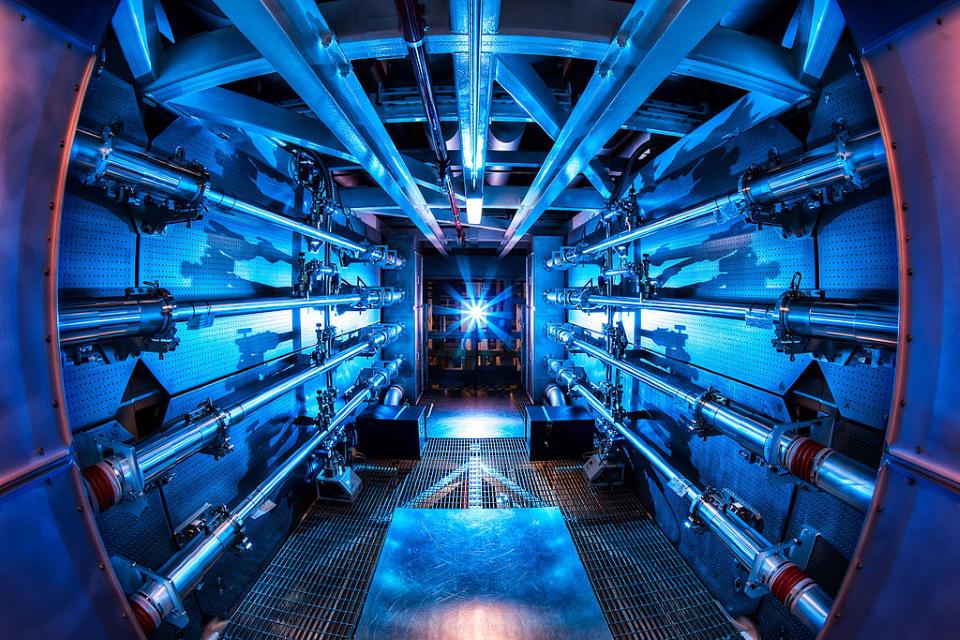
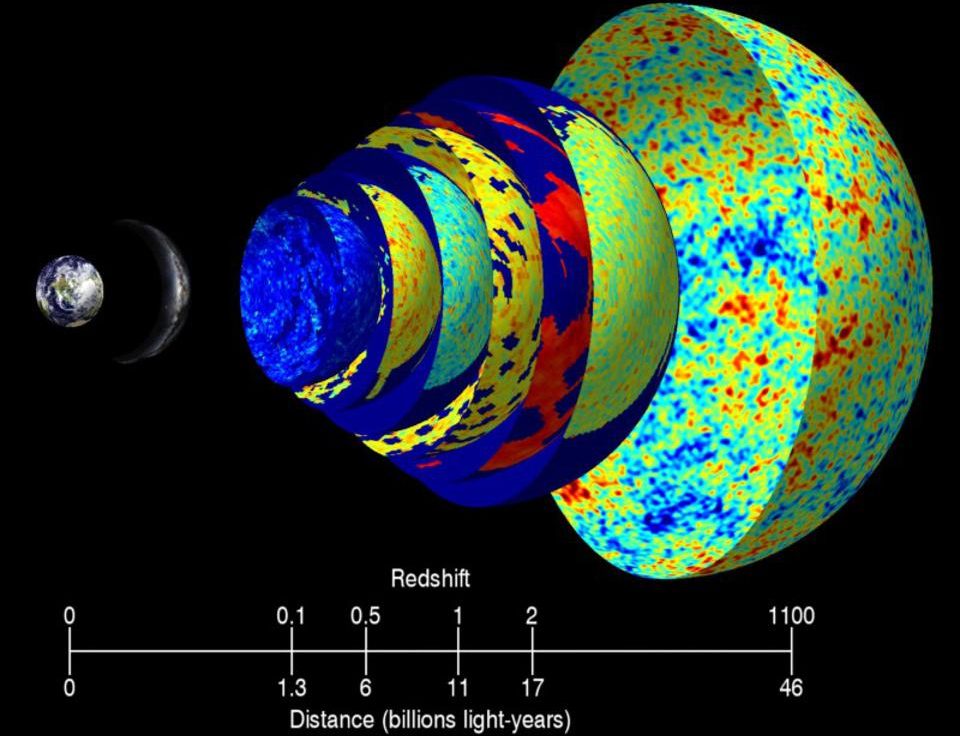
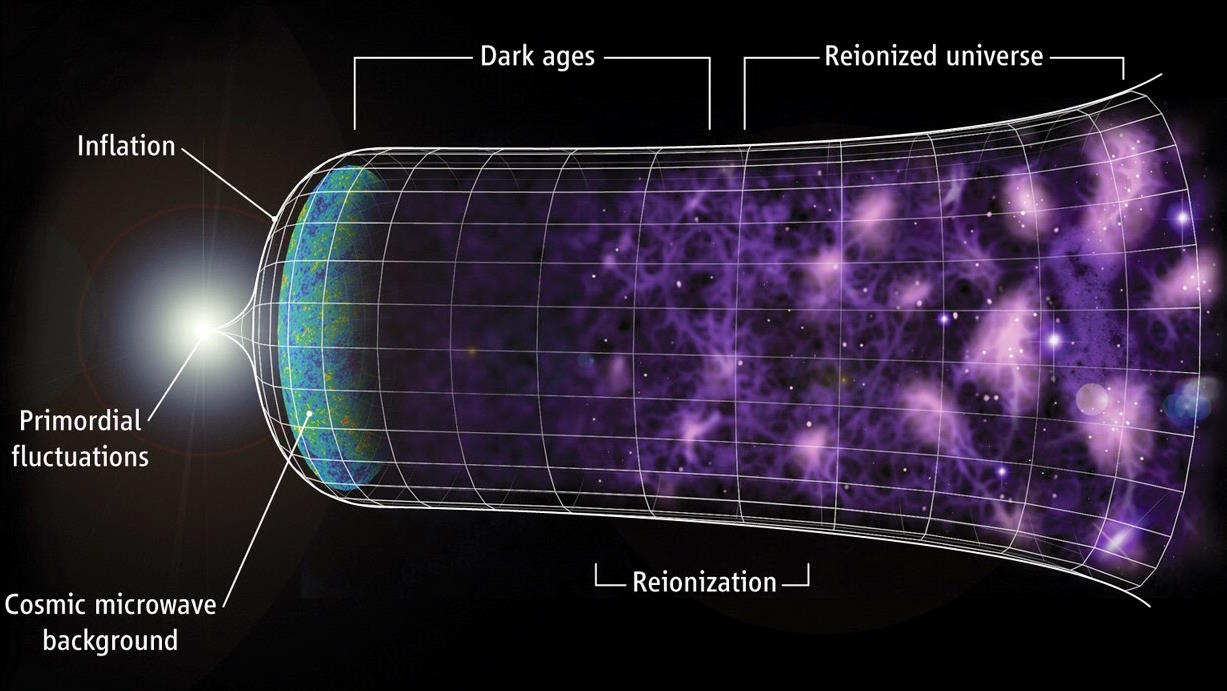
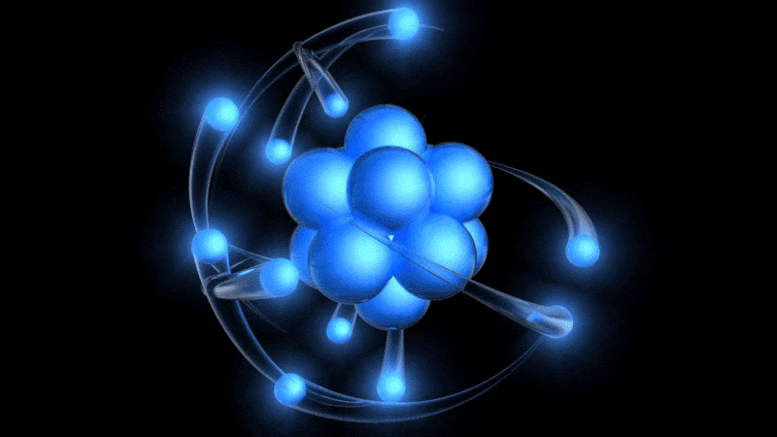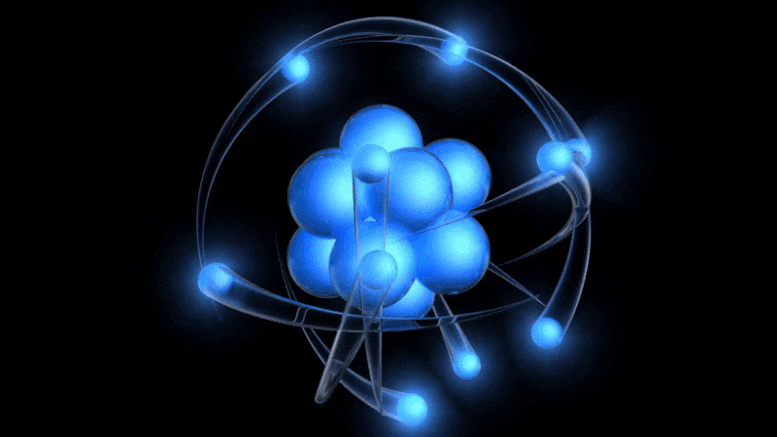