Surprising Science
All Stories
A new study on virtual embodiment explores the “surprising plasticity of the brain’s body representation,” and suggests that virtual reality representations can improve cognition.
As temperatures rise, your brain’s processing power declines.
NASA recorded an interplanetary exchange. And it sounds not entirely unlike the beginning to a certain Daft Punk song.
For millions of years, this popular color dominated the world.
Animal extinction is, after all, inevitable in the natural world — some have even called it the “engine of evolution”. So why should extinction matter to us?
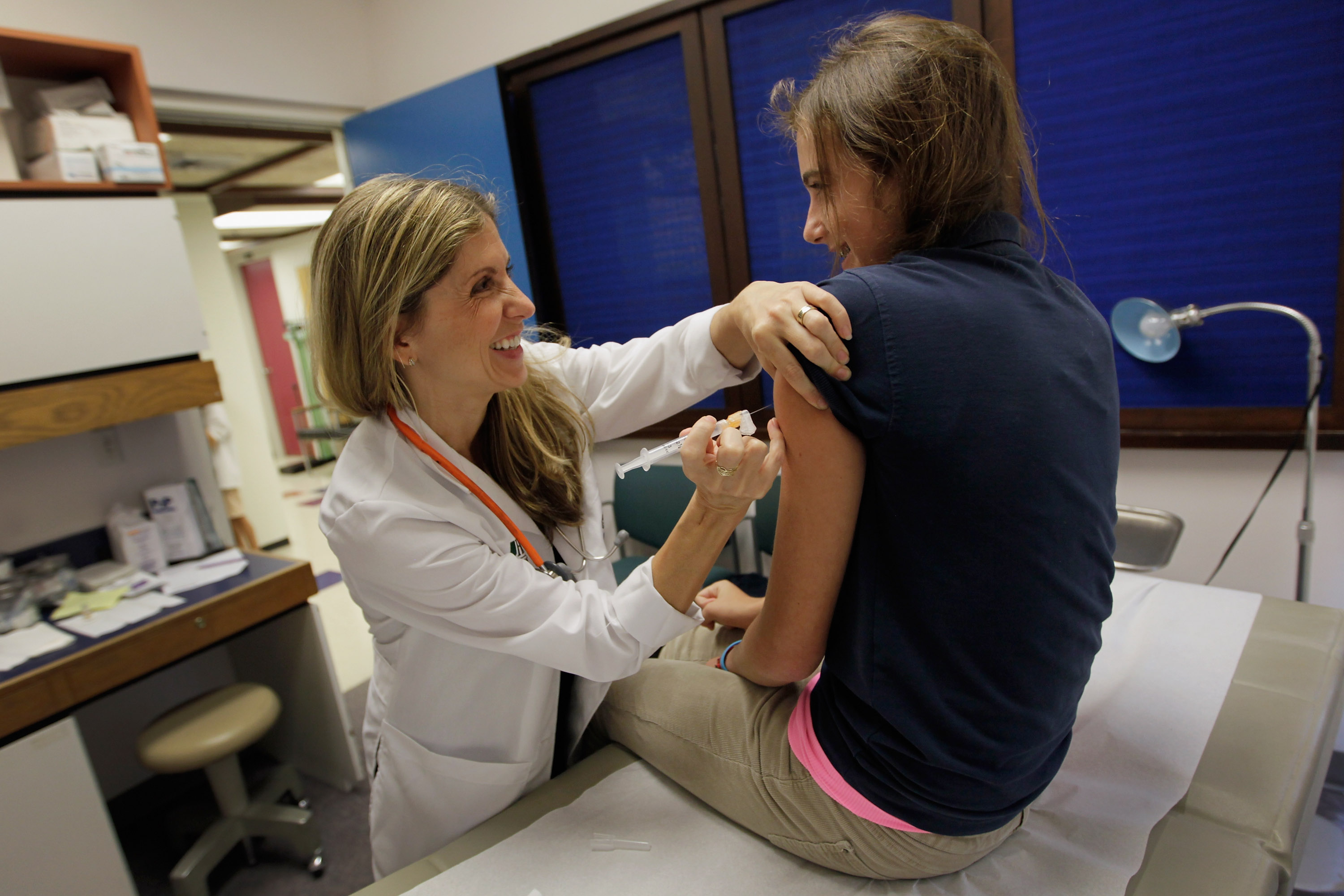
There is a reason why anti-vaxx attitudes are hard to shake, explains a new study.
When crows and ravens fight, it’s the smaller crows being the aggressor about 97% of the time. It may be them being protective of their nest or it may be competition, but ravens are the ones being bullied.
But there were some serious oversights.
