Space & Astrophysics
To know how to protect its astronauts, NASA needs to first understand the threat.
From forming bound states to normal scattering, many possibilities abound for matter-antimatter interactions. So why do they annihilate?
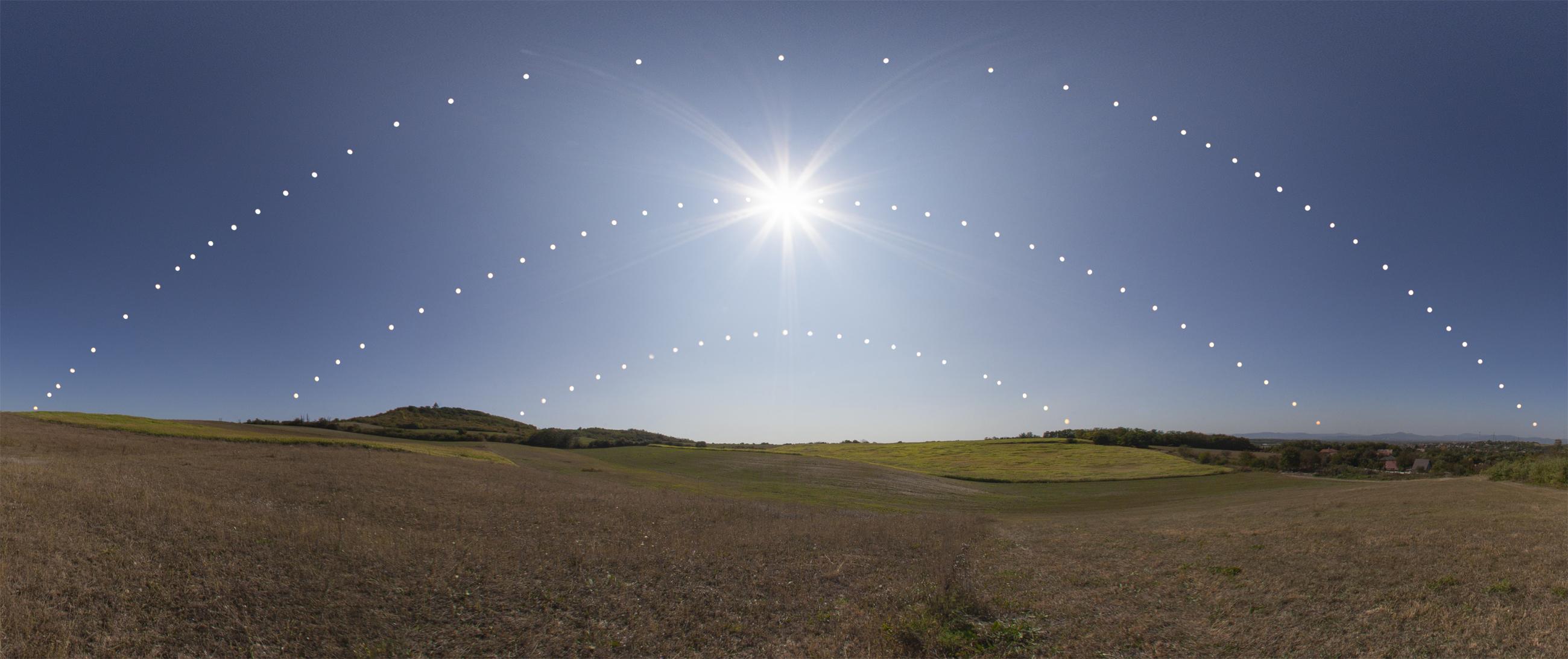
On June 20, 2024, the summer solstice occurs at its earliest moment since 1796: when George Washington was President of the USA. Here’s why.
There are two different ways to measure the expansion rate of the Universe, and they don’t agree. And no, new measurements don’t help.
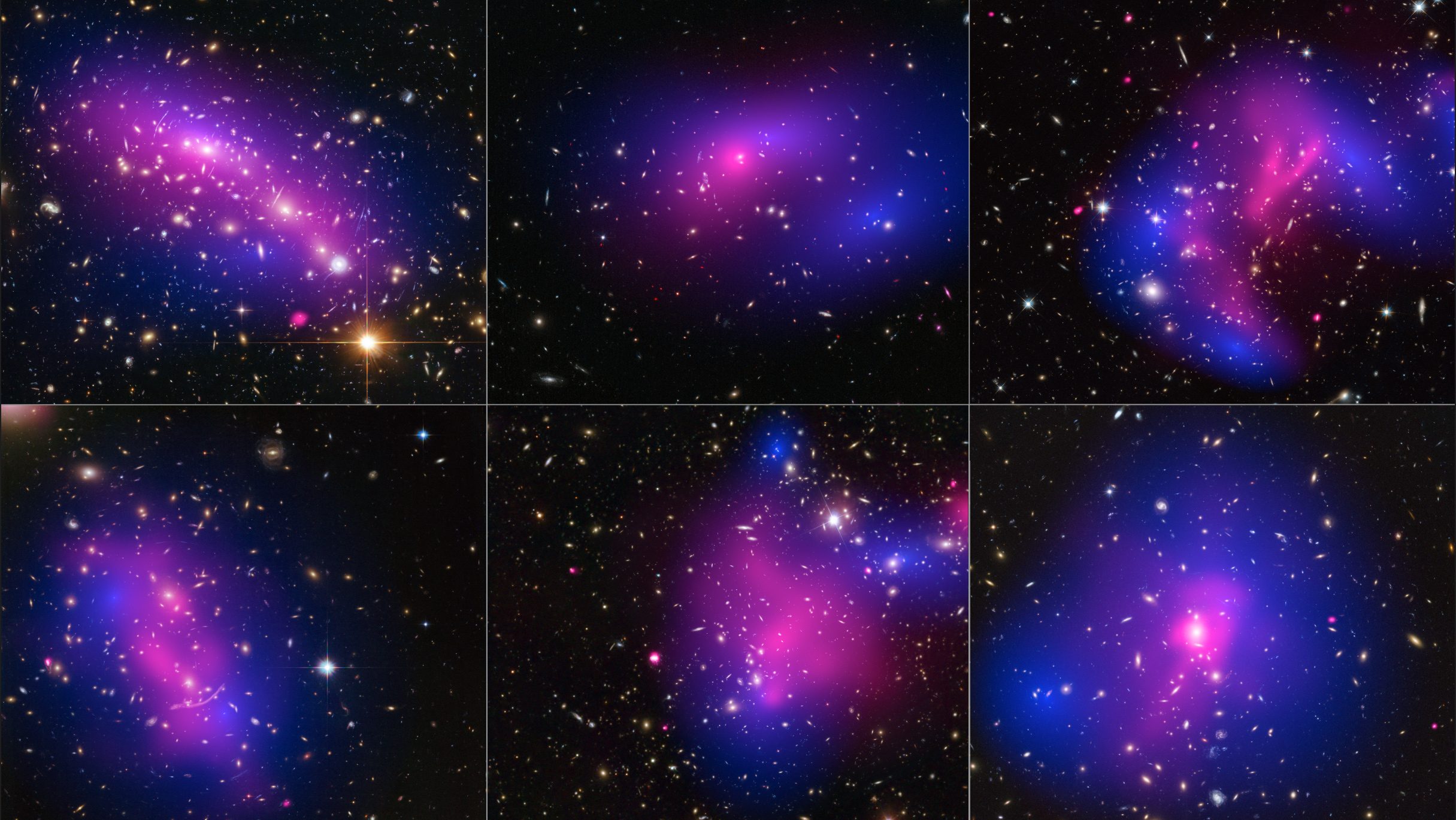
Is gravity weaker over distances of billions of light-years?
