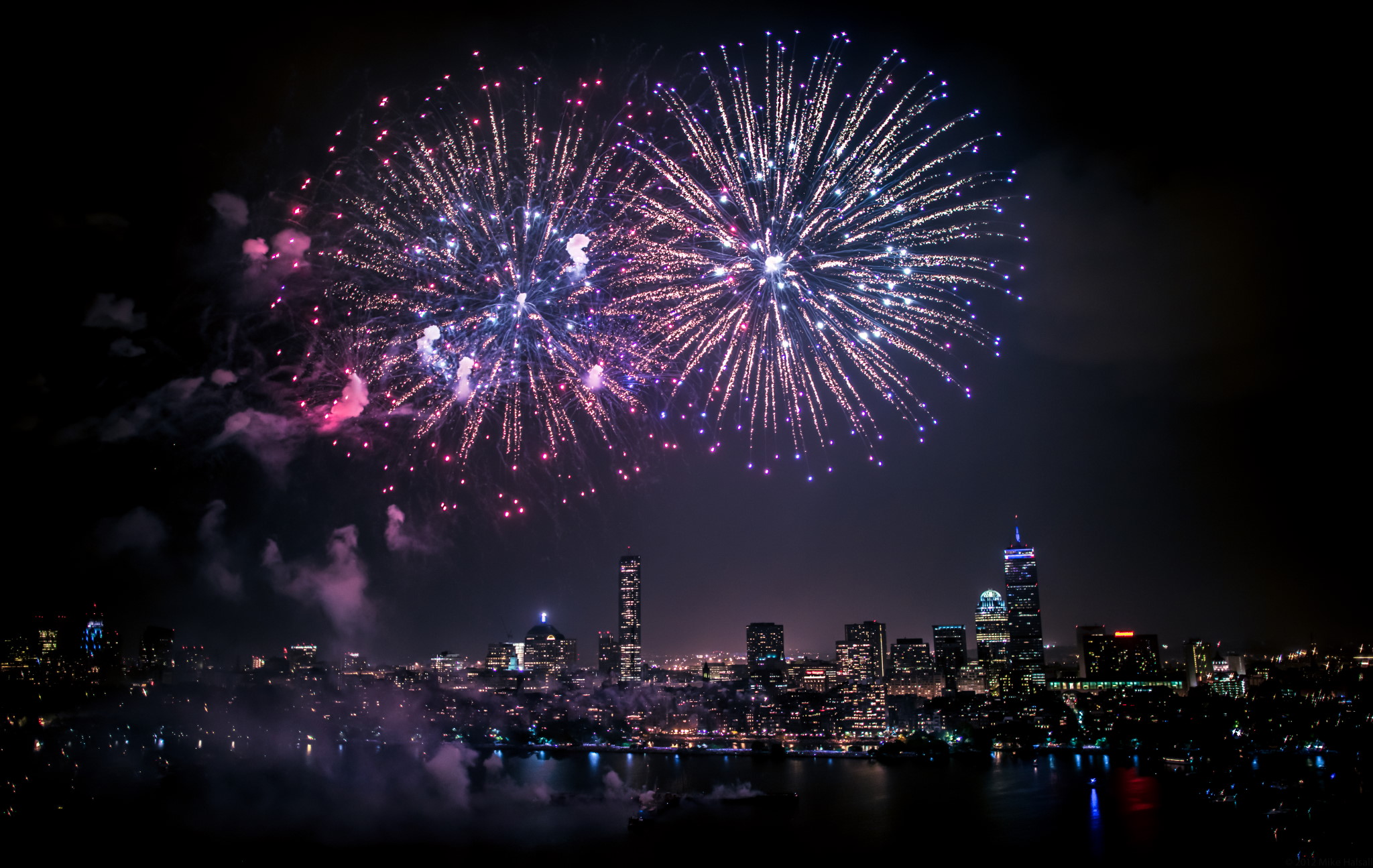
The biggest nuclear blast in history came courtesy of Tsar Bomba. We could make something at least 100 times more powerful.
