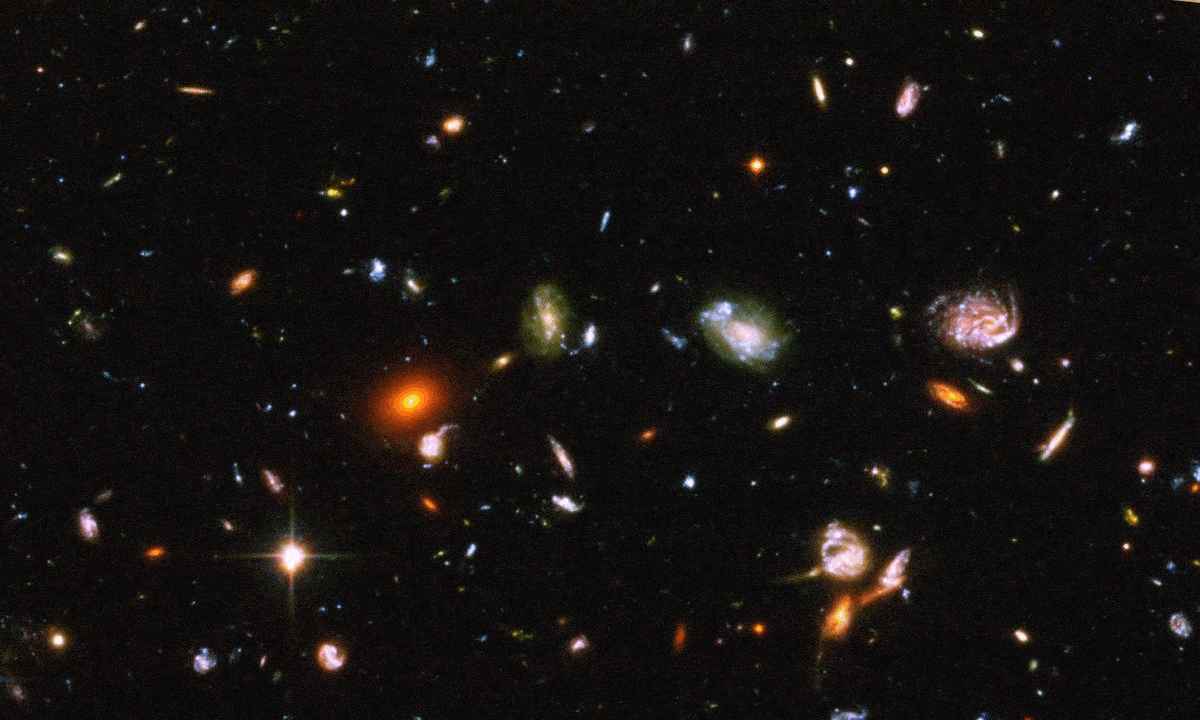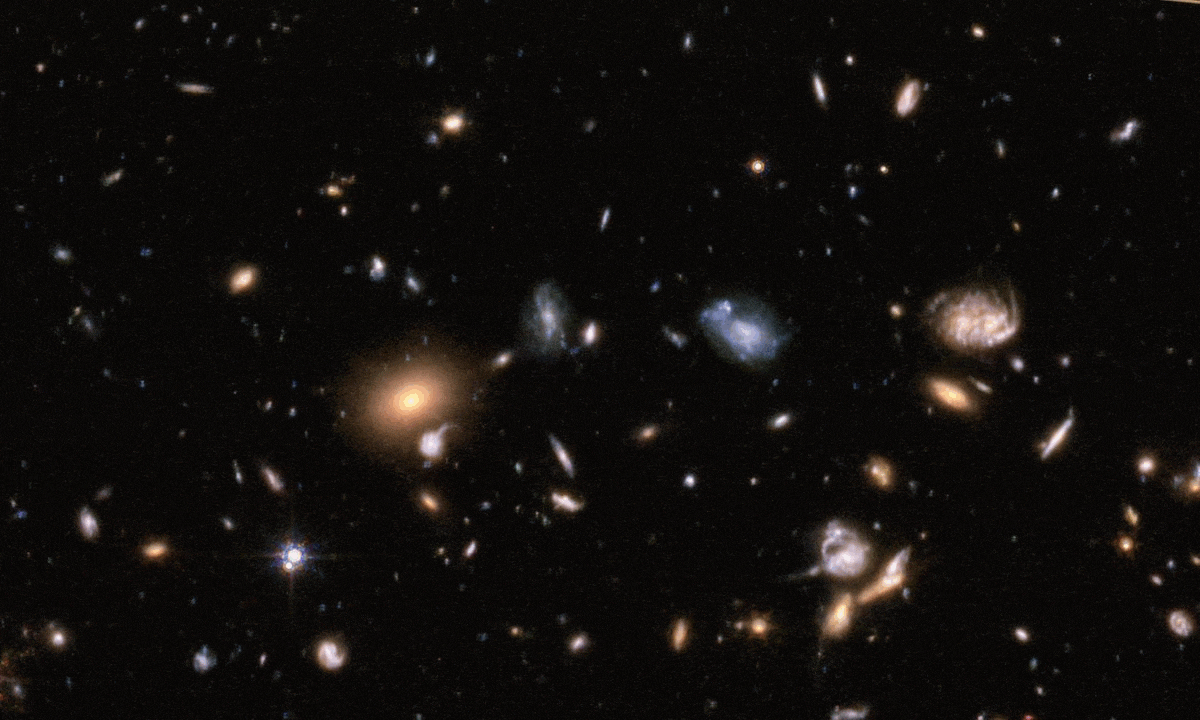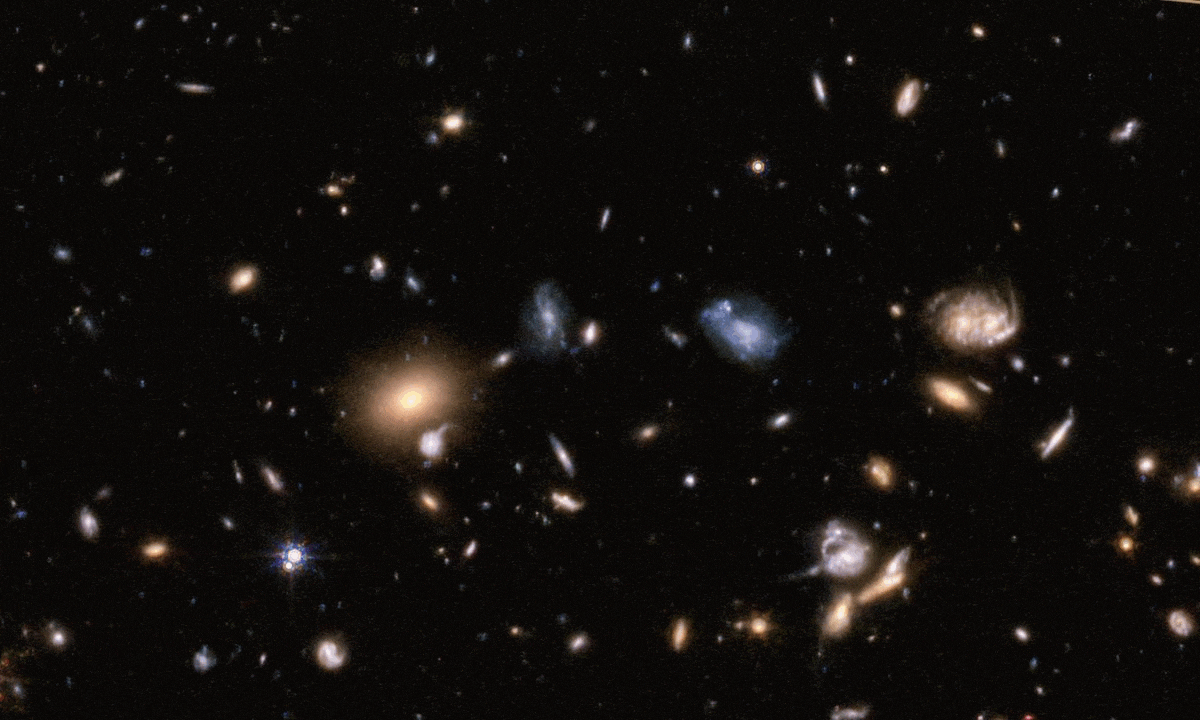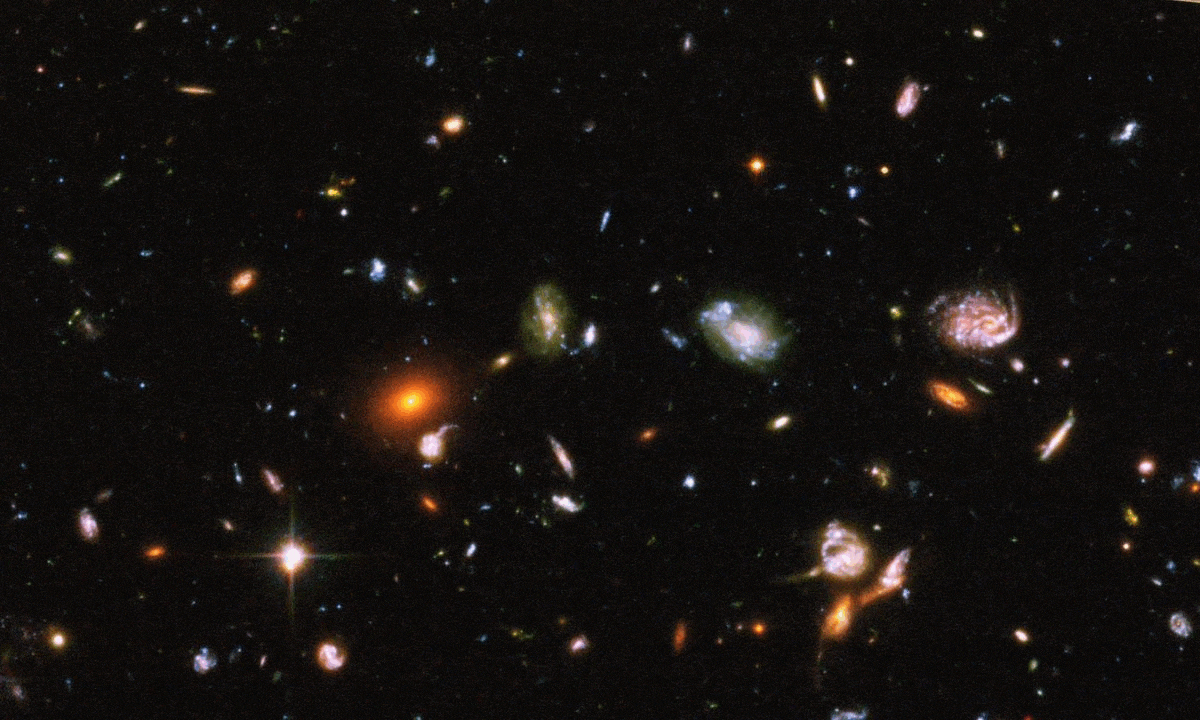Science cannot help us understand or describe first-person experience. Zen koans are a powerful form for helping us reach that description.
Search Results
You searched for: Physical Constants
