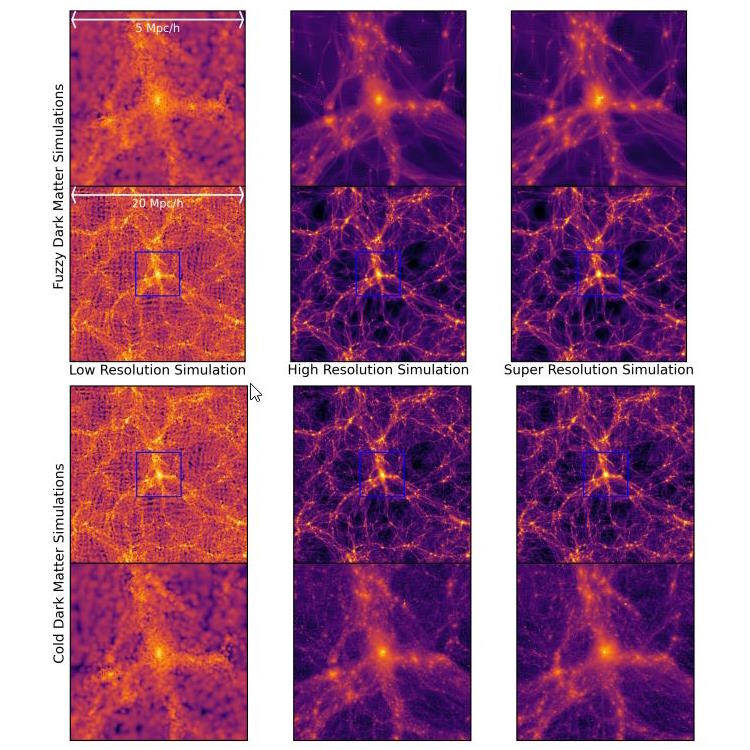
Space & Astrophysics
Headlines have blared that quasar ticking confirms that time passed more slowly in the early Universe. That’s not how any of this works.
For thousands of years, we puzzled at how far away the Moon was. Today we know its distance, at any time, to within millimeters.
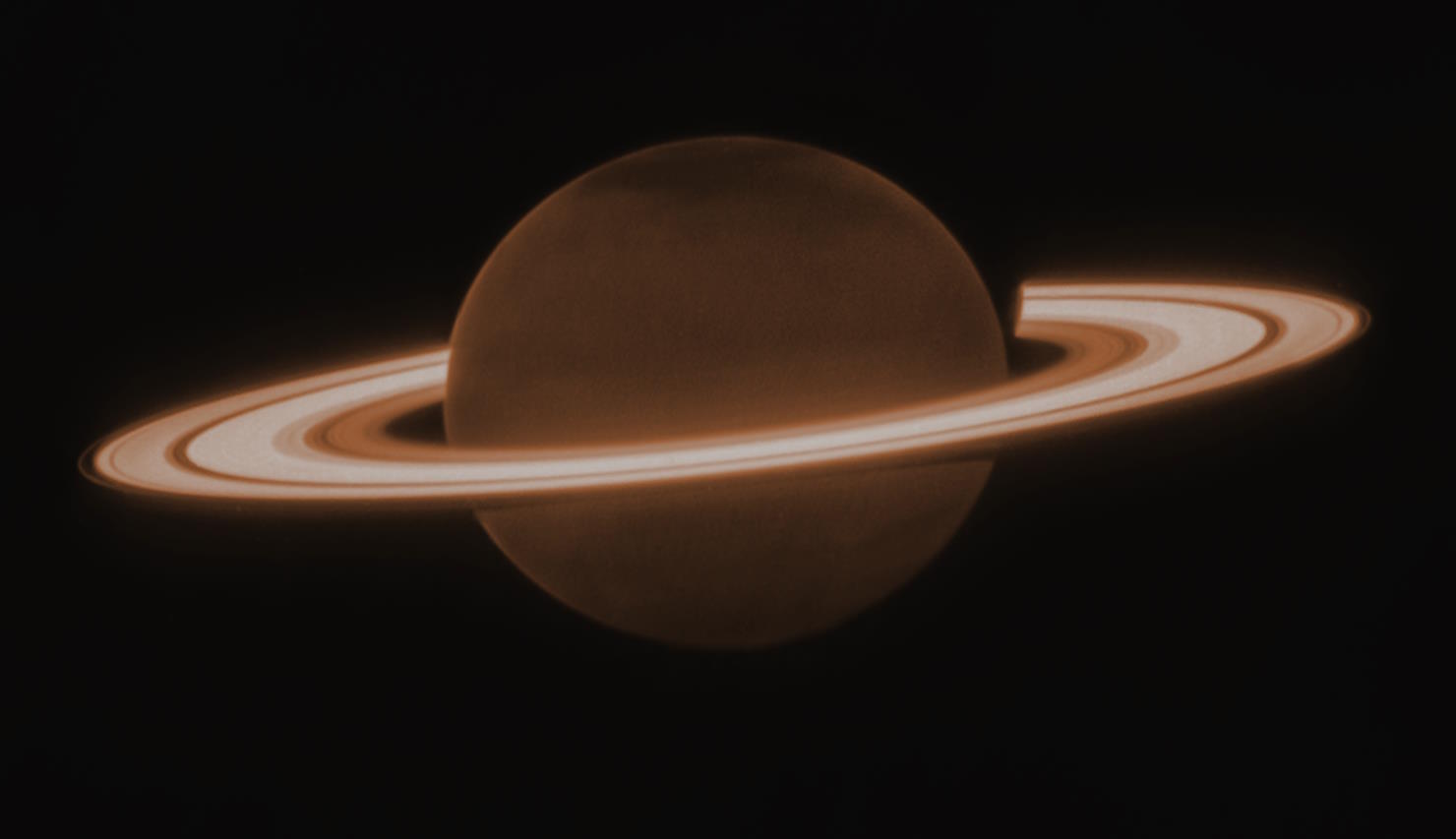
While Saturn and its moons all appear faint and cloudy to JWST, Saturn’s rings are the star of the show. Here’s the big scientific reason.
