particle physics
The National Ignition Facility just repeated, and improved upon, their earlier demonstration of nuclear fusion. Now, the true race begins.
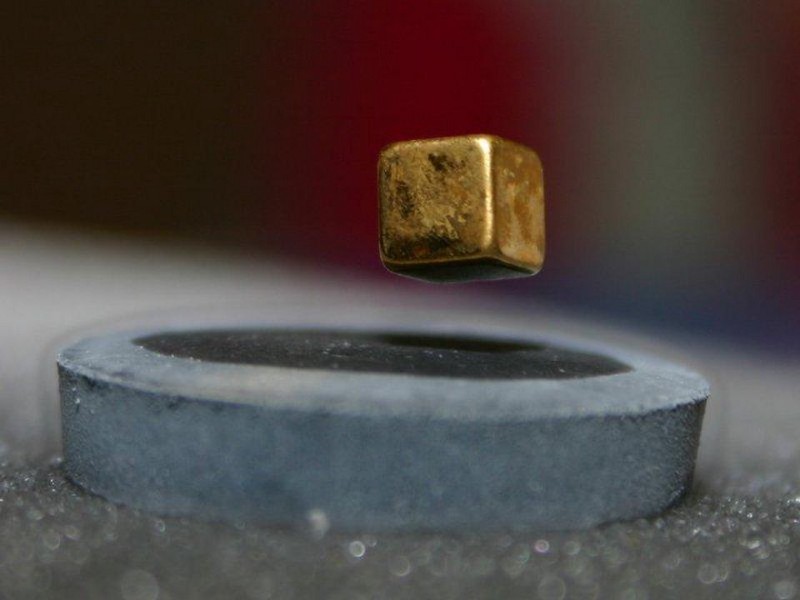
Recent claims put LK-99 as the first room temperature, ambient pressure superconductor ever. Has the game changed, or is it merely hype?
