Space & Astrophysics
Here in our Universe, stars shine brightly, providing light and heat to planets, moons, and more. But some objects get even hotter, by far.
Most stars shine with properties, like brightness, that barely change at all with time. The ones that do vary help us unlock the Universe.
Astronomer Adam Frank reflects on some responses to his recent appearance on the Lex Fridman Podcast.
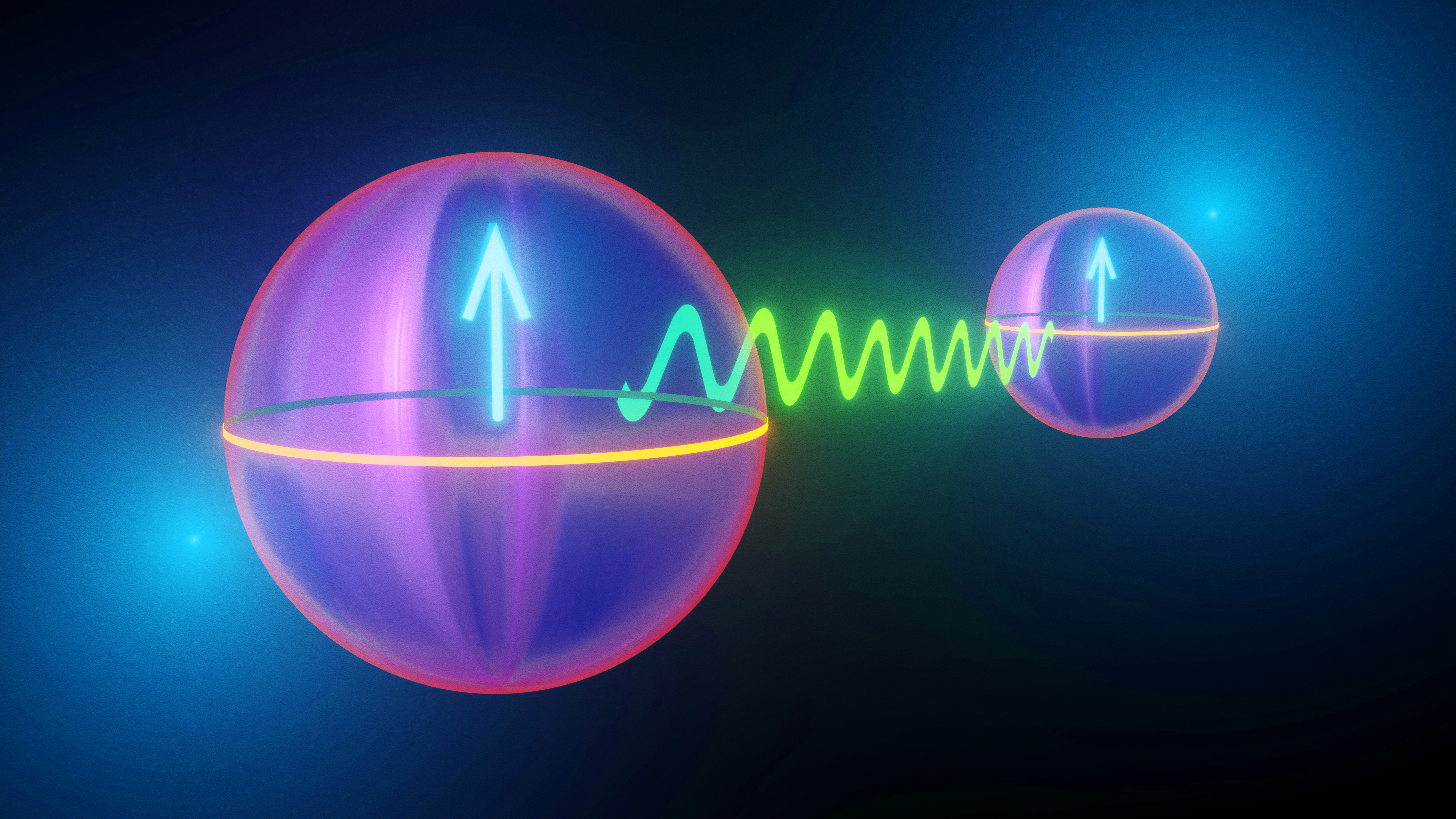
Despite no experimental evidence showing that gravitons exist, they remain a respectable concept in the world of professional physicists.