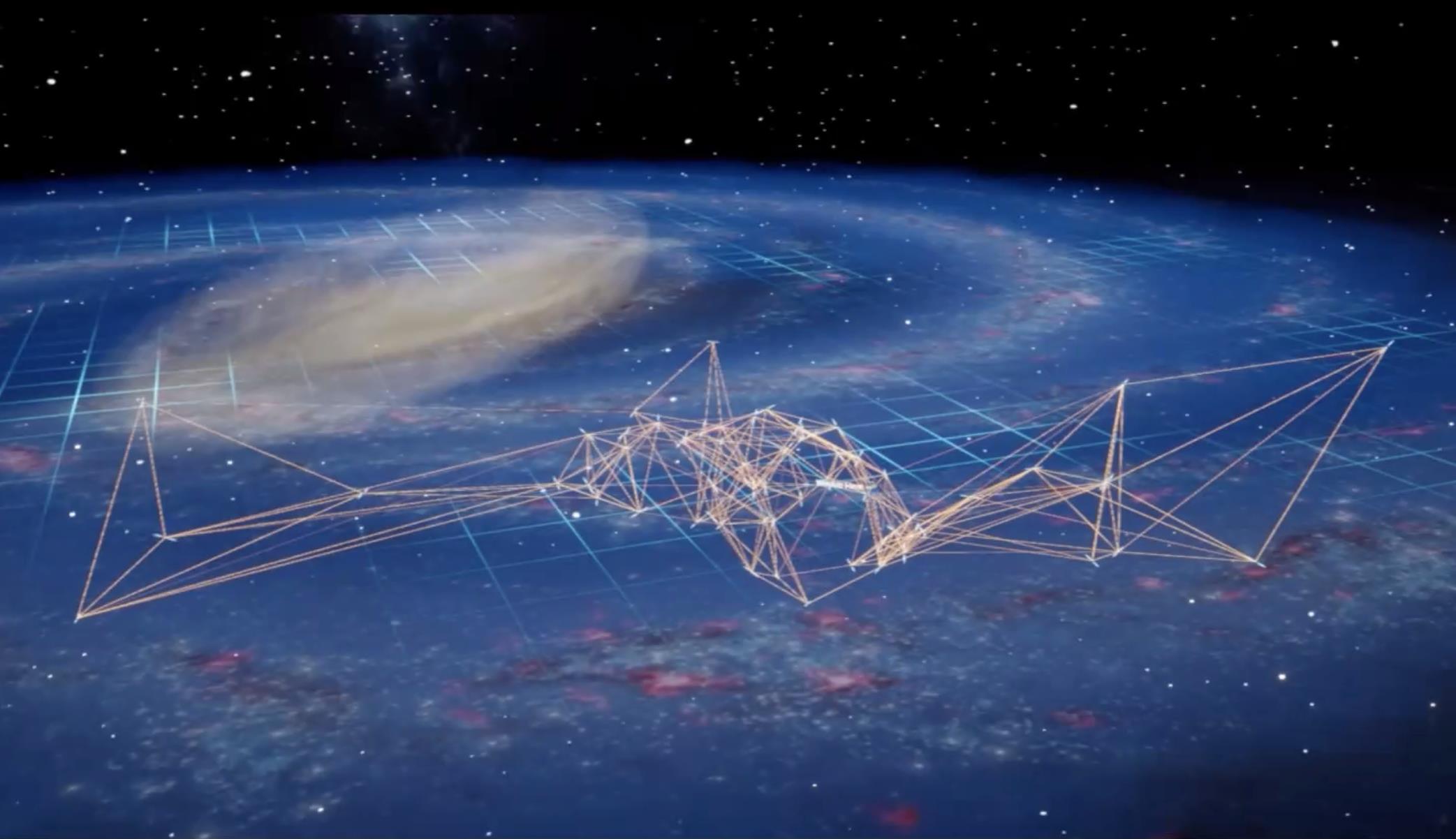
Lost in a building or underwater? A new muon-based navigation system could be your guide.