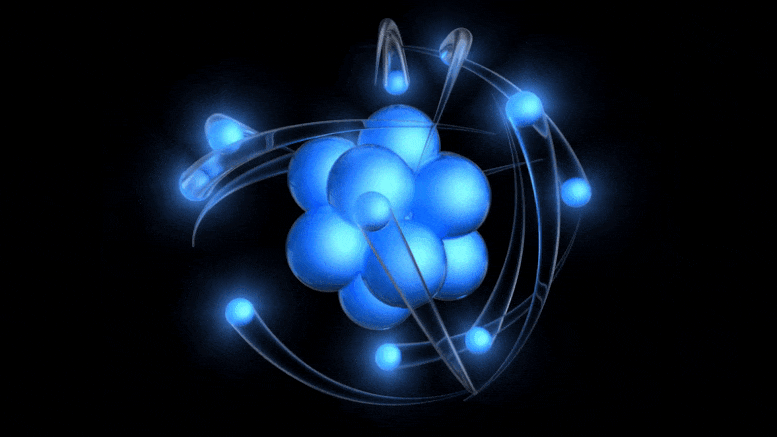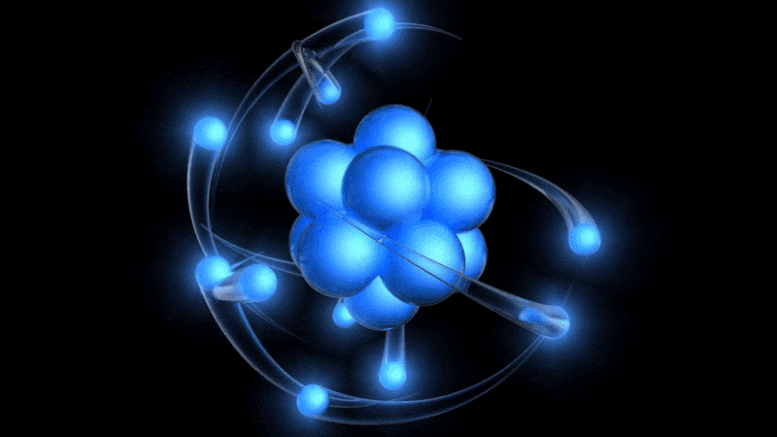
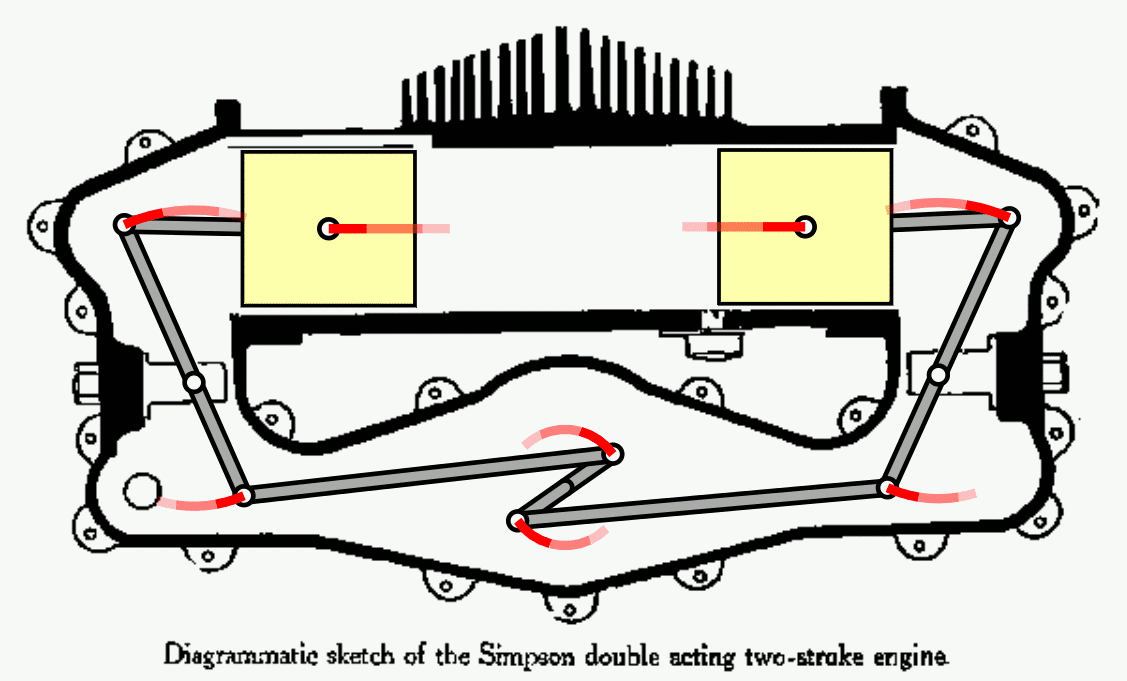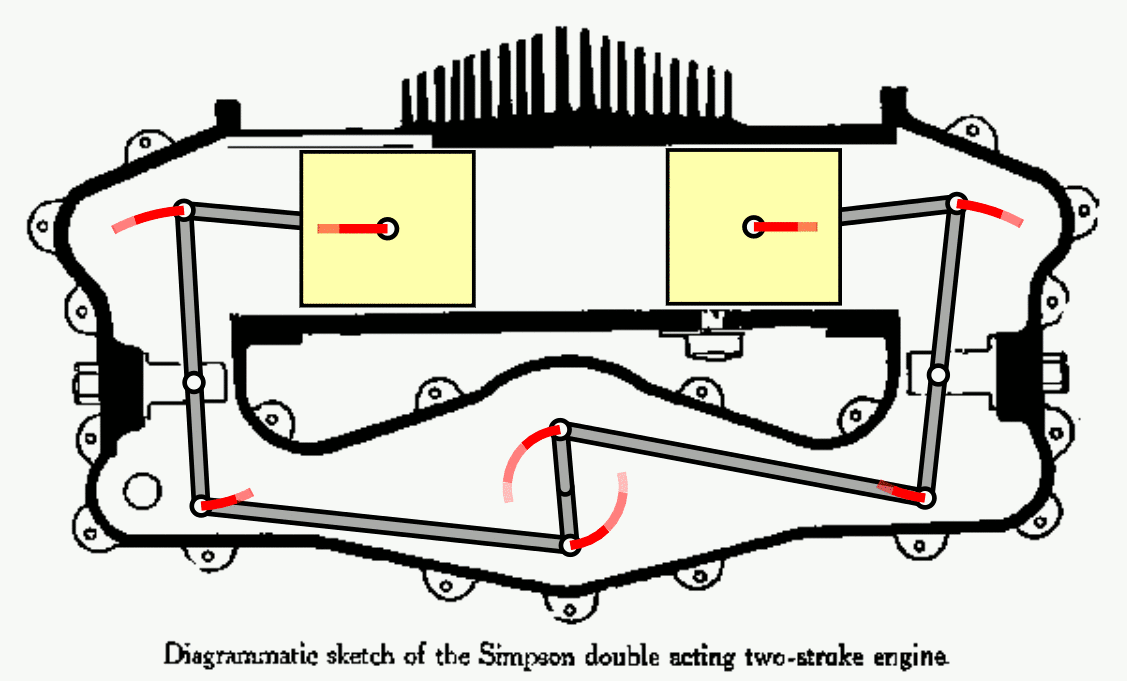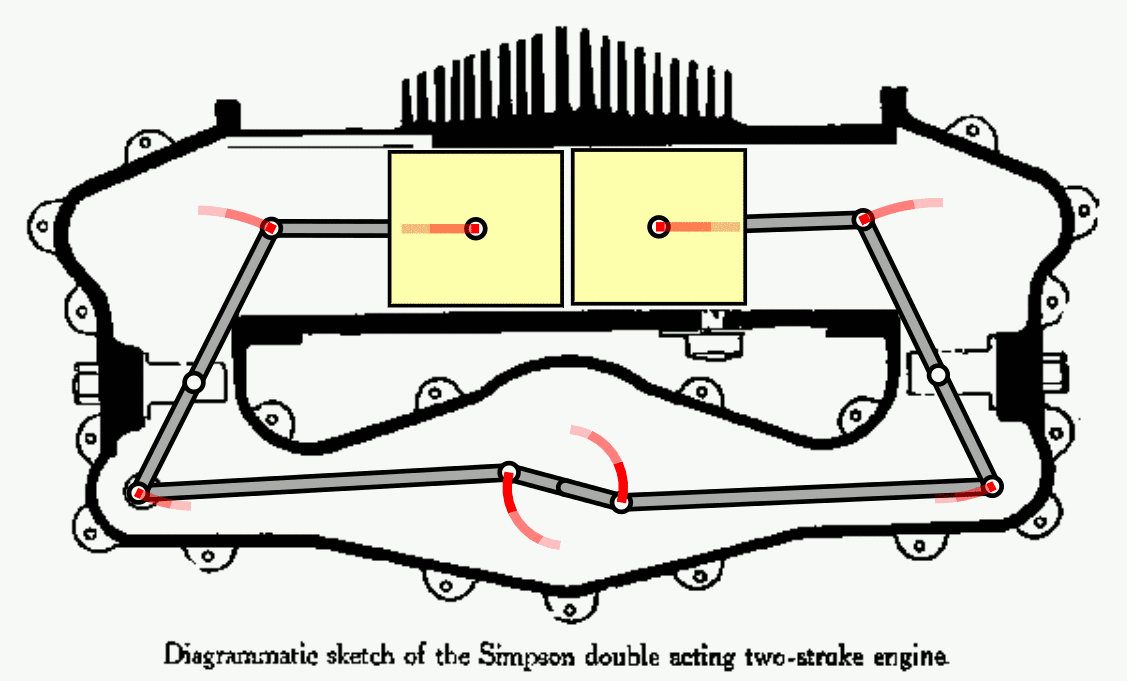