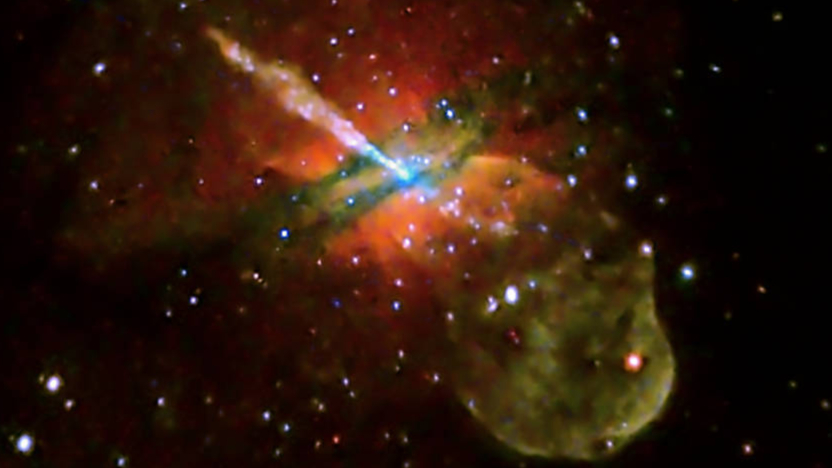
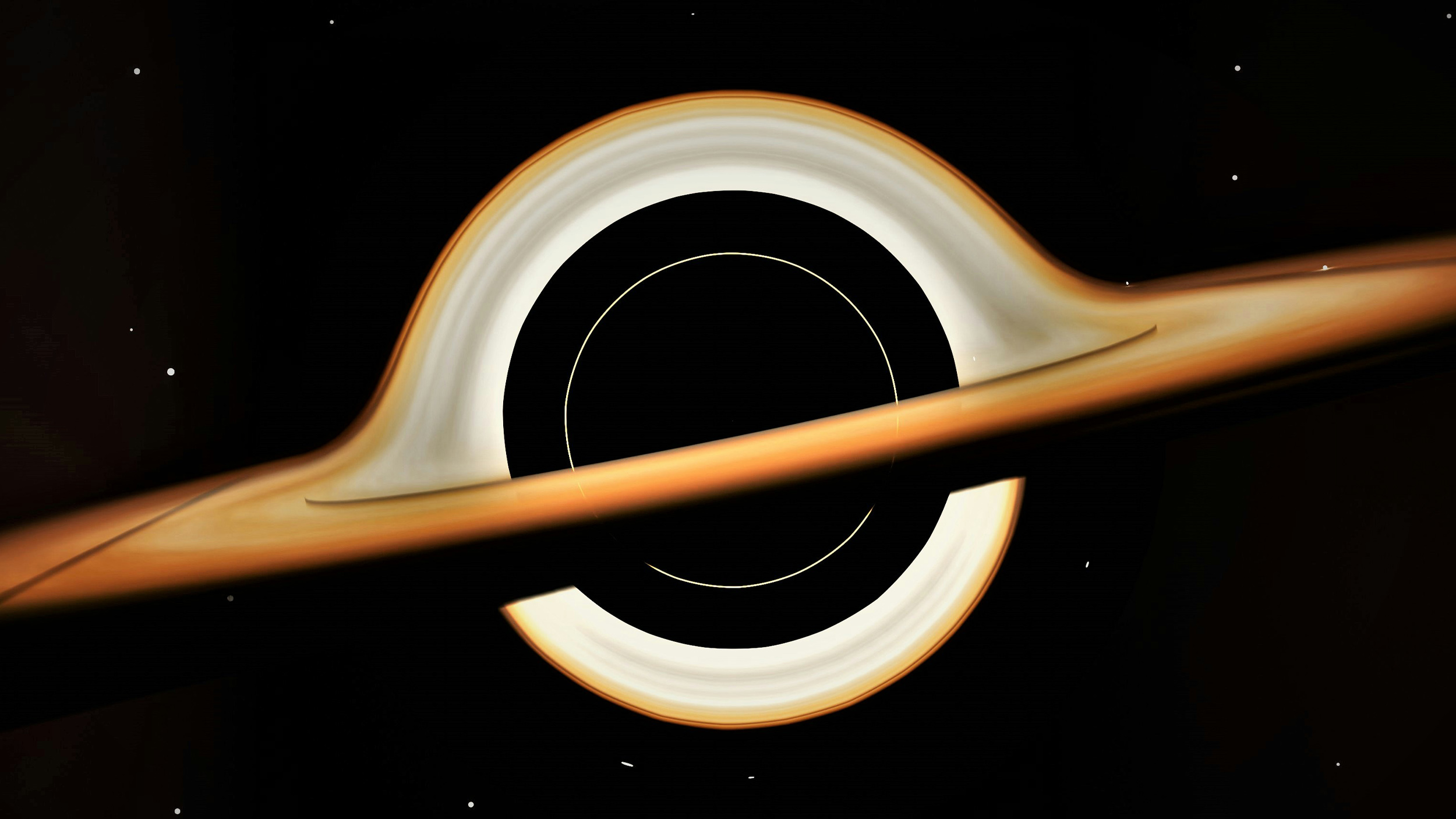
Many of us look at black holes as cosmic vacuum cleaners: sucking in everything in their vicinity. But it turns out they don’t suck at all.
