Japanese car maker introduces self-driving chairs to eliminate lines.
Search Results
You searched for: Museum Objects
And England almost burned themselves down as a result. “When Benjamin Franklin inveted the lightning rod, the clergy, both in England and America, with enthusiastic support of George III, condemned it […]
The US Air Force’s Space Horizons Team wants to juice America’s space program. Here’s how.
We are only just beginning to understand how easy access to information is reshaping how we think.
Rather than life arising on Earth, did it already exist in space prior to our planet’s formation? “When you arise in the morning, think of what a precious privilege it […]
Sotheby’s will auction off 380 pieces from Bowie’s collection later this year. The collection is “eclectic, unscripted, [and] understated,” according to Sotheby’s European chairman Oliver Barker.
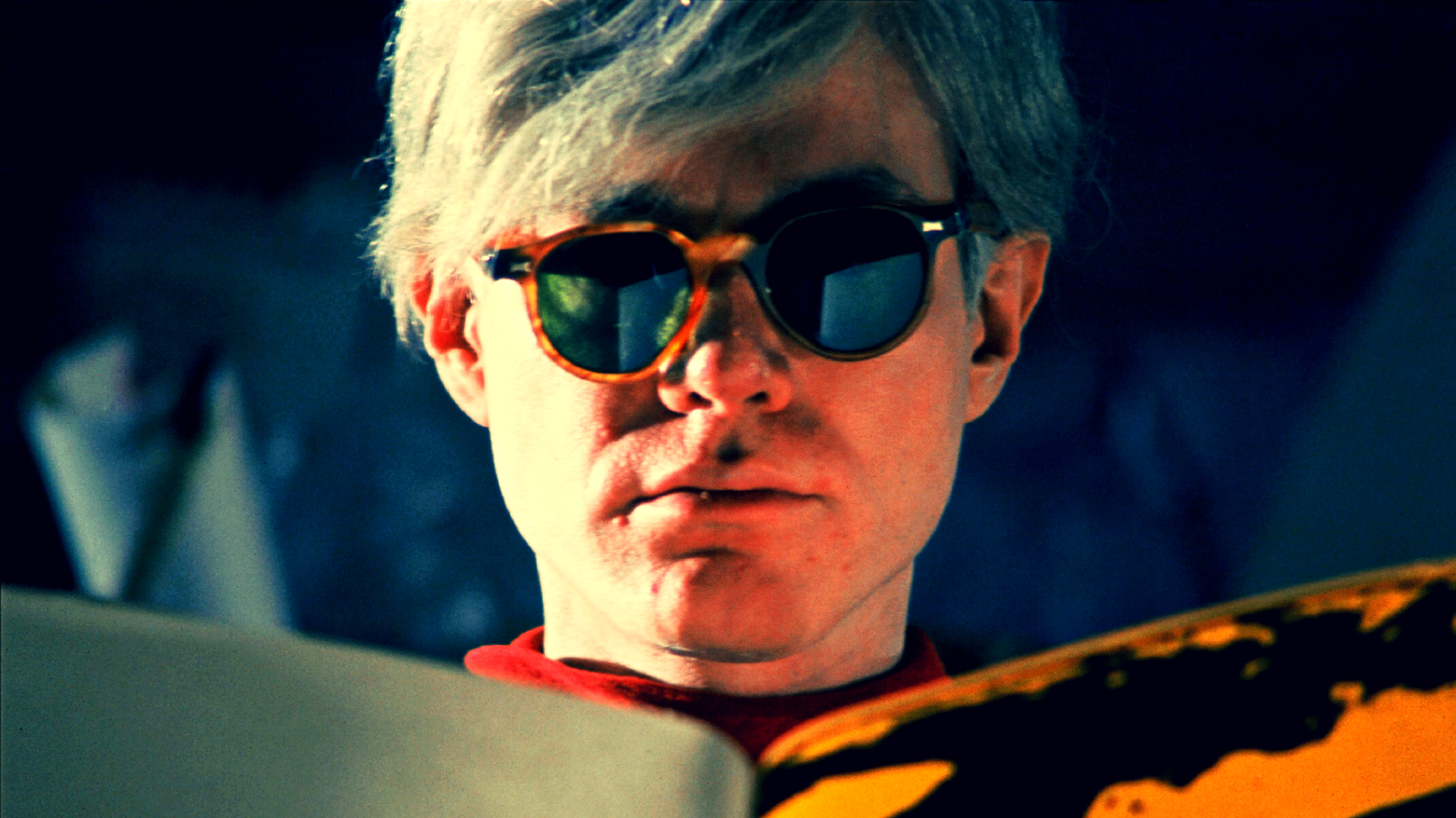
Warhol may be dead, but Pop Art is not—it’s more international, relevant, and alive than ever.
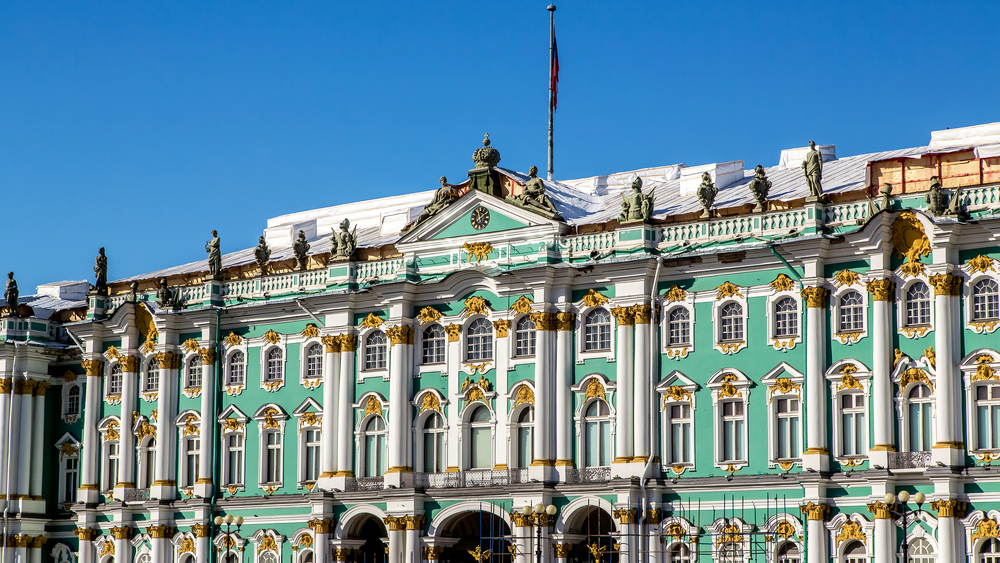
No national museum captures its country’s greatness as perfectly as Russia’s Hermitage.
Impressionist master or indulgent misogynist? Why do people either love Renoir or love to hate him?
American stuff is the stuff of American history, as recorded in still life painting.