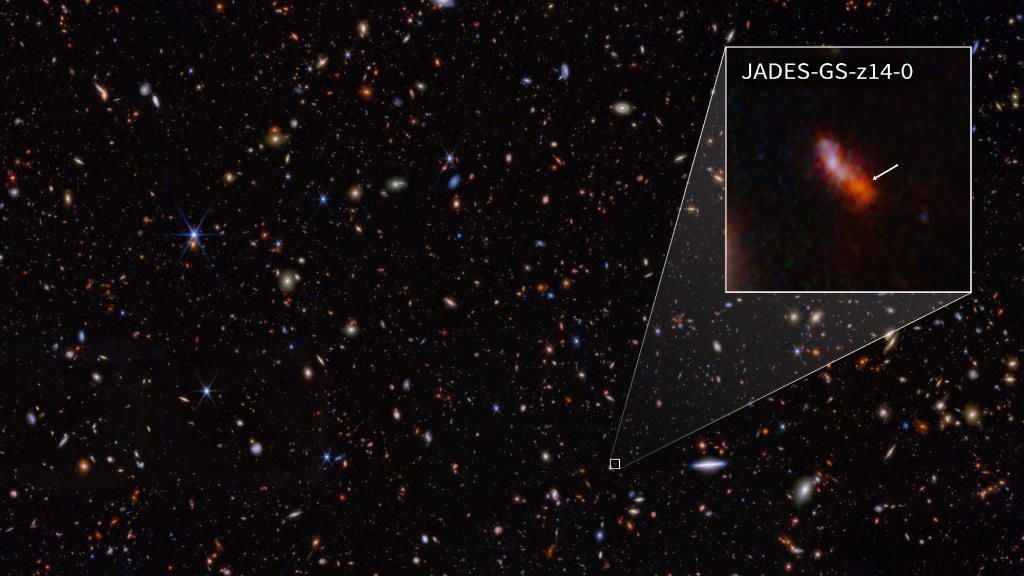
A new all-time record! JWST’s discovery of JADES-GS-z14-0 pushes the earliest galaxy ever seen to just 290 million years after the Big Bang.
If you bring too much mass or energy together in one location, you’ll inevitably create a black hole. So why didn’t the Big Bang become one?
The Universe is precisely dated at 13.8 billion years old, but astronomers claim the Methuselah star is 14.5 billion years old. What gives?
Ancient currents seemed to move in concert with a 2.4 million-year dance between the Red Planet and Earth.
The threats Mars astronauts face — and how NASA is working to solve them.
