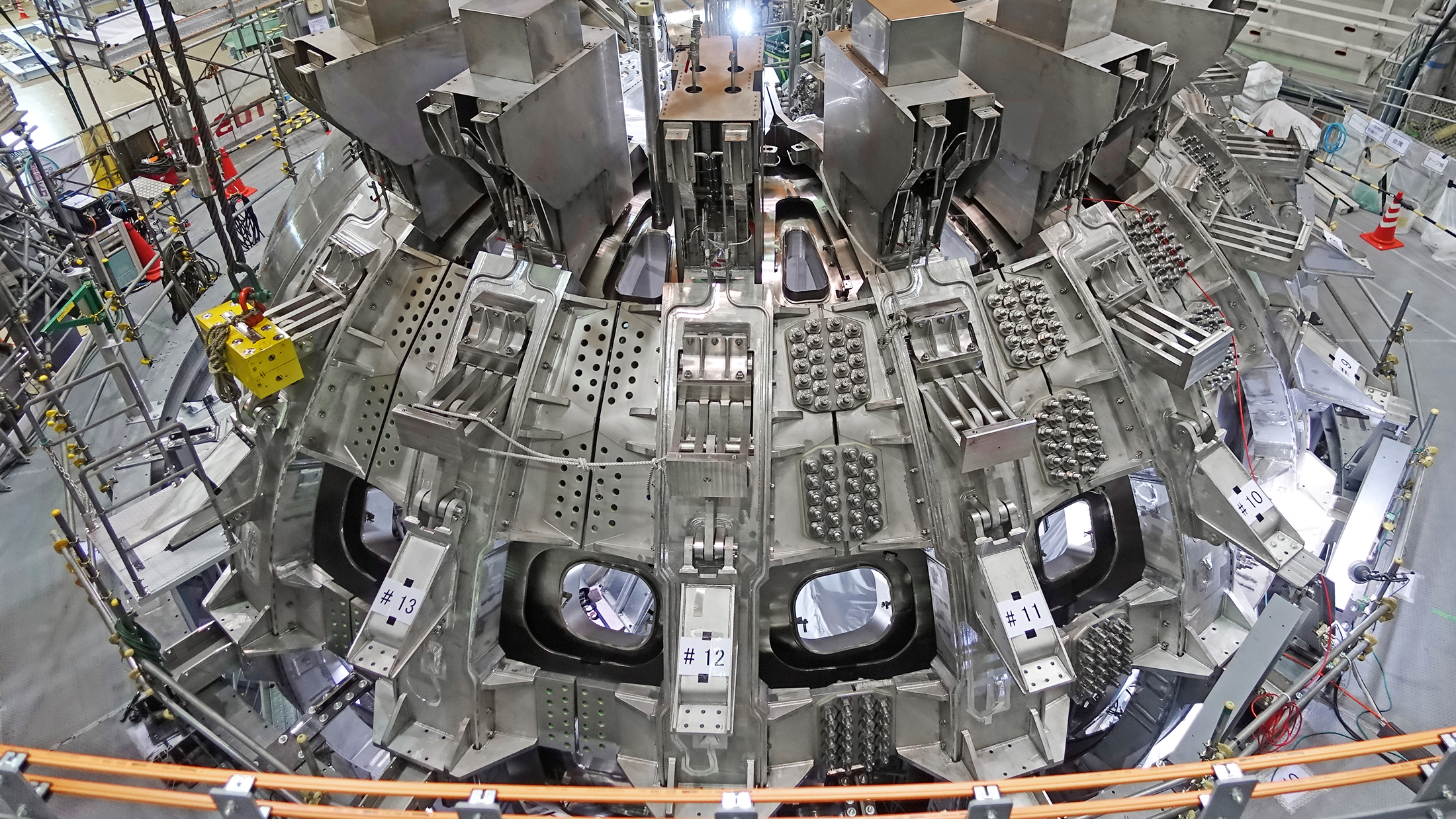
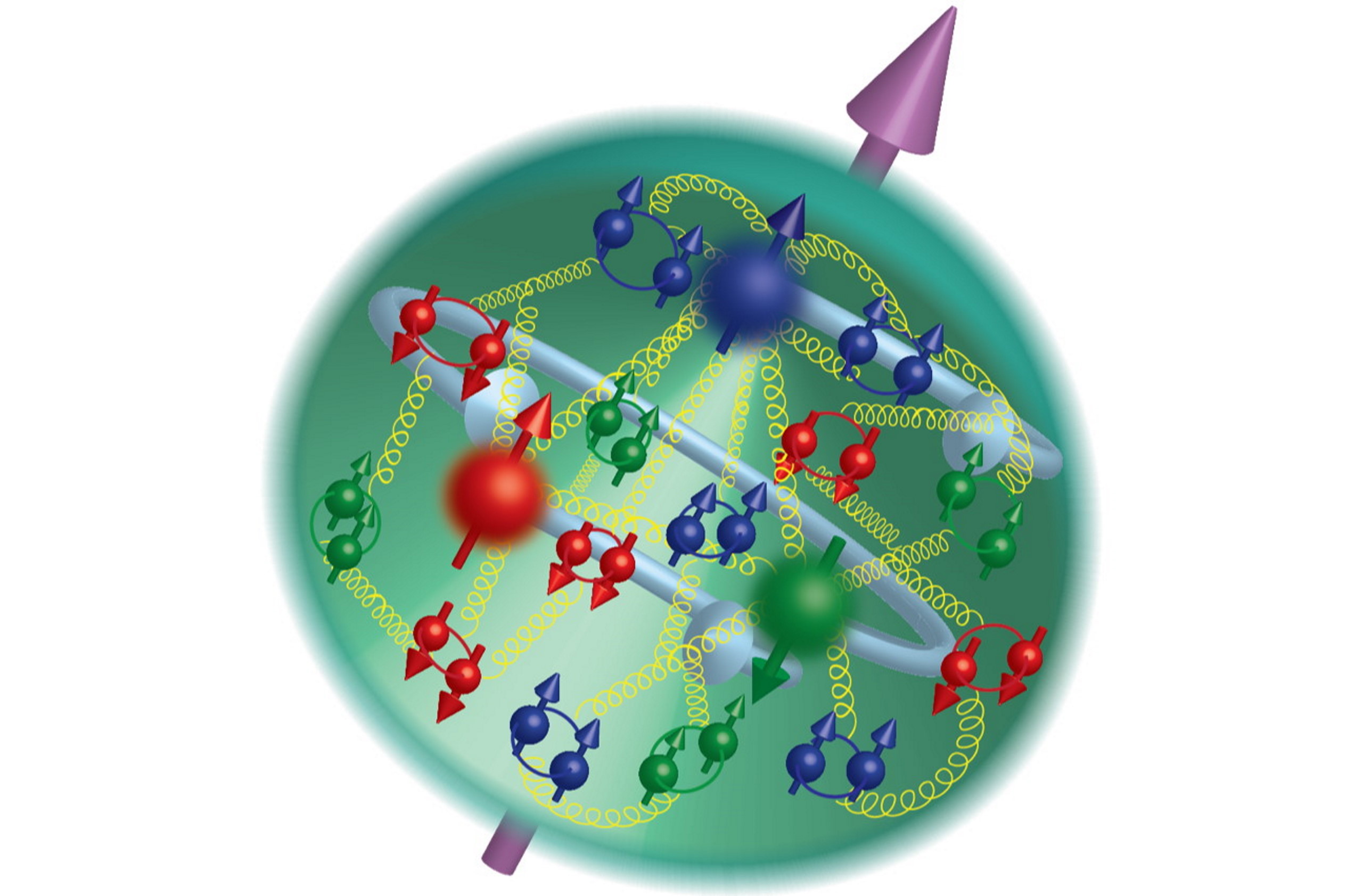
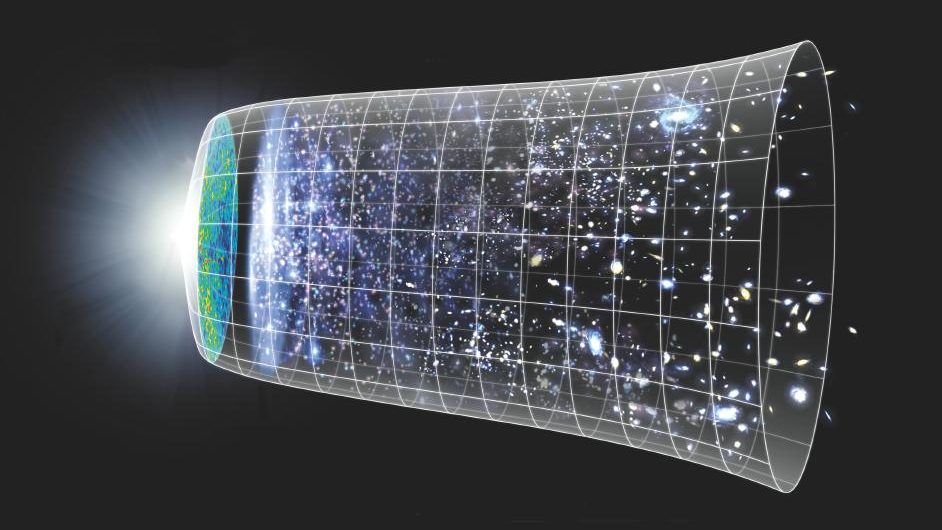
A massive nuclear fusion experiment just hit a major milestone, potentially putting us a little closer to a future of limitless clean energy.
Search Results
You searched for: quantum
