neuroscience
A healthy lifestyle even protects those who are genetically predisposed to depression.
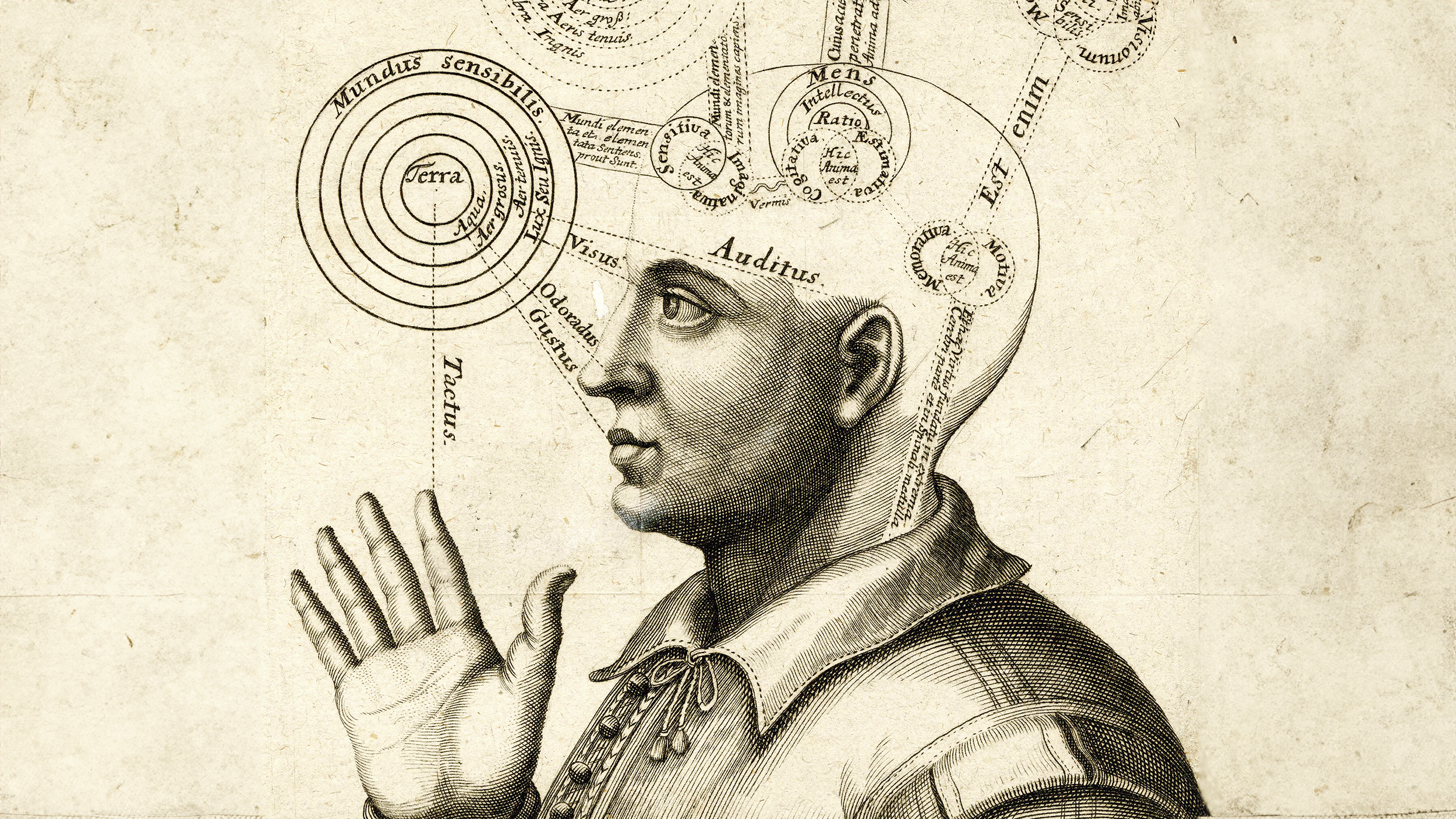
Neural imaging has shown that the brain has “decided” what we’re going to do before we make a conscious choice — but is this even relevant to free will?
According to neuropsychologist Julia DiGangi, no one can live a life free of emotional pain. We can only choose how those emotions empower us.