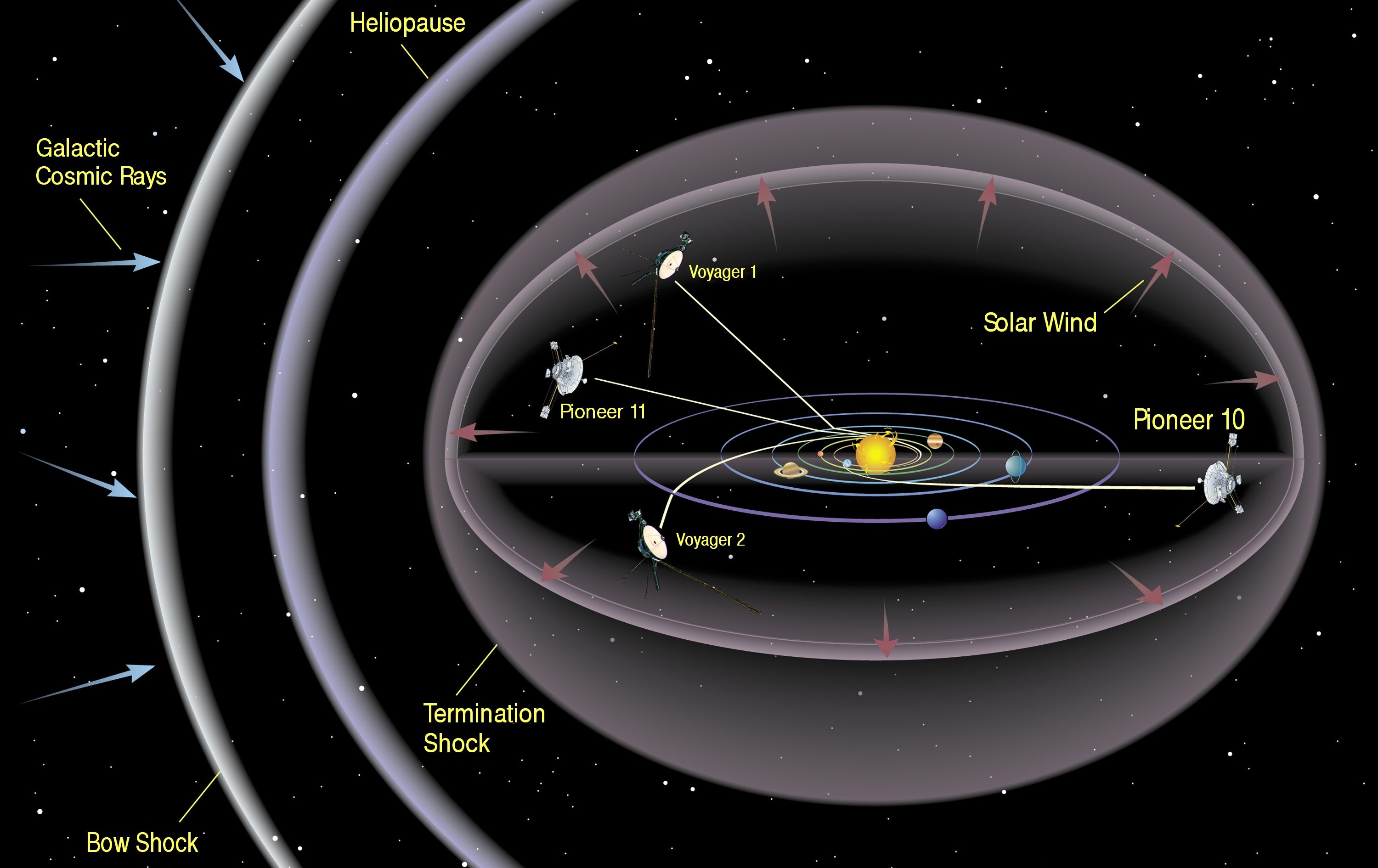
The expanding Universe, in many ways, is the ultimate out-of-equilibrium system. After enough time passes, will we eventually get there?
Some think the reason fundamental scientific revolutions are so rare is because of groupthink. It’s not; it’s hard to mess with success.
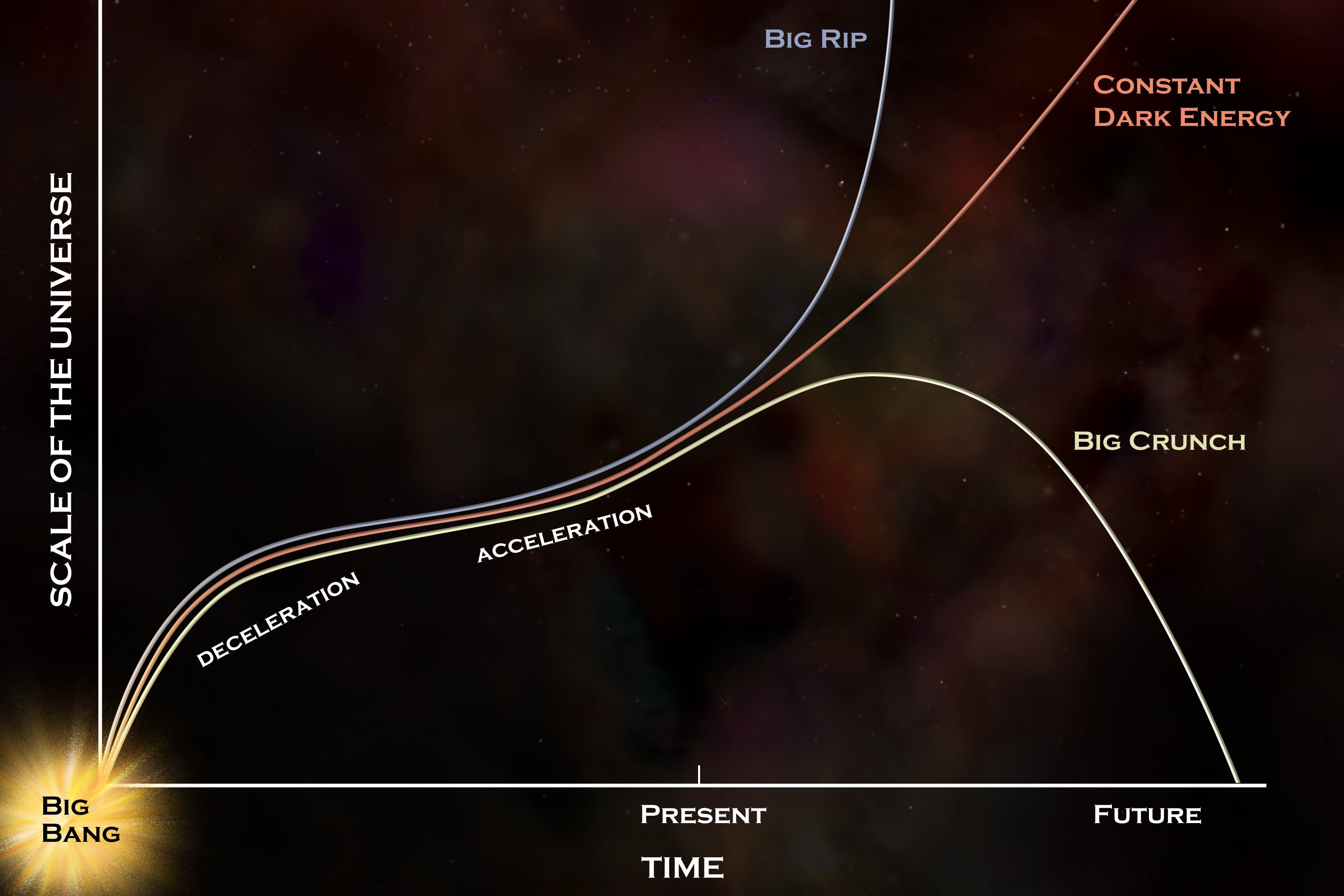
For nearly 25 years, we thought we knew how the Universe would end. Now, new measurements point to a profoundly different conclusion.
