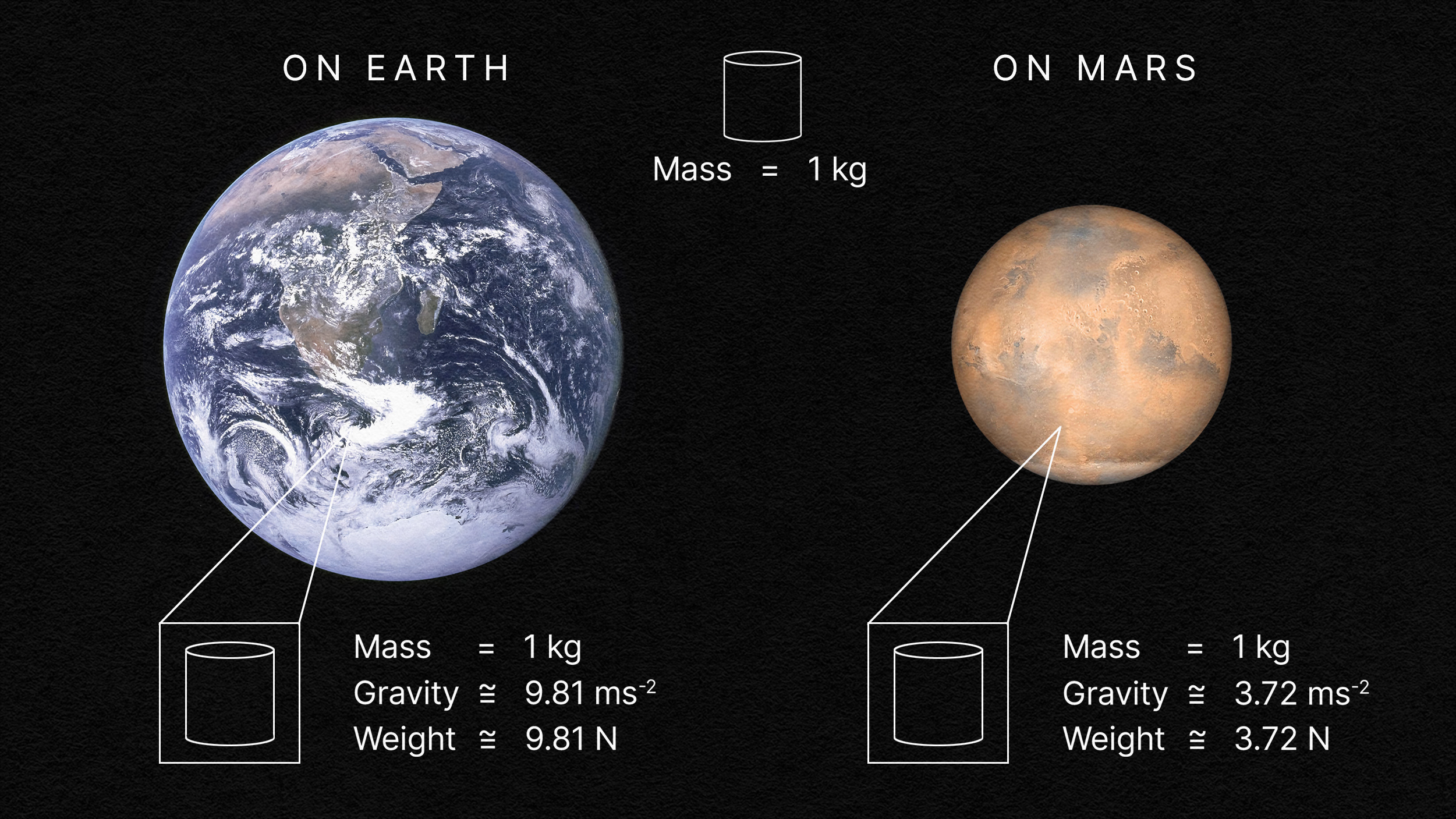
Here on Earth, we commonly use terms like weight (in pounds) and mass (in kilograms) as though they’re interchangeable. They’re not.