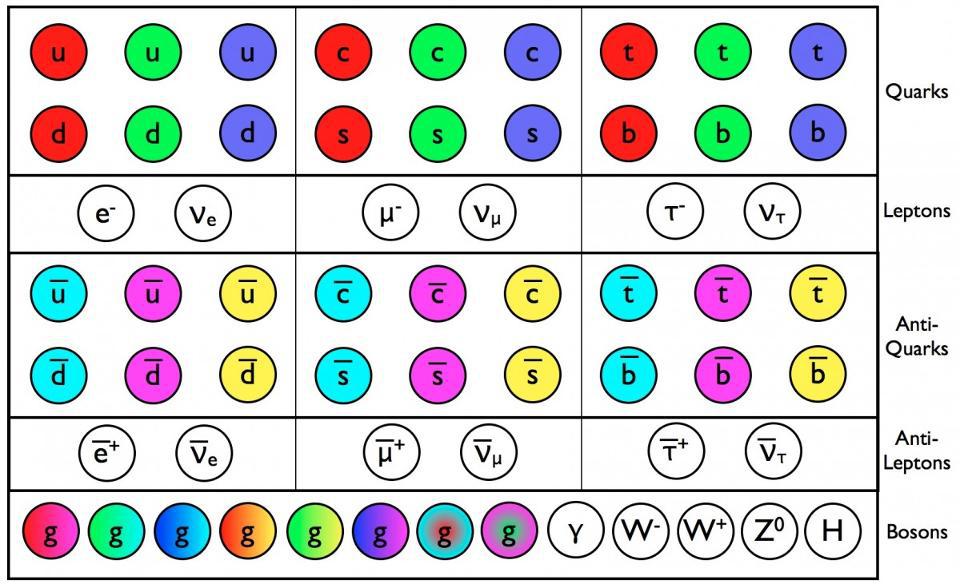
Every proton contains three quarks: two up and one down. But charm quarks, heavier than the proton itself, have been found inside. How?
Unless you confront your theory with what’s actually out there in the Universe, you’re playing in the sandbox, not engaging in science.