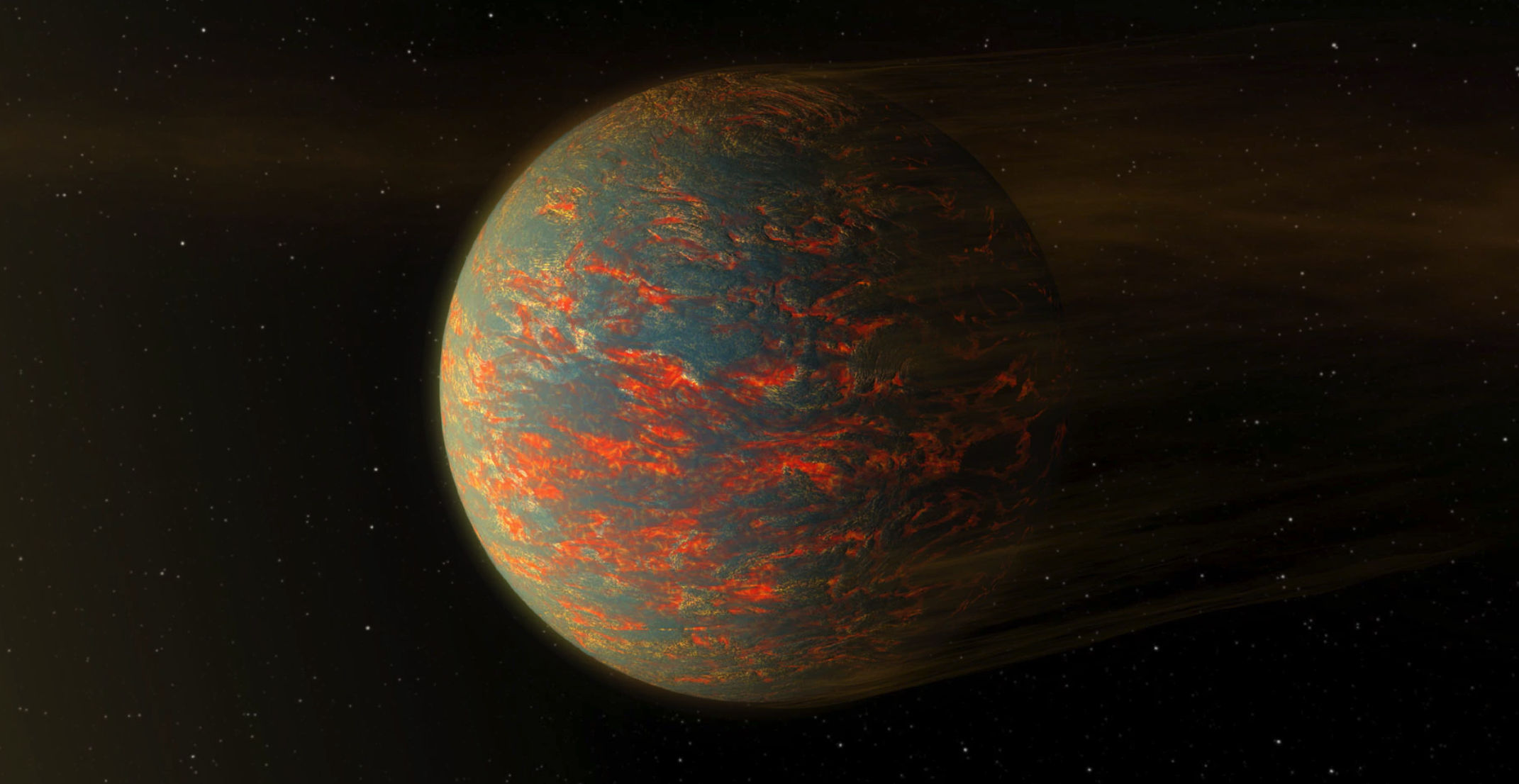
Bright pink? Lava? Liquid planets that could hold water? Some far-out planets are truly… out of this world.
The quest to find another Earth may be in vain.
Researchers study wolves in the area contaminated by the Chernobyl nuclear disaster and what happens when they leave.
An even better reason to eschew alpha-male office culture.
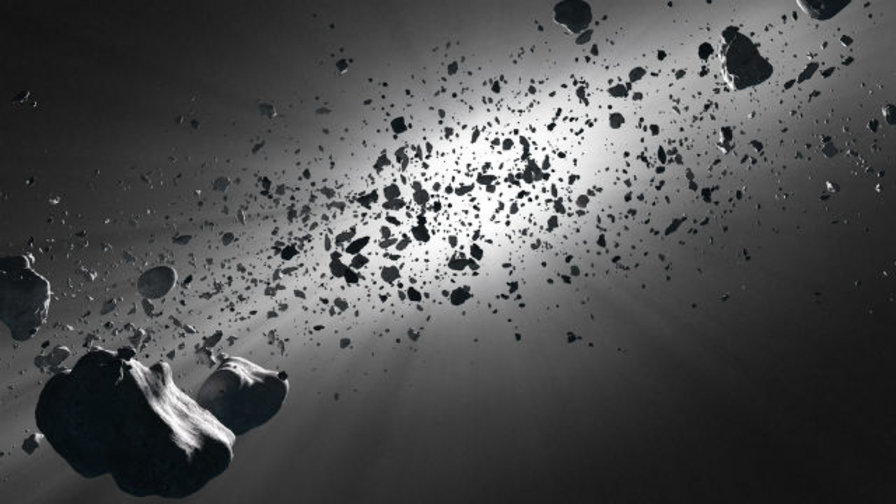
There are millions of asteroids in the solar system. A new study might tell us where they came from.
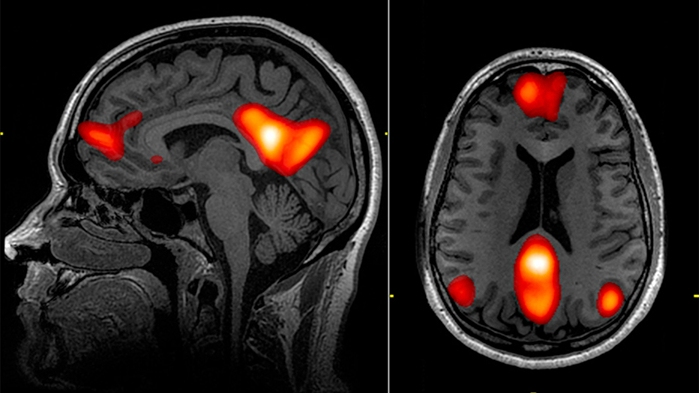
Psychopathy is a “wildly misunderstood corner of mental health research,” according to the author of a new study on psychopathy and attention mechanisms in the brain.
