The Universe is out there, waiting for you to discover it.
Our mission: to answer, scientifically, the biggest questions of all.
- What is our Universe made of?
- How did it become the way it is today?
- Where did everything come from?
- What is the ultimate fate of the cosmos?
For countless generations, these were questions without resolutions. Now, for the first time in history, we have scientific answers. Starts With A Bang, written by Dr. Ethan Siegel, brings these stories — of what we know and how we know it — directly to you.
Get Starts With A Bang in your inbox
Featured
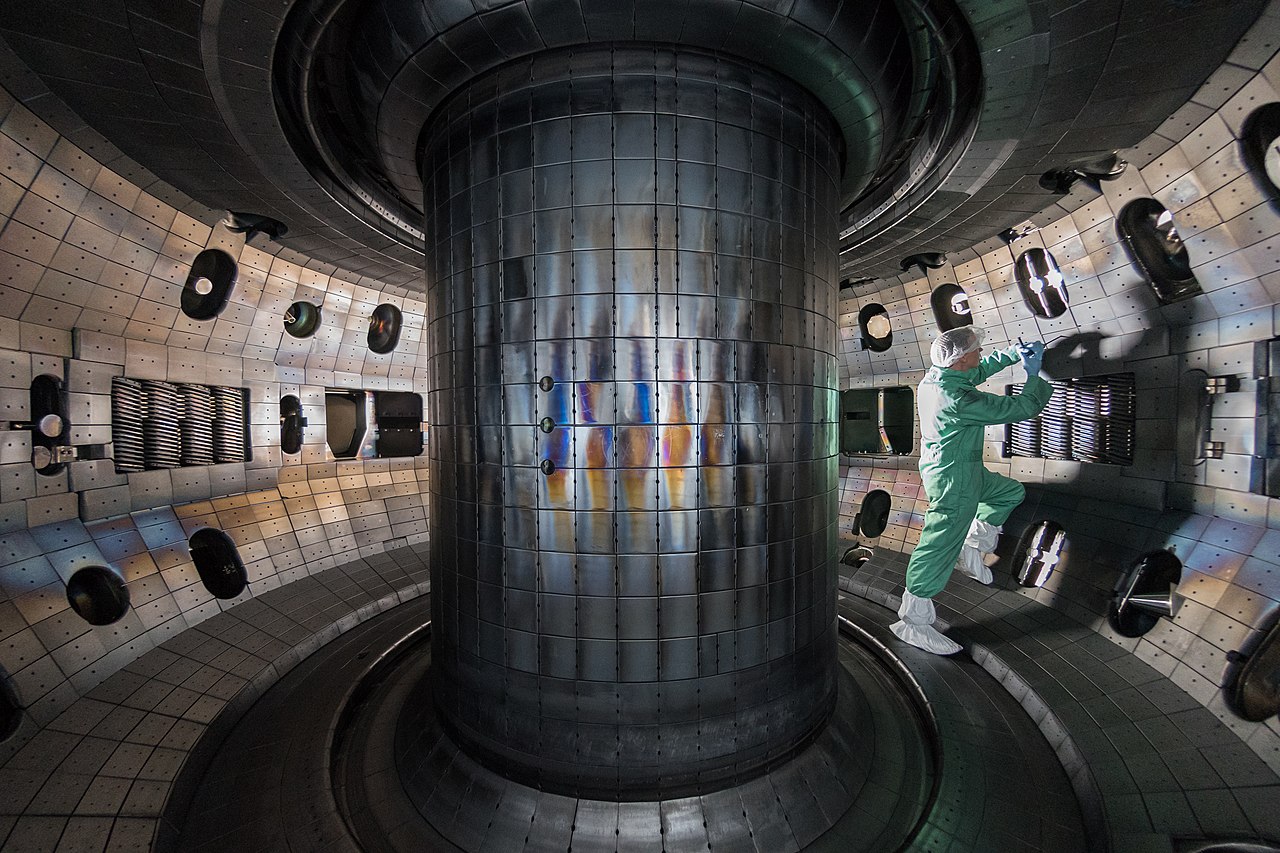
Why power generated through nuclear fusion will be the future, but not the present, solution to humanity’s energy needs.
It’s a strange idea to consider: that a tiny building block of matter, the atomic nucleus, holds the greatest potential for energy release.
And yet, it’s true; while electron transitions in atoms or molecules typically release energy on the order of ~1 electron-Volt, nuclear transitions between different configurations release energies a million times as great, on the order of ~1 Mega-electron-Volt.
Popular
From before the Big Bang to the present day, the Universe goes through many eras. Dark energy heralds the final one.
A wild, compelling idea without a direct, practical test, the Multiverse is highly controversial. But its supporting pillars sure are stable.
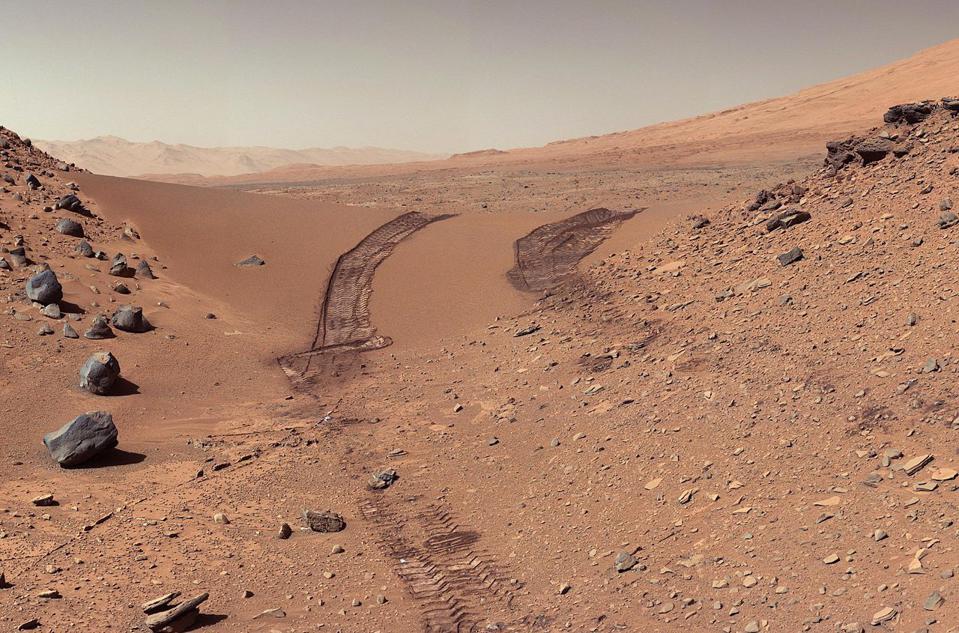
The surface and atmosphere is colored by ferric oxides. Beneath a very thin layer, mere millimeters deep in places, it’s not red anymore.
