Ethan Siegel
A theoretical astrophysicist and science writer, host of popular podcast "Starts with a Bang!"
Ethan Siegel is a Ph.D. astrophysicist and author of "Starts with a Bang!" He is a science communicator, who professes physics and astronomy at various colleges. He has won numerous awards for science writing since 2008 for his blog, including the award for best science blog by the Institute of Physics. His two books "Treknology: The Science of Star Trek from Tricorders to Warp Drive" and "Beyond the Galaxy: How humanity looked beyond our Milky Way and discovered the entire Universe" are available for purchase at Amazon. Follow him on Twitter @startswithabang.

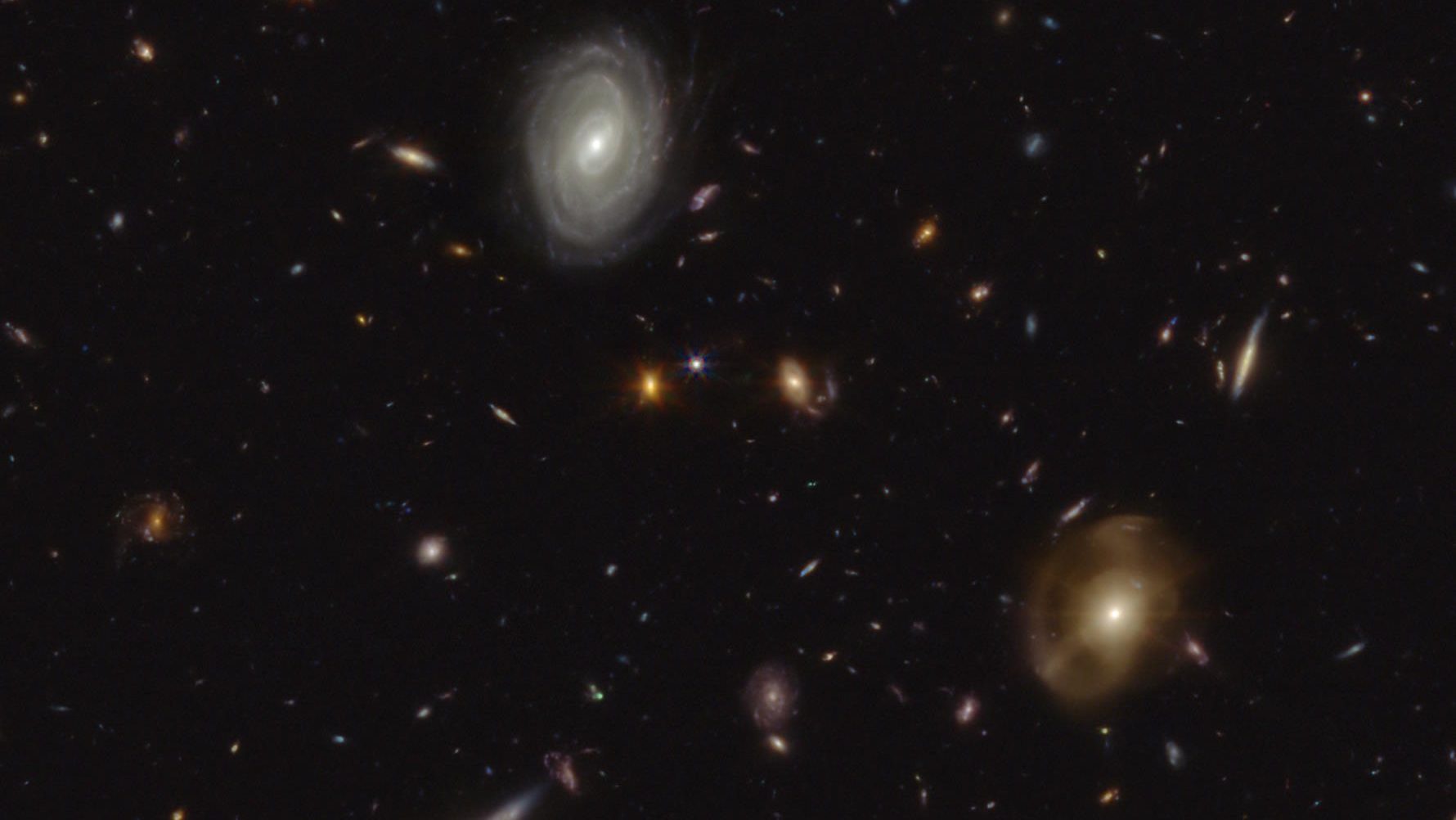
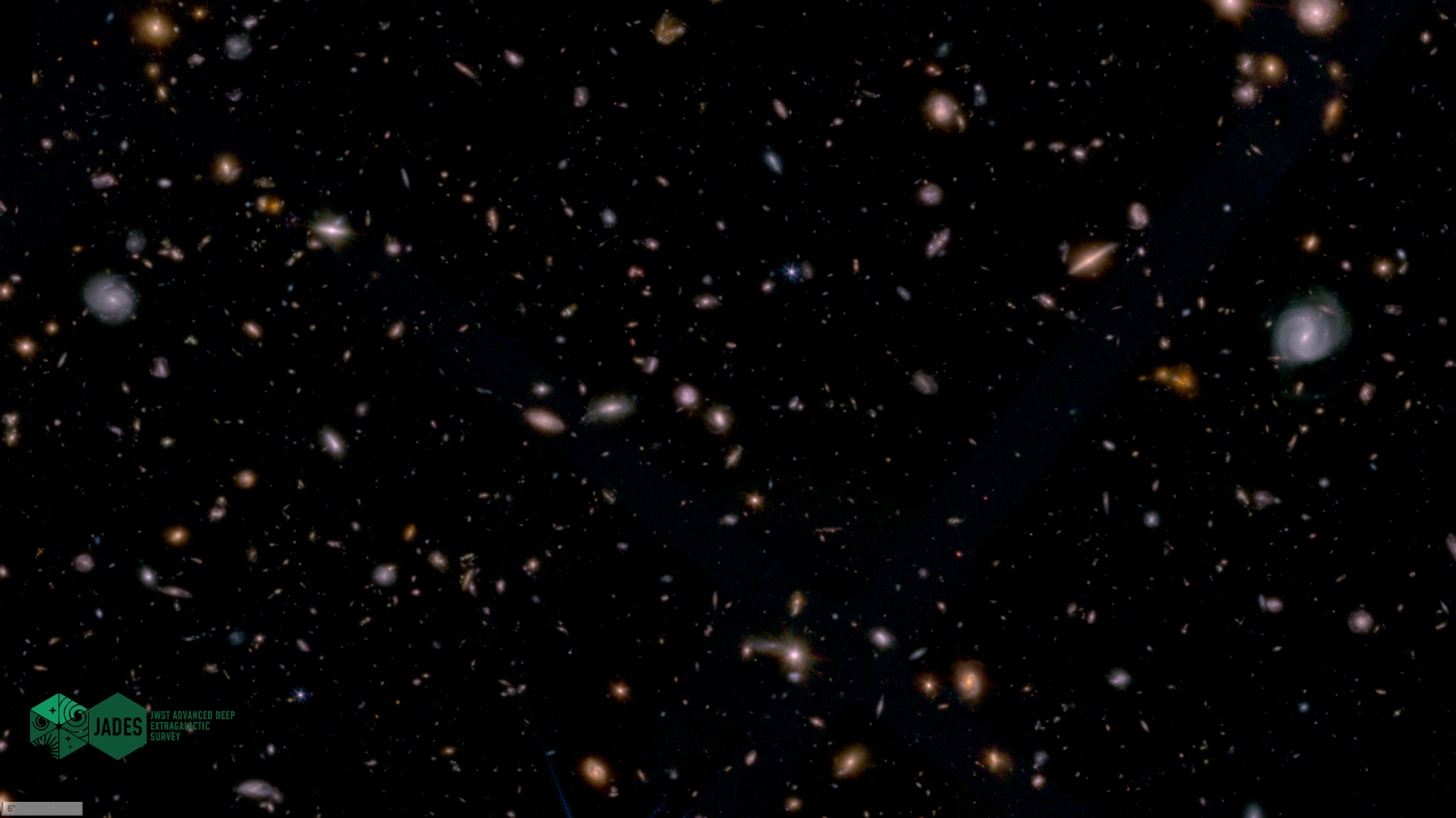
In 2022, Hubble owned the record for most distant galaxy. Today, that galaxy is down to the 9th most distant object. Thanks, JWST.
