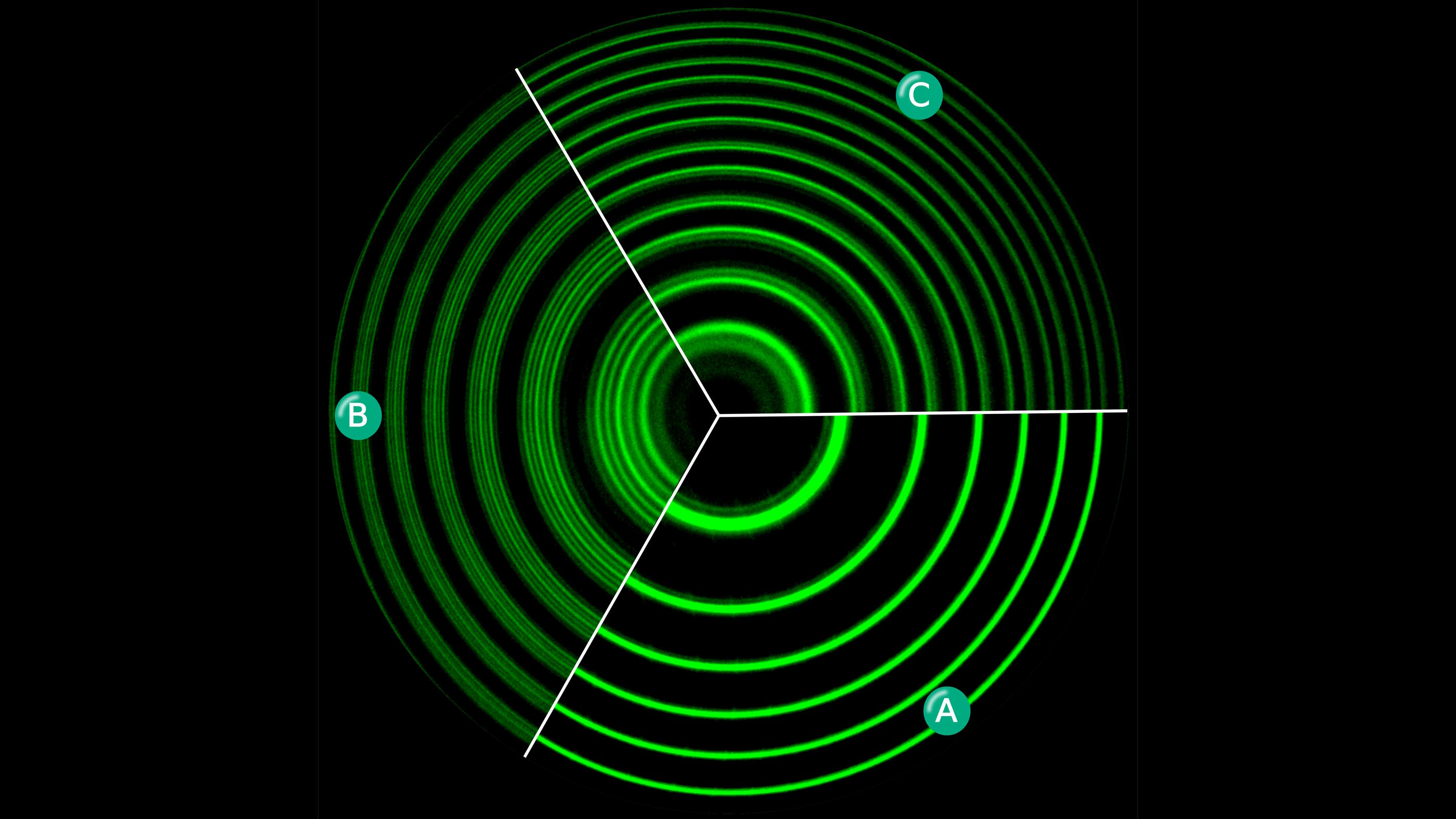
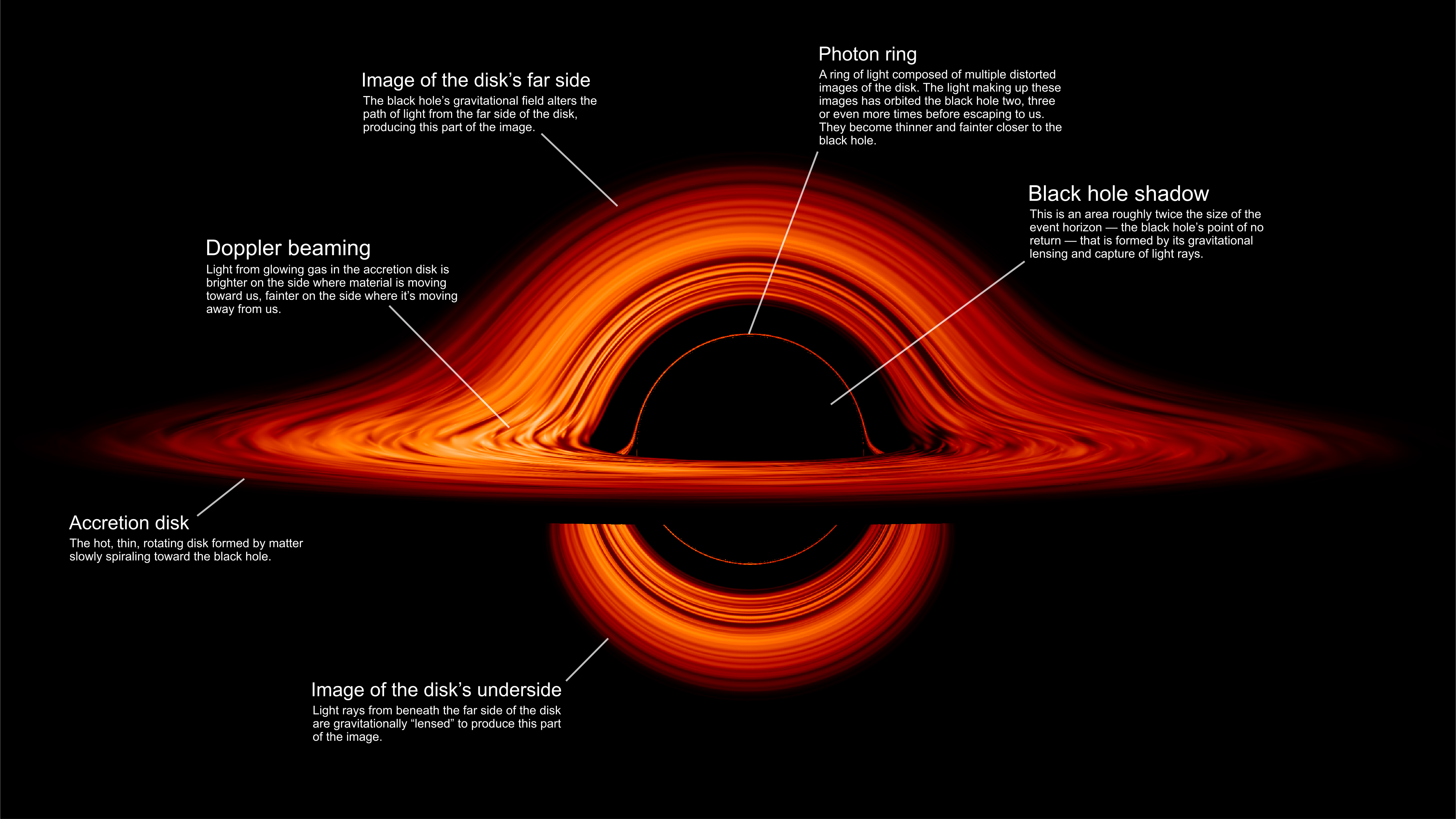
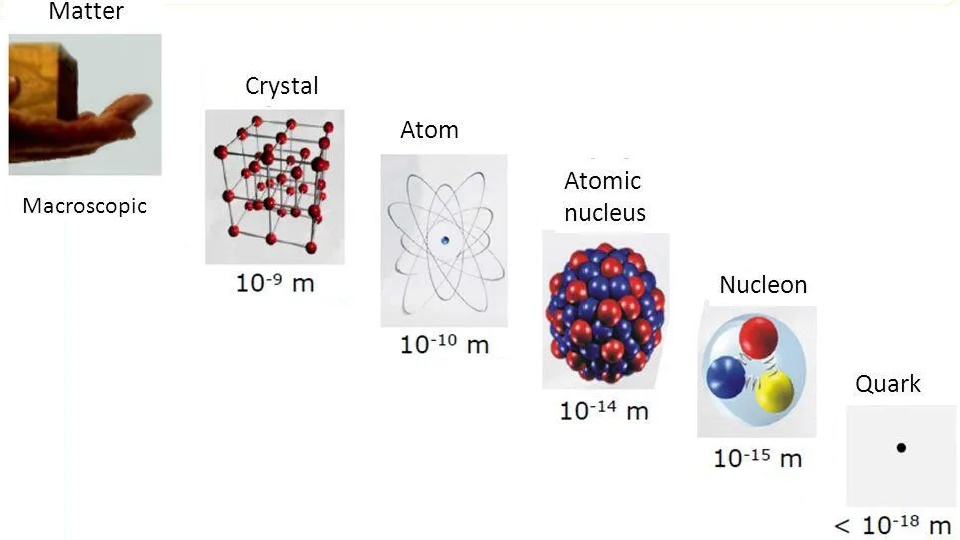
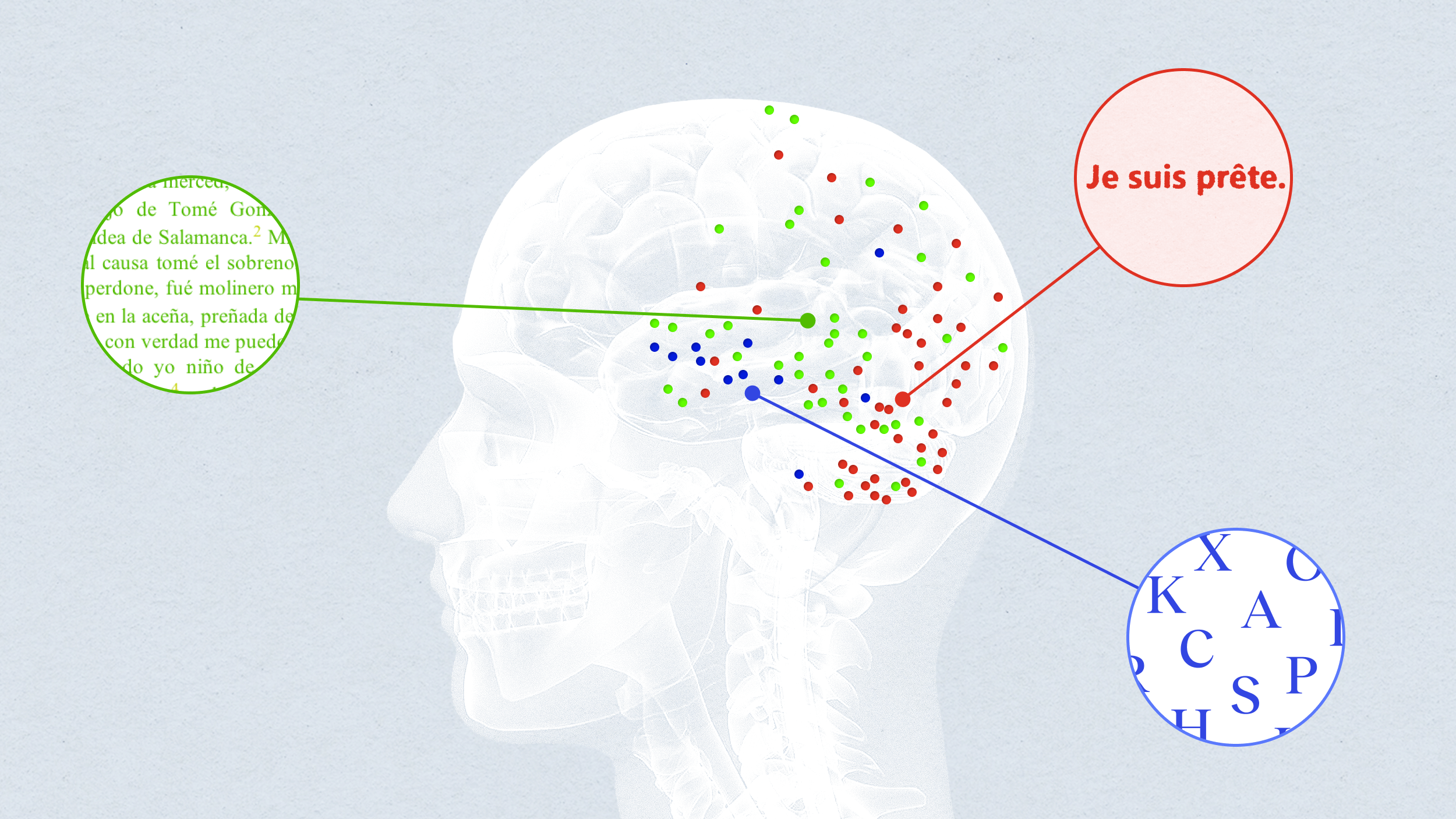
If light can’t be bent by electric or magnetic fields (and it can’t), then how do the Zeeman and Stark effects split atomic energy levels?
