Are these 100 people killing the planet?
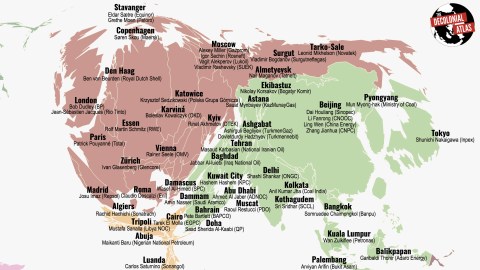
Image source: Jordan Engel, reused via Decolonial Media License 0.1
- Just 100 companies produce 71% of the world’s greenhouse gases.
- This map lists their names and locations, and their CEOs.
- The climate crisis may be too complex for these 100 people to solve, but naming and shaming them is a good start.
Editorial note: Big Think has issued a retraction regarding this article. This map was originally based on a July 2017 report entitled The Carbon Majors Database by CDP and all of the names shown may no longer be up to date.
Image source: Jordan Engel, reused via Decolonial Media License 0.1 / Edited by Big Think.
Do you carry your shopping home in a reusable bag? Close the tap while you brush your teeth? Well done! But saving the planet will require a more systemic approach.
A new UN-sponsored report (1,500 pages in full — consider the environment before printing!) details how the accelerating decline of biodiversity is threatening humanity’s very survival.
It’s not the first report of its kind, and despite their increasingly alarmist tones, unlikely to be the last.
What to do?
Between the relative futility of individual do-goodery and the seemingly unstoppable forces degrading earth’s ecosystems lies a whole world of despair, paralysis, and tuned-out apathy.
But if those forces seem unstoppable, it’s perhaps because they appear to be nameless and faceless. As this map points out, they aren’t. The harm that’s being done to the planet can be pinpointed, to a very specific list of companies. And those companies have CEOs that can be named and shamed.
Image source: Jordan Engel, reused via Decolonial Media License 0.1 / Edited by Big Think.
The map shows the 100 companies responsible for the biggest share of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions, and their CEOs. Countries are inflated to represent their share of CO2 emissions since the beginning of industrialisation.
If we want to make a serious dent in the amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gases we’re emitting, this map suggests, it’s these companies — and more specifically, these CEOs — we need to hold to account. Naming and shaming them is a first step.
The basis for this map is the Carbon Majors report from 2017 by CDP (formerly the Carbon Disclosure Project), listing the top 100 fossil fuel producers in the world, responsible for 71 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions since 1988.
In fact, more than 50 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions since 1988 can be traced to just the top 25 entities on that list.
Those are, in descending order: China (state coal production), Aramco, Gazprom, National Iranian Oil, ExxonMobil, Coal India, Pemex, Russia (state coal production), Shell, China National Petroleum, BP, Chevron, PDVSA, Abu Dhabi National Oil, Poland Coal, Peabody Energy, Sonatrach, Kuwait Petroleum, Total, BHP Billiton, ConocoPhilips, Petrobras, Lukoil, RioTinto, Nigerian National Petroleum.

Even oil companies are now turning to invest in sustainable energy — but is it just window dressing? Image source: Jordan Engel, reused via Decolonial Media License 0.1
If fossil-fuel extraction over the next quarter century continues at the same rate as the previous 25 years, the Carbon Majors report claims we’re on course for a 4°C rise in average temperatures by the end of this century — accelerating the loss of biodiversity and the rise of food insecurity, to name but two consequences.
Granted, even oil companies are aware that the wind is blowing from a different direction now and have initiated programmes to produce energy in a more sustainable way. But in many cases, the discrepancy between the size of those programmes and the attention they are given in corporate PR makes them little more than window dressing.

Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia, is the wider region’s capital of greenhouse gas-emitting companies. Image source: Jordan Engel, reused via Decolonial Media License 0.1
This overview refocuses the attention on the main issue — the emission of CO2 and other greenhouse gases. And by naming each company’s CEO, the issue is personalized.
That personalization should come with a few caveats.
First, these corporations thrive only because consumers buy their product — although it must be said that demand for energy is fairly inelastic: most people can’t do without fuel to get from A to B, or to heat their homes.
Second, in all fairness: the true captains of industry are not the CEOs, but the majority shareholders. It’s those shareholders’ priorities — profit only or planet also — that drive corporate decision-making.
Those shareholders include large institutional investors, but also national governments. Up to 20 percent of investment in hydrocarbon extraction is done by public funding — i.e. us.

Africa counts relatively little CO2 culprits, while the tally is much higher in the Middle East (as could have been expected). Image source: Jordan Engel, reused via Decolonial Media License 0.1
On the other hand, we’re running into the same problem mentioned above again. Big institutions, even if they include you and me, are nameless/faceless. These CEOs are picked to run and represent their companies. Perhaps they should get used to a new job: being the lightning rod for our growing concern about global warming.
The Decolonial Atlas, which published this map, quotes U.S. folk artist and labor organizer Utah Phillips: “The earth is not dying, it is being killed, and those who are killing it have names and addresses.”
On that list is your name and address, and mine; because we could all do a lot more. But not nearly as much as these 100 people. Let this map be an invitation to acquaint ourselves with their intentions, good or otherwise.
Map released by The Decolonial Atlas. Many thanks to Roger Huisman for sending it in.
Strange Maps #973
Got a strange map? Let me know at [email protected].