In ~7 billion years, our Sun will run out of fuel and die. So will every star, eventually. Here are the different fates they’ll encounter.
In 2023, data from the James Webb Space Telescope soured hopes that TRAPPIST-1 c had an atmosphere. That disappointment might have been premature.
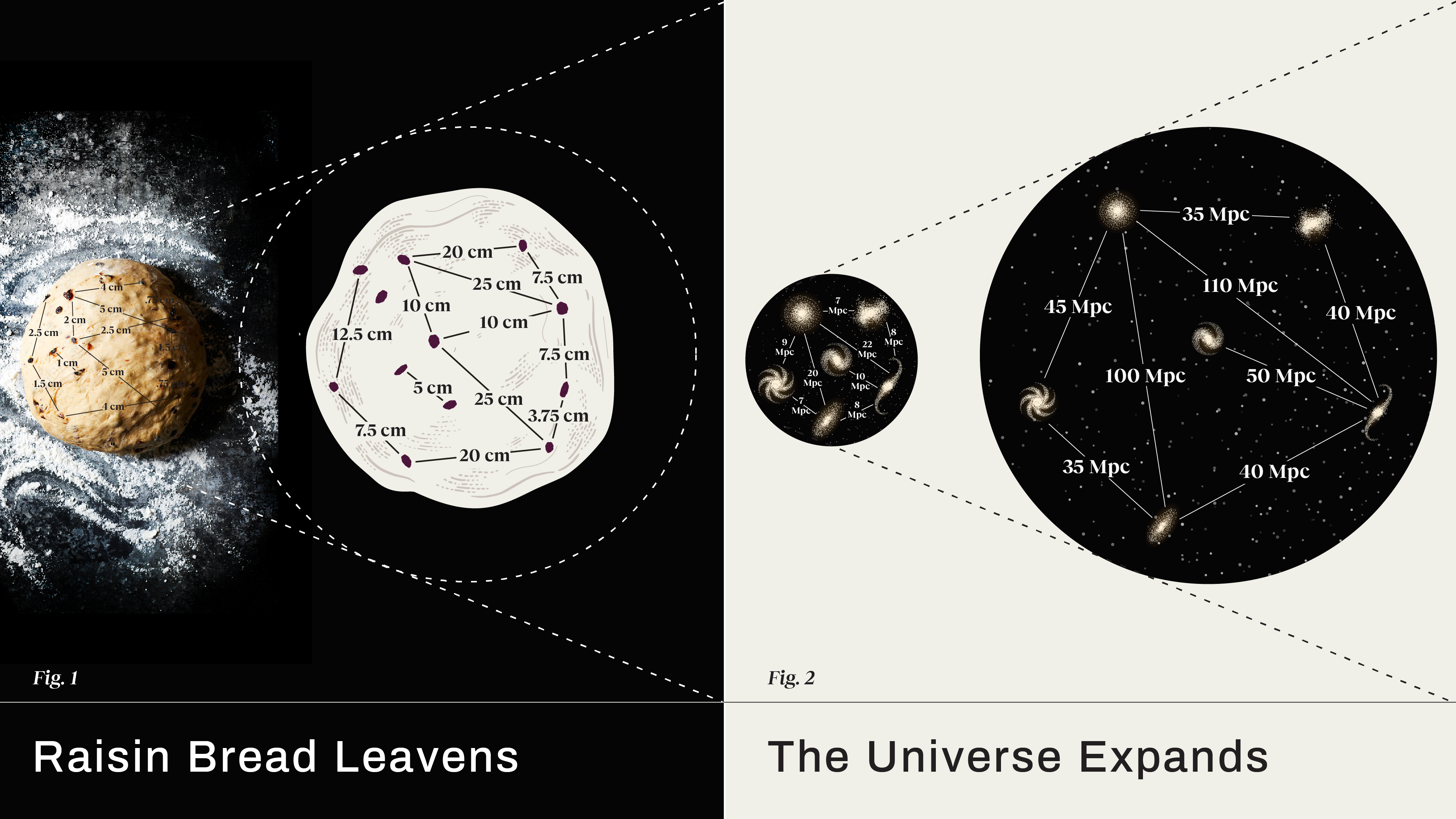
The mutual distance between well-separated galaxies increases with time as the Universe expands. What else expands, and what doesn’t?
