A wave of innovation is coursing through the nuclear industry — but ingrained opposition is the biggest roadblock.
Search Results
You searched for: energy
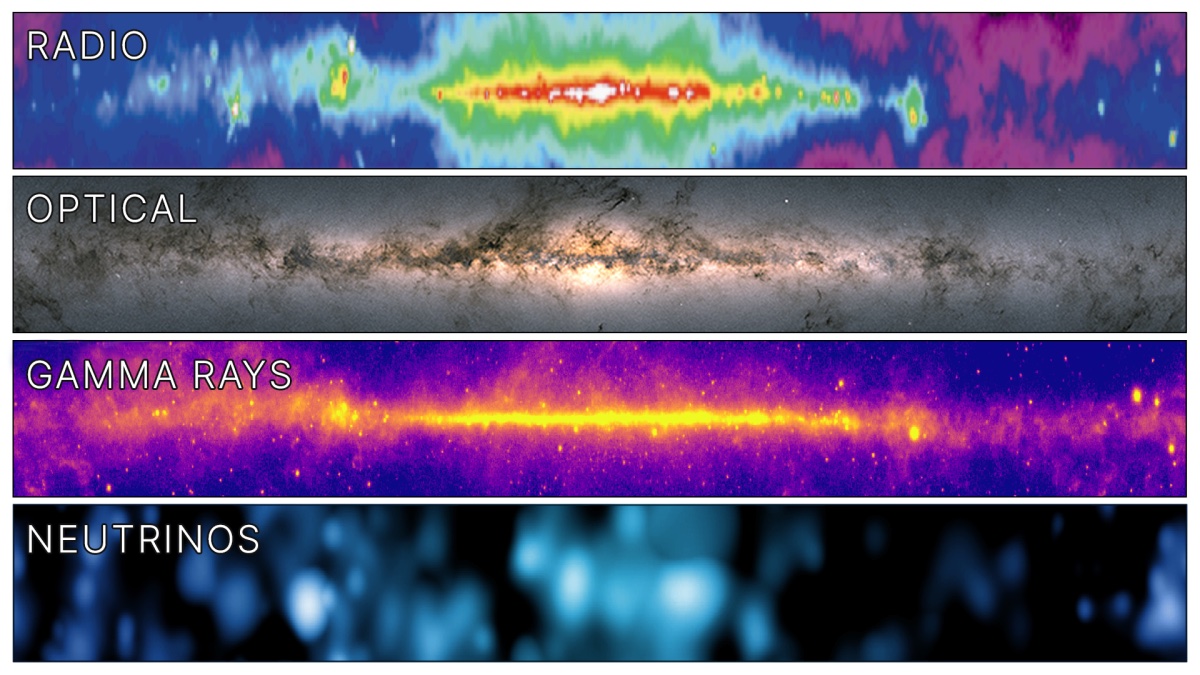
Back during the hot Big Bang, it wasn’t just charged particles and photons that were created, but also neutrinos. Where are they now?
In the early stages of the hot Big Bang, matter and antimatter were (almost) balanced. After a brief while, matter won out. Here’s how.
The National Ignition Facility just repeated, and improved upon, their earlier demonstration of nuclear fusion. Now, the true race begins.
Behind America’s hunt for a superior semiconductor.
The closest known star that will soon undergo a core-collapse supernova is Betelgeuse, just 640 light-years away. Here’s what we’ll observe.
If the Universe is expanding, and the expansion is accelerating, what does that tell us about the cause of the expanding Universe?
From ancient Greek cosmology to today’s mysteries of dark matter and dark energy, explore the relentless quest to understand the Universe’s invisible forces.
