Space & Astrophysics
Sixty years ago, the Soviet Union was way ahead of the USA in the space race. Then one critical event changed everything.
The problem for galactic-scale civilizations comes down to two numbers.
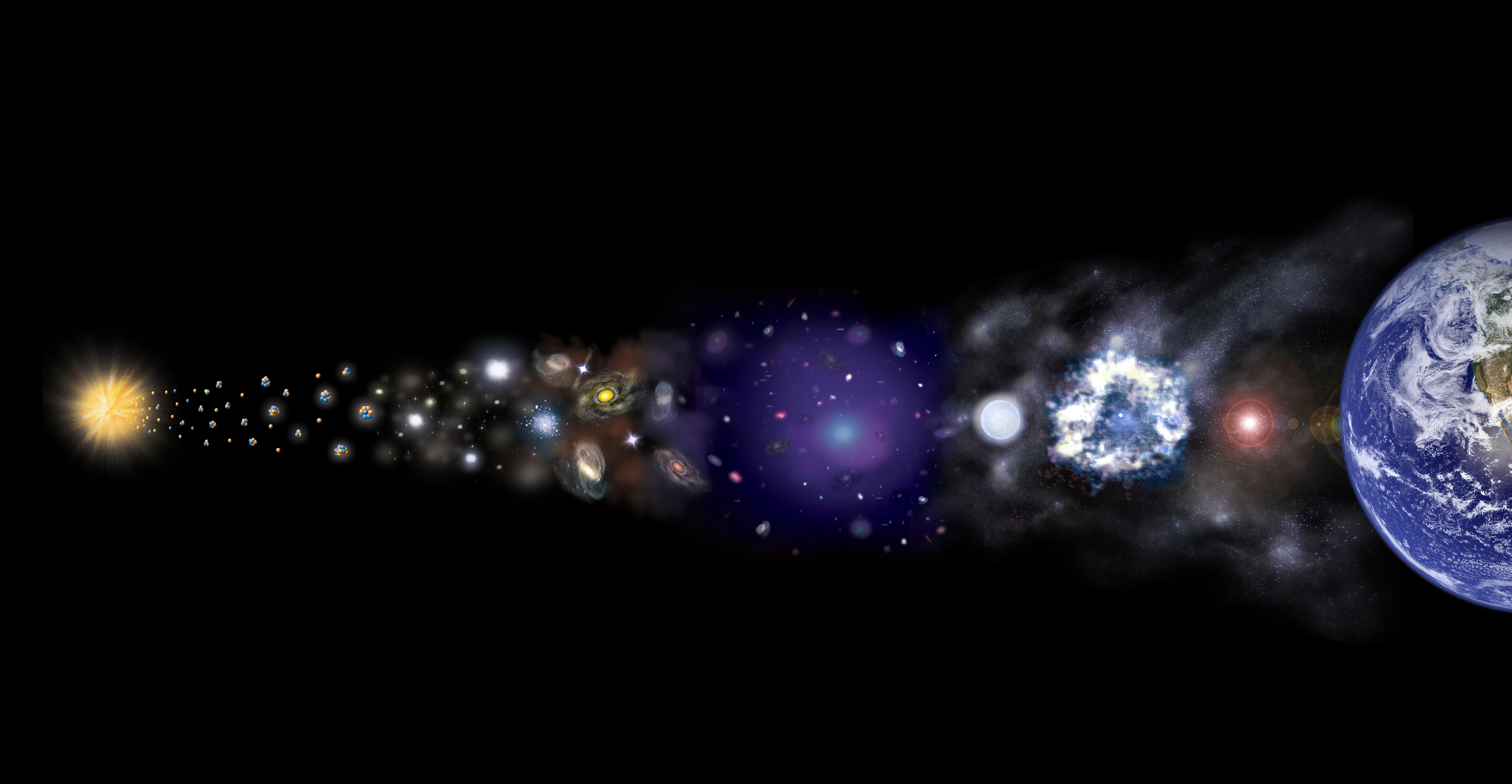
From a hot, dense, uniform state in its earliest moments, our entire known Universe arose. These unavoidable steps made it all possible.
It was barely a century ago that we thought the Milky Way encompassed the entirety of the Universe. Now? We’re not even a special galaxy.
