Space & Astrophysics
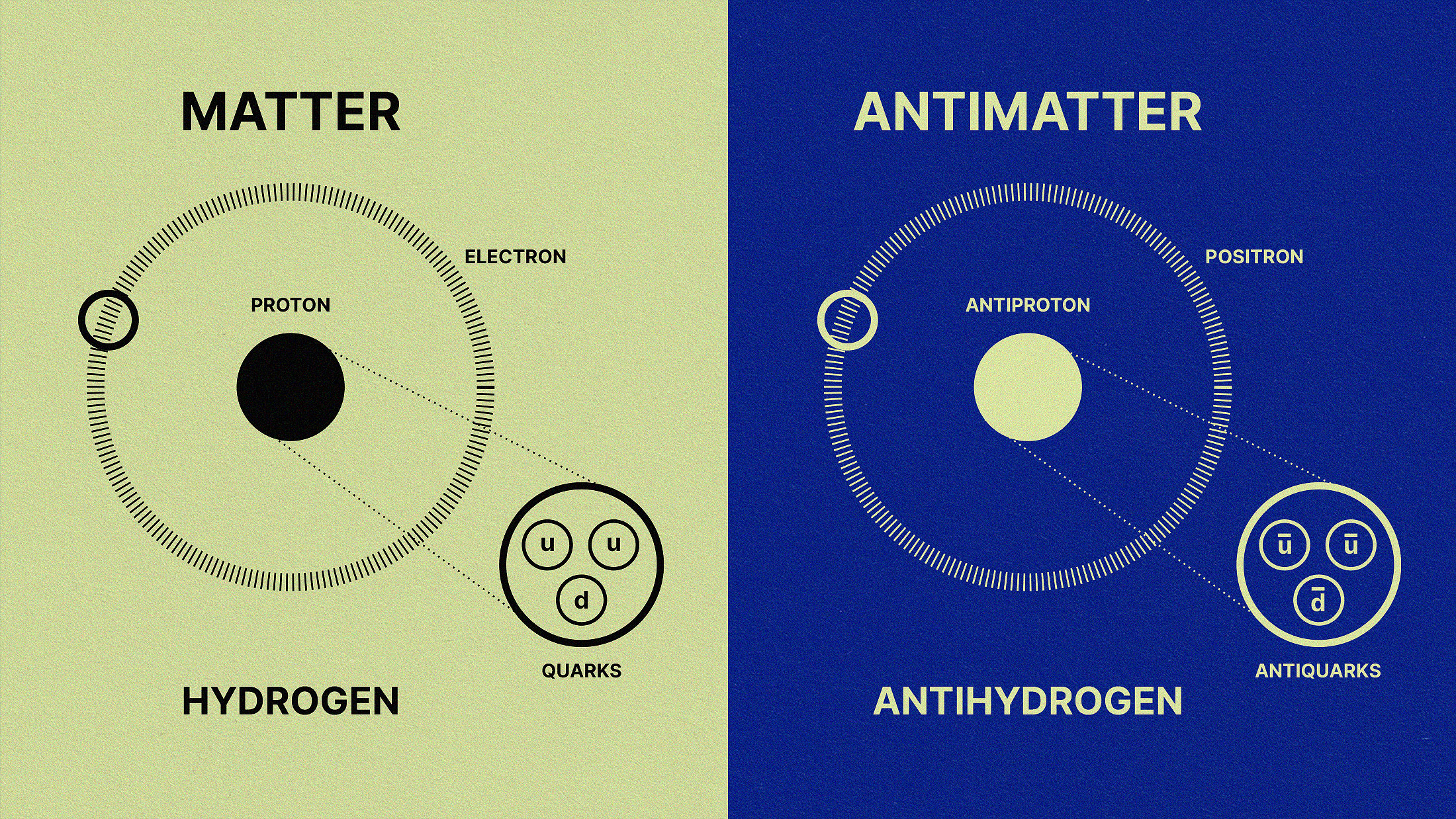
In the earliest stages of the hot Big Bang, equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have existed. Why aren’t they equal today?
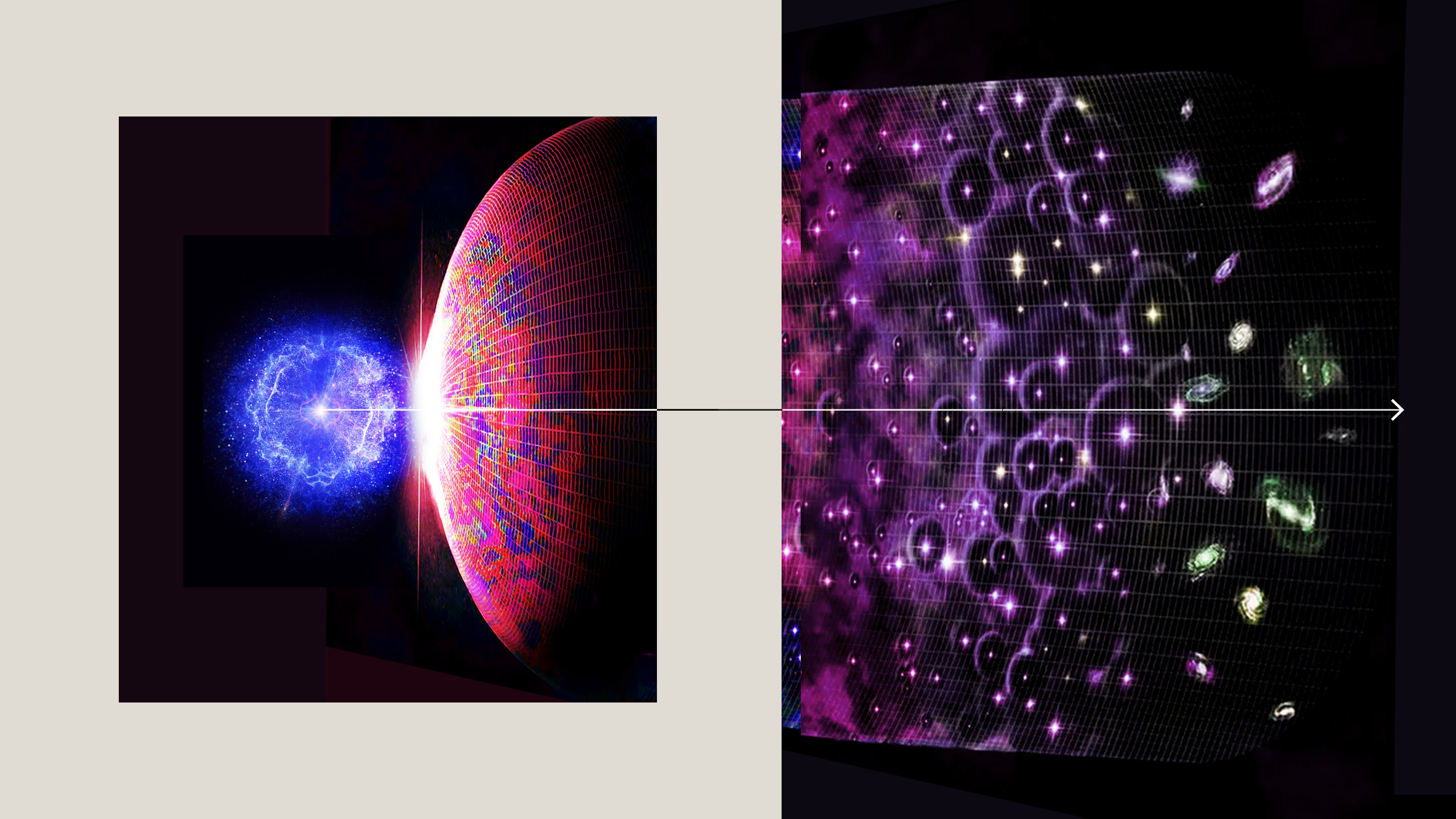
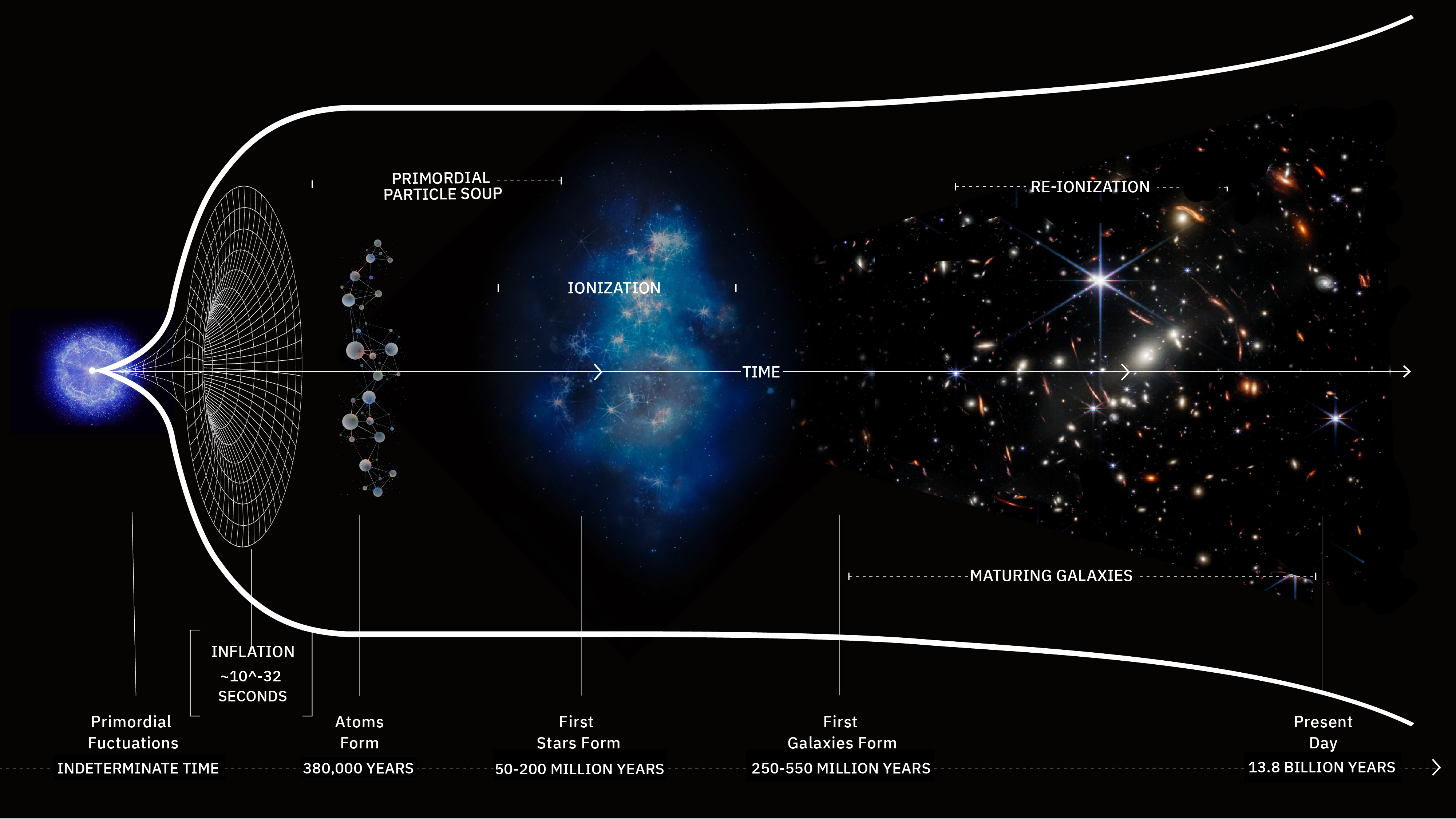