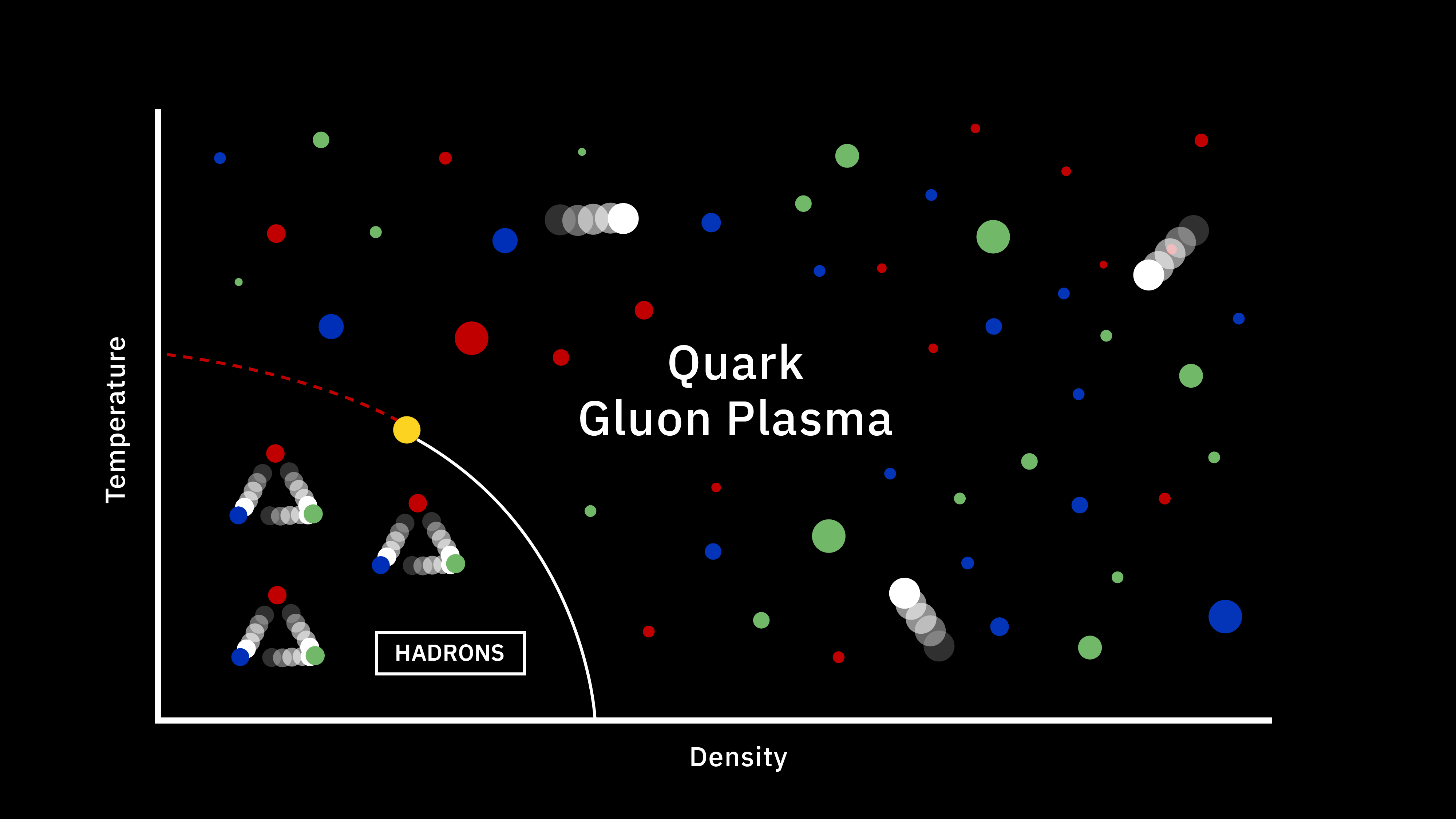
For a substantial fraction of a second after the Big Bang, there was only a quark-gluon plasma. Here’s how protons and neutrons arose.
In the very early Universe, practically all particles were massless. Then the Higgs symmetry broke, and suddenly everything was different.
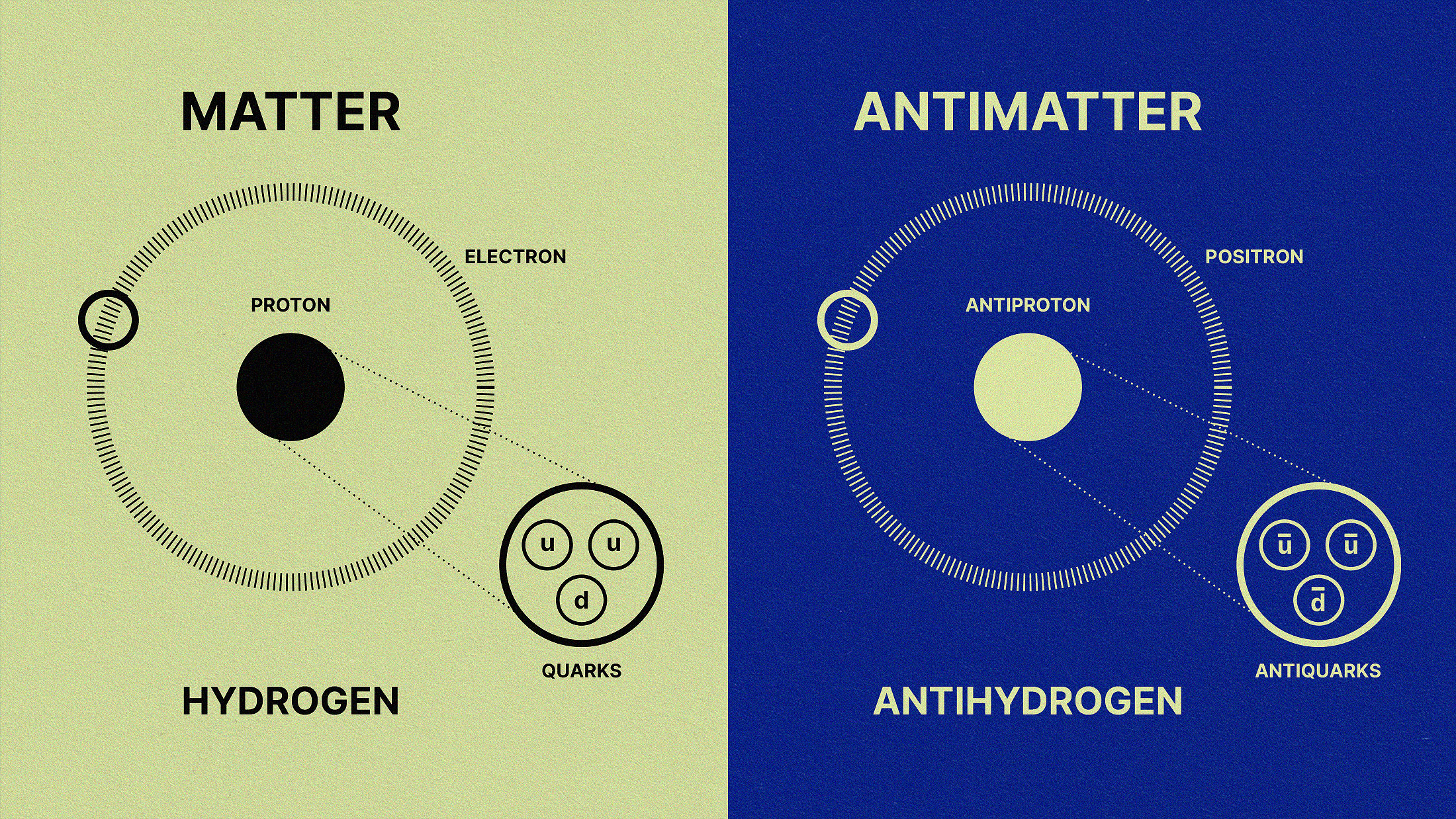
In the earliest stages of the hot Big Bang, equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have existed. Why aren’t they equal today?