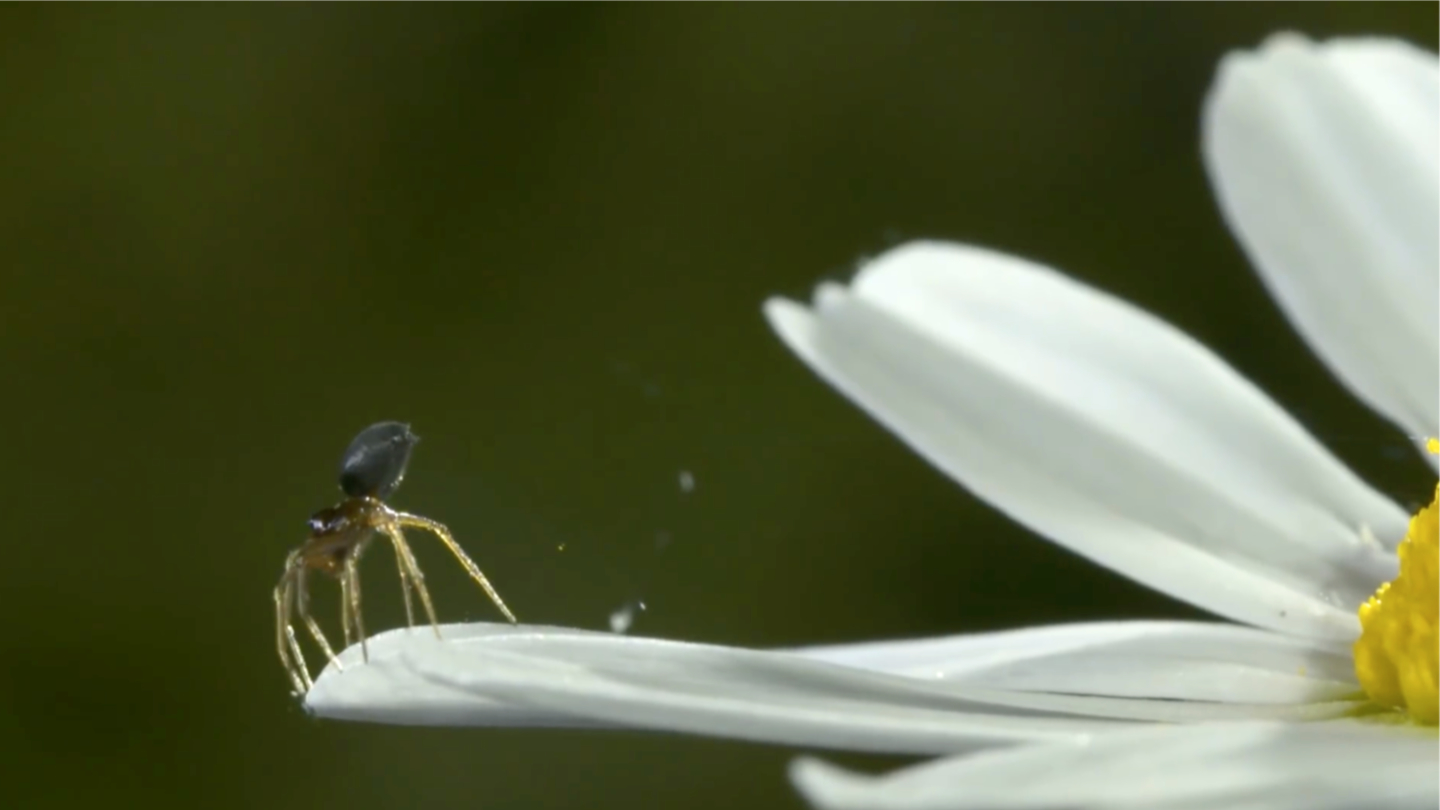
Biologists at the University of Bristol demonstrate how the mysterious phenomenon of spider ballooning for great distances and at great heights works.
Rates of centenarians are going to increase eightfold in the next three decades.
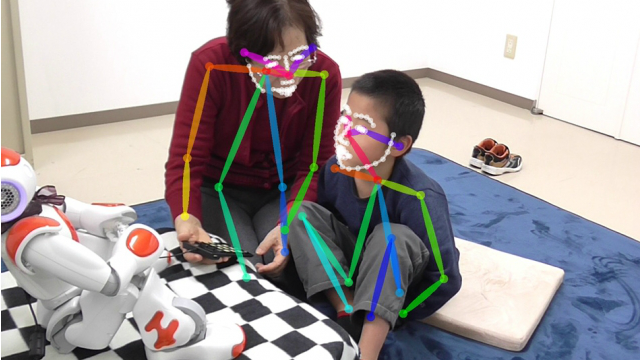
A child-friendly robot demonstrates human emotions and engages children with autism in responding appropriately. MIT researchers have now developed a type of personalized machine learning that helps robots estimate the engagement and interest of each child during these interactions.