Search Results
You searched for: energy
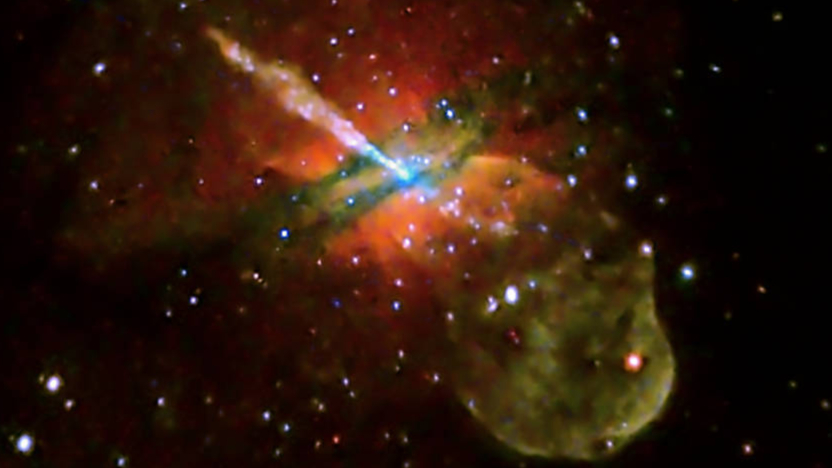
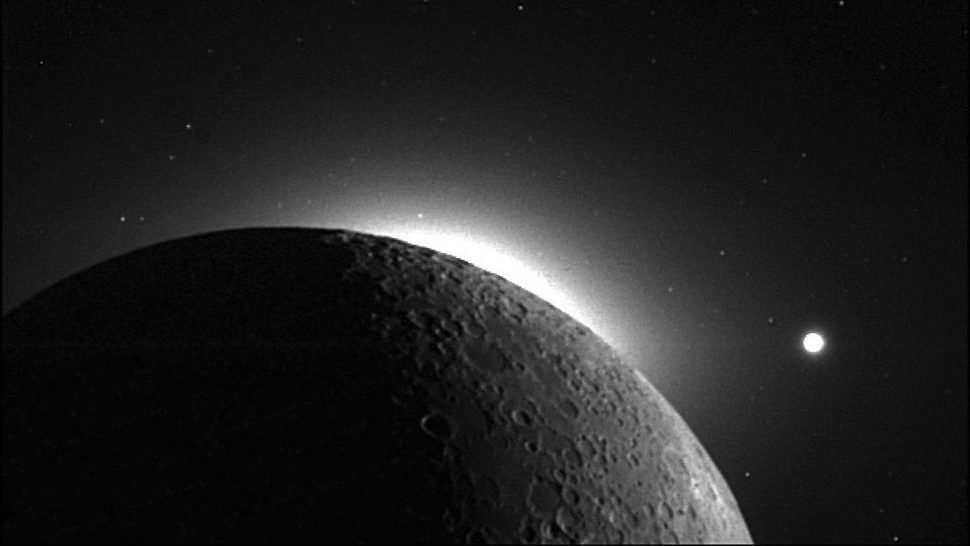
Here in our Universe, stars shine brightly, providing light and heat to planets, moons, and more. But some objects get even hotter, by far.
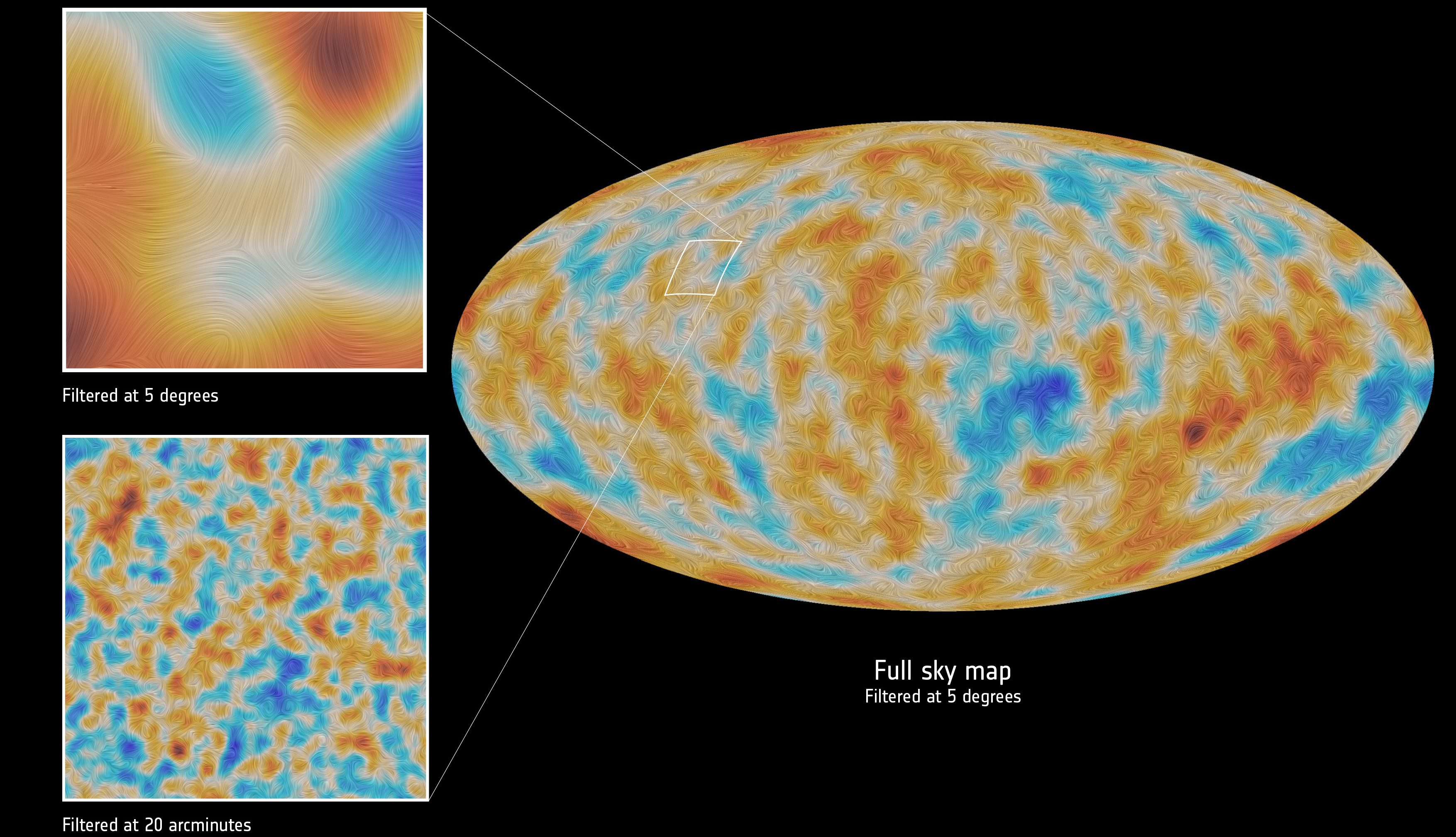
Although the Big Bang occurred at an instant in time long ago, we still see the light from it. Will the evidence ever disappear completely?