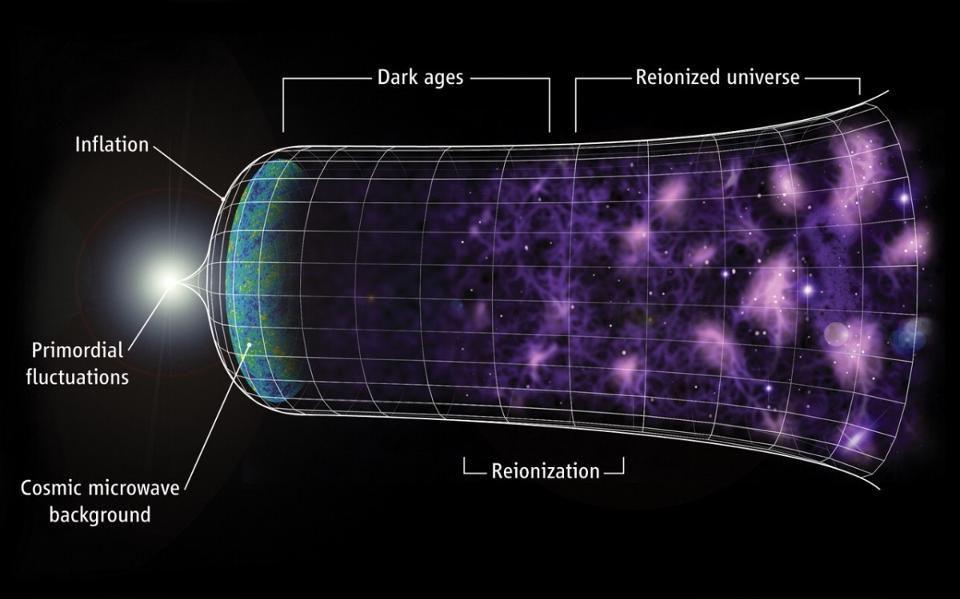
Cosmic inflation is the state that preceded and set up the hot Big Bang. Here’s what the Universe was like during that time period.
In the expanding Universe, different ways of measuring its rate give incompatible answers. Nobel Laureate Adam Riess explains what it means.
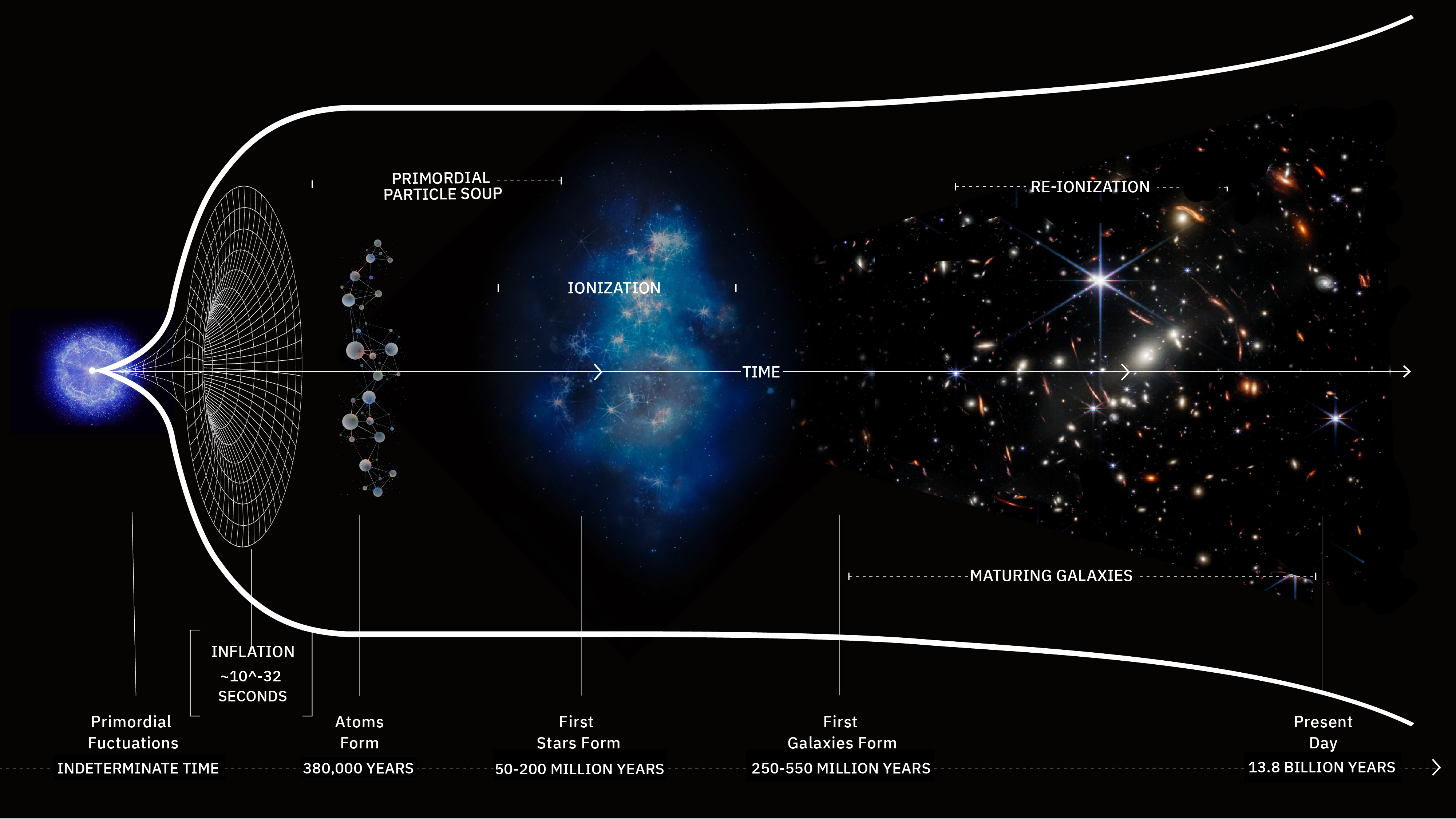
The first elements in the Universe formed just minutes after the Big Bang, but it took hundreds of thousands of years before atoms formed.