Even if a leading theory of consciousness is wrong, it can still be useful to science.
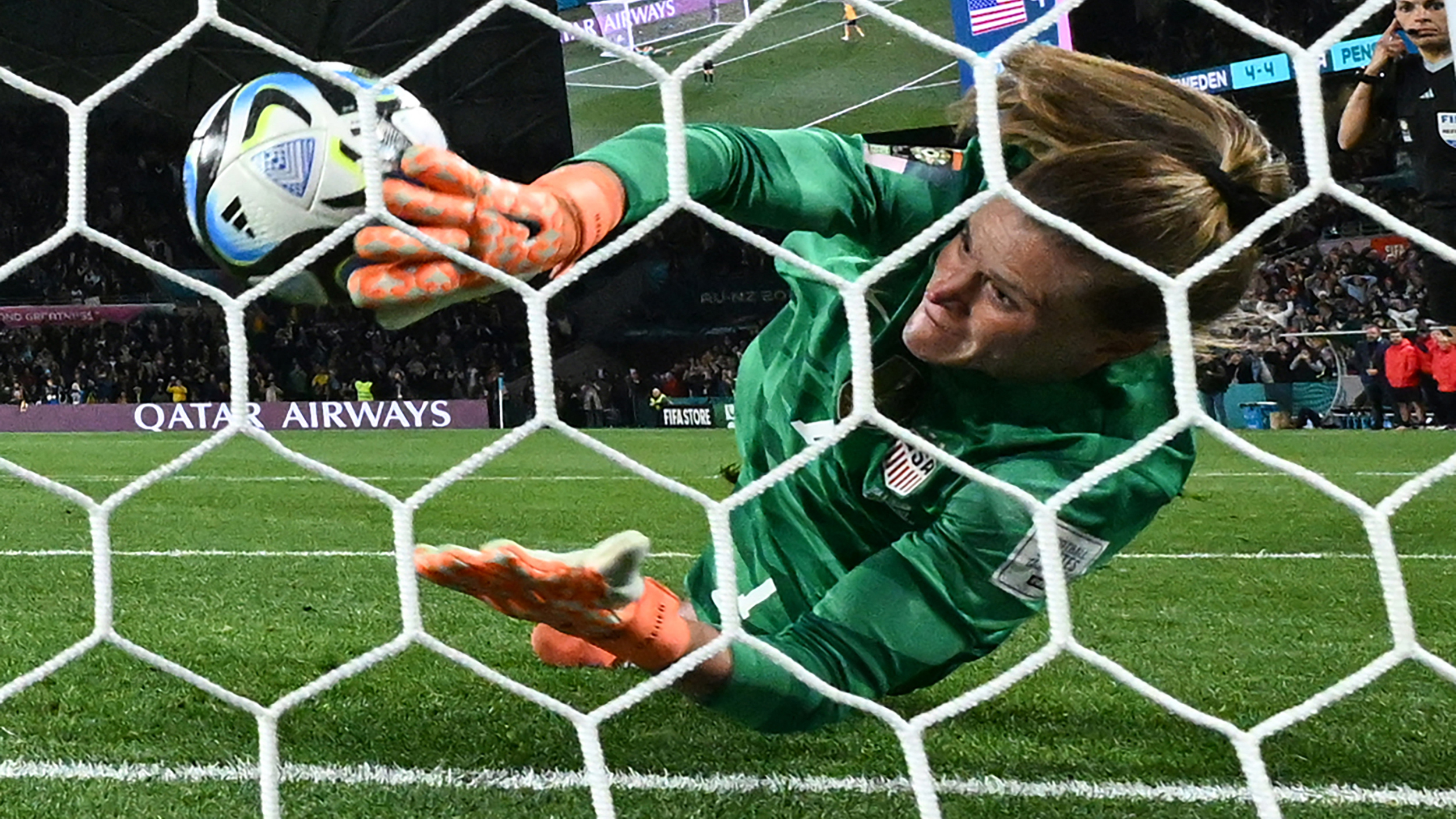
Goalkeepers have an enhanced ability to integrate auditory and visual information compared to other players.
If the “self” is not real, then we are slaves to a billiard ball universe, trapped in a nihilistic nightmare in which we cannot change our fate.
