From the coldest planets to spacecraft that have exited the Solar System, these little-known facts stump even many professional astronomers.
Search Results
You searched for: Jupiter
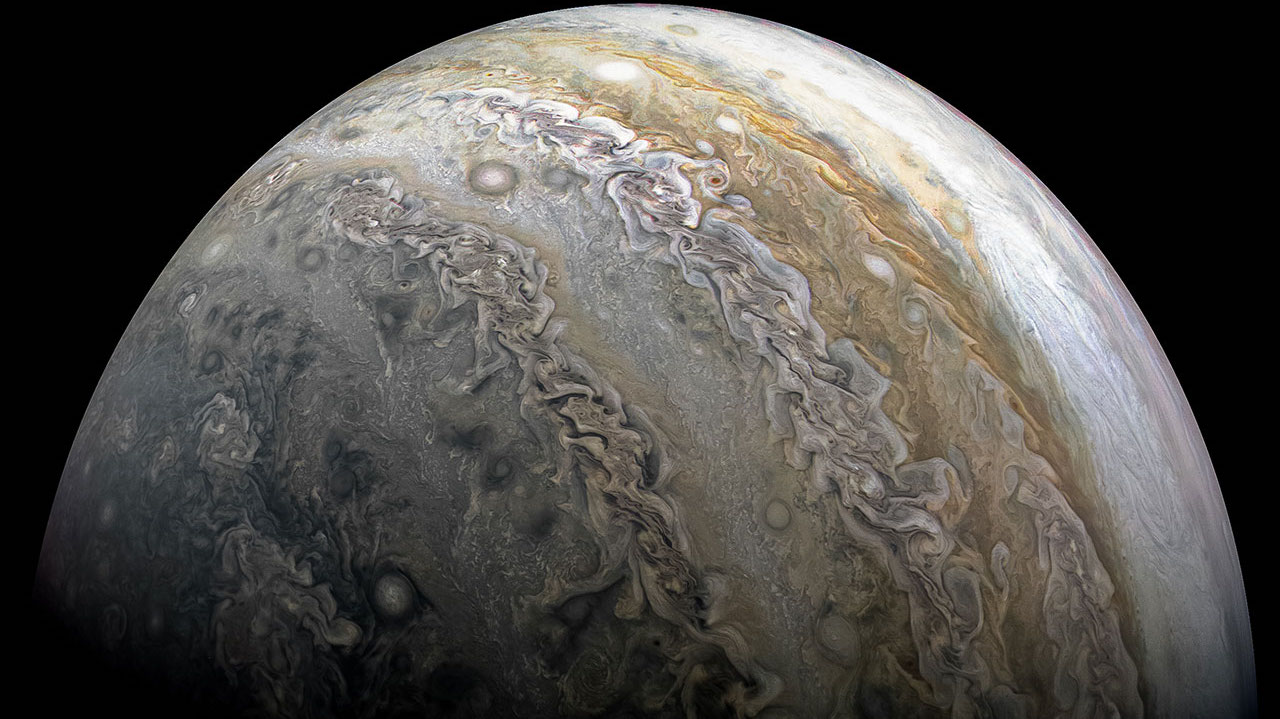
The classic picture of Jupiter’s great rocky core might be entirely wrong.
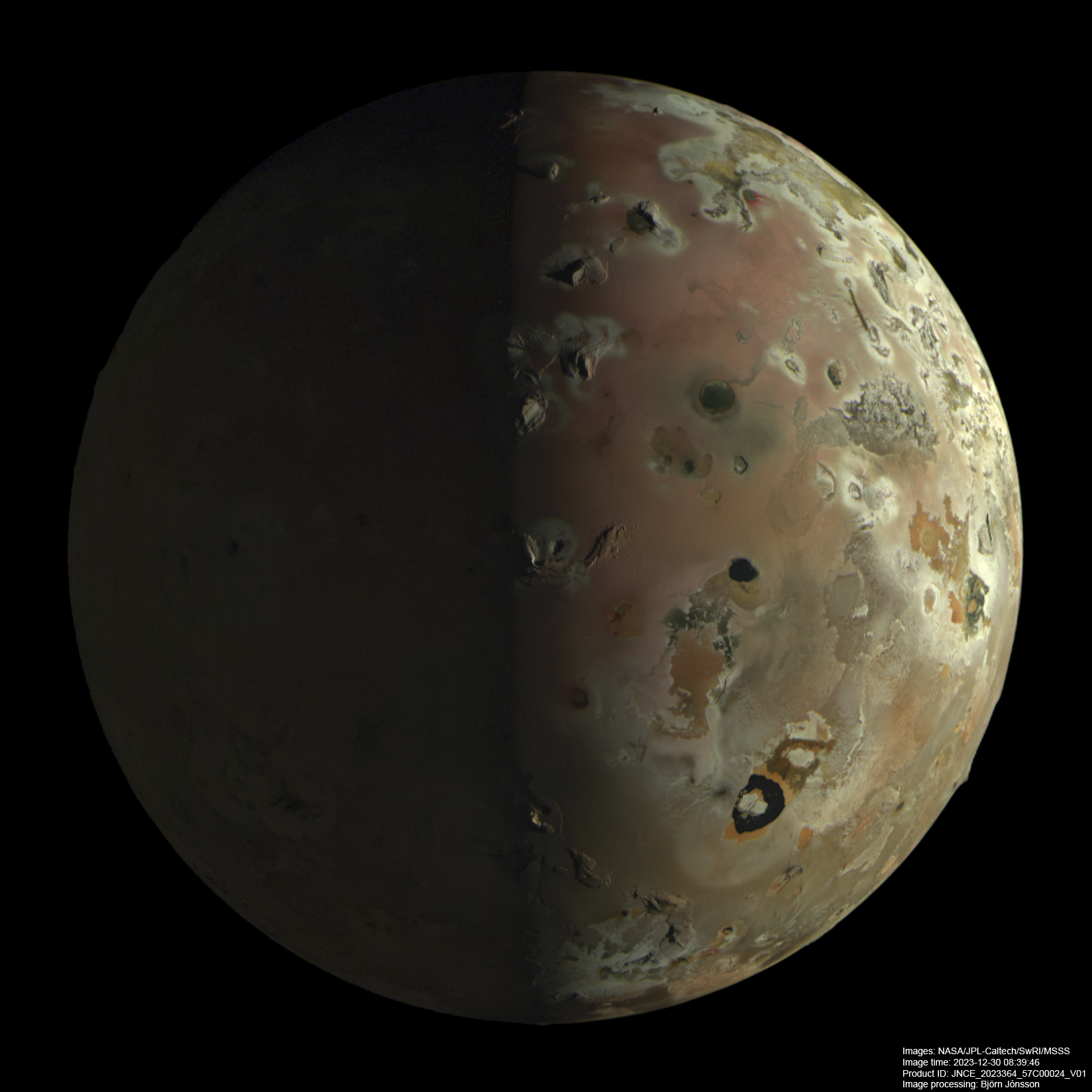
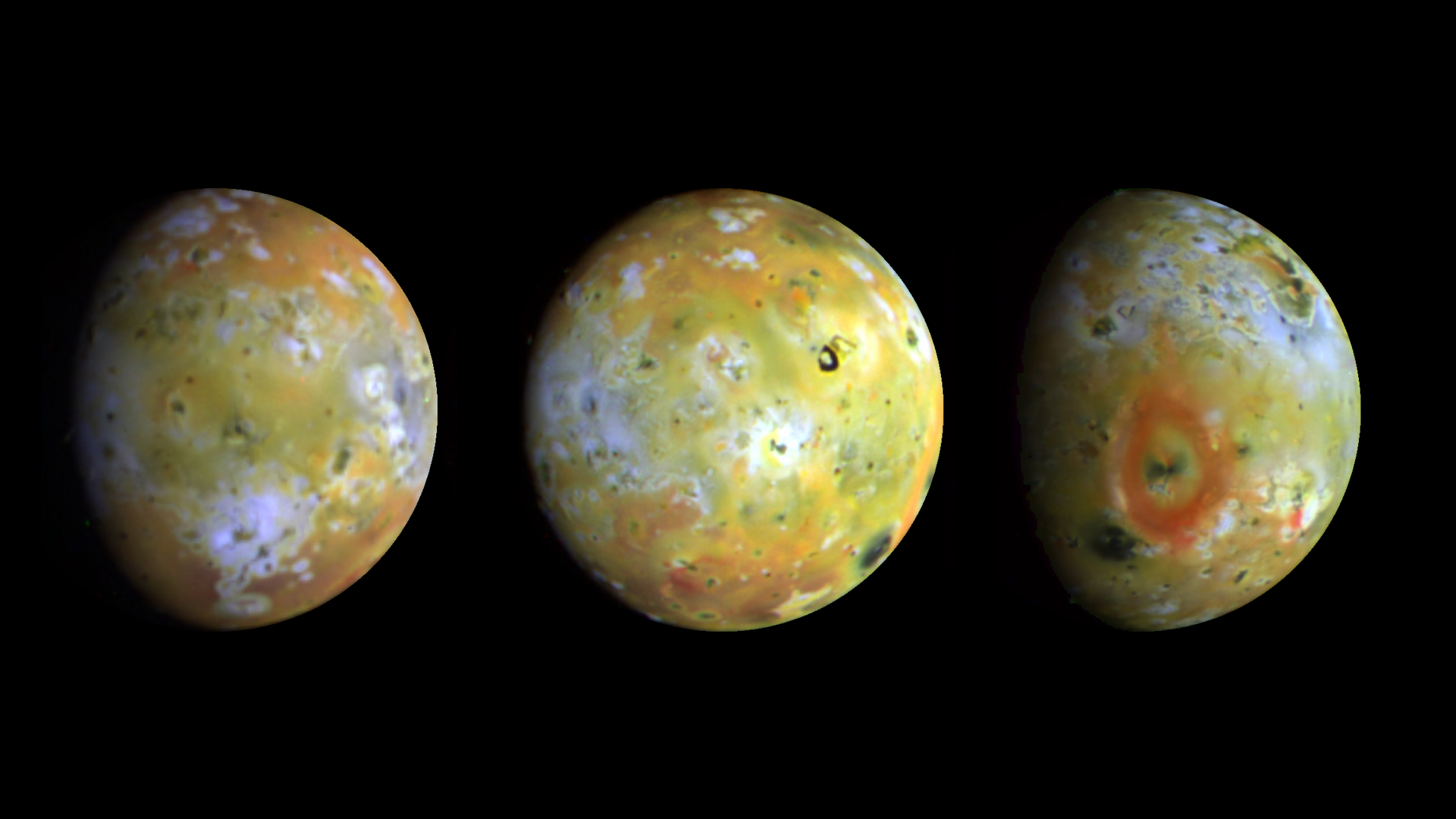
NASA’s Juno mission, in orbit around Jupiter, occasionally flies past its innermost large moon: Io. The volcanic activity is unbelievable.