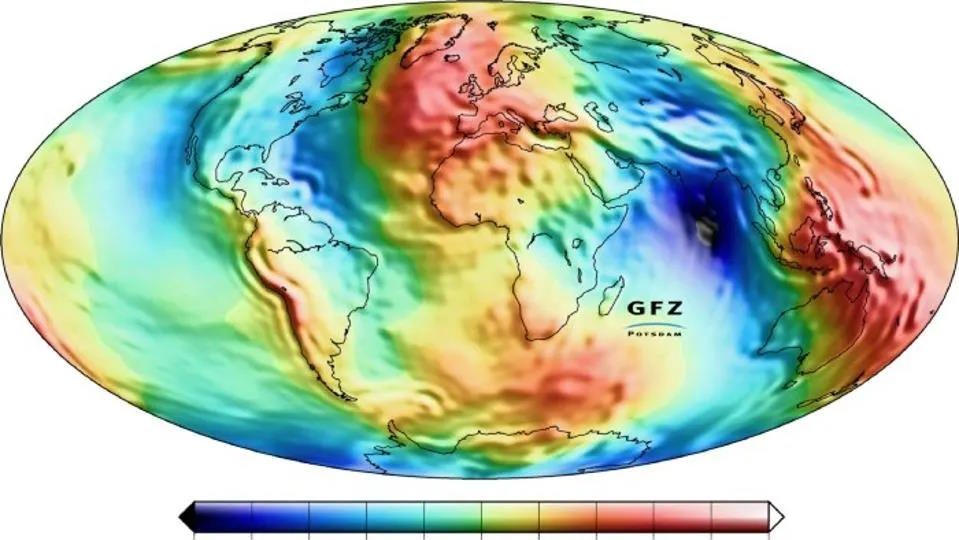
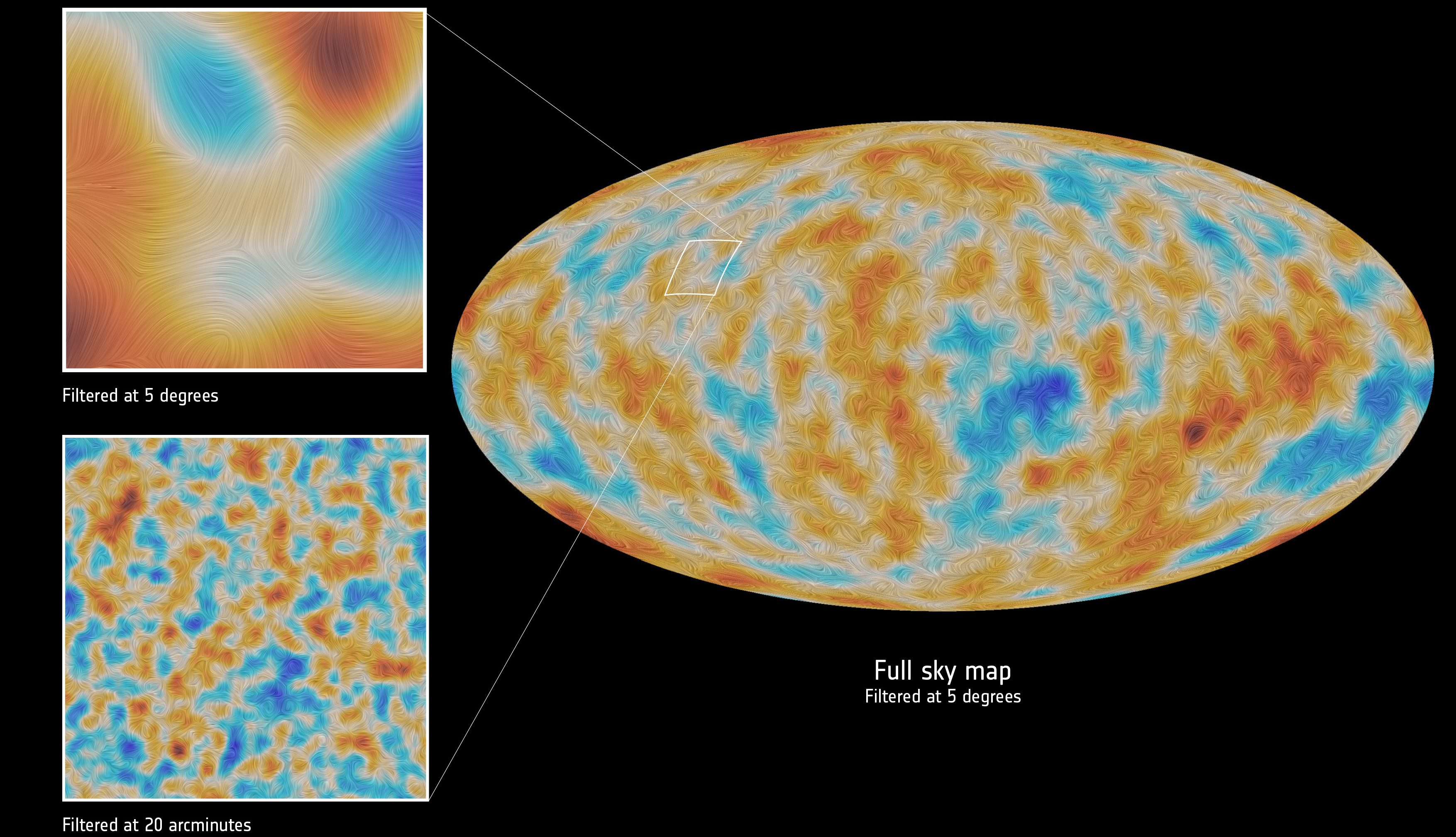
Even with just a momentary view of our galaxy right now, the data we collect enables us to reconstruct so much of our past history.
50 years ago, Stephen Hawking showed that black holes emit radiation and eventually