When the hot Big Bang first occurred, the Universe reached a maximum temperature never recreated since. What was it like back then?
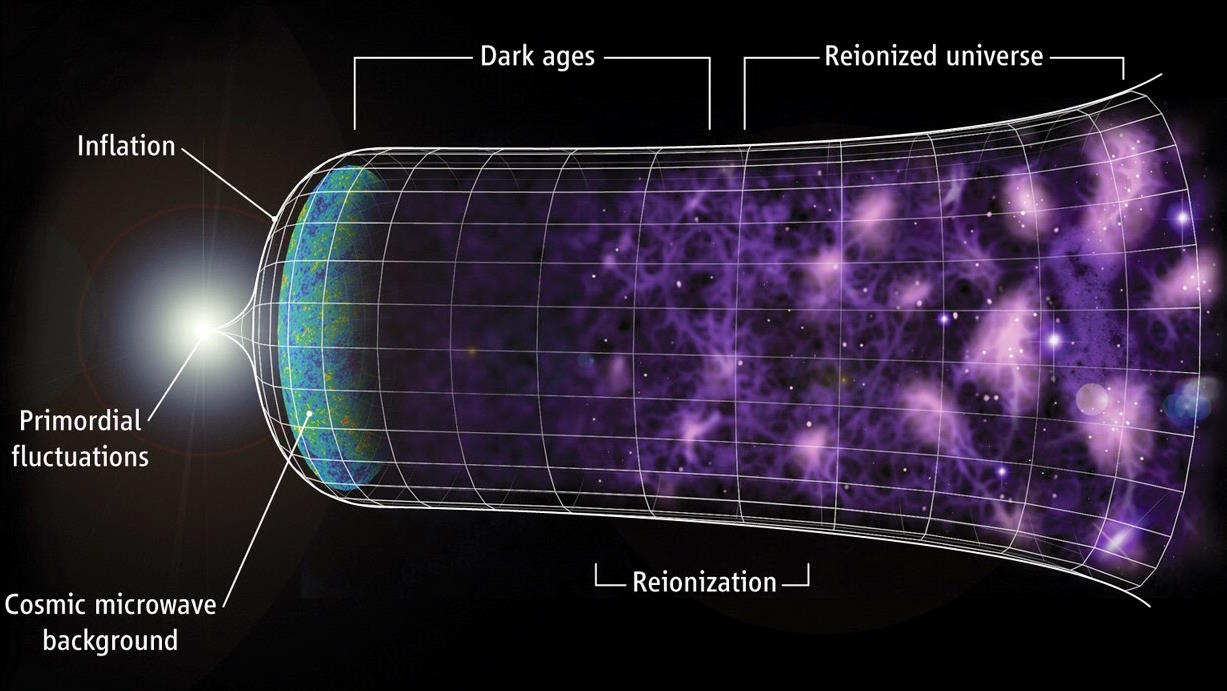
Some 13.8 billion years ago, the Universe became hot, dense, and filled with high-energy quanta all at once. Here’s what it was like.