When the hot Big Bang first occurred, the Universe reached a maximum temperature never recreated since. What was it like back then?
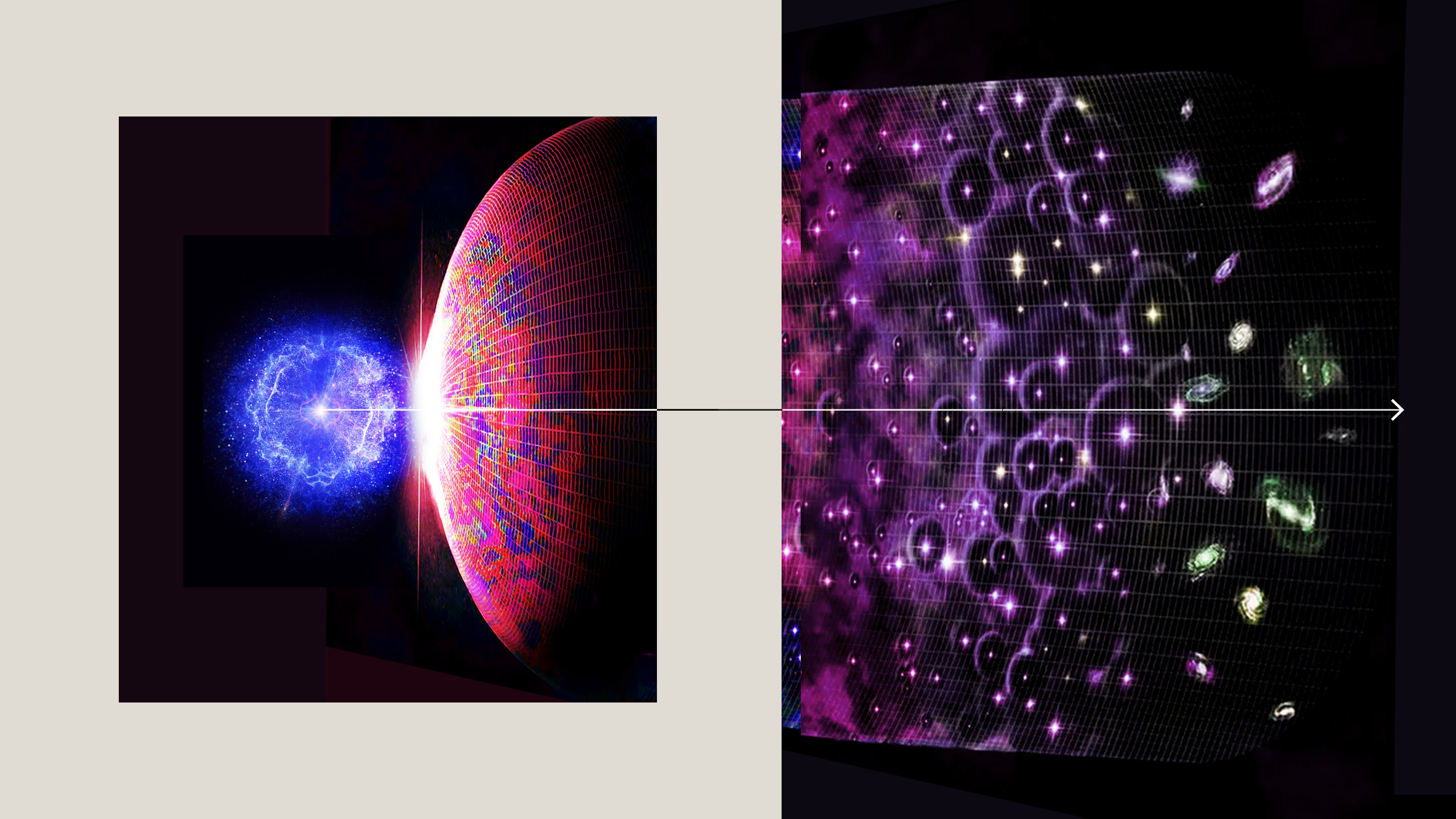
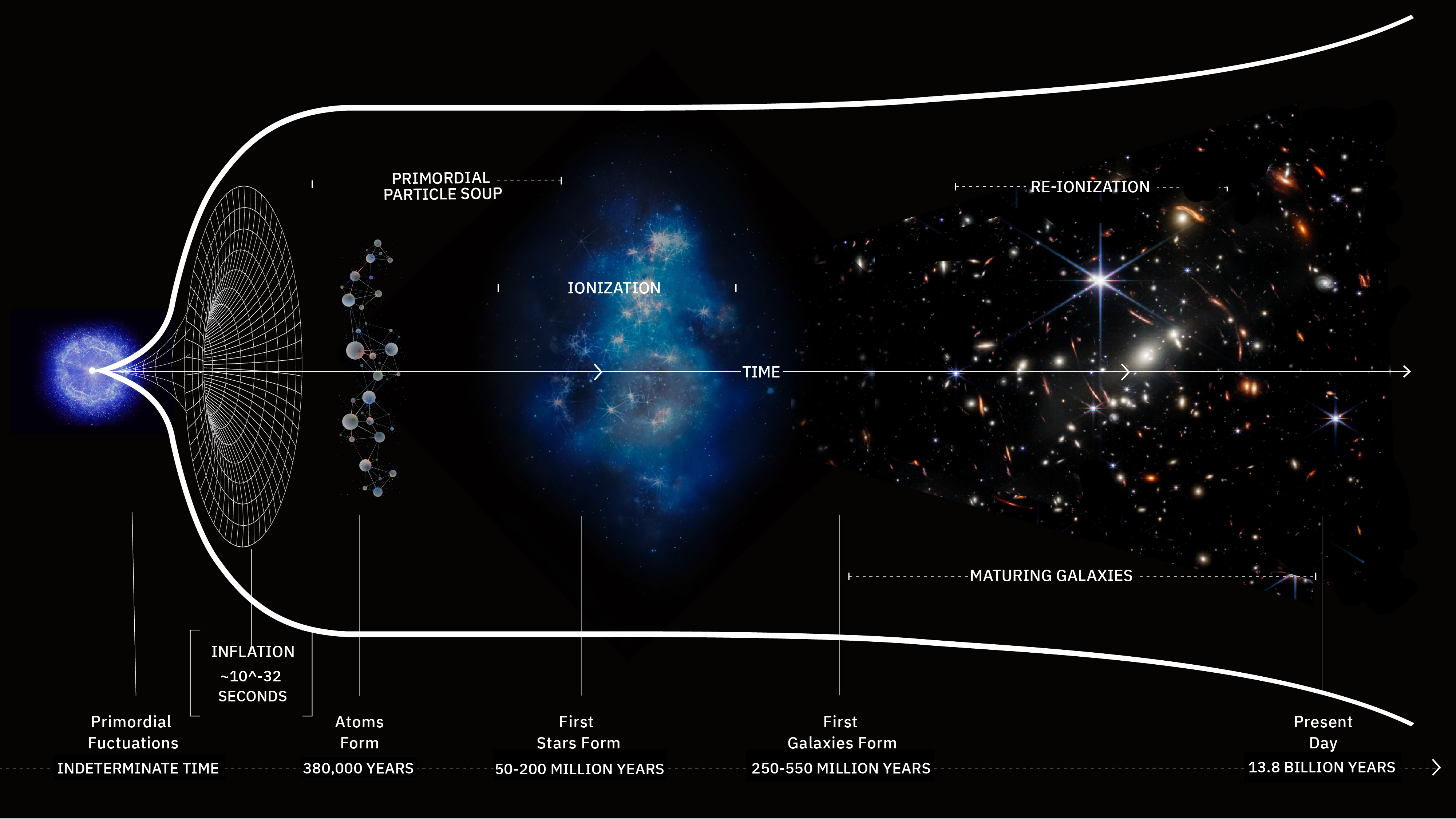
Some 13.8 billion years ago, the Universe became hot, dense, and filled with high-energy quanta all at once. Here’s what it was like.