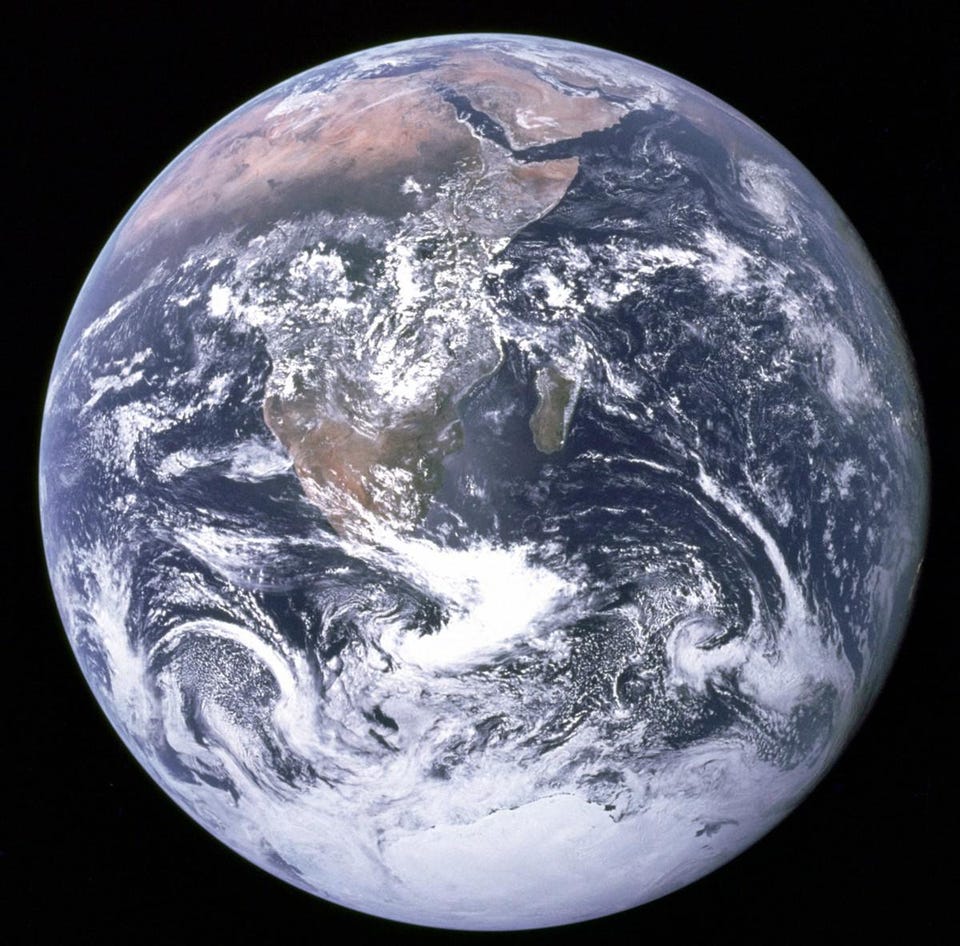
There’s an entire Universe out there. So, with all that space, all those planets, and all those chances at life, why do we all live here?
After 15 years of monitoring 68 objects known as millisecond pulsars, we’ve found the Universe’s background gravitational wave signal!