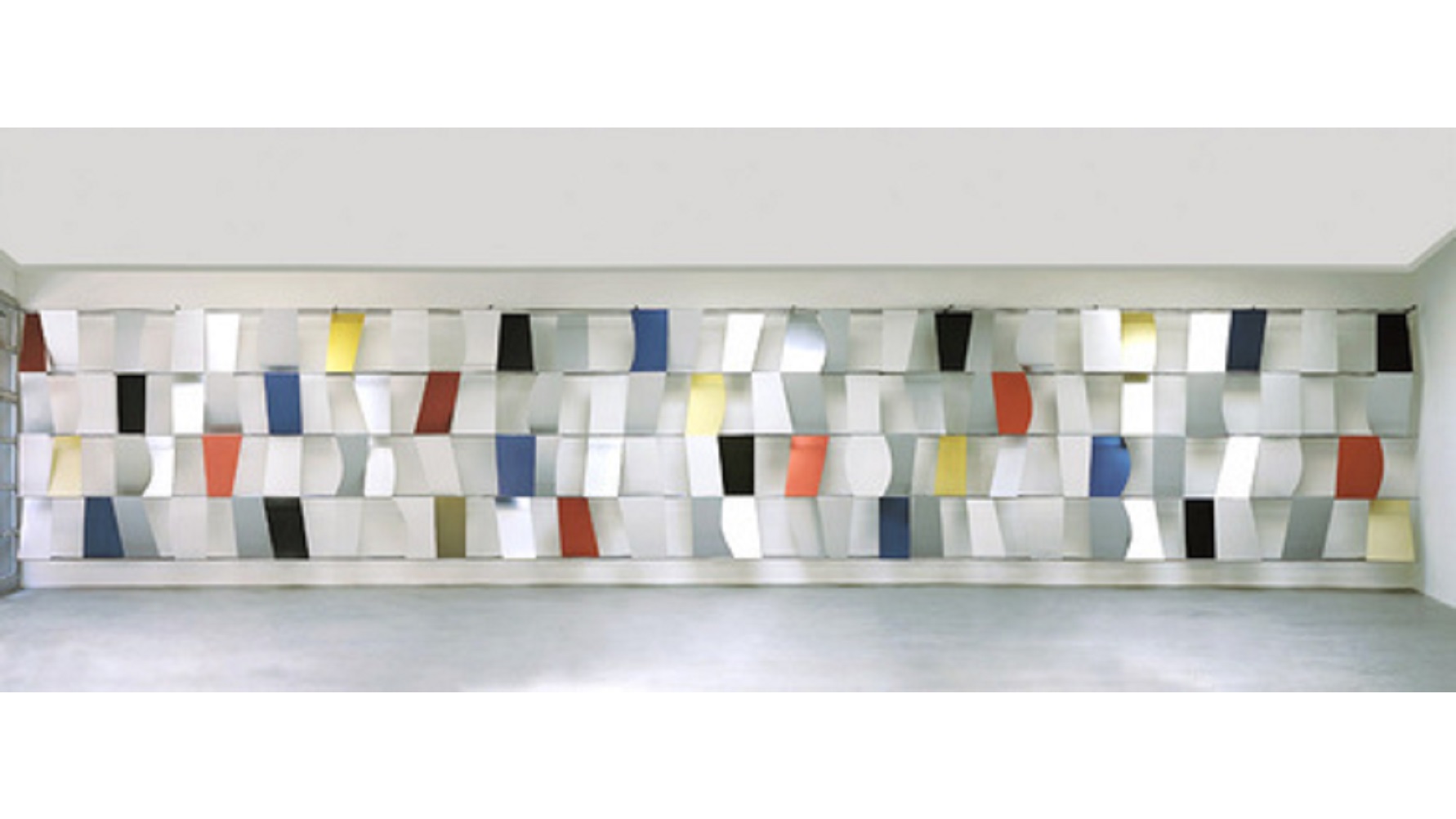
Don’t know Ellsworth Kelly or his art? Now’s your chance — he’s dead.
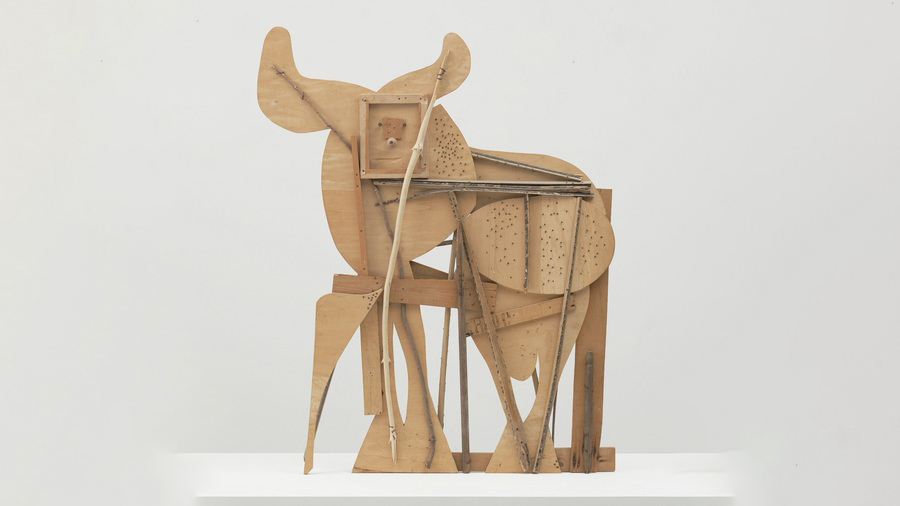
Painting for Picasso was rule-breaking, serious business, but sculpture was rule-innocent child’s play.
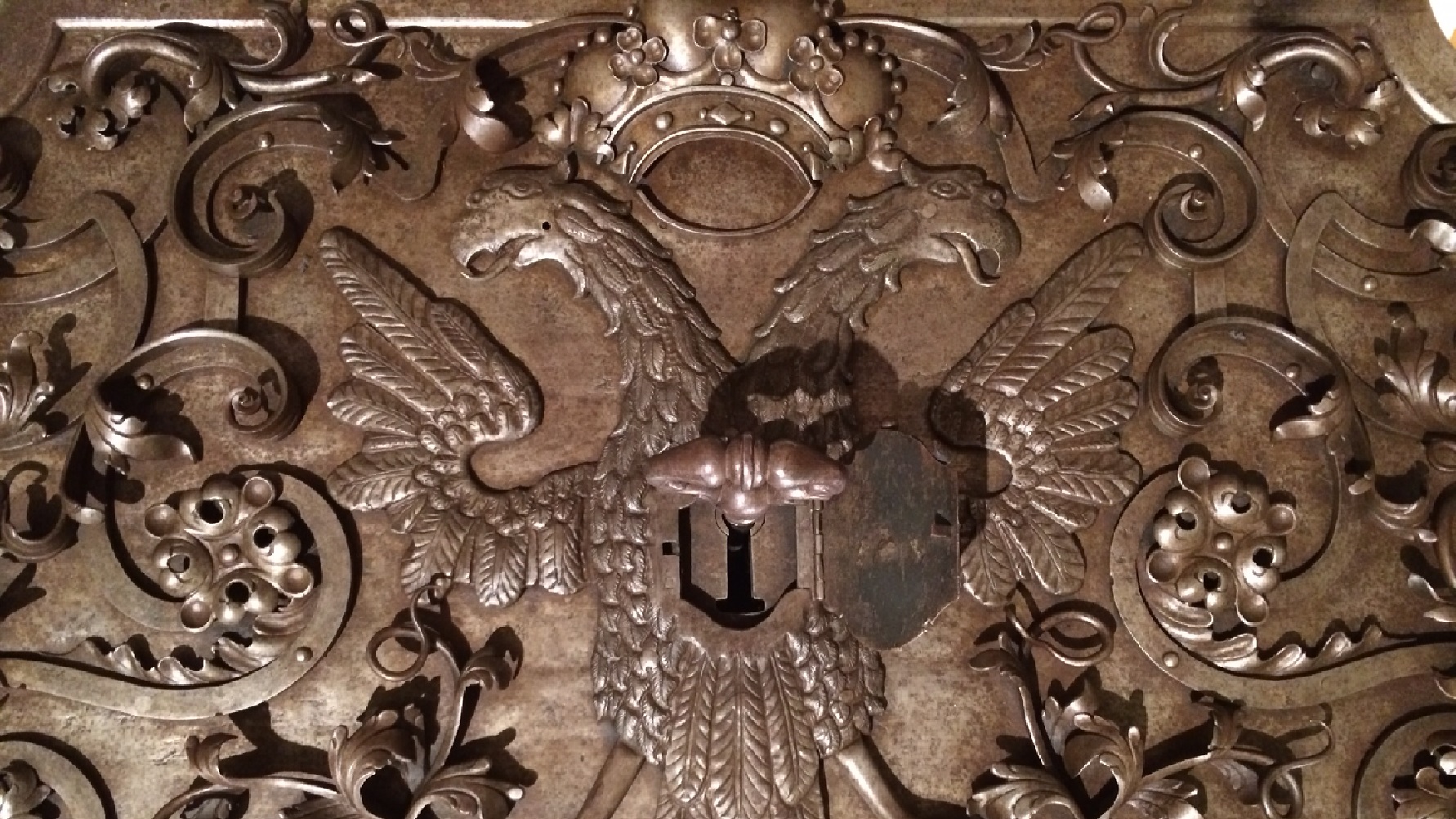
A new Barnes Foundation show highlights the connections between ancient artisanal ironwork and modern art.