Search Results
You searched for: Structure
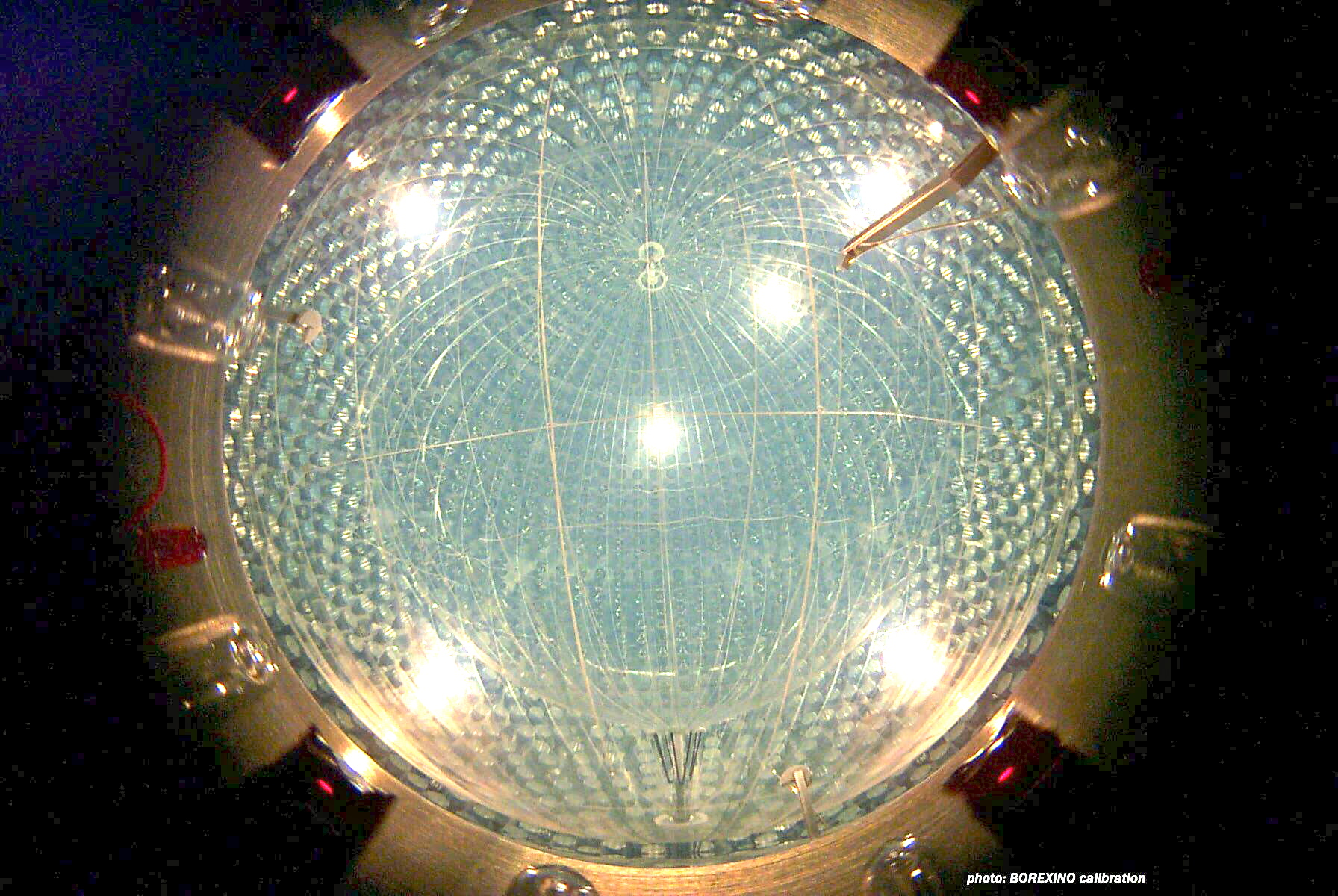
Back during the hot Big Bang, it wasn’t just charged particles and photons that were created, but also neutrinos. Where are they now?
According to Stephen Hawking, spontaneously emitted radiation should cause all black