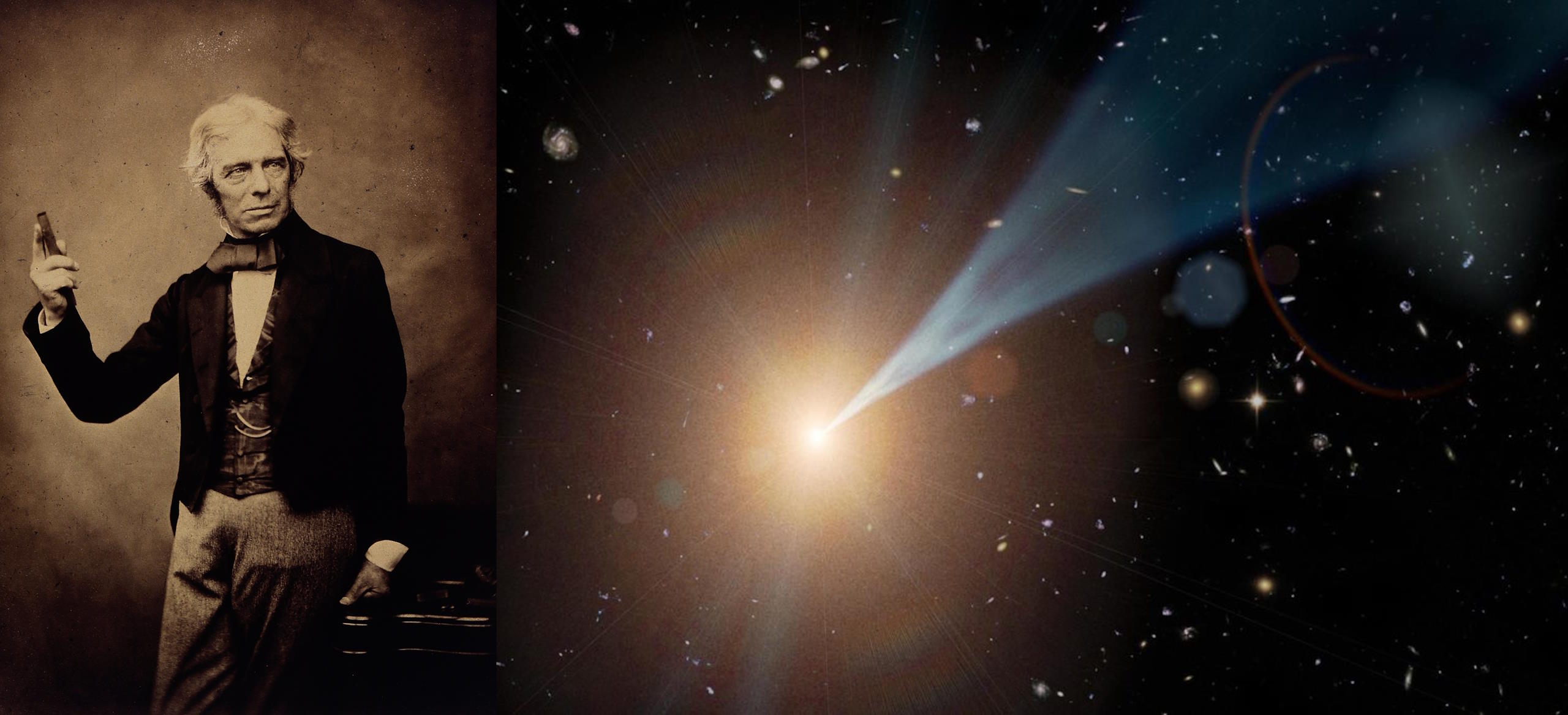
Michael Faraday’s 1834 law of induction was the key experiment behind the eventual discovery of relativity. Einstein admitted it himself.
In one experiment, the Viking landers added water to Martian soil samples. That might have been a very bad idea.