Perhaps the most remarkable fact about the Universe is simply that it, and everything in it, exists. But what’s the reason why?
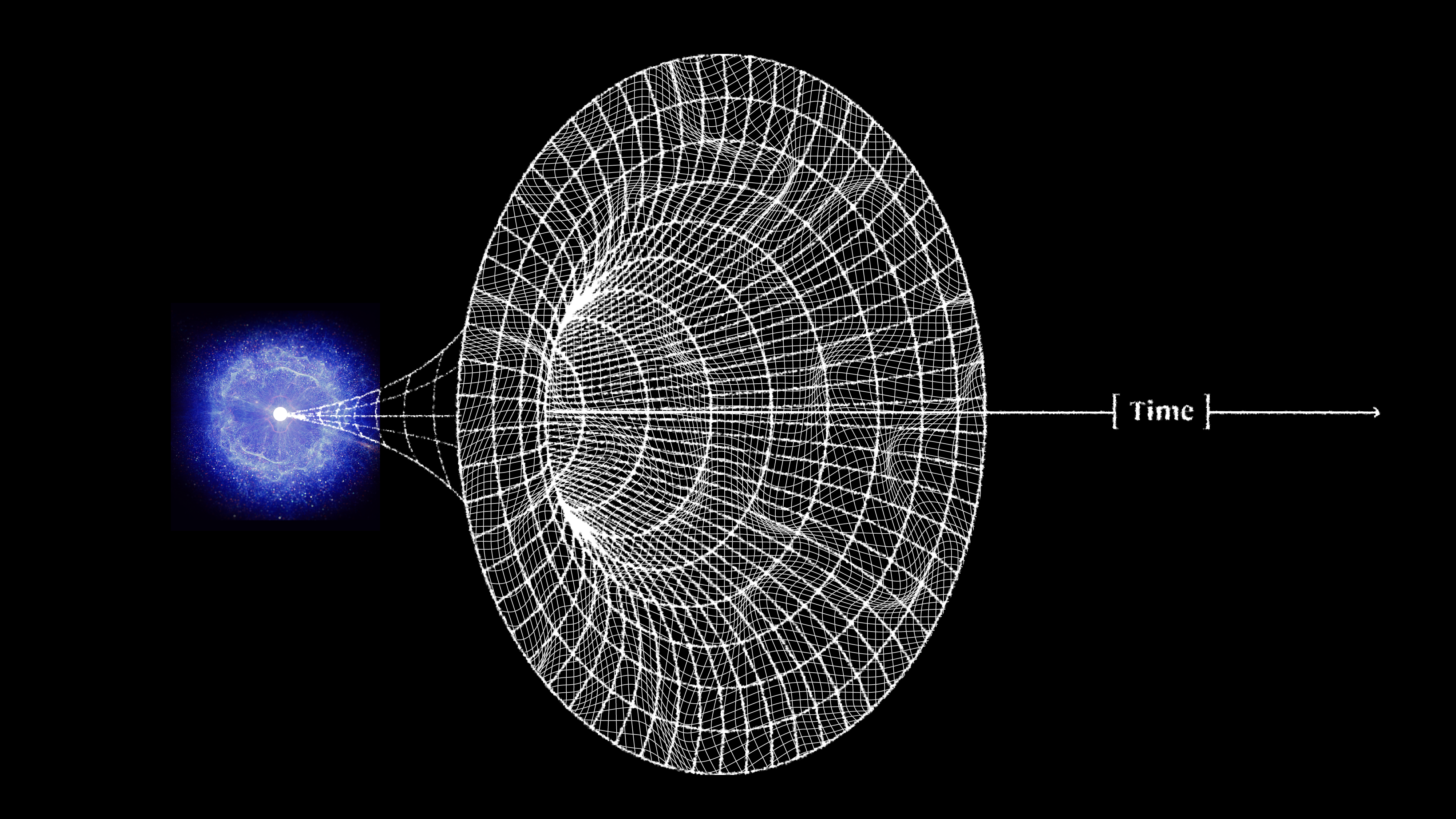
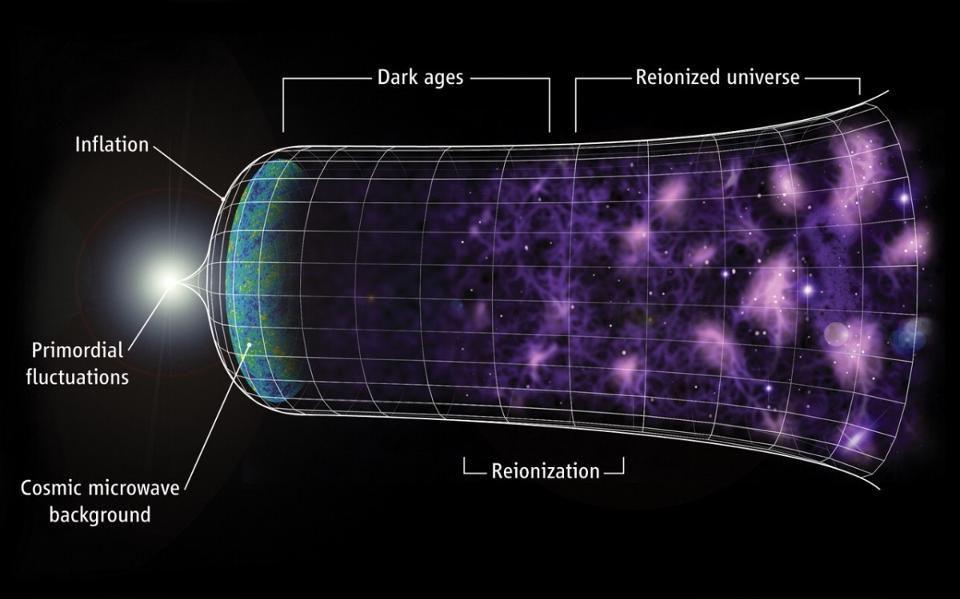
Cosmic inflation is the state that preceded and set up the hot Big Bang. Here’s what the Universe was like during that time period.
Two of the answers add a dimension to physics that doesn’t belong there. Maybe we could call it “astrotheology.”