Search Results
You searched for: Physical Constants
Headlines have blared that quasar ticking confirms that time passed more slowly in the early Universe. That’s not how any of this works.
“It is healthy and normal to be afraid of death.”
Since its observation discovery in the 1990s, dark energy has been one of science’s biggest mysteries. Could black holes be the cause?
Nature may not allow us full access to the weirdness of quantum mechanics.
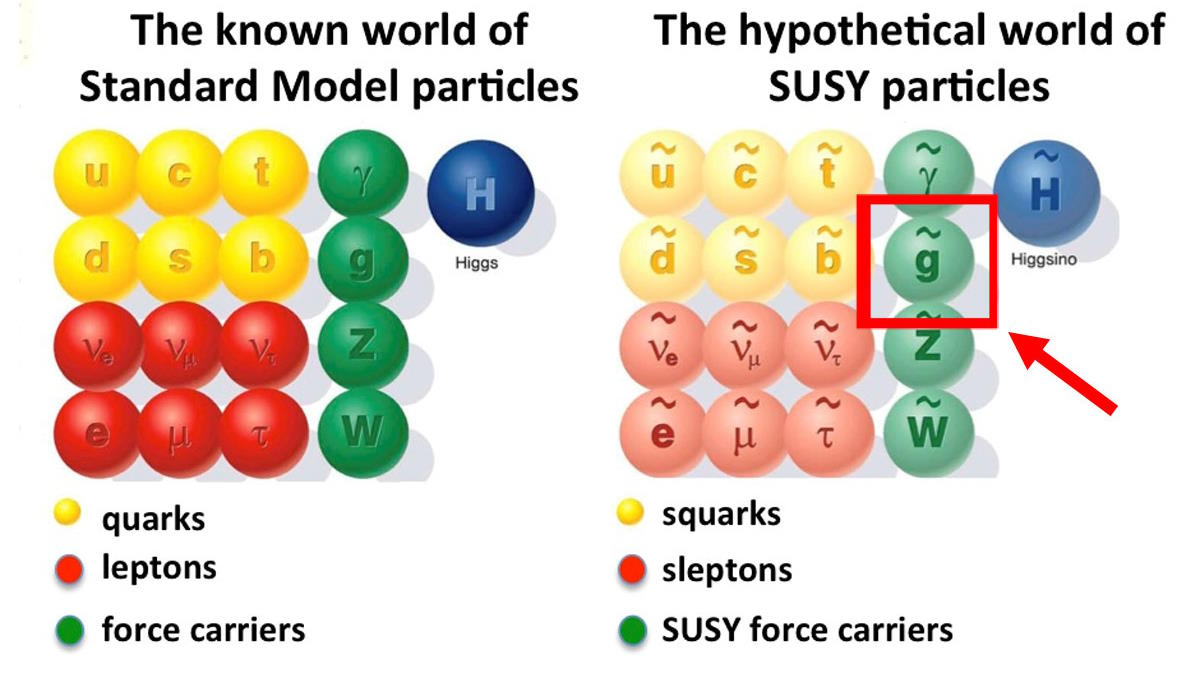
Almost 100 years ago, an asymmetric pathology led Dirac to postulate the positron. A similar pathology could lead us to supersymmetry.
The Multiverse fuels some of the 21st century’s best fiction stories. But its supporting pillars are on extremely stable scientific footing.
The multiverse is an idea that has gained a lot of traction in popular culture. But what does science have to say about it?
For every proton, there were over a billion others that annihilated away with an antimatter counterpart. So where did all that energy go?
Science cannot help us understand or describe first-person experience. Zen koans are a powerful form for helping us reach that description.
The concept of ‘relativistic mass’ has been around almost as long as relativity has. But is it a reasonable way to make sense of things?
Our greatest tool for exploring the world inside atoms and molecules, and specifically electron transitions, just won 2023’s Nobel Prize.