A cute mathematical trick can “rescale” the Universe so that it isn’t actually expanding. But can that “trick” survive all our cosmic tests?
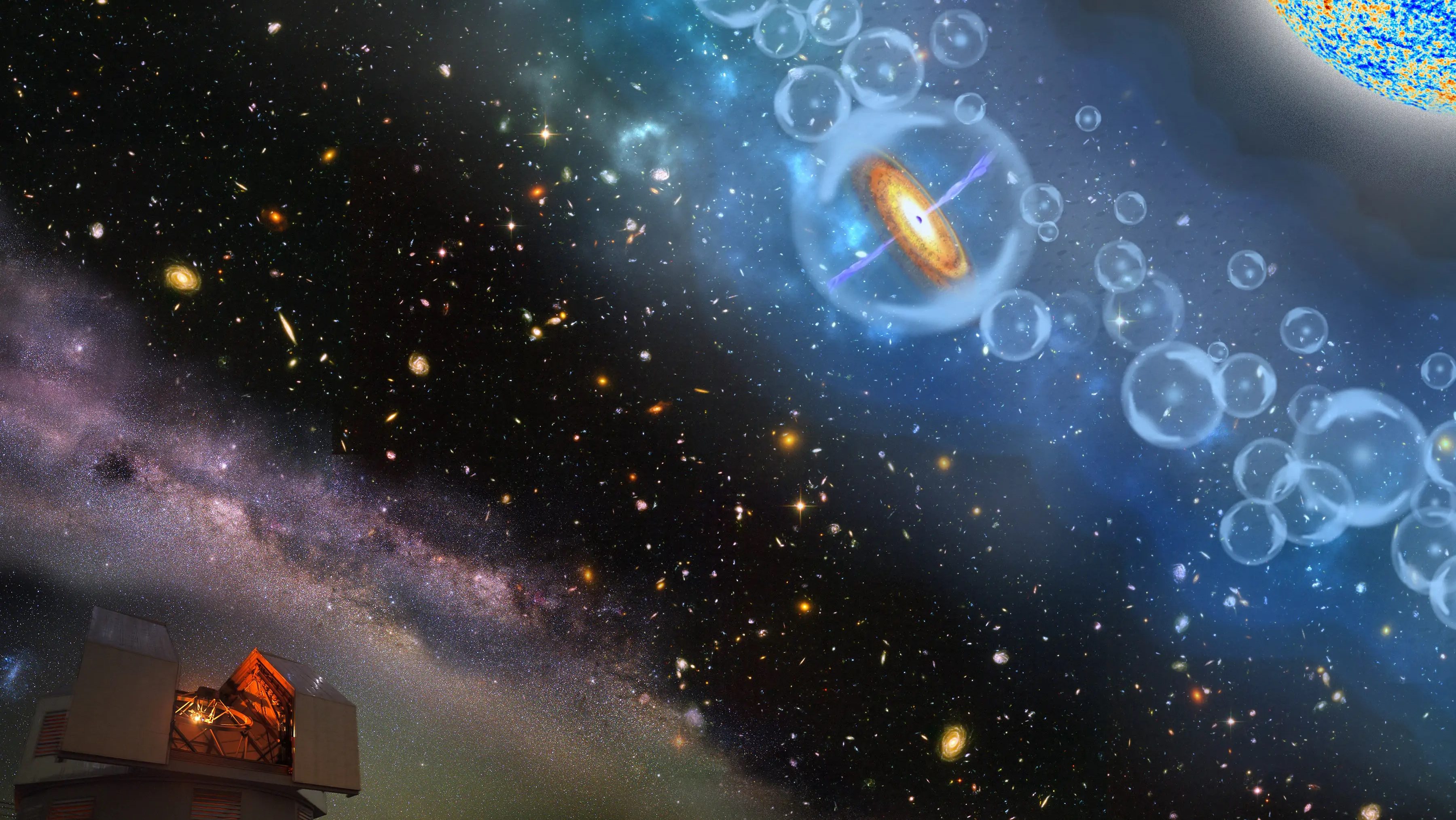
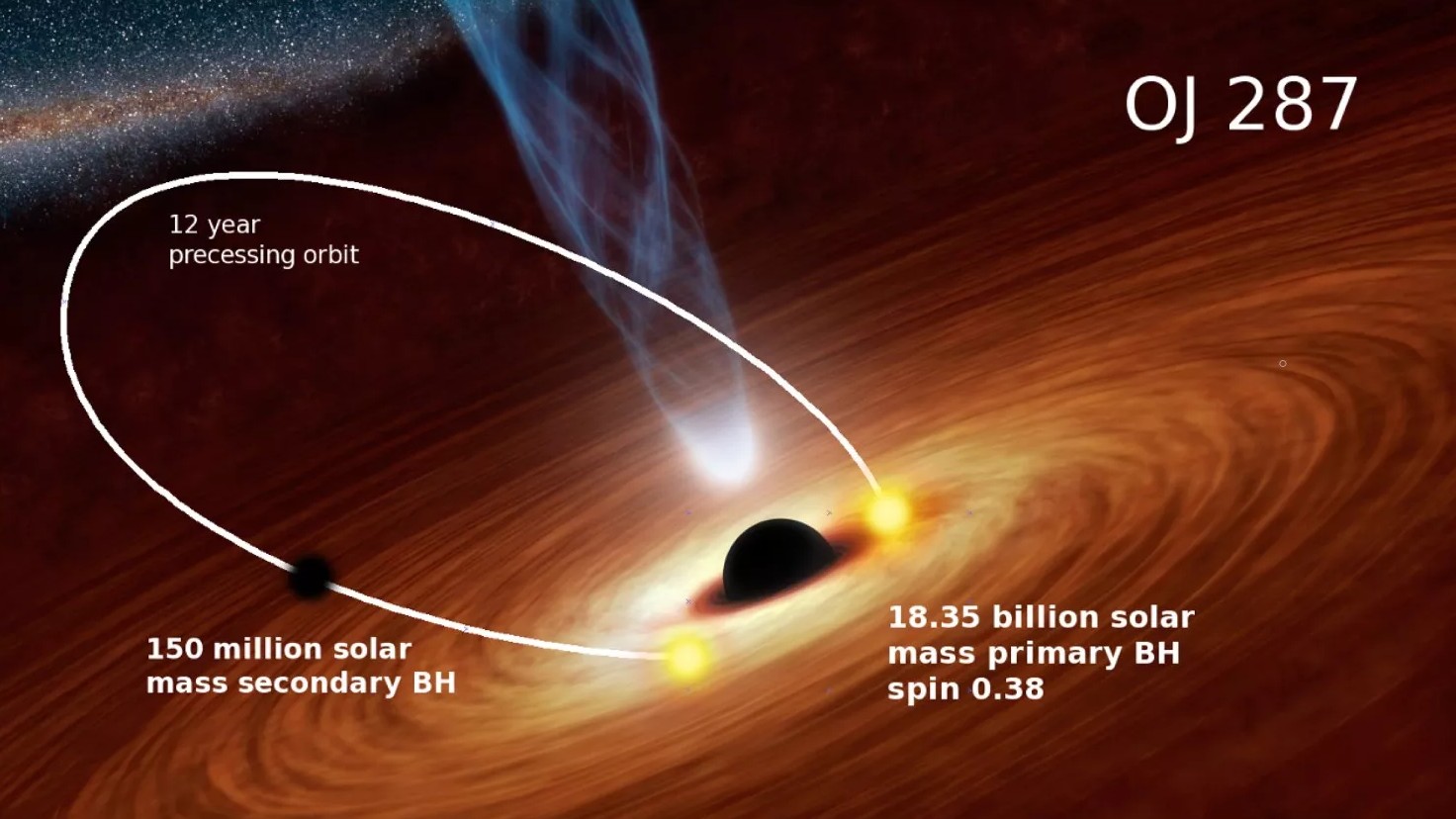
In a distant galaxy, a cosmic dance between two supermassive black holes emits periodic flashes of light.