How (not) to end up in the ash heap of history.
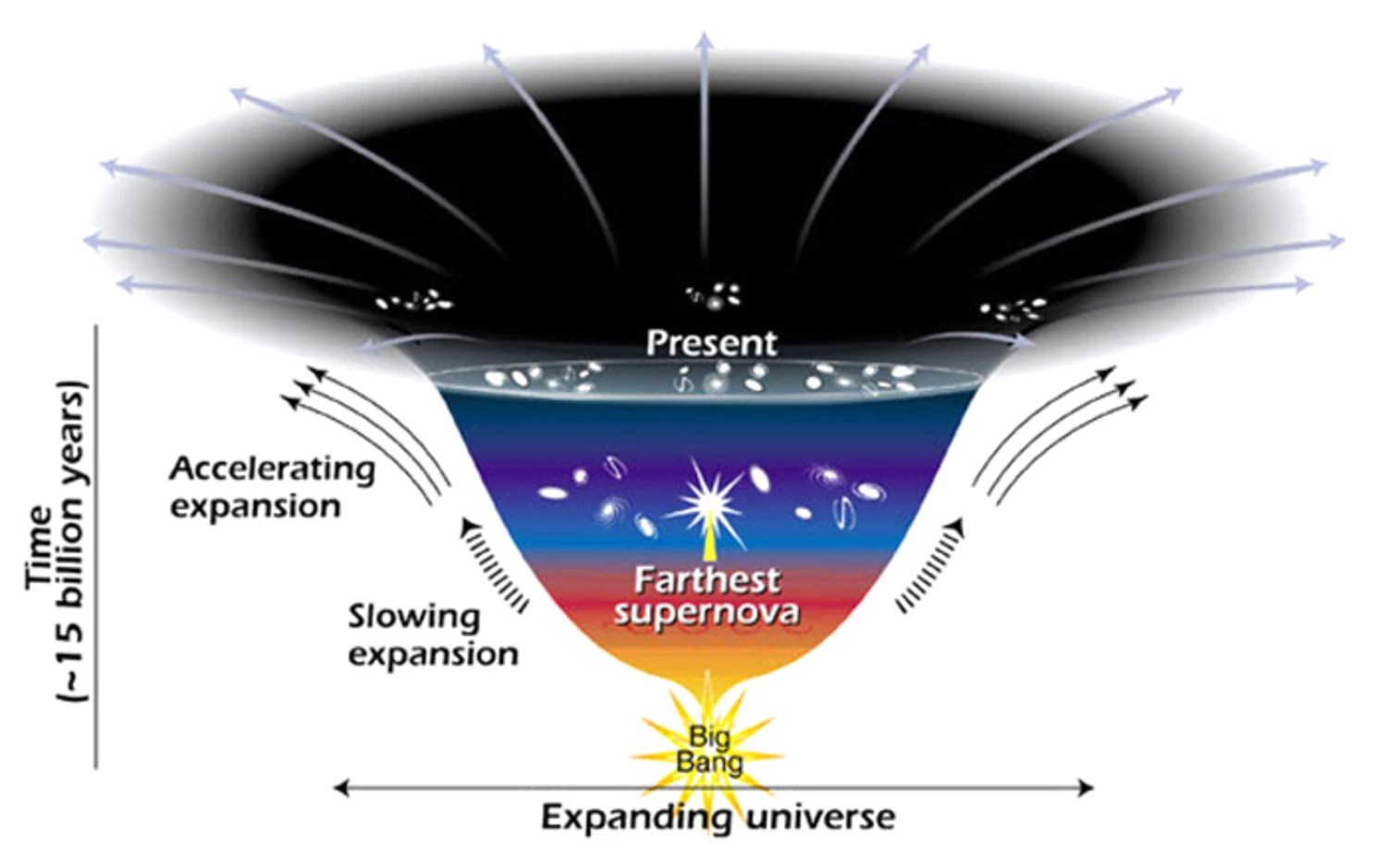
As time goes on, dark energy makes distant galaxies recede from us ever faster in our expanding Universe. But nothing truly disappears.