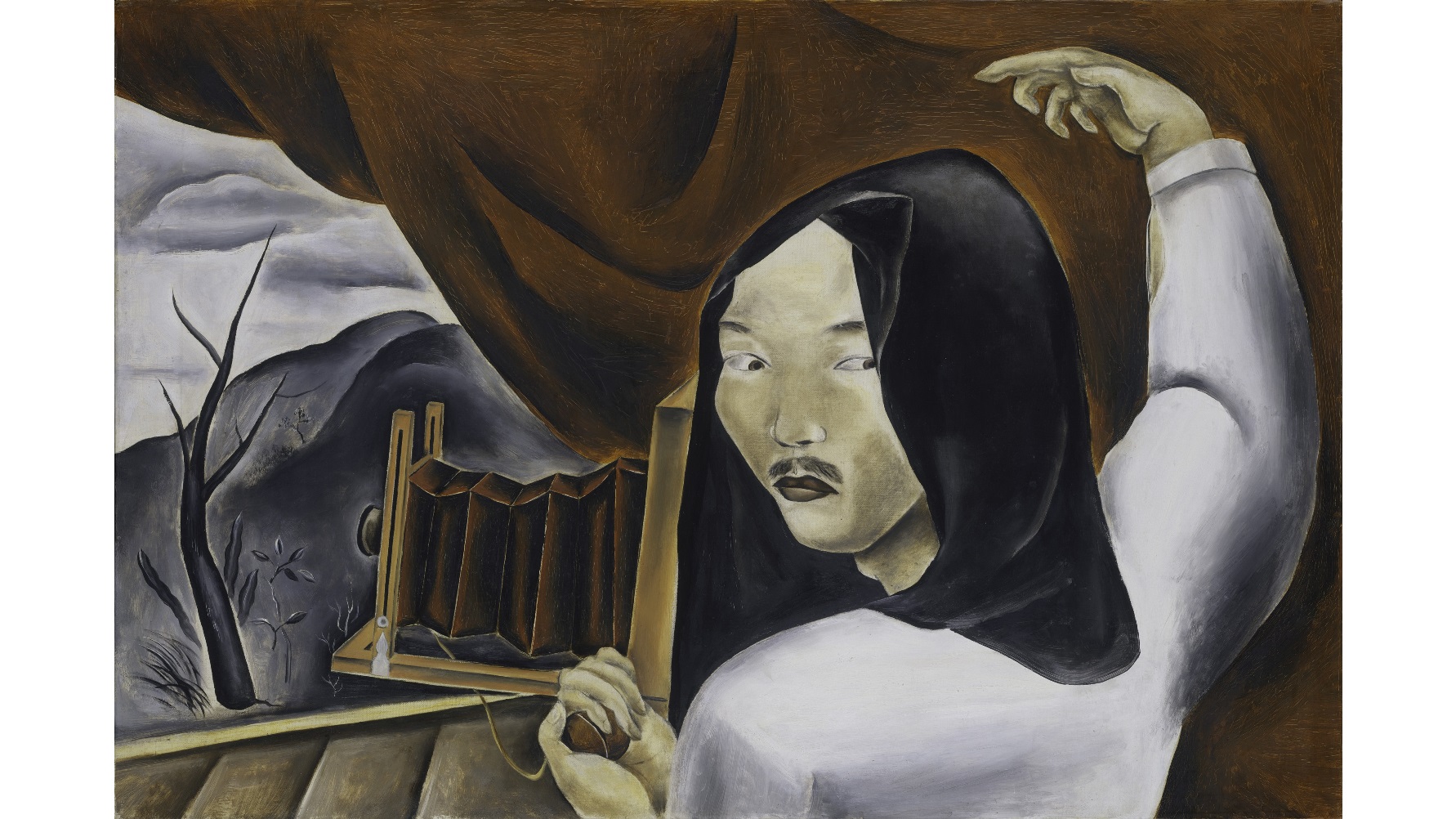
When the Whitney Museum of American Art decided to stage in 1948 their first exhibition of a living American artist, they chose someone who wasn’t even an American citizen, but only legally could become one just before his death. Painter Yasuo Kuniyoshi came to America as a teenager and immersed himself in American culture and art while rising to the top of his profession, all while facing discrimination based on his Japanese heritage. The exhibition The Artistic Journey of Yasuo Kuniyoshi, which runs through August 30, 2015 at the Smithsonian American Art Museum in Washington, DC, unveils an amazing story of an artist who lived between two worlds — East and West — while bridging them in his art that not only synthesized different traditions, but also mirrored the joys and cruelties of them.