As the Earth spins and wobbles on its axis and revolves elliptically around the Sun, each day changes from the last. “24 hours” isn’t right.
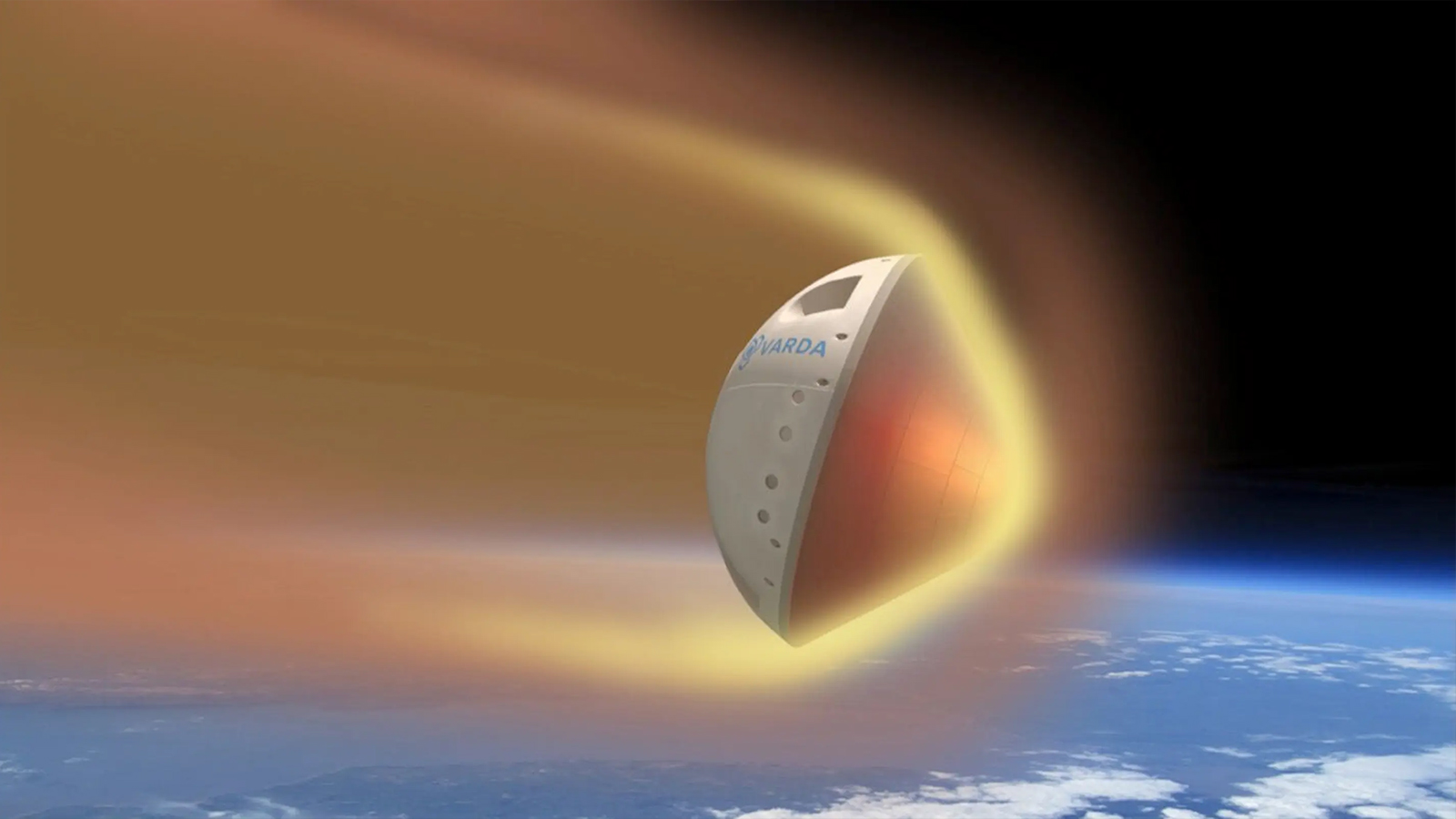
Particles behave differently when freed from the force of gravity. A new space factory aims to use this to synthesize pharmaceuticals.