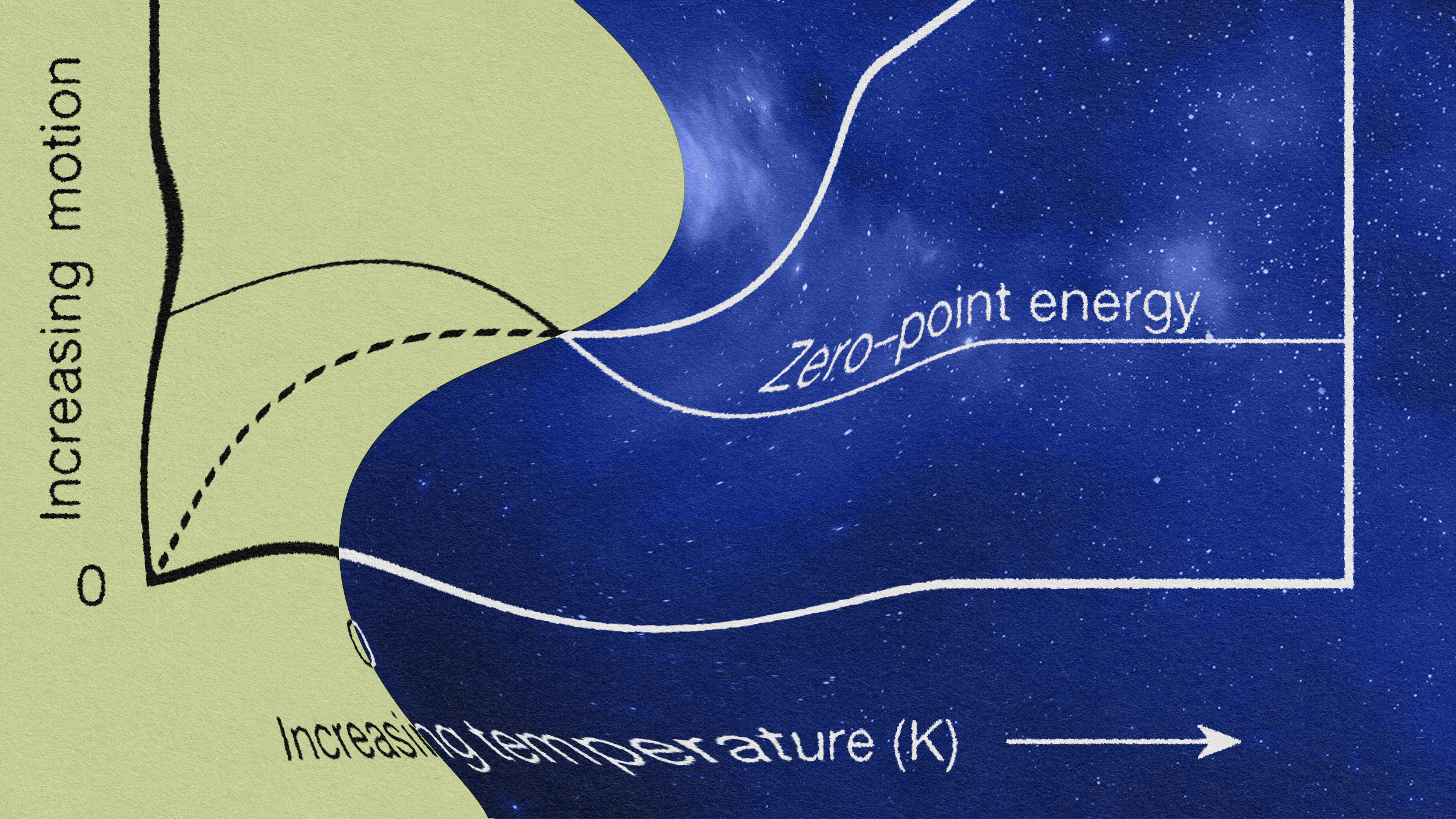
The term “zero-point energy” has at least two meanings, one that is innocuous and one that is a great deal sexier (and scammier).
With LEDs bringing brighter nighttime lighting than ever before, and thousands of new satellites polluting the skies, astronomy needs help.
Bang bang all over the Universe.
Finding alien technology on the seafloor would be truly incredible. This extraordinary claim, however, is debunked by the actual evidence.
Our host Kmele went inside Fermilab, America’s premiere particle accelerator facility, to find out how the smallest particles in the universe can teach us about its biggest mysteries.
▸
38 min
—
with
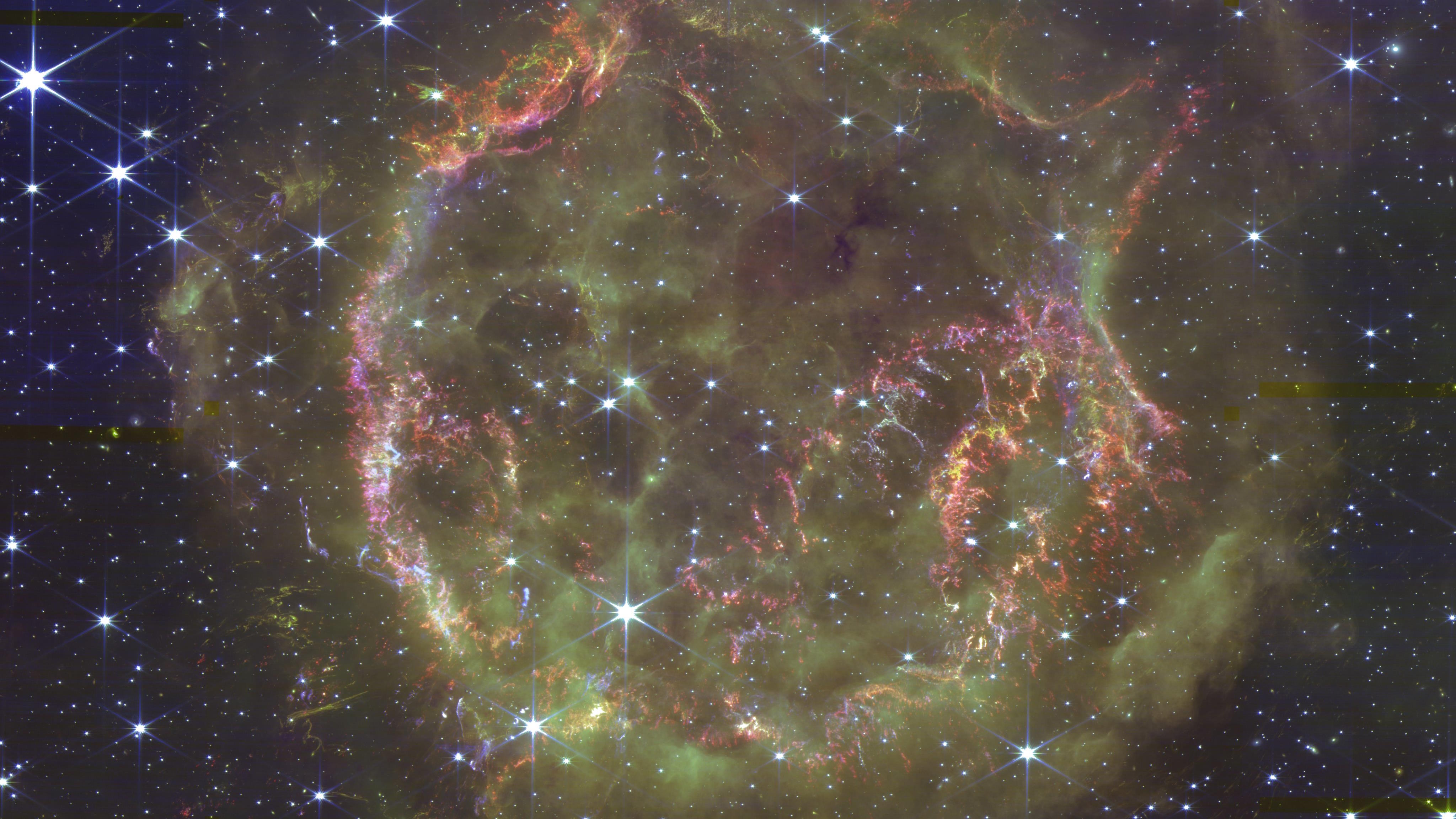
In 1667, a core-collapse supernova happened right here in the Milky Way, invisible to all humans. ~350 years later, here’s what JWST sees.
