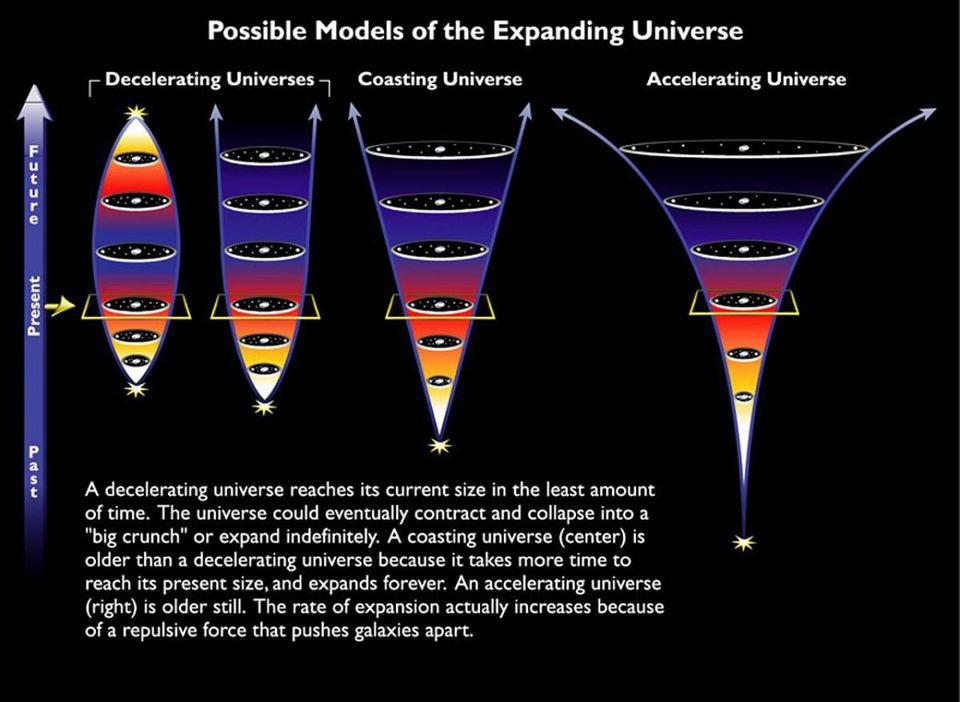
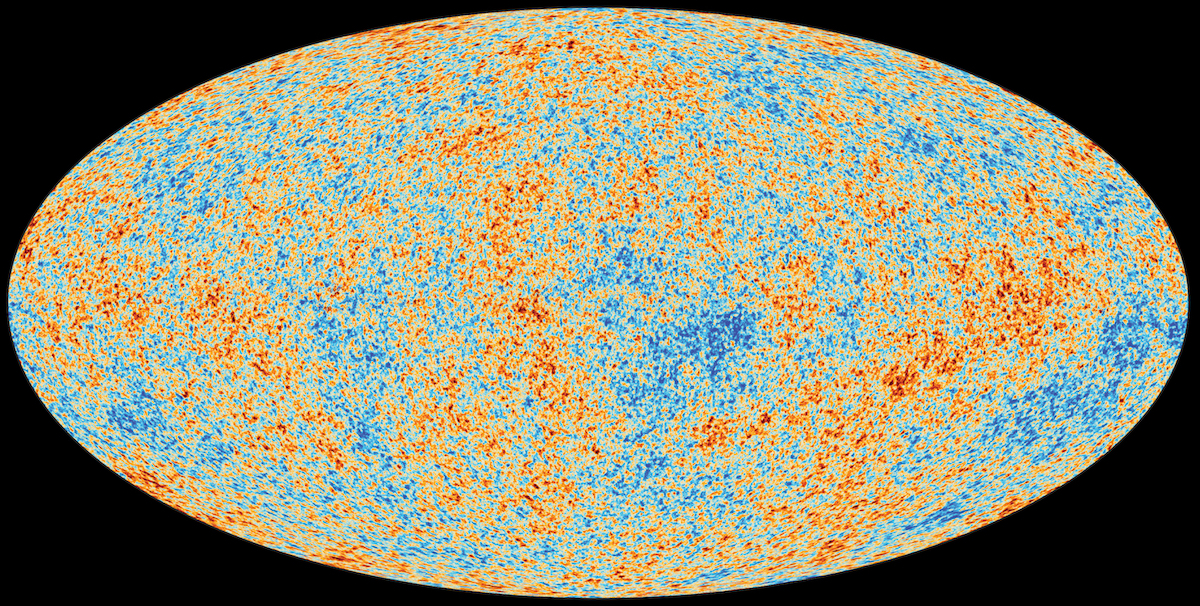
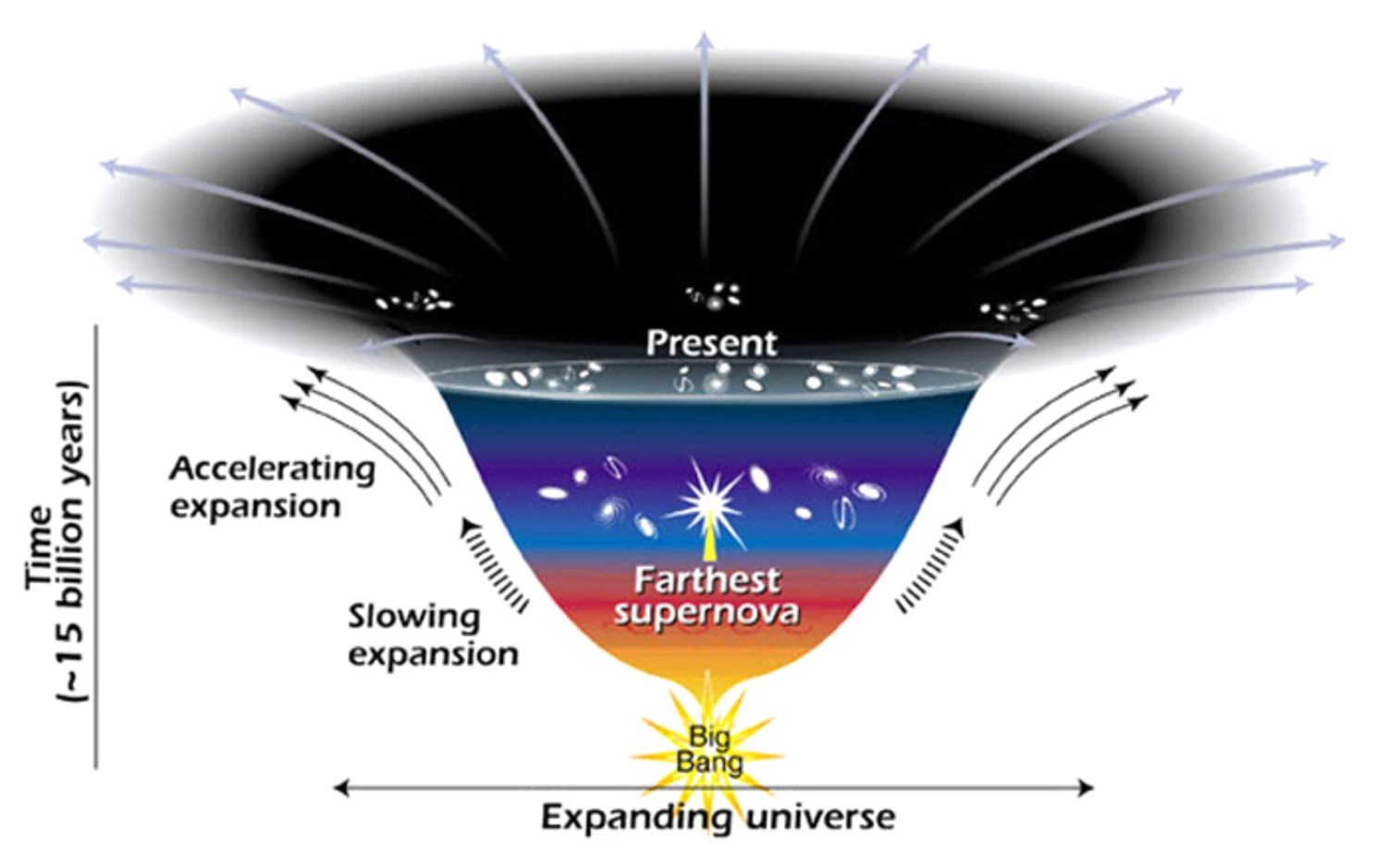
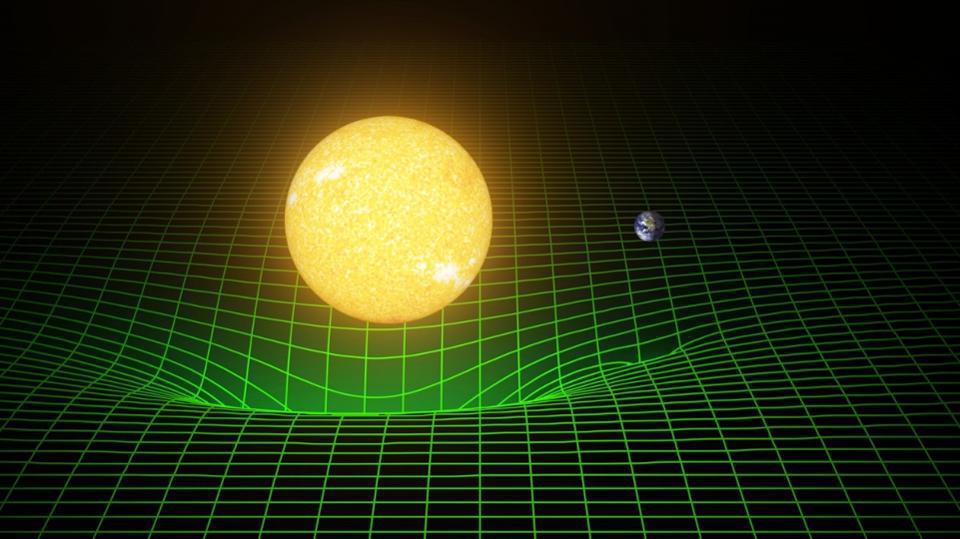
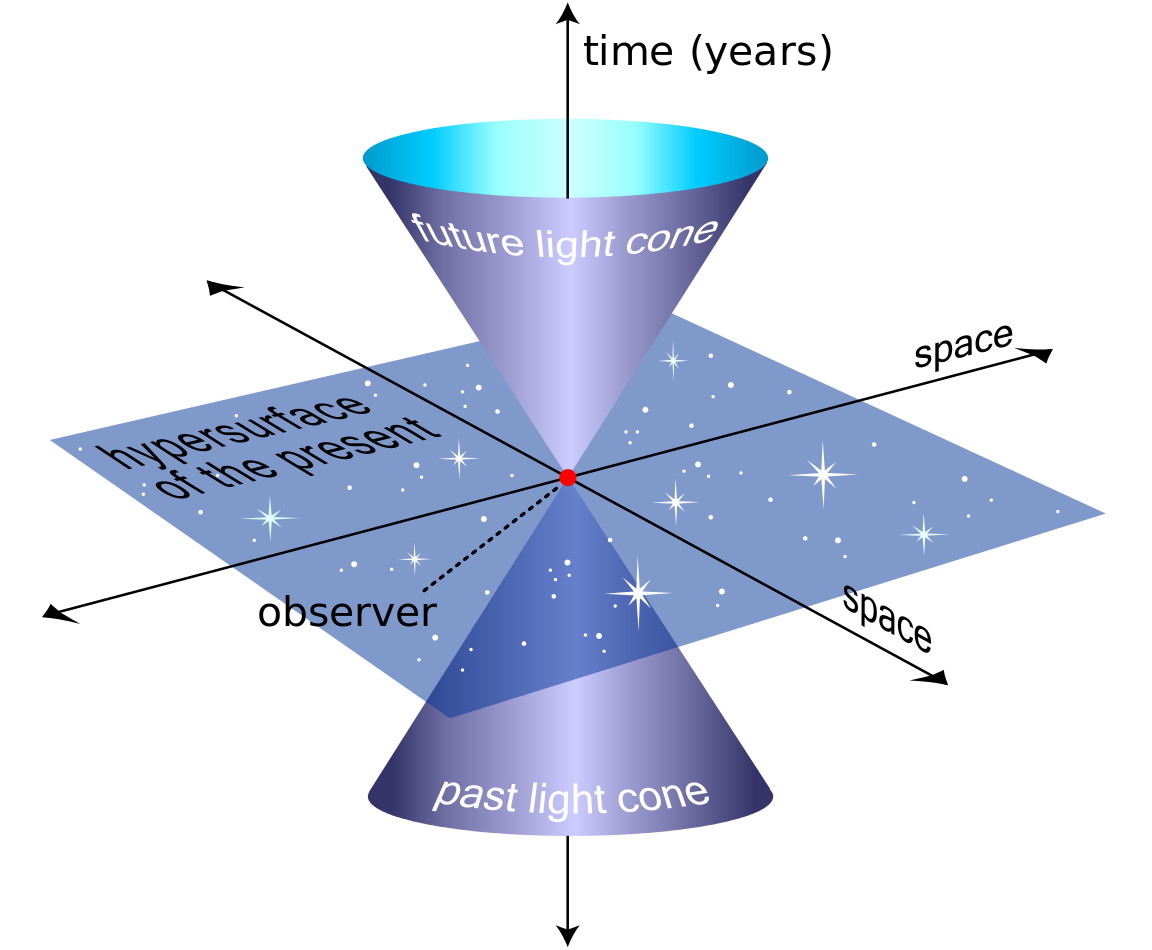
Dark energy is one of the biggest mysteries in all the Universe. Is there any way to avoid “having to live with it?”
Search Results
You searched for: gravity
The first stars took tens or even hundreds of millions of years to form, and then died in the cosmic blink of an eye. Here’s how.