The farther away they get, the smaller distant galaxies look. But only up to a point, and beyond that, they appear larger again. Here’s how.
From a photon’s viewpoint, the Universe is timeless and dimensionless.
The truth is out there, but it’s probably not in the latest whistleblower’s report.
The multiverse pushes beyond the limits of the scientific method. From our vantage point in the Universe, we cannot know if it’s real.
The familiar terrain of solids, liquids, and gases gives way to the exotic realms of plasmas and degenerate matter.
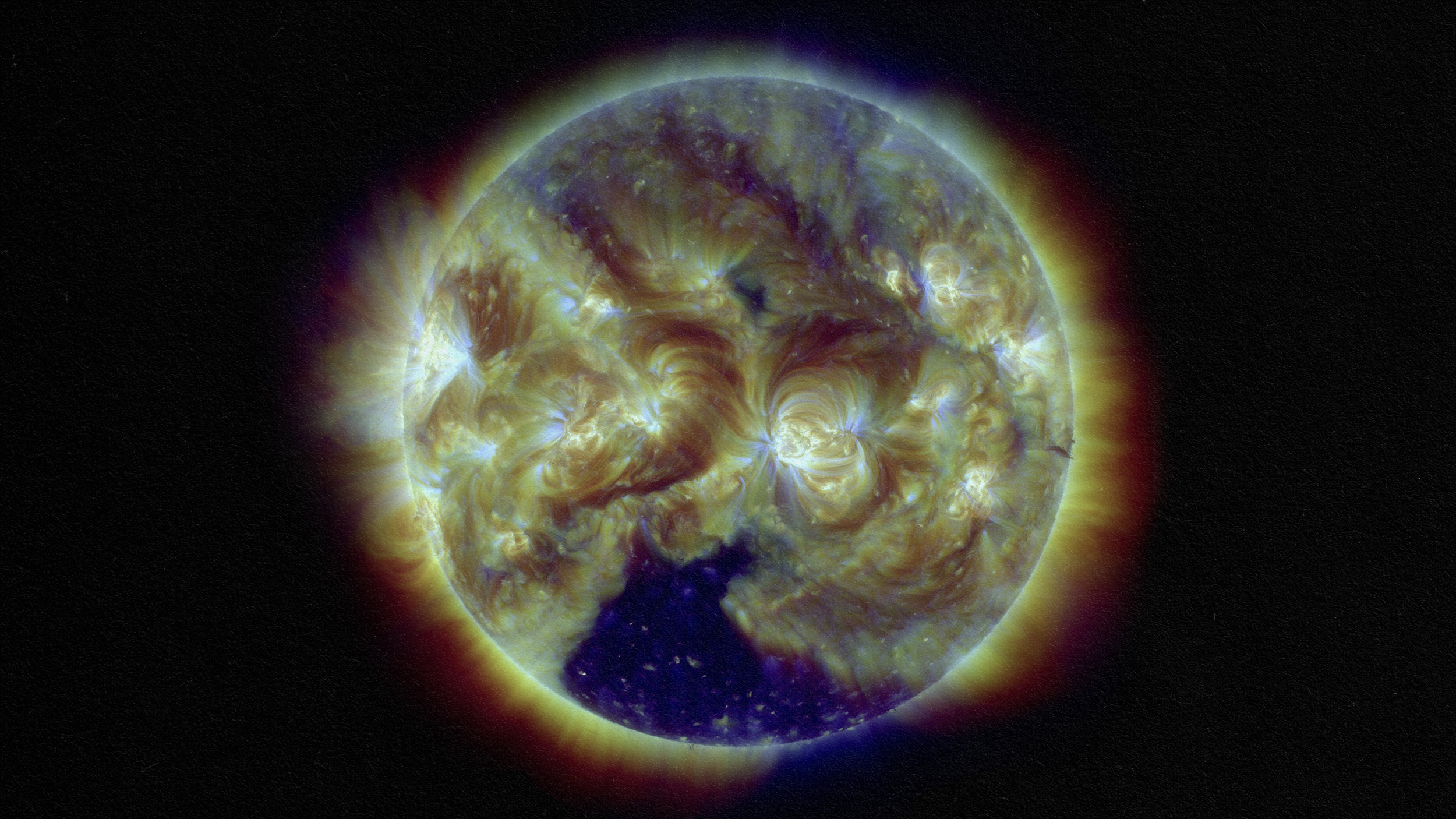
In many ways, we are still novices playing with toy models seeking to understand the stars.
