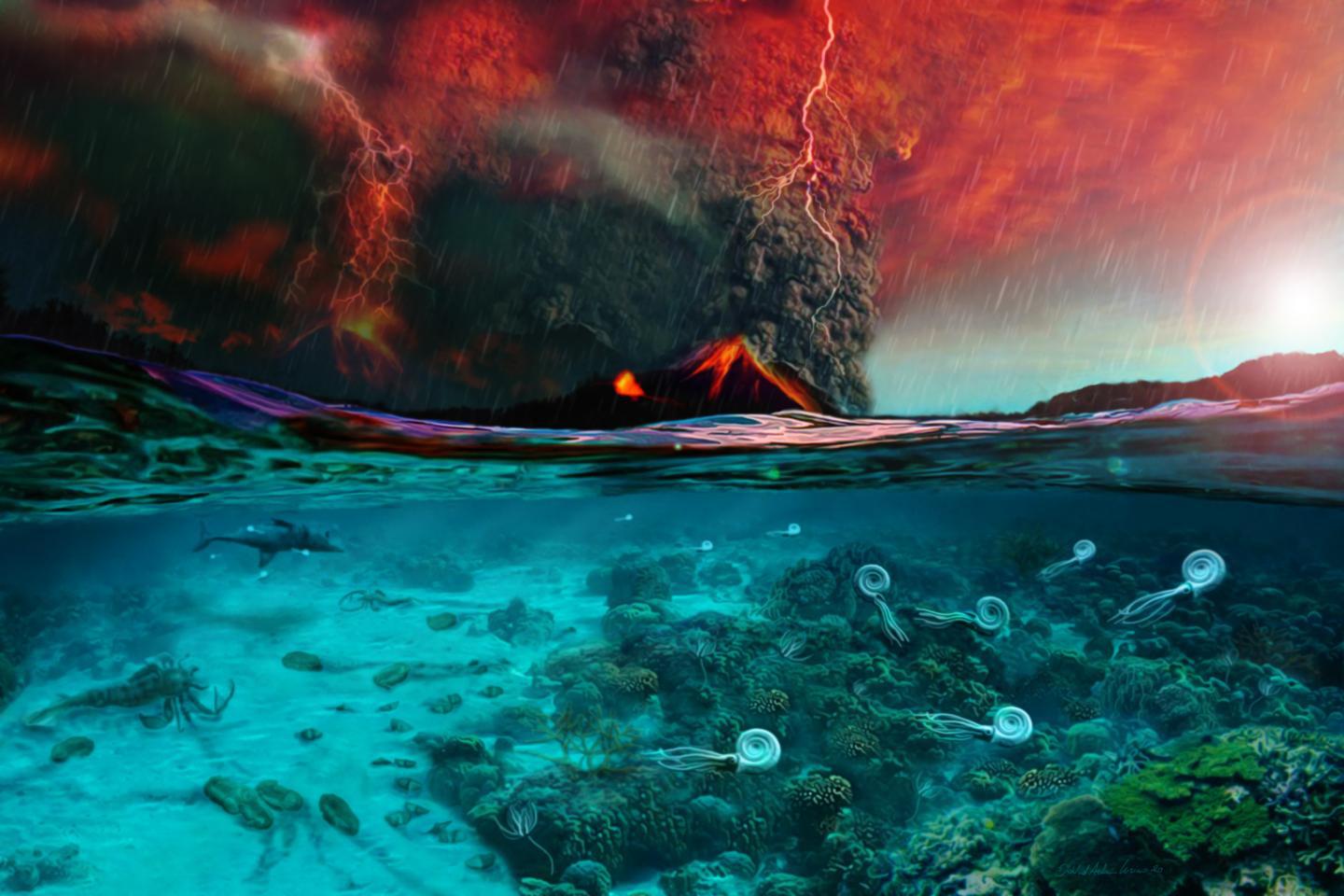
A new study reveals what caused most life on Earth to die out during the end-Permian extinction, also known as the Great Dying.
An analysis of the gravitational wave data from black hole mergers show that the event horizon area, and entropy, always increases.
Geologists discover a rhythm to major geologic events.
Researchers discovered a galactic wind from a supermassive black hole that sheds light on the evolution of galaxies.
Every star we can see, including our sun, was born in one of these violent clouds.
Tiny specks of space debris can move faster than bullets and cause way more damage. Cleaning it up is imperative.
▸
6 min
—
with
The following is an excerpt from Viruses, Pandemics, and Immunity by Arup K. Chakraborty and Andrey S. Shaw. Reprinted with Permission from The MIT PRESS. Copyright 2021. Koch’s Postulates, Anthrax, […]
Astronomers possibly solve the mystery of how the enormous Oort cloud, with over 100 billion comet-like objects, was formed.
Can one equation unite all of physics?
▸
6 min
—
with
The helicopter’s sixth mission almost went down in disaster.