There’s no upper limit to how massive galaxies or black holes can be, but the most massive known star is only ~260 solar masses. Here’s why.
In the year 2000, physicists created a list of the ten most important unsolved problems in their field. 25 years later, here’s where we are.
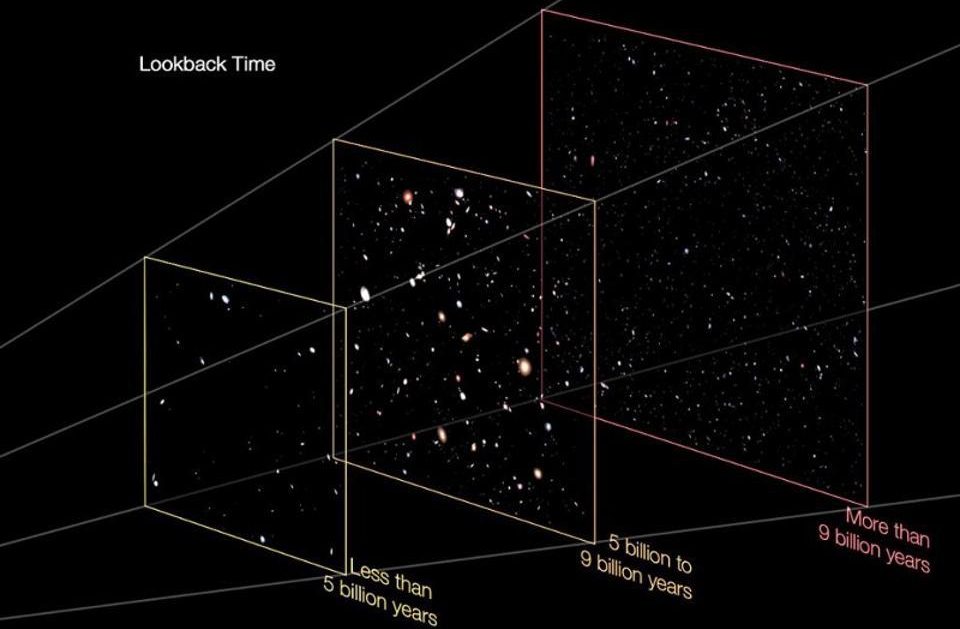
We see objects whose light only arrives just now. But we see them as they were in the past: when that now-arriving light was first emitted.
Featuring SpaceX’s “Mechazilla,” a first-of-its-kind spacewalk, and more.
Our Universe isn’t just expanding, the expansion is accelerating. Instead of dark energy, could a “lumpy” Universe be at fault?
Despite the Sun’s high core temperatures, atomic nuclei repel each other too strongly to fuse together. Good thing for quantum physics!
A recent measurement has simultaneously settled an ongoing scientific debate while puzzling scientists.