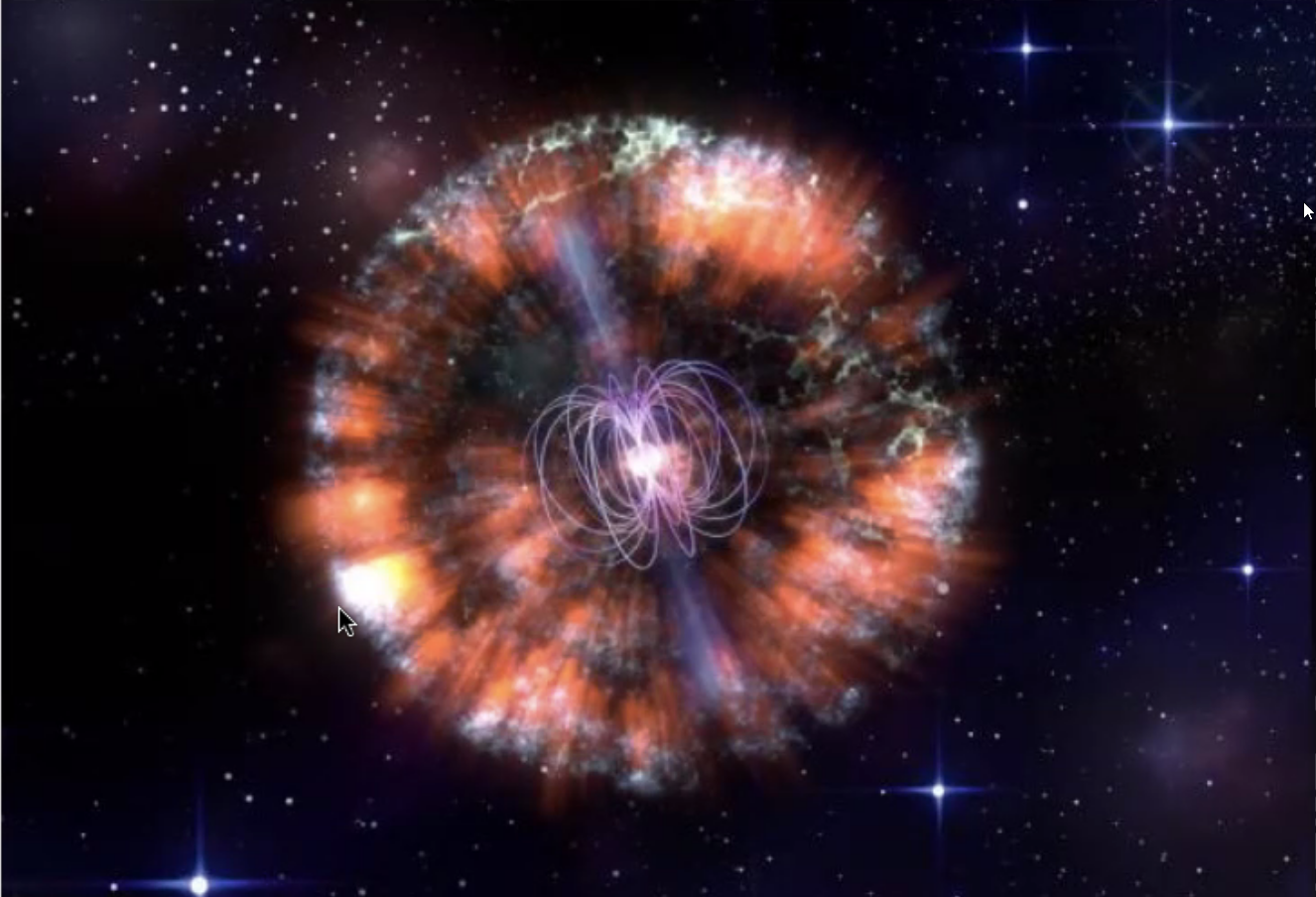
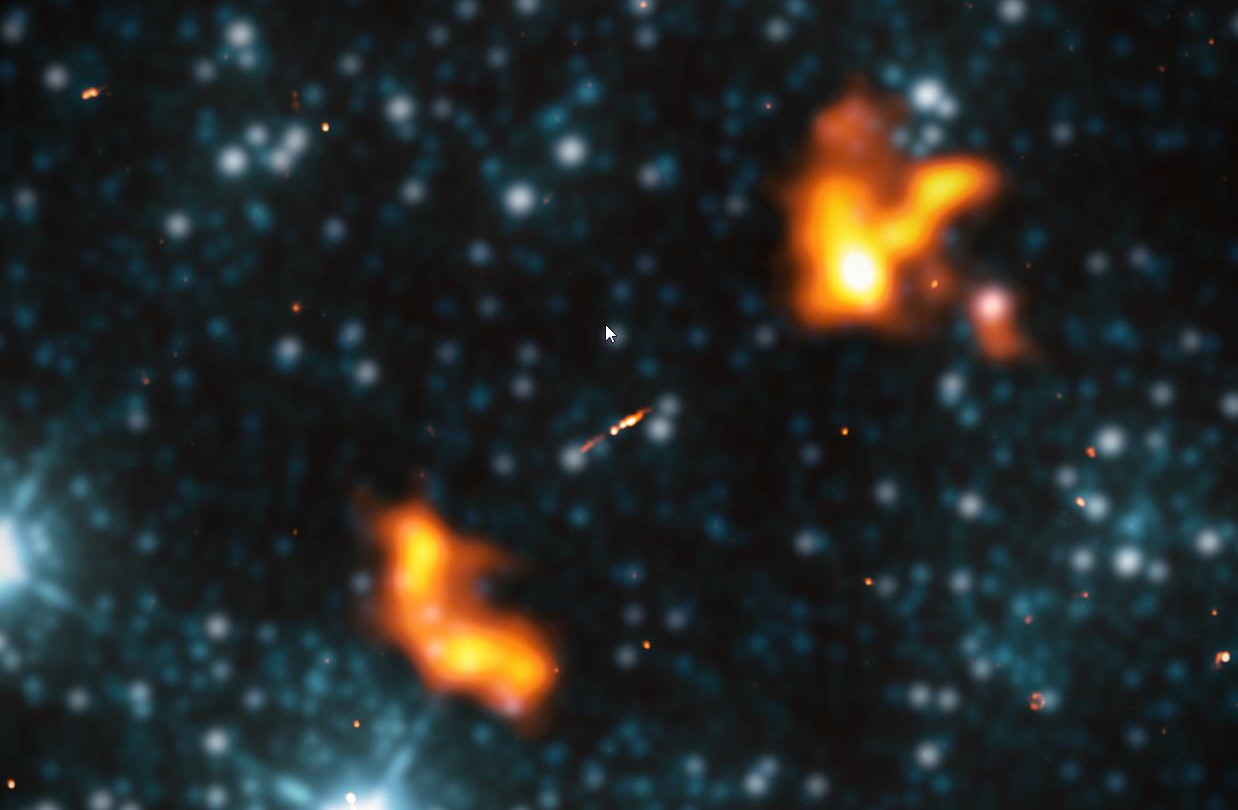
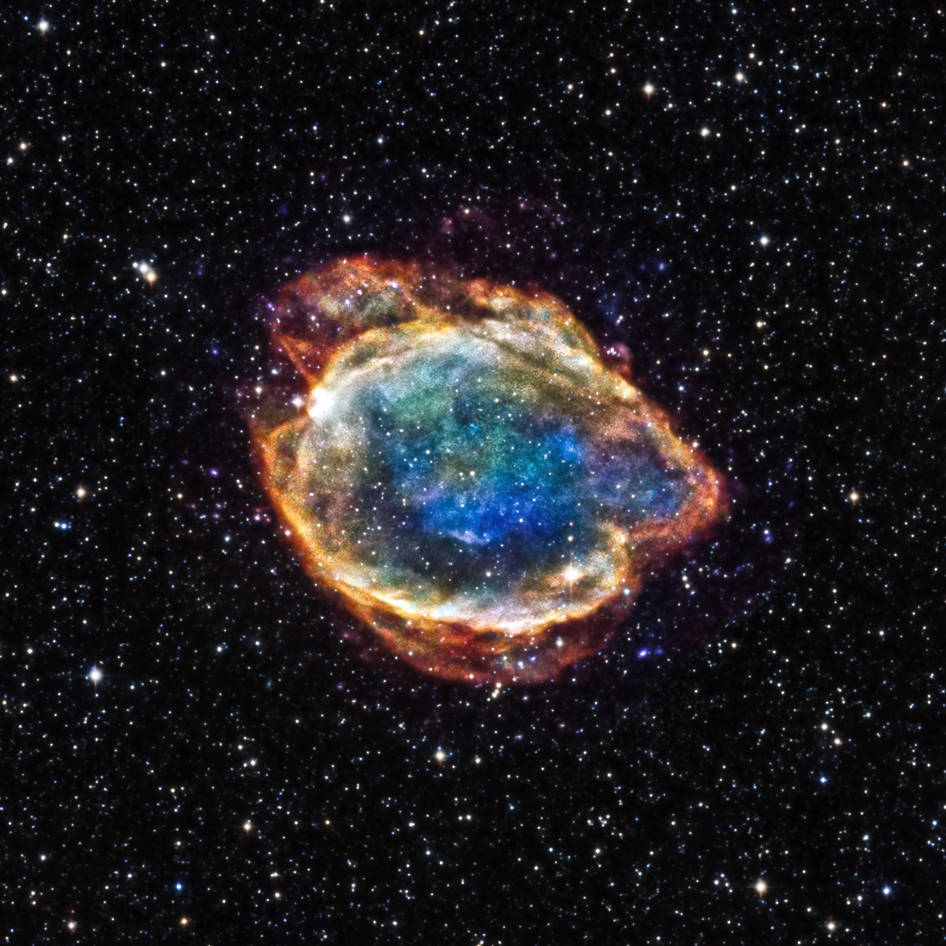
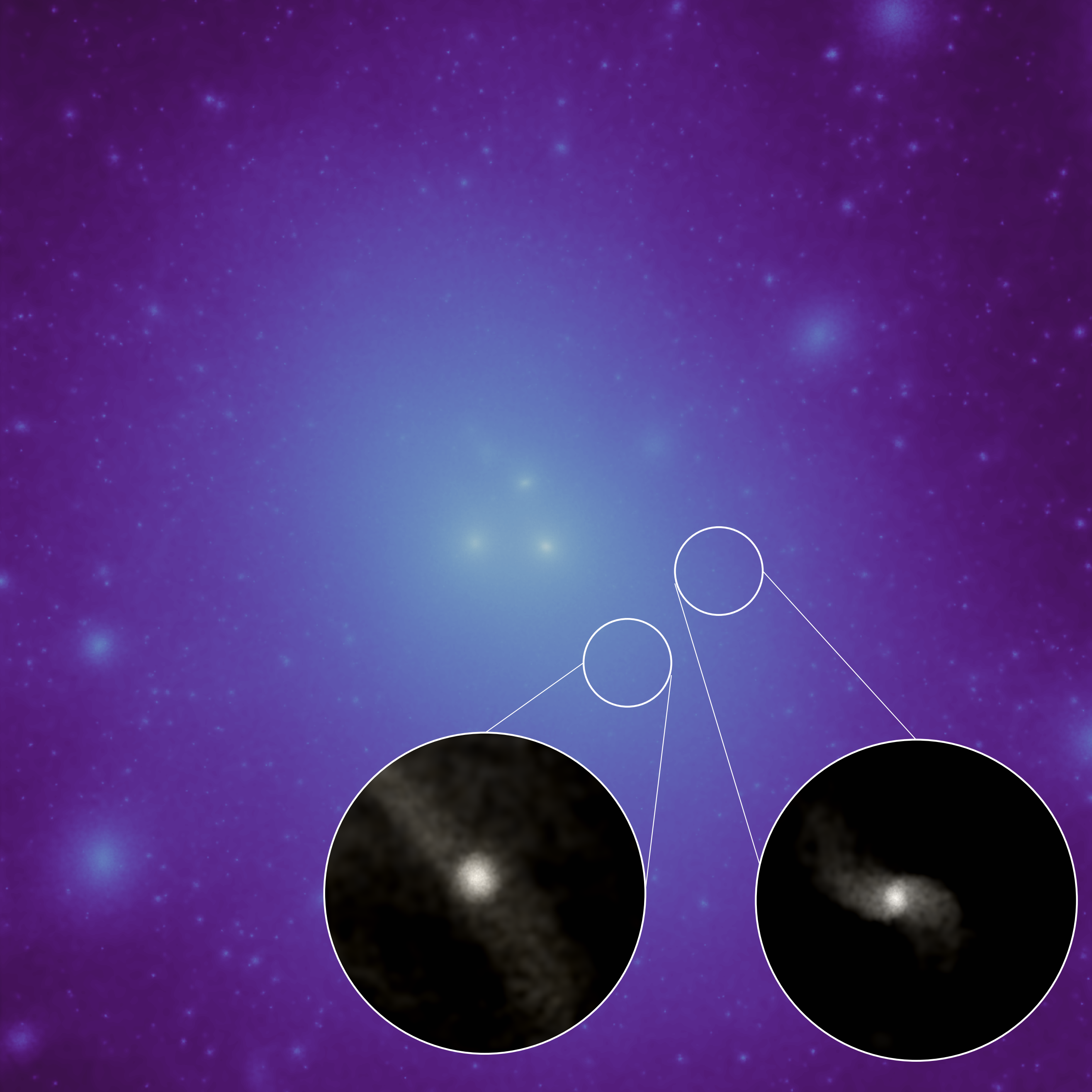
The first supernova ever discovered through its X-rays has an enormously powerful engine at its core. It’s unlike anything ever seen.
Just 13.8 billion years after the hot Big Bang, we can see 46.1 billion light-years away in all directions. Doesn’t that violate…something?