holes to decay. But we’ve never seen it: not even once.
The new corporate landscape demands an approach to leadership based on empowering the “inner CEO.”
When we divide matter into its fundamental, indivisible components, are those particles truly point-like, or is there a finite minimum size?
In the brain’s language-processing centers, some cells respond to one word, while others respond to strings of words together.
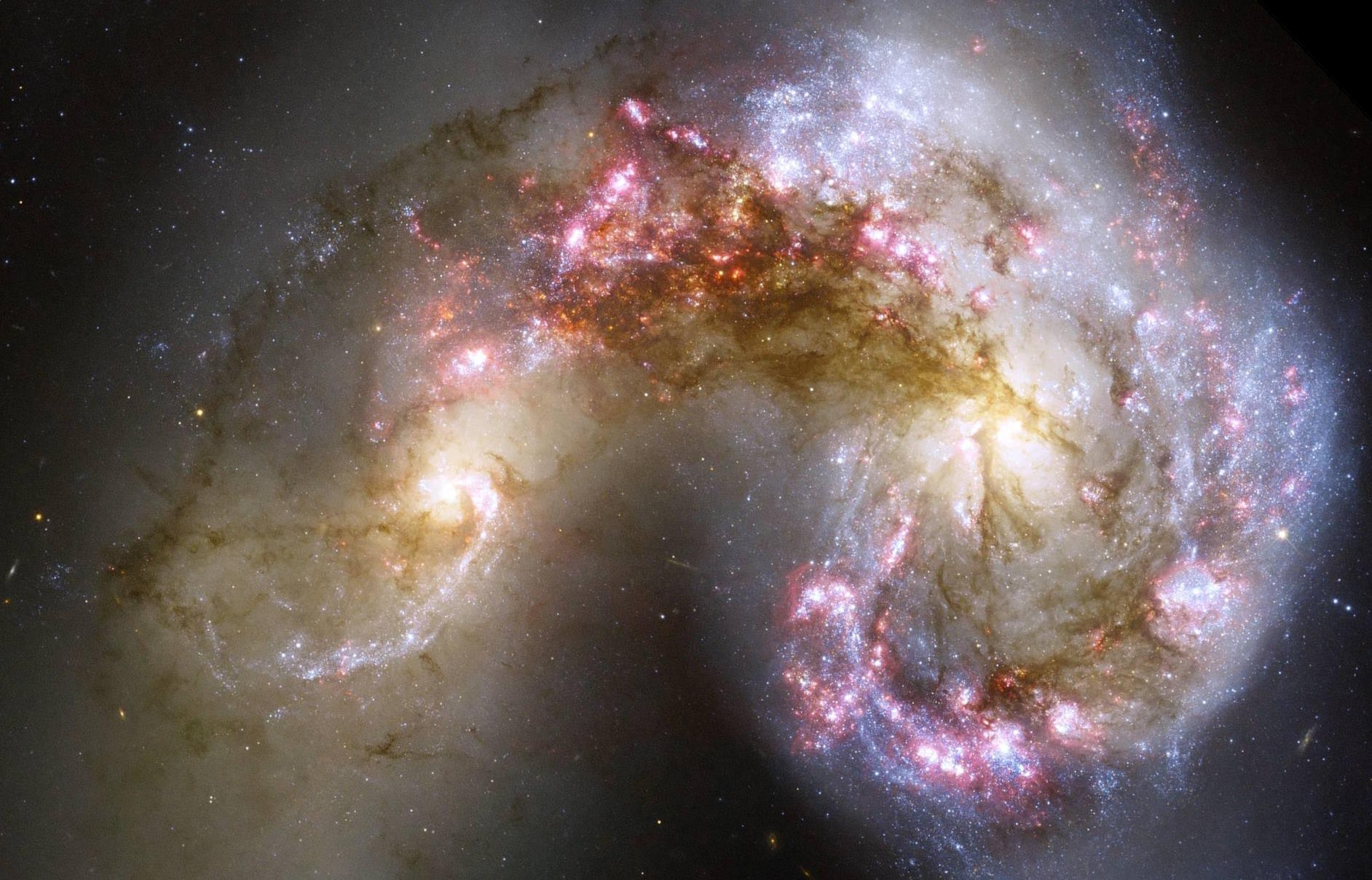
Ring galaxies are rare, but we think we know how they form. A new, early-stage version, the Bullseye galaxy, provides a new testing ground.