decay away. That fate may now apply to everything.
The closest known star that will soon undergo a core-collapse supernova is Betelgeuse, just 640 light-years away. Here’s what we’ll observe.
Most waves need a medium to travel through. But the way that light and gravitational waves travel shows that space can’t be a medium at all.
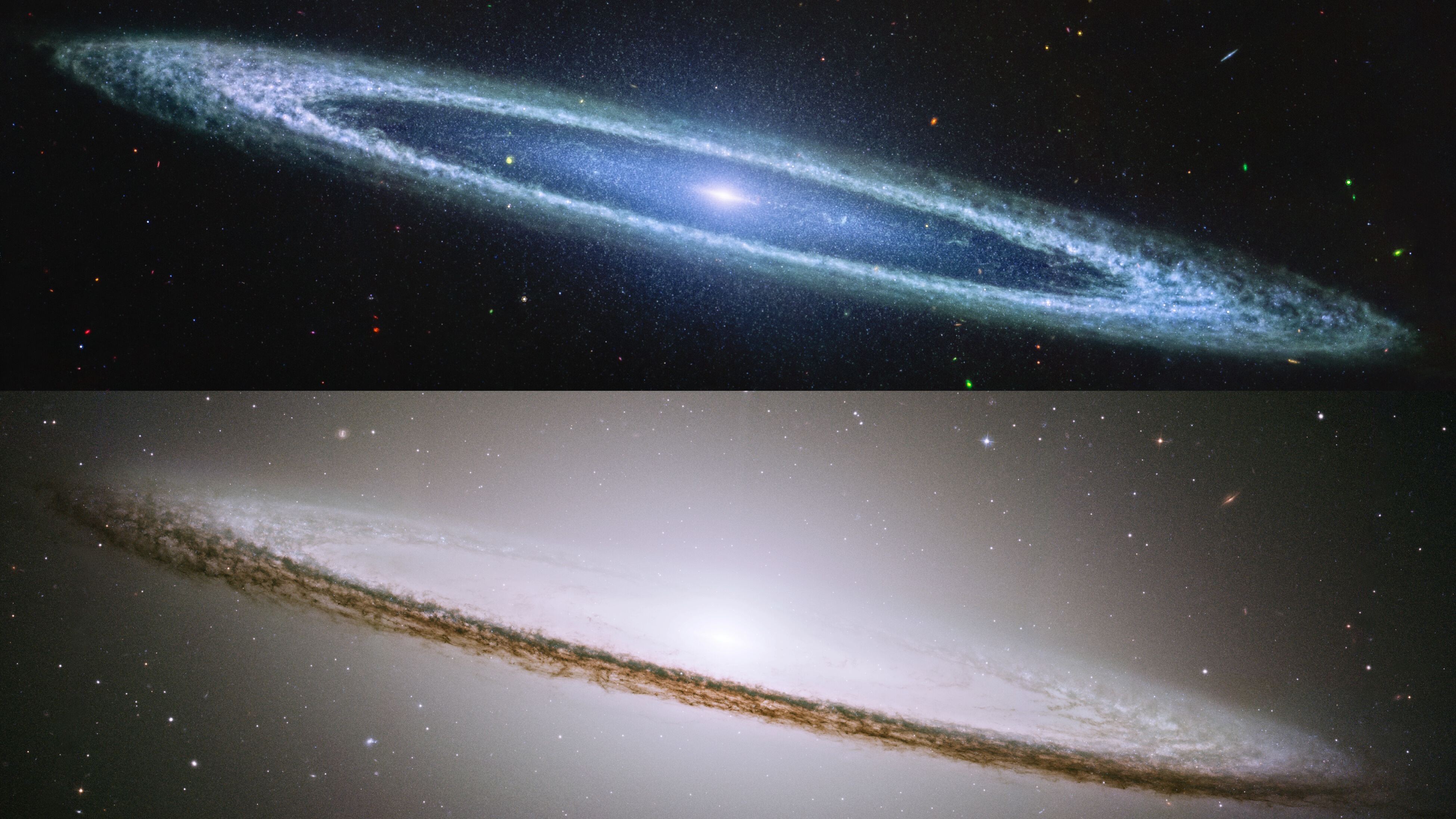
The Sombrero is the closest bright, massive, edge-on galaxy to us. JWST’s new image, taken with MIRI, finally shows what’s under its hat.
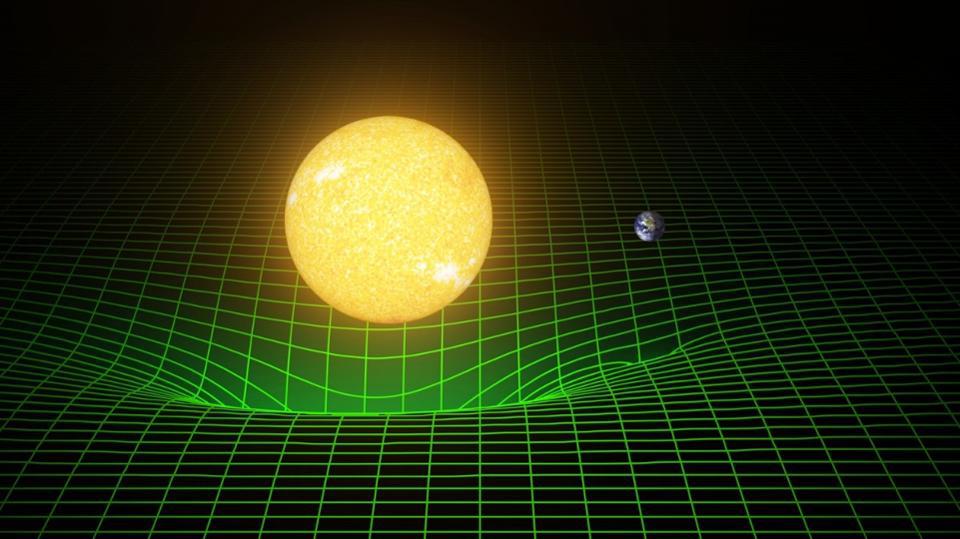
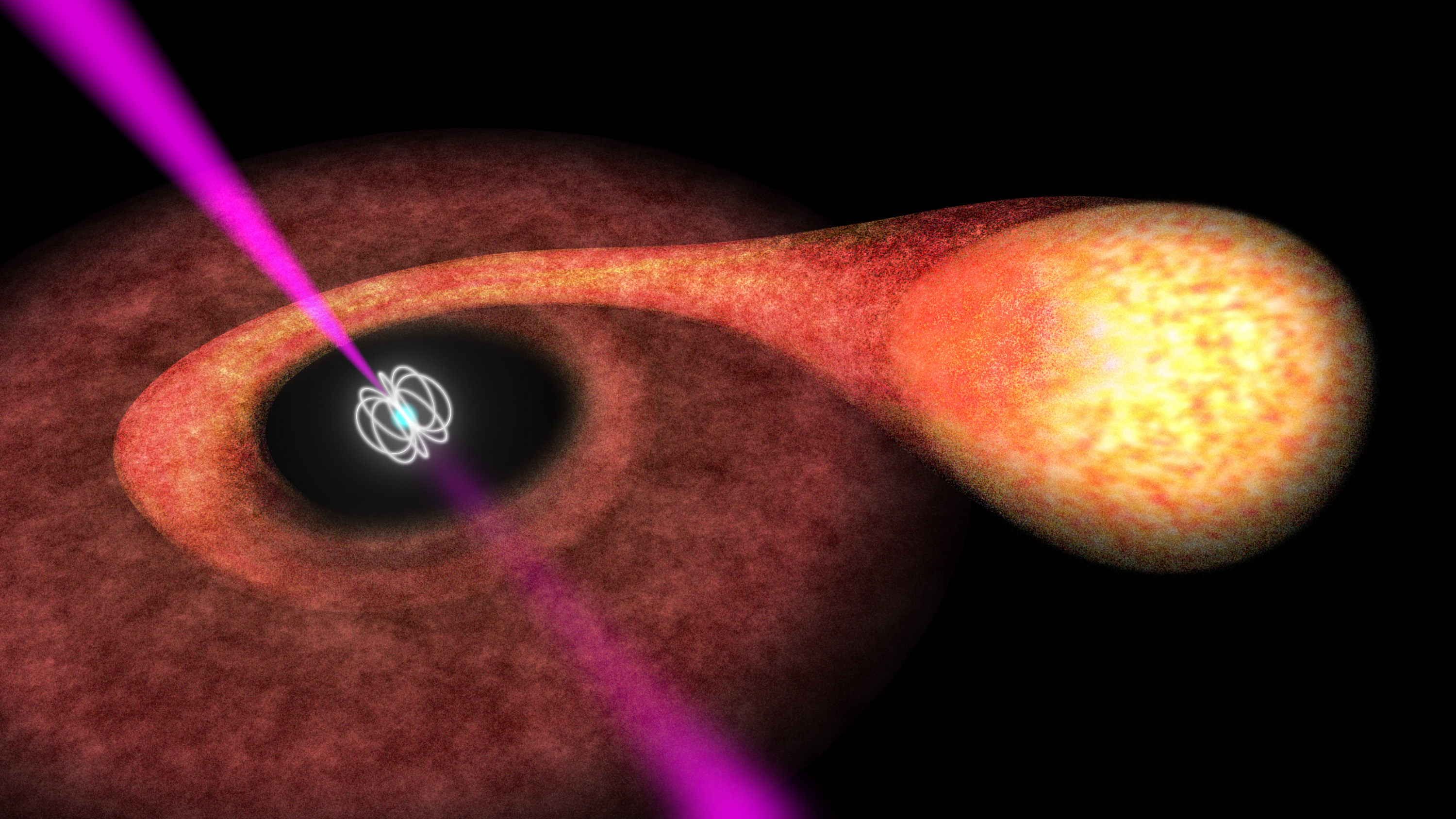