All Stories
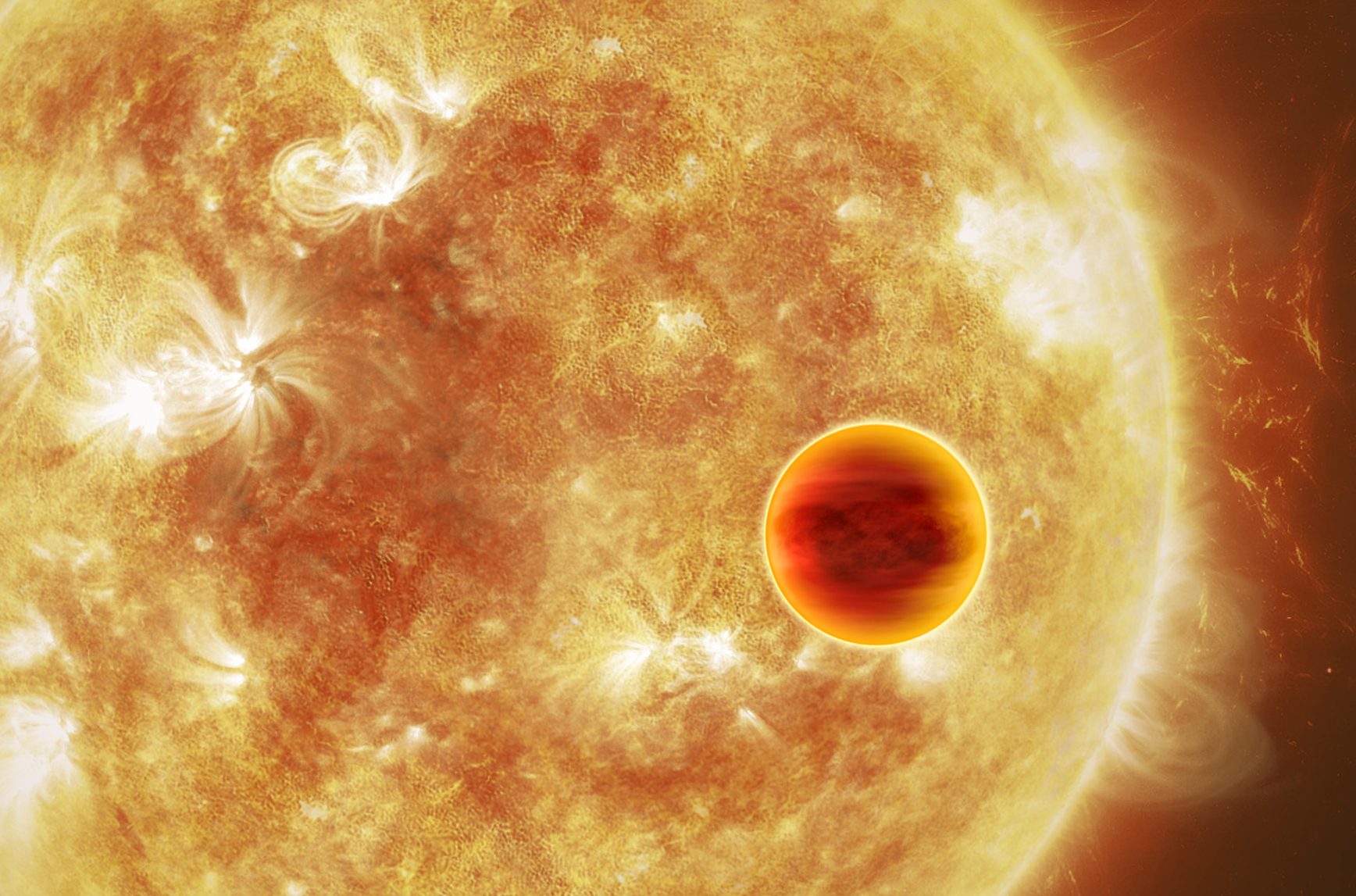
There’s a limit to how large planets can be, and it’s only about double the radius of Jupiter. At least, so far.
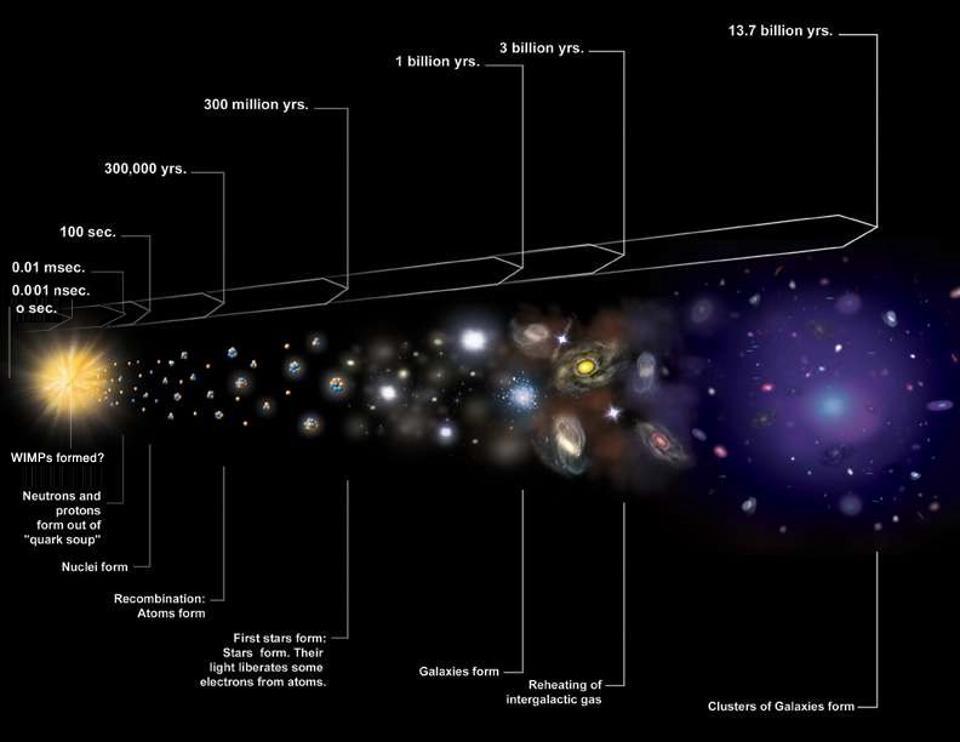
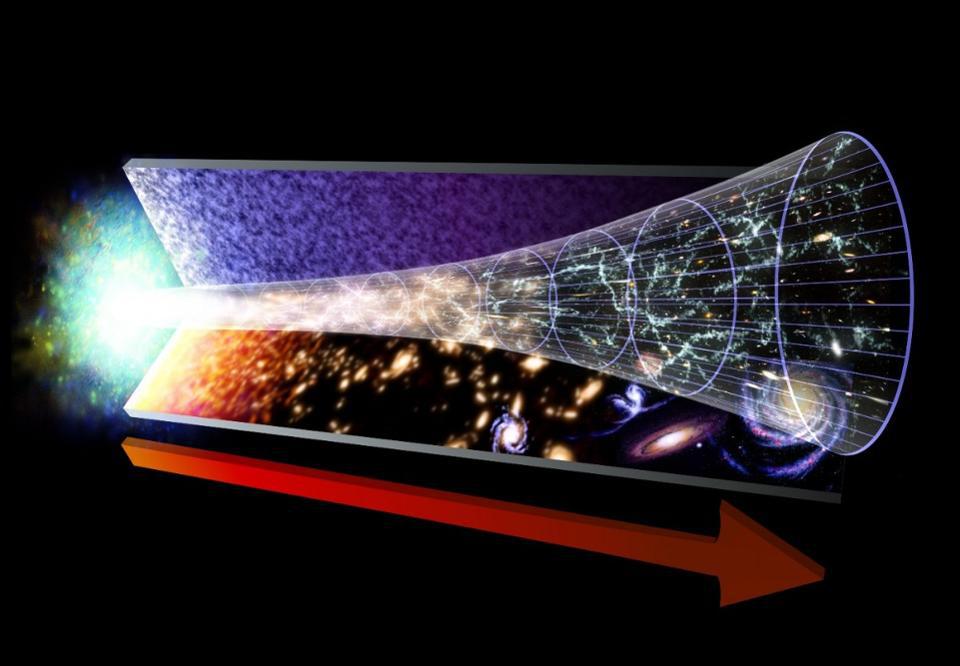
The Big Bang was hot, dense, uniform, and filled with matter and energy. Before that? There was nothing. Here’s how that’s possible.