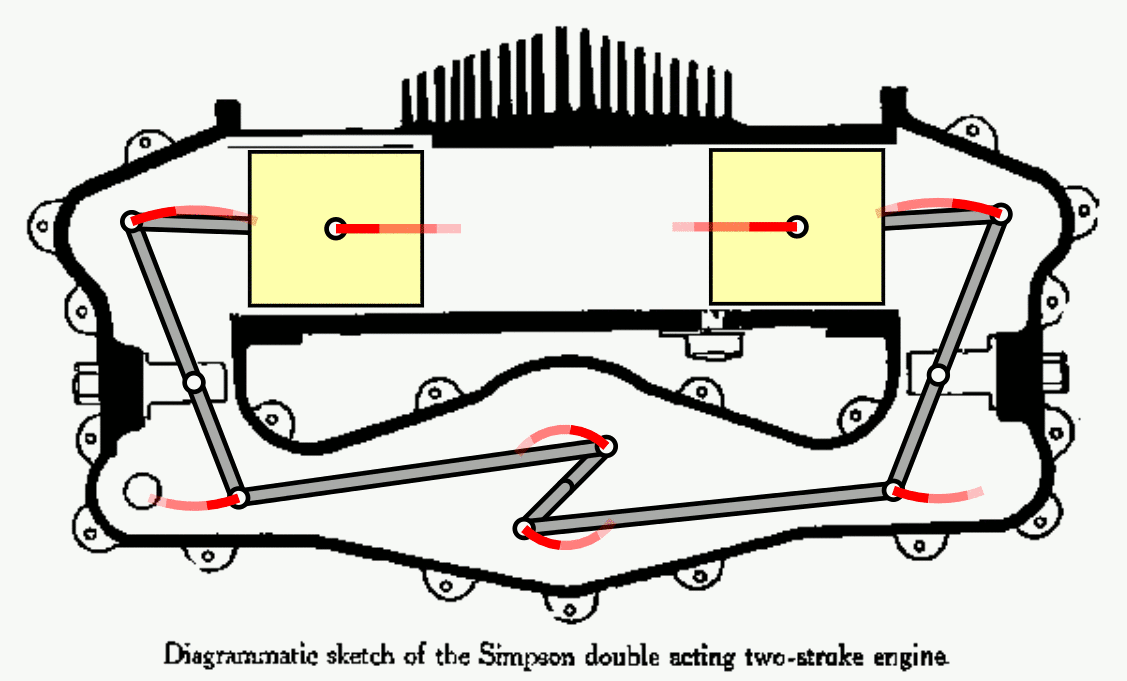
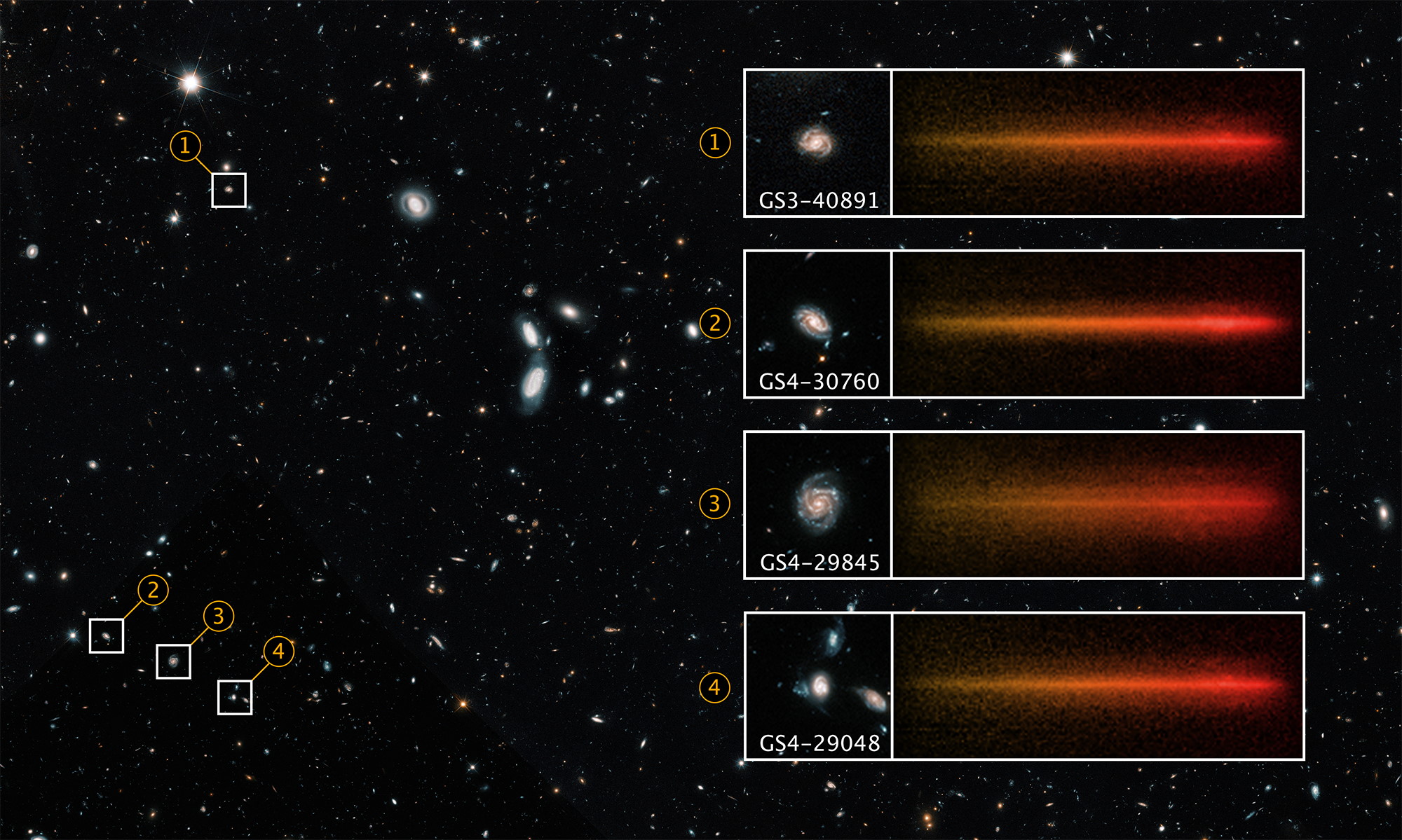
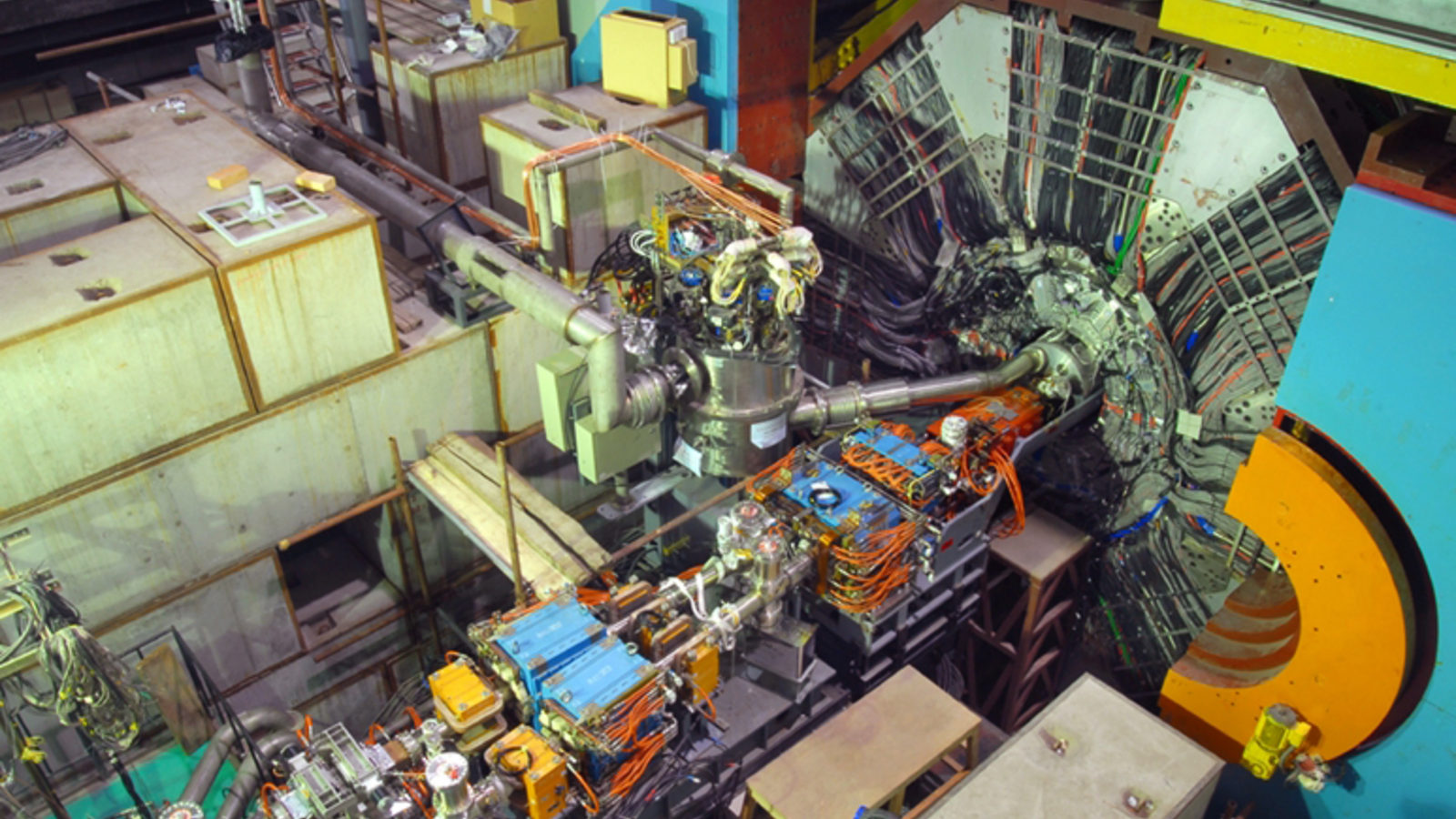
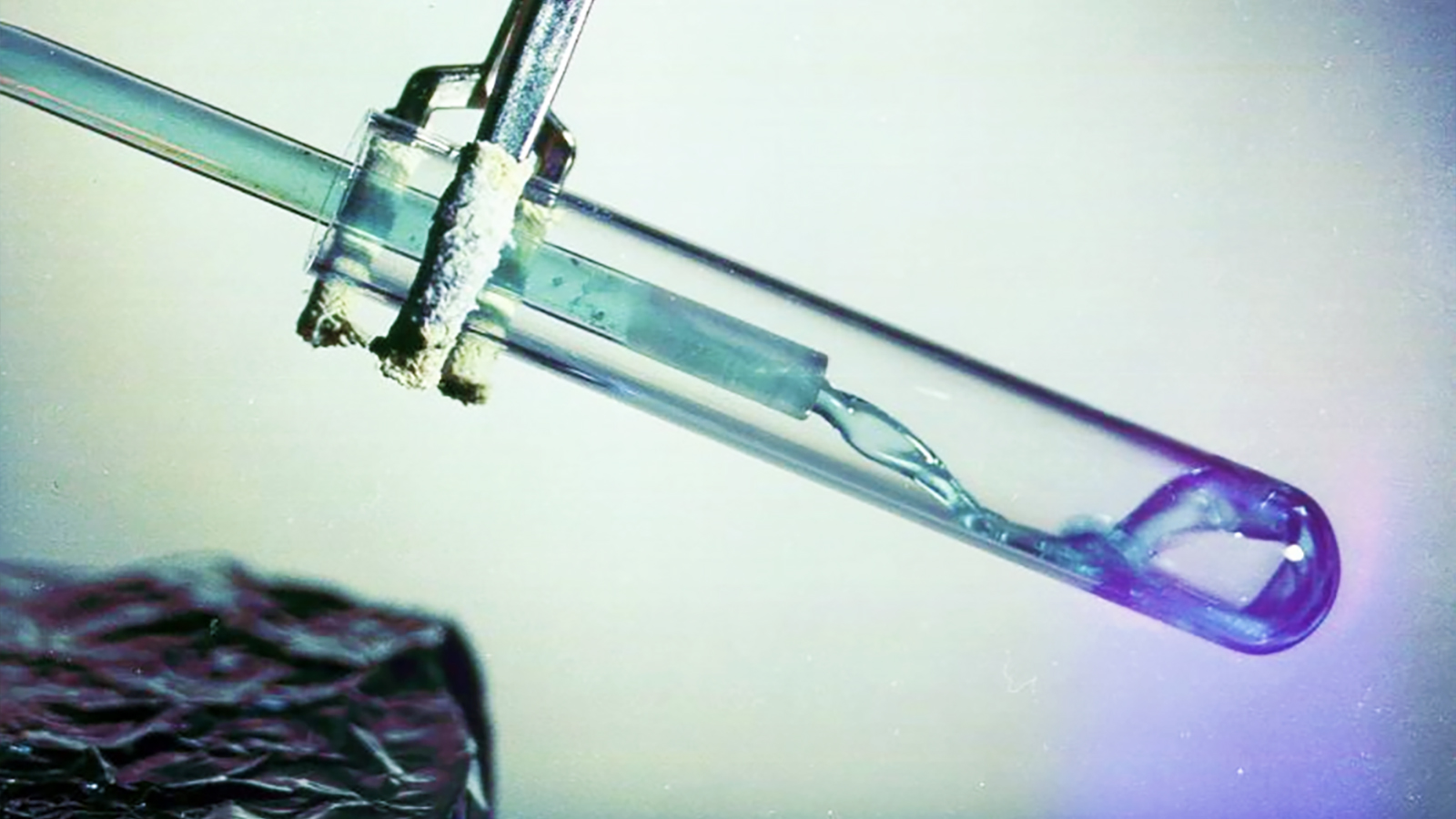
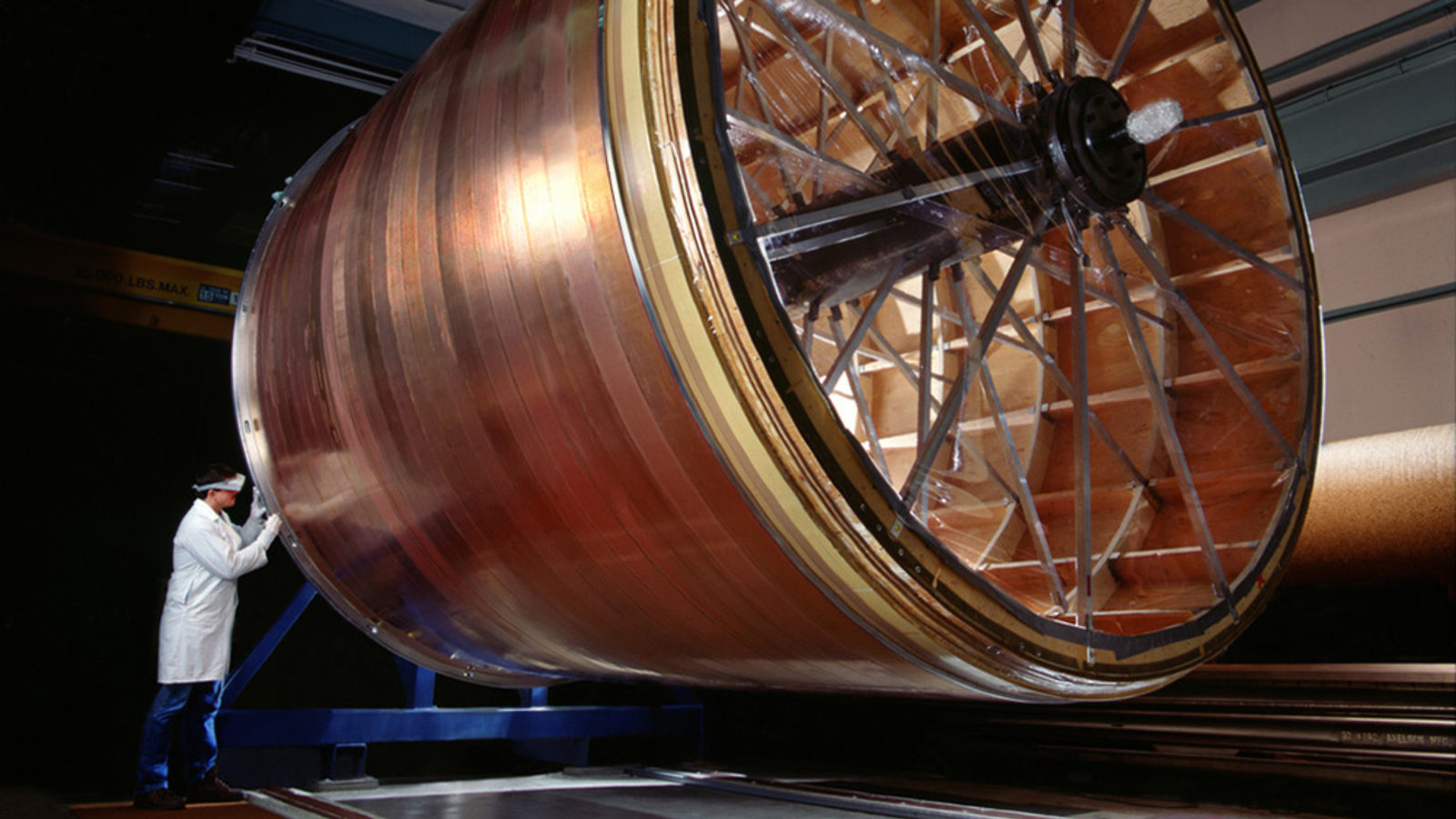
Nuclear fusion has long been seen as the future of energy. As the NIF now passes the breakeven point, how close are we to our ultimate goal?
Search Results
You searched for: energy
The evolution of quantum technology is far from over.
In the 20th century, many options abounded as to our cosmic origins. Today, only the Big Bang survives, thanks to this critical evidence.