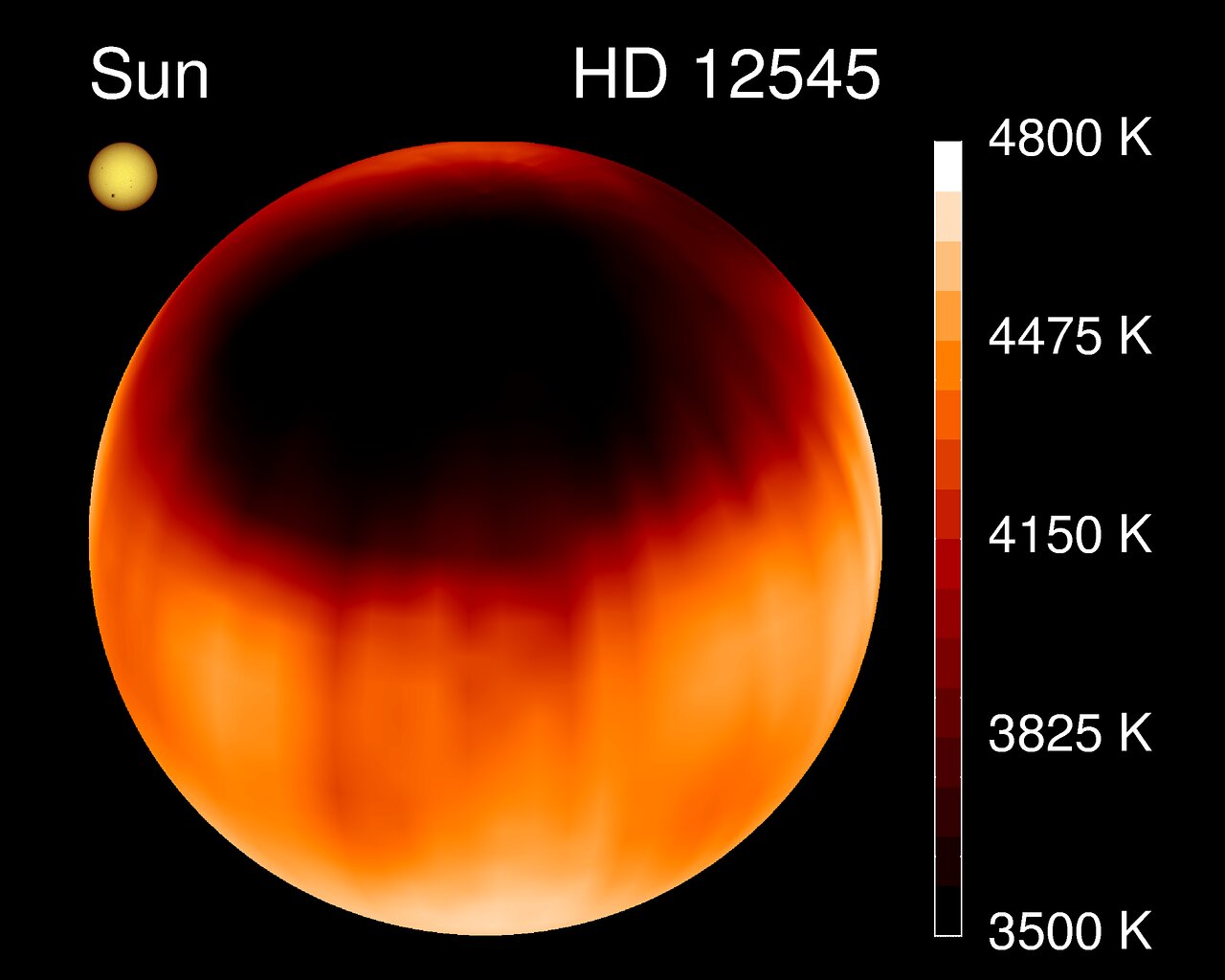
When we look at our Sun, its properties are incredibly constant, varying by merely ~0.1% over time. But all stars don’t play by those rules.
Light can be turned into heat, which can then be turned into motion, and the effect of that motion can be turned into a big squeeze.
All matter particles can act as waves, and massless light waves show particle-like behavior. Can gravitational waves also be particle-like?
We need a hypothesis that accounts for both the fine-tuning of physics for life but also the arbitrariness and gratuitous suffering we find in the world.