More than any other of Einstein’s equations, E = mc² is the most recognizable to people. But what does it all mean?
Despite being the closest planet to the Sun, Mercury “only” reaches 800 °F at its hottest. Venus is always hotter, even at night.
Planet Earth has been around for over 4.5 billion years, but humans? For 99.998% of our planet’s history, humans were nowhere to be found.
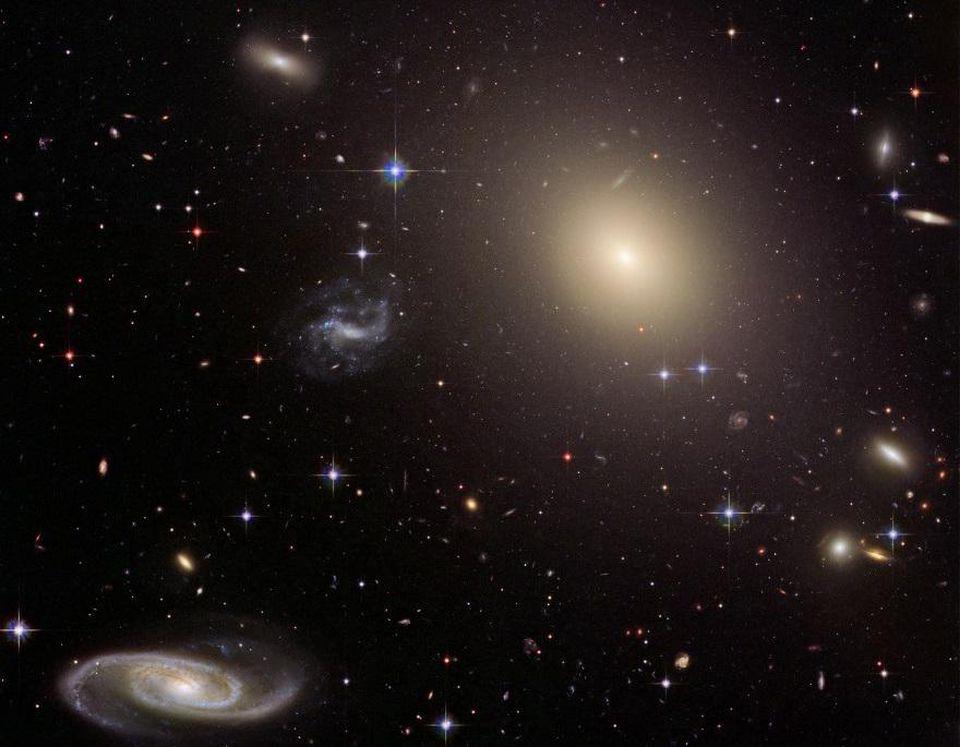
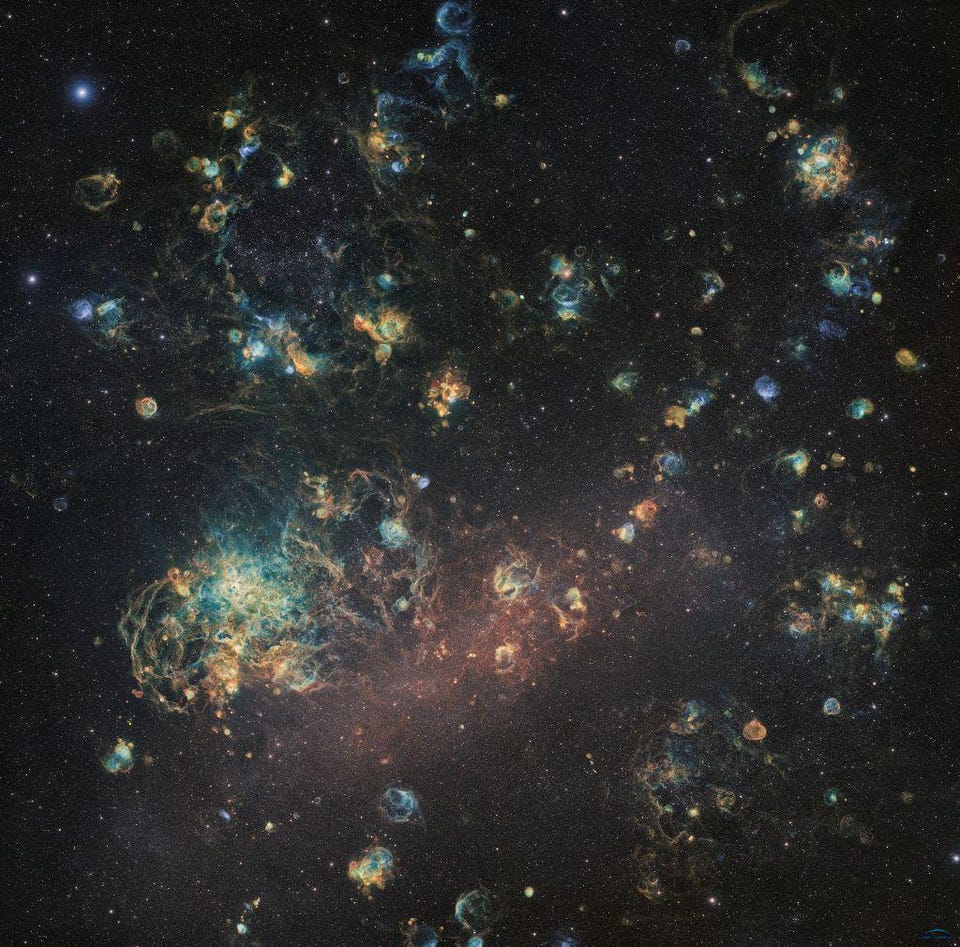
Professional astronomy images are the gold standard. But this Large Magellanic Cloud composite is the amateur community’s best image ever.
If you think of the Big Bang as an explosion, we can trace it back to a single point-of-origin. But what if it happened everywhere at once?