Scientists are notoriously resistant to new ideas. Are they falling prey to groupthink? Or are our current theories just that successful?
Even with the quantum rules governing the Universe, there are limits to what matter can withstand. Beyond that, black holes are unavoidable.
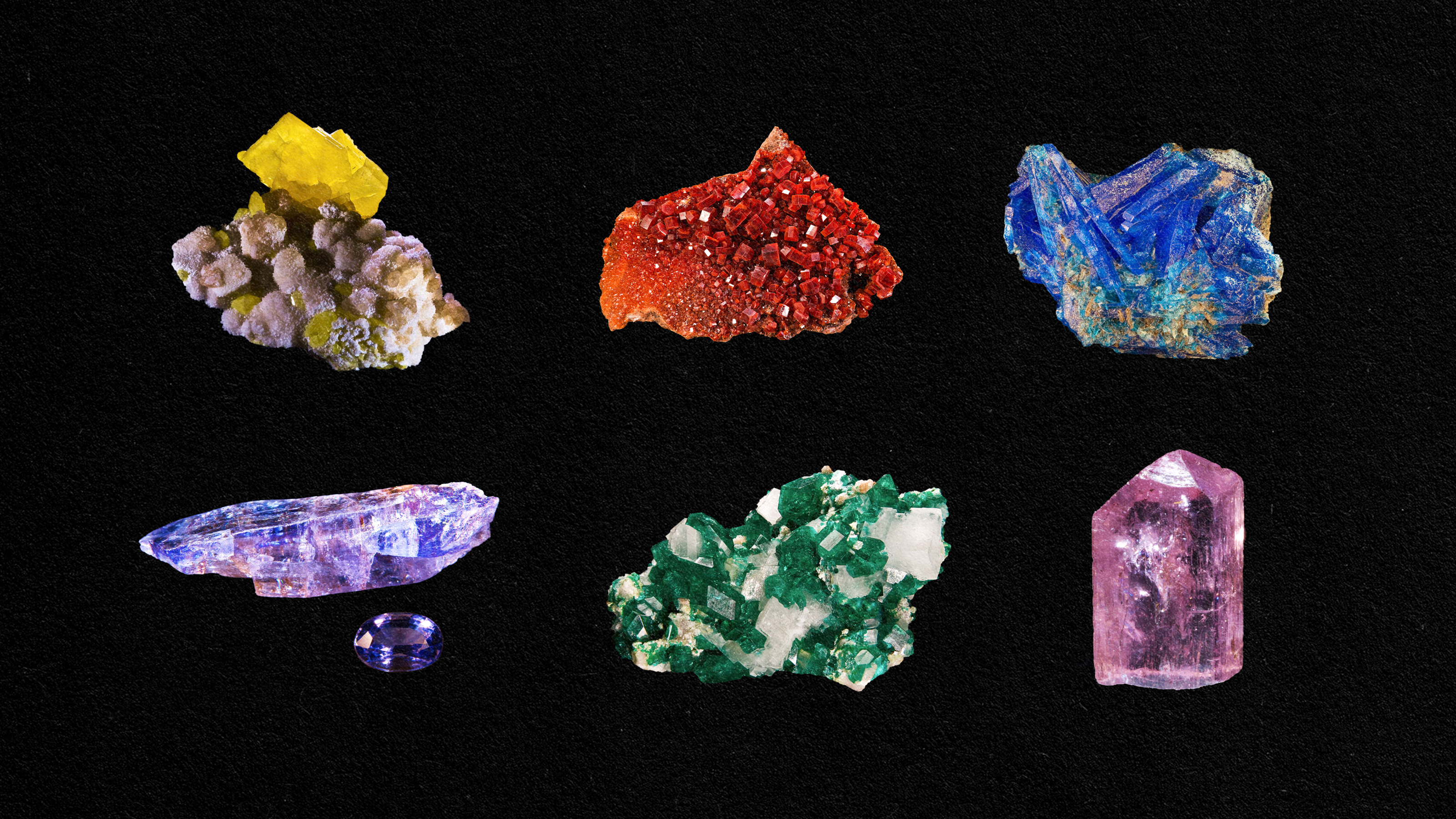
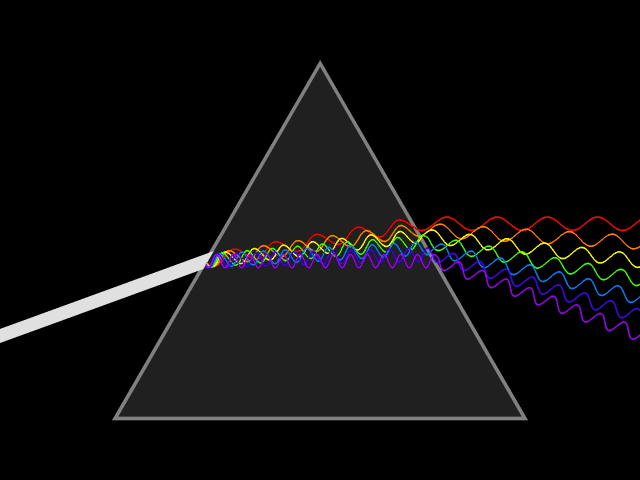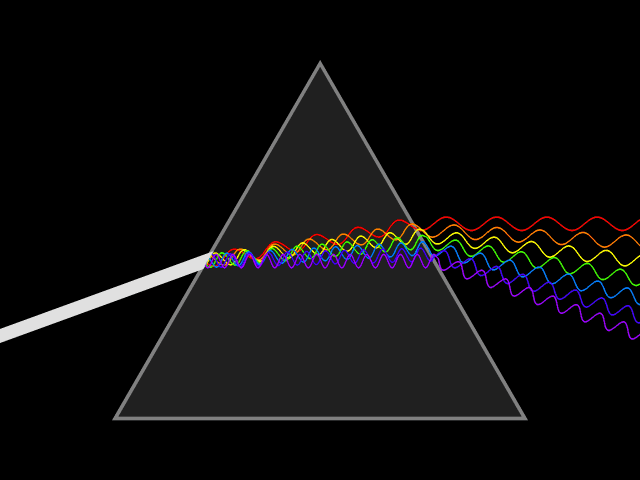