Perhaps the most remarkable fact about the Universe is simply that it, and everything in it, exists. But what’s the reason why?
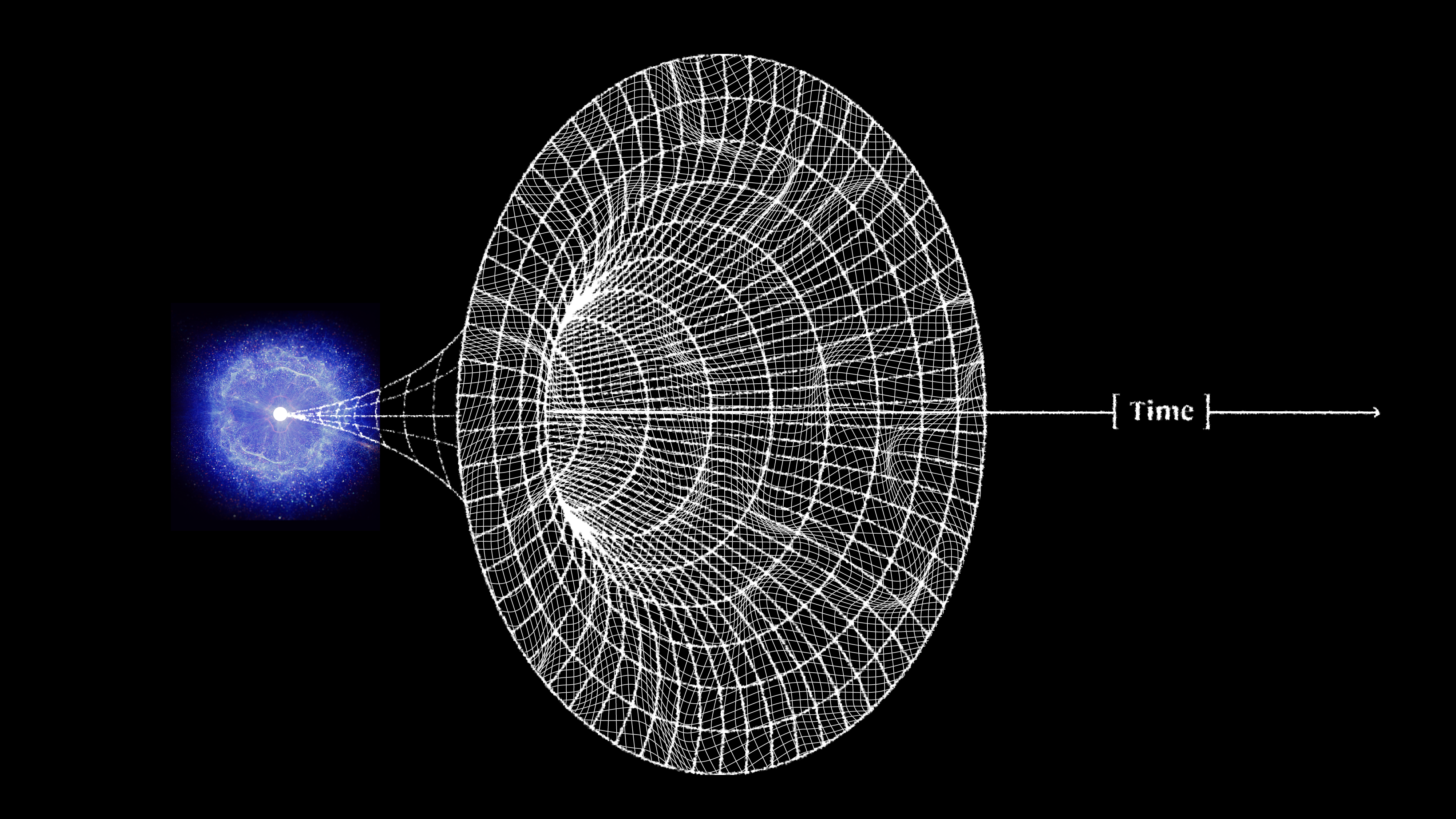
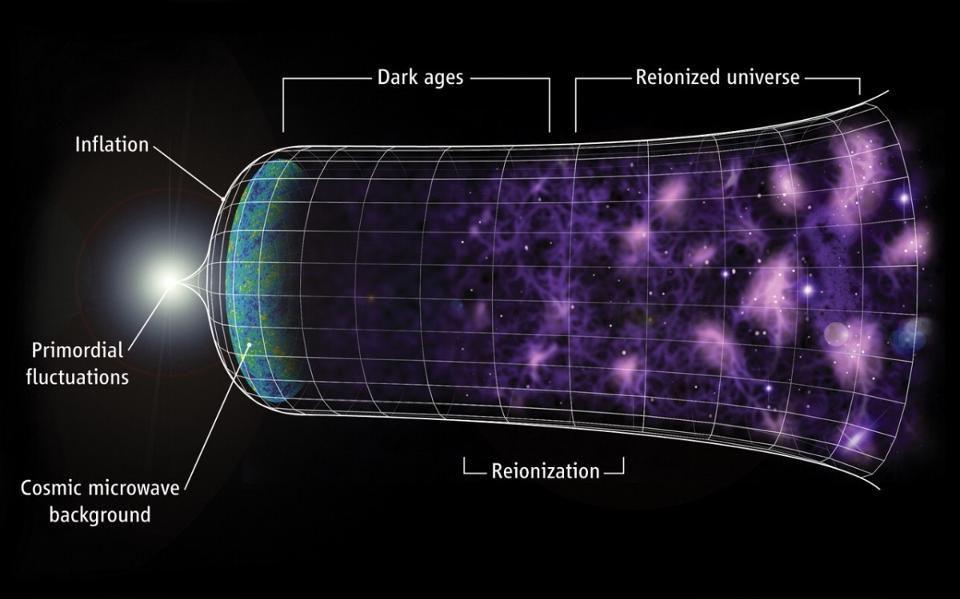
Cosmic inflation is the state that preceded and set up the hot Big Bang. Here’s what the Universe was like during that time period.
With LEDs bringing brighter nighttime lighting than ever before, and thousands of new satellites polluting the skies, astronomy needs help.
Finding alien technology on the seafloor would be truly incredible. This extraordinary claim, however, is debunked by the actual evidence.