Researchers devise a record-breaking laser transmission that avoids atmospheric interference.
This is especially true for three key groups.
The quantum world — and its inherent uncertainty — defies our ability to describe it in words.
Leaders ideally intertwine their own success with that of their teams — if that’s not the case at your workplace, here’s what to do.
Whether you’re a leader looking to ramp up team output or just trying to improve your skill set, hard work alone is not enough.
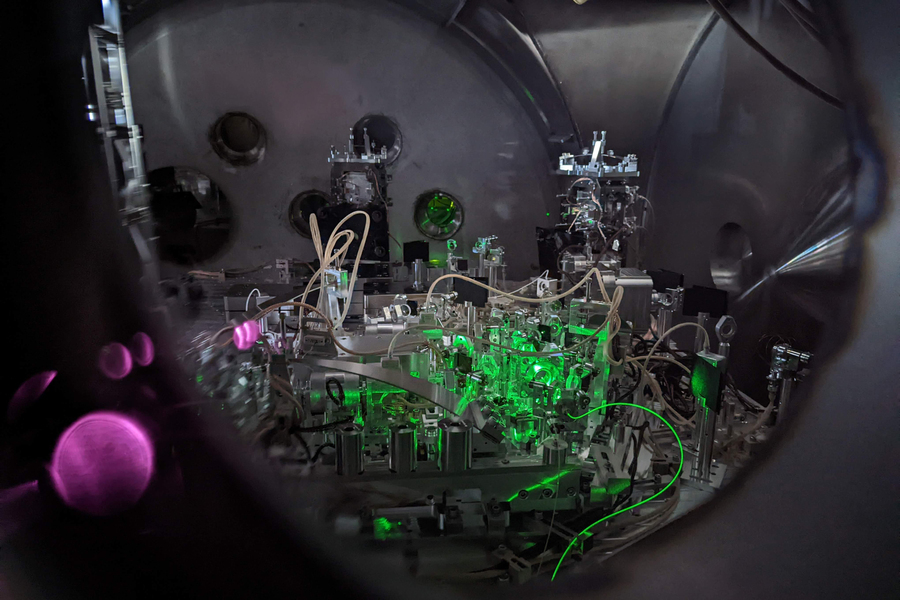
There’s a quantum limit to how precisely anything can be measured. By squeezing light, LIGO has now surpassed all previous limitations.