Event
The L&D team at S&P Global discuss how they build a culture of learning at their organization.
Your organization won’t become a “data democracy” organically — shared knowledge is key.
The Universe’s history, from cosmic inflation to the Big Bang to the present, is known. But whether it’s infinite or not is still a mystery.
Two parts of our Universe that seem to be unavoidable are dark matter and dark energy. Could they really be two aspects of the same thing?
Even with the best technology imaginable, you’d probably never be able to exist as a consciously aware brain in a vat.
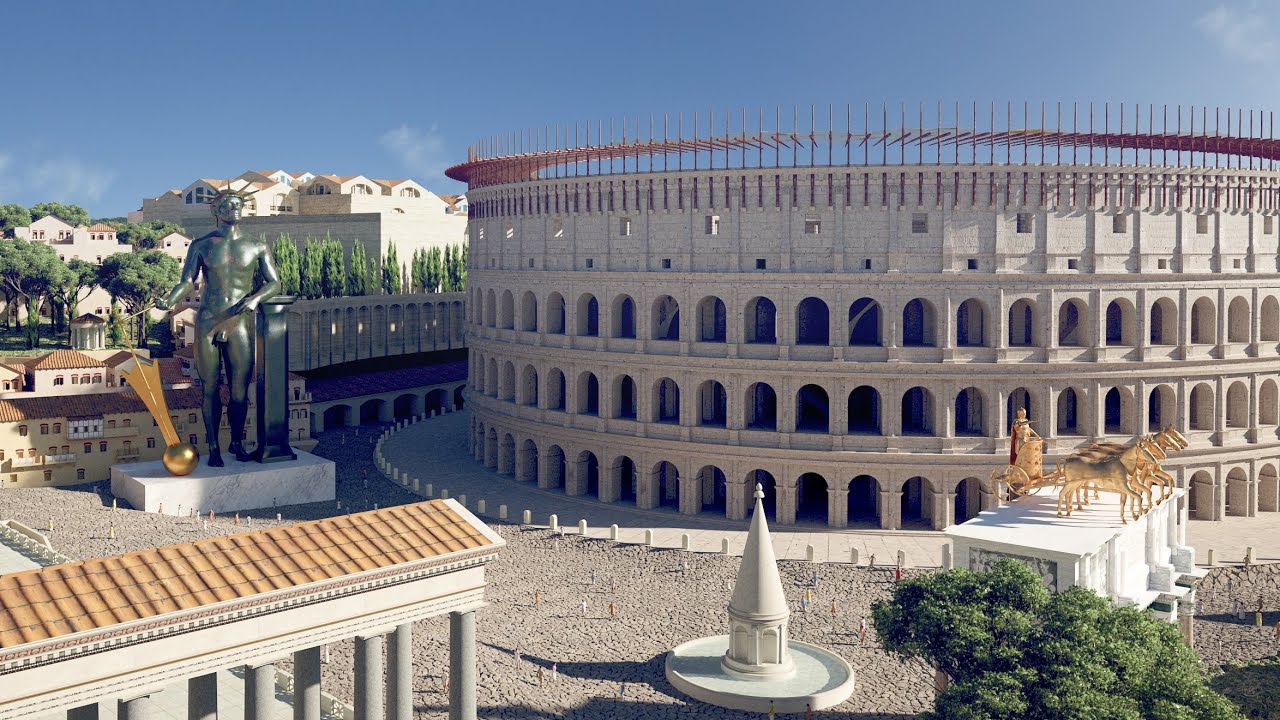
Archaeologist Bernard Frischer spent decades uploading the ruins of the Eternal City to the cloud. Here’s what it looks like.
Today, the star-formation rate across the Universe is a mere trickle: just 3% of what it was at its peak. Here’s what it was like back then.
One of the most promising dark matter candidates is light particles, like axions. With JWST, we can rule out many of those options already.
The arsons were no accident, archaeological evidence suggests.