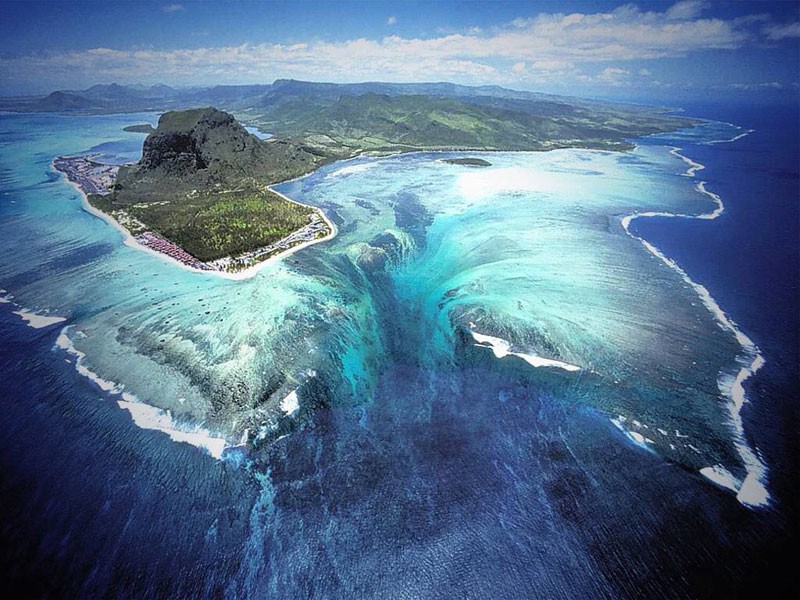
The natural wonders of Mauritius include the spectacular sight of an underwater waterfall. Here’s the science of how it works.
Out of all the galaxies we know, only a few little ones are missing dark matter. At last, we finally understand why.
The odds are slim, but the consequences would be devastating. Here’s what would happen, plus how to avoid it.
Move over, IC 1101. You may be impressively large, but you never stood a chance against the largest known galaxy: Alcyoneus.
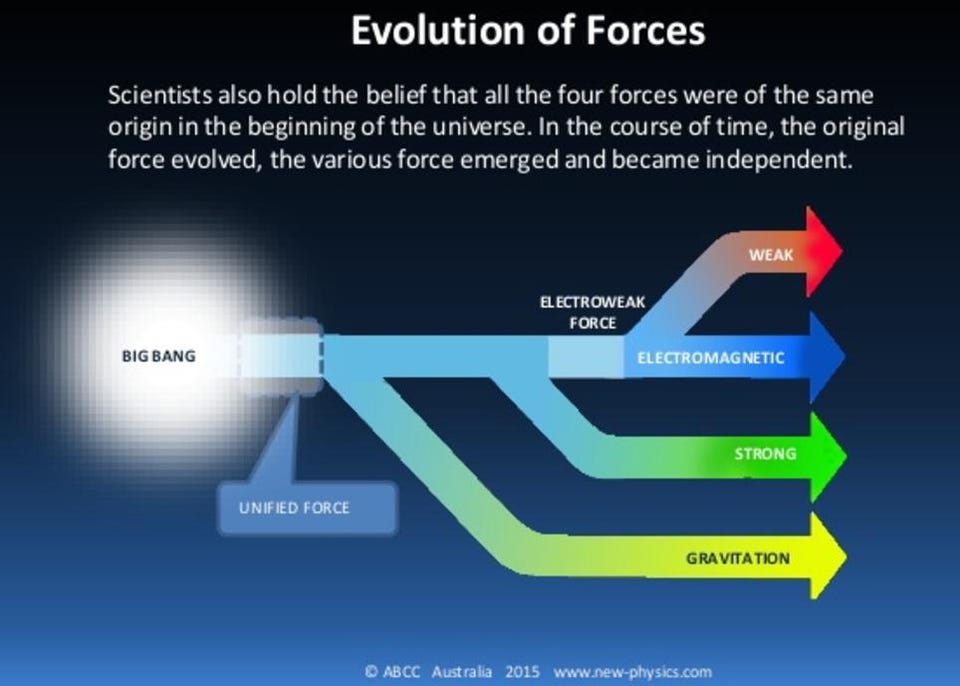
If the electromagnetic and weak forces unify to make the electroweak force, maybe, at even higher energies, something even greater happens?
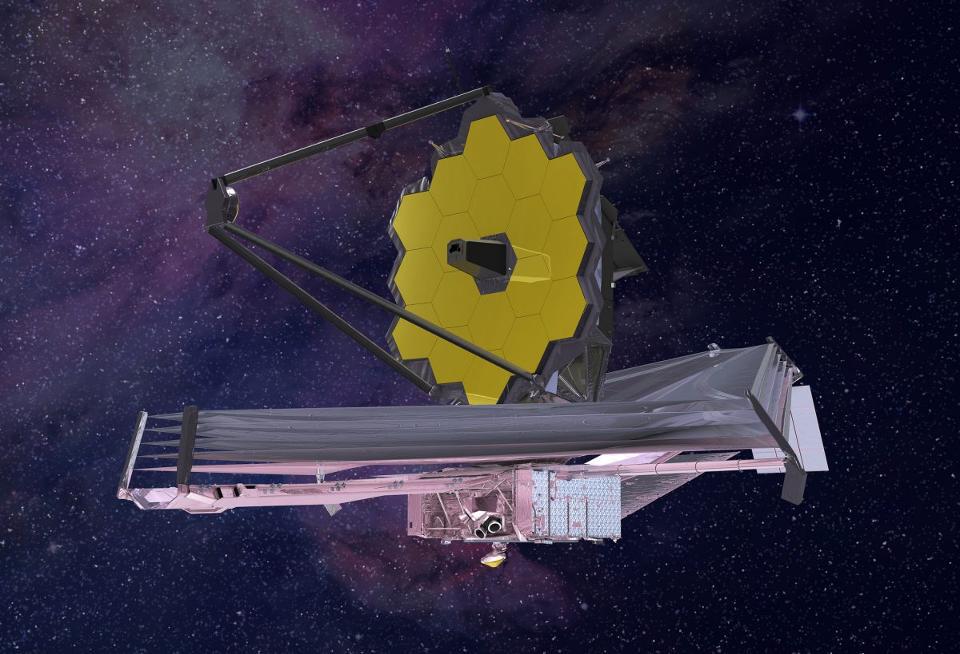
Once science operations begin for James Webb, we’ll never look at the Universe the same way again. Here’s what everyone should know.