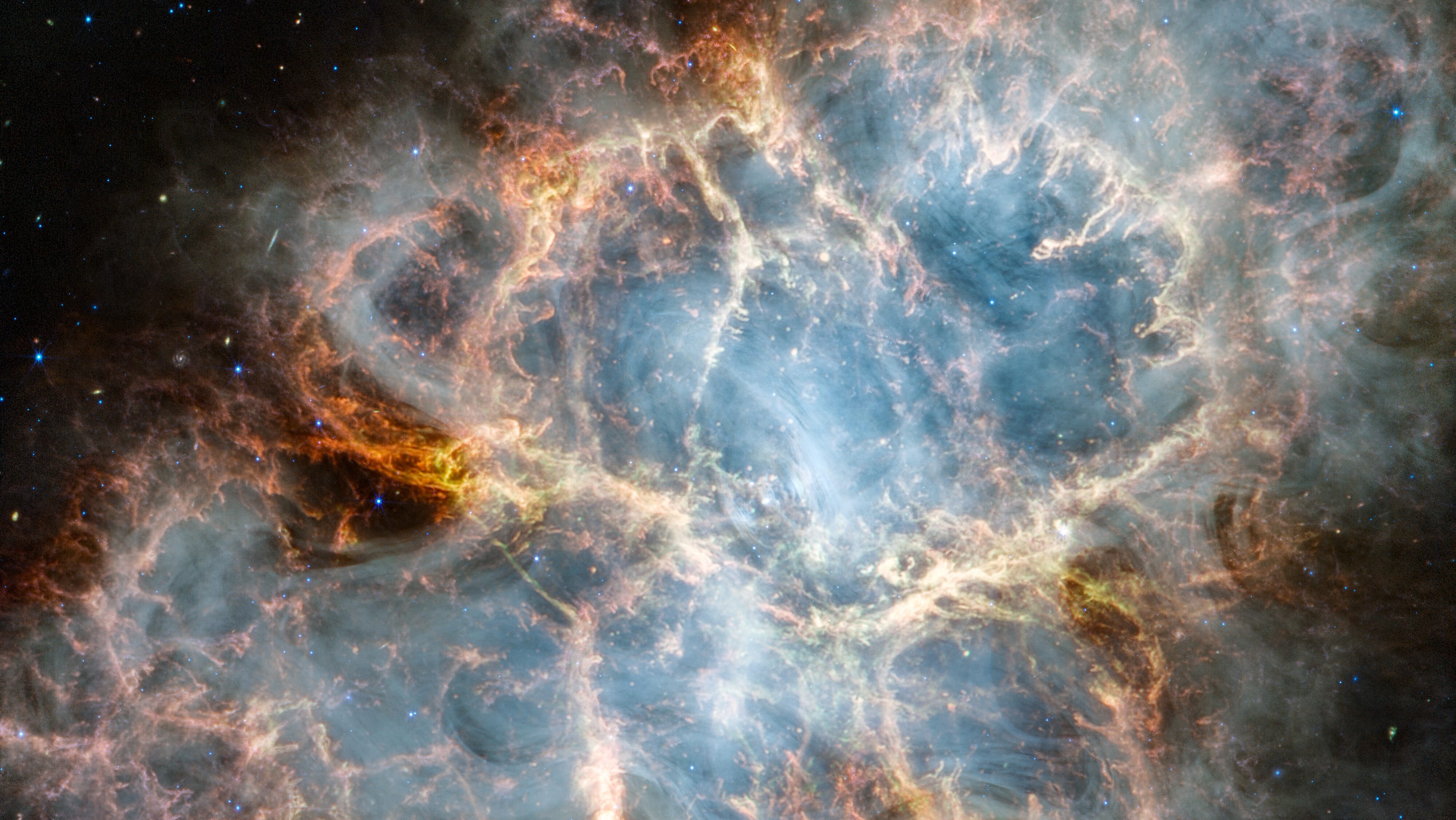
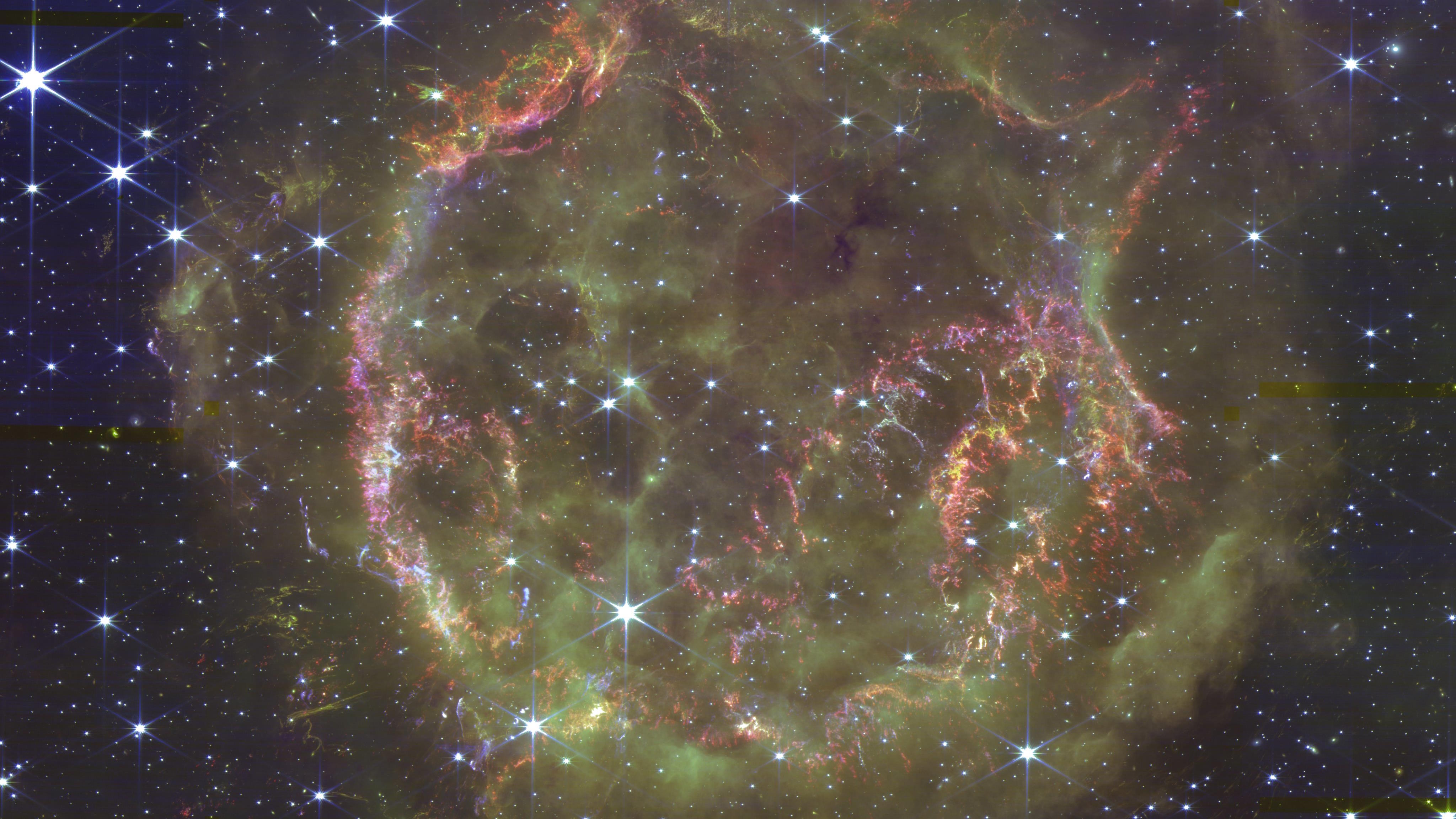
In 1667, a core-collapse supernova happened right here in the Milky Way, invisible to all humans. ~350 years later, here’s what JWST sees.