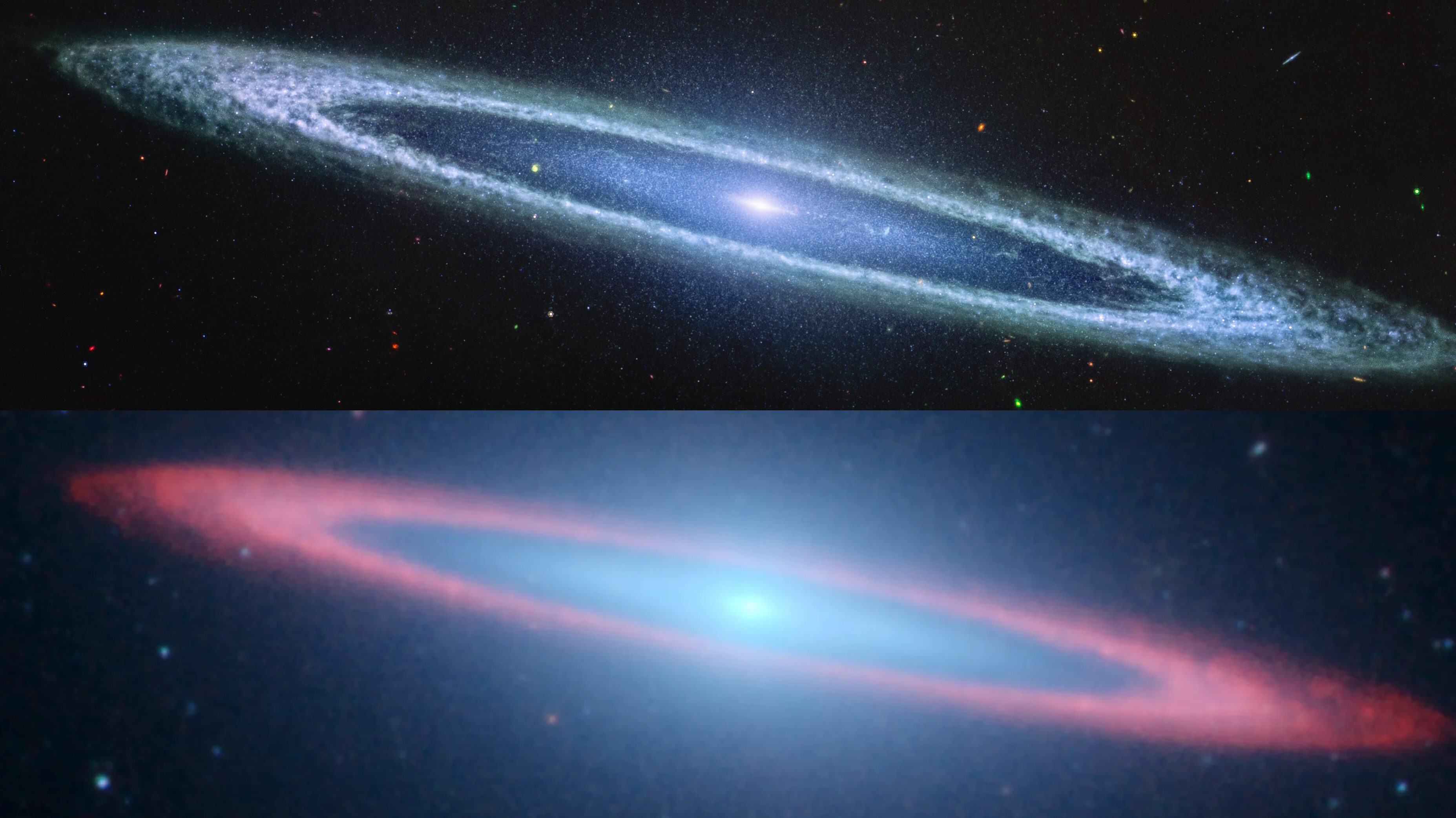
The Universe isn’t just expanding, the expansion is also accelerating. If that’s true, how will the Milky Way and Andromeda eventually merge?
The history of catastrophe shows that true resilience comes not from restoration, but from reinvention.
Cosmic inflation, proposed back in 1980, is a theory that precedes and sets up the hot Big Bang. After thorough testing, is it still valid?