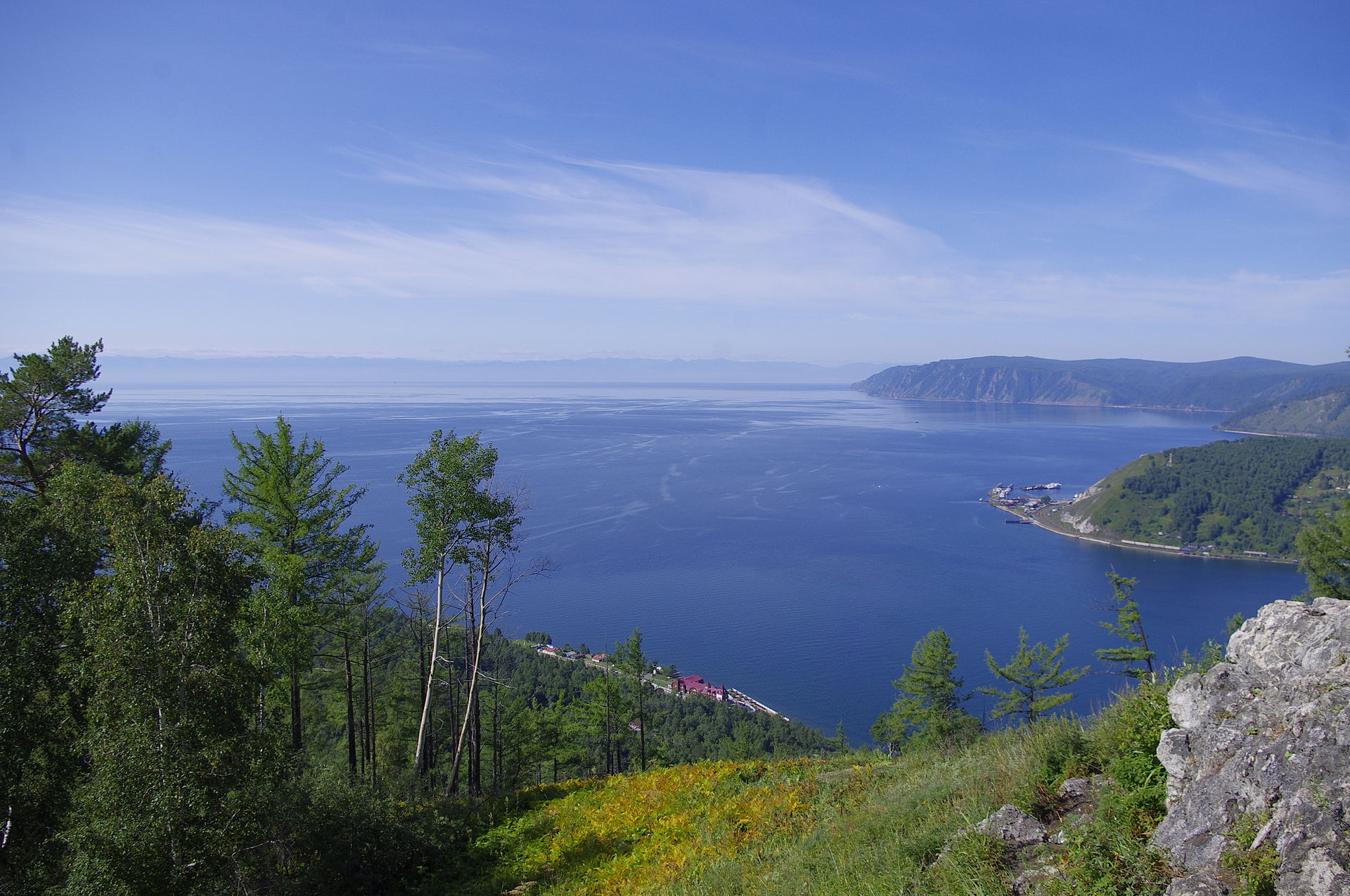
Lake Baikal holds nearly one-fourth of Earth’s fresh surface water and is the most scientifically interesting lake on our planet.
With 1550 distinct type Ia supernovae measured across ~10 billion years of cosmic time, the Pantheon+ data set reveals our Universe.
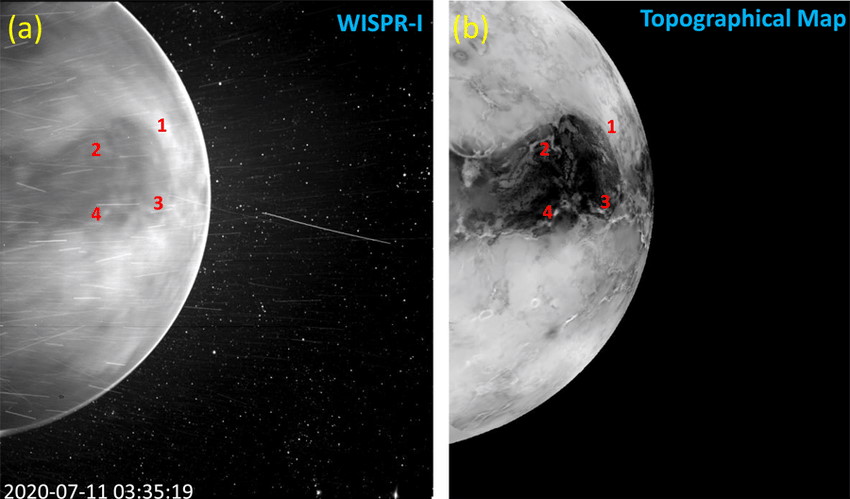
Until recently, we were only able to view Venus’s surface with radar or by landing on the planet. It was believed that Venus’s surface was entirely obscured by clouds; NASA’s Parker Solar Probe proved otherwise.
Yes, the Universe is expanding, but you might wonder, “How fast is it expanding?”
65 million years ago, an asteroid strike caused the 5th great mass extinction. Could we save Earth, today, from a similar event?
The ANITA experiment found cosmic rays shooting out of Antarctica. One interpretation claims “parallel Universes,” but is that right?
Why power generated through nuclear fusion will be the future, but not the present, solution to humanity’s energy needs.
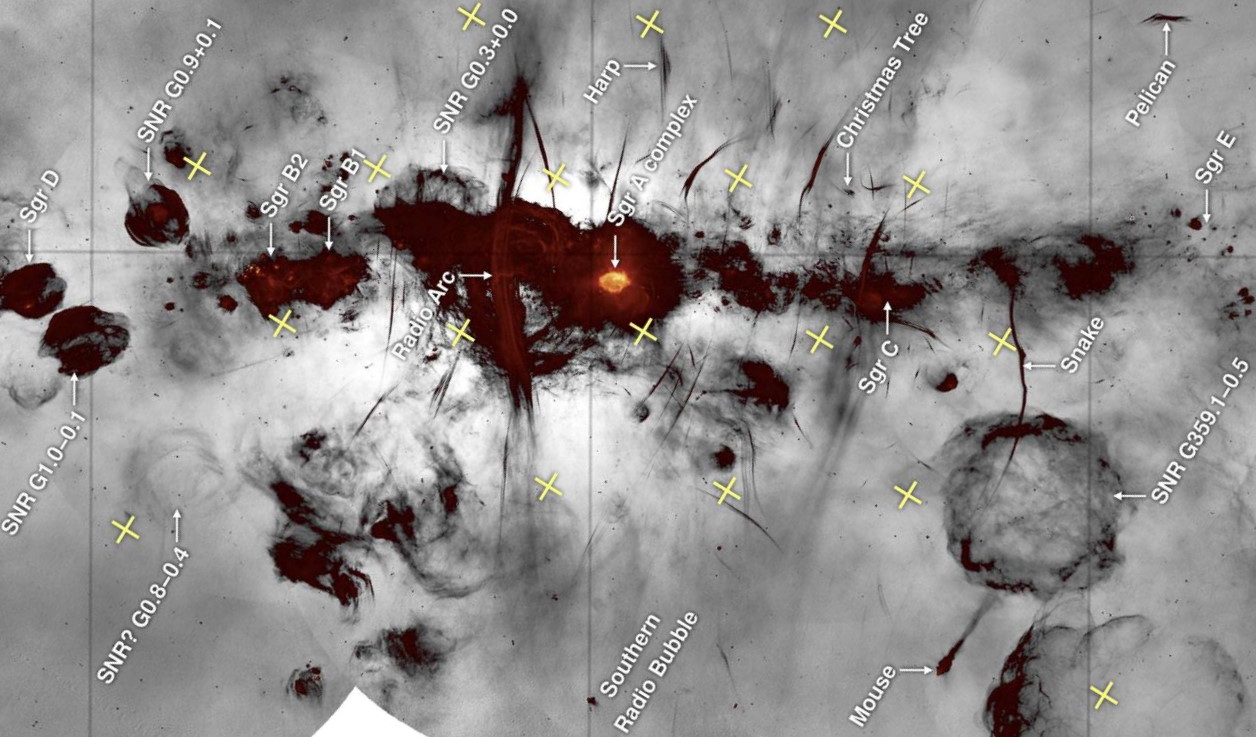
As viewed by the MeerKAT telescope, this radio view of the Milky Way blows away every other way we’ve ever seen our home galaxy.