His grandfather, a member of Oppenheimer’s atomic bomb team, foresaw the potential of nuclear energy to power cities — not destroy them.
In a recent paper, biologists outlined a three-part hypothesis for how all life as we know it began.
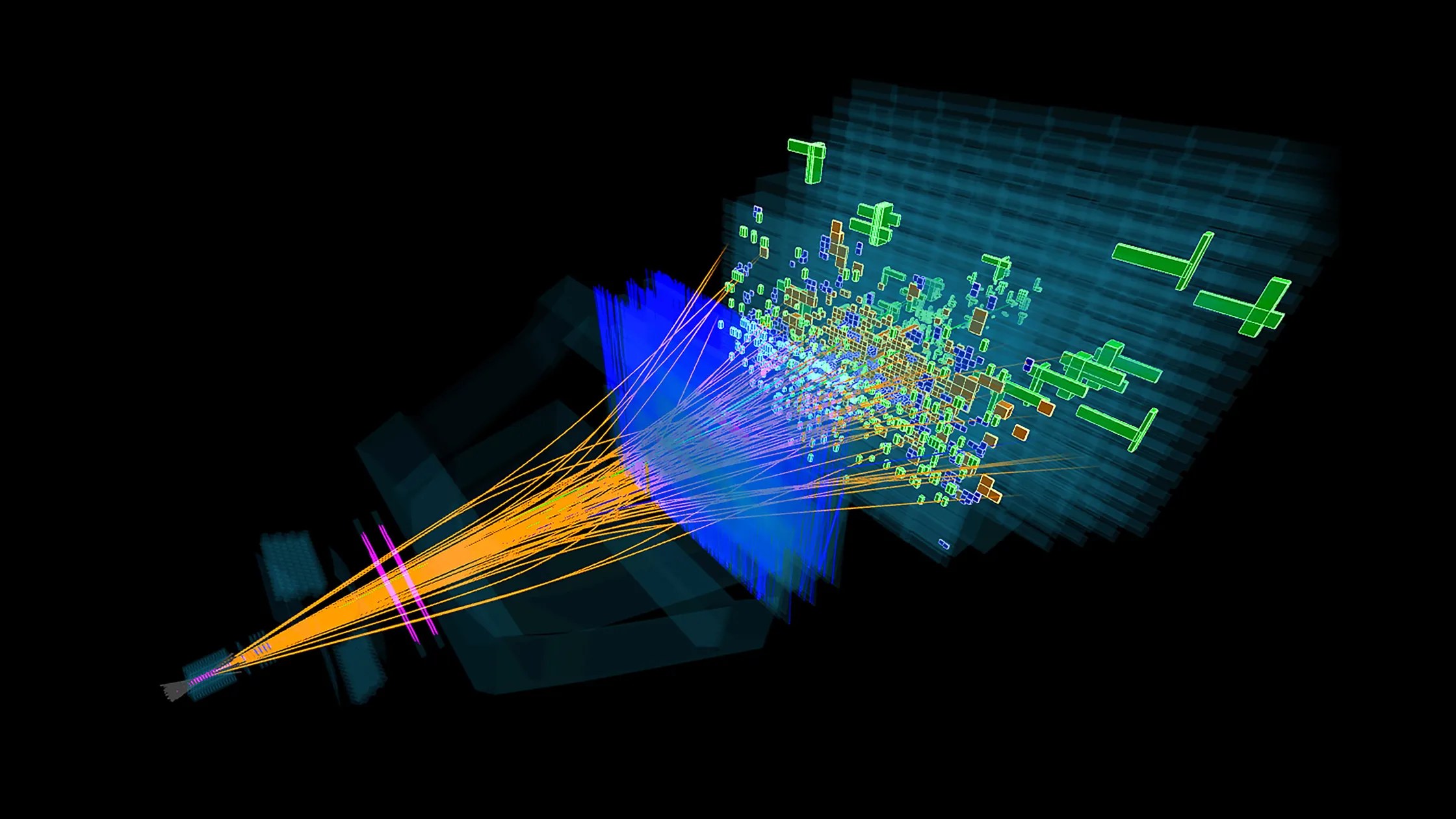
In the infant Universe, particle physics reigned supreme.