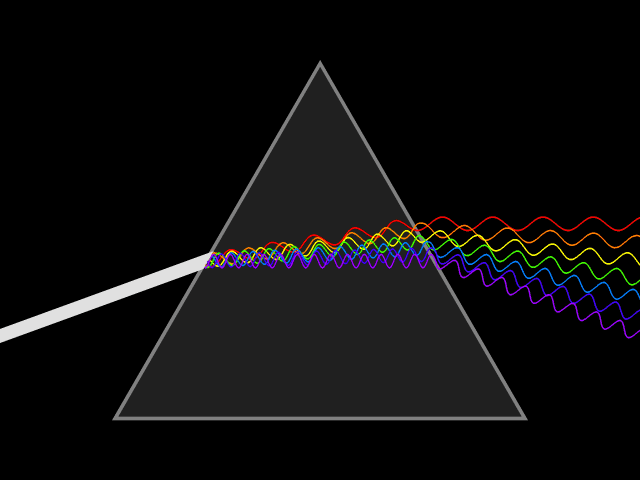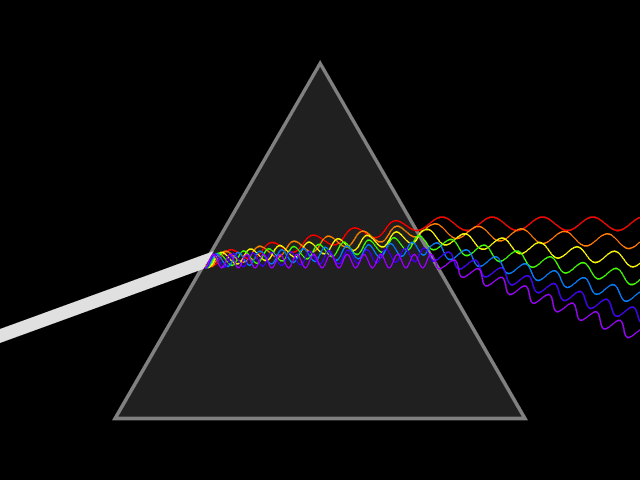
Rocks and minerals don’t simply reflect light. They play with it and interact with light as both a wave and a particle.
Ultracold gases in the lab could help scientists better understand the universe.
The hunt for the elusive particles continues.