Gravitational waves are the last signatures that are emitted by merging black holes. What happens when these two phenomena meet in space?
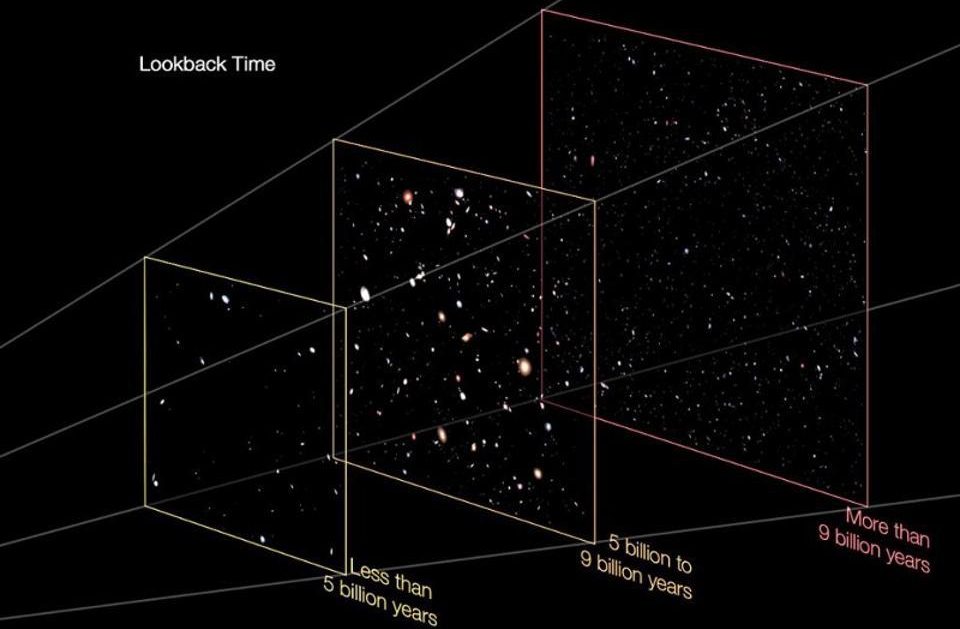
DESI has allowed astronomers to create an unprecedented 3D map of the Universe representing 20% of the entire sky.