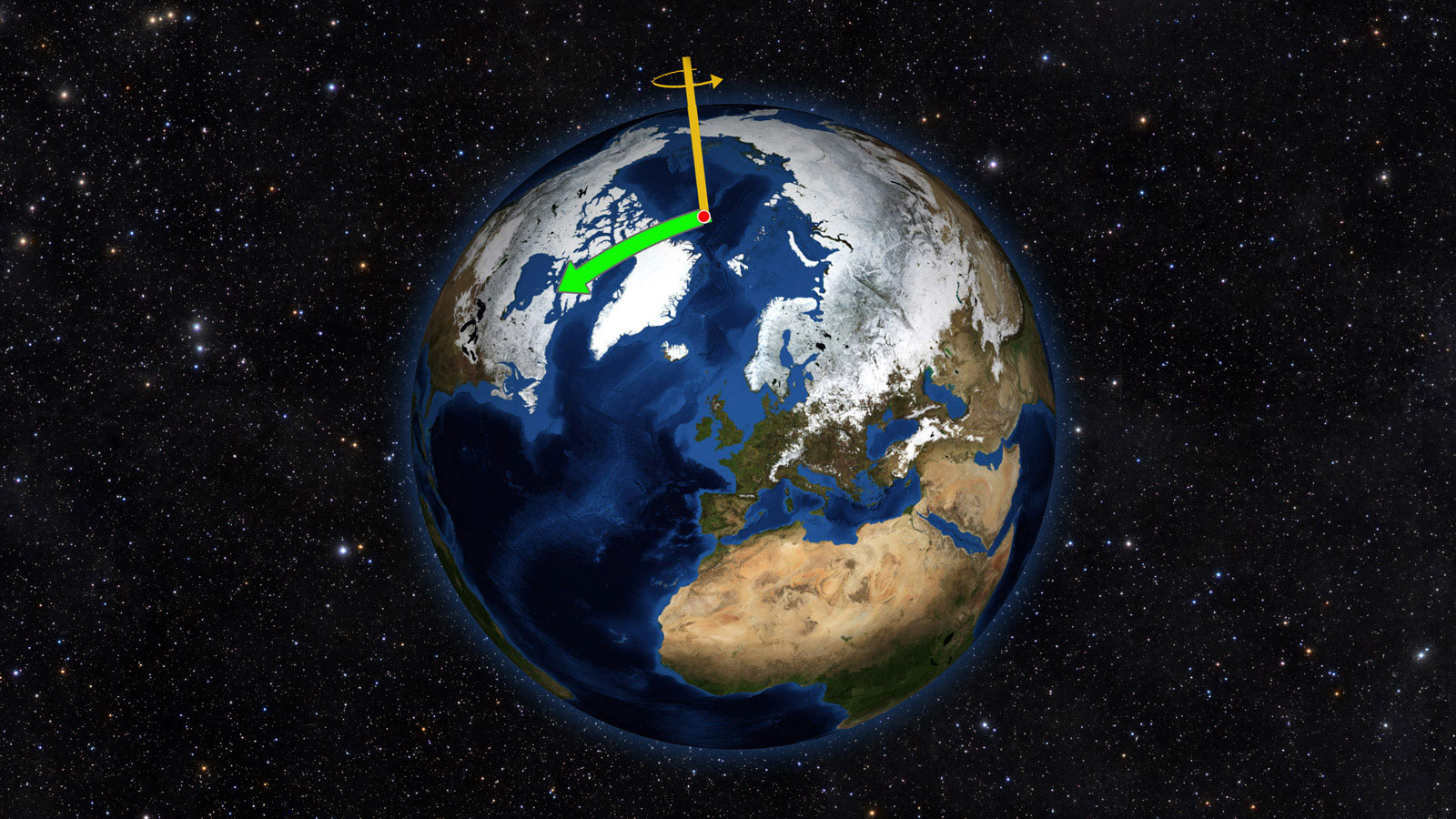
Despite the enormous mass of the Earth, simply depleting our groundwater is changing our axial tilt. Simple Newtonian physics explains why.
In physics, we reduce things to their elementary, fundamental components, and build emergent things out of them. That’s not the full story.
If you can identify a foreground star, the spike patterns are a dead giveaway as to whether it’s a JWST image or any other observatory.
In a far-reaching discovery with astrophysicist Karolina Garcia, we discuss what’s in the Universe and how it grew up.
What do the dark recesses of the early Universe and Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom have in common? More than you could have ever hoped for.
How are we to deal with the quantization of spacetime and gravity?
The brightest gamma-ray burst ever observed, GRB 221009A behaved in unexpected ways that might help us understand how they occur.
Sun-like stars live for around 10 billion years, but our Universe is only 13.8 billion years old. So what’s the maximum lifetime for a star?
Neuroscientist and author Bobby Azarian explores the idea that the Universe is a self-organizing system that evolves and learns.
With hundreds of billions of stars burning bright, some galaxies are already dead. Their inhabitants might not know it, but we’re certain.
There are 40 billion billion black holes in the universe. Here’s how our Solar System stacks up against ten of them.
We don’t know what causes Miyake events, but these great surges of energy can help us understand the past — while posing a threat to our future.