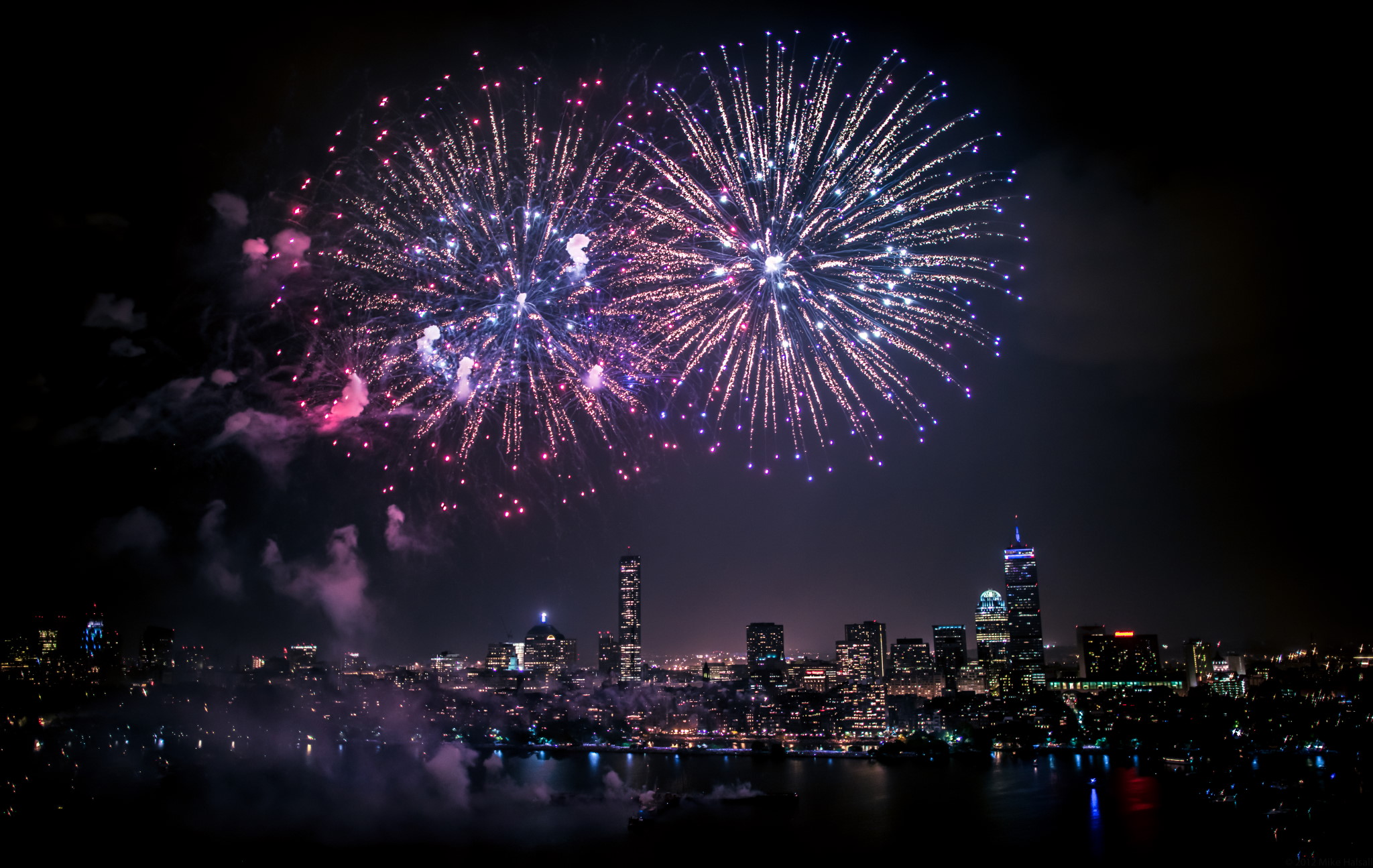
From the explosions themselves to their unique and vibrant colors, the fireworks displays we adore require quantum physics.
Quantum mechanics has taught us that even empty space contains energy. “Negative energy” is the state of having less energy than empty space.
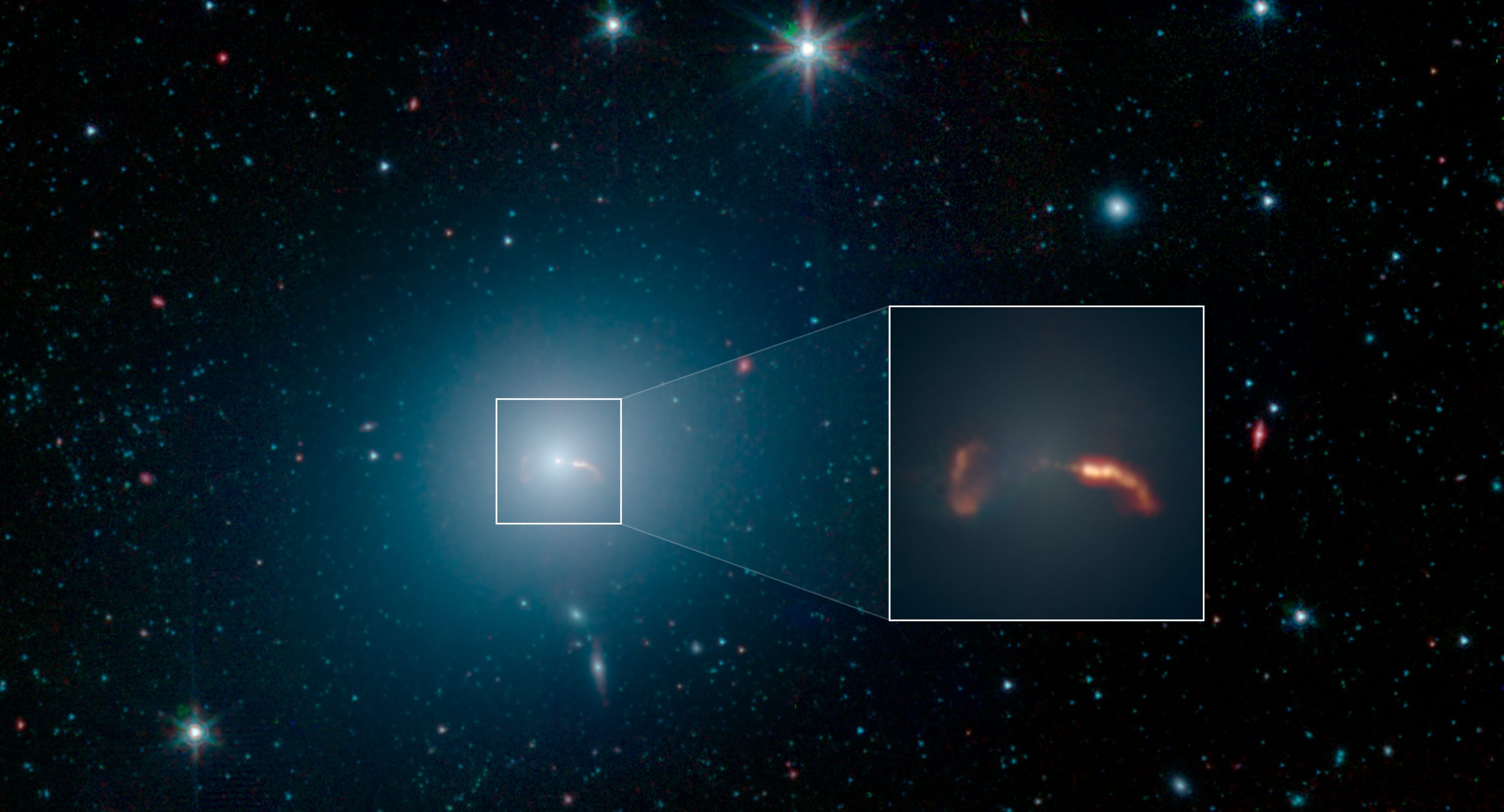
Nothing can escape from a black hole. So where do Hawking radiation, relativistic jets, and X-ray emissions around black holes come from?