The existence of another watery world in the outer solar system may offer clues to how such seas form — and hope for another spot to search for life.
If there’s life lurking on the moons of Saturn and Jupiter, could our instruments even detect it?
The outer planets’ clouds hide the weirdness within.
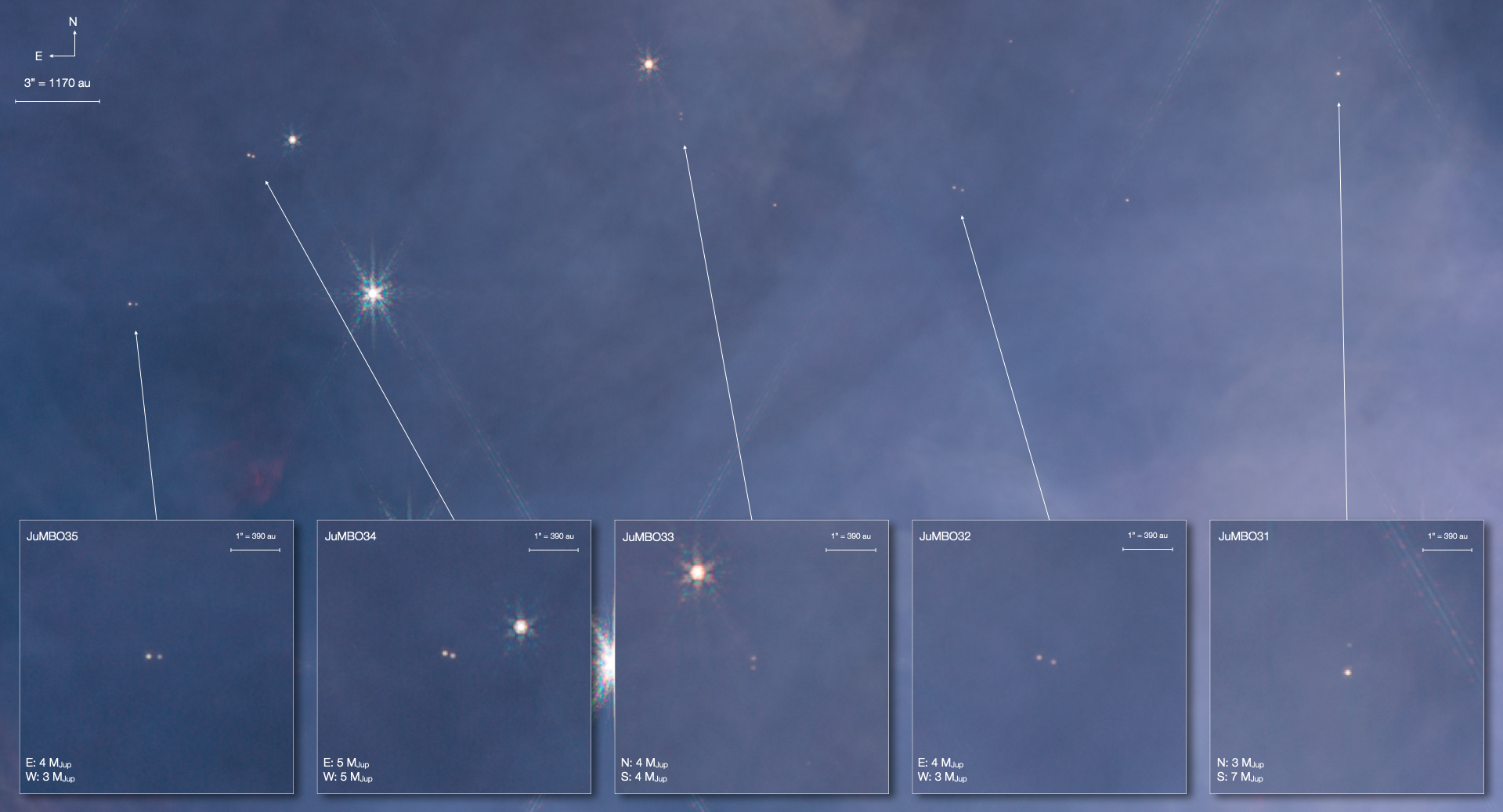
In the largest star-forming region close to Earth, JWST found hundreds of planetary-mass objects. How do these free-floating planets form?
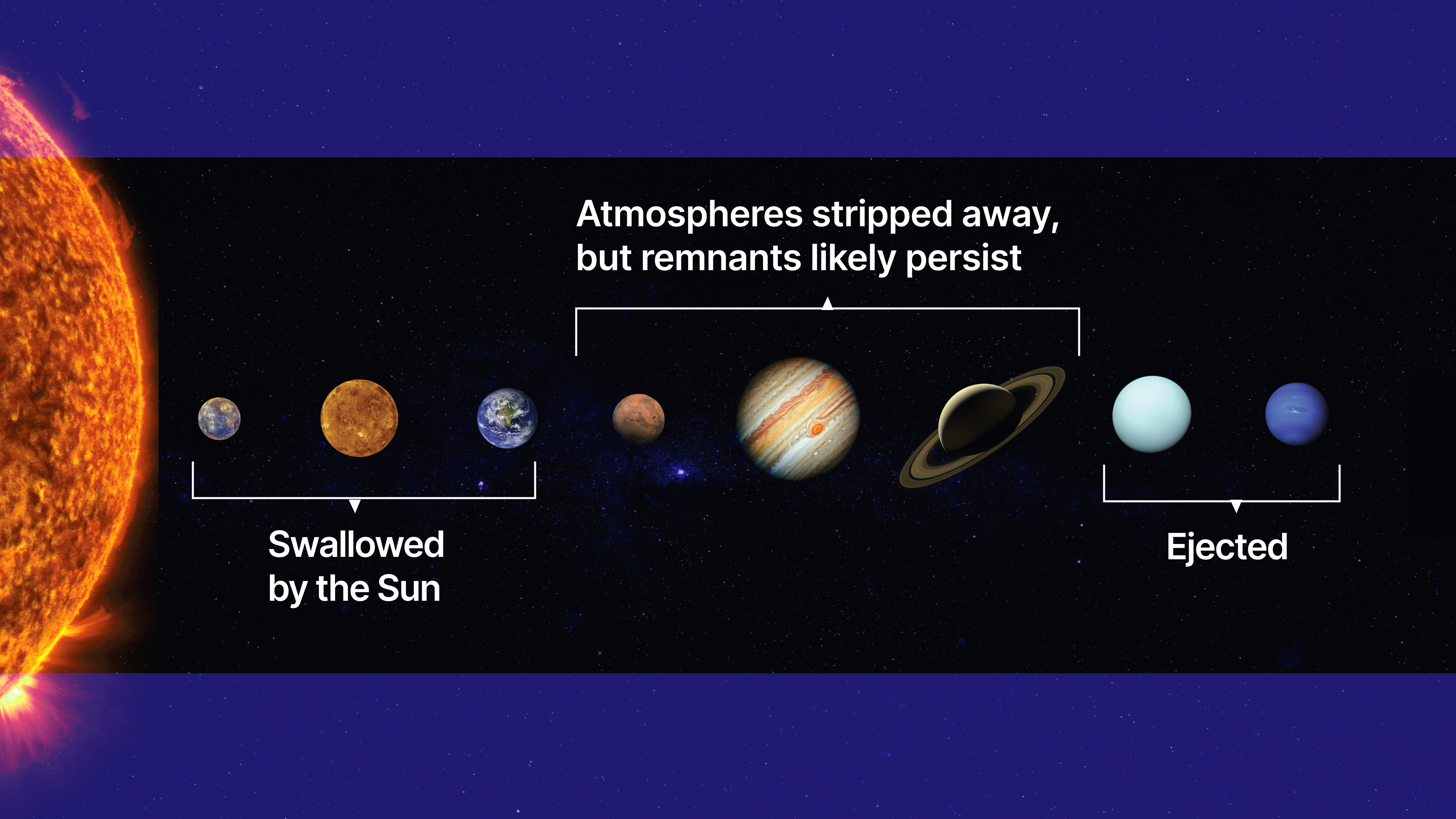
For now, our Solar System’s eight planets are all safe, and relatively stable. Billions of years from now, everything will be different.