The origin of life is one of the biggest open questions. Could it all have started before our planet was even born? “When you arise in the morning, think of […]
The glorious meteor shower peaking this week is the most consistent, year after year. Here’s why. “Men of genius are often dull and inert in society; as the blazing meteor, […]
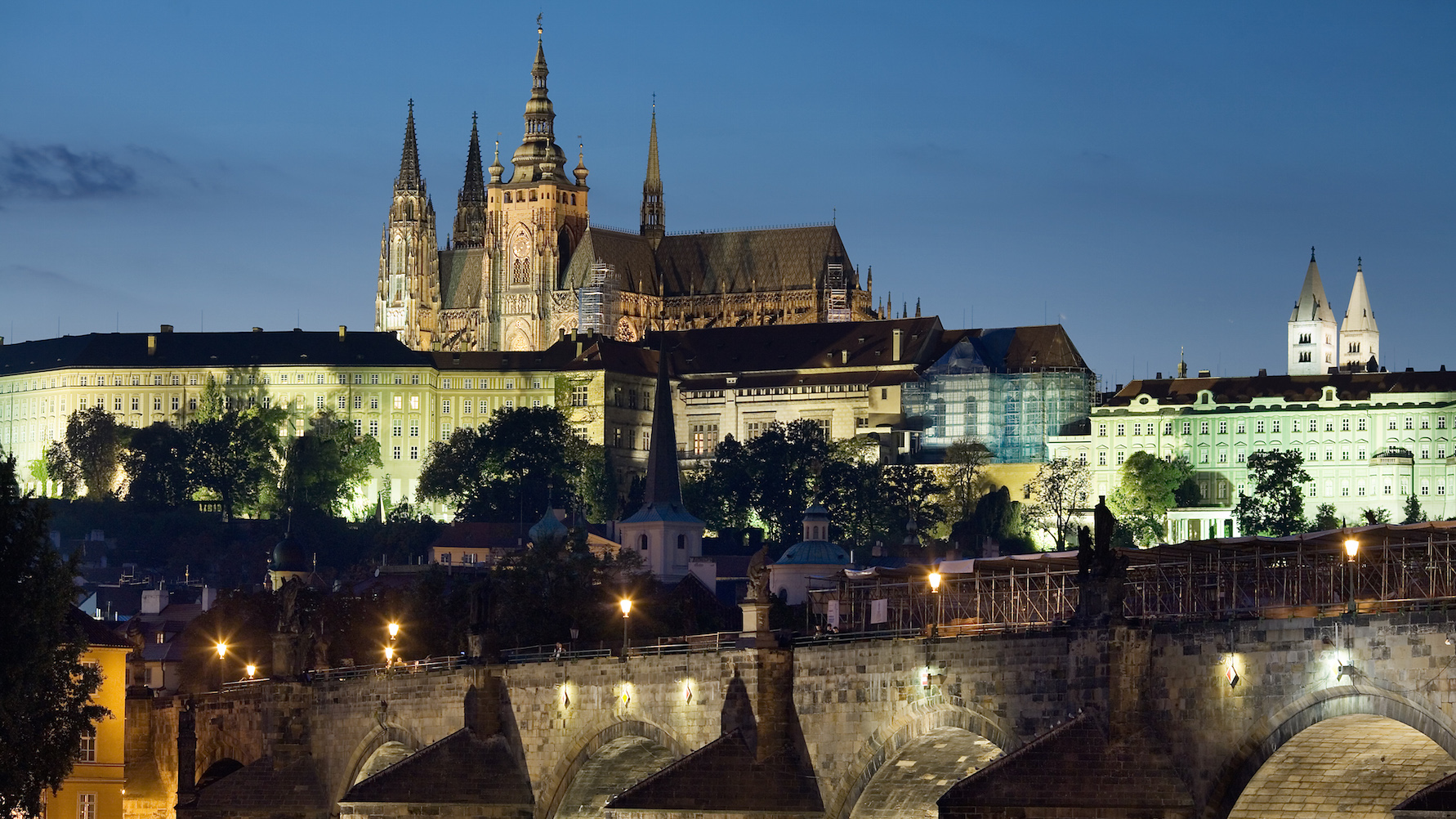
The beautiful and intricate Czech capital is like an anti-Silicon Valley.
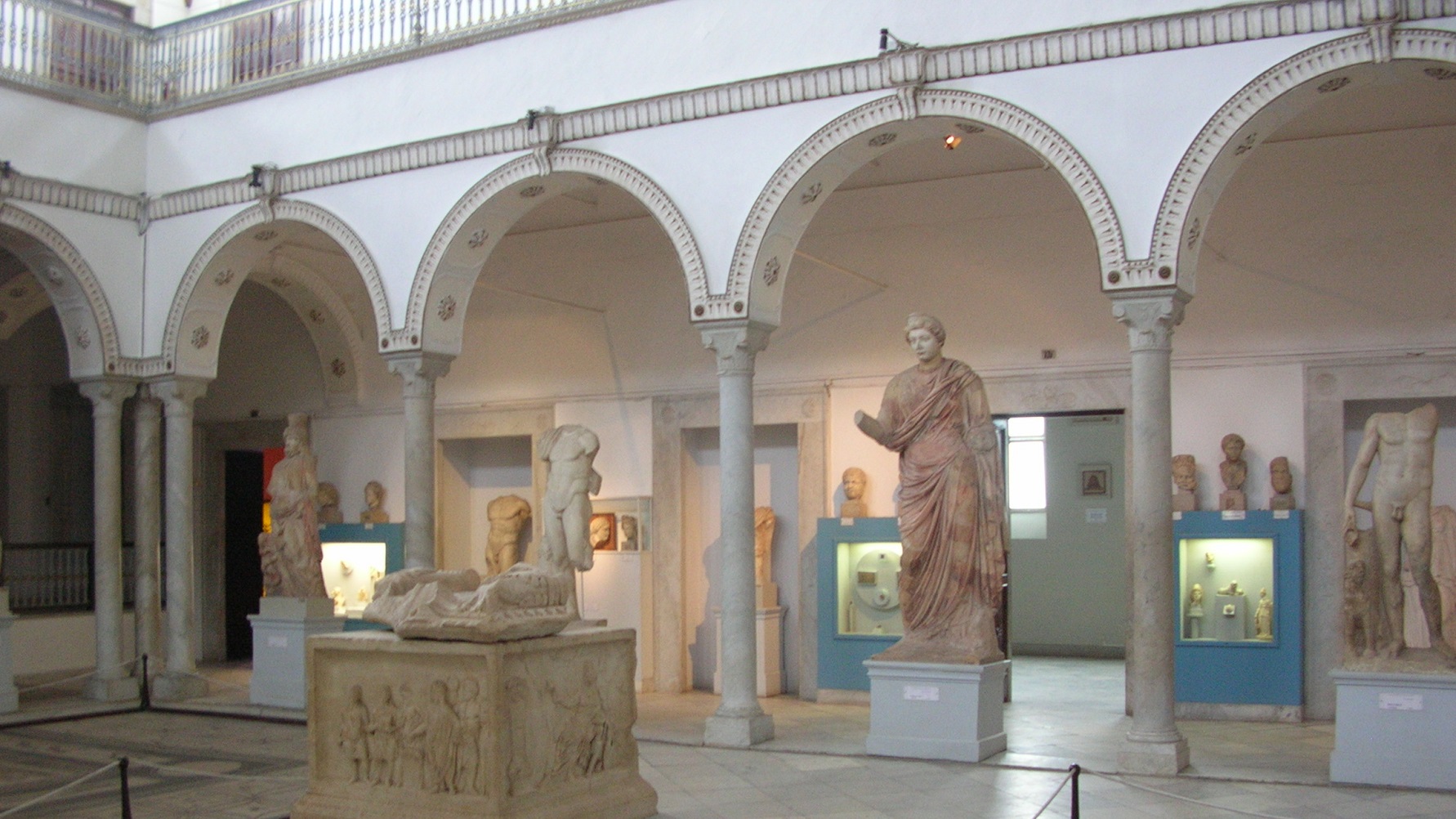
The attack at the Bardo National Museum in Tunis, Tunisia, on March 18, 2015, was an attack on civilization itself. Not just Tunisian civilization or Western civilization or Islamic civilization or Christian civilization — ALL civilization. ISIS may not have been directly involved in the Tunisian attack, but its iconoclastic, its “year zero” philosophy certainly was present. The fact that these attackers targeted tourists seeking out ancient civilizations rather than the artifacts of those ancient civilizations makes this latest tragedy even more chilling. The Bardo National Museum attacks may one day emerge as the first battle in the ultimate fight for civilization’s survival.
