Space & Astrophysics
Our own galaxy, the Milky Way, is both completely normal and absolutely remarkable in a number of ways. Here’s the story of our cosmic home.
Millennia ago, philosophers like Anaximander grasped that nature is the ultimate recycler.
On the largest cosmic scales, galaxies line up along filaments, with great clusters forming at their intersection. Here’s how it took shape.
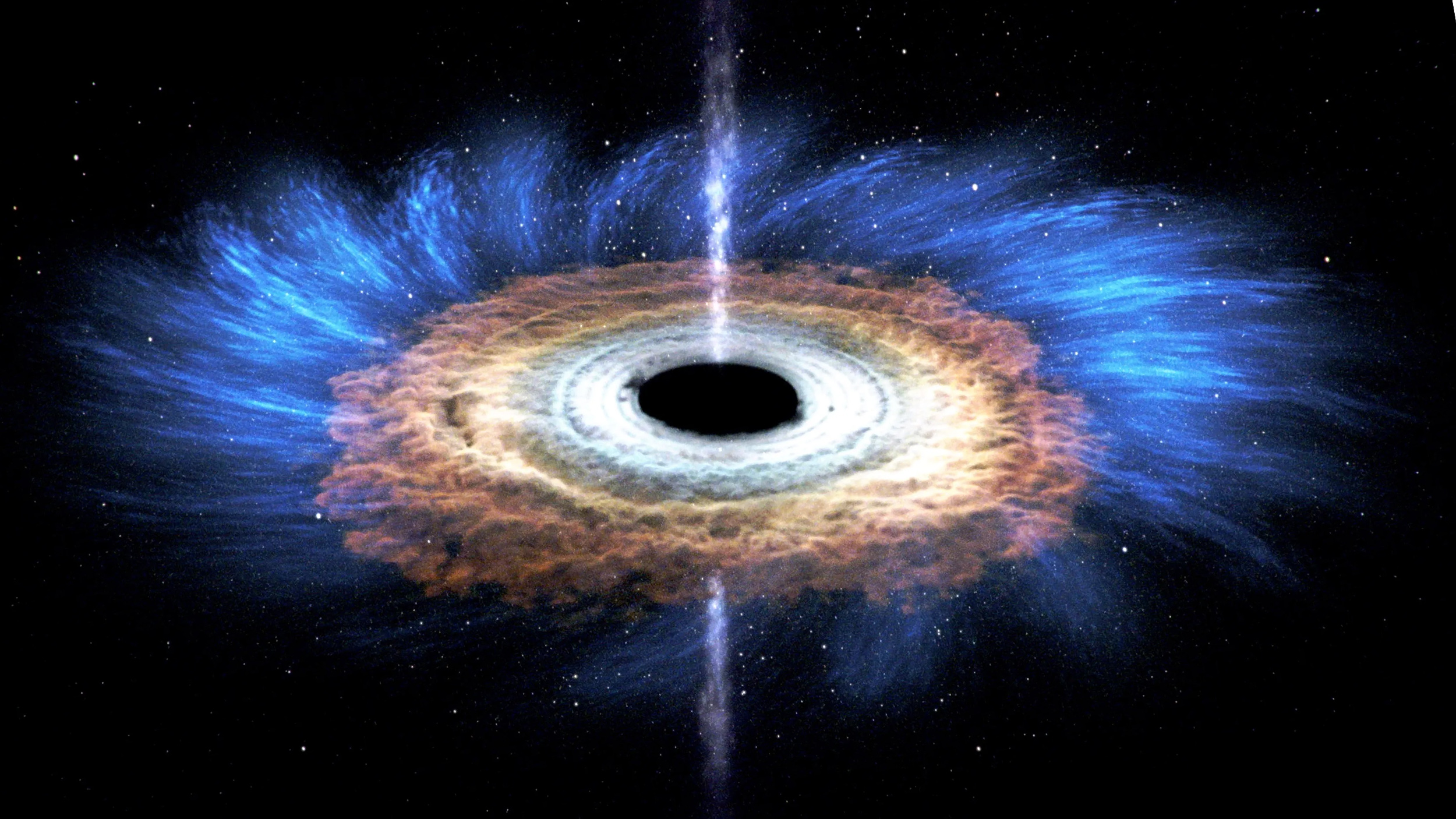
Want to avoid getting “spaghettified” by a black hole? Steer clear of the smaller ones.
Astronomers claim to have found structures so large, they shouldn’t exist. With such biased, incomplete observations, perhaps they don’t.
Here in our Solar System, we only have one star: a singlet. For many systems, including the highest-mass ones, that’s anything but the norm.
The answer is set to change in the year 2113, a recent estimate suggests.
The pattern 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, etc., is the Fibonacci sequence. It shows up all over nature. But what’s the full explanation behind it?
Two scientists recently wagered a bottle of whiskey. The bet? Whether we’ll find evidence of advanced extraterrestrial life in the next 15 years.
Life became a possibility in the Universe as soon as the raw ingredients were present. But living, inhabited worlds required a bit more.