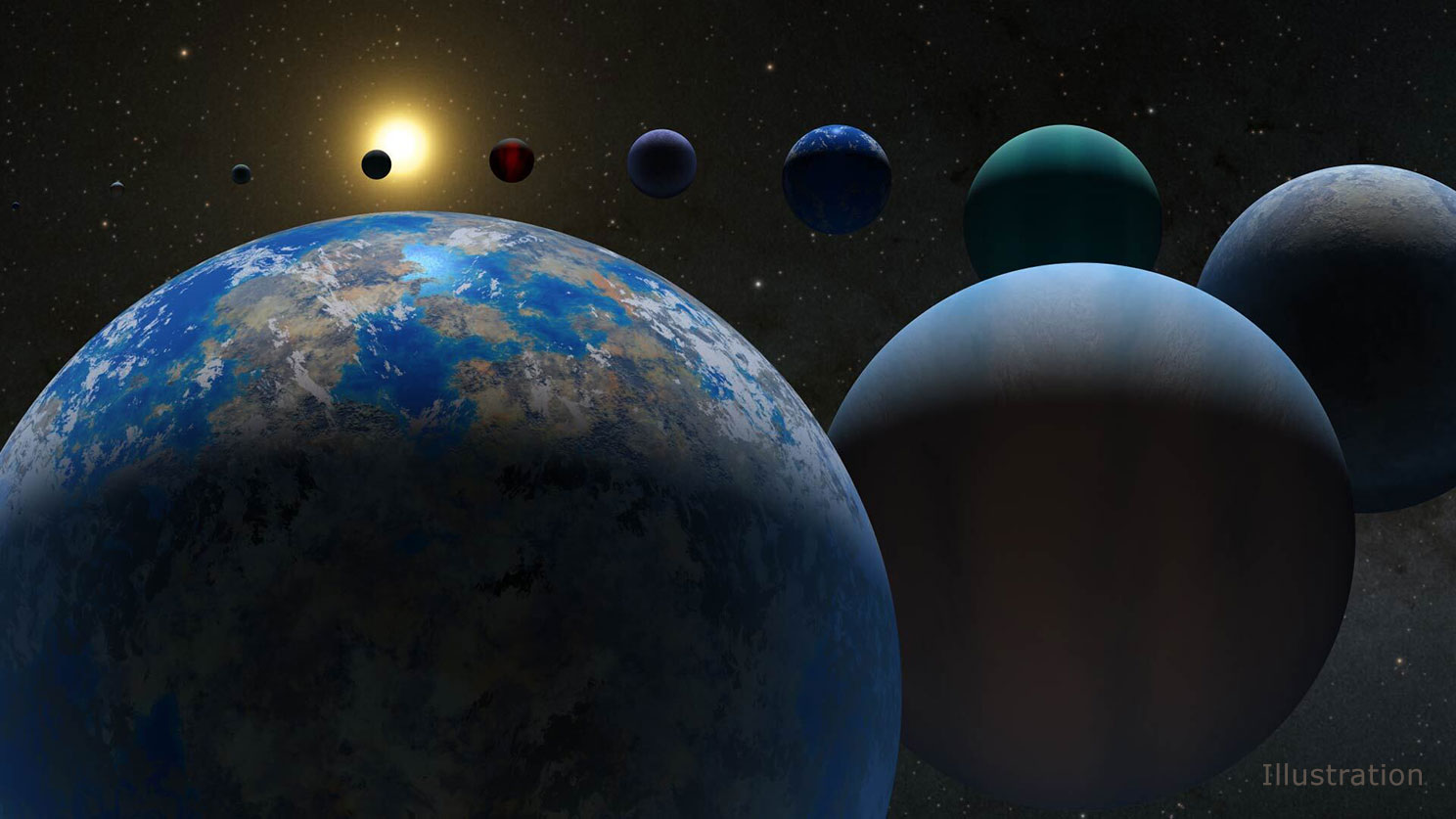
Planets can be Earth-like or Neptune-like, but only rarely are in between. This hot, Saturn-like planet hints at a solution to this puzzle.
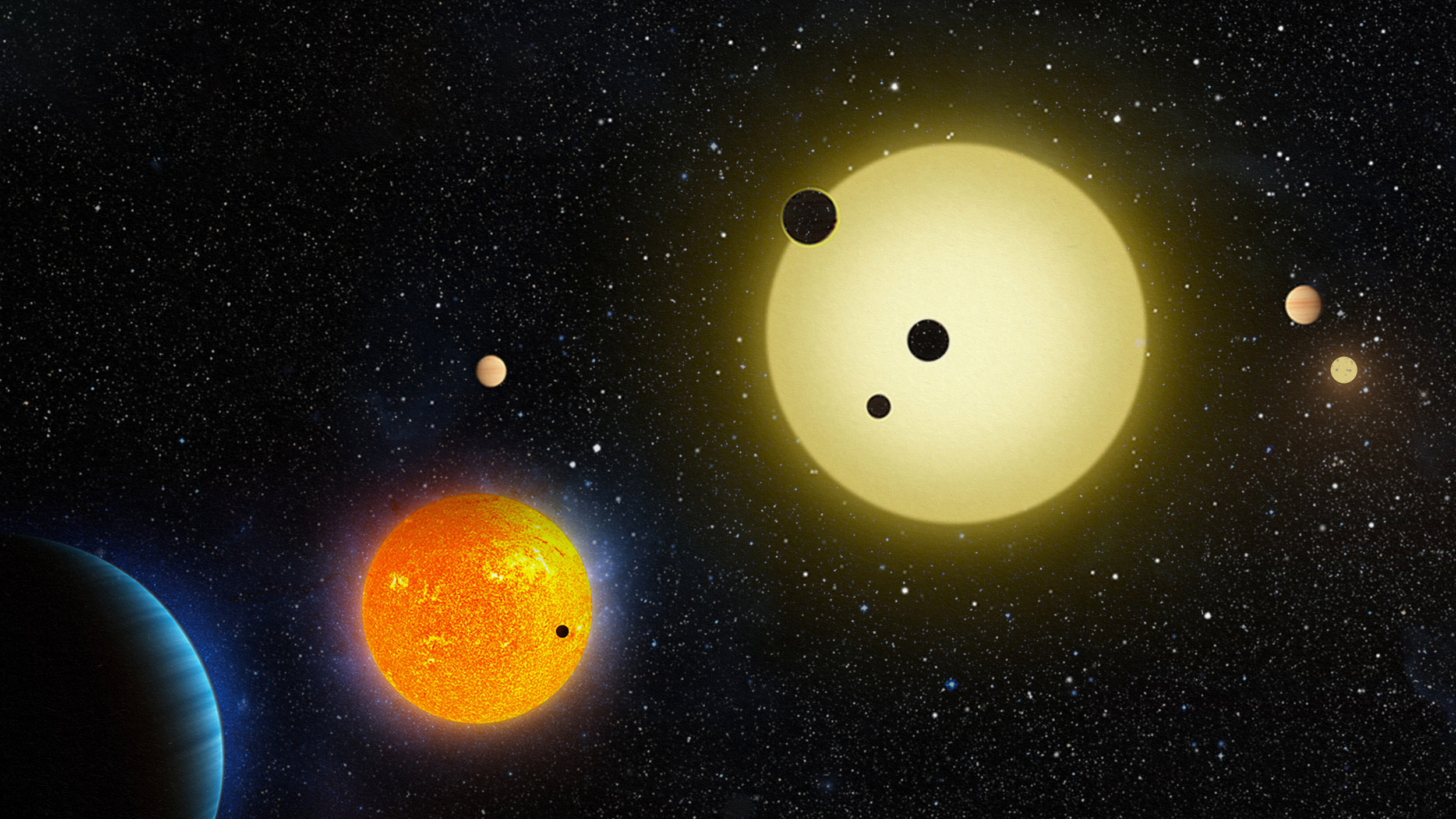
The structure of our Solar System has been known for centuries. When we finally started finding exoplanets, they surprised everyone.
As planets with too many volatiles and too little mass orbit their parent stars, their atmospheres photoevaporate, spelling doom for some.
On Earth, microbial growth is common in lava tubes no matter the location and climate, whether it’s ice-volcano interactions in Iceland or hot, sand-floored lava tubes in Saudi Arabia.