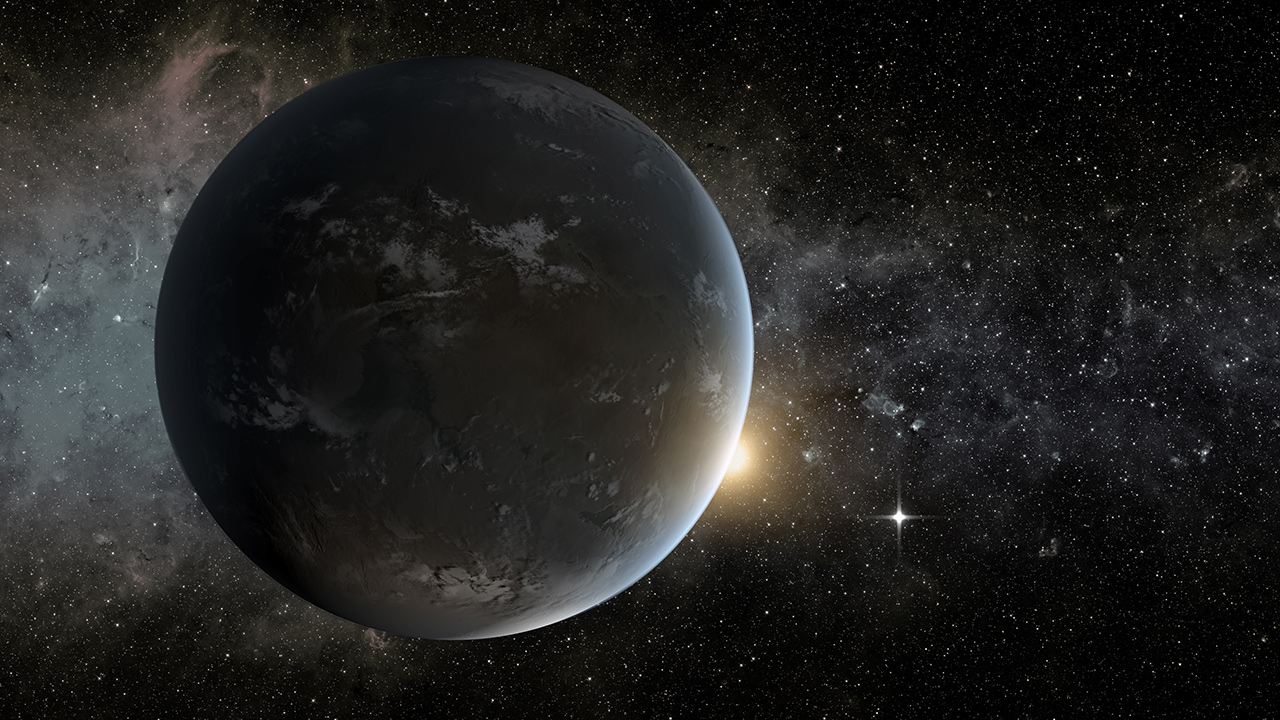
The number of planets that could support life may be far greater than previously thought, a recent discovery suggests.
It’s not a gambit. It’s not fraud. It’s not driven by opinion, prejudice, or bias. It’s not unchallengeable. And it’s more than facts alone.
The most iconic, longest-lived space telescope of all, NASA’s Hubble, is experiencing orbital decay as the solar cycle peaks. Here’s why.
The galactic center is home to the most powerful engine in the Milky Way: a supermassive black hole. How does its energy ultimately escape?
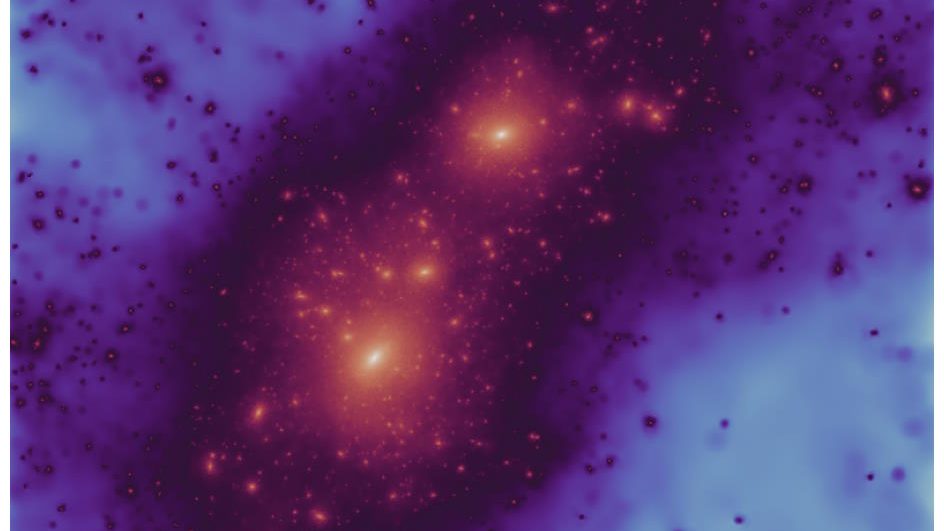
We normally think of dark matter as the “glue” that holds galaxies and larger structures together. But it’s so much more than that.