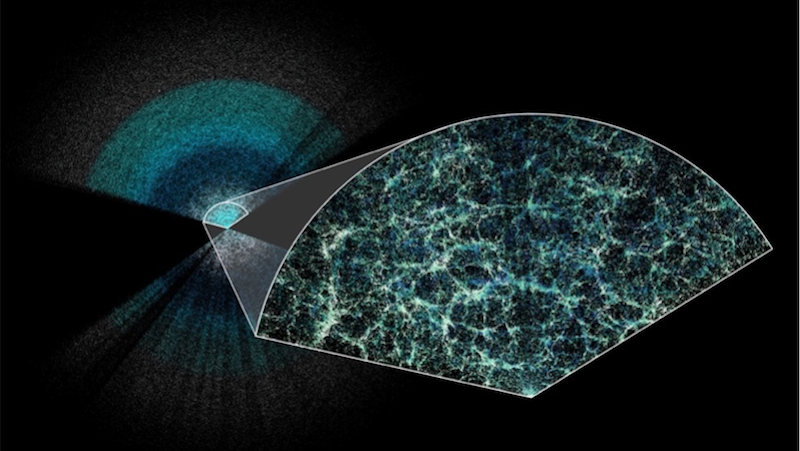
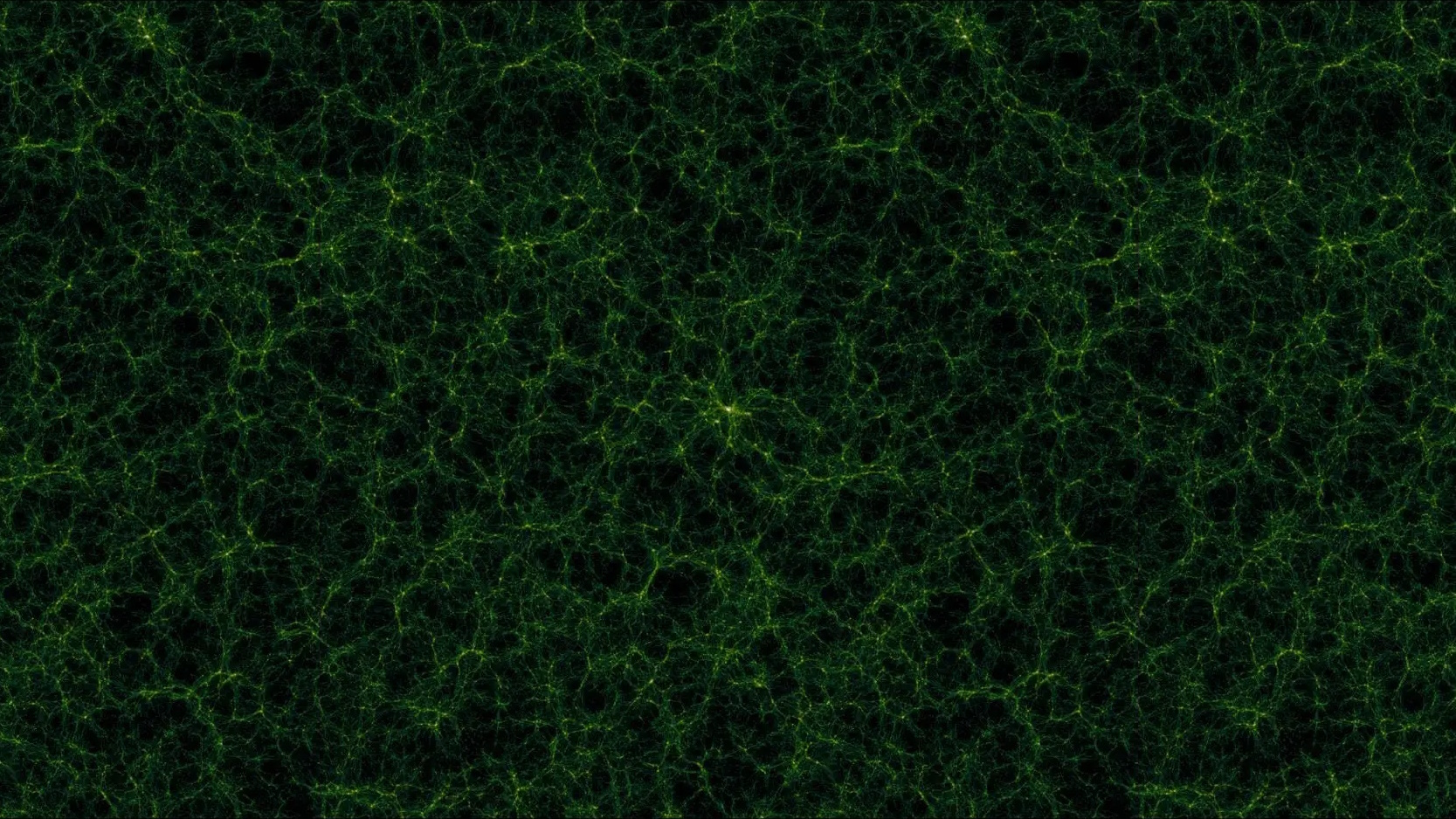
On larger and larger scales, many of the same structures we see at small ones repeat themselves. Do we live in a fractal Universe?