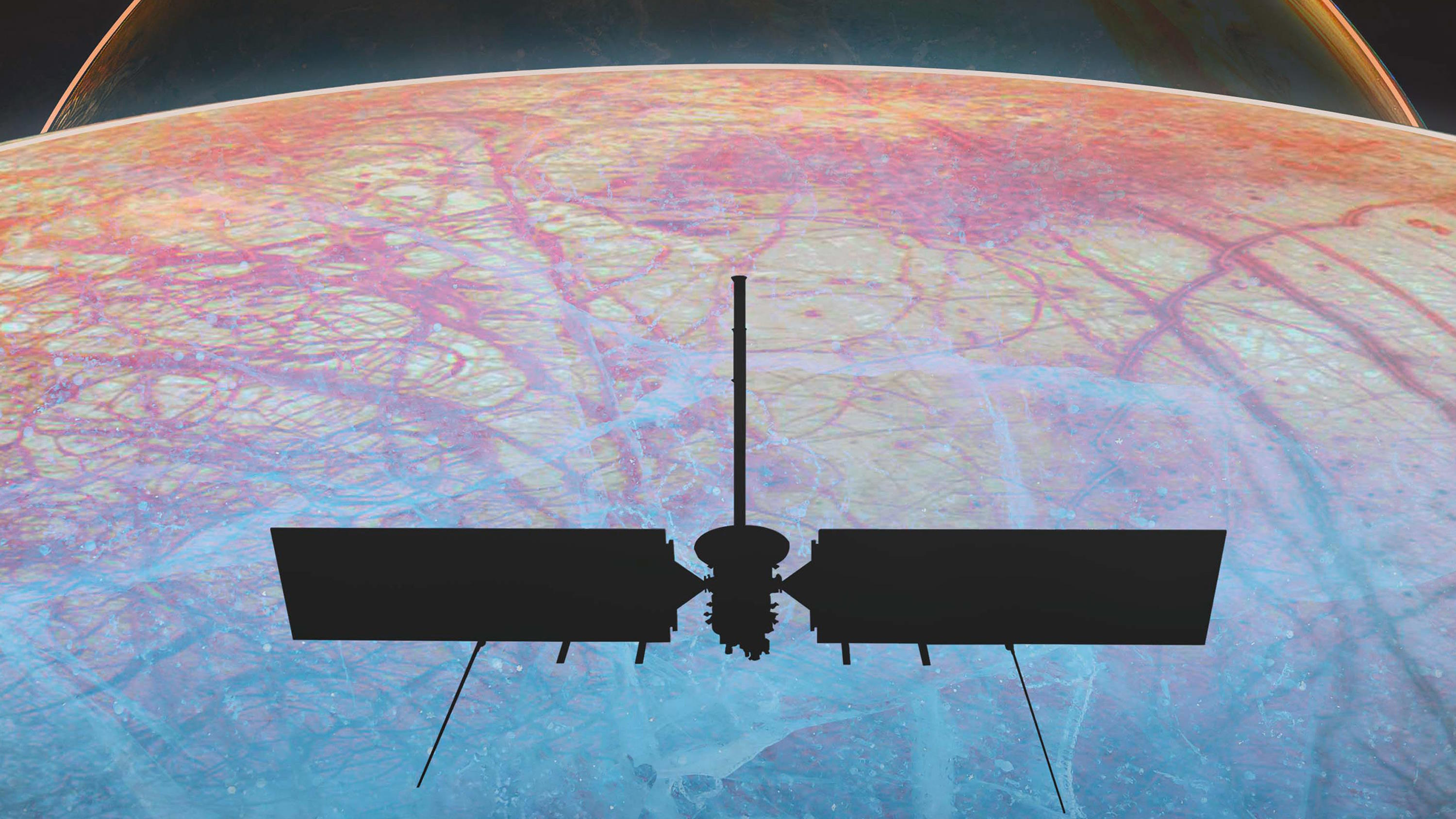
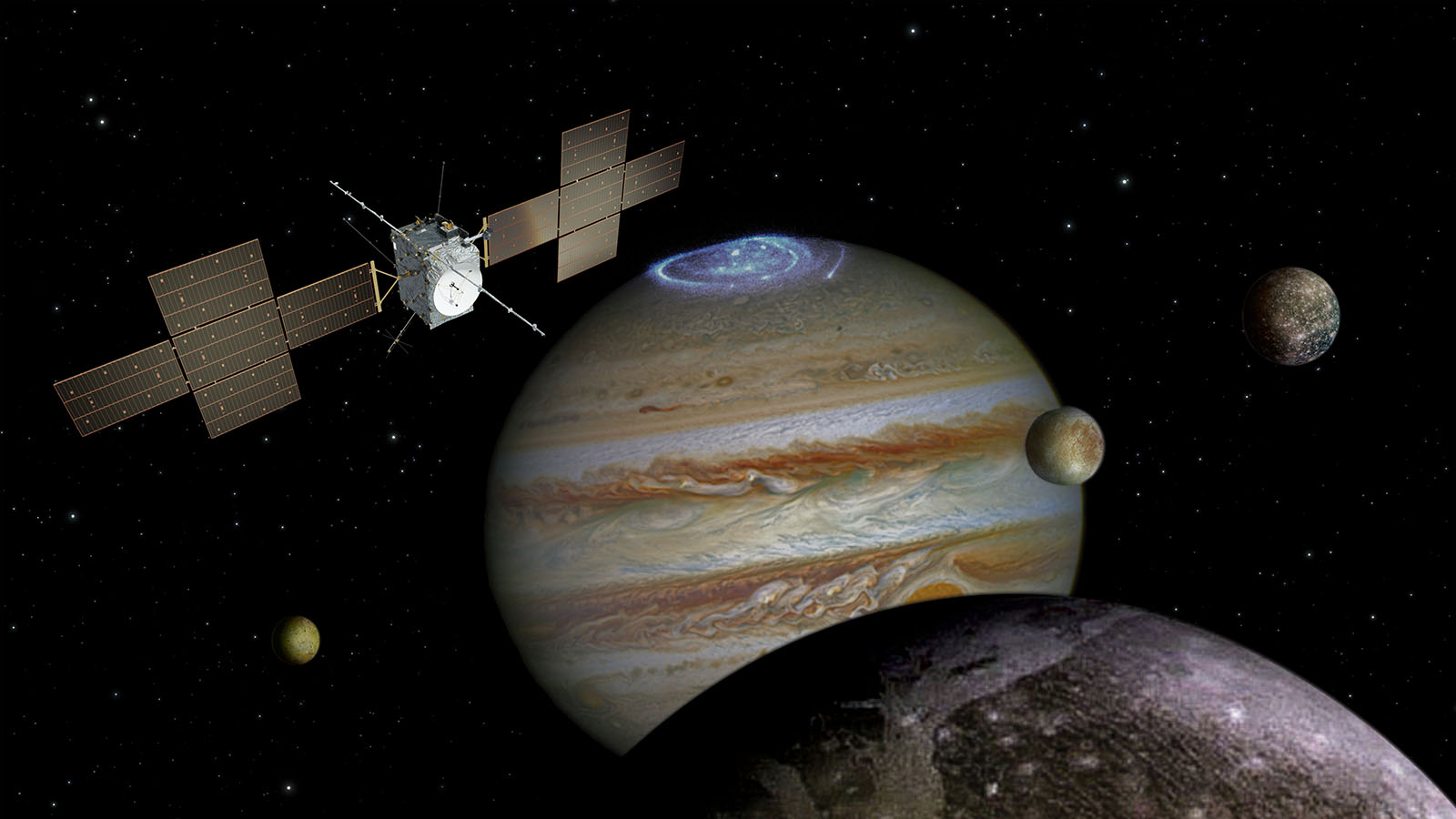
Could life be widespread throughout the cosmos, in the subsurface oceans of ice-covered worlds? NASA’s Europa Clipper mission investigates.
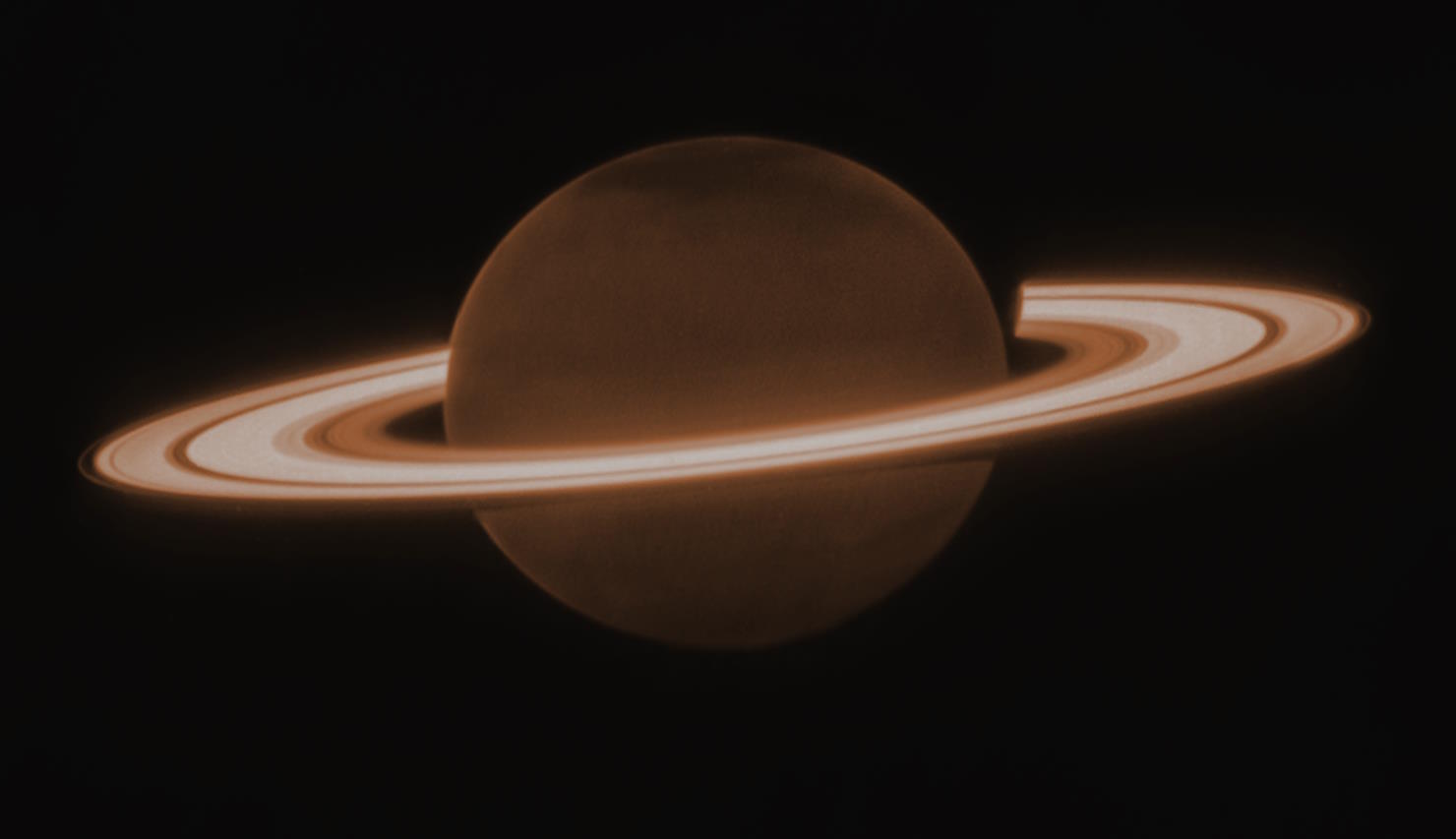
While Saturn and its moons all appear faint and cloudy to JWST, Saturn’s rings are the star of the show. Here’s the big scientific reason.
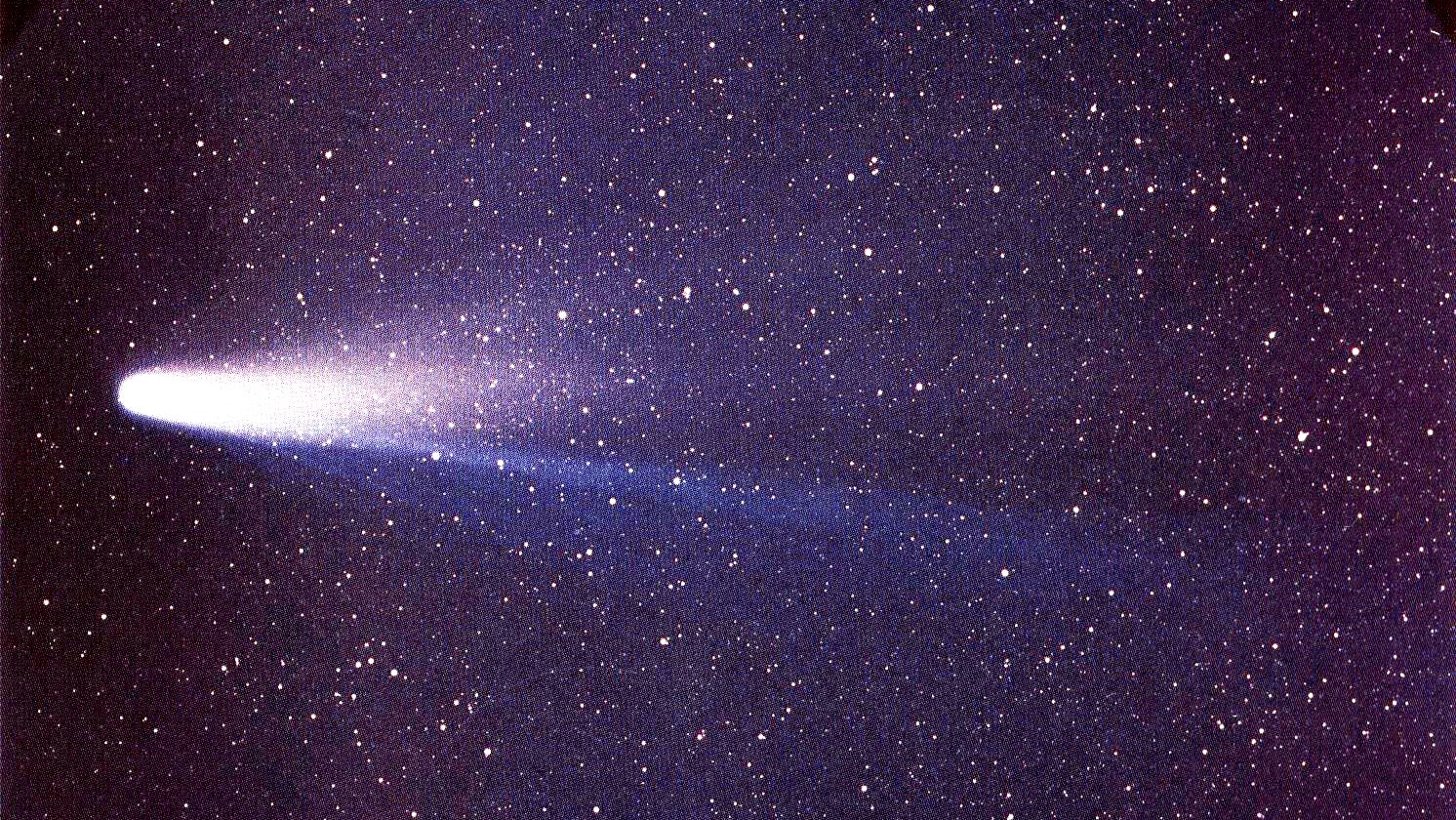
On December 9, 2023, Halley’s Comet reached aphelion: its farthest point from the Sun. As it returns, here are 10 facts you should know.