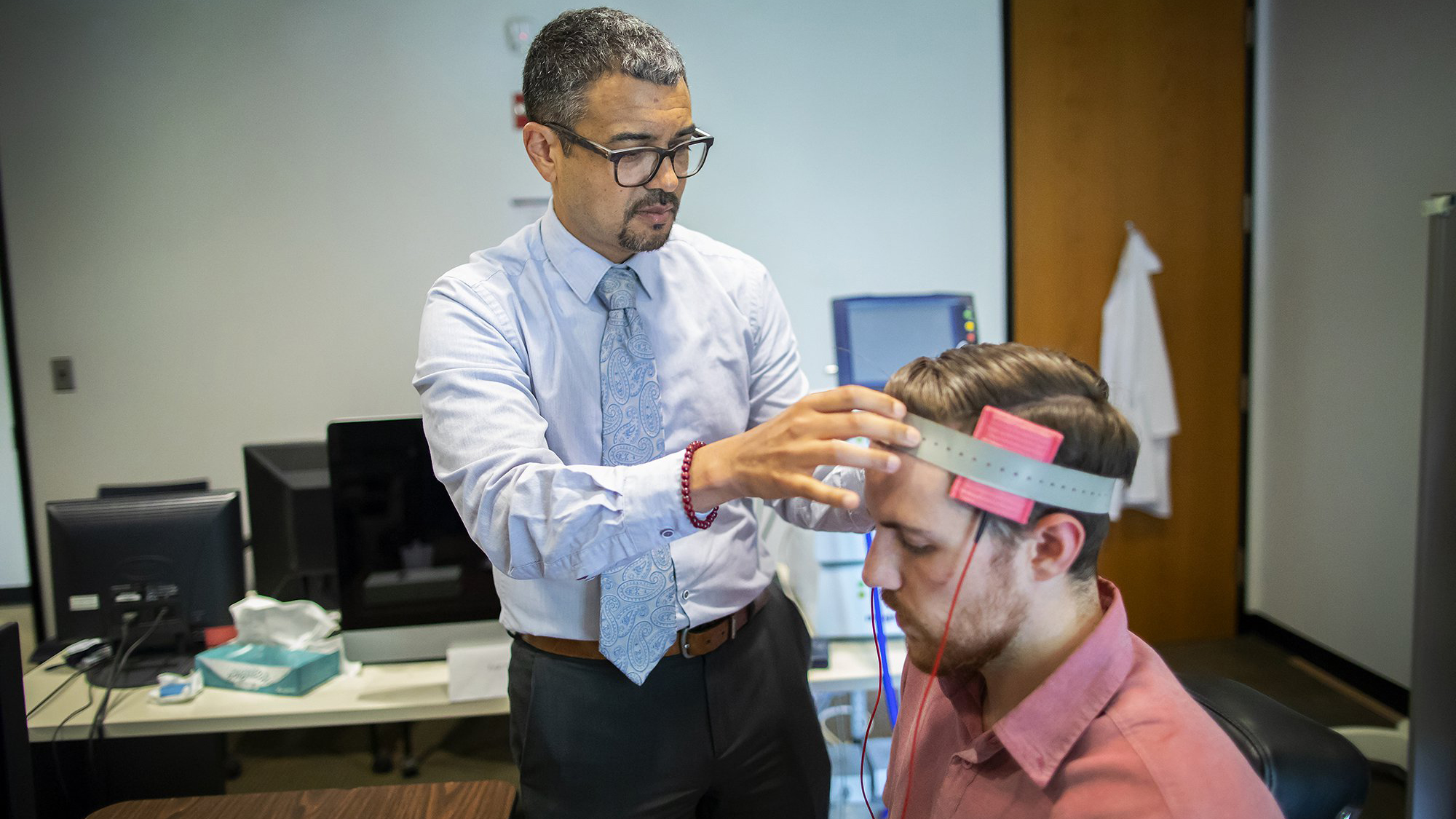
In a fascinating and somewhat unexpected result, mild electrical stimulation of the prefrontal cortex part of the brain can reduce violent urges and even raise moral awareness.
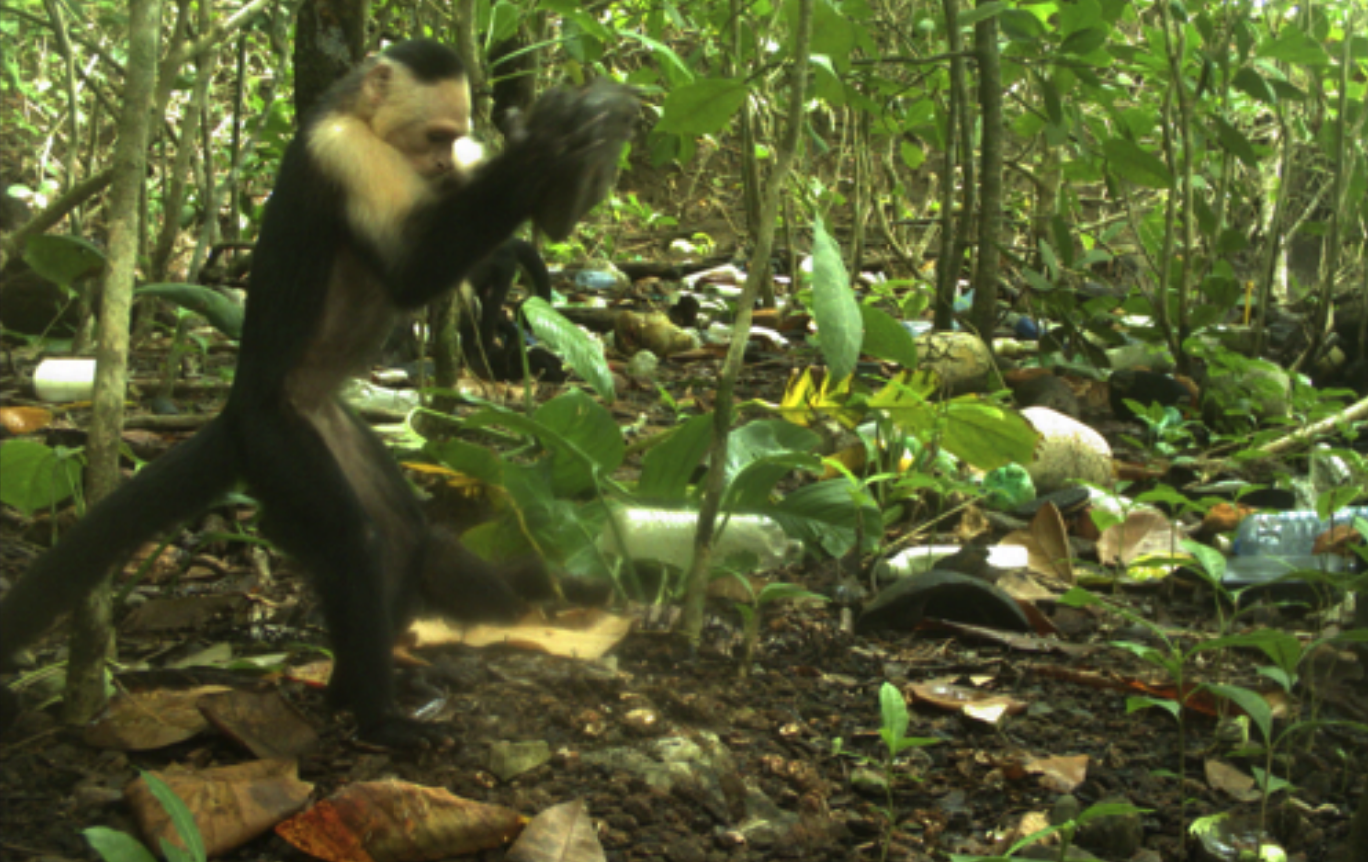
This is a remarkably rare case of non-human primate tool use in the wild. We’re witnessing another species dawn of their Stone Age.
CEO time has never been studied in this kind of detail.