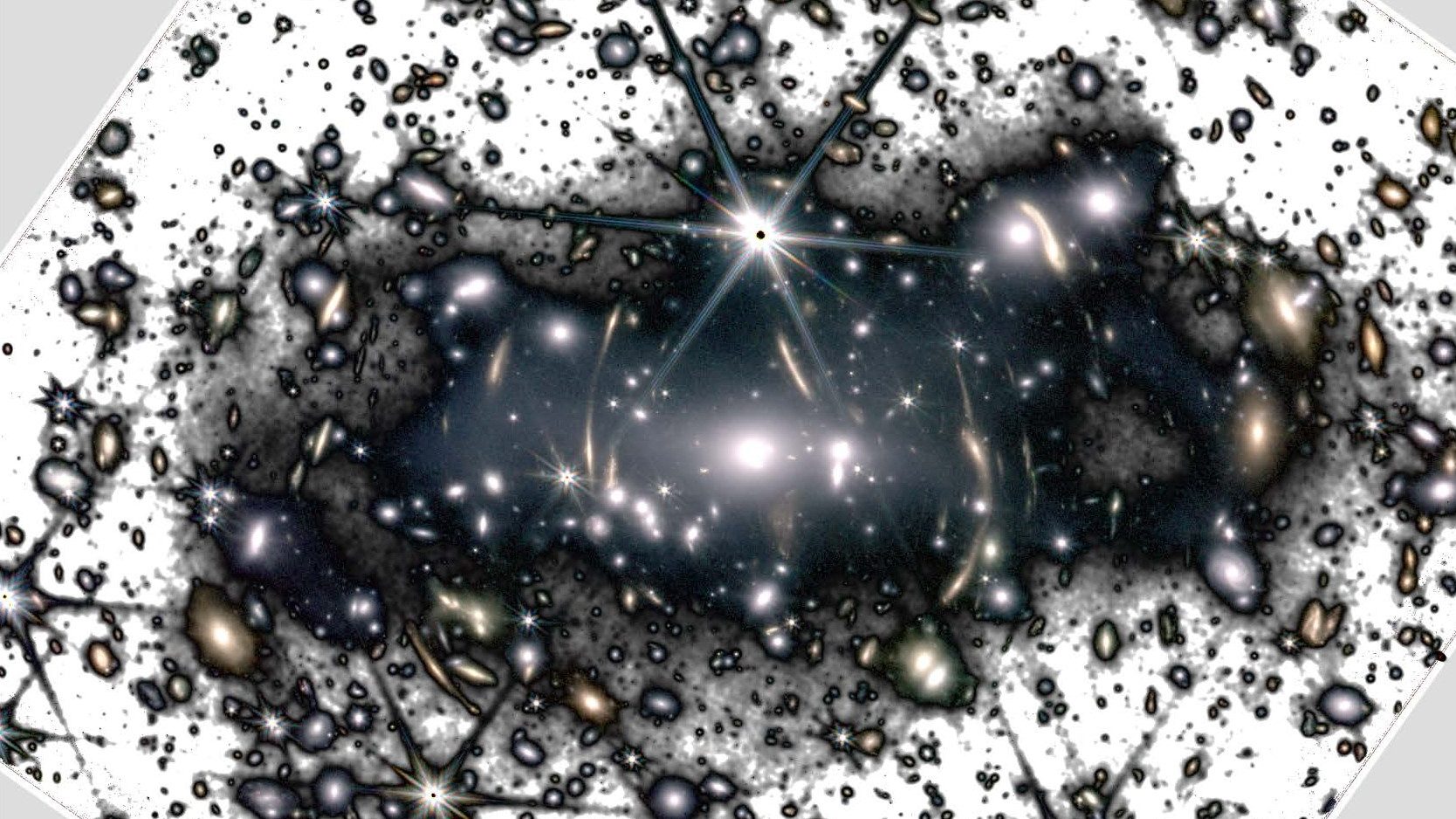
It’s not only the gravity from galaxies in a cluster that reveals dark matter, but the ejected, intracluster stars actually trace it out.
Experts answer 10 big questions about the nightmare scenario that could send us back to the pre-Space Age.
Earth is actively broadcasting and actively searching for intelligent civilizations. But could our technology even detect ourselves?
Did the Milky Way form by slowly accreting matter or by devouring its neighboring galaxies? At last, we’re uncovering our own history.
Forget billions and billions. When it comes to the number of galaxies in the Universe, both theorists’ and observers’ estimates are too low.
Known as orphaned planets, rogue planets, or planets without parent stars, these “outliers” might be the most common type of planet overall.
Our galactic home in the cosmos — the Milky Way — is only one of trillions of galaxies within our Universe. Is one of them truly our “twin?”