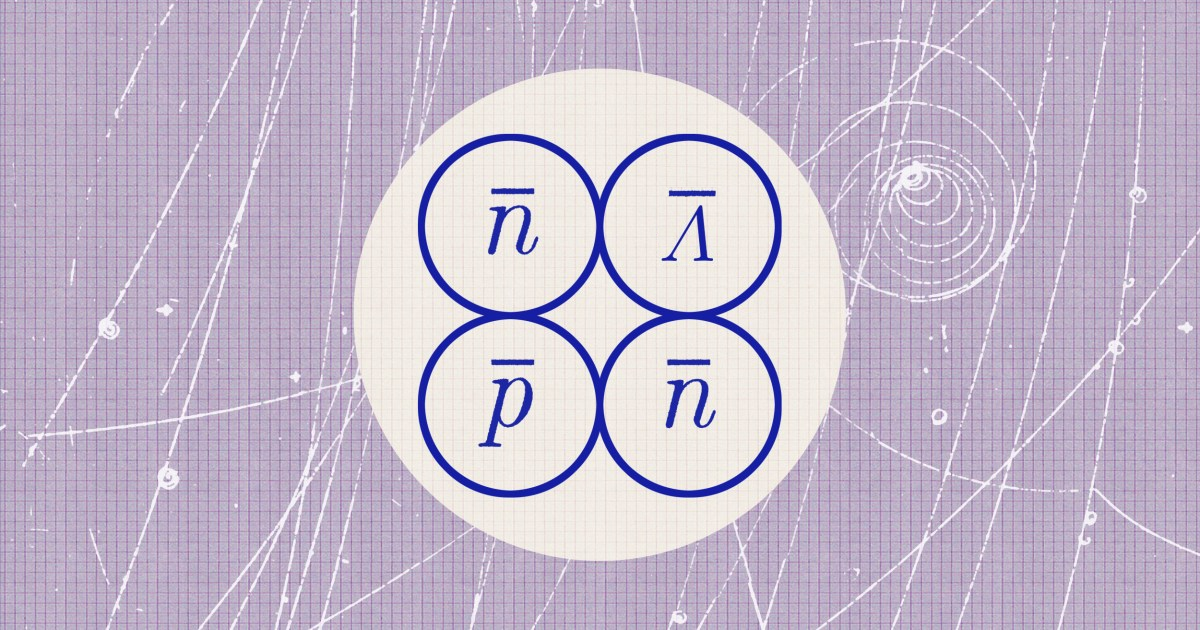
Researchers at the Brookhaven National Laboratory recently created the heaviest exotic antimatter hypernucleus ever observed.
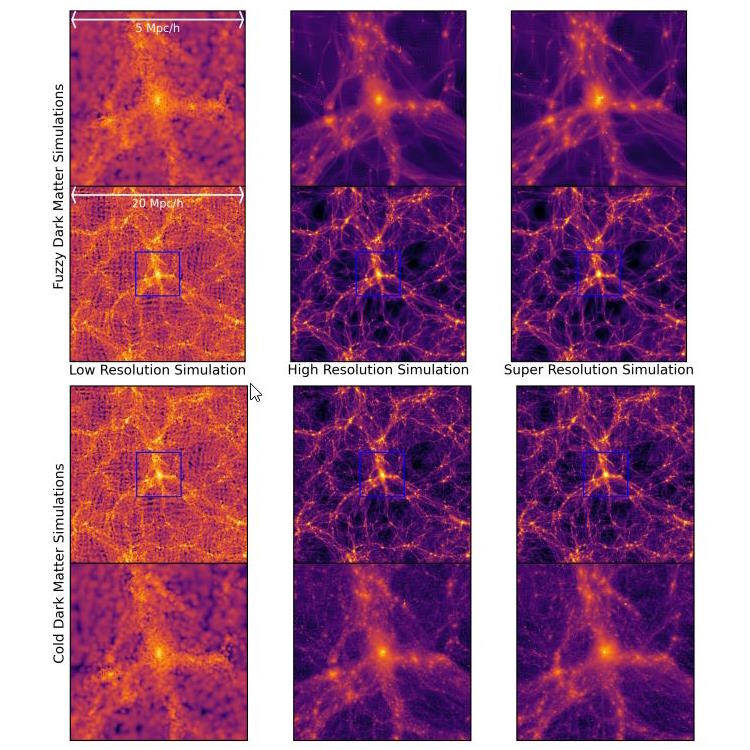
In a far-reaching discovery with astrophysicist Karolina Garcia, we discuss what’s in the Universe and how it grew up.
Welcome to The Nightcrawler — a weekly newsletter from Eric Markowitz covering tech, innovation, and long-term thinking.
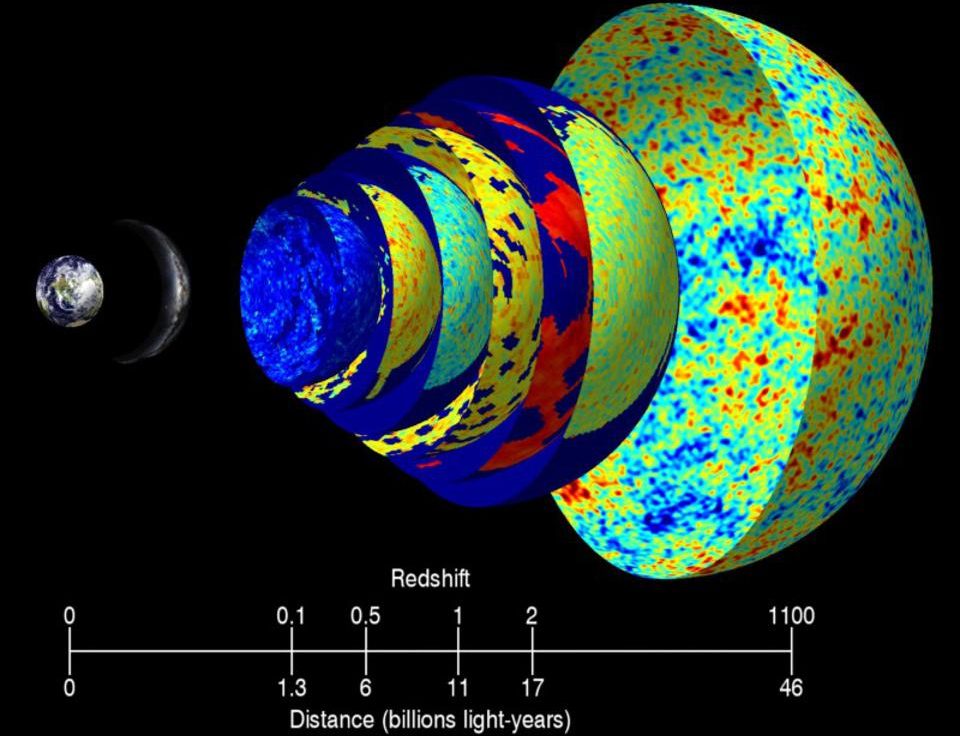
Just 13.8 billion years after the hot Big Bang, we can see objects up to 46.1 billion light-years away. No, this doesn’t violate relativity.