Carrie Berk reveals how she transformed her struggle with anxiety and internet fame by changing her perception and finding her true voice as a writer.
▸
5 min
—
with
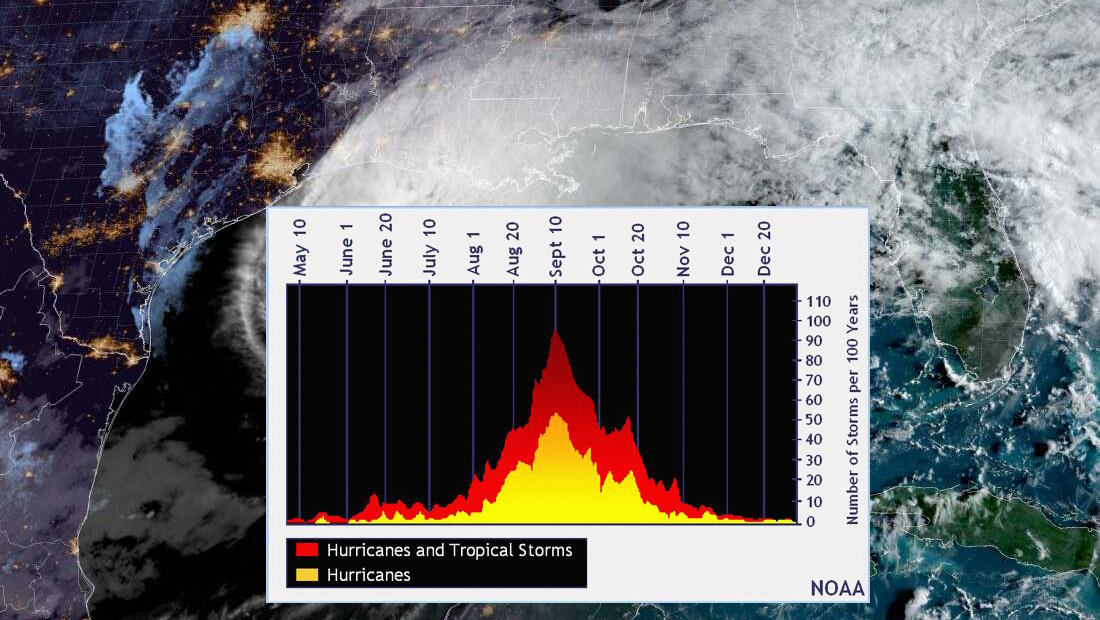
The laws of physics aren’t changing. But the Earth’s conditions are different than what they used to be, and so are hurricanes as a result.
From forming bound states to normal scattering, many possibilities abound for matter-antimatter interactions. So why do they annihilate?
The quantum world — and its inherent uncertainty — defies our ability to describe it in words.
Successful alpha leadership is more about caring and healing than dog-eat-dog supremacy.
The Universe is expanding, and the Hubble constant tells us how fast. But how can it be a constant if the expansion is accelerating?
The science fiction dream of a traversable wormhole is no closer to reality, despite a quantum computer’s suggestive simulation.
The quantum world is one in which rules that are completely foreign to our everyday experience dictate bizarre behavior.
There are a wide variety of theoretical studies that call our Standard Model of cosmology into question. Here’s what they really mean.