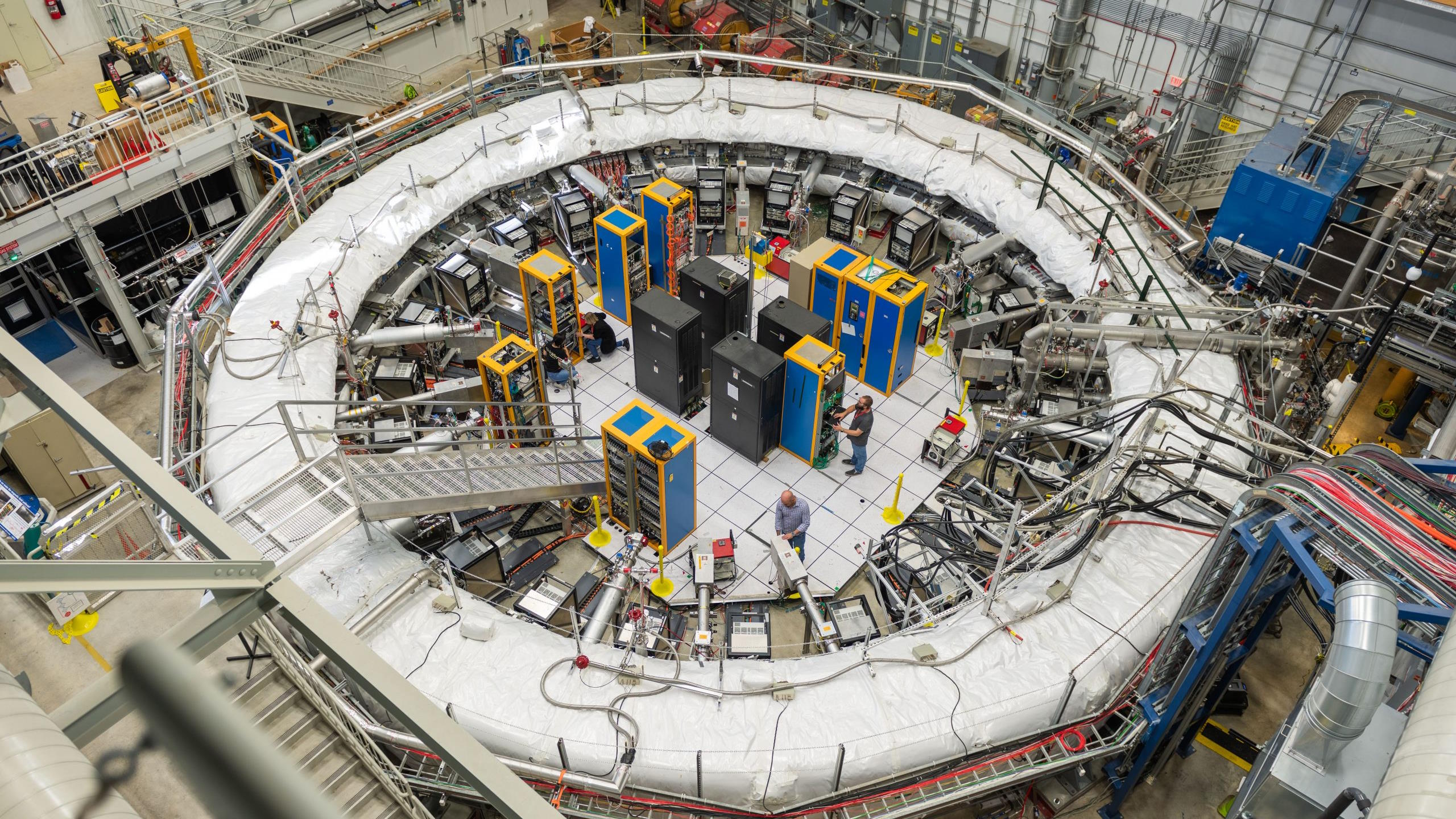
A longstanding mismatch between theory and experiment motivated an exquisite muon measurement. At last, a theoretical solution has arrived.