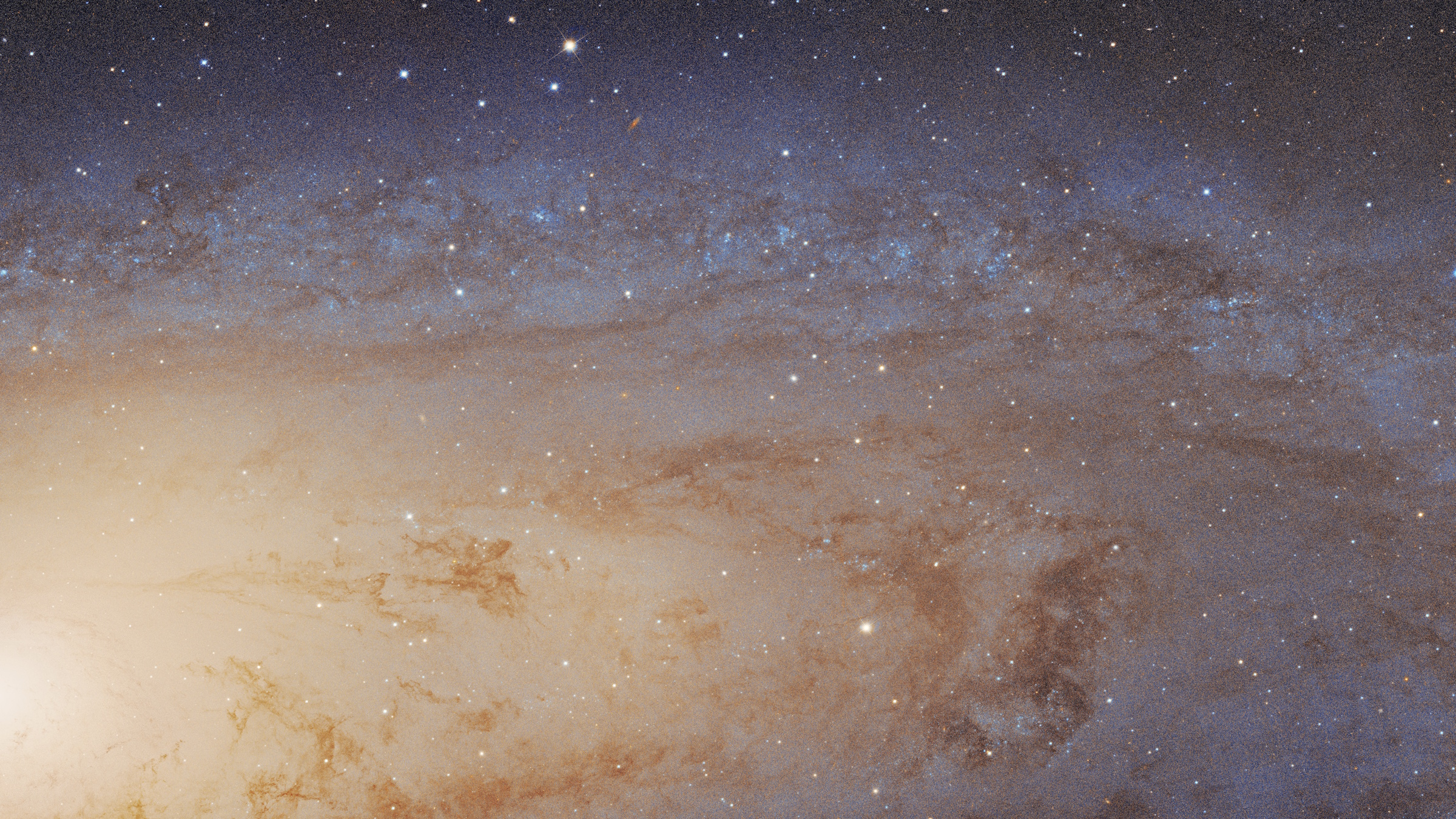
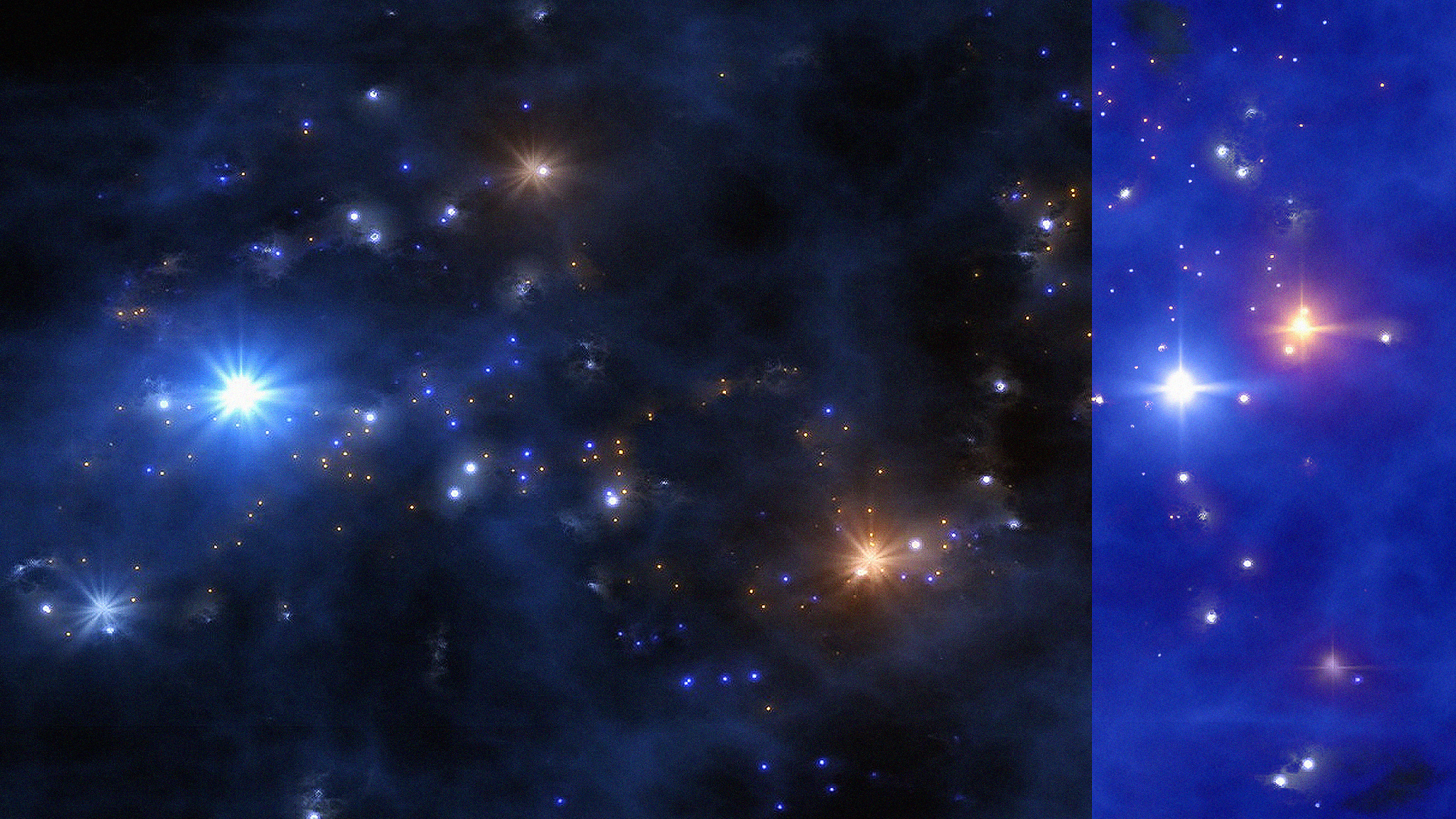
The full extent of the Andromeda galaxy, the nearest large galaxy to our own, has been entirely imaged with Hubble’s exquisite cameras.