Scientists find two 30-second techniques that prevent dizziness upon standing.
Embedded in a cell phone or in accessories such as rings, bracelets or watches, the novel tools aim to make it easier to manage hypertension. But they must still pass several tests before hitting the clinic.
Do the laws of physics place a hard limit on how far technology can advance, or can we re-write those laws?
Since 1930, type Ia supernovae have been thought to arise from white dwarfs exceeding the Chandrasekhar mass limit. Here’s why that’s wrong.
A crowdsourced “final exam” for AI promises to test LLMs like never before. Here’s how the idea, and its implementation, dooms us to fail.
Ever since the start of the hot Big Bang, time ticks forward as the Universe expands. But could time ever run backward, instead?
Today, the deepest depths of intergalactic space aren’t at absolute zero, but at a chill 2.73 K. How does that temperature change over time?
It’s possible to remove all forms of matter, radiation, and curvature from space. When you do, dark energy still remains. Is this mandatory?
Symmetries aren’t just about folding or rotating a piece of paper, but have a profound array of applications when it comes to physics.
Earth, the only rocky planet with a large, massive satellite, is greatly affected by the Moon. Destroying it would cause 7 major changes.
A longstanding mismatch between theory and experiment motivated an exquisite muon measurement. At last, a theoretical solution has arrived.