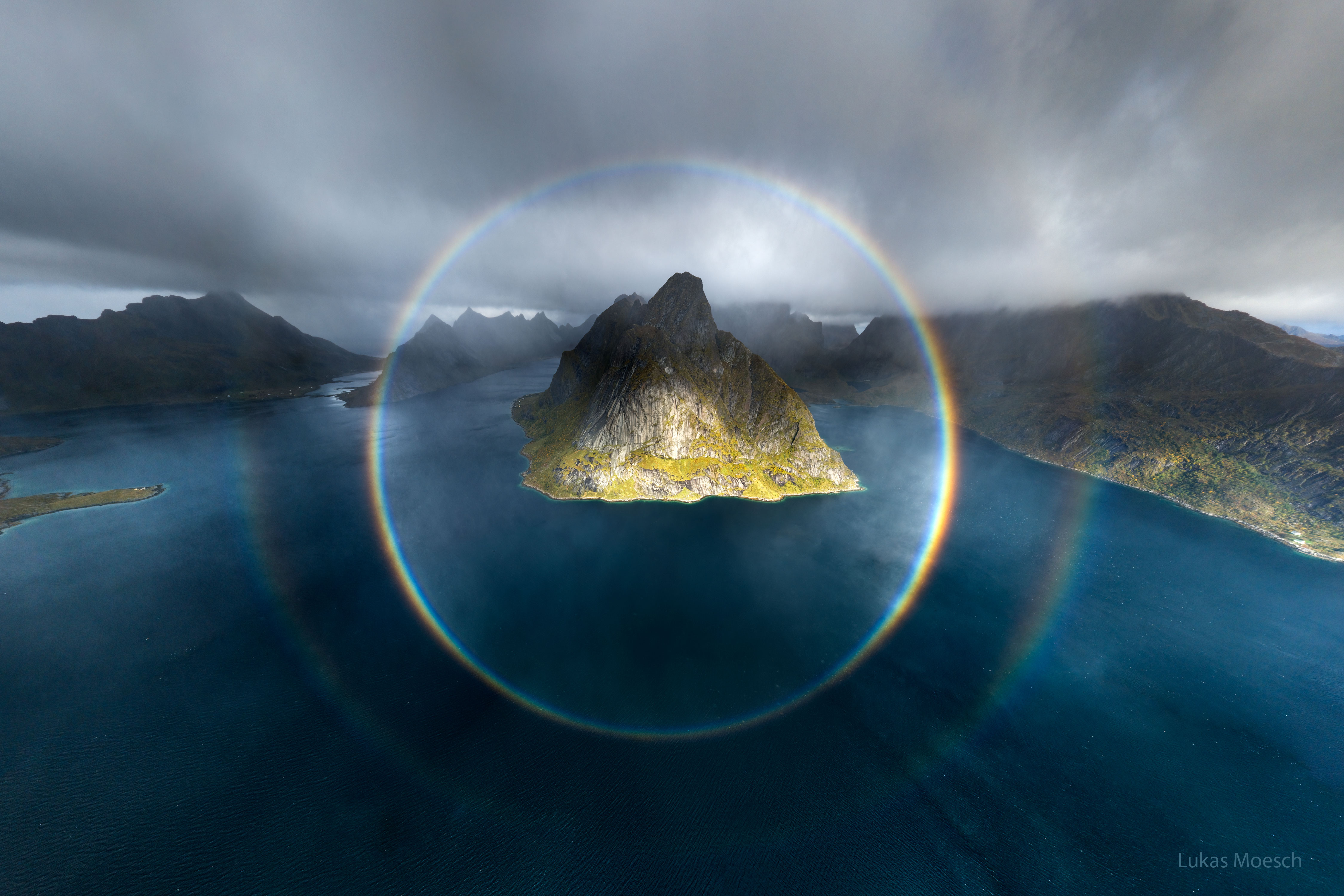
Most of us only ever see a fraction of a full rainbow: an arc. But optically, a full rainbow makes a complete circle. Physics explains why.
The science fiction dream of a traversable wormhole is no closer to reality, despite a quantum computer’s suggestive simulation.
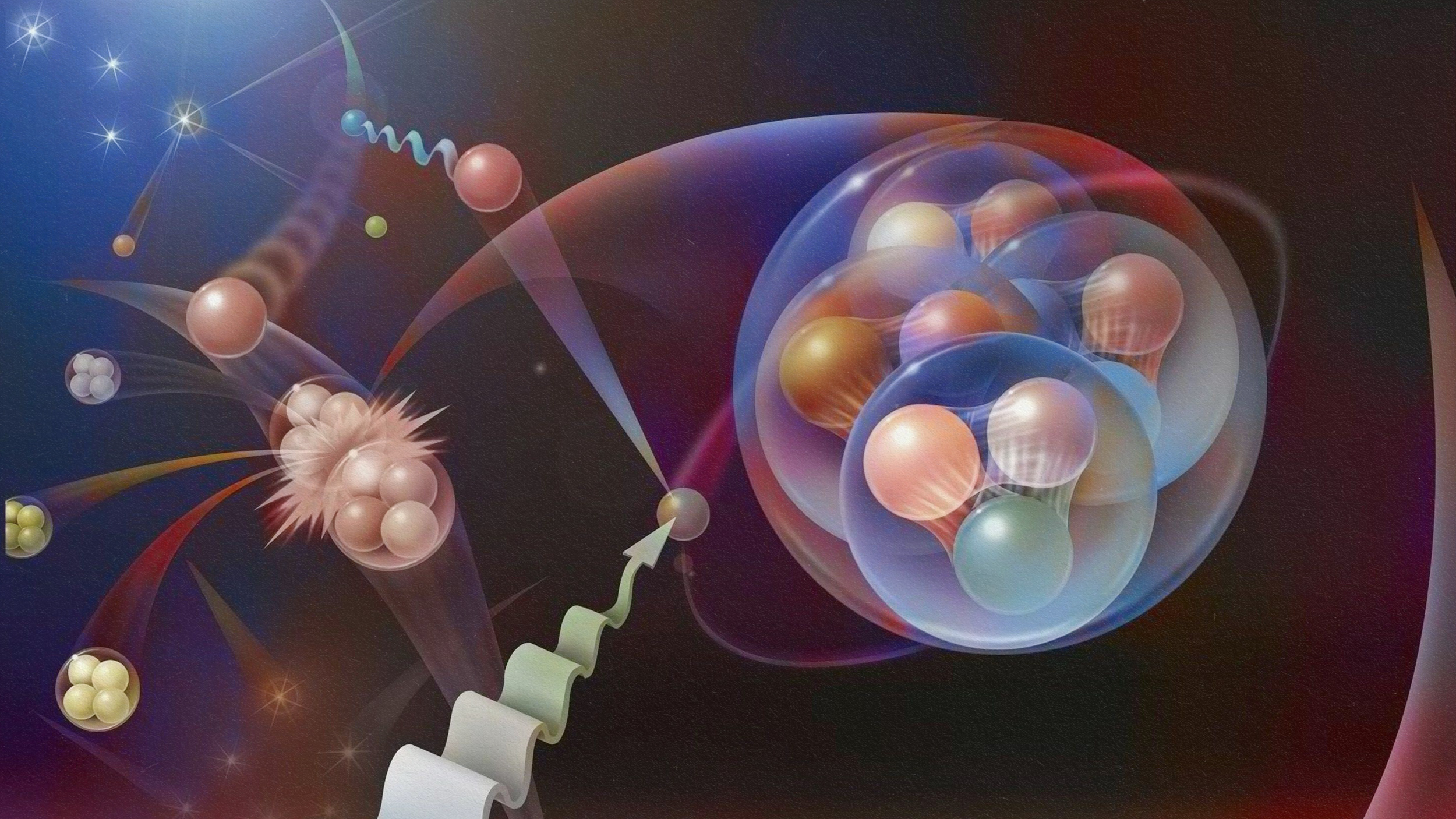
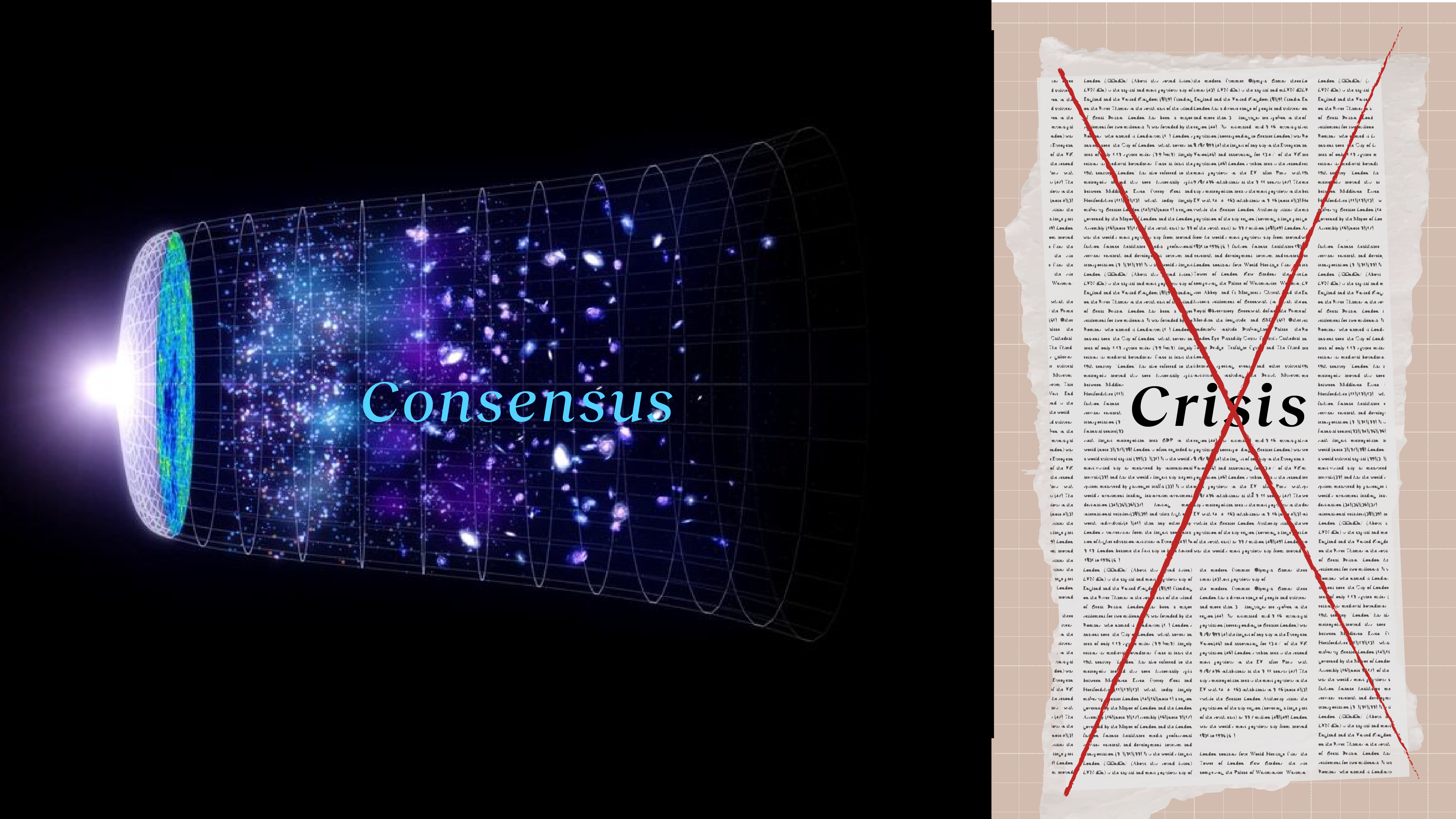
There are a few clues that the Universe isn’t completely adding up. Even so, the standard model of cosmology holds up stronger than ever.
The quantum world is one in which rules that are completely foreign to our everyday experience dictate bizarre behavior.
Yushiro Kato — the 32-year-old co-founder and CEO of manufacturing platform CADDi — offers his most valuable leadership learnings.