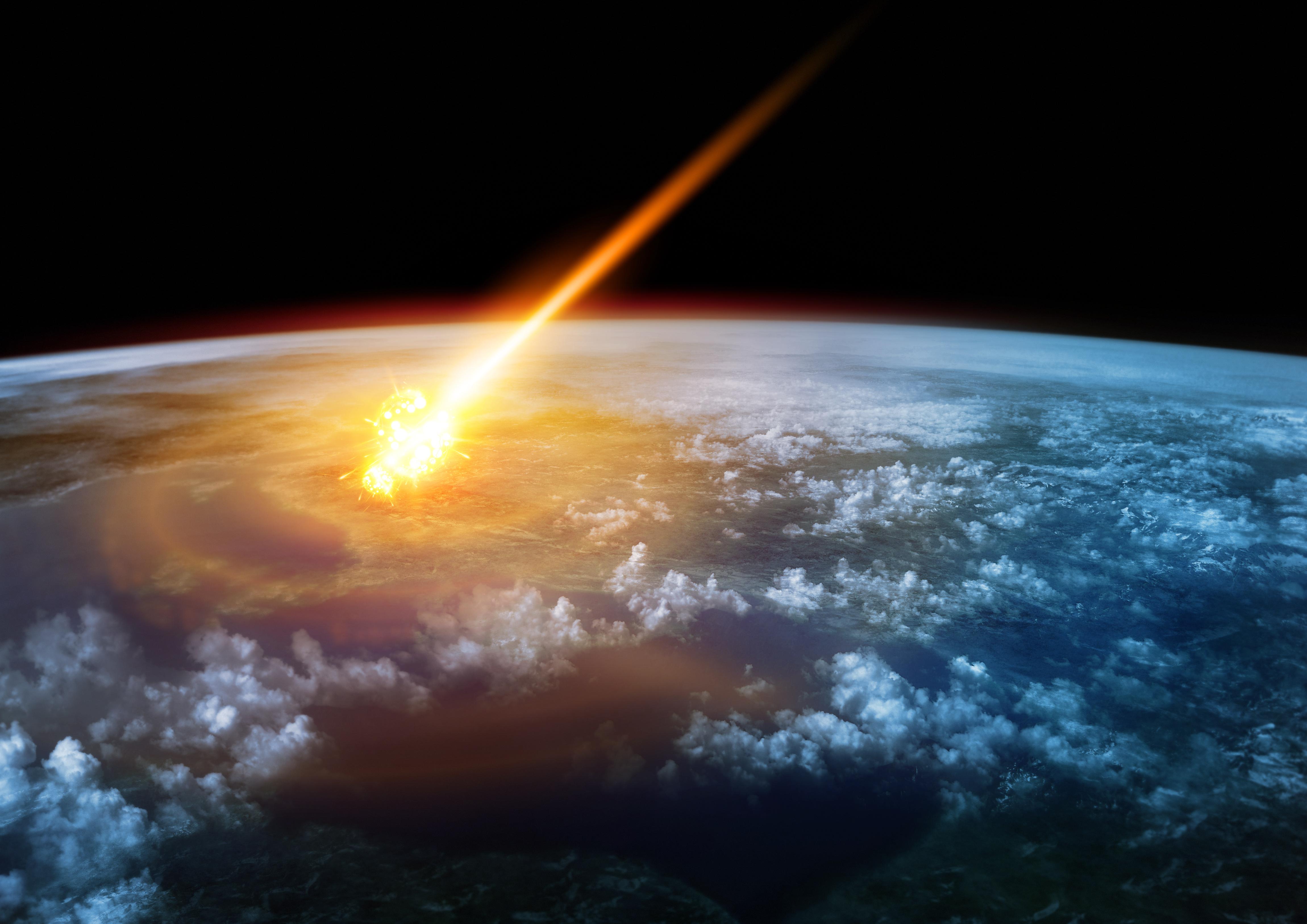
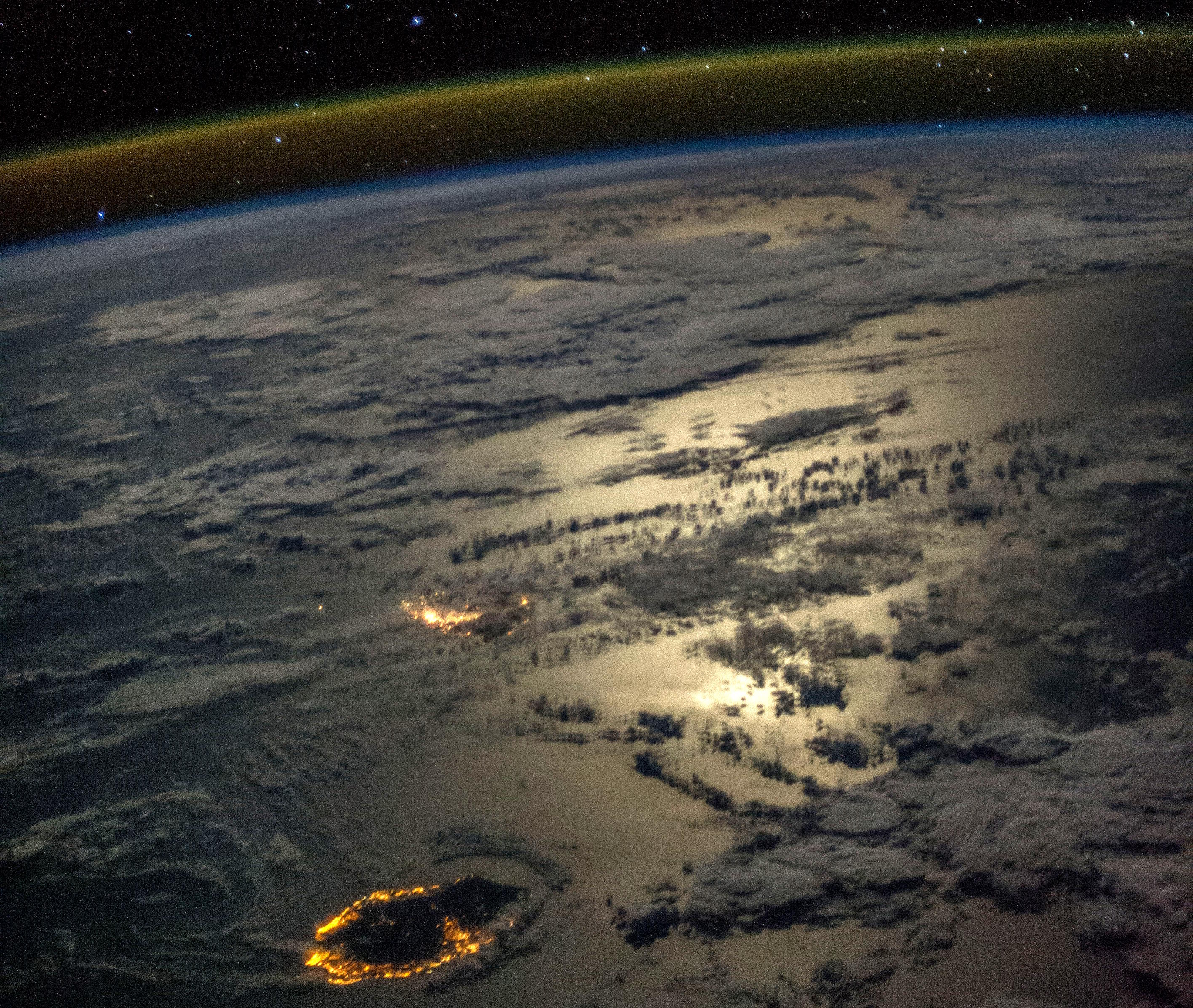
65 million years ago, a massive asteroid struck Earth. Not only did Jupiter not stop it, but it probably caused the impact itself.