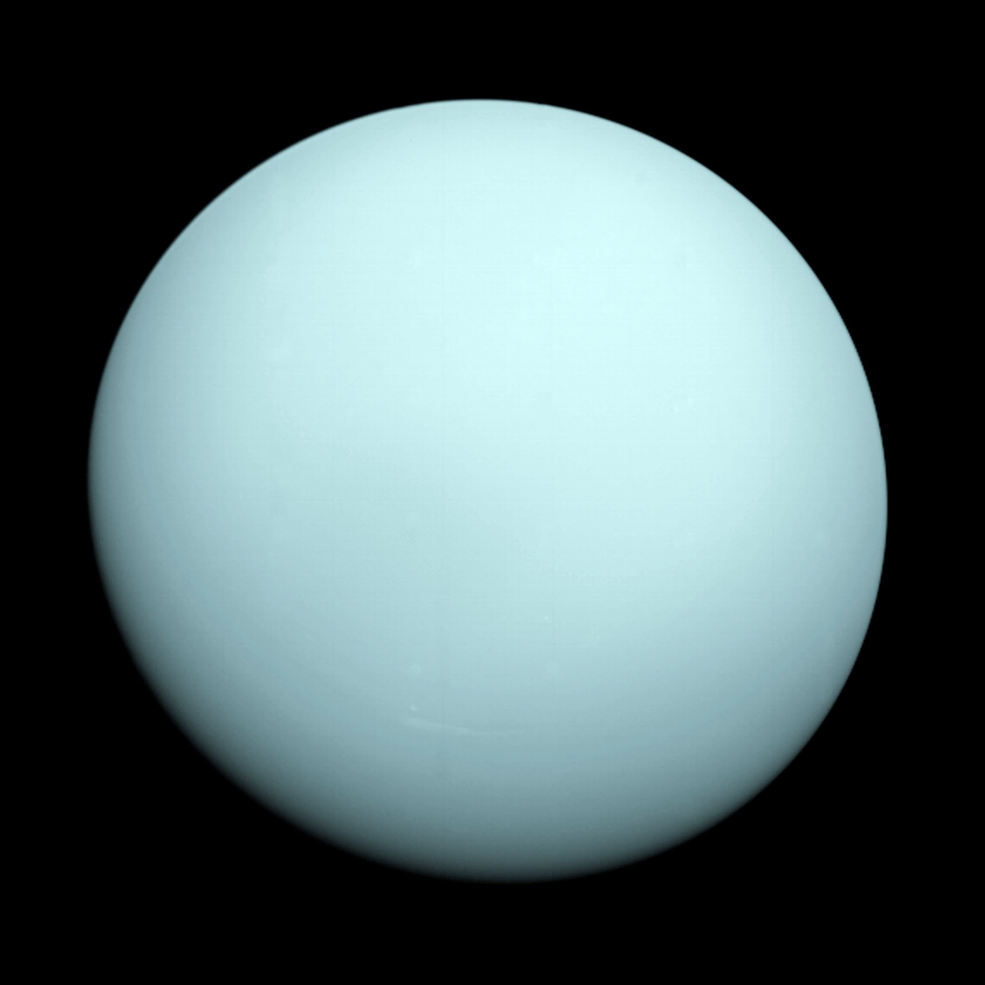
We’ve only seen Uranus up close once: from Voyager 2, back in 1986. The next time we do it, its features will look entirely different.
The information we have in the Universe is finite and limited, but our curiosity and wonder is forever insatiable. And always will be.
Just 13.8 billion years after the hot Big Bang, we can see objects up to 46.1 billion light-years away. No, this doesn’t violate relativity.
We know of stellar mass and supermassive black holes, but intermediate mass ones have long proved elusive. Until now.
Mathematically, it is a monster, but we can understand it in plain English.
Maybe our understanding of quantum entanglement is incomplete, or maybe there is something fundamentally unique about consciousness.
It took 9.2 billion years of cosmic evolution before our Sun and Solar System even began to form. Such a small event has led to so much.