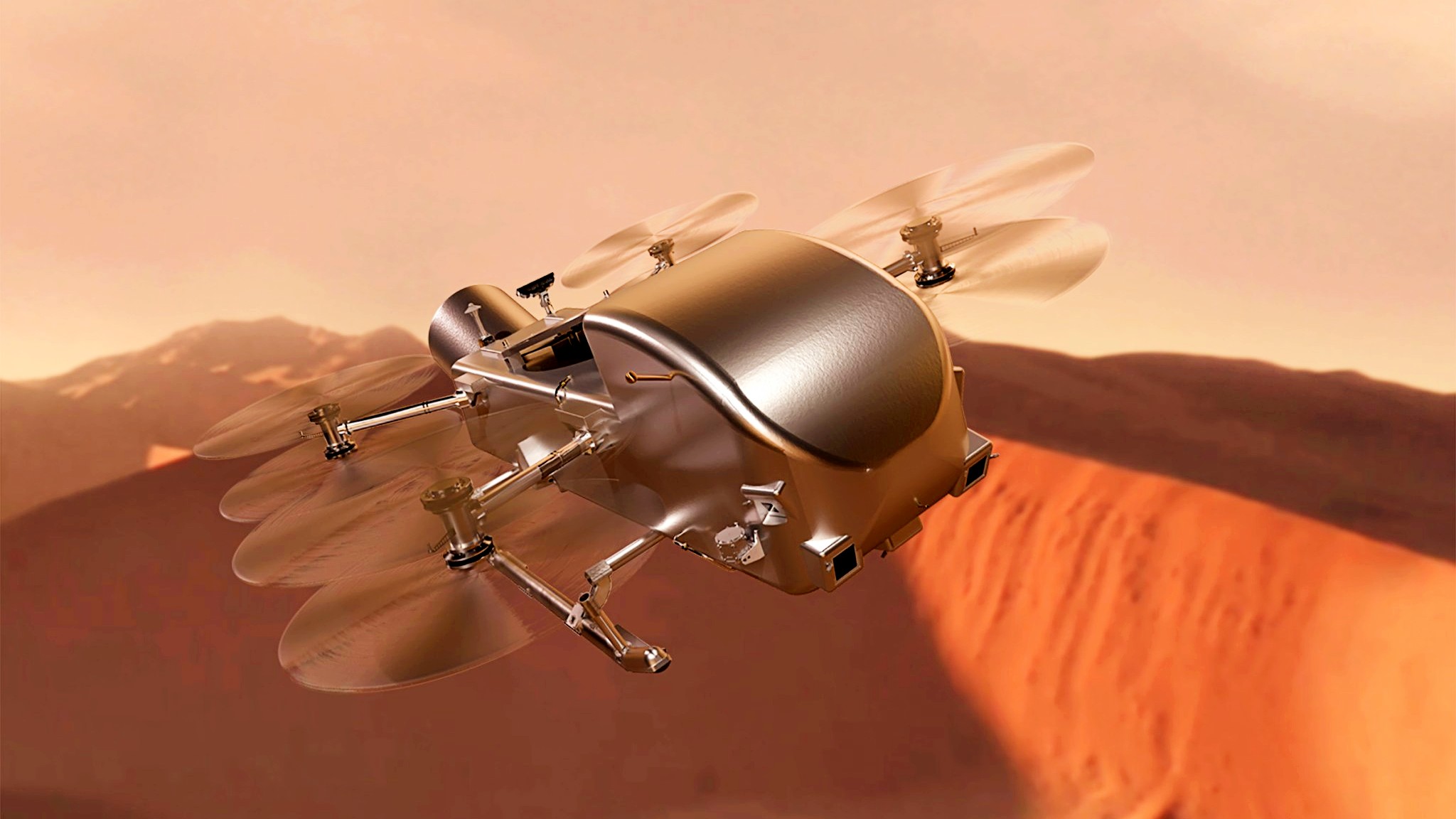
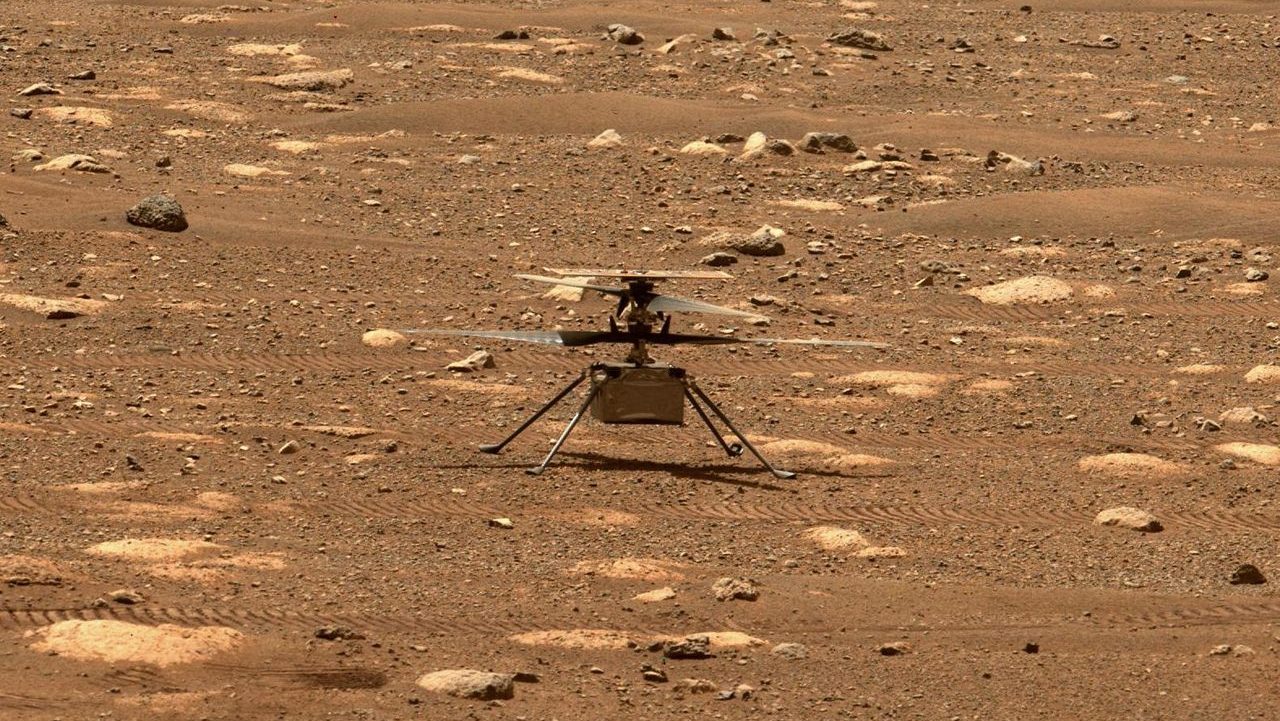
NASA’s minivan-sized drone is scheduled to search for signs of life on Titan in 2034.