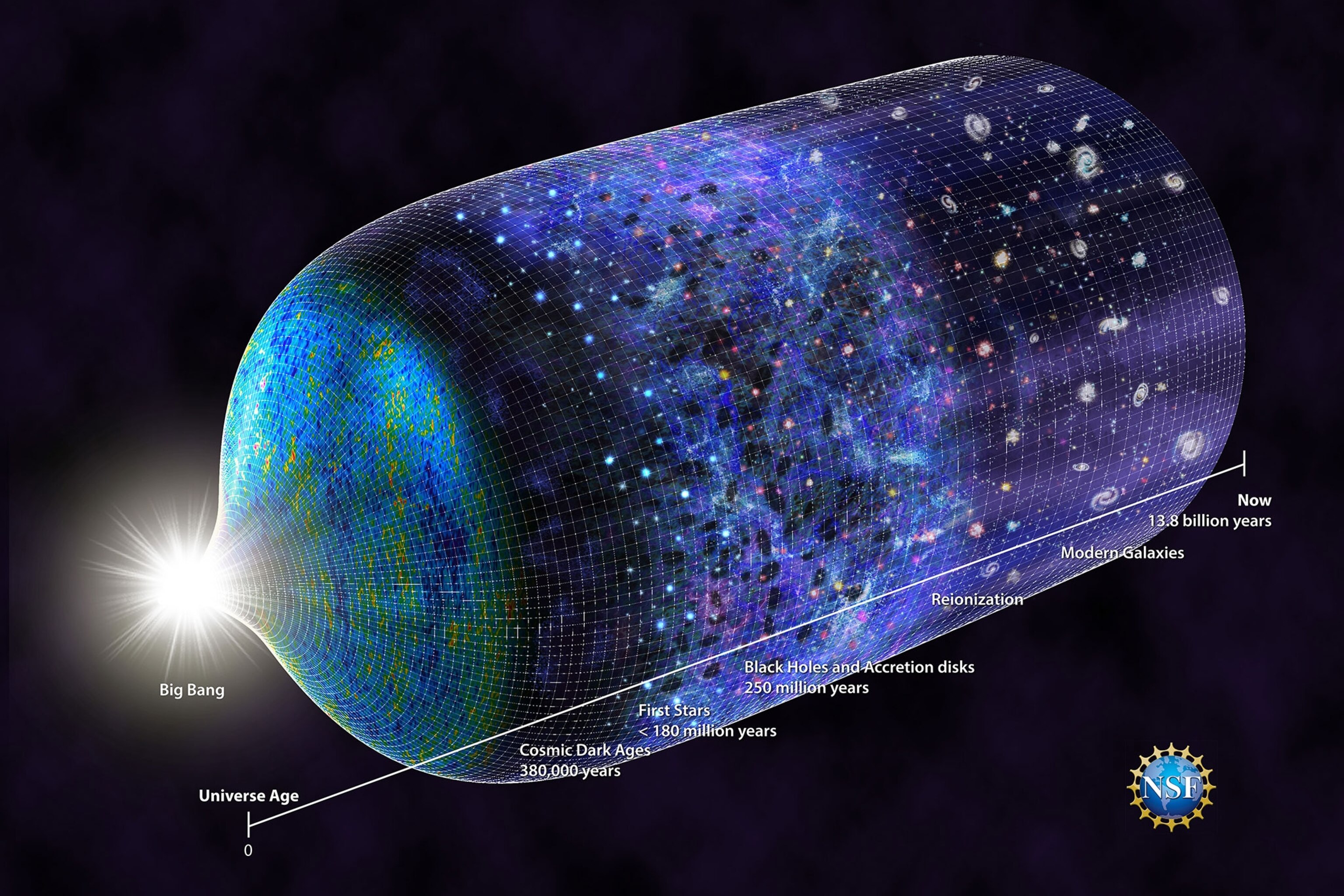
If you said “with the Big Bang,” congratulations: that was our best answer as of ~1979. Here’s what we’ve learned in all the time since.
When the average person has a “theory,” they’re just guessing. But for a scientist, a theory is the pinnacle of what we can achieve.