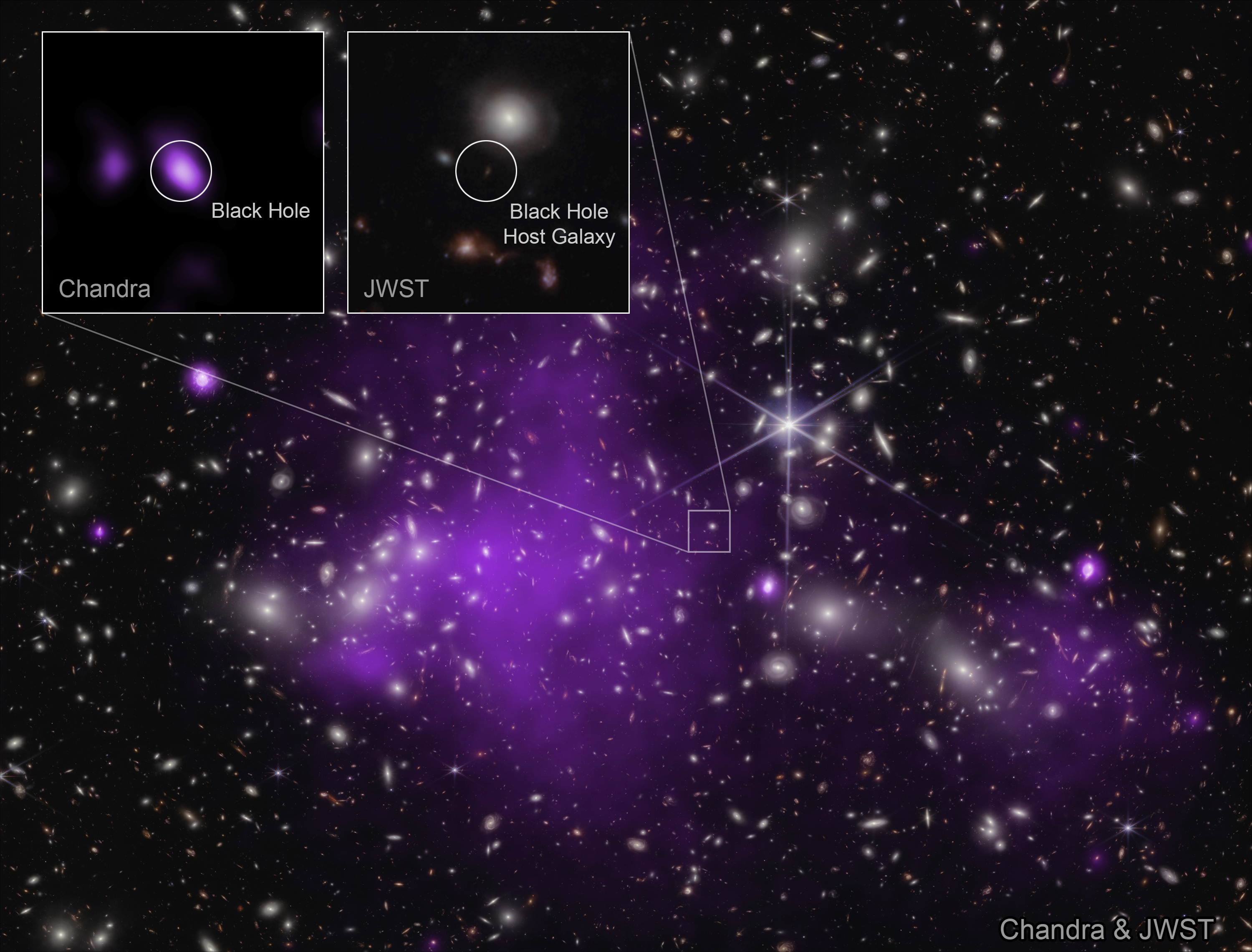
With JWST, Chandra, and gravitational lensing combined, evidence has emerged for the earliest black hole ever. And wow, is it a surprise!
What do ghosts and anomalous galaxy rotation rates have in common? Some sci-fi enthusiasts believe the answer involves “parallel universes.”
Sometimes, going “deeper” doesn’t reveal the answers you seek. By viewing more Universe with better precision, ESA’s Euclid mission shines.
While humanity has been skywatching since ancient times, much of our cosmic understanding has come about only recently. Very recently.
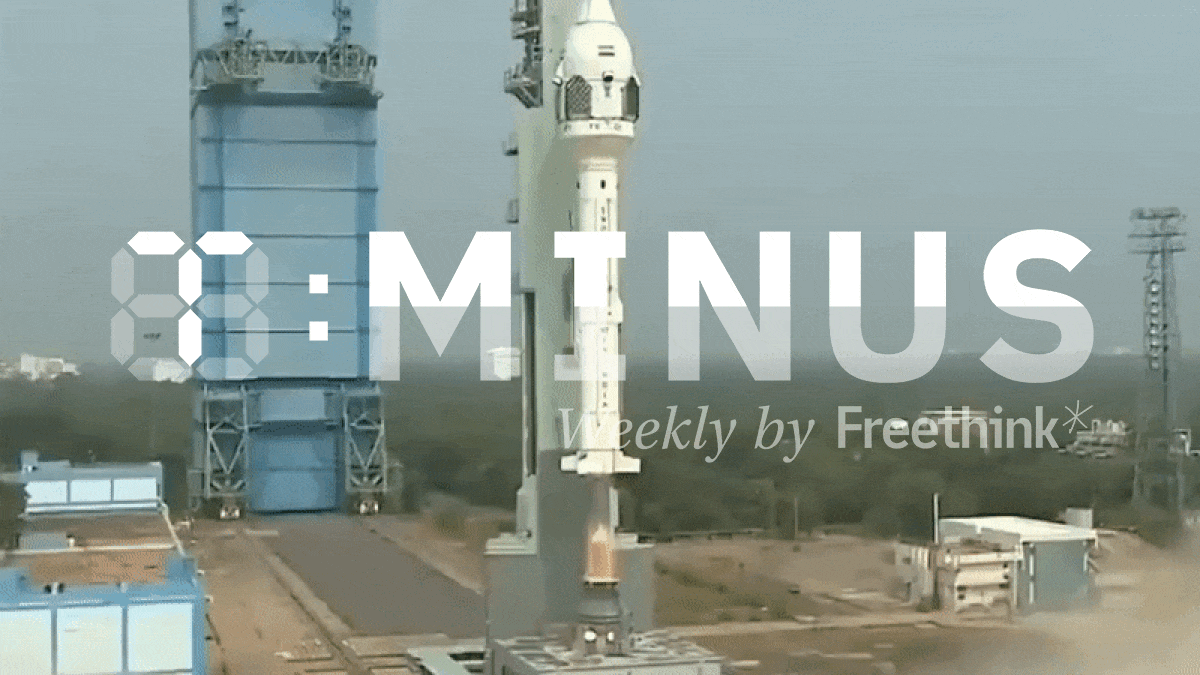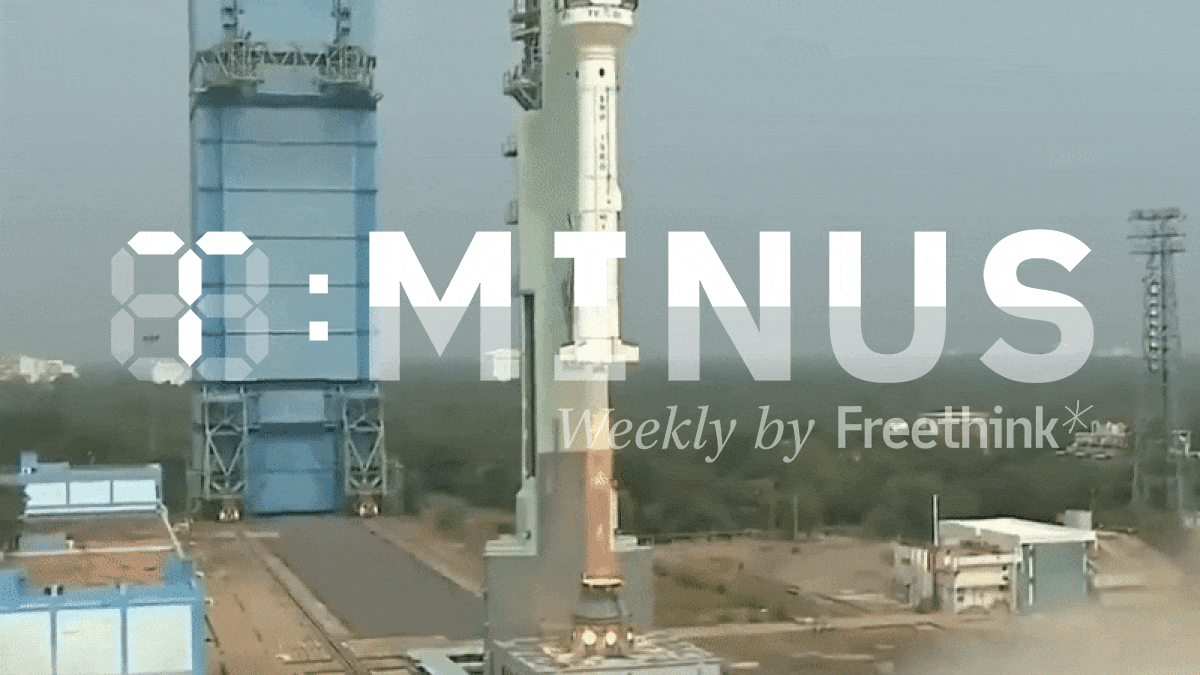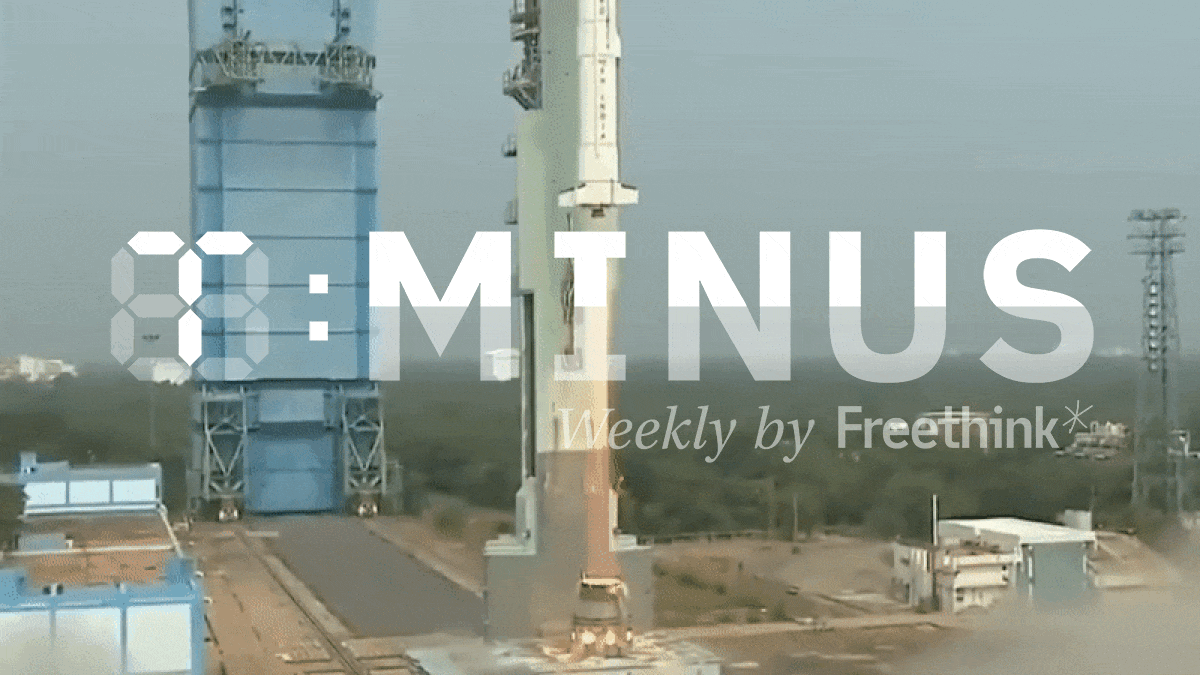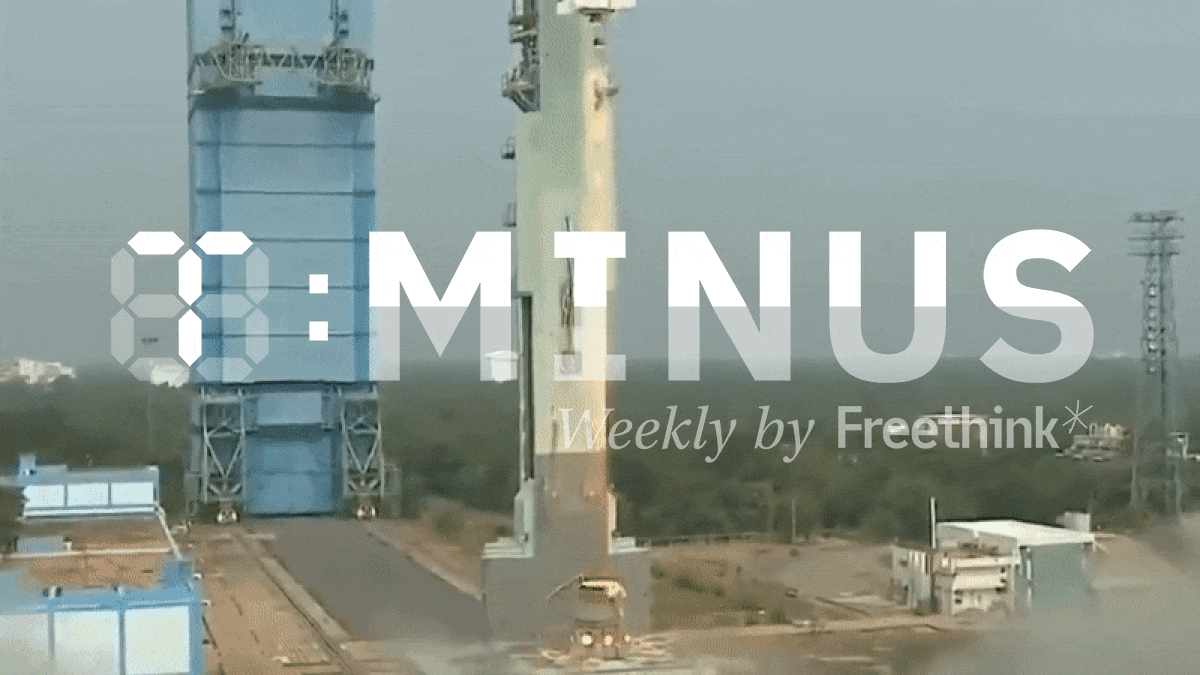
Freethink’s weekly countdown of the biggest space news, featuring a stranded space factory, Jeff Bezos’ new moon lander, and more.
The TRAPPIST-1 system is a treasure trove of possibilities and questions. Observations by JWST have just begun.
If the Universe is expanding, and the expansion is accelerating, what does that tell us about the cause of the expanding Universe?
Everything we observe beyond our Local Group is speeding away from us, omnidirectionally. If the Universe is expanding, where is the center?
In 1054, a core-collapse supernova occurred 6500 light-years away. In 2023, JWST imaged the remnant, and might solve a massive mystery.