Today, supermassive black holes and their host galaxies tell a specific story in terms of mass. But JWST reveals a different story early on.
Observations of an enormous cosmic structure, dubbed the “Big Ring,” seem to violate the Copernican principle.
The most celebrated genius in human history didn’t just revolutionize physics, but taught many valuable lessons about living a better life.
Our cosmic home, planet Earth, has been through a lot over the past 4.5 billion years. Here are some of its most spectacular changes
Fire was crucial to the evolution of human technology. That’s why alien species stuck in the “oxygen bottleneck” may be forever primitive.
For every proton, there were over a billion others that annihilated away with an antimatter counterpart. So where did all that energy go?
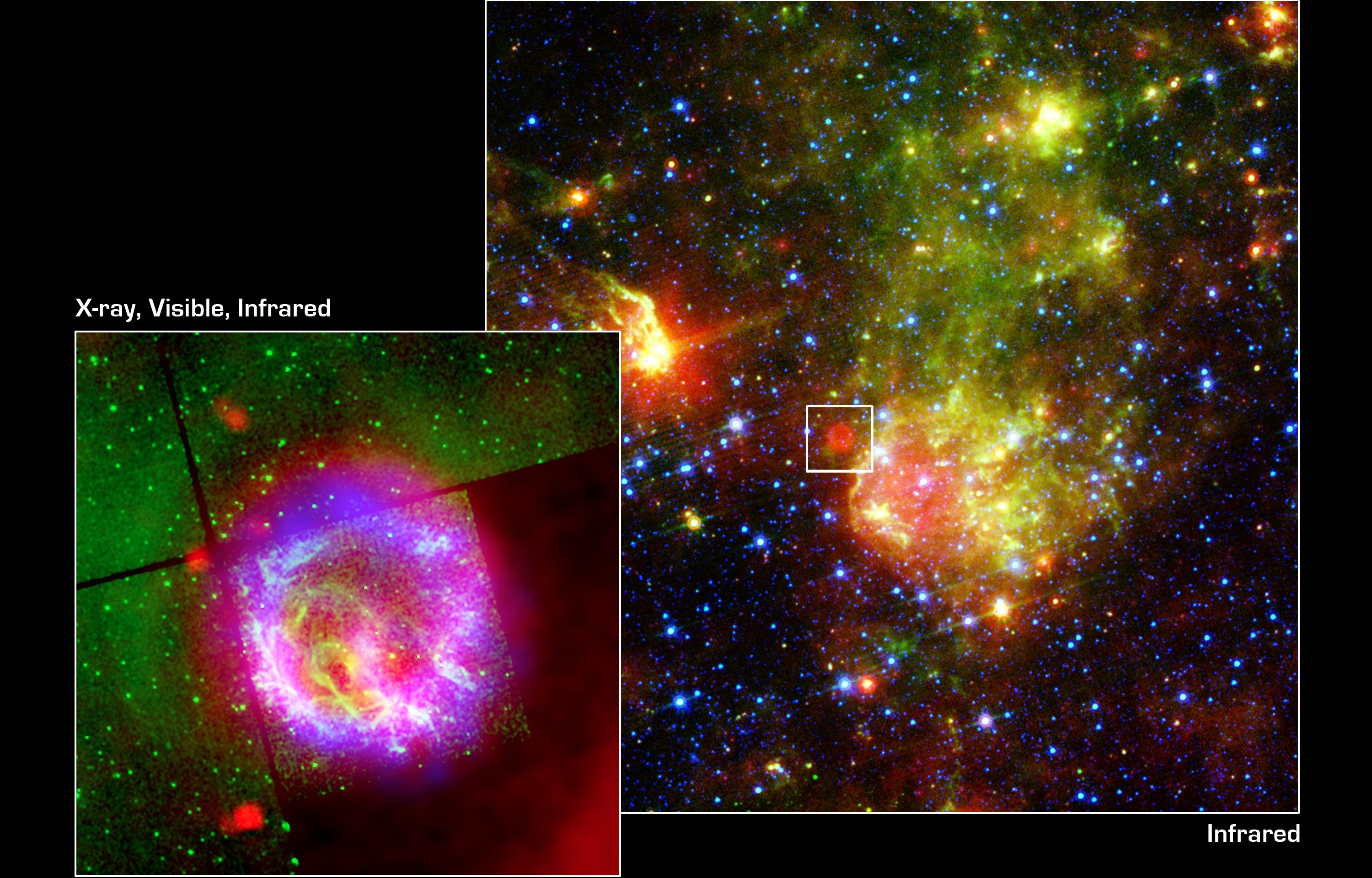
One newly discovered, ancient star has a composition unlike any other. Explaining its existence is already blowing astronomers’ minds.
Planets can be Earth-like or Neptune-like, but only rarely are in between. This hot, Saturn-like planet hints at a solution to this puzzle.
Finding it at all was a happy accident. Examining it further may help unlock the secrets hiding within the earliest galaxies of all.