Invisible cloaks. Ghost imaging. Scientists are manipulating light in ways that were once only science fiction.
Scientists can make substantial progress without fully understanding exactly what they’re doing.
Science fiction met nuclear fission when Hungarian physicist Leó Szilárd pondered the explosive potential of nuclear energy.
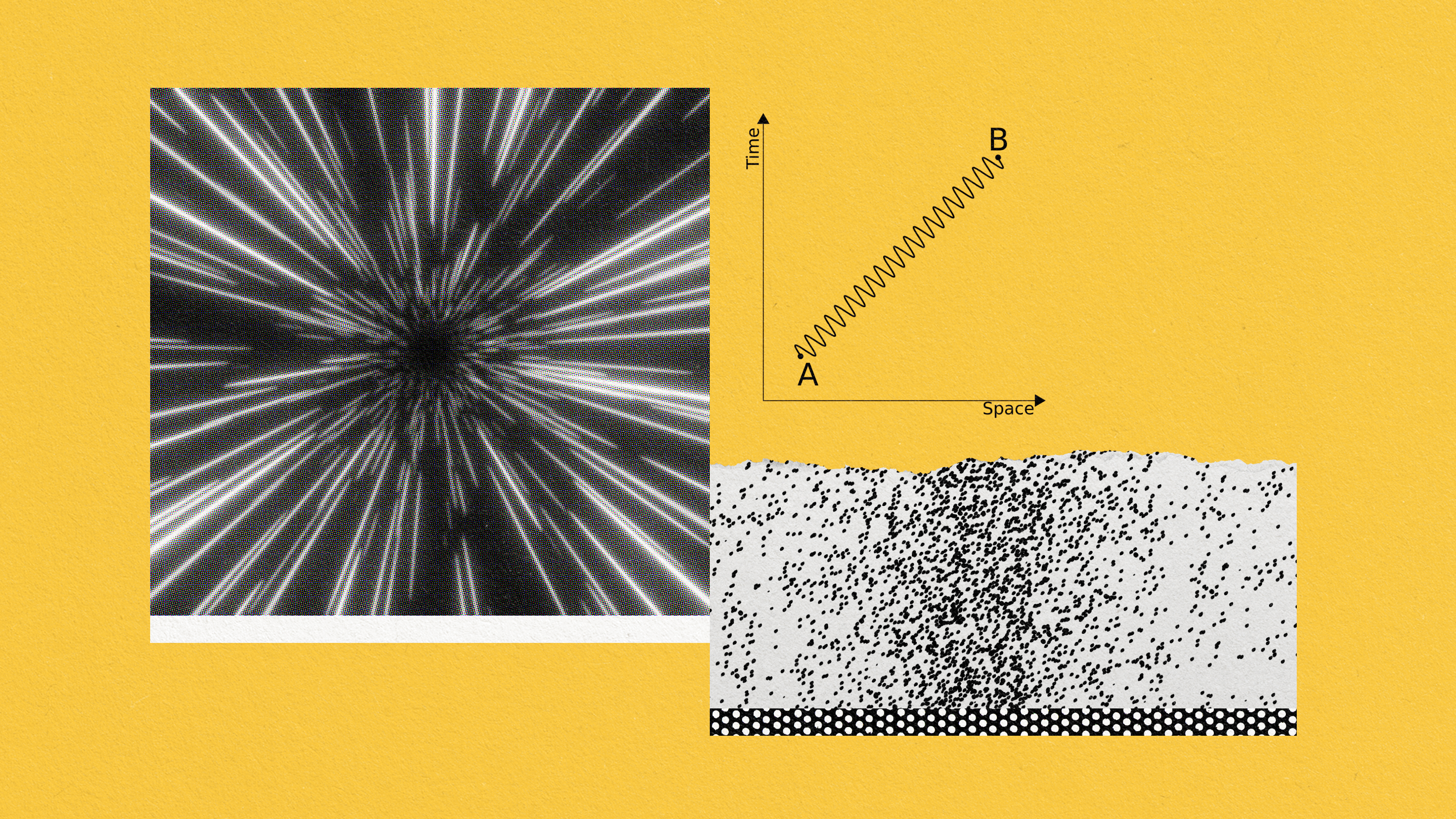