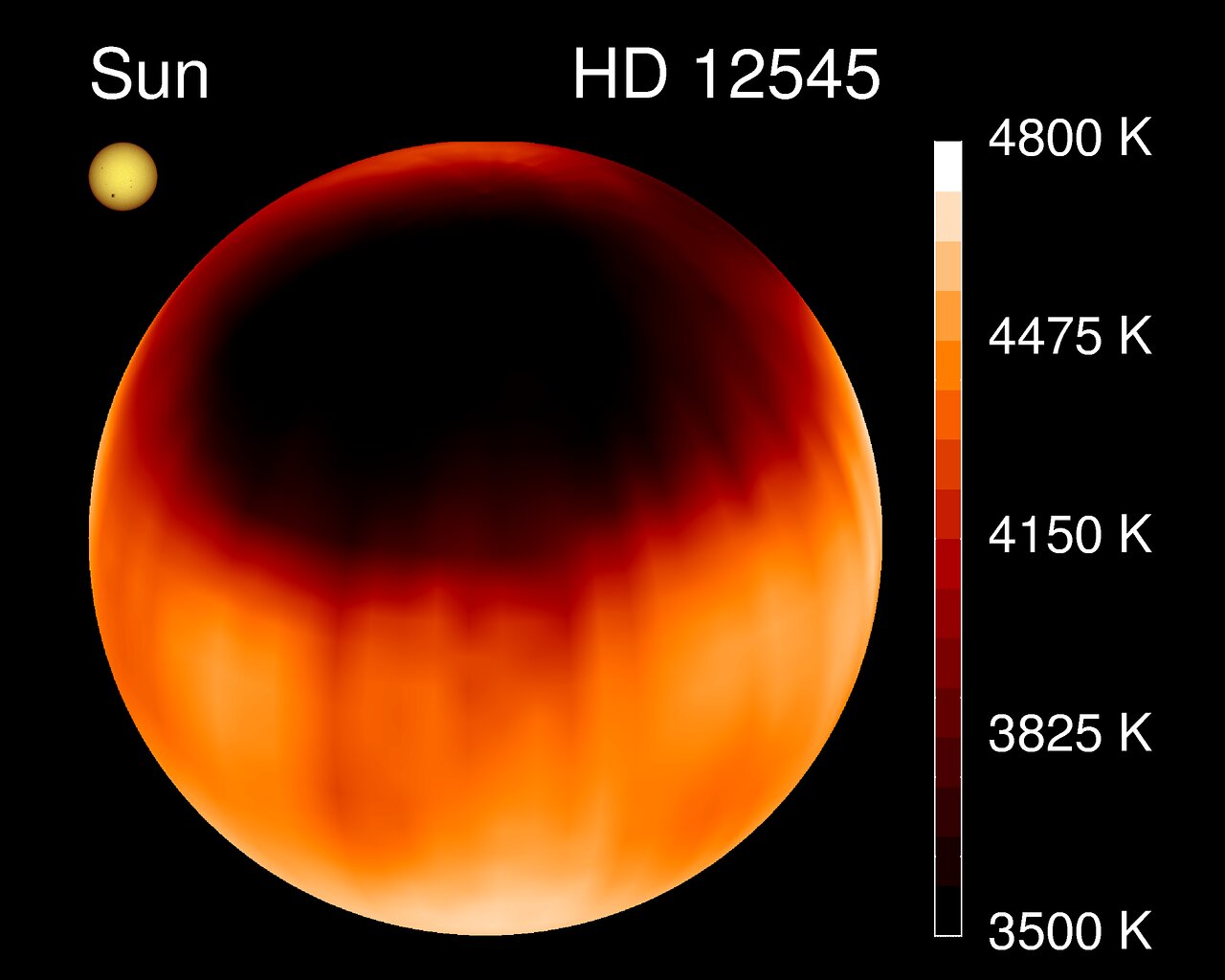
When we look at our Sun, its properties are incredibly constant, varying by merely ~0.1% over time. But all stars don’t play by those rules.
In our Universe, all stable atomic nuclei have protons in them; there’s no stable “neutronium” at all. But what’s the reason why?
All matter particles can act as waves, and massless light waves show particle-like behavior. Can gravitational waves also be particle-like?
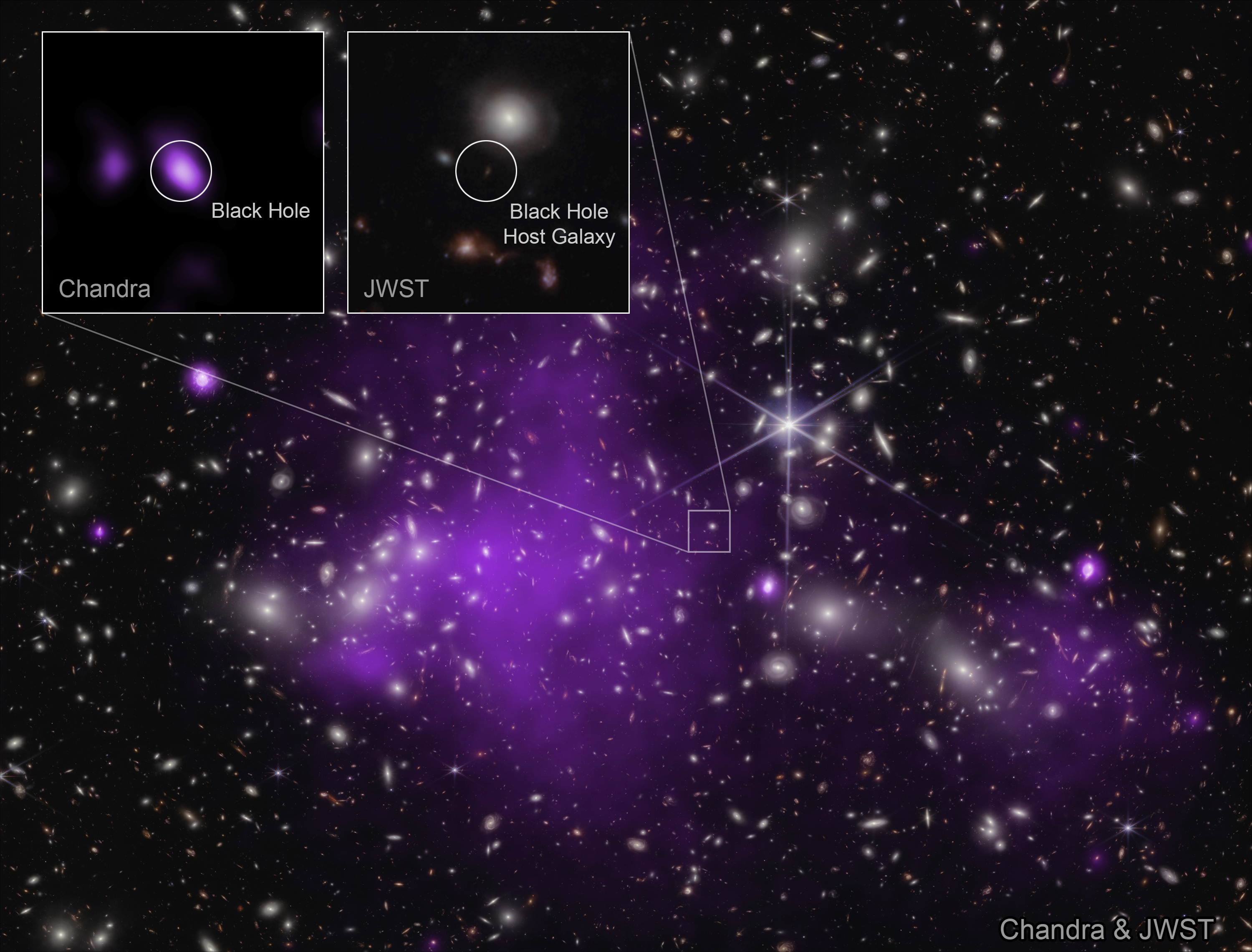
With JWST, Chandra, and gravitational lensing combined, evidence has emerged for the earliest black hole ever. And wow, is it a surprise!