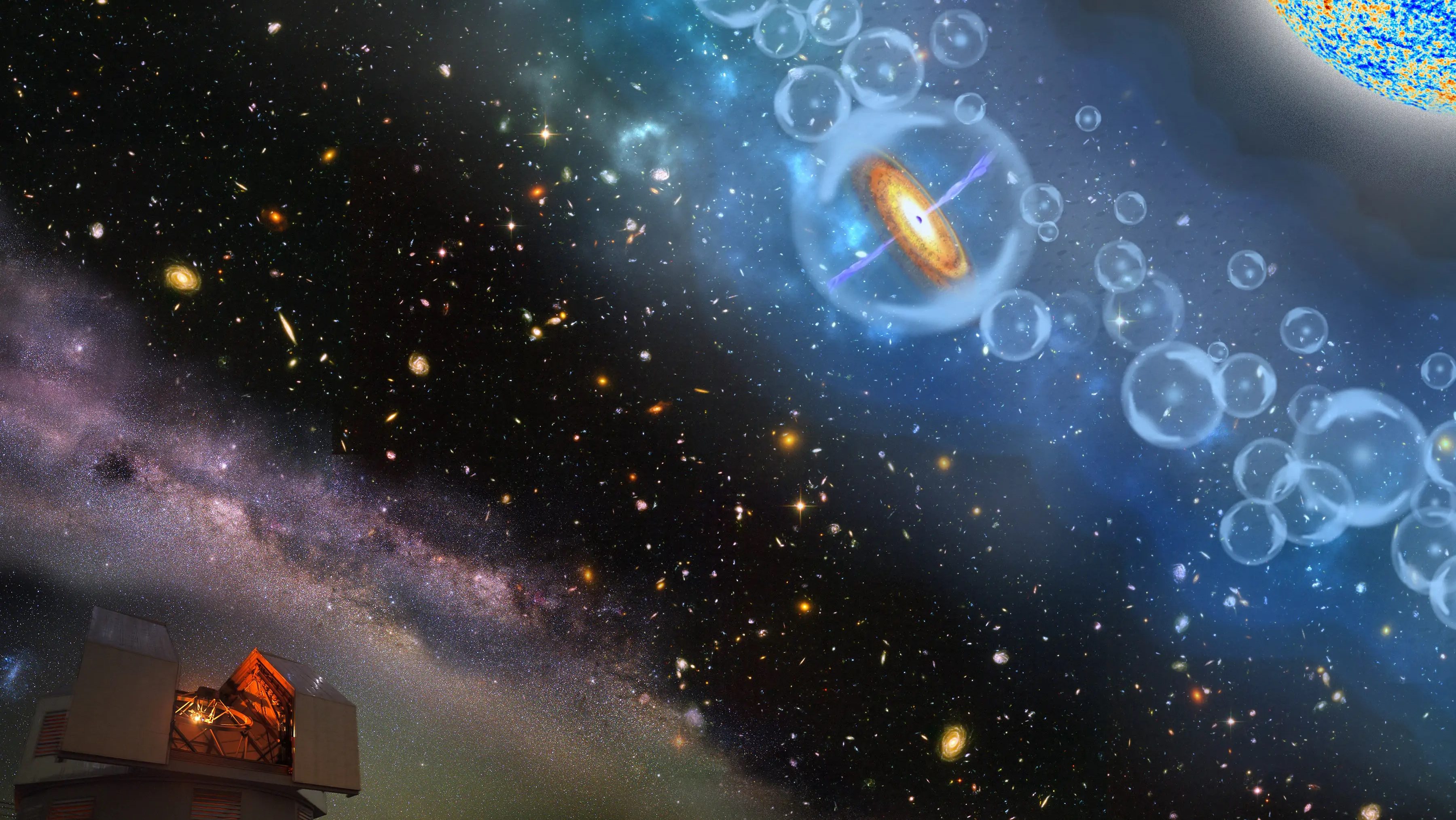
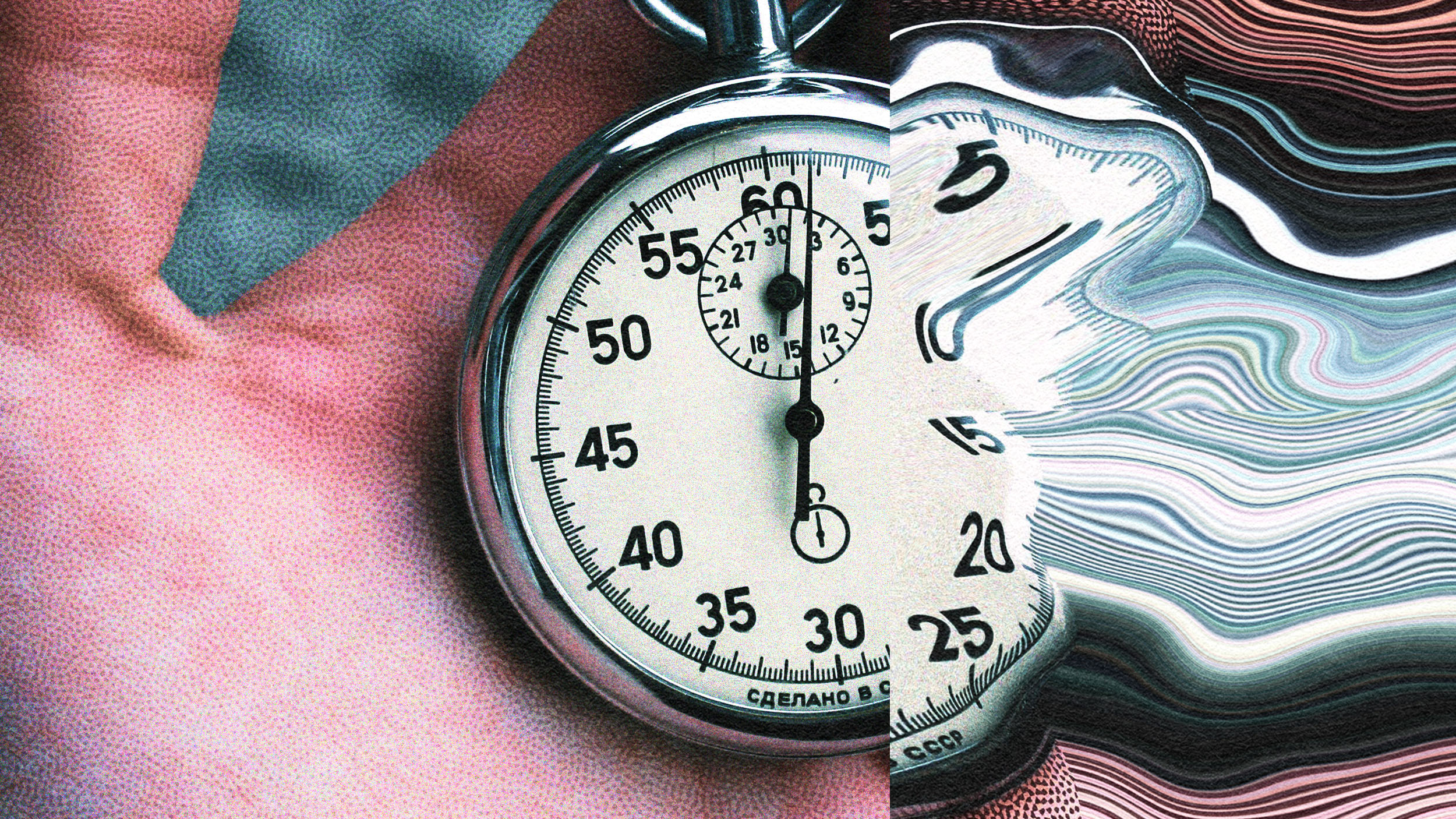
Headlines have blared that quasar ticking confirms that time passed more slowly in the early Universe. That’s not how any of this works.