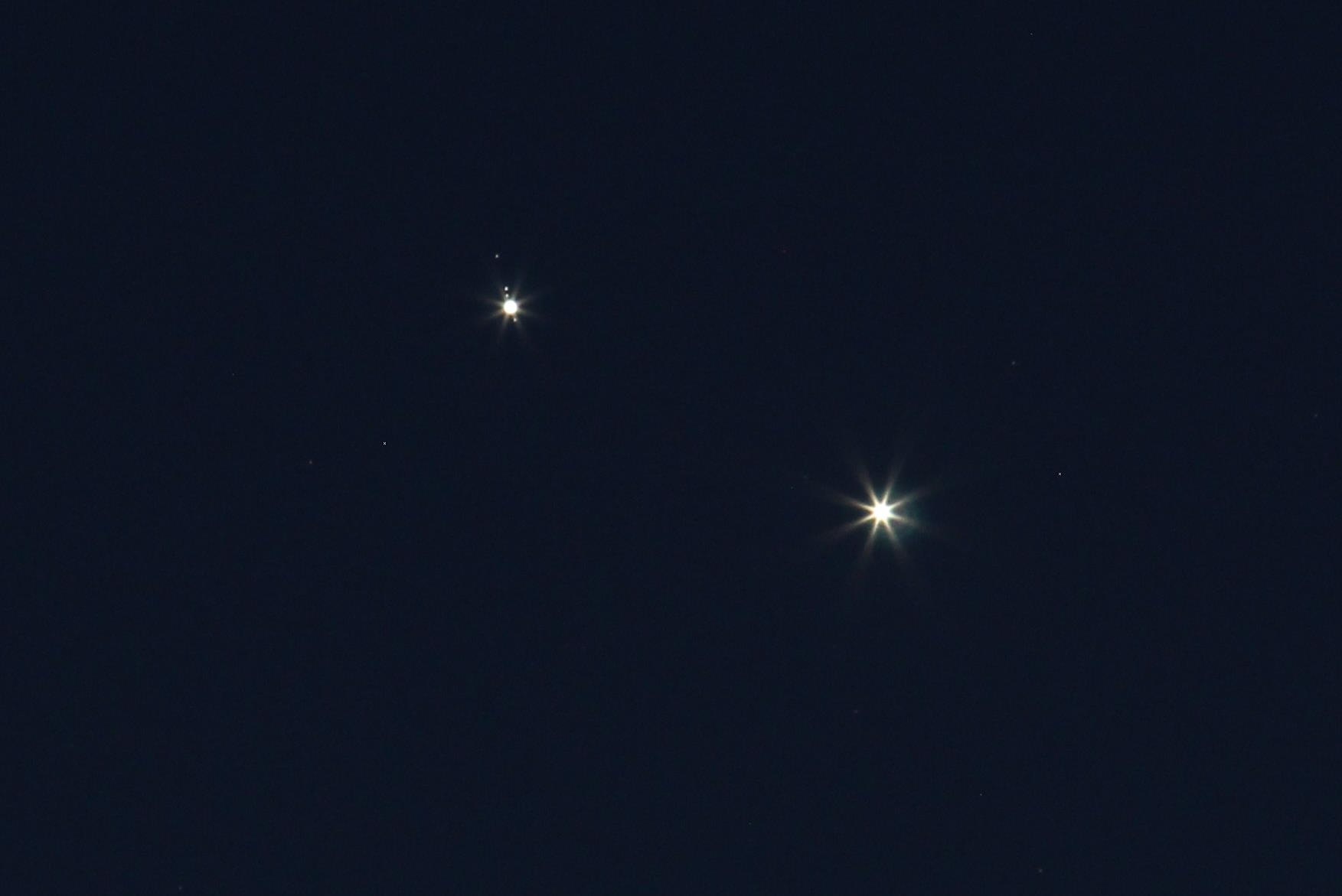
In our Solar System, even the two brightest planets frequently align in our skies. But only rarely is it spectacularly visible from Earth.
Finding a tiny planet around bright stars dozens or hundreds of light-years from Earth is extremely difficult.
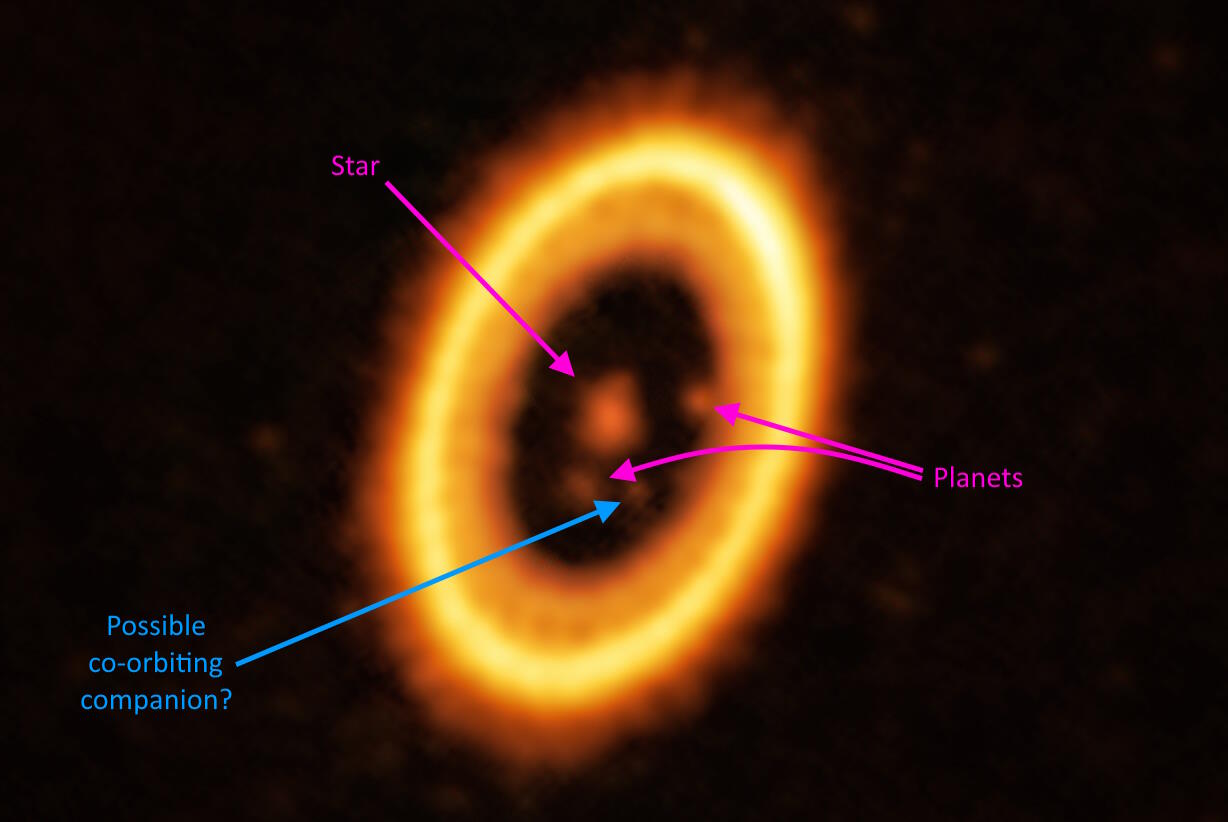
The secret ingredient is violence, and it just might indicate that “moonmoons” aren’t as uncommon as most astronomers think.
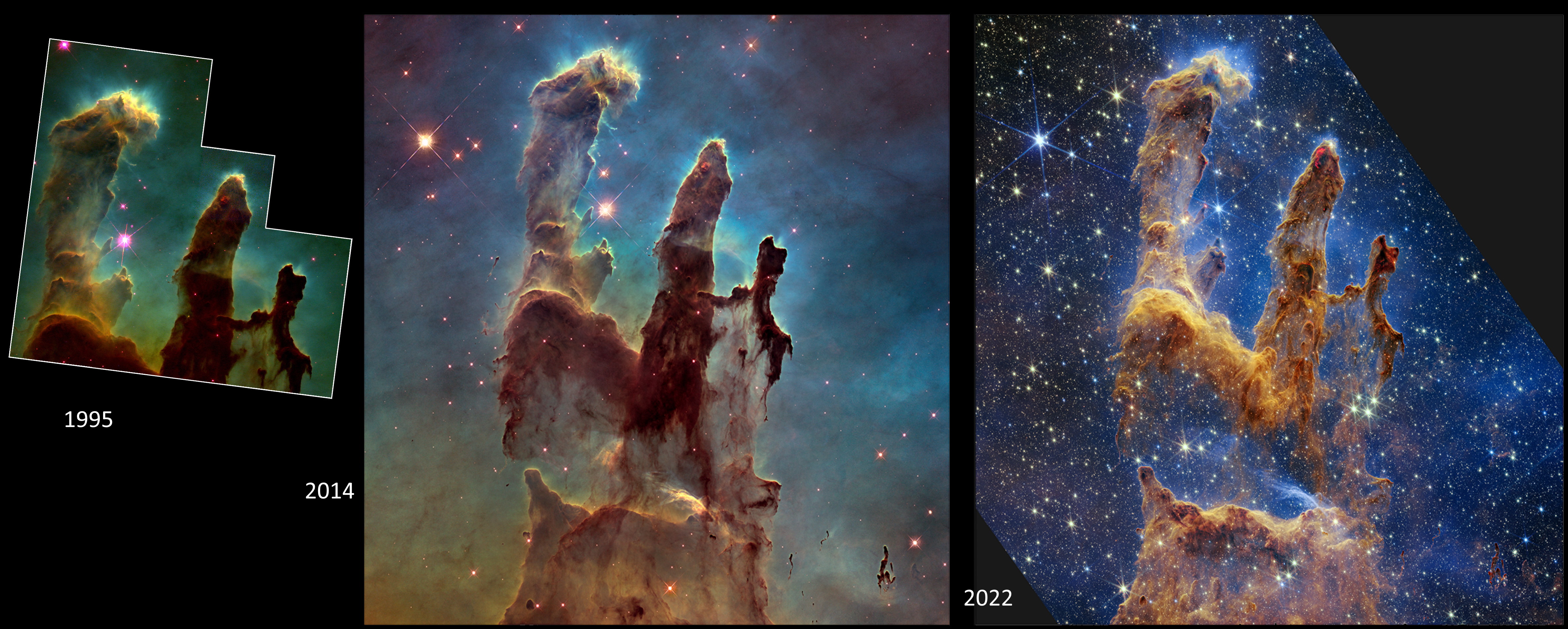
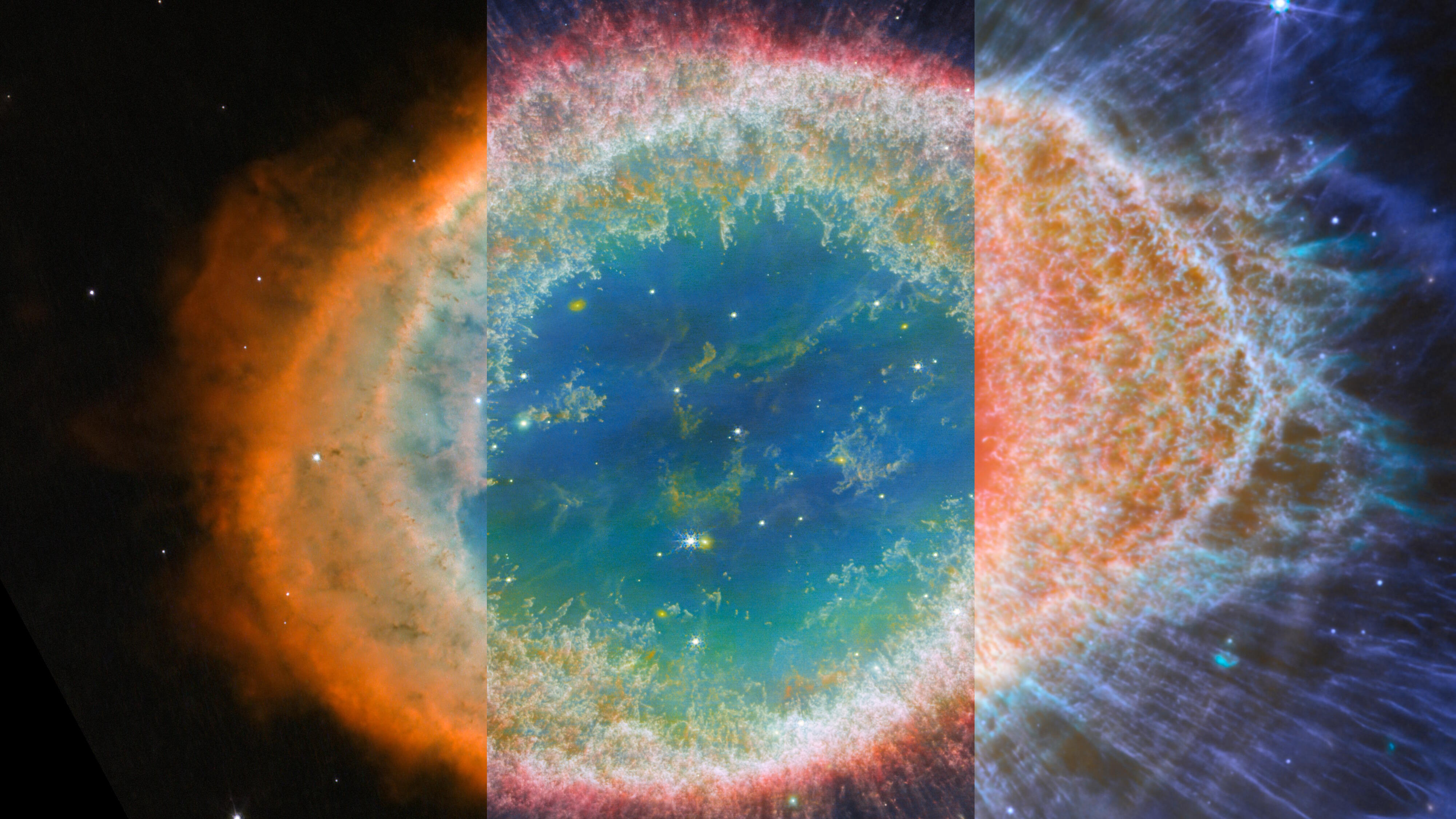
The last infant stars are finishing their formation inside these pillars of gas. The evaporation of those columns is almost complete.