Some processes, like quantum tunneling, have been shown to occur instantaneously. But the ultimate cosmic speed limit remains unavoidable.
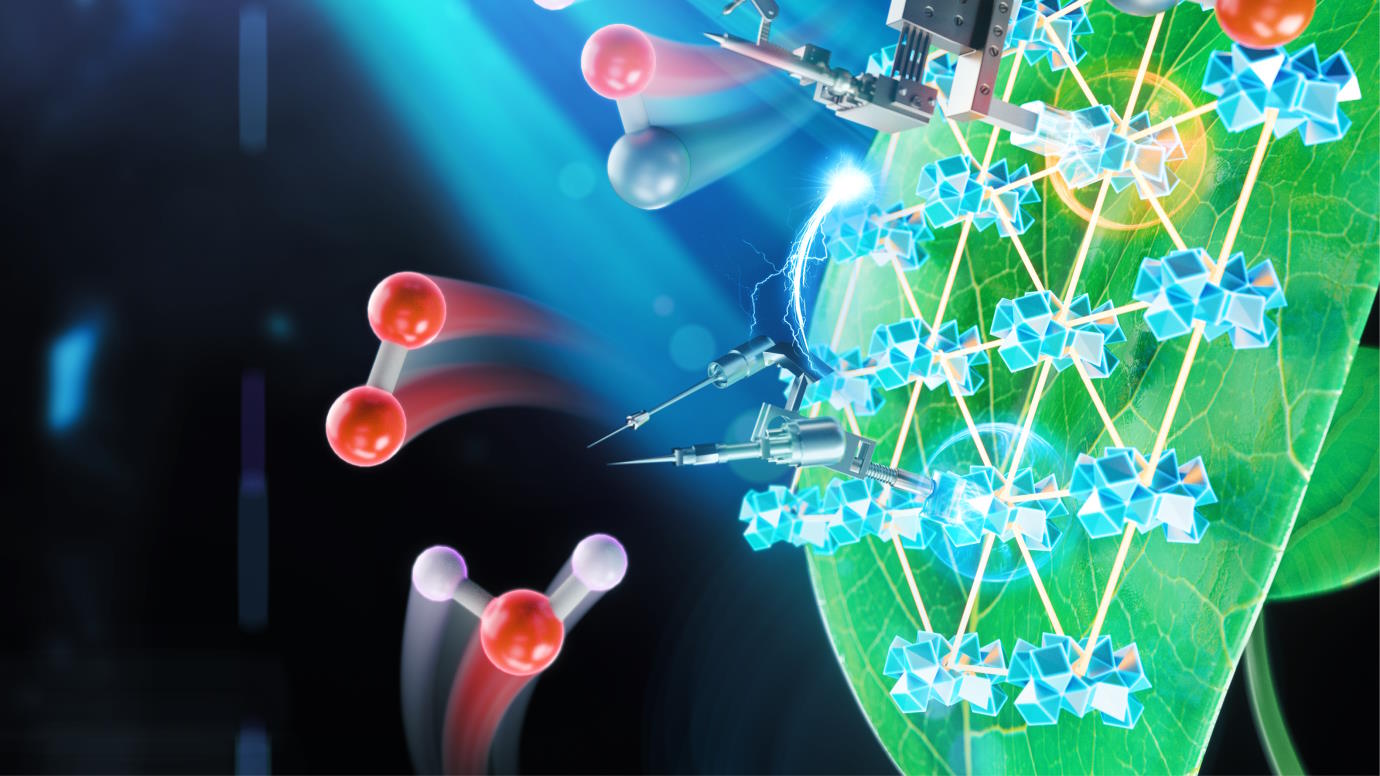
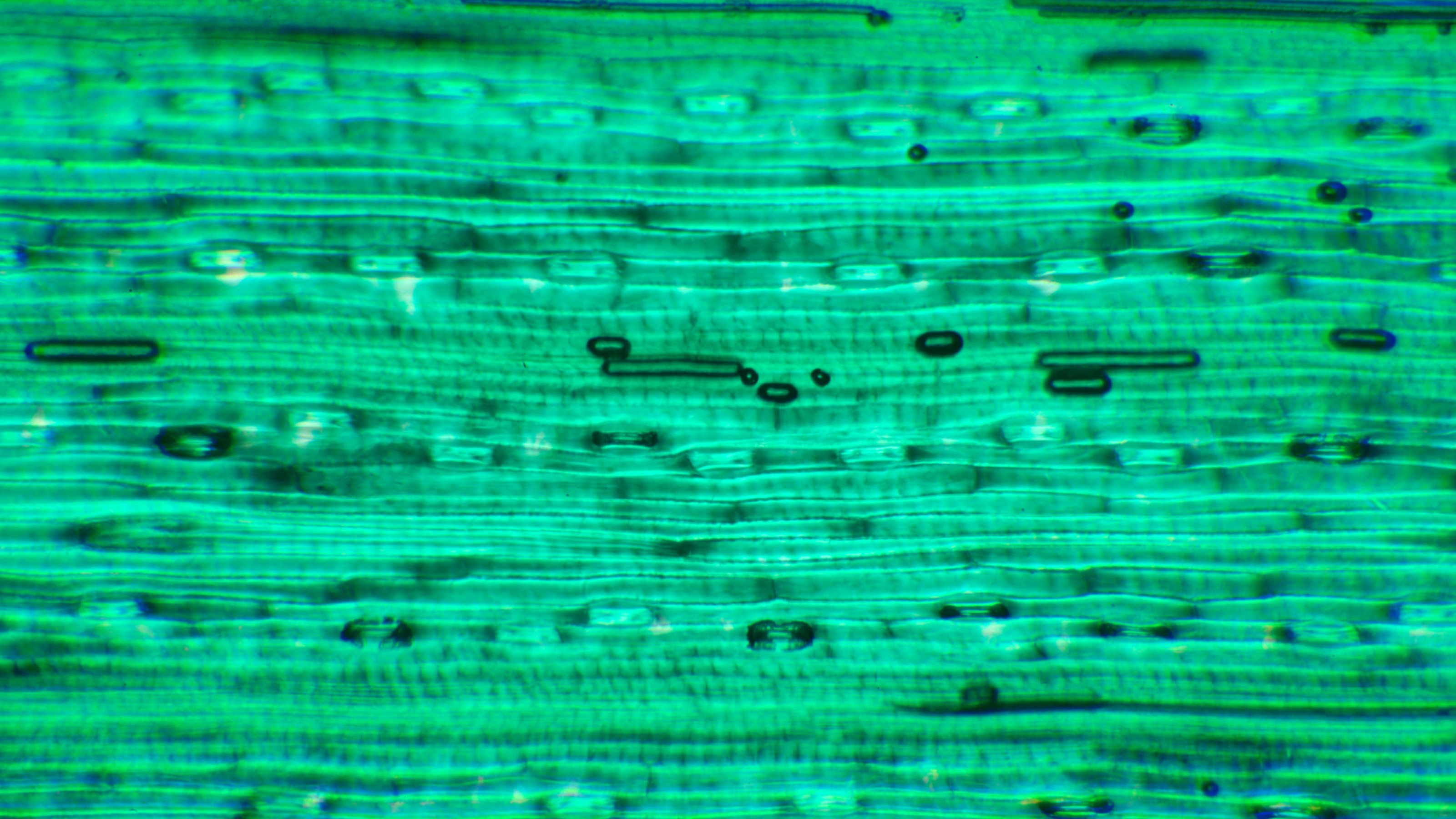
All biological systems are wildly disordered. Yet somehow, that disorder enables plant photosynthesis to be nearly 100% efficient.