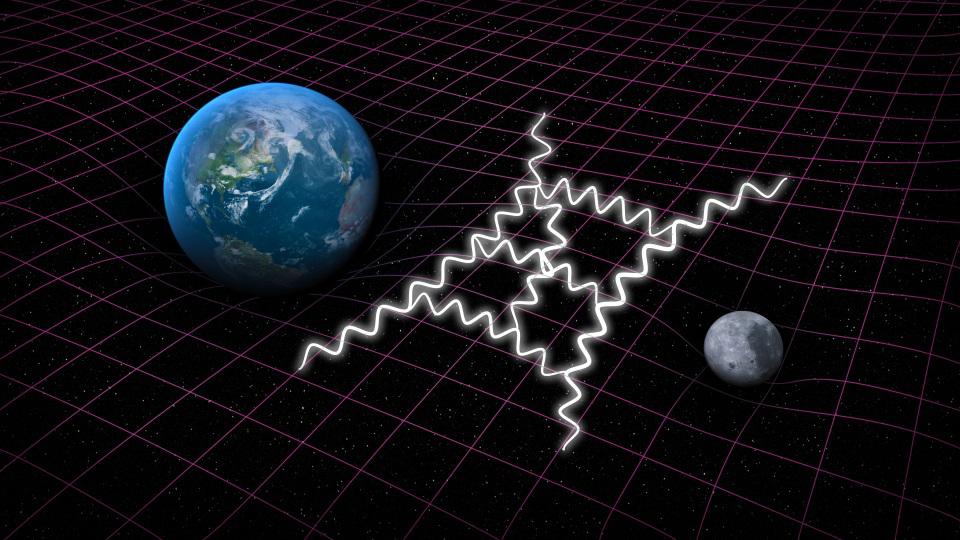
Electromagnetism, both nuclear forces, and even the Higgs force are mediated by known bosons. What about gravity? Does it require gravitons?
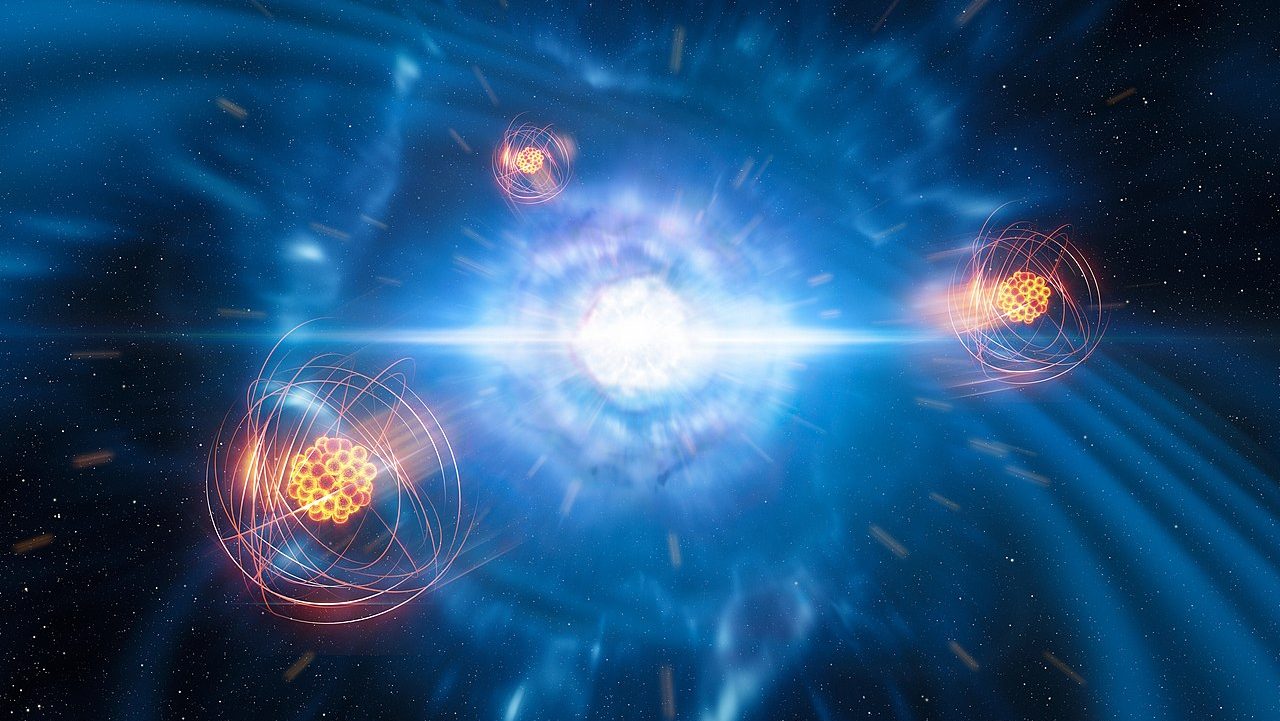
When three wise men gifted baby Jesus with gold, frankincense, and myrrh, they had no idea one was made from colliding neutron stars.