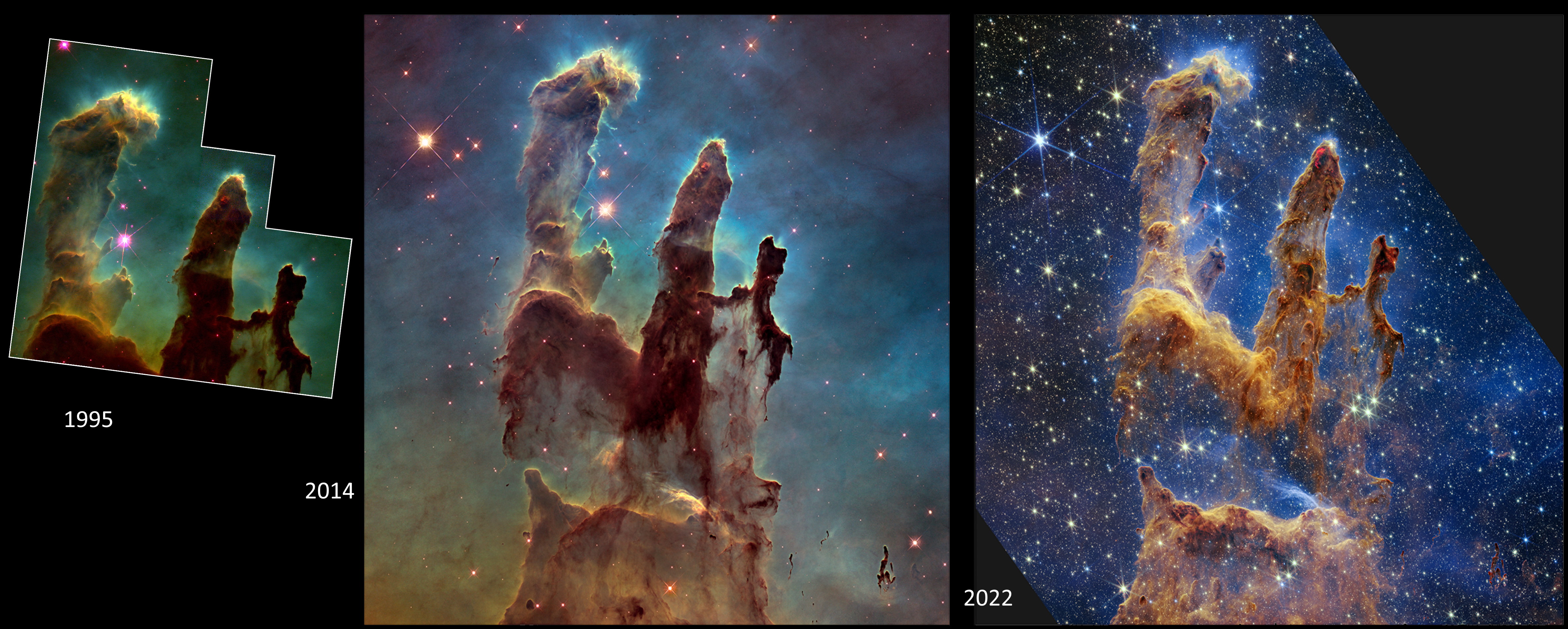
The last infant stars are finishing their formation inside these pillars of gas. The evaporation of those columns is almost complete.
If atoms are mostly empty space, then why can’t two objects made of atoms simply pass through each other? Quantum physics explains why.
New research from Big Think+ shows that leaders crave more feedback on their leadership and management skills.
Neuroscientist and author Bobby Azarian explores the idea that the Universe is a self-organizing system that evolves and learns.
There was a time where no starlight was visible throughout the entire cosmos. That time was short-lived: shorter than astronomers imagined.
We are prone to false memories. One reason is that we are biased toward remembering tidy endings for events, even if they didn’t exist.
It’s not just fun: DNA origami has the potential to revolutionize engineering at the nanoscopic scale.
Out beyond Neptune are some fascinating bodies left over from our Solar System’s formation. Could one of them truly be spectacular?
The future belongs to complexity.
Joseph Campbell argued that nearly every myth can be boiled down to a hero’s journey. Was he right?