A study finds that when checking genetic ancestry, people cherry-pick which ancestors they identify with and which ignore.
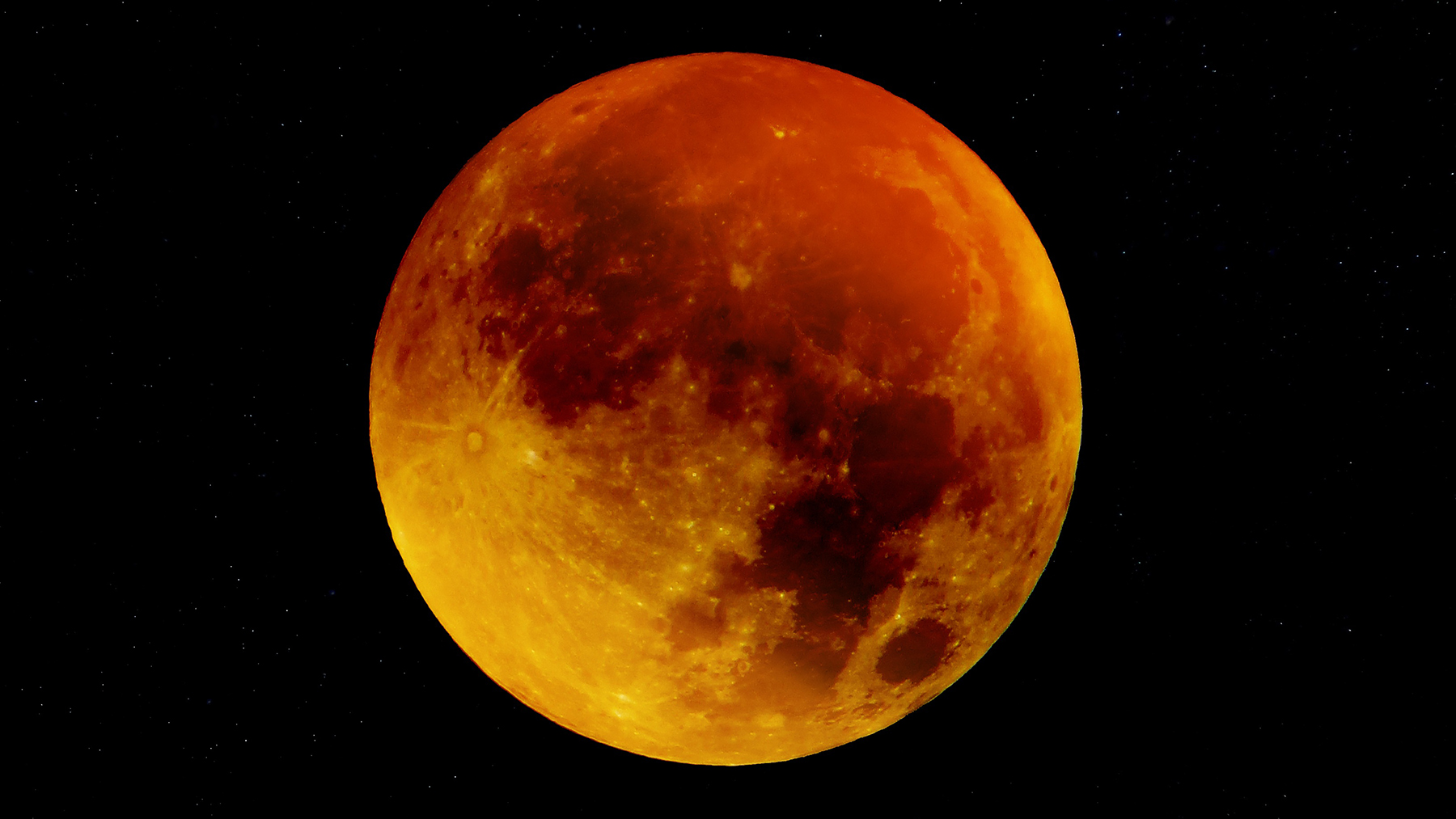
As we’ve come to expect, conspiracy theorists and fringe Christian evangelicals are heralding the July 27 blood moon as a sign of the imminent apocalypse. But what is the blood moon prophecy, and why does it appeal to a certain type of believer?