For nearly 60 years, the hot Big Bang has been accepted as the best story of our cosmic origin. Could the Steady-State theory be possible?
In November 1974, astronomers used the radio telescope at Puerto Rico’s Arecibo Observatory to send a hello to the universe.
Two parts of our Universe that seem to be unavoidable are dark matter and dark energy. Could they really be two aspects of the same thing?
“I was stunned. Here in front of me was the original apparatus through which a new vision of the world was slowly and painfully brought to light.”
Scalars, vectors, and tensors come up all the time in physics. They’re more than mathematical structures. They help describe the Universe.
Since the mid-1960s, the CMB has been identified with the Big Bang’s leftover glow. Could any alternative explanations still work?
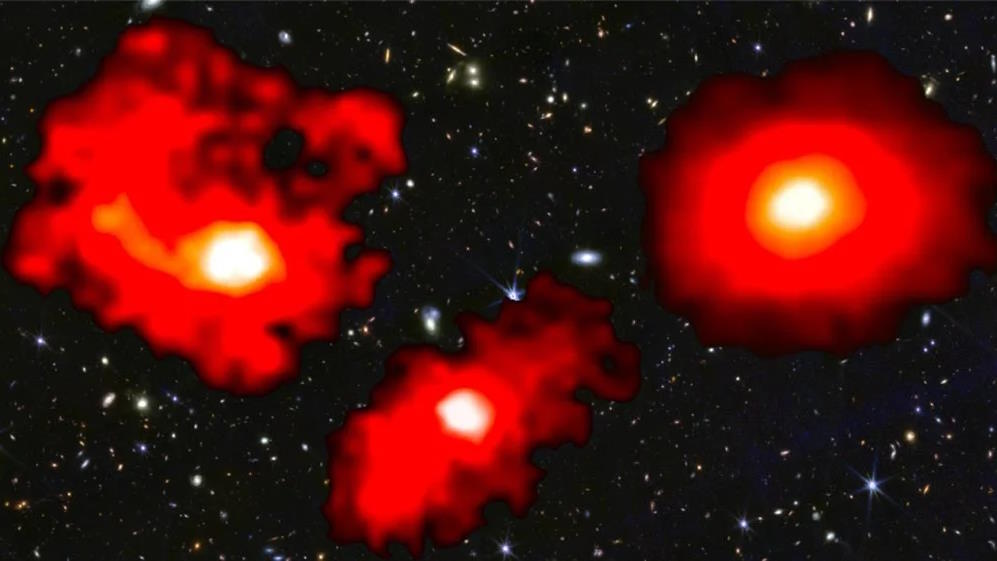
The most massive early galaxies grew up faster, and have more stars, than astronomers expected, according to JWST. What does it all mean?
There are a few small cosmic details that, if things were just a little different, wouldn’t have allowed our existence to be possible.
Recent controversies bode ill for the effort to detect life on other planets by analyzing the gases in their atmospheres.