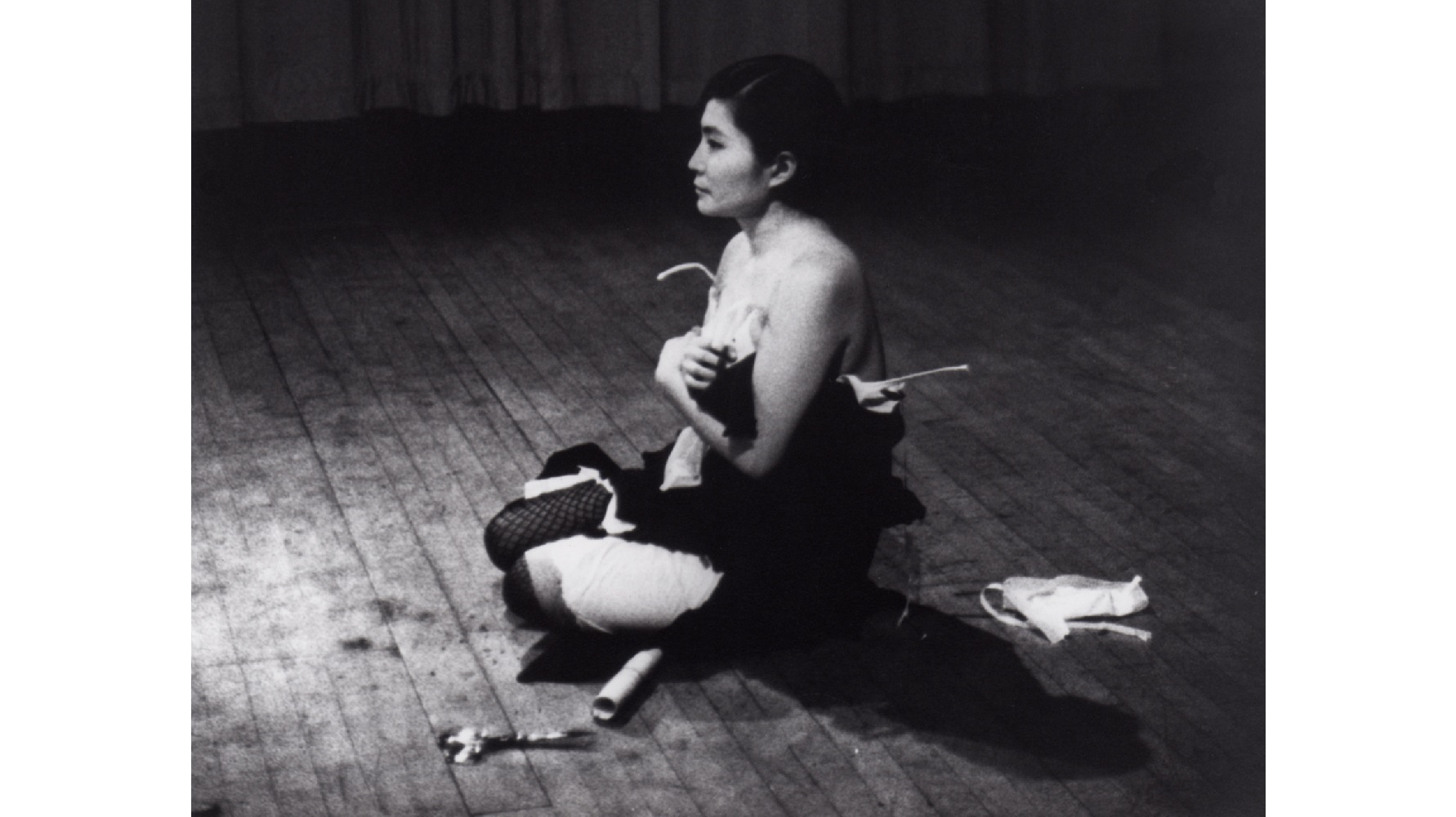
John Lennon liked to joke that Yoko Ono was “the world’s most famous unknown artist.” Before she infamously “broke up the Beatles” (but not really), Ono built an internationally recognized career as an artist in the developing fields of Conceptual art, experimental film, and performance art. Unfairly famous then and now for all the wrong reasons, Ono’s long fought in her own humorously sly way for recognition, beginning with her self-staged 1971 “show” Museum of Modern (F)art, a performance piece in which she dreamed of a one-woman exhibition of her work at the Museum of Modern Art, New York. Now, more than 40 years later, the MoMA makes that dream come true with the exhibition Yoko Ono: One Woman Show, 1960–1971. Better late than never, this exhibition of the pre-Lennon and early-Lennon Ono establishes her not just as the world’s most famous unknown artist, but the most unfairly unknown one, too.
By the 1960s the two most criticized art forms in America were modern art and television. Some critics called modern art mystifying junk, while others targeted TV as anything from trash to a threat to democracy. Revolution of the Eye: Modern Art and the Birth of American Television at The Jewish Museum, New York, hopes to redeem both media by exploring how modern art provided an ethos and aesthetic for early television — a debt repaid later as television, in turn, inspired a new generation of modern artists, including Andy Warhol, who began as a modernist-influenced graphic designer for, among other clients, television networks. By looking back at modern art and television’s mutual love affair from the 1940s to the 1970s, Revolution of the Eye challenges us to reflect on the artistic aspirations of TV’s latest golden age.
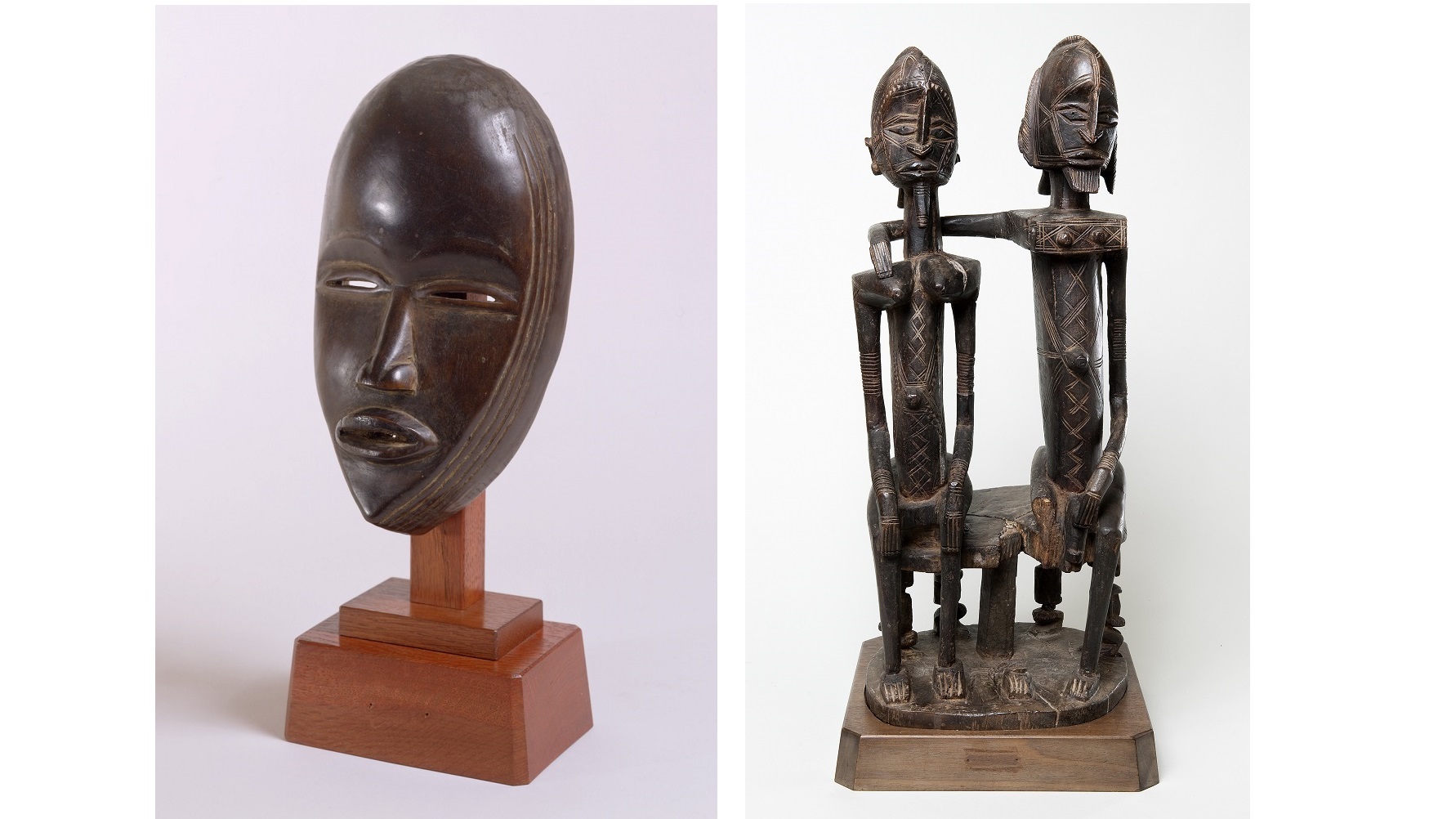