Carl Sagan was far from the first to declare we are the children of ancient stars.
There was a lot of hype and a lot of nonsense, but also some profoundly major advances. Here are the biggest ones you may have missed.
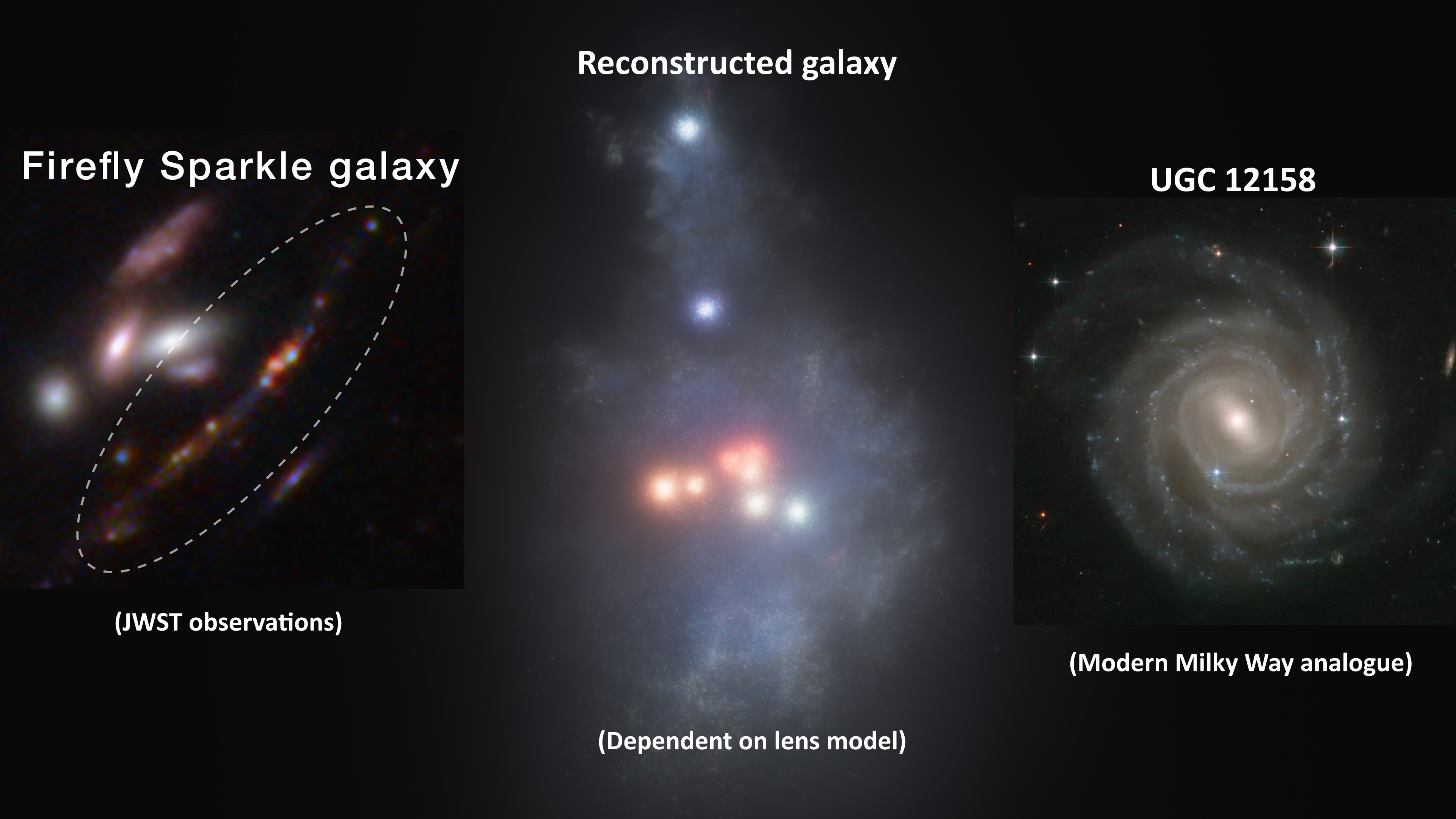
The Firefly Sparkle galaxy was only spotted because of gravitational lensing’s effects. Yet galaxies like these brought us a visible cosmos.