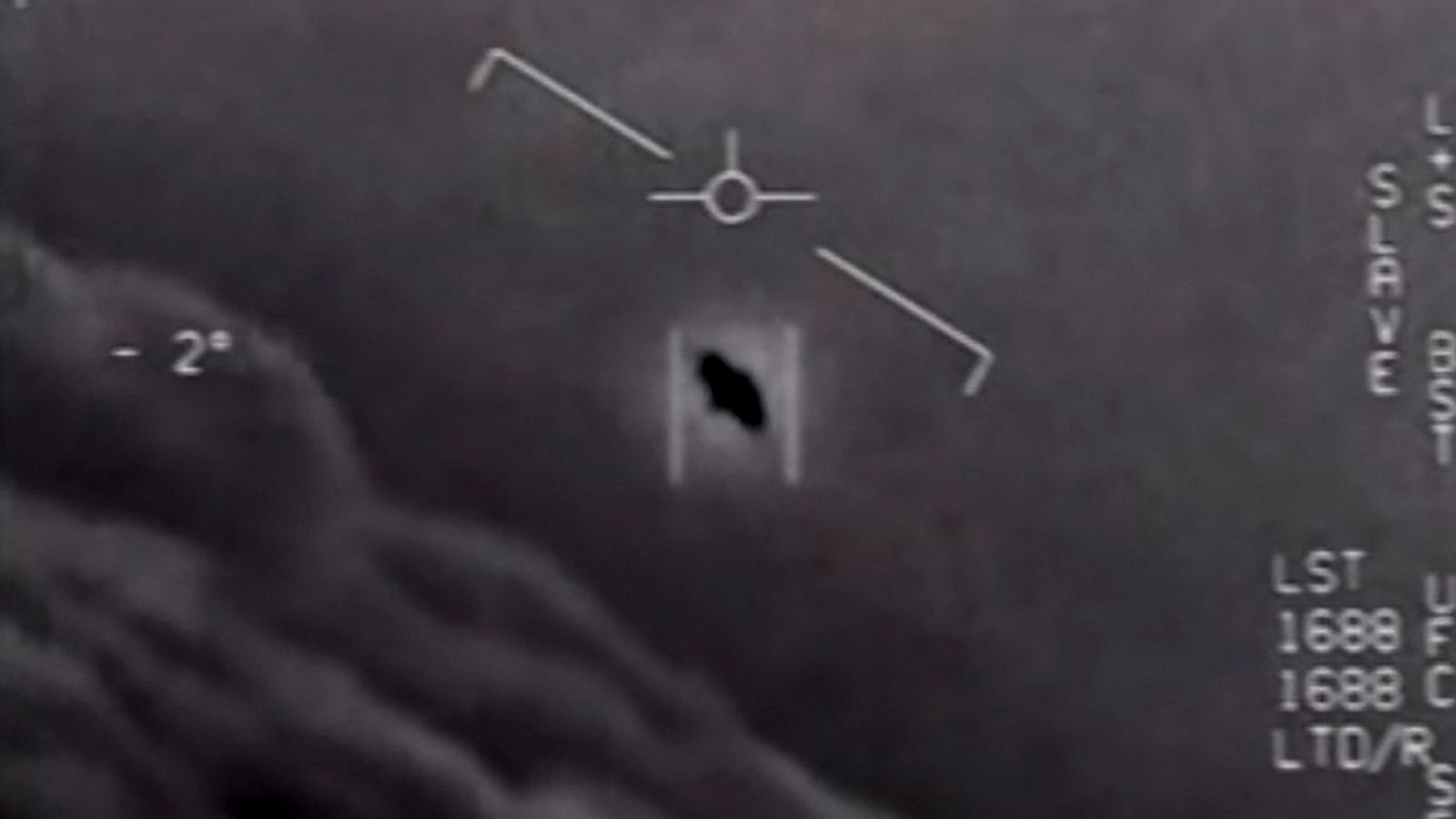
Astronomer Adam Frank asks: With so many extraordinary claims, why can’t anybody produce the proof?