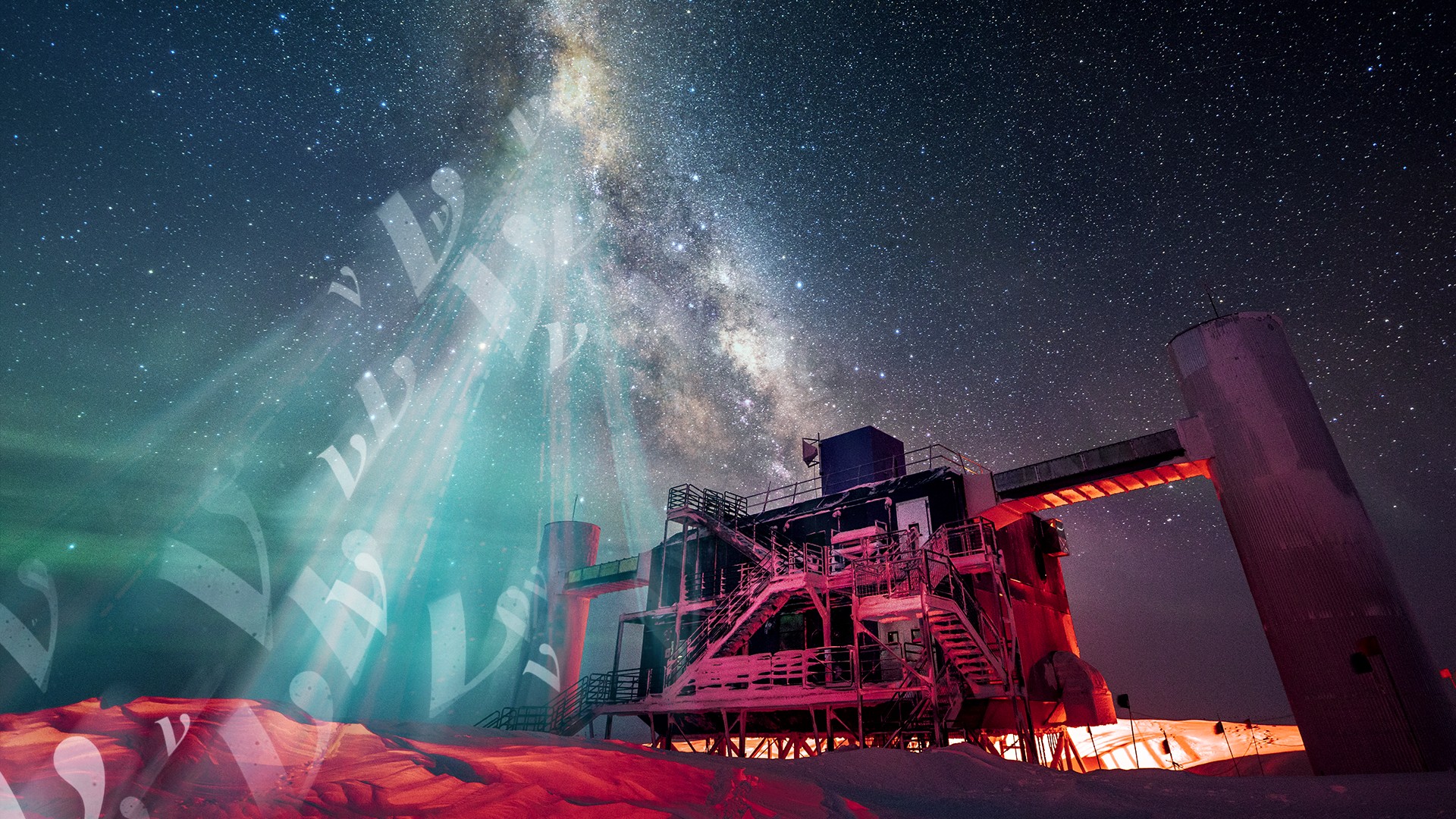
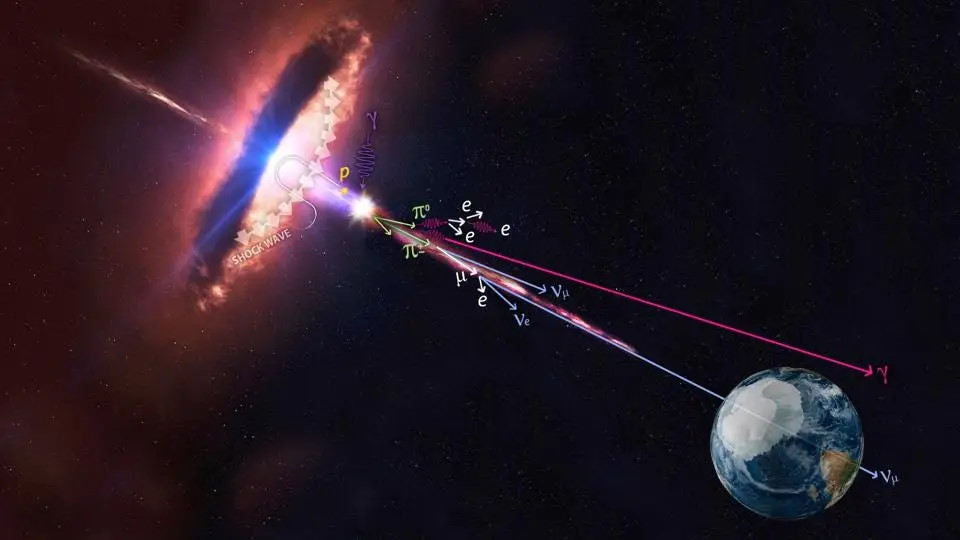
IceCube scientists have detected high-energy tau neutrinos from deep space, suggesting that neutrino transformations occur not only in lab experiments but also over cosmic distances.
Bang bang all over the Universe.
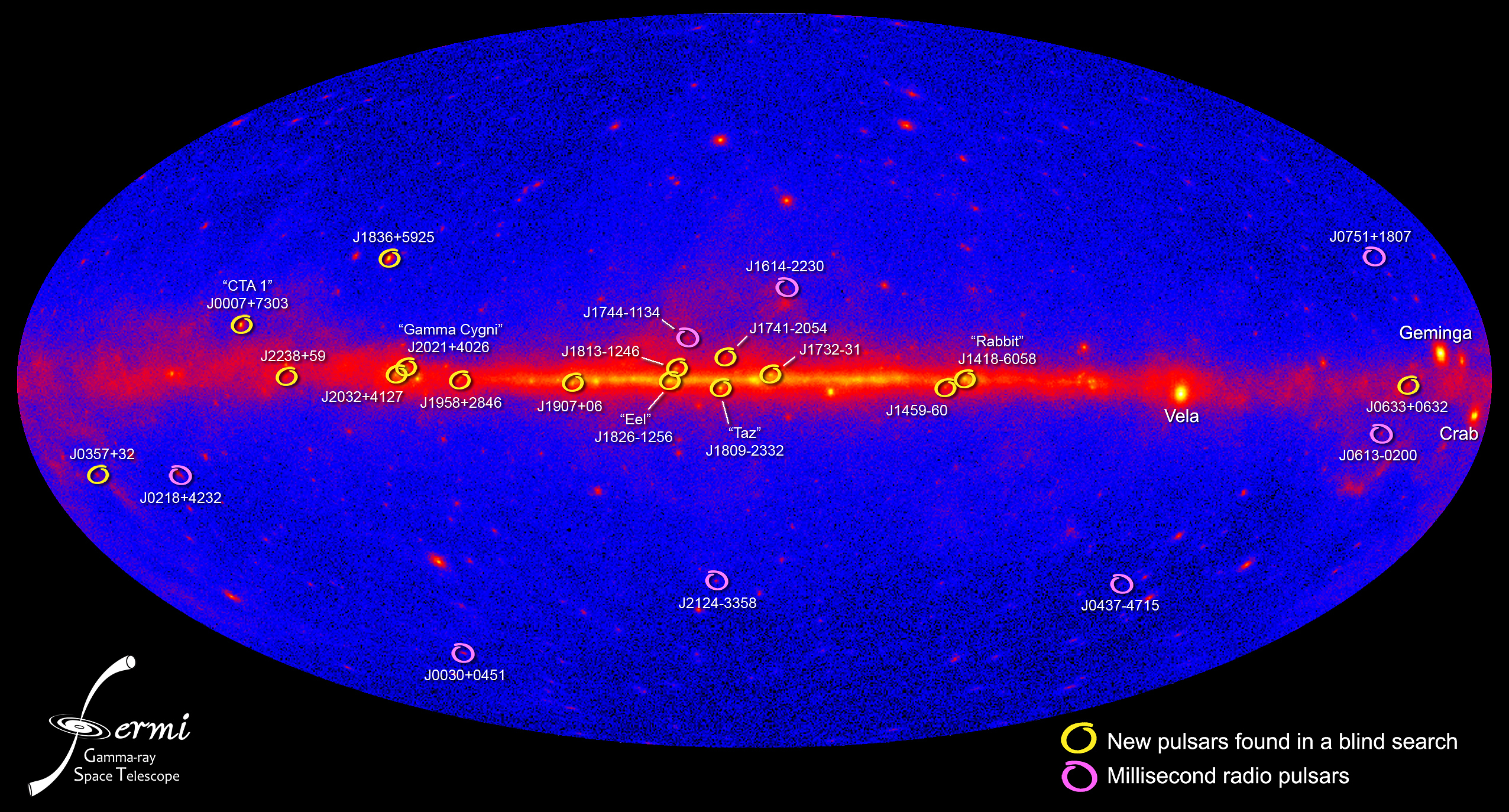
An enormous amount of antimatter is coming from our galactic center. But the culprit probably isn’t dark matter, but merely neutron stars.