The Barnes Foundation’s current exhibition, Mark Dion, Judy Pfaff, Fred Wilson: The Order of Things, epitomizes the business buzz phrase “disruptive innovation” like few other museum shows (which I wrote about here). Disrupt or die, the thinking goes. Old orders must make way for new. Coincidentally, as the Barnes Foundation, home of Dr. Albert Barnes’ meticulously and idiosyncratically ordered collection of Impressionist and Post-Impressionist masterpieces left just so since his death in 1951, invites outsider artists to question and challenge Dr. Barnes’ old order, it also publishes their own insider’s critical “warts and all” assessment of Dr. Barnes’ relationship to African art and African-Americans. In African Art in the Barnes Foundation: The Triumph of L’Art nègre and the Harlem Renaissance, scholar Christa Clarke reassesses Dr. Barnes intentions and results in his building of the first great African art collection in America. “More than just formal accents to modernist paintings and other Western art in the collection,” Clarke argues, “African art deserves to be seen as central to the aesthetic mission and progressive vision that was at the very heart of the Barnes Foundation.”
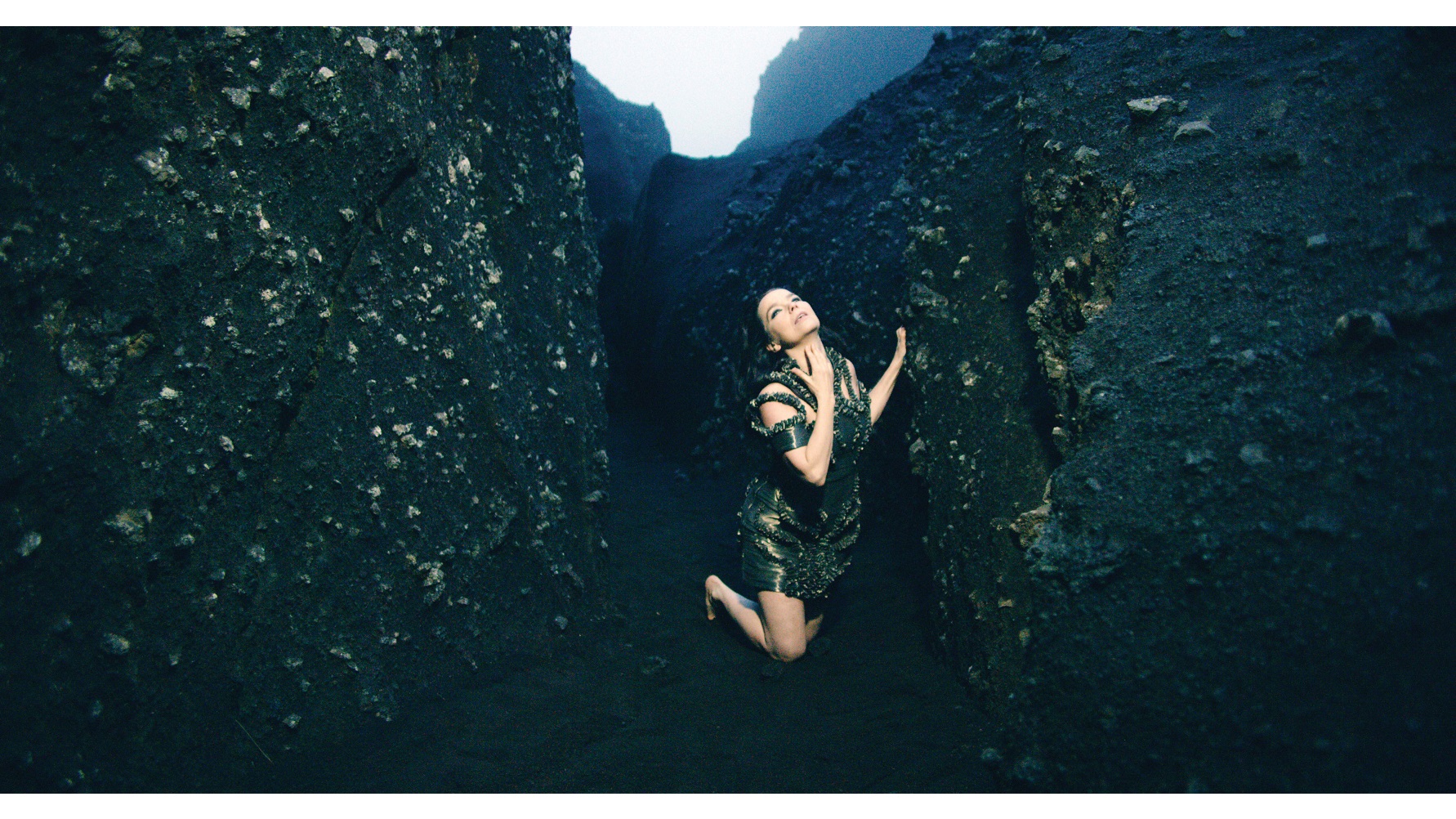
It’s hard to remember a major show at a major American museum generating so much angst as Björk at The Museum of Modern Art, New York. Some arts sites quickly began aggregating art critics’ aggravation over almost every detail of the show. What began as art criticism evolved into a media lynching of the MoMA, American museums, and pandering-to-the-public curators (in this case, Klaus Biesenbach). New York art world critics, and husband-and-wife team, Jerry Saltz and Roberta Smith hated the show in different ways, but both connected to their love of Björk and her music. ArtNews’ M.H. Miller wins the poison pen prize, however, for coining the new critical term “starf@#king” to describe the MoMA’s treatment of Björk as much as its treatment of the viewing public. The question of whether Björk is good or not might really be a question of what Björk is really about.