The biggest nuclear blast in history came courtesy of Tsar Bomba. We could make something at least 100 times more powerful.
Quantum physics is starting to show up in unexpected places. Indeed, it is at work in animals, plants, and our own bodies.
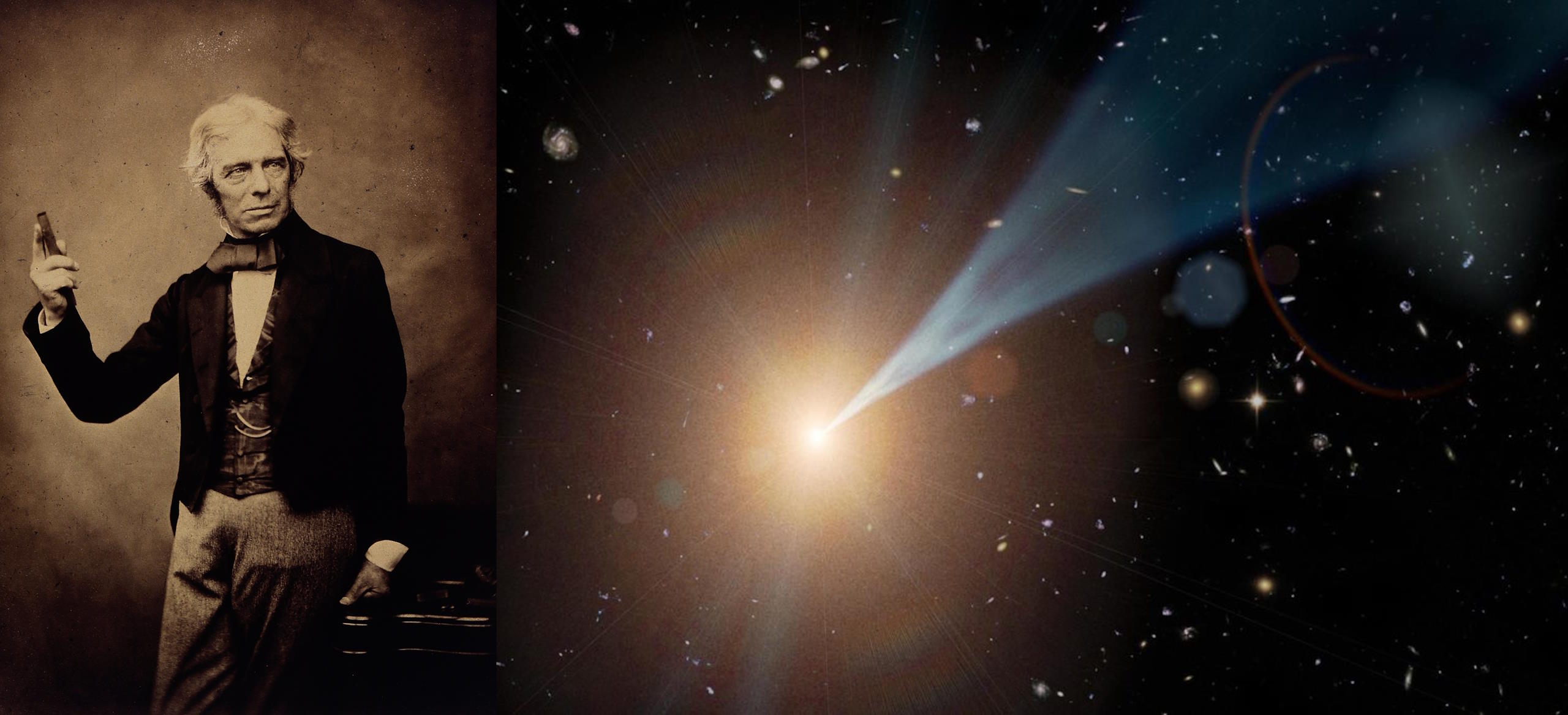
Michael Faraday’s 1834 law of induction was the key experiment behind the eventual discovery of relativity. Einstein admitted it himself.
From a photon’s viewpoint, the Universe is timeless and dimensionless.
Whether you run the clock forward or backward, most of us expect the laws of physics to be the same. A 2012 experiment showed otherwise.
The familiar terrain of solids, liquids, and gases gives way to the exotic realms of plasmas and degenerate matter.