Sometimes, going “deeper” doesn’t reveal the answers you seek. By viewing more Universe with better precision, ESA’s Euclid mission shines.
While humanity has been skywatching since ancient times, much of our cosmic understanding has come about only recently. Very recently.
If the Universe is expanding, and the expansion is accelerating, what does that tell us about the cause of the expanding Universe?
Everything we observe beyond our Local Group is speeding away from us, omnidirectionally. If the Universe is expanding, where is the center?
In 1054, a core-collapse supernova occurred 6500 light-years away. In 2023, JWST imaged the remnant, and might solve a massive mystery.
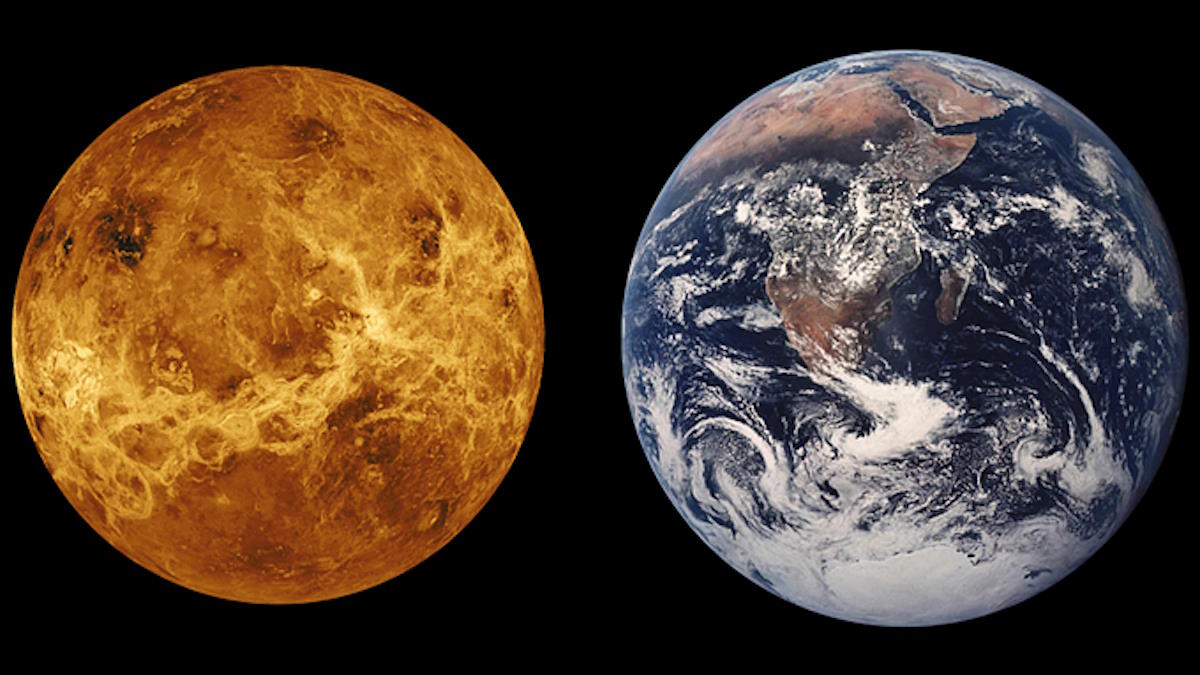
Out of the four rocky planets in our Solar System, only Earth presently has plate tectonics. But billions of years ago, Venus had them, too.
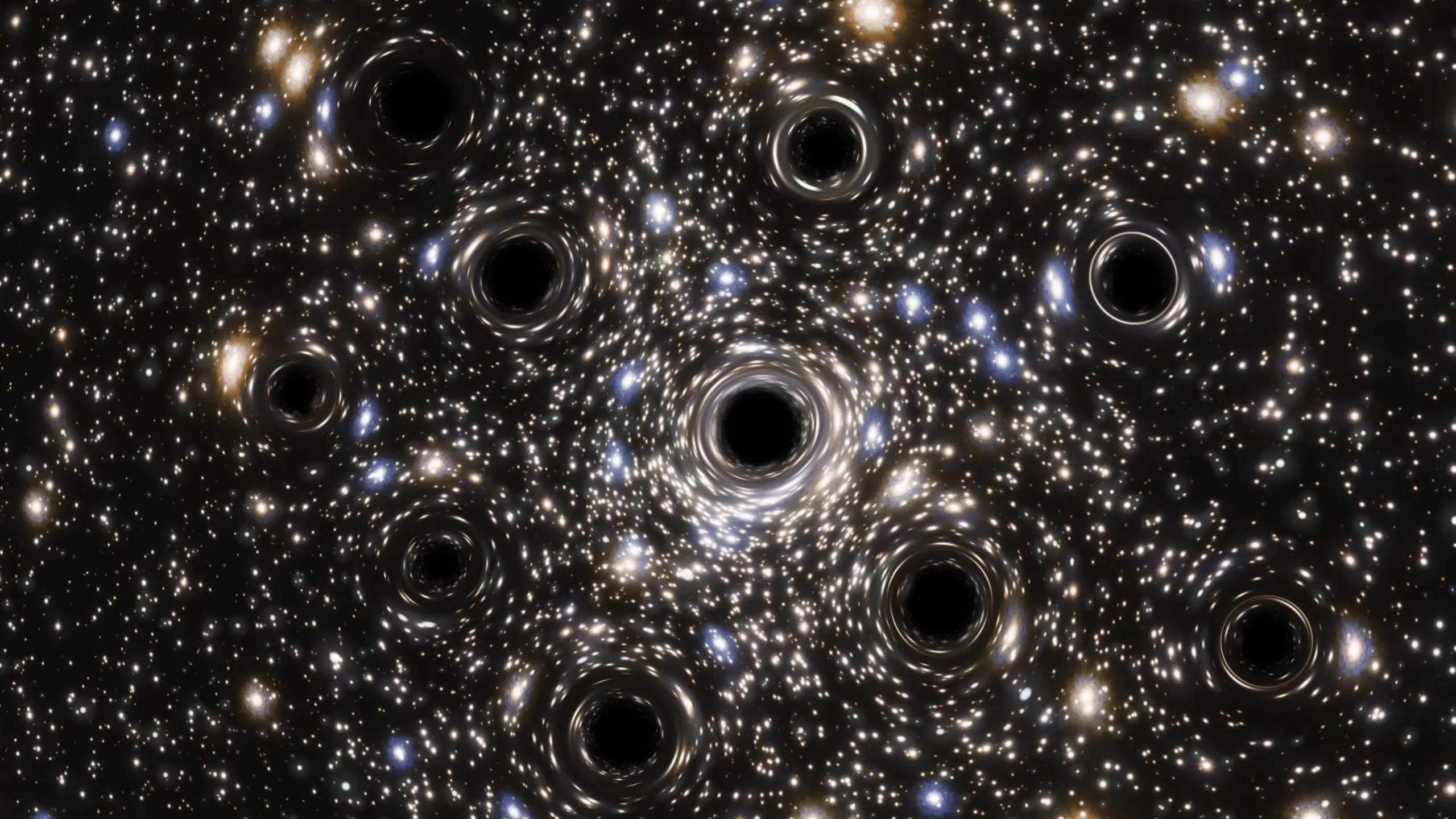
For the first time, astronomers have created a data-driven estimate for how many black holes are in our Universe: more than anyone expected.