We take for granted that time is real. But what if it’s only an illusion, and a relative illusion at that? Does time even exist?
An in-depth interview with astronomer Kelsey Johnson, whose new book, Into the Unknown, explores what remains unknown about the Universe.
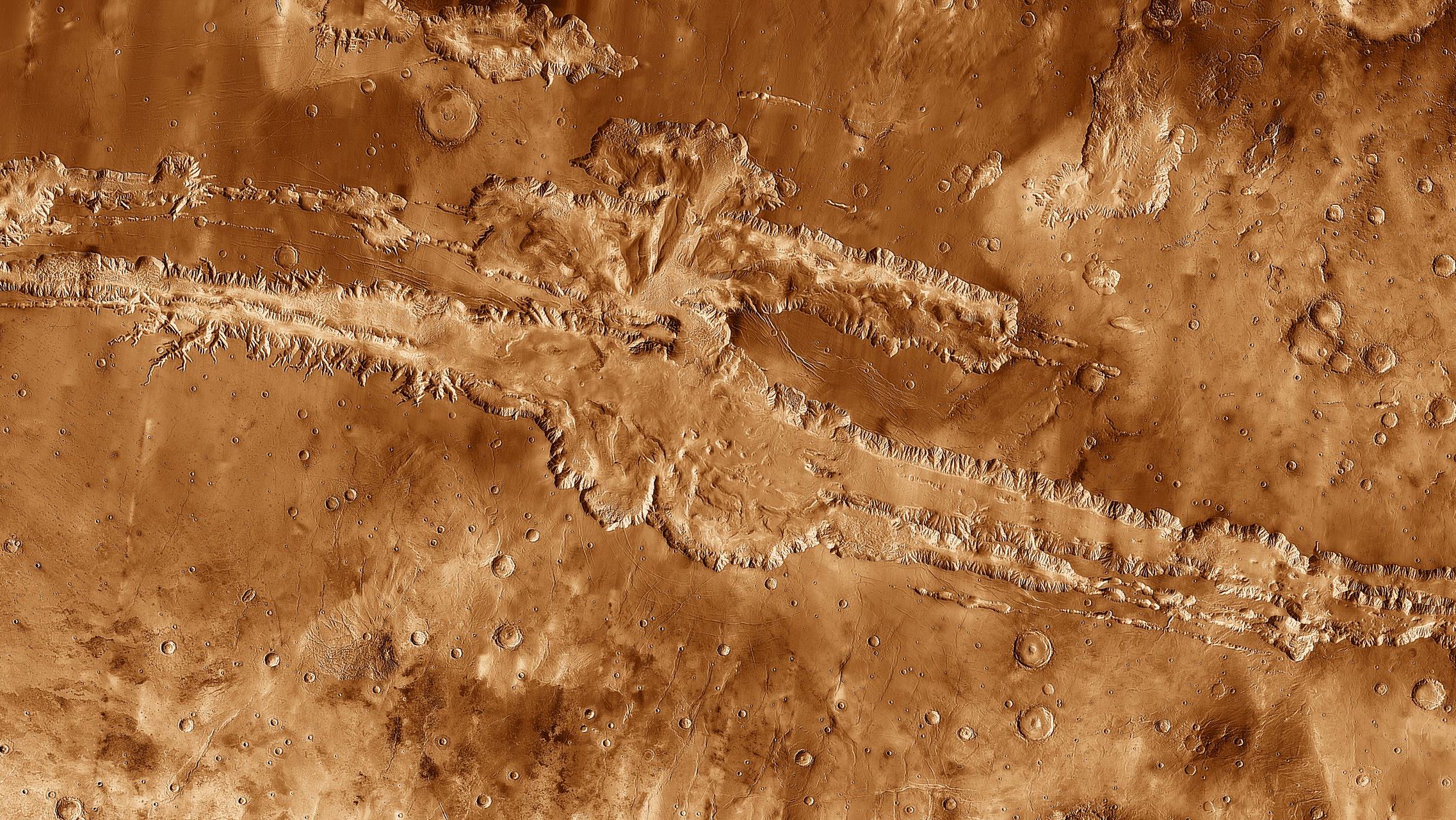
Valles Marineris is the Solar System’s grandest canyon, many times longer, wider, and deeper than the Grand Canyon. What scarred Mars so?