Sixty years ago, the Soviet Union was way ahead of the USA in the space race. Then one critical event changed everything.
The problem for galactic-scale civilizations comes down to two numbers.
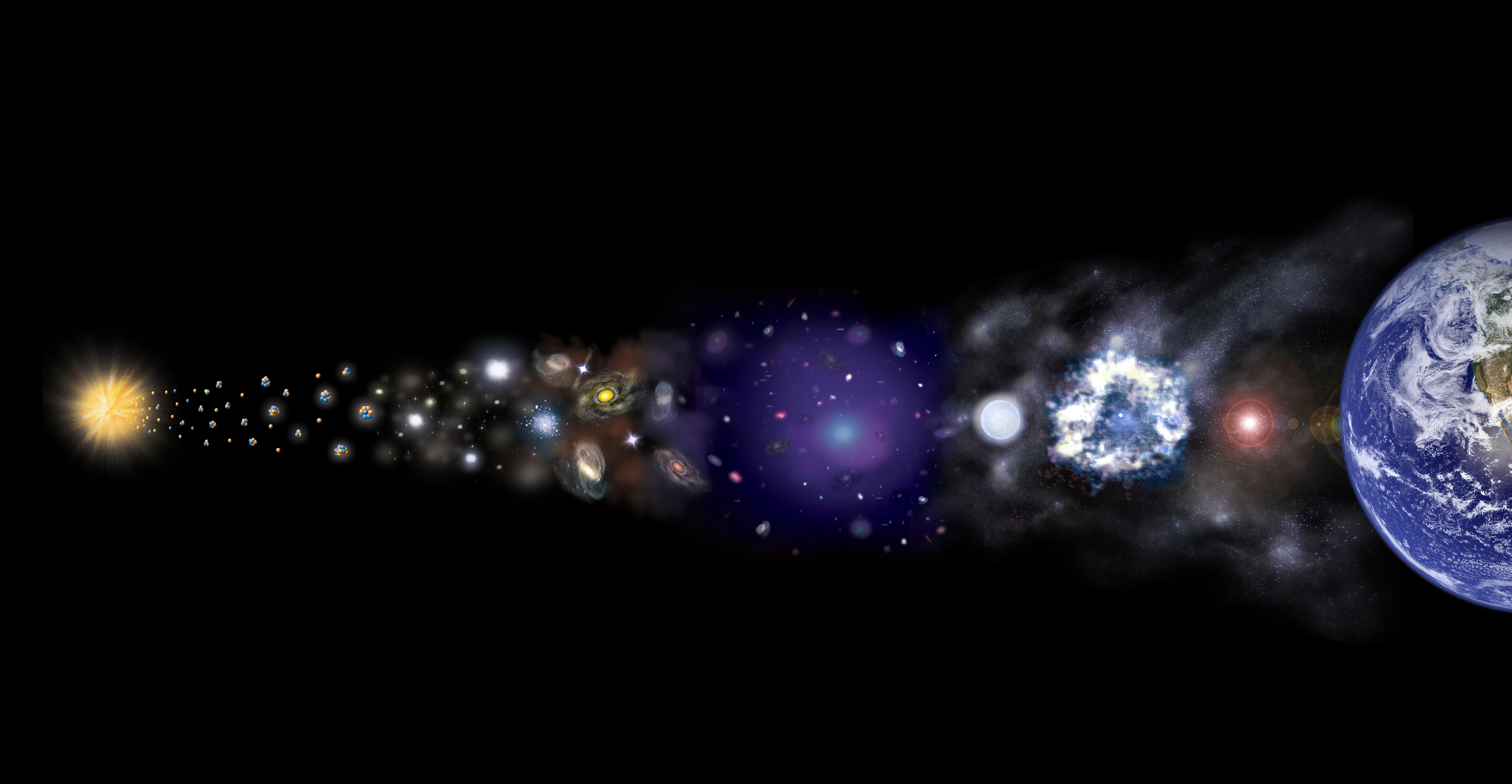
From a hot, dense, uniform state in its earliest moments, our entire known Universe arose. These unavoidable steps made it all possible.
It was barely a century ago that we thought the Milky Way encompassed the entirety of the Universe. Now? We’re not even a special galaxy.
Even with just a momentary view of our galaxy right now, the data we collect enables us to reconstruct so much of our past history.