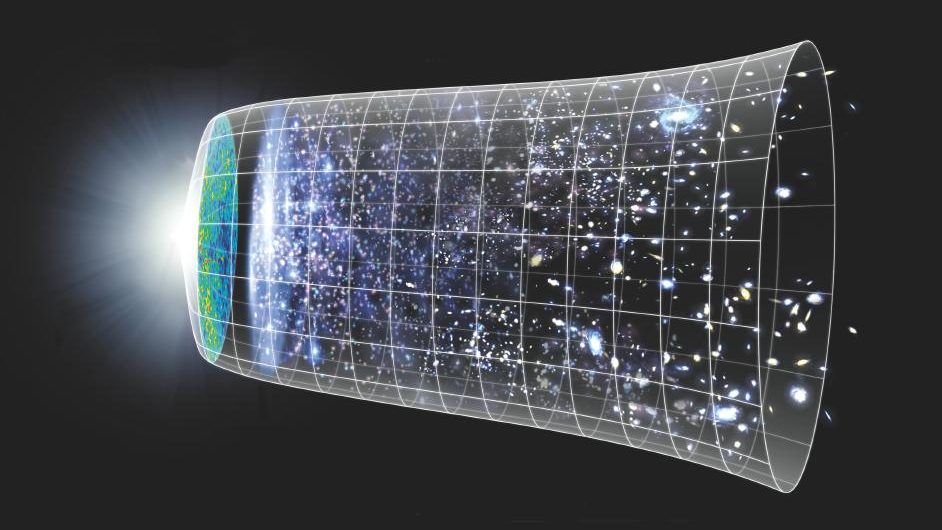
If you said “with the Big Bang,” congratulations: that was our best answer as of ~1979. Here’s what we’ve learned in all the time since.
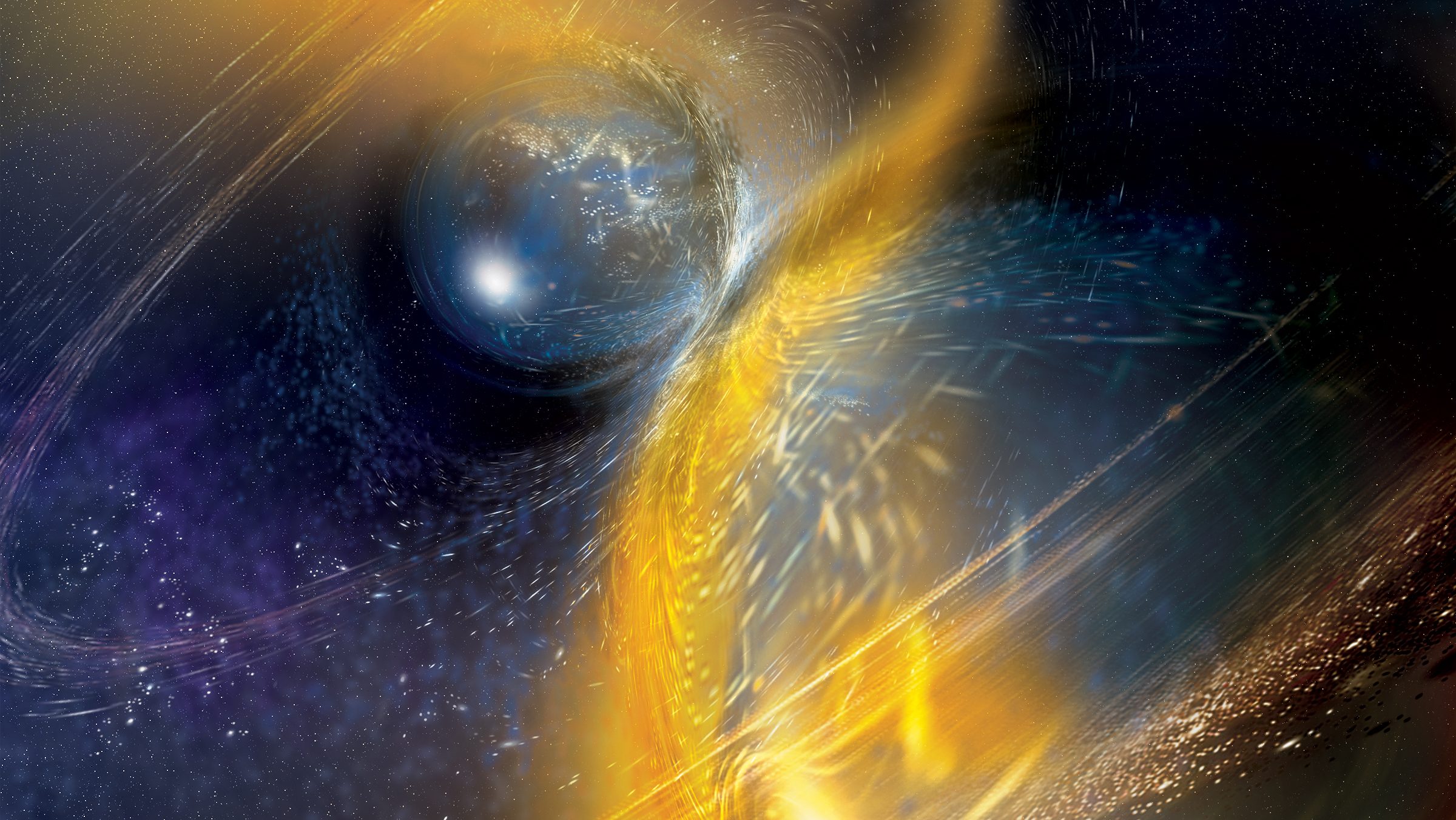
In 2017, a kilonova sent light and gravitational waves across the Universe. Here on Earth, there was a 1.7 second signal arrival delay. Why?
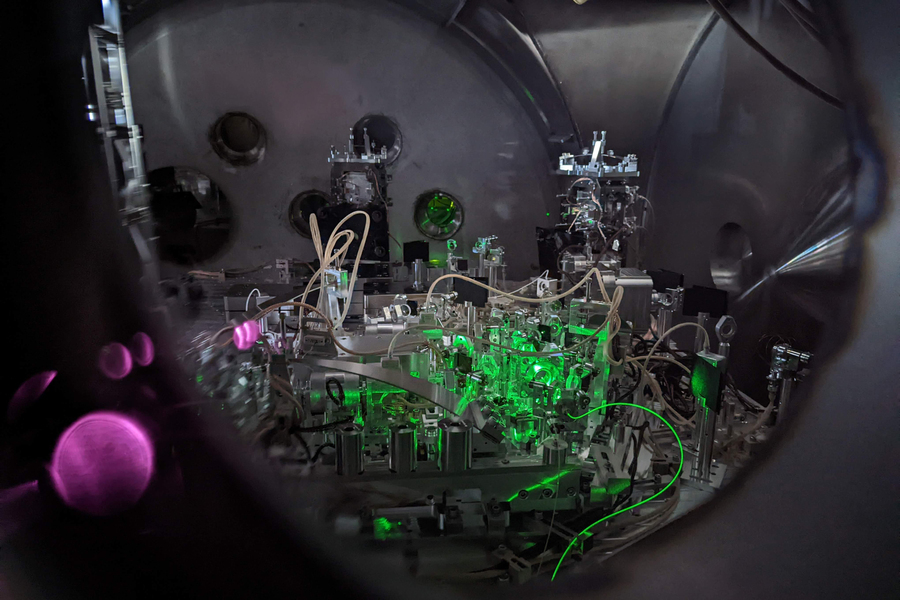
There’s a quantum limit to how precisely anything can be measured. By squeezing light, LIGO has now surpassed all previous limitations.
The second law of thermodynamics is an inviolable law of reality. Here’s what everyone should know about closed, open, and isolated systems.
JWST has already broken many of Hubble’s cosmic records. Perhaps additional record-breakers already exist within this data-rich image?
Back during the hot Big Bang, it wasn’t just charged particles and photons that were created, but also neutrinos. Where are they now?
Although we still don’t know the question, we know that the answer to life, the Universe, and everything is 42. Here are 5 possibilities.
Nothing lives forever, at least, not in the physical Universe. But relativity allows us to get closer than ever, from one perspective.