Light carries with it the secrets of reality in ways we cannot completely understand.
Matt Strassler’s journey into fundamental physics culminates in a brilliant explanation of the Higgs field. Enjoy this exclusive interview.
Dive into a realm where time, space, and even reality itself are put into question.
In the quest to measure how antimatter falls, the possibility that it fell “up” provided hope for warp drive. Here’s how it all fell apart.
From the tiniest subatomic scales to the grandest cosmic ones, solving any of these puzzles could unlock our understanding of the Universe.
Tumor cells traverse many different types of fluids as they travel through the body.
The Universe is expanding, and the Hubble constant tells us how fast. But how can it be a constant if the expansion is accelerating?
A group of prominent scientists shares how research has changed them.
The Michelson-Morley experiment of 1887, despite expectations, revealed a null result: no effect. The implications were revolutionary.
The farther away they get, the smaller distant galaxies look. But only up to a point, and beyond that, they appear larger again. Here’s how.
The Universe isn’t just expanding, the expansion is also accelerating. If that’s true, how will the Milky Way and Andromeda eventually merge?
The laws of physics don’t prefer matter over antimatter. So how can we be certain that distant stars & galaxies aren’t made of antimatter?
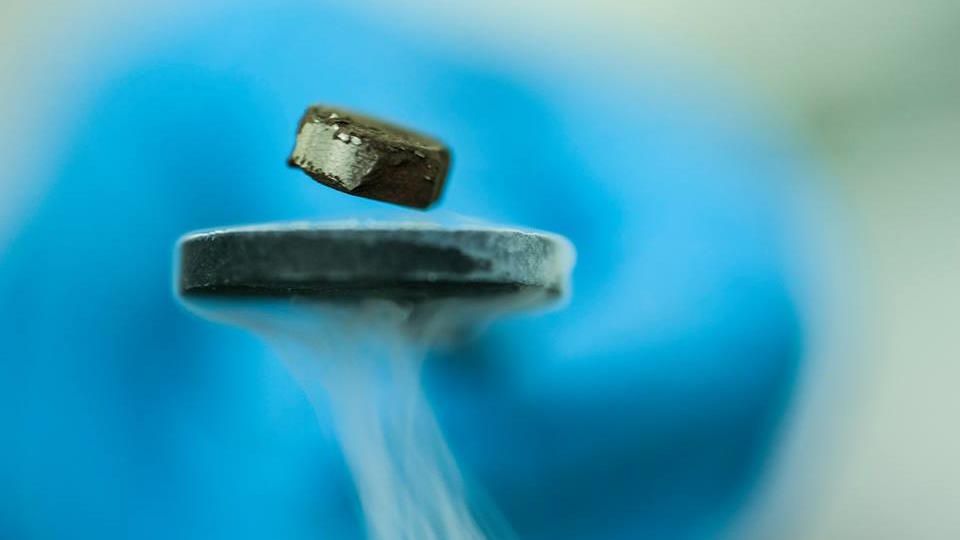
Is LK-99 truly a room temperature superconductor? These 4 tests, none of which have yet been passed, will separate fact from fiction.