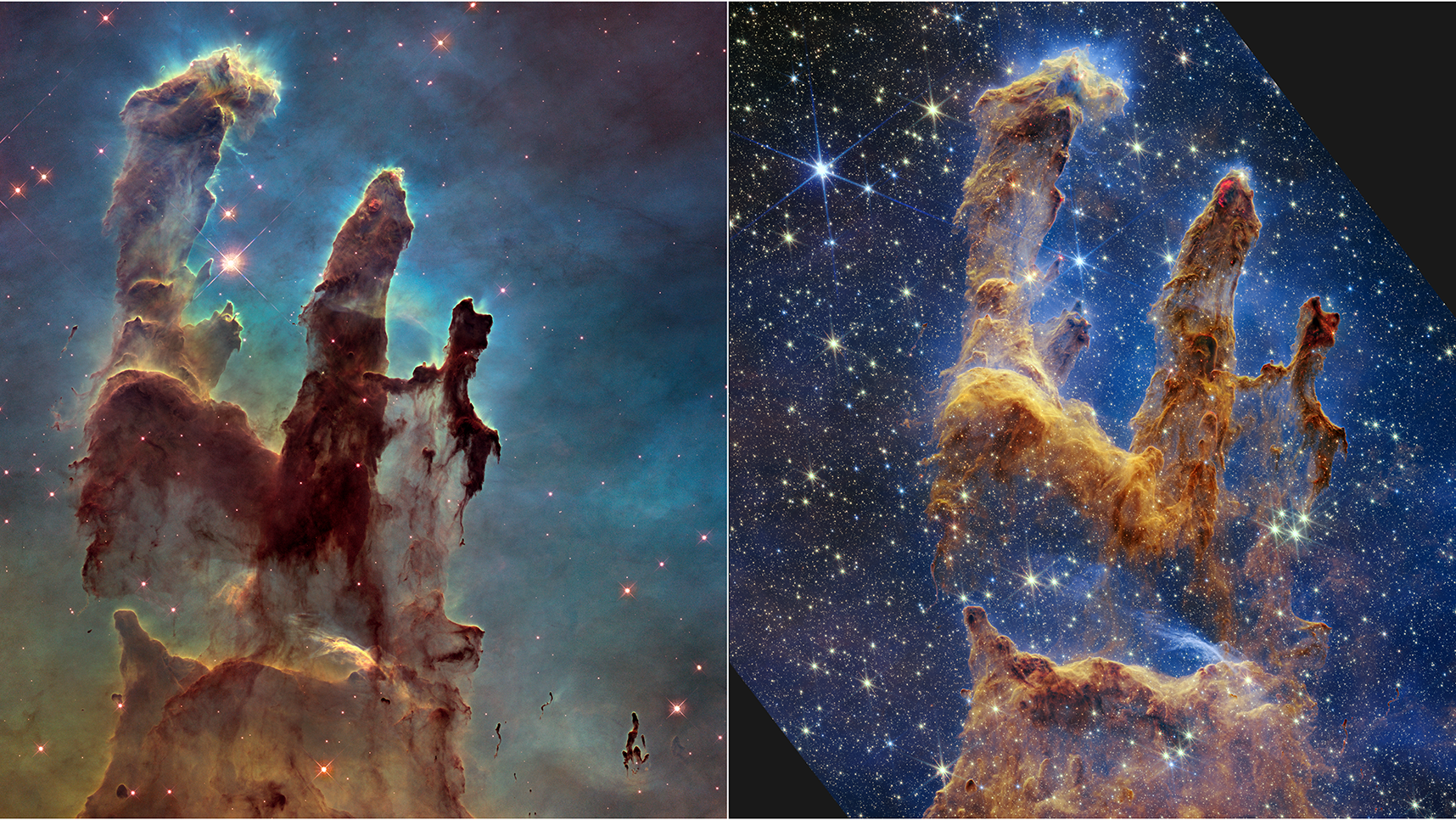
When we see pictures from Hubble or JWST, they show the Universe in a series of brilliant colors. But what do those colors really tell us?
The last naked-eye Milky Way supernova happened way back in 1604. With today’s detectors, the next one could solve the dark matter mystery.
How did life on Earth begin? Is there life on other worlds? An answer to either question will reflect heavily on the other.
Since 1930, type Ia supernovae have been thought to arise from white dwarfs exceeding the Chandrasekhar mass limit. Here’s why that’s wrong.
In partisan political times, recognizing the scientific truth is more important than ever. Scientists must be vocal and clear about reality.
In astronomy, a star’s initial mass determines its ultimate outcome in life. Unless, that is, a stellar companion alters the deal.
Black holes are the most massive individual objects, spanning up to a light-day across. So how do they make jets that affect the cosmic web?
Humans, when we consider space travel, recognize the need for gravity. Without our planet, is artificial or antigravity even possible?
All the stars, stellar corpses, planets, and other large, massive objects take on spherical or spheroidal shapes. Why is that universal?