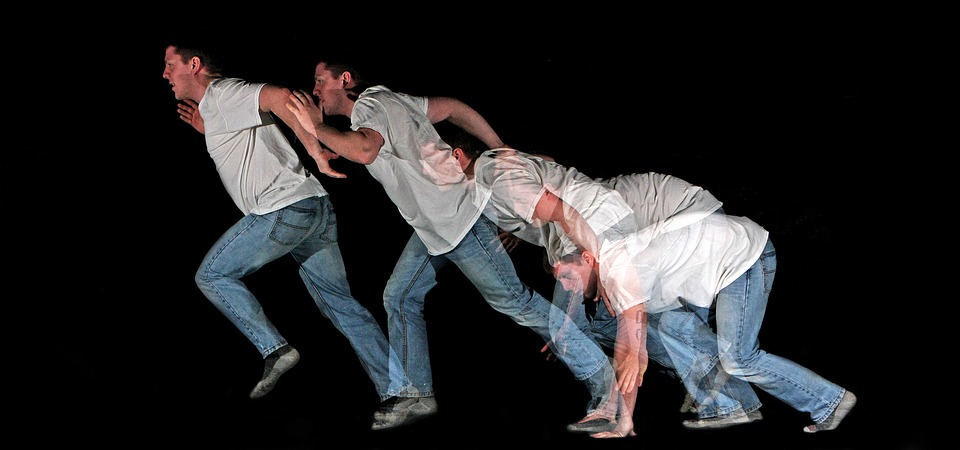
The passage of time is something we all experience, as it takes us from one moment to the next. But could it all just be an illusion?
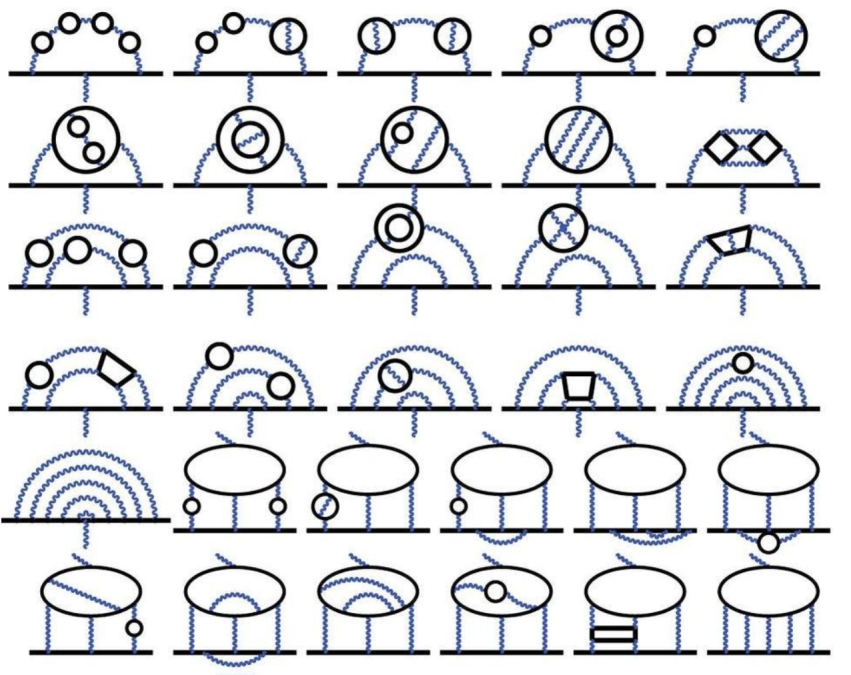
Predicted way back in the 1960s, the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012 completed the Standard Model. Here’s why it remains fascinating.
The conservation of energy is one of the most fundamental laws governing our reality. But in the expanding Universe, that’s just not true.
Time is relative, not absolute, as gravity and motion both cause time to dilate. Your head and feet, therefore, don’t age at the same rate.
The game of Plinko perfectly illustrates chaos theory. Even with indistinguishable initial conditions, the outcome is always uncertain.
At a fundamental level, nobody knows whether gravity is truly quantum in nature. A novel experiment strongly hints that it is.
The simulation hypothesis is fun to talk about, but believing it requires an act of faith.
Neuroscientist and author Bobby Azarian explores the idea that the Universe is a self-organizing system that evolves and learns.