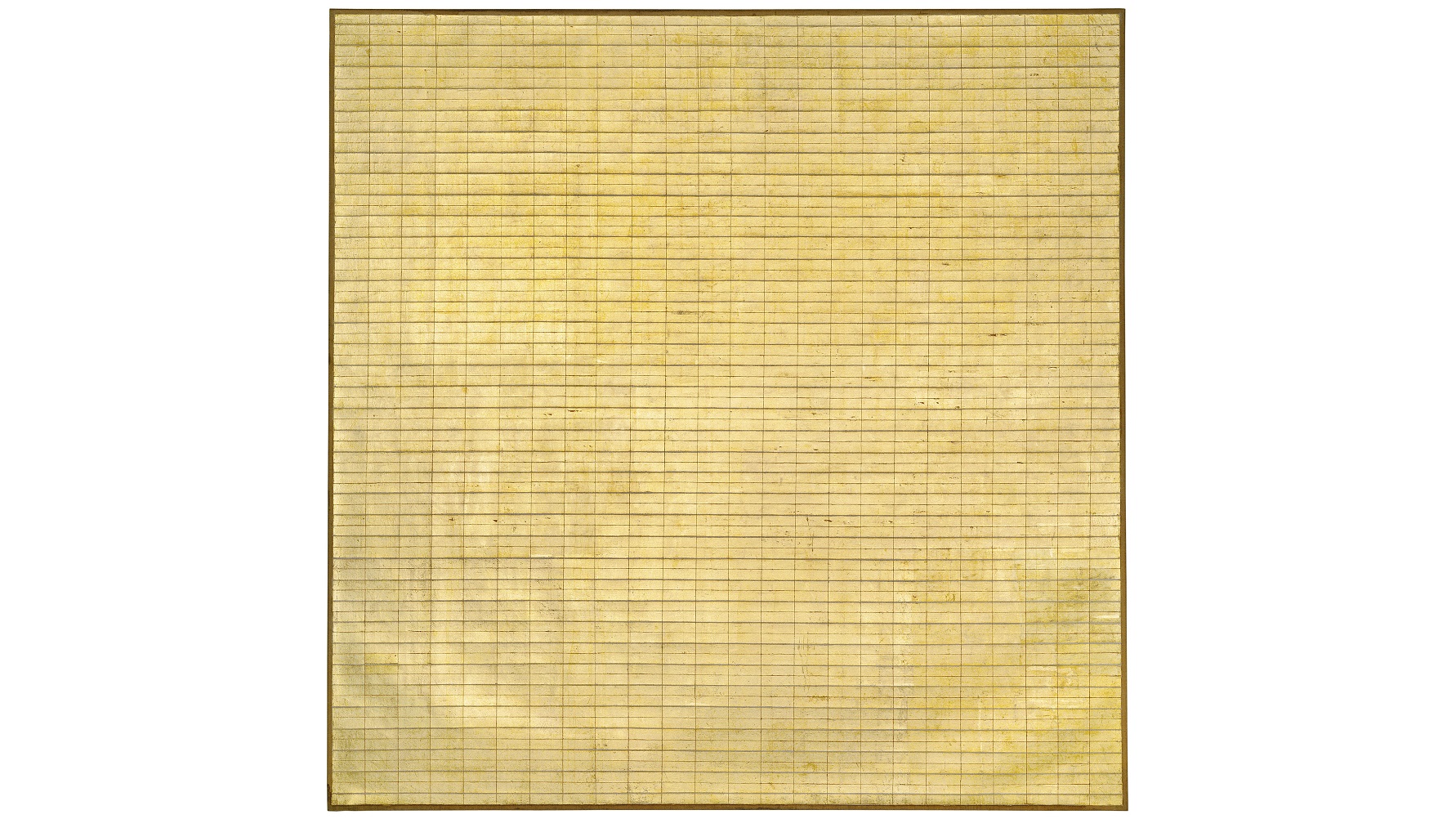
“When I think of art, I think of beauty. Beauty is the mystery of life,” minimalist artist Agnes Martin once explained. “It is not in the eye; it is in my mind. In our minds there is awareness of perfection.” In the first comprehensive survey of her art at the Tate Modern, in London, England, the exhibition Agnes Martin strives to guide viewers to that “awareness of perfection” Martin strove to embody in her minimalist, geometrically founded art. Rather than the cold, person-less brand of modernist minimalism, Martin’s work personifies the warm humanity of Buddhist editing down to essentials. At the same time, surveying Martin’s art and thinking allows us to revisit the feminist critiques of minimalism and shows how Martin’s stepping back from the bustle of the New York art scene freed her to find “a beautiful mind” — not just for women, but for everyone.
Few business buzzphrases draw as much interest (and ire) as “disruptive innovation.” Disrupt or die, the thinking goes. Old orders must make way for new. At the Barnes Foundation, home of Dr. Albert Barnes’ meticulously and idiosyncratically ordered collection of Impressionist and Post-Impressionist masterpieces left just so since his death in 1951, three artistic innovators aim at questioning and challenging Dr. Barnes’ old order. Mark Dion, Judy Pfaff, Fred Wilson: The Order of Things invites three award-winning, contemporary installation artists to disrupt the existing paradigm at the Barnes and assist us in seeing Dr. Barnes and his collection in a whole new way.
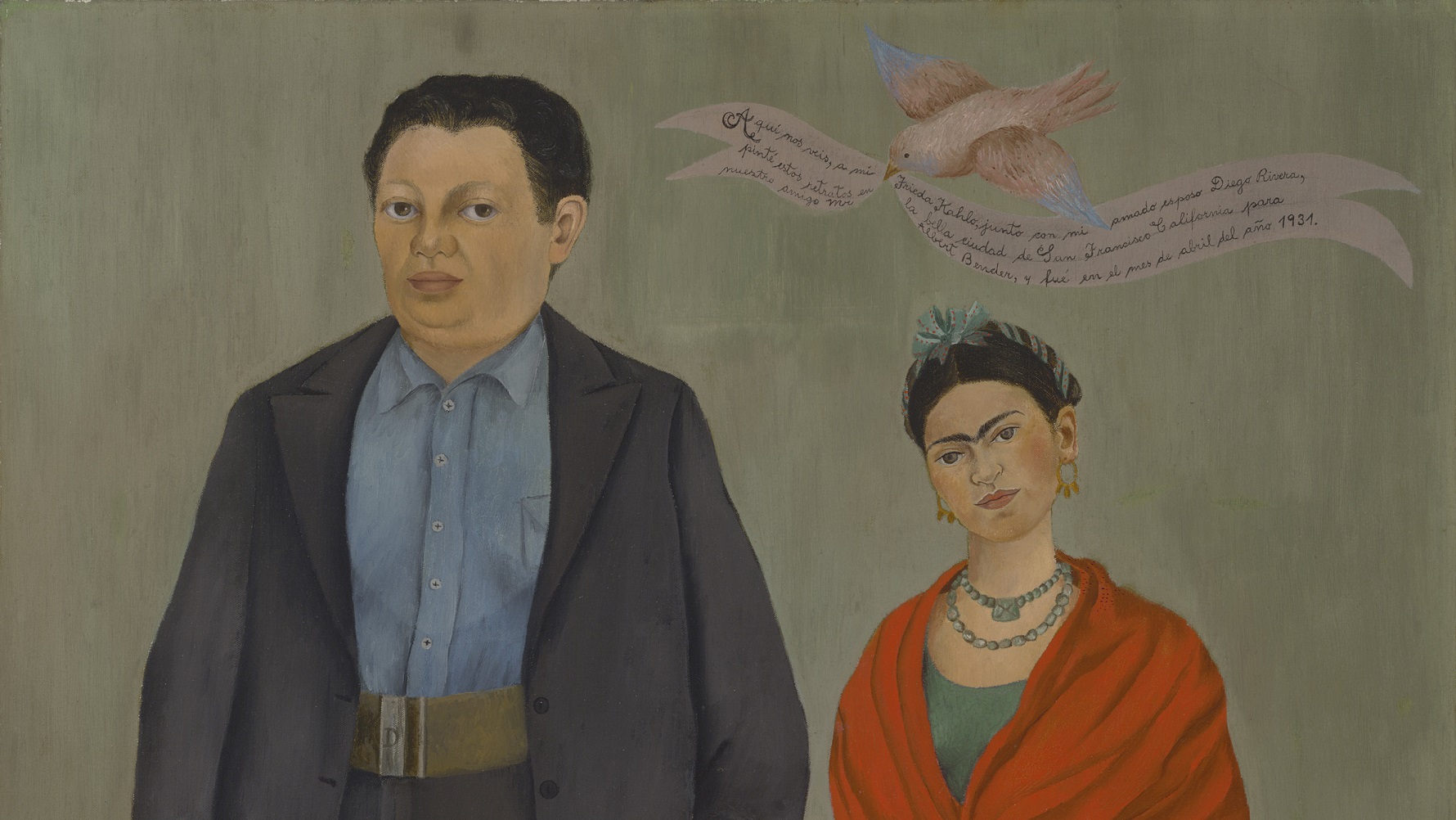
Few American cultural institutions stared as deep into the yawning, austerity-driven abyss of large-scale deaccessioning as The Detroit Institute of Arts. When the City of Detroit declared bankruptcy in 2013, vulturous creditors circled the DIA’s collection, estimated worth (depending on the estimator) of $400 million to over $800 million. Some experts see signs of a Detroit comeback, however, but one very visible sign is the new DIA exhibition Diego Rivera and Frida Kahlo in Detroit, a showcase of the city’s ties to Mexican artists Frida Kahlo and Diego Rivera as well as a tribute to Kahlo’s and Rivera’s own artistic comebacks. Few exhibitions truly capture the spirit of a city at a critical moment in its history, but Diego Rivera and Frida Kahlo in Detroit is a show of comebacks that will have you coming back for more.