A new study suggests that it’s possible to replace anxiety-producing unpleasant memories with new ones implanted under hypnosis.
The death rate cut in half for people who kept the same doctor.
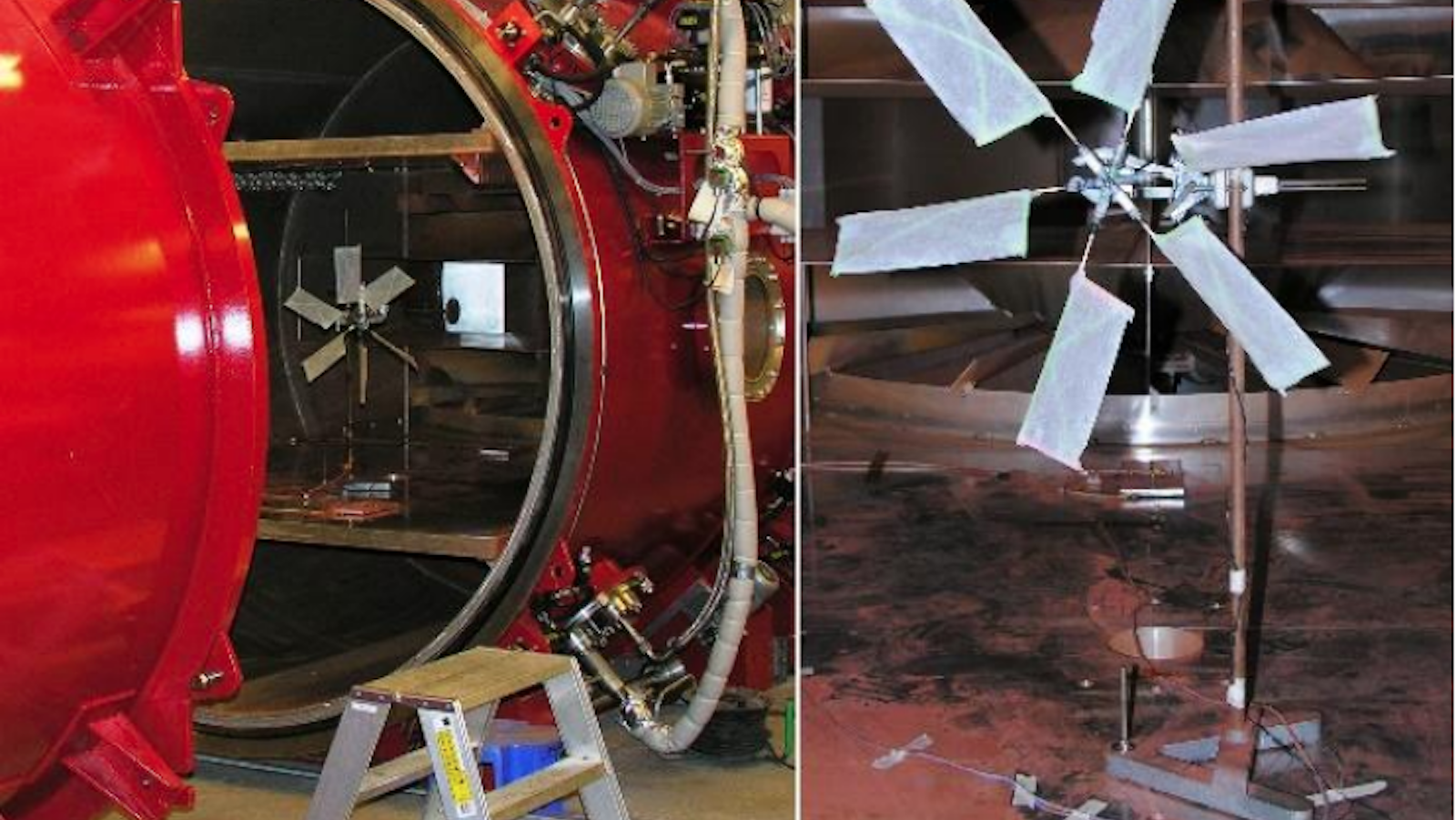
Wind power on Mars makes it possible for any rover or other craft to collect power at the poles or other areas on the planet that don’t get constant sunlight.
Despite little clinical evidence of efficacy, a growing number of parents are giving their children supplements that could prove dangerous.