There are many theories of gravity out there, and many interpretations of wide binary star data. What have we really learned from it all?
The evidence that the Universe is expanding is overwhelming. But how? By stretching the existing space, or by creating new space itself?
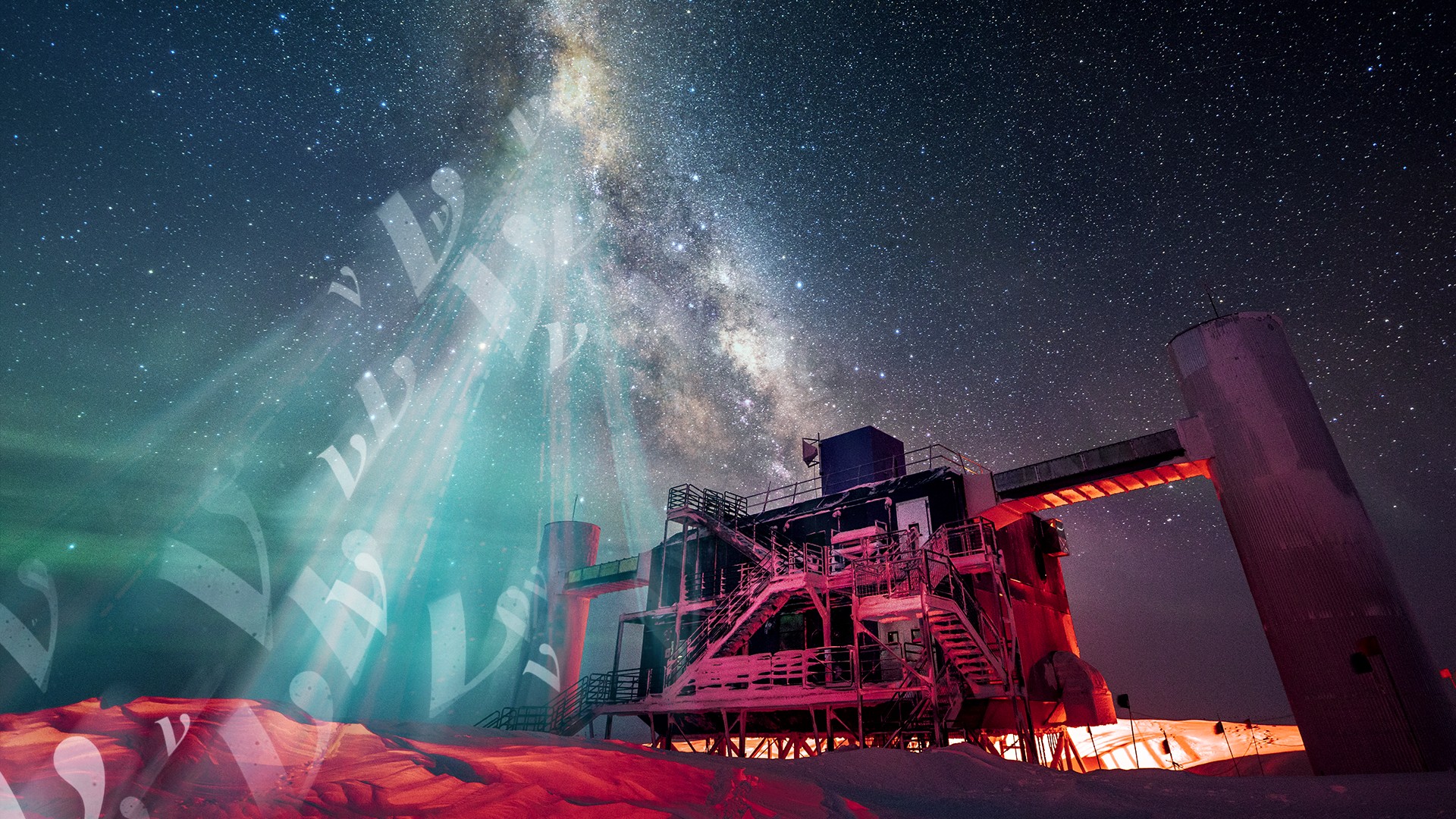
IceCube scientists have detected high-energy tau neutrinos from deep space, suggesting that neutrino transformations occur not only in lab experiments but also over cosmic distances.
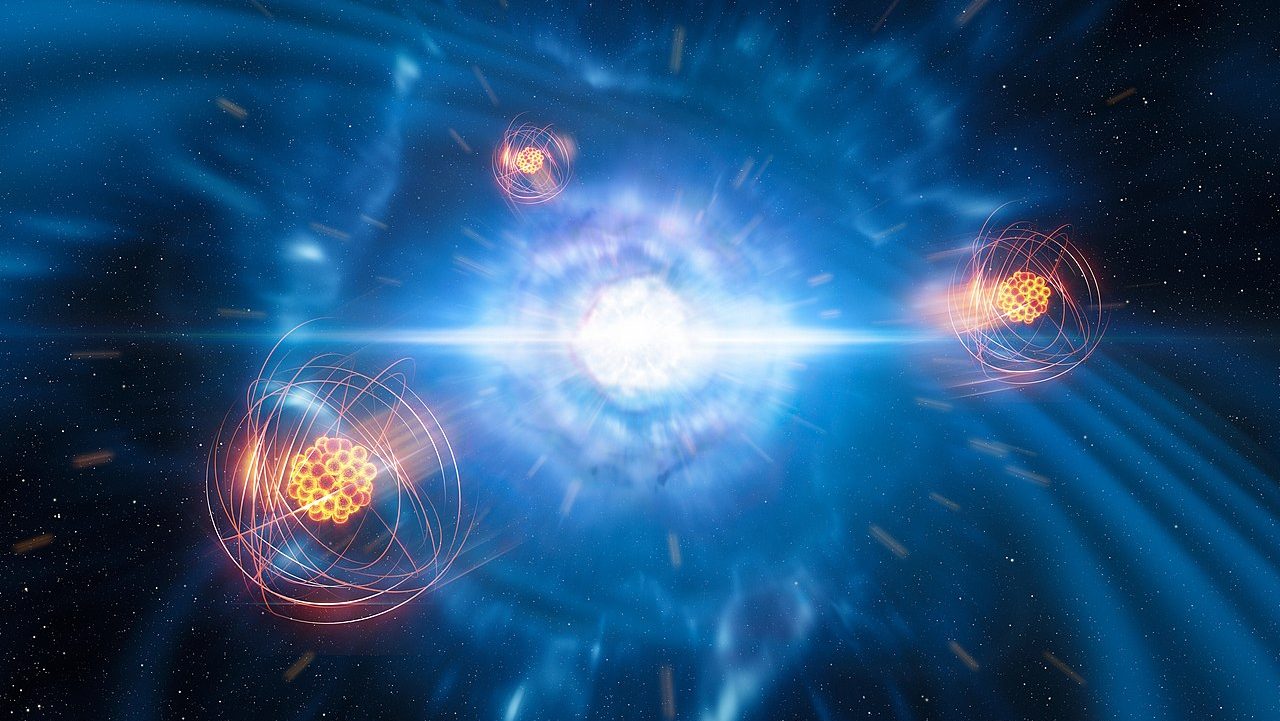
In 2017, we detected gold being forged in a neutron star-neutron star merger. Now, in 2024, the amounts created simply don’t add up.