The relationship between these two ways of thinking about the world deserves deeper exploration.
At a fundamental level, only a few particles and forces govern all of reality. How do their combinations create human consciousness?
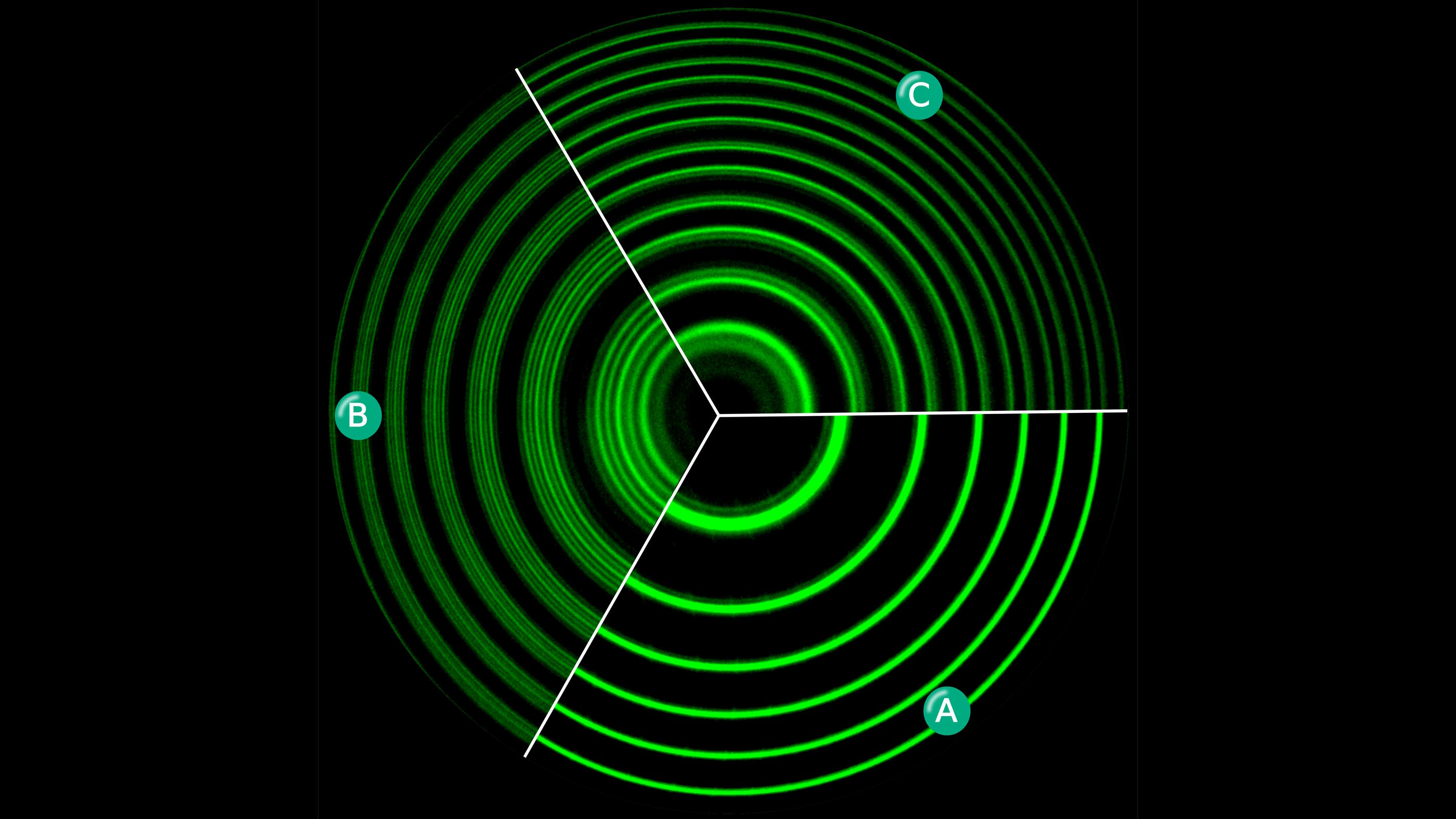
If light can’t be bent by electric or magnetic fields (and it can’t), then how do the Zeeman and Stark effects split atomic energy levels?
The answer to the age-old philosophical question of whether there is meaning in the Universe may ultimately rest upon the power of information.
Inflation, dark matter, and string theory are all proposed extensions to the prior consensus picture. But what does the evidence say?
No matter what physical system we consider, nature always obeys the same fundamental laws. Must it be this way, and if so, why?
Holograms preserve all of an object’s 3D information, but on a 2D surface. Could the holographic Universe idea lead us to higher dimensions?
The zero-point energy of empty space is not zero. Even with all the physics we know, we have no idea how to calculate what it ought to be.
When you bring two fingers together, you can feel them “touch” each other. But are your atoms really touching, and if so, how?