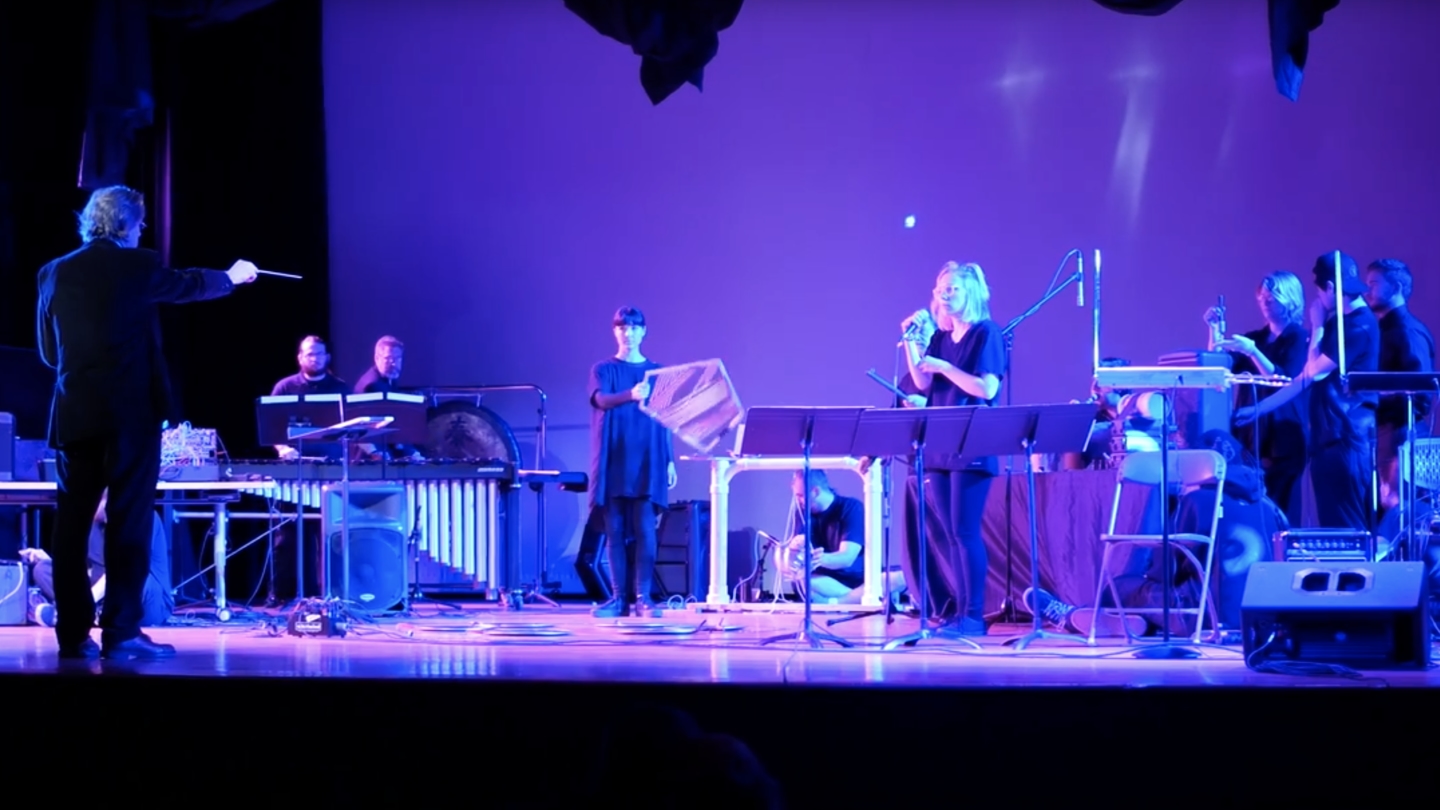
To help dramatize the need for us to open our minds about the potential nature of extraterrestrial life, experimental philosopher Jonathon Keats has built instruments and composed music for aliens.
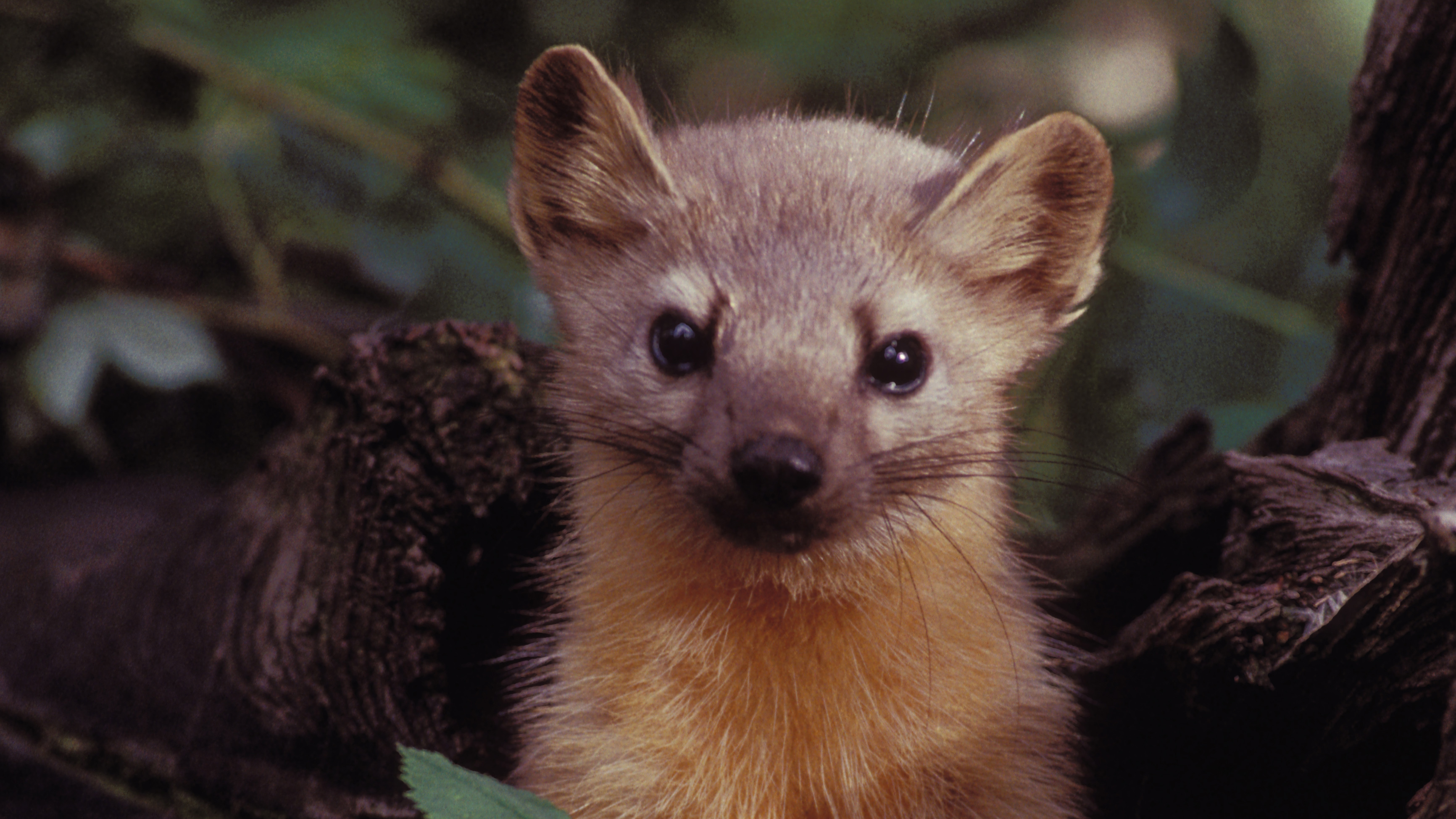
The Humboldt marten, a (much cuter) cousin of the weasel, has been placed on the endangered species list thanks to marijuana croppers.