When it comes to predicting the energy of empty space, the two leading theories disagree by a factor of 100 googol quintillion.
Across all wavelengths of light, the Sun is brighter than the Moon. Until we went to the highest energies and saw a gamma-ray surprise.
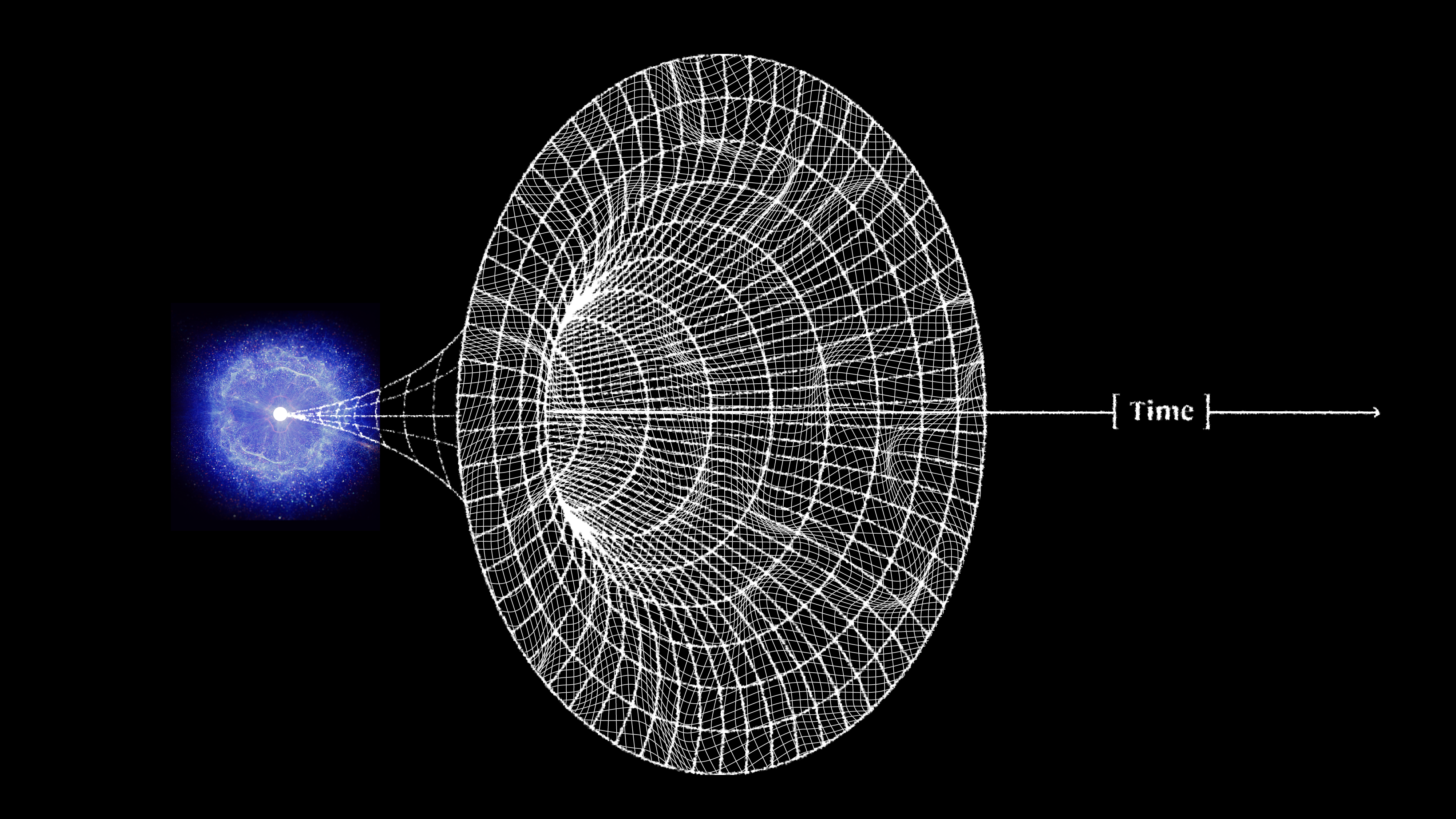
When the hot Big Bang first occurred, the Universe reached a maximum temperature never recreated since. What was it like back then?
Almost everyone asserts that the Big Bang was the beginning of everything, followed by inflation. Has everyone gotten the order wrong?
Within our observable Universe, there’s only one Earth and one “you.” But in a vast multiverse, so much more becomes possible.
Most fundamental constants could be a little larger or smaller, and our Universe would still be similar. But not the mass of the electron.