Learning to decode complex communication on Earth may give us a leg up if intelligent life from space makes contact.
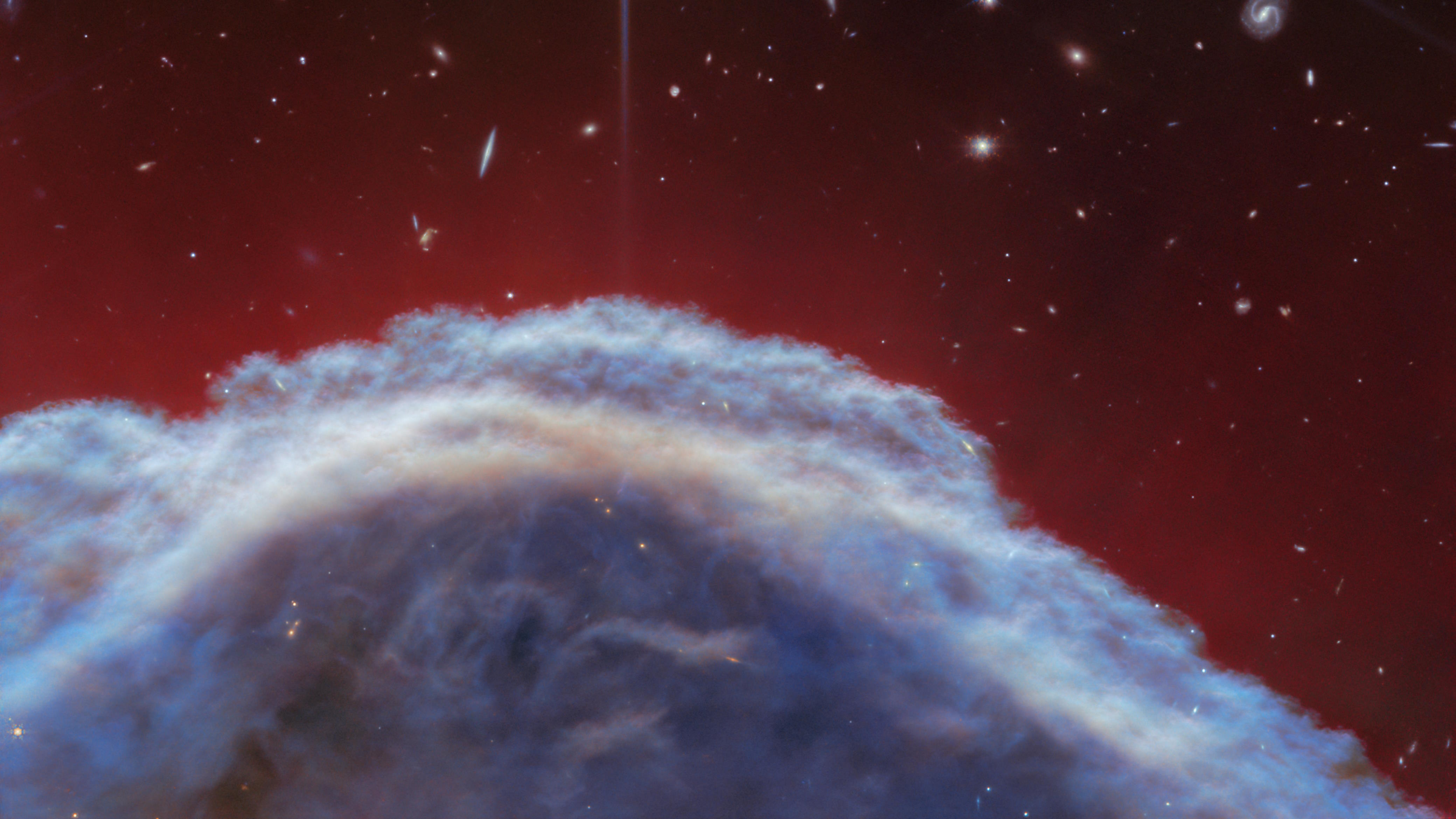
The most iconic “dark nebula” of all lights up under JWST’s infrared gaze. Here’s what’s newly discovered inside.
If the past is any guide, things are going to take off quickly.
Holograms preserve all of an object’s 3D information, but on a 2D surface. Could the holographic Universe idea lead us to higher dimensions?