The conservation of energy is one of the most fundamental laws governing our reality. But in the expanding Universe, that’s just not true.
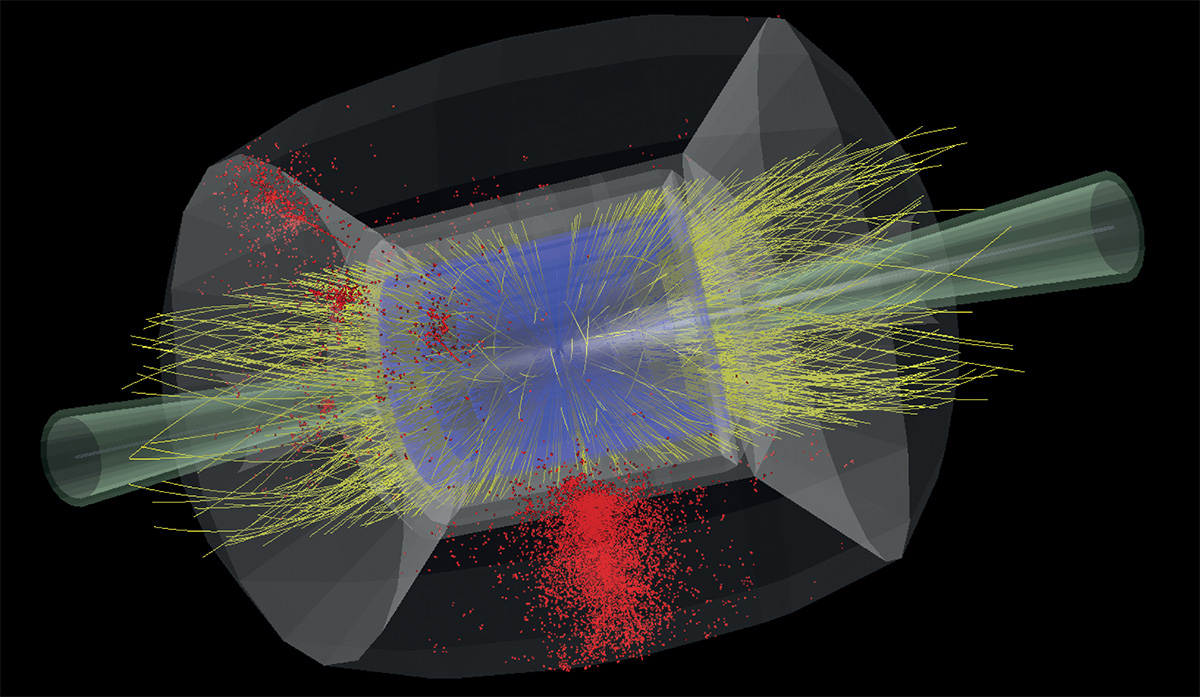
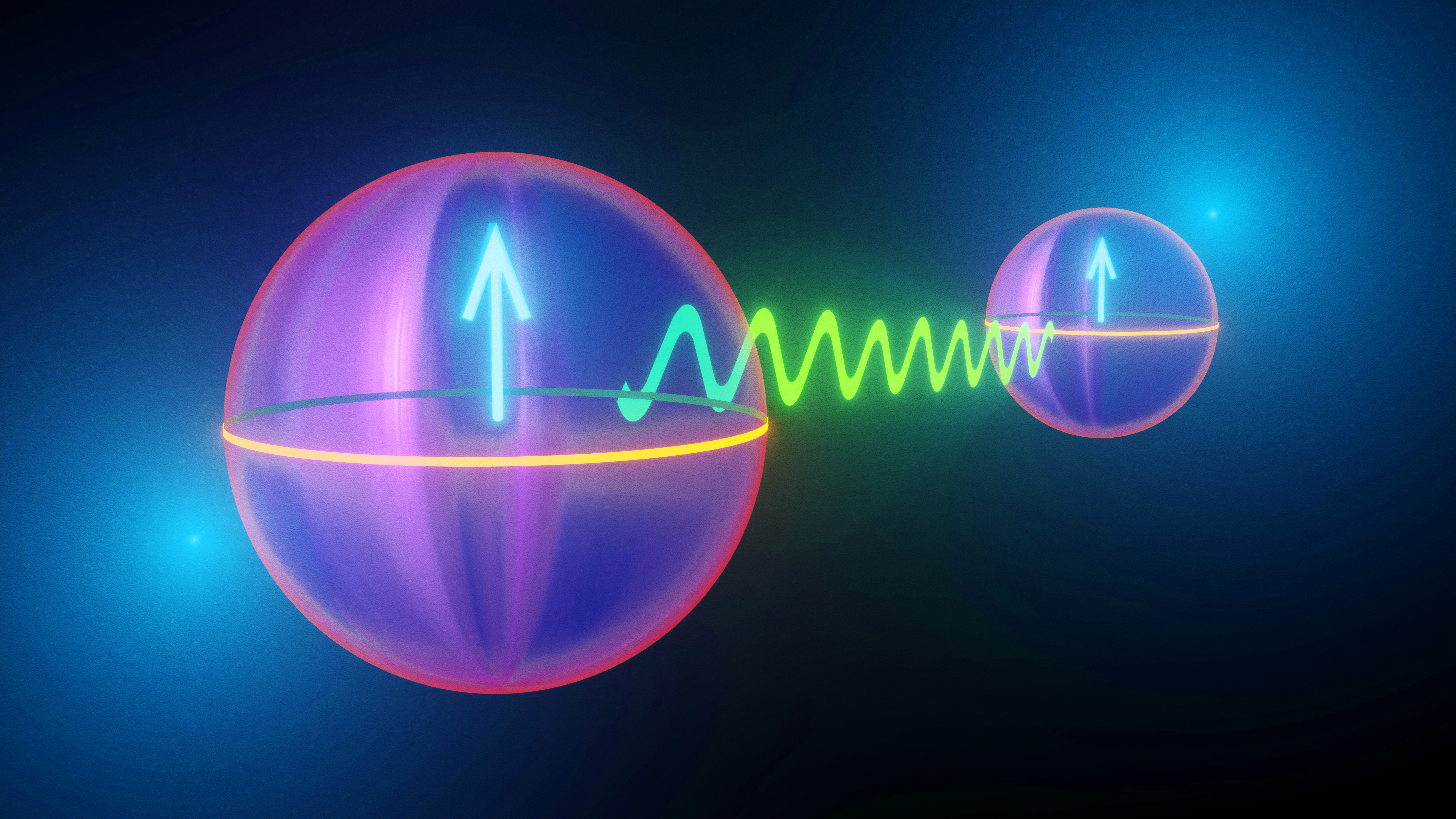
We have very specific predictions for how particles ought to decay. When we look at B-mesons all together, something vital doesn’t add up.
If you eat a diet full of refined grains, high-sugar drinks, and sweets, there’s a good chance you have too much insulin.
Today, the Large Hadron Collider is the most powerful particle physics experiment in history. What would a new, successor collider teach us?
If nature were perfectly deterministic, atoms would almost instantly all collapse. Here’s how Heisenberg uncertainty saves the atom.
From the explosions themselves to their unique and vibrant colors, the fireworks displays we adore require quantum physics.