A large analysis shows that many species are completely changing their habits to avoid humans.
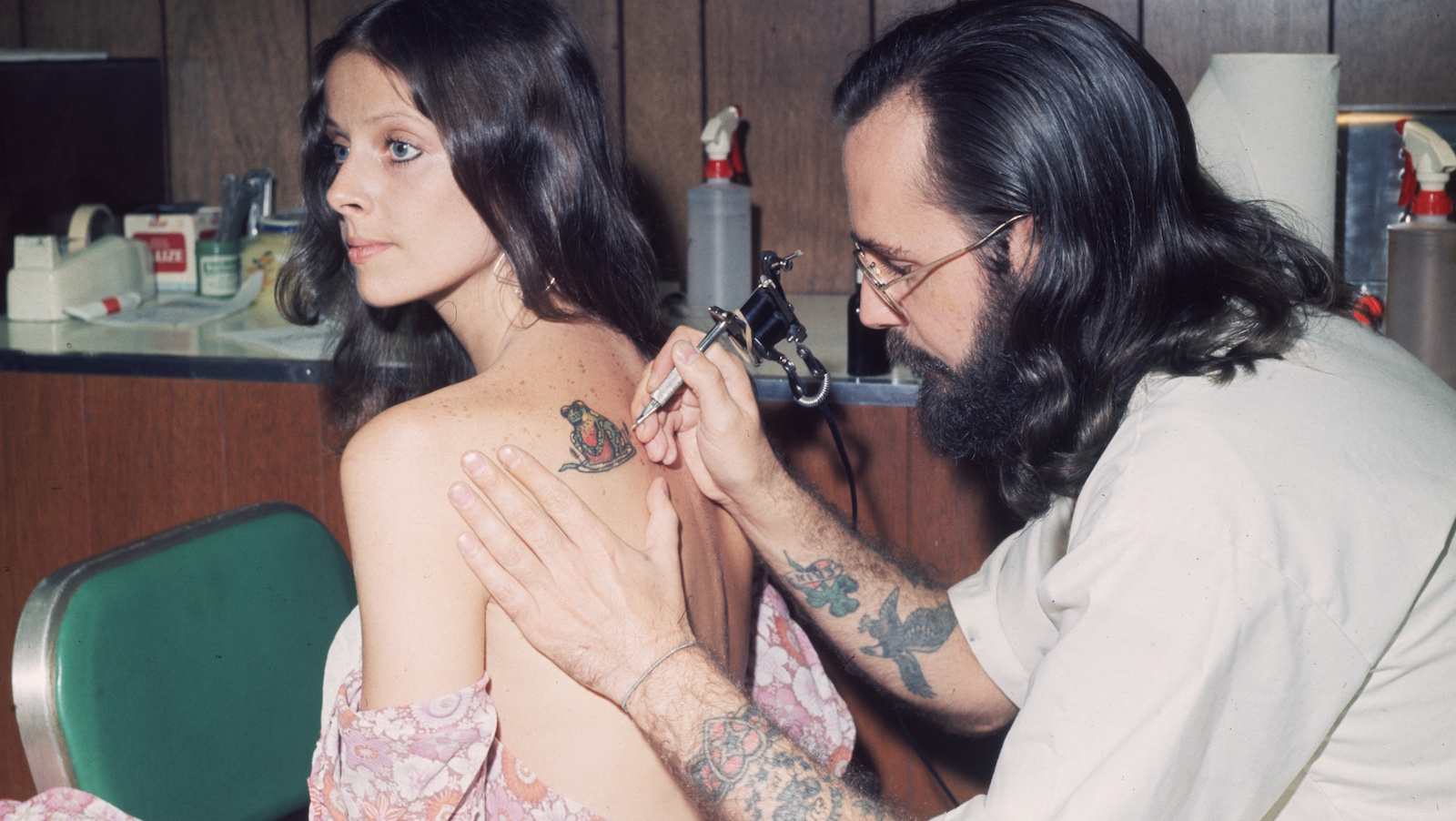
It turns out, that tattoo ink can travel throughout your body and settle in lymph nodes.