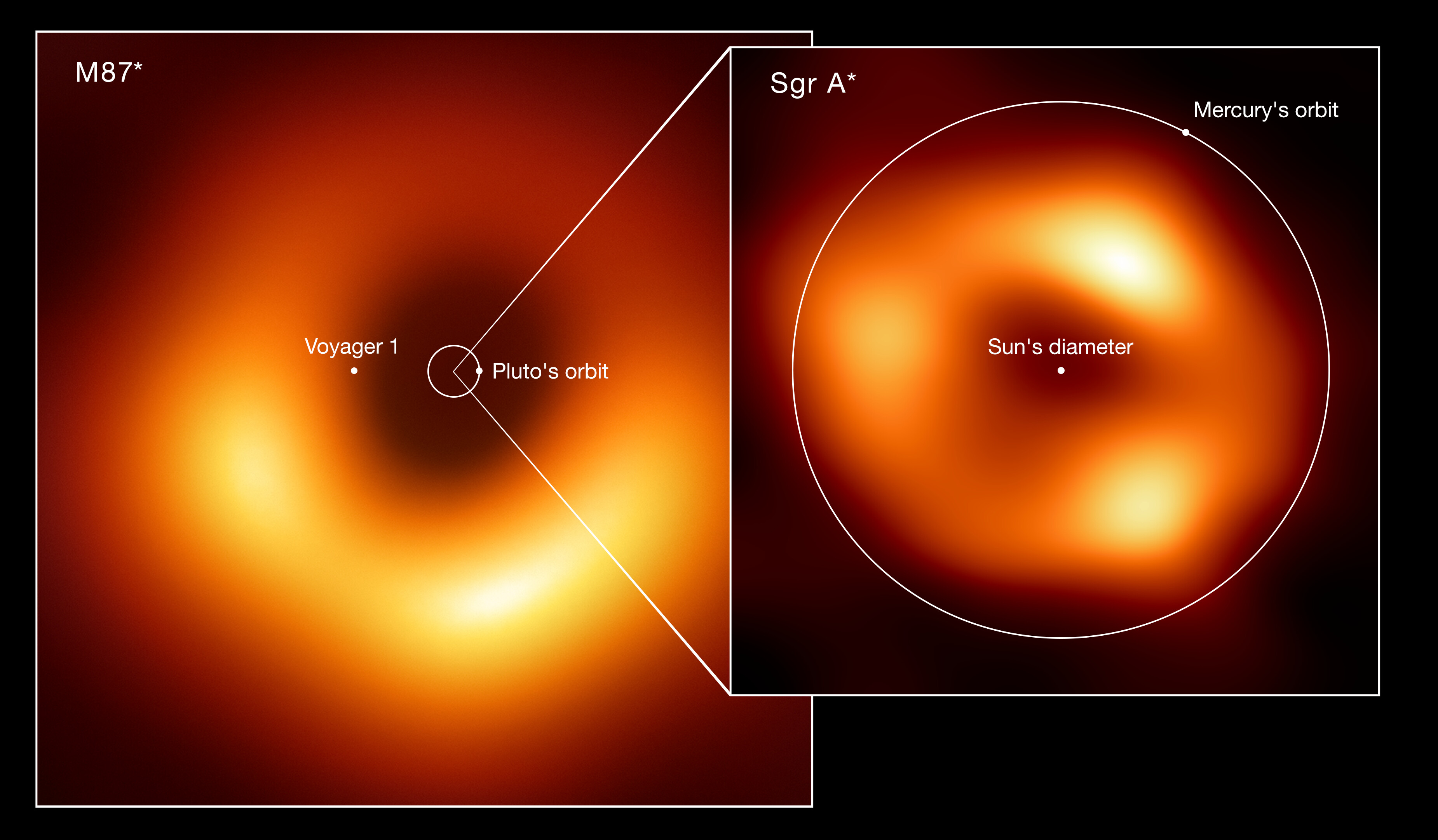
From the tiniest subatomic scales to the grandest cosmic ones, solving any of these puzzles could unlock our understanding of the Universe.
This is especially true for three key groups.
Whenever someone waxes poetic about terraforming alien worlds, it’s worth taking a moment to consider the ethical implications of the proposal.
Light carries with it the secrets of reality in ways we cannot completely understand.
Traveling back in time is a staple of science fiction movies. But according to Einstein, it’s a physical possibility that’s truly allowed.