The giant impact theory suggests our Moon was formed from proto-Earth getting a Mars-sized strike. An exoplanet system shows it’s plausible.
Mercury, Venus, and Mars are all uni-plate planets, and may always have been. Here’s what’s known about why Earth, uniquely, has plate tectonics.
Instead of worshipping Yahweh, the devotees were perhaps dedicated to Mars and Jupiter.
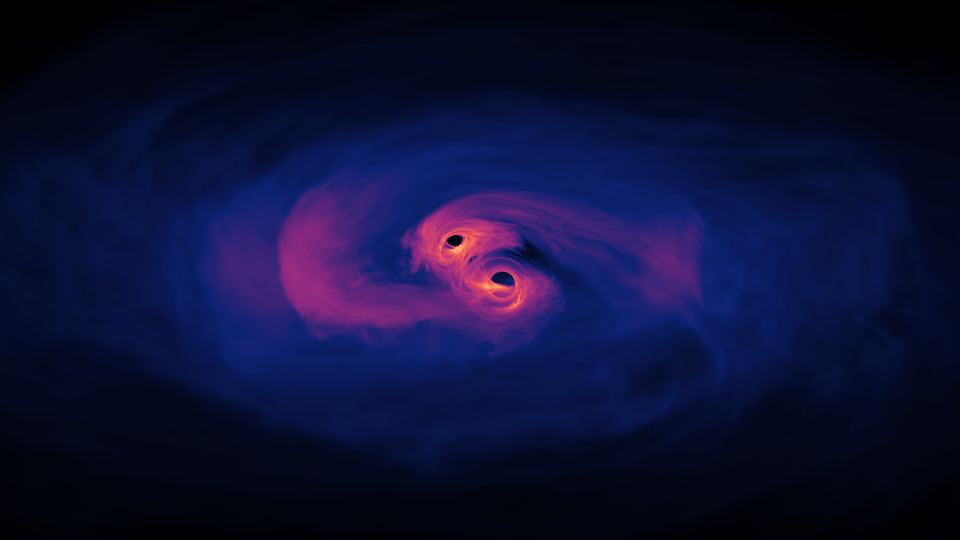
Newton thought that gravitation would happen instantly, propagating at infinite speeds. Einstein showed otherwise; gravity isn’t instant.
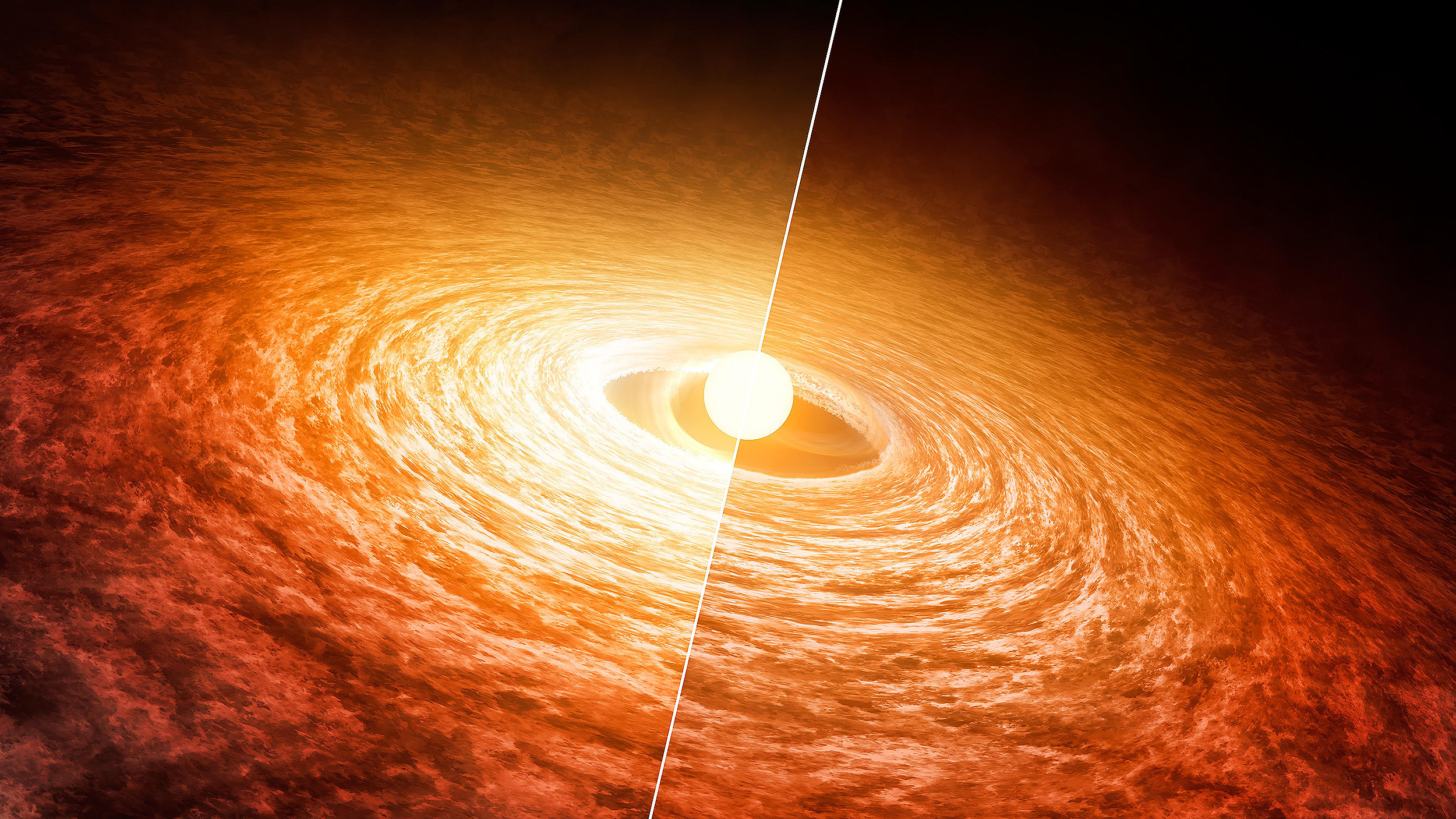
Newborn stars are surrounded only by a featureless disk. Debris disks persist for hundreds of millions of years. So when do planets form?
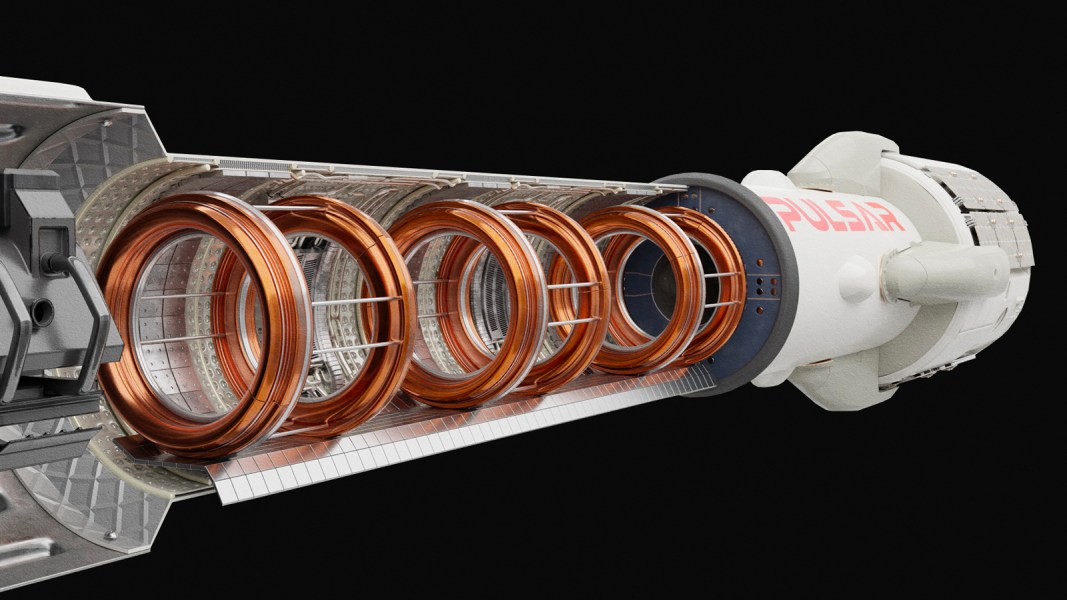
It could cut the time needed to reach Mars in half.