As Marcel Proust said, “The real voyage of discovery… consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes.”
In our Universe, all stable atomic nuclei have protons in them; there’s no stable “neutronium” at all. But what’s the reason why?
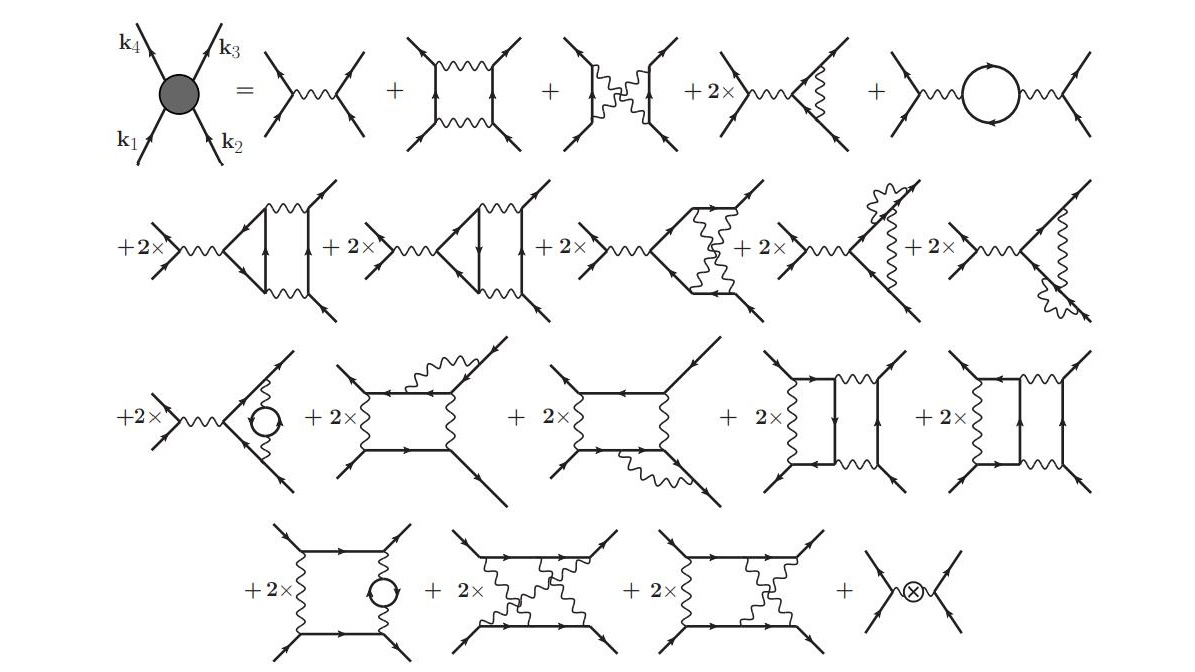
It’s 2024, and we still only know of the fundamental particles of the Standard Model: nothing more. But these 8 unanswered questions remain.
According to neuropsychologist Julia DiGangi, no one can live a life free of emotional pain. We can only choose how those emotions empower us.
The electromagnetic force can be attractive, repulsive, or “bendy,” but is always mediated by the photon. How does one particle do it all?
LK-99, almost certainly, isn’t a room-temperature superconductor. The underlying physics of the phenomenon helps us understand why.
The miniaturization of particle accelerators could disrupt medical science.
All biological systems are wildly disordered. Yet somehow, that disorder enables plant photosynthesis to be nearly 100% efficient.
What if we could harvest energy from human heat, sweat, or vibrations?