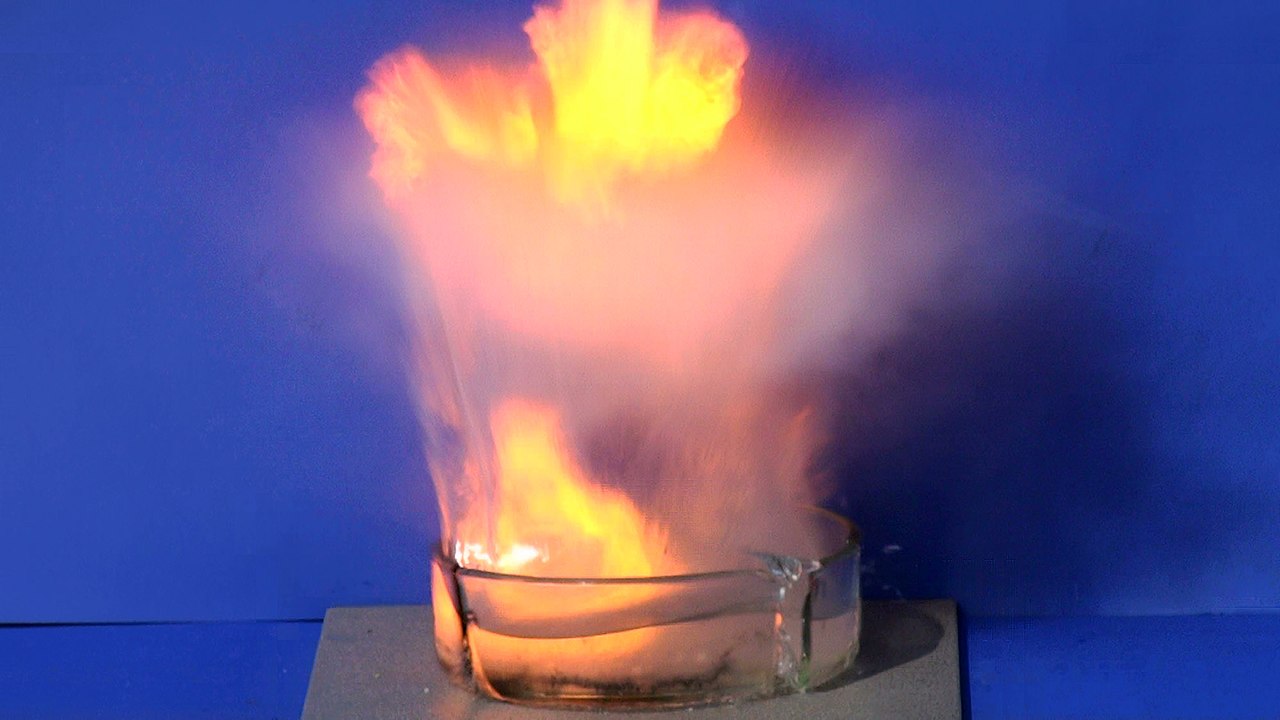
Drop sodium in water, and a violent, even explosive reaction will occur. But quantum physics is needed to explain why.
Could we finally detect the elusive Unruh effect?
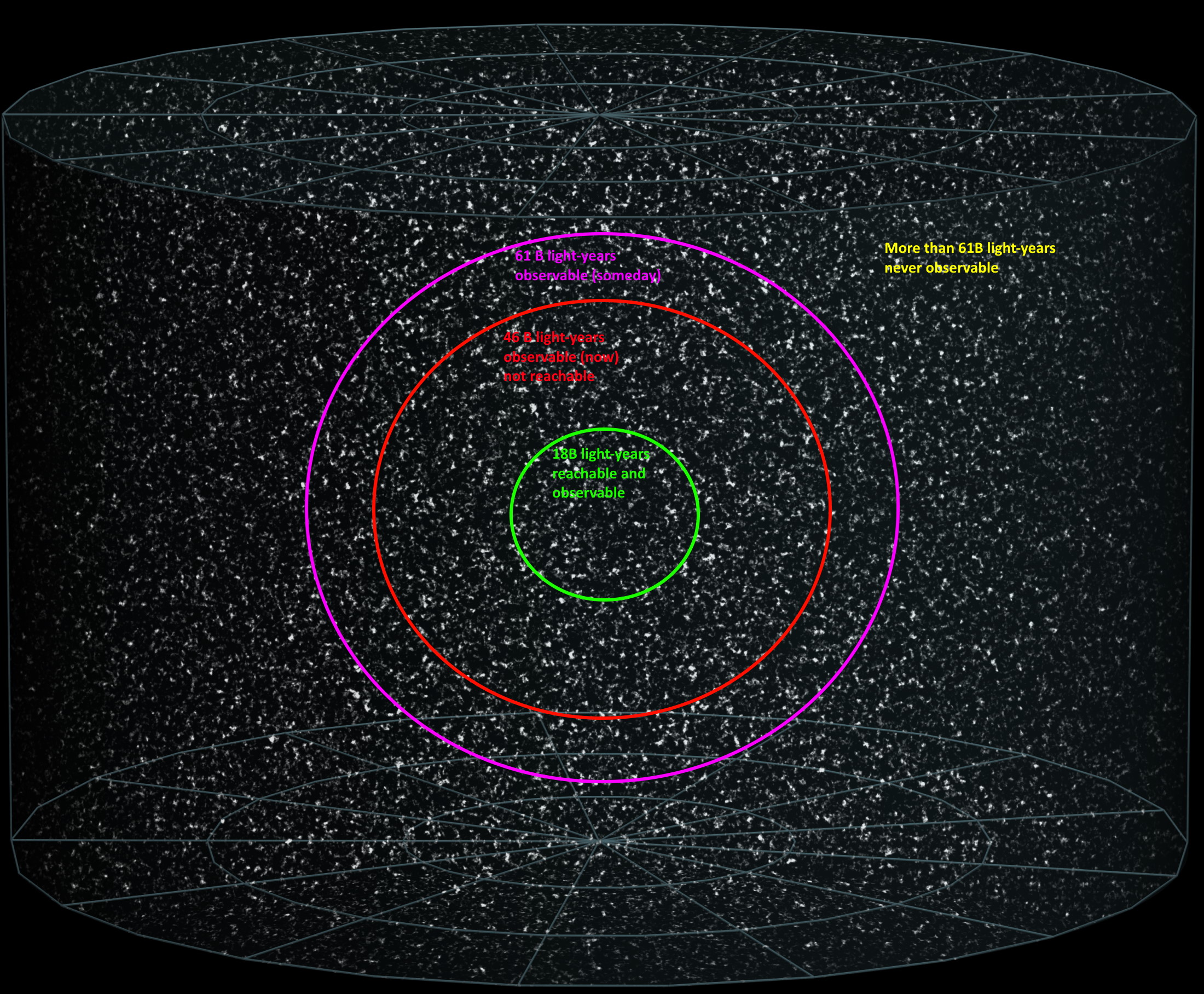
From the earliest stages of the hot Big Bang (and even before) to our dark energy-dominated present, how and when did the Universe grow up?