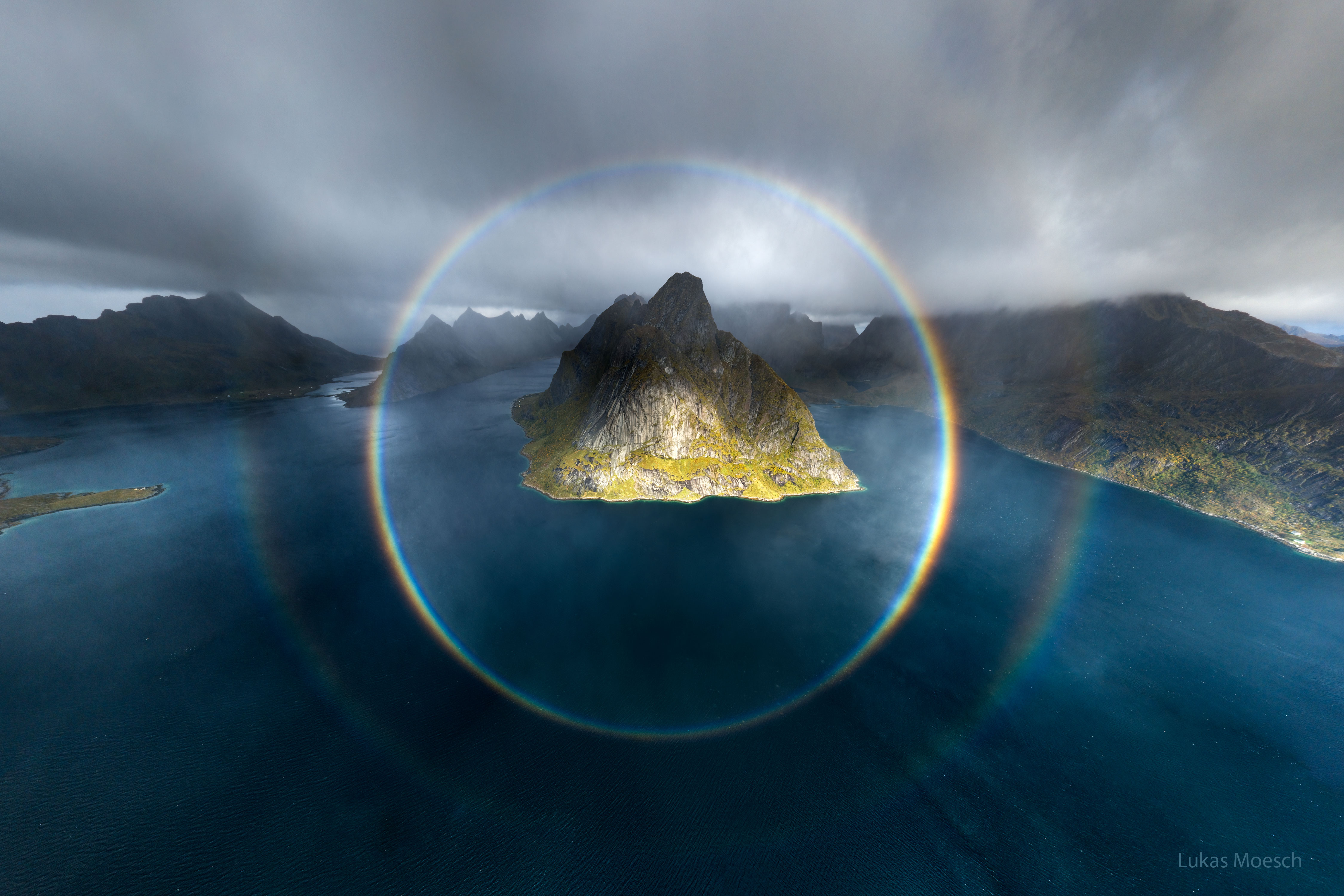
Most of us only ever see a fraction of a full rainbow: an arc. But optically, a full rainbow makes a complete circle. Physics explains why.
Whether you’re a leader looking to ramp up team output or just trying to improve your skill set, hard work alone is not enough.
A group of prominent scientists shares how research has changed them.
Tumor cells traverse many different types of fluids as they travel through the body.