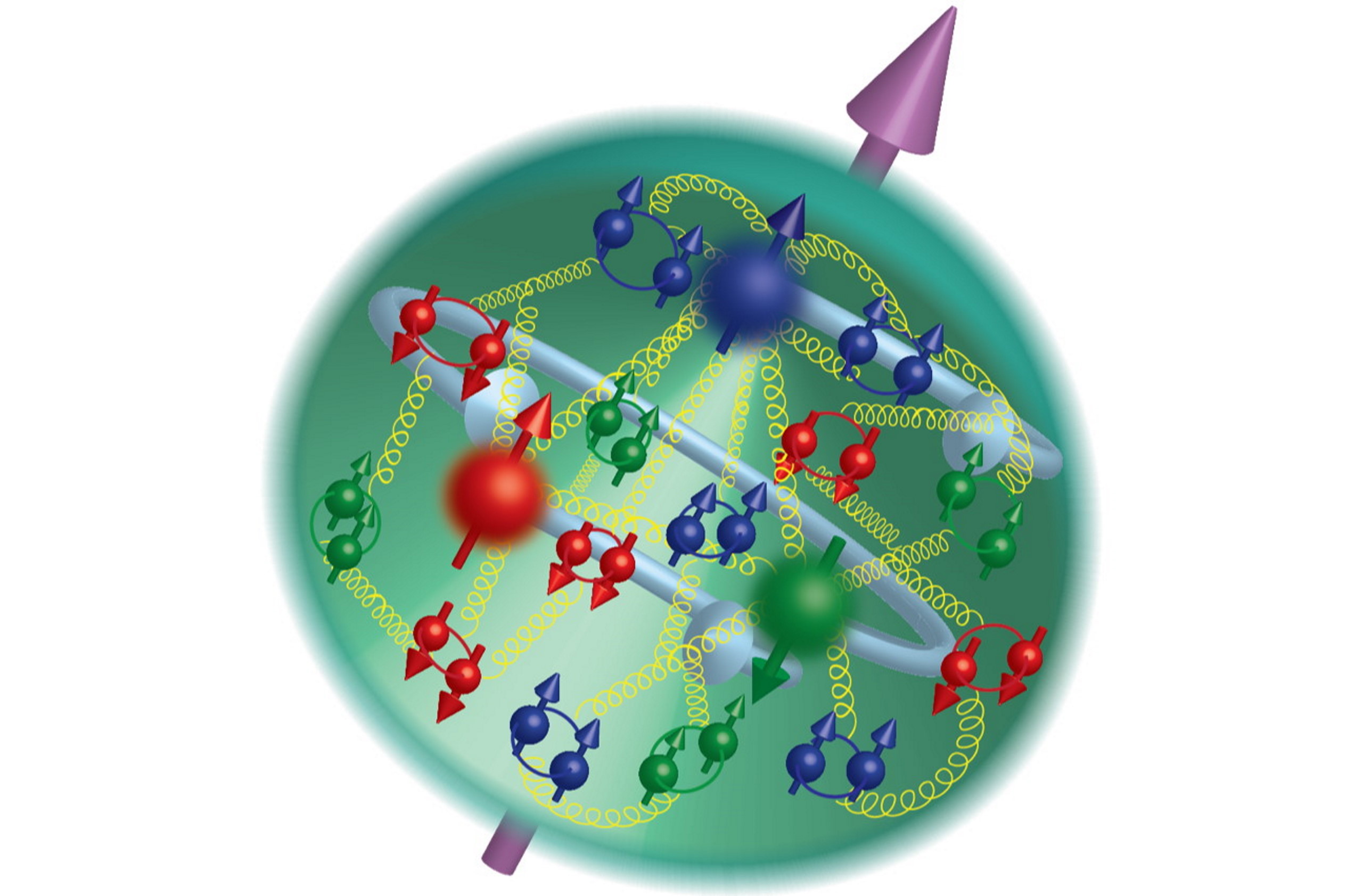
In physics, we reduce things to their elementary, fundamental components, and build emergent things out of them. That’s not the full story.
If we waited long enough, would even protons themselves decay? The far future stability of the Universe depends on it.
How are we to deal with the quantization of spacetime and gravity?