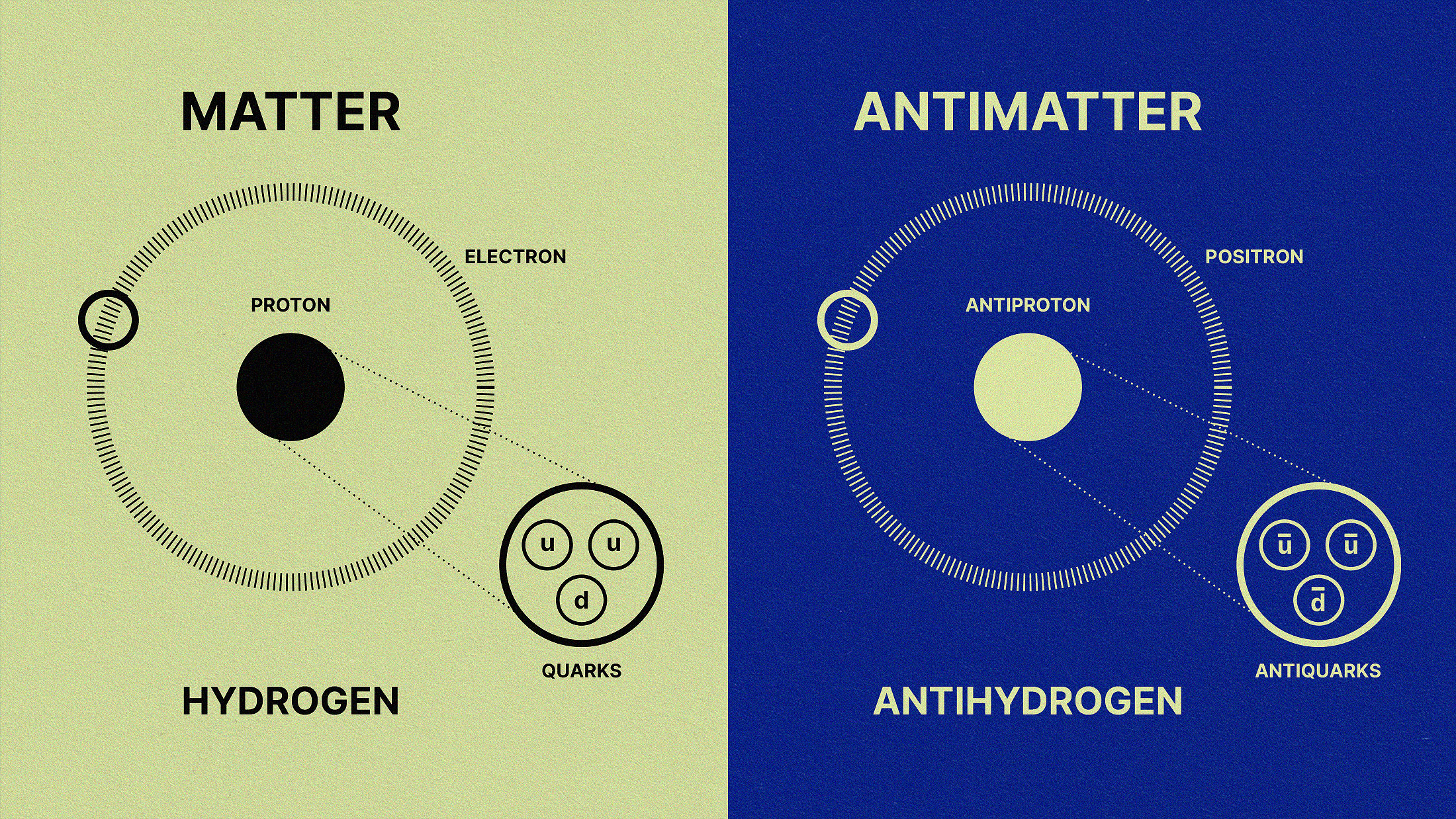
In the earliest stages of the hot Big Bang, equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have existed. Why aren’t they equal today?
The lithium-ion alternatives could help create a safer, greener future.
The observation that everything we know is made out of matter and not antimatter is one of nature’s greatest puzzles. Will we ever solve it?
Our thermodynamic arrow of time explains why the entropy of any isolated system always increases. But it can’t explain what we perceive.
The zero-point energy of empty space is not zero. Even with all the physics we know, we have no idea how to calculate what it ought to be.
There are a wide variety of theoretical studies that call our Standard Model of cosmology into question. Here’s what they really mean.
The last naked-eye Milky Way supernova happened way back in 1604. With today’s detectors, the next one could solve the dark matter mystery.
Our Universe requires dark matter in order to make sense of things, astrophysically. Could massive photons do the trick?
The second law of thermodynamics is an inviolable law of reality. Here’s what everyone should know about closed, open, and isolated systems.
Time is relative, not absolute, as gravity and motion both cause time to dilate. Your head and feet, therefore, don’t age at the same rate.
It would get rid of our hazardous, radioactive, and pollutive waste for good, but physics tells us it’s a losing strategy for elimination.
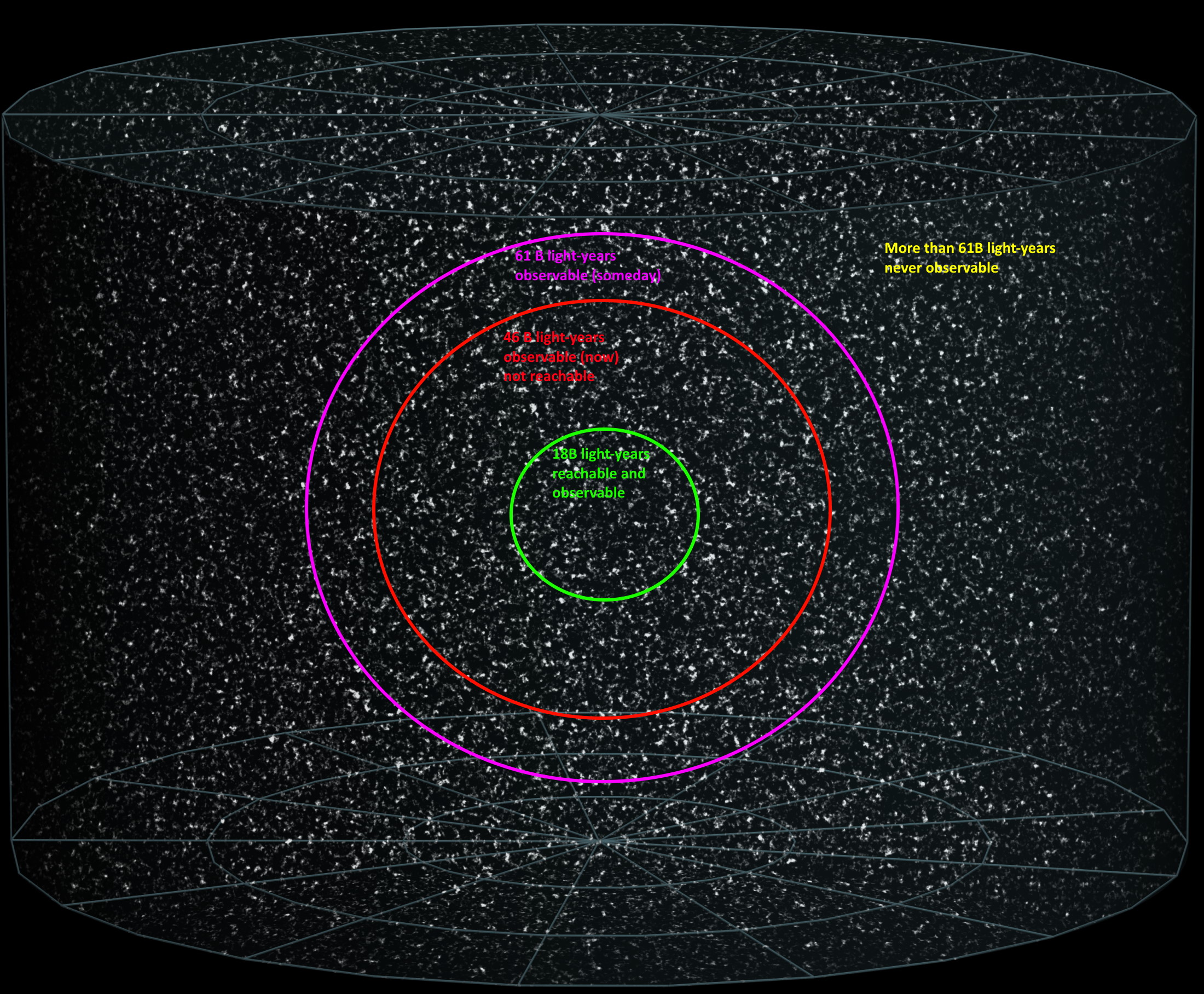
Because of dark energy, distant objects speed away from us faster and faster as time goes on. How long before every galaxy is out of reach?
The mass that gravitates and the mass that resists motion are, somehow, the same mass. But even Einstein didn’t know why this is so.
Scientific surprises, driven by experiment, are often how science advances. But more often than not, they’re just bad science.
They are expected to be cheaper to build and even more reliable than today’s nuclear plants.
Traveling back in time is a staple of science fiction movies. But according to Einstein, it’s a physical possibility that’s truly allowed.
Dark matter’s hallmark is that it gravitates, but shows no sign of interacting under any other force. Does that mean we’ll never detect it?
Measurements of the acceleration of the universe don’t agree, stumping physicists working to understand the cosmic past and future. A new proposal seeks to better align these estimates — and is likely testable.