For many people, art museums feel like a foreboding foreign nation with a language all its own. Frederick Wiseman’s new documentary, National Gallery, offers an immersion class in how to speak fluent “museum.”
Before you tout the next exoplanet as “the most Earth-like ever,” ask whether that’s true, and whether that’s even a good thing. “You can spend too much time wondering which […]
If Mona Lisa is the smile, Madame Cézanne is the scowl. Hortense Fiquet, Paul Cézanne’s model turned mistress turned mother of his child turned metaphorical millstone around his neck, endures as a standard art history punch line—the muse whose misery won immortality through the many masterpiece portraits done of her. Or at least that’s how the joke usually goes. The Metropolitan Museum of Art’s current exhibition Madame Cézanne, which gathers together 24 of the 29 known portraits Cézanne painted of Hortense over a period of more than 20 years, tries to rewrite that joke as it hopes to solve the riddle of Madame Cézanne, aka, The Case of the Miserable Muse.
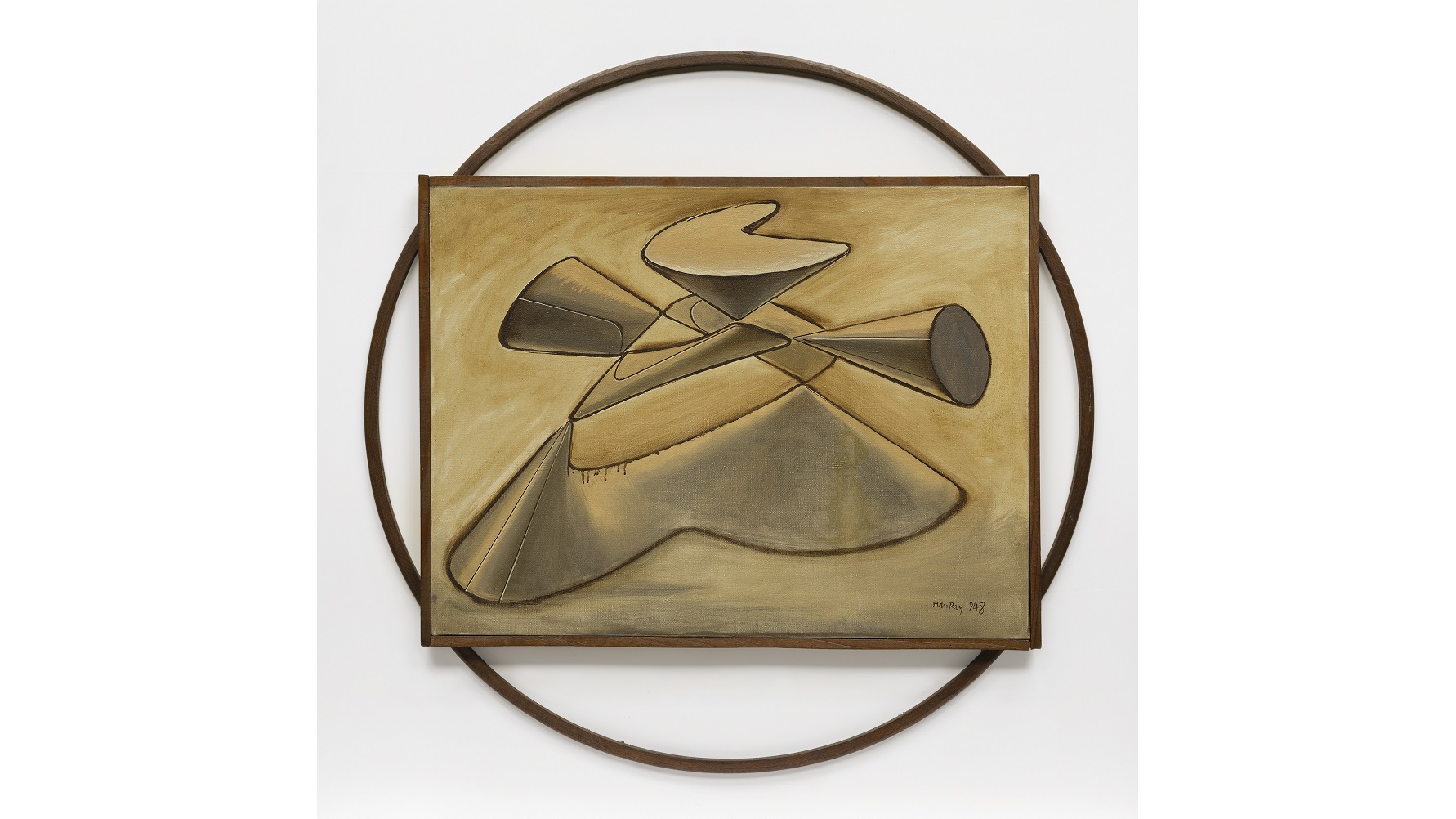
While advanced math and Shakespeare combine to make a nightmare curriculum for some students, for artist Man Ray, one of the most intriguing minds of 20th century art, they were “such stuff as dreams are made on,” or at least art could be made from. A new exhibition at The Phillips Collection reunites the objects and photographs with the suite of paintings they inspired Man Ray to create and title Shakespearean Equations. Man Ray—Human Equations: A Journey from Mathematics to Shakespeare traces the artist’s travels between disciplines, between war-torn continents, and between media that became not only a journey from arithmetic to the Bard, but also a journey of artistic self-discovery.
Originating out beyond Neptune, thousands of world originate. Who’s the largest? It’s not who you expect, Pluto-lovers! “It is not when truth is dirty, but when it is shallow, that […]