There really might be extraterrestrials out there, attempting to make contact. Here’s how science, not fiction, is attempting to find them.
With launch costs dropping and enormous numbers of new satellites filling the sky, can’t we just do it all from space?
There are ~400 billion stars in the Milky Way, and ~2 trillion galaxies in the visible Universe. But what if we aren’t typical?
Travel half the distance to your destination, and there’s always another half to go. Despite Zeno’s Paradox, you always arrive right on time.
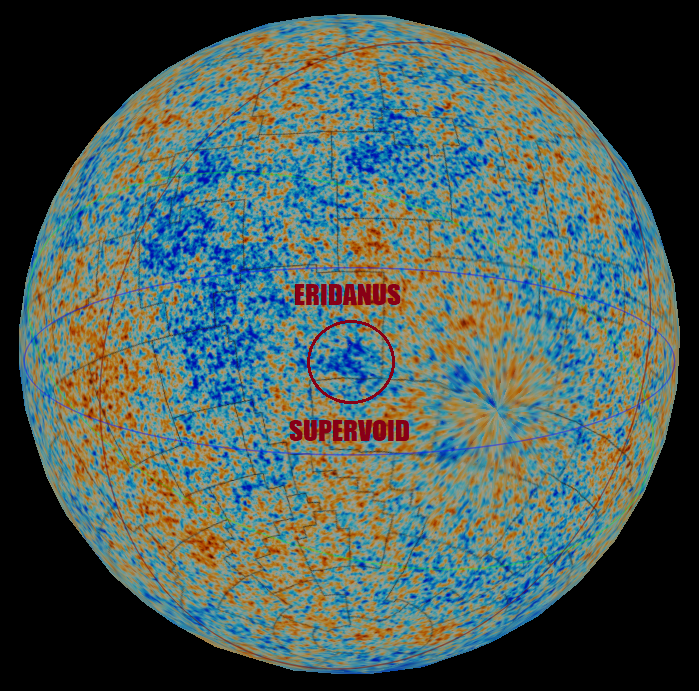
The Universe is supposed to be the same everywhere and in all directions. So what’s that giant “cold spot” doing out there?
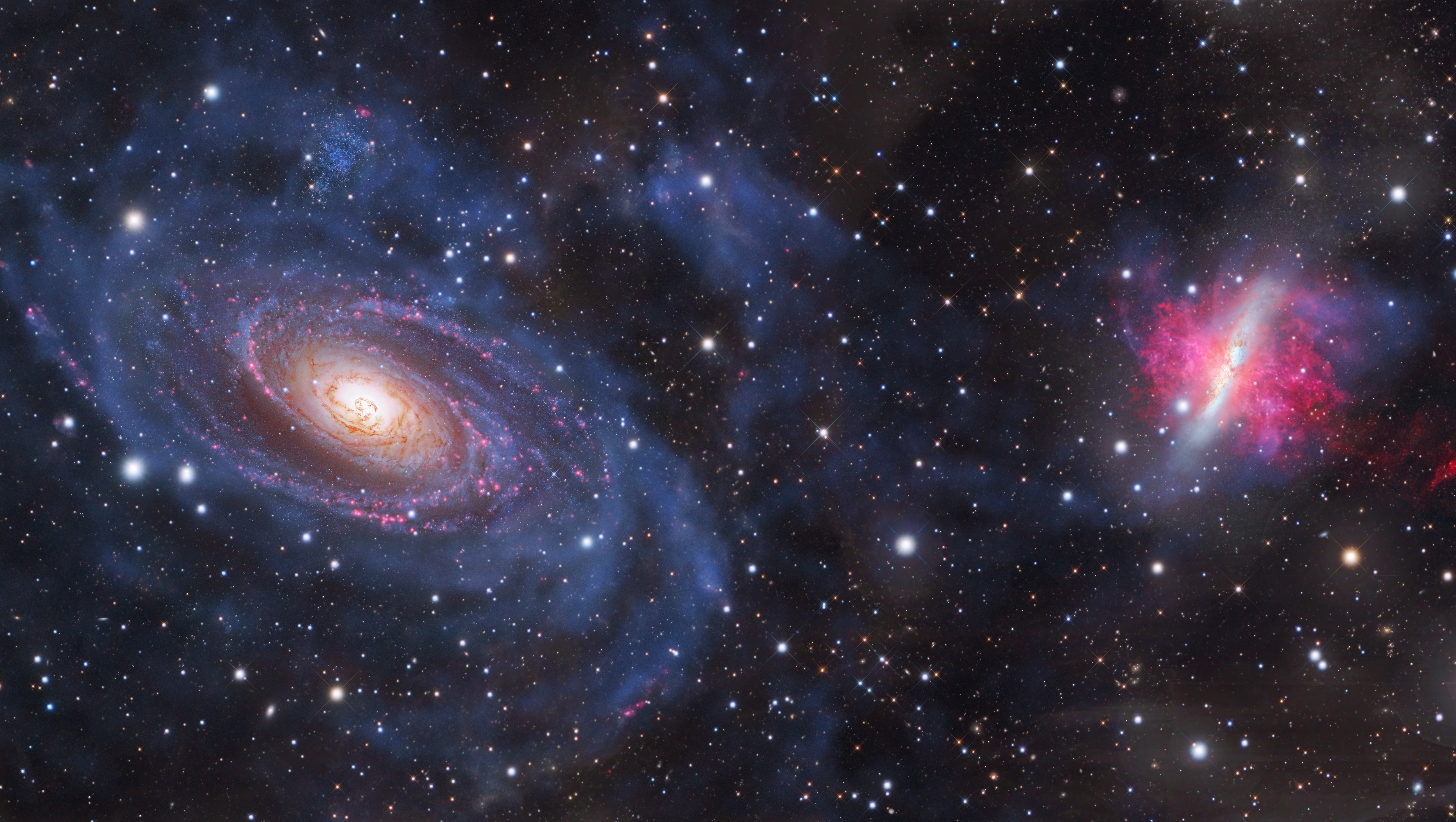
Just 12 million light-years away, the galaxies Messier 81 and 82 offer a nearby preview of the Milky Way-Andromeda merger.
Is the Universe finite or infinite? Does it go on forever or loop back on itself? Here’s what would happen if you traveled forever.
There are an estimated two trillion galaxies within the observable Universe. Most are already unreachable, and the situation only gets worse.
The laws of physics obey certain symmetries and defy others. It’s theoretically tempting to add new ones, but reality doesn’t agree.