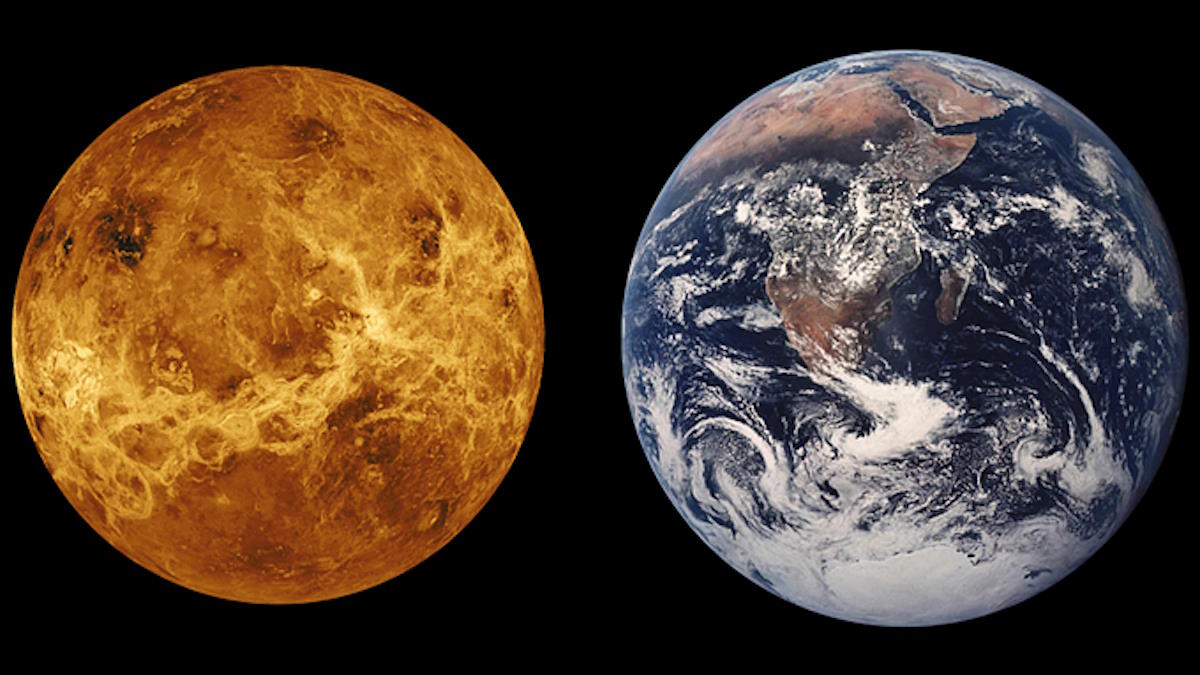
Out of the four rocky planets in our Solar System, only Earth presently has plate tectonics. But billions of years ago, Venus had them, too.
Dispatches host Kmele Foster is on a journey to understand humanity’s role in the cosmos. His first stop? The Atacama Plateau in Northern Chile, home to the darkest deserts and largest telescopes on earth.
▸
35 min
—
with
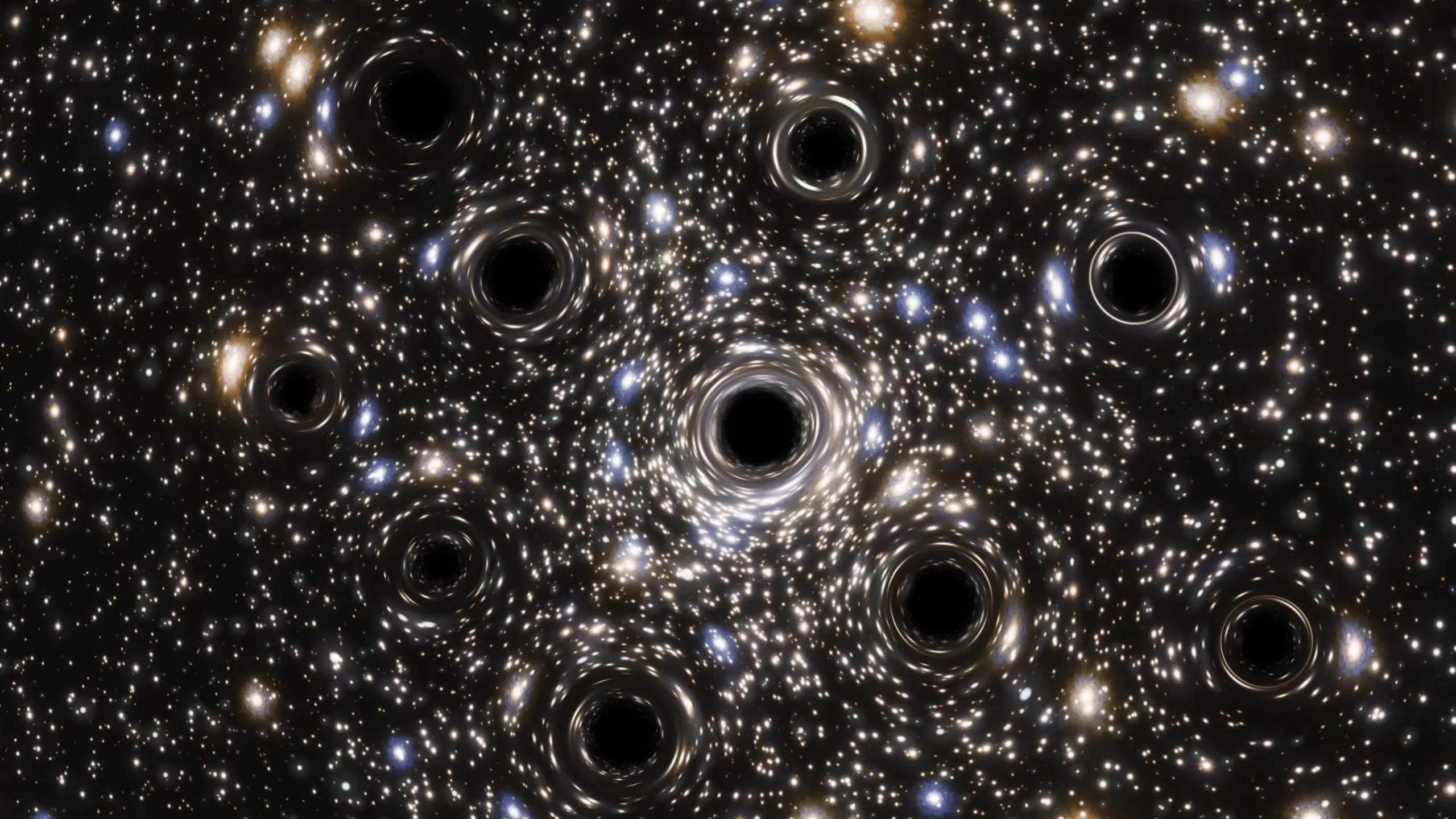
For the first time, astronomers have created a data-driven estimate for how many black holes are in our Universe: more than anyone expected.
See the 3 biggest space stories from October 16-22, 2023.
Sophisticated rovers have found the conditions for Martian life, as well as the building blocks of life, but never life itself. AI can help.