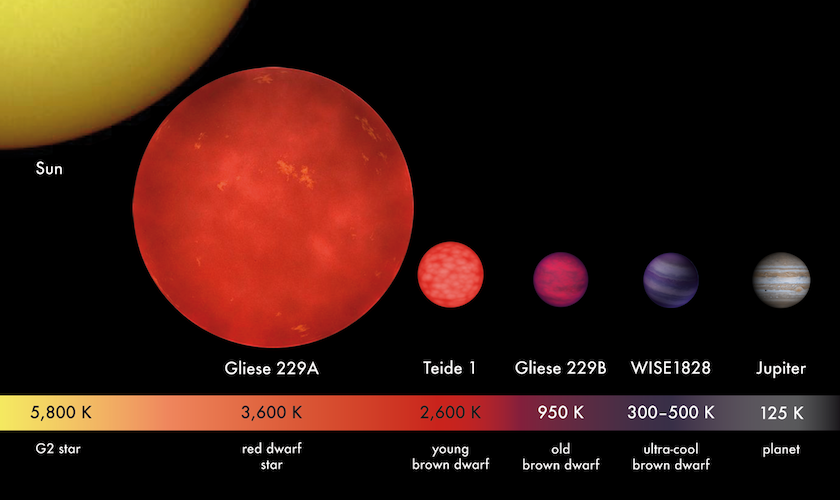
Between the least massive star and most massive planet lies the mysterious brown dwarf: a class of objects that are neither star nor planet.
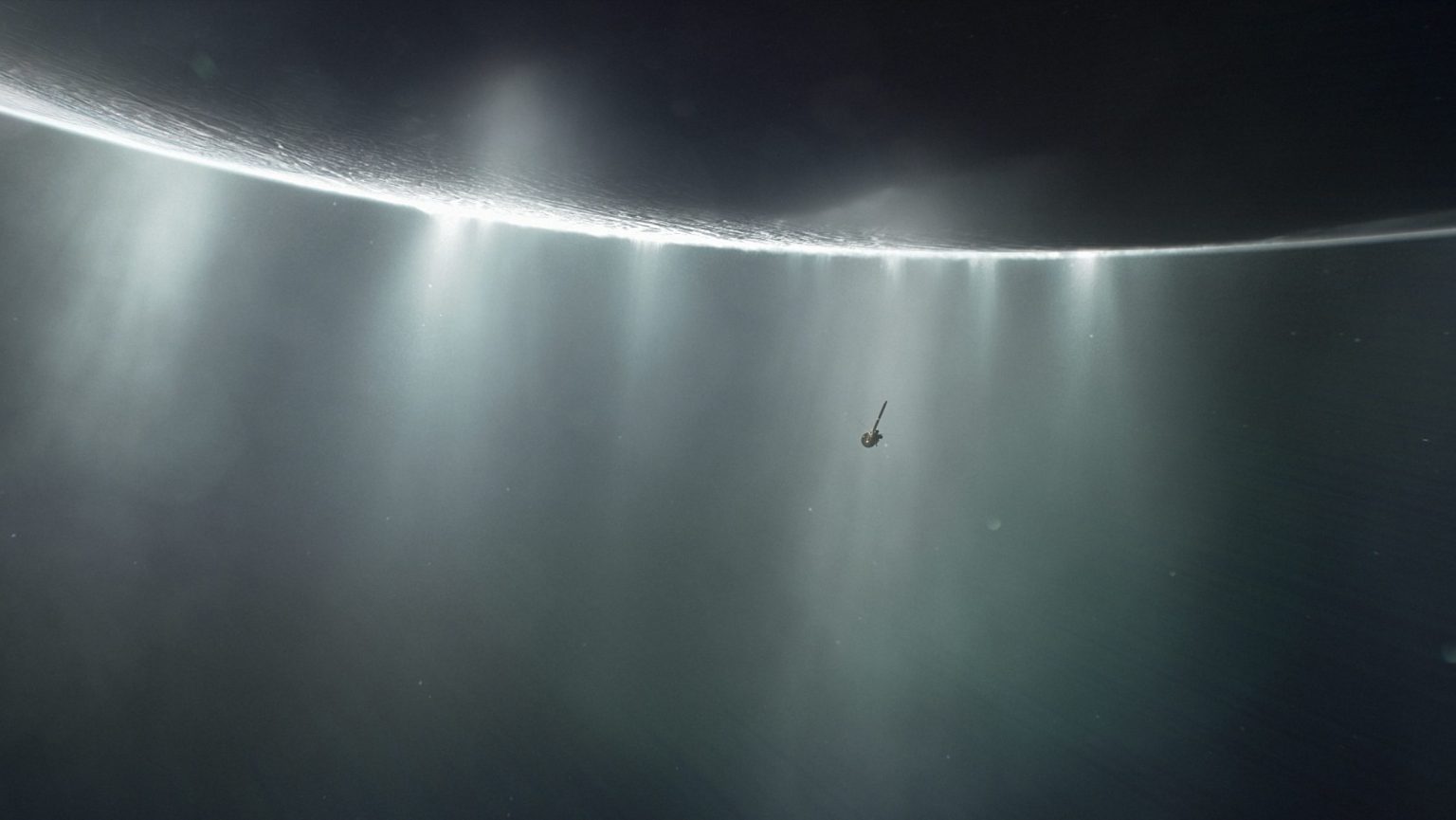
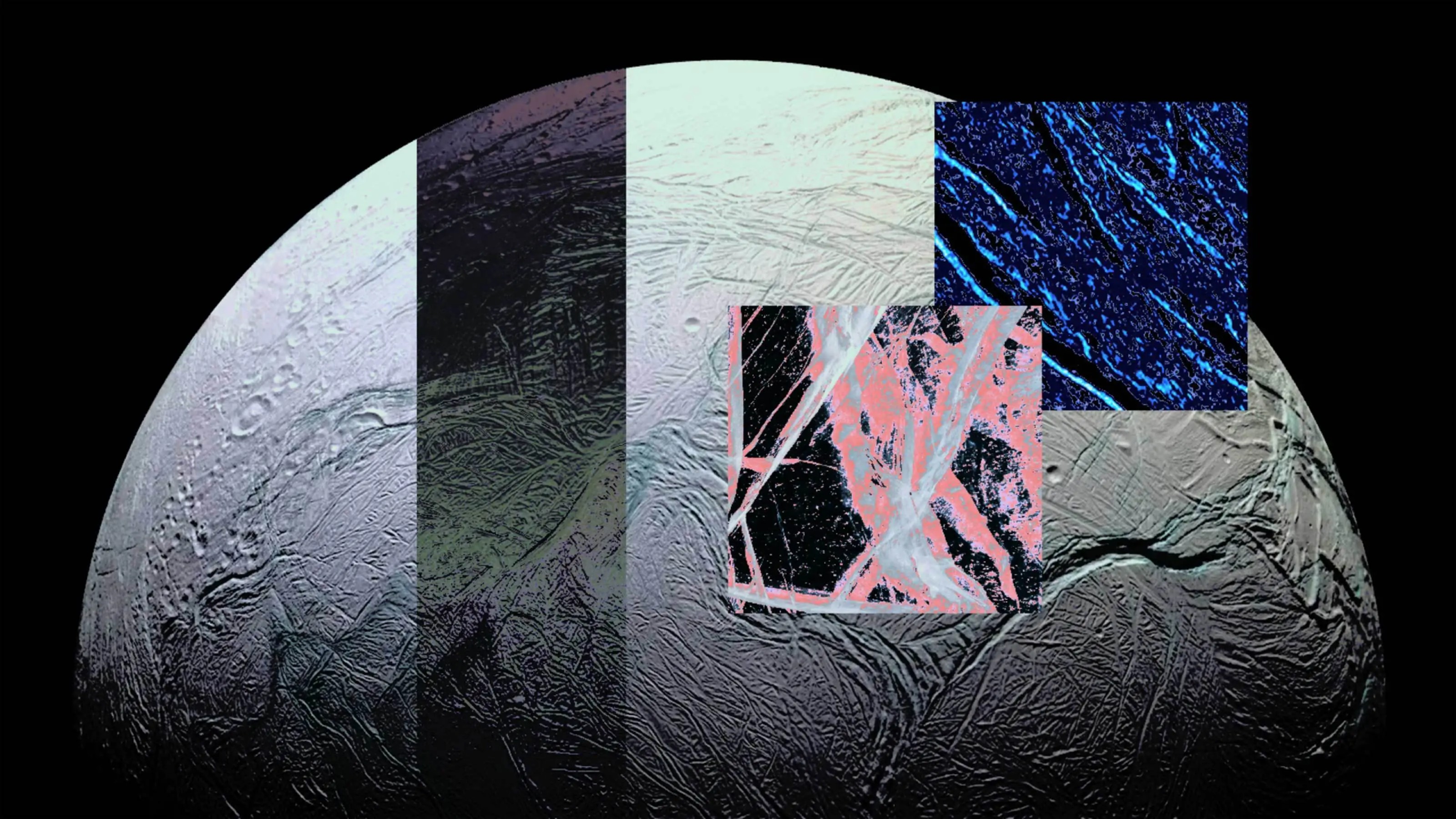
This research team is working out how to detect extraterrestrial cells in the liquid water ocean hidden beneath Enceladus’s icy crust.
More than two years after JWST began science operations, our Universe now looks very different. Here are its biggest science contributions.
2023 will see the launch of new rockets, the return of OSIRIS-REx, and a mission to Jupiter that could help us find extraterrestrial life.