A new measurement offers insights on the density of the mysterious force driving the Universe’s expansion.
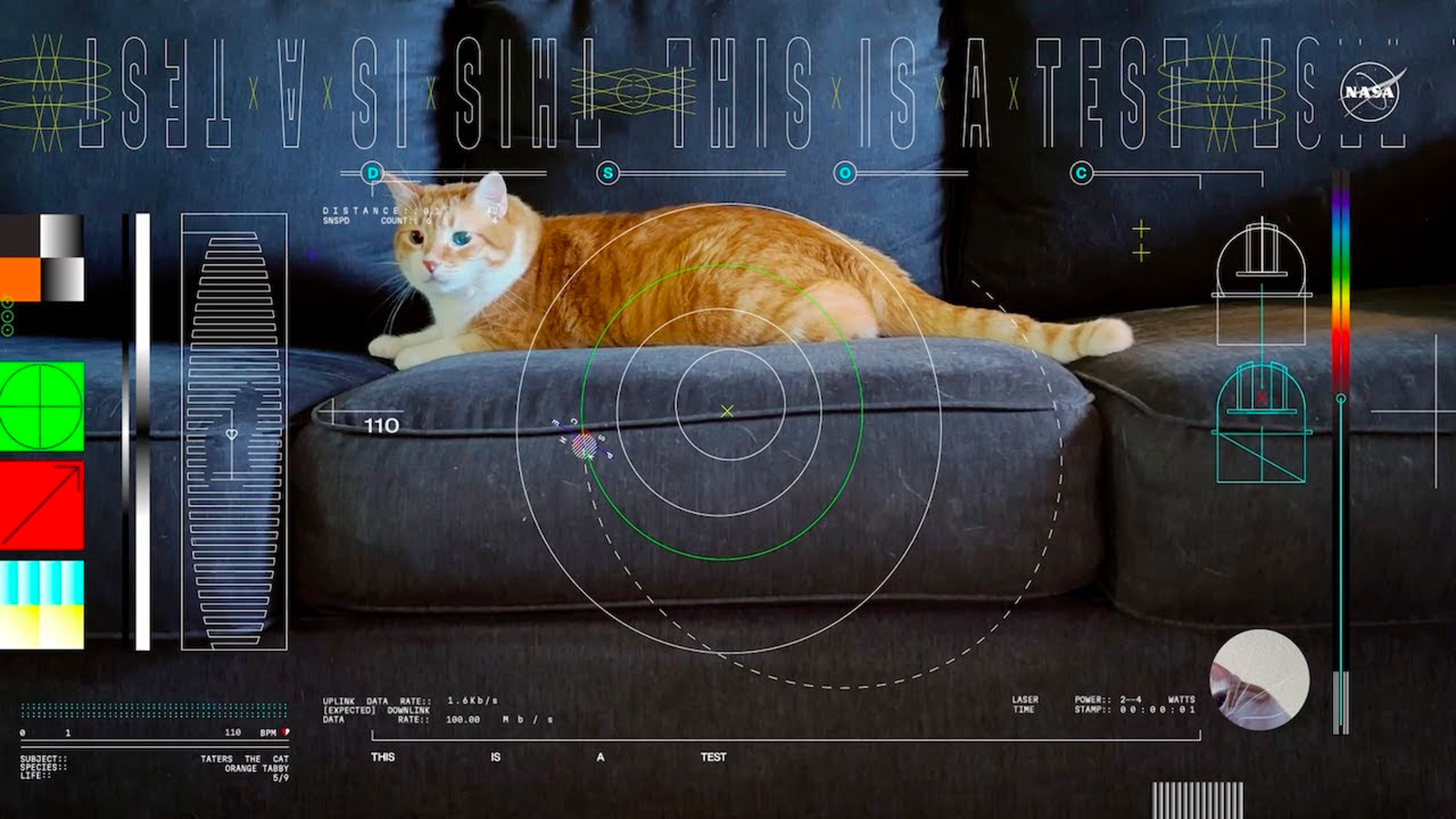
The record-breaking transmission could revolutionize deep space communication.
The cosmic scales governing the Universe are almost unbelievably large. What if we shrunk the Sun down to be just a grain of sand?
Figuring out the answer involved a prism, a pail of water, and a 50 year effort by the most famous father-son astronomer duo ever.
Here’s why the answer may forever elude scientists.
With the invention of the leap year, the Julian calendar was used worldwide for over 1500 years. Over time, it led only to catastrophe.
Today, the star-formation rate across the Universe is a mere trickle: just 3% of what it was at its peak. Here’s what it was like back then.
Earth wasn’t created until more than 9 billion years after the Big Bang. In some lucky places, life could have arisen almost right away.
As early as we’ve been able to identify them, the youngest galaxies seem to have large supermassive black holes. Here’s how they were made.
For 550 million years, neutral atoms blocked the light made in stars from traveling freely through the Universe. Here’s how it then changed.
Even after the first stars form, those overdense regions gravitationally attract matter and also merge. Here’s how they grow into galaxies.