All the things that surround and compose us didn’t always exist. But describing their origin depends on what ‘nothing’ means.
Even with the best technology imaginable, you’d probably never be able to exist as a consciously aware brain in a vat.
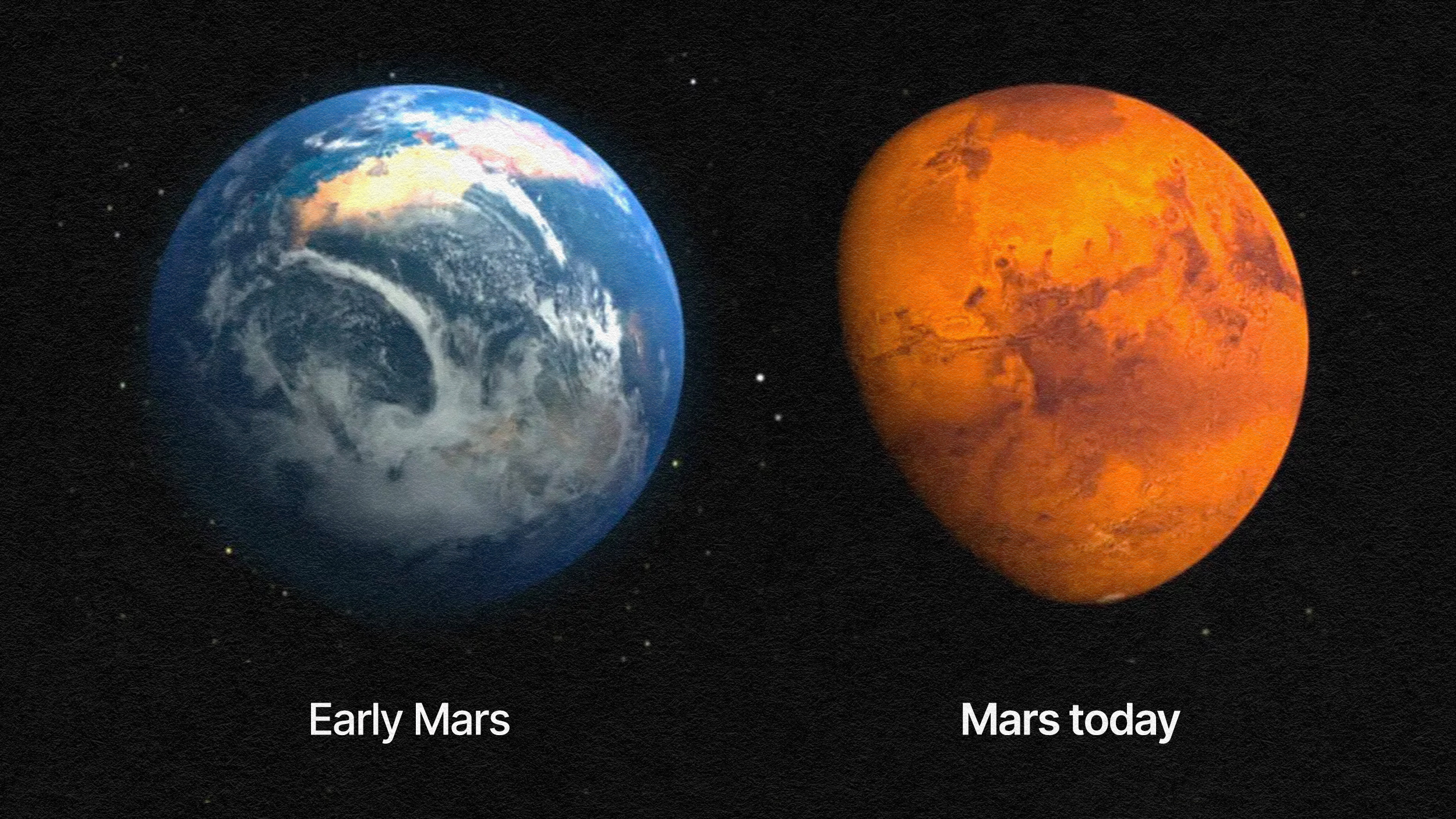
Mars and Earth were sister planets in many ways, with early similar conditions. Why did Mars die? The leading explanation isn’t universal.
The largest particle accelerator and collider ever built is the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. Why not go much, much bigger?