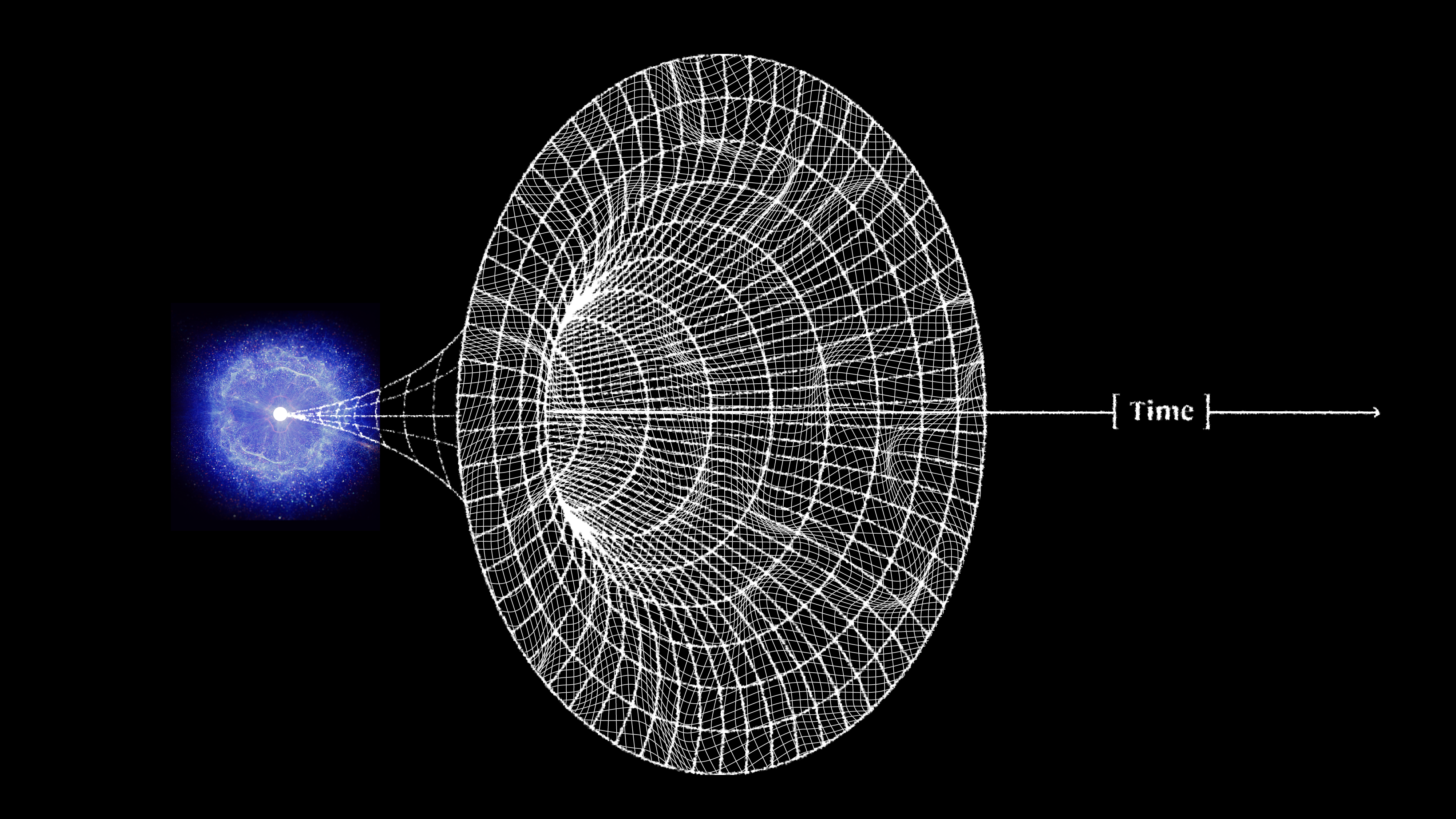
All of the matter and radiation we measure today originated in a hot Big Bang long ago. The Universe was never empty, not even before that.
Some 13.8 billion years ago, the Universe became hot, dense, and filled with high-energy quanta all at once. Here’s what it was like.
Science fiction met nuclear fission when Hungarian physicist Leó Szilárd pondered the explosive potential of nuclear energy.
50 years ago, Stephen Hawking showed that black holes emit radiation and eventually decay away. That fate may now apply to everything.
The Multiverse fuels some of the 21st century’s best fiction stories. But its supporting pillars are on extremely stable scientific footing.
Although a great many unidentified sights have been seen in the skies, none have conclusively demonstrated the presence of aliens. So far.
In the very early Universe, practically all particles were massless. Then the Higgs symmetry broke, and suddenly everything was different.
Welcome to The Nightcrawler — a weekly newsletter from Eric Markowitz covering tech, innovation, and long-term thinking.
On larger and larger scales, many of the same structures we see at small ones repeat themselves. Do we live in a fractal Universe?
The second law of thermodynamics tells us that entropy always increases. But that doesn’t mean it was zero at the start of the Big Bang.