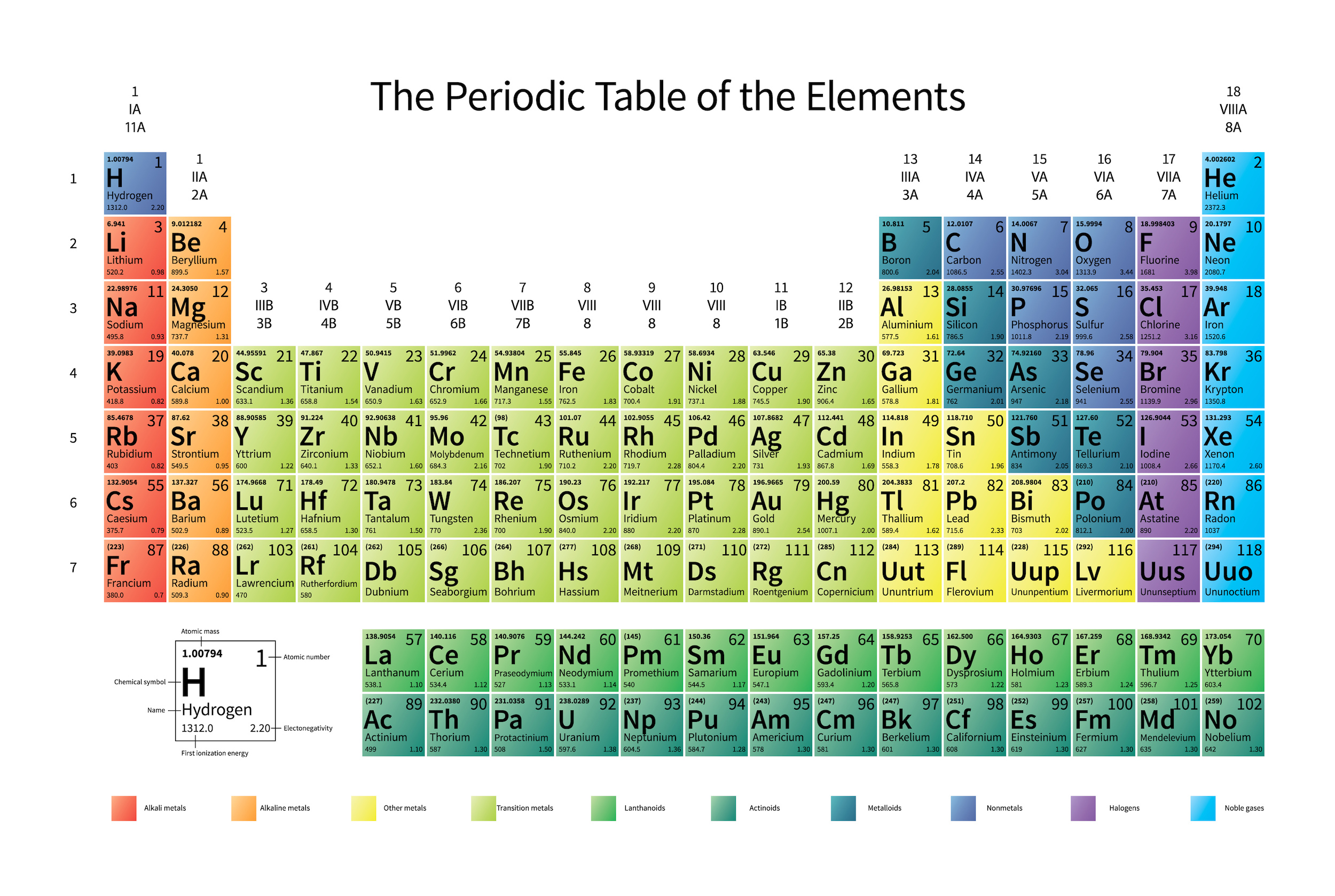
Up until 2002, we thought that the heaviest stable element was bismuth: #83 on the periodic table. That’s absolutely no longer the case.
Just by observing the tiny amount of deuterium left over from the Big Bang, we can determine that dark matter and dark energy must exist.
There is no such thing as a void in the Universe.
Gamma-ray bursts are so powerful they could vaporize the Earth from 200 light-years away. Recreating them in the lab is not easy.
If light can’t be bent by electric or magnetic fields (and it can’t), then how do the Zeeman and Stark effects split atomic energy levels?
In 1974, Hawking showed that black holes aren’t stable, but emit radiation and decay. Nearly 50 years later, it isn’t just for black holes.
The concept of ‘relativistic mass’ has been around almost as long as relativity has. But is it a reasonable way to make sense of things?
Plants at room temperature show properties we had only seen near absolute zero.