In general relativity, white holes are just as mathematically plausible as black holes. Black holes are real; what about white holes?
The future belongs to complexity.
Since the mid-1960s, the CMB has been identified with the Big Bang’s leftover glow. Could any alternative explanations still work?
In many ways, it was worse than Chernobyl.
There was a lot of hype and a lot of nonsense, but also some profoundly major advances. Here are the biggest ones you may have missed.
Smarter building materials can control indoor temperatures without external power.
To know how to protect its astronauts, NASA needs to first understand the threat.
Earth, the only rocky planet with a large, massive satellite, is greatly affected by the Moon. Destroying it would cause 7 major changes.
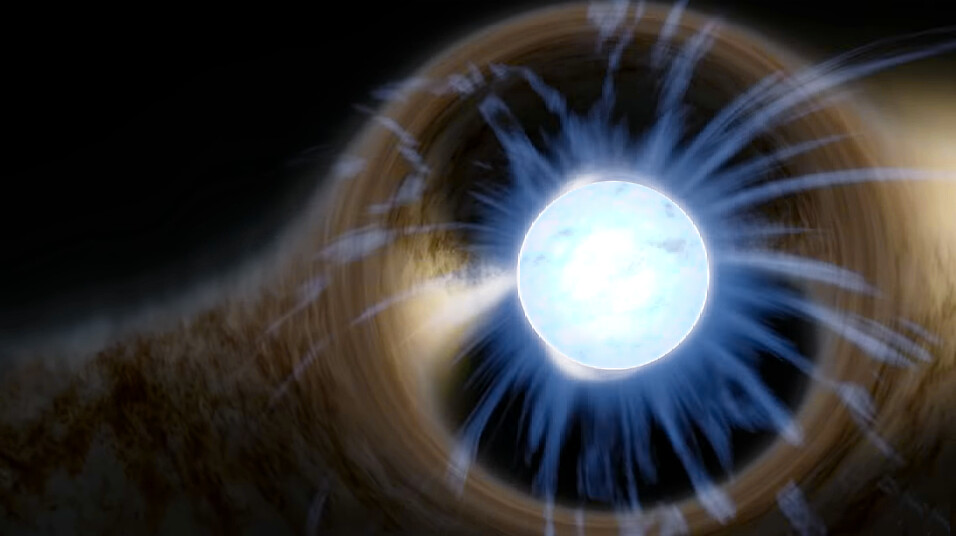
Neutrons can be stable when bound into an atomic nucleus, but free neutrons decay away in mere minutes. So how are neutron stars stable?