Astronomers claim to have found structures so large, they shouldn’t exist. With such biased, incomplete observations, perhaps they don’t.
There are two different ways to measure the expansion rate of the Universe, and they don’t agree. And no, new measurements don’t help.
If something is “true,” it needs to be shown to work in the real world.
Today, supermassive black holes and their host galaxies tell a specific story in terms of mass. But JWST reveals a different story early on.
If nature were perfectly deterministic, atoms would almost instantly all collapse. Here’s how Heisenberg uncertainty saves the atom.
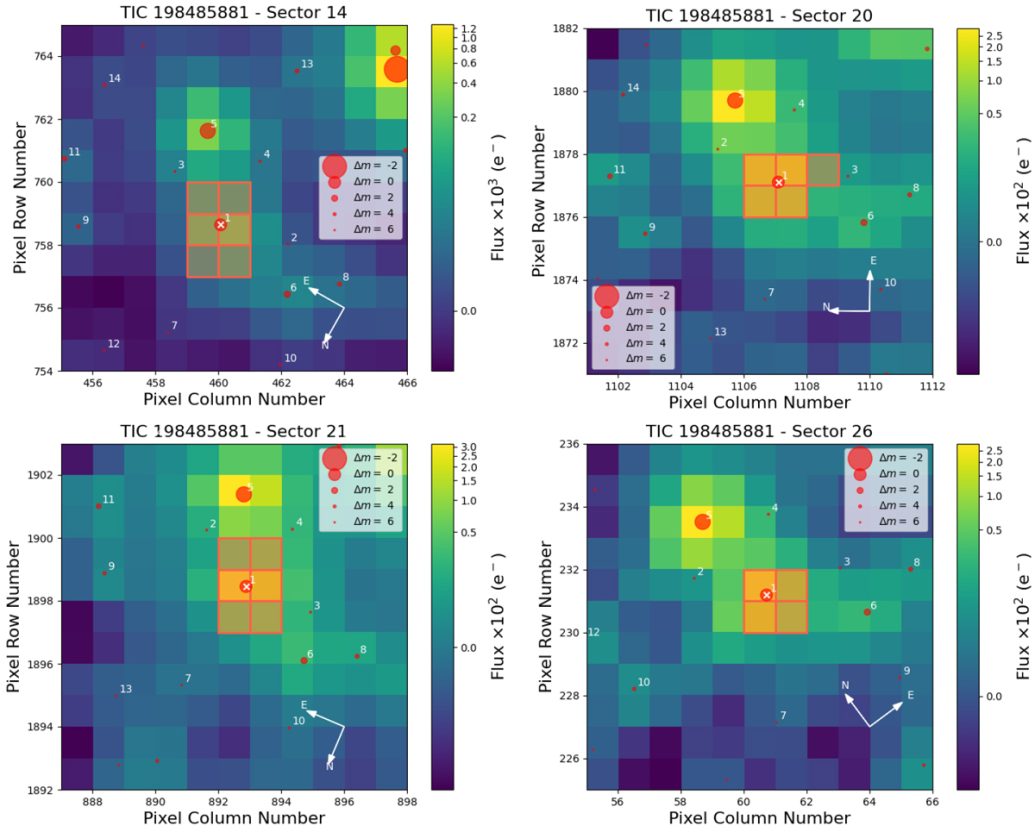
The search for worlds outside our solar system has just turned up a planet, TOI-2257 b, with a truly extreme orbit.
We are traveling in a realm that once exclusively belonged to the gods. Space travel will force humanity to rethink everything.