NASA’s only flagship X-ray telescope ever, Chandra, still works and has no planned successor. So why does the President want to kill it?
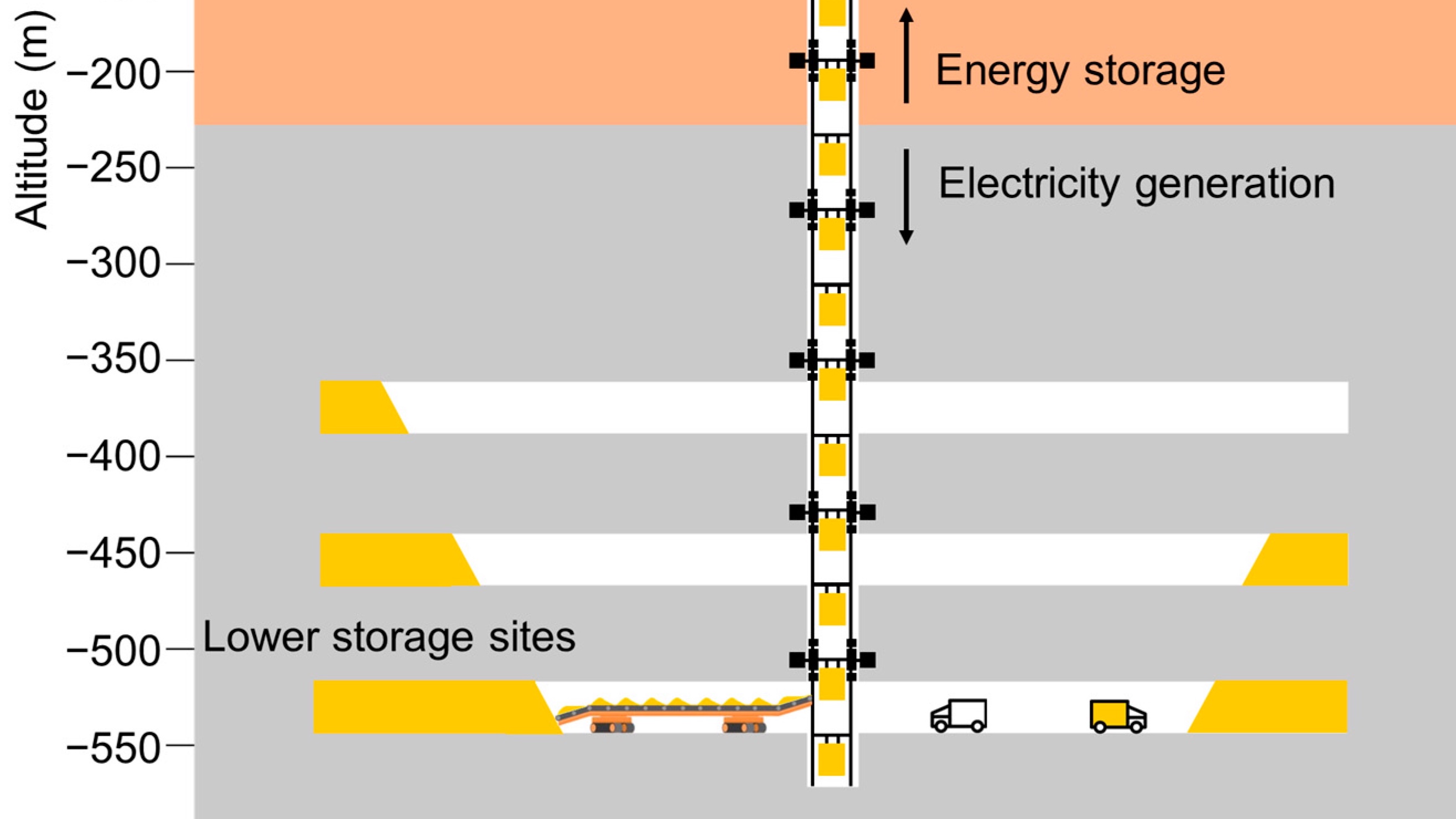
Old coal mines can be converted into “gravity batteries” by retrofitting them with equipment that raises and lowers giant piles of sand.
Practically all of the matter we see and interact with is made of atoms, which are mostly empty space. Then why is reality so… solid?