Only about 10% of patients survive cardiac arrest. Of the ones who do, many have amazing stories to tell.
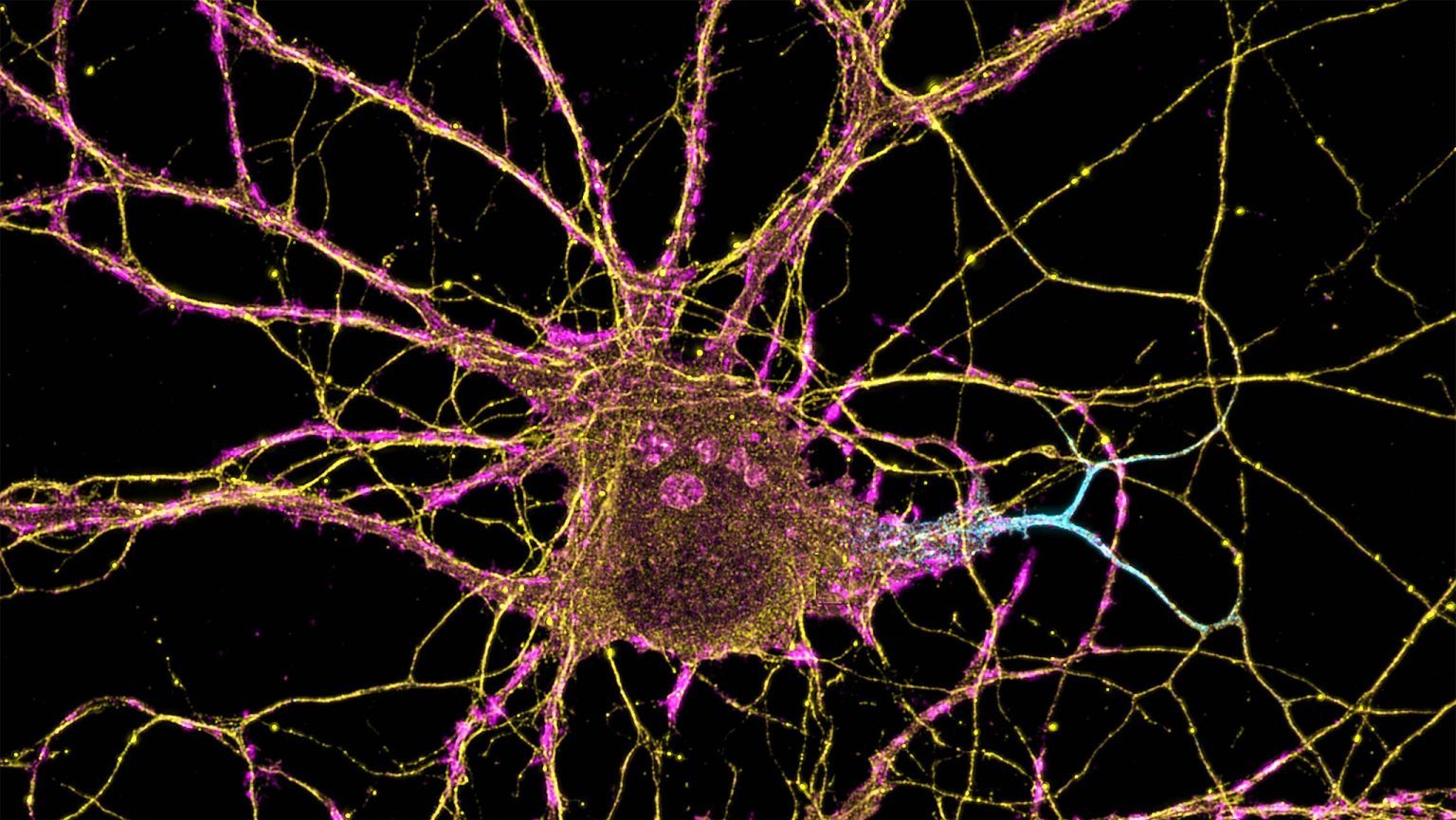
If you want to achieve new goals, harness your brain’s ability to change chemically, structurally, and functionally.
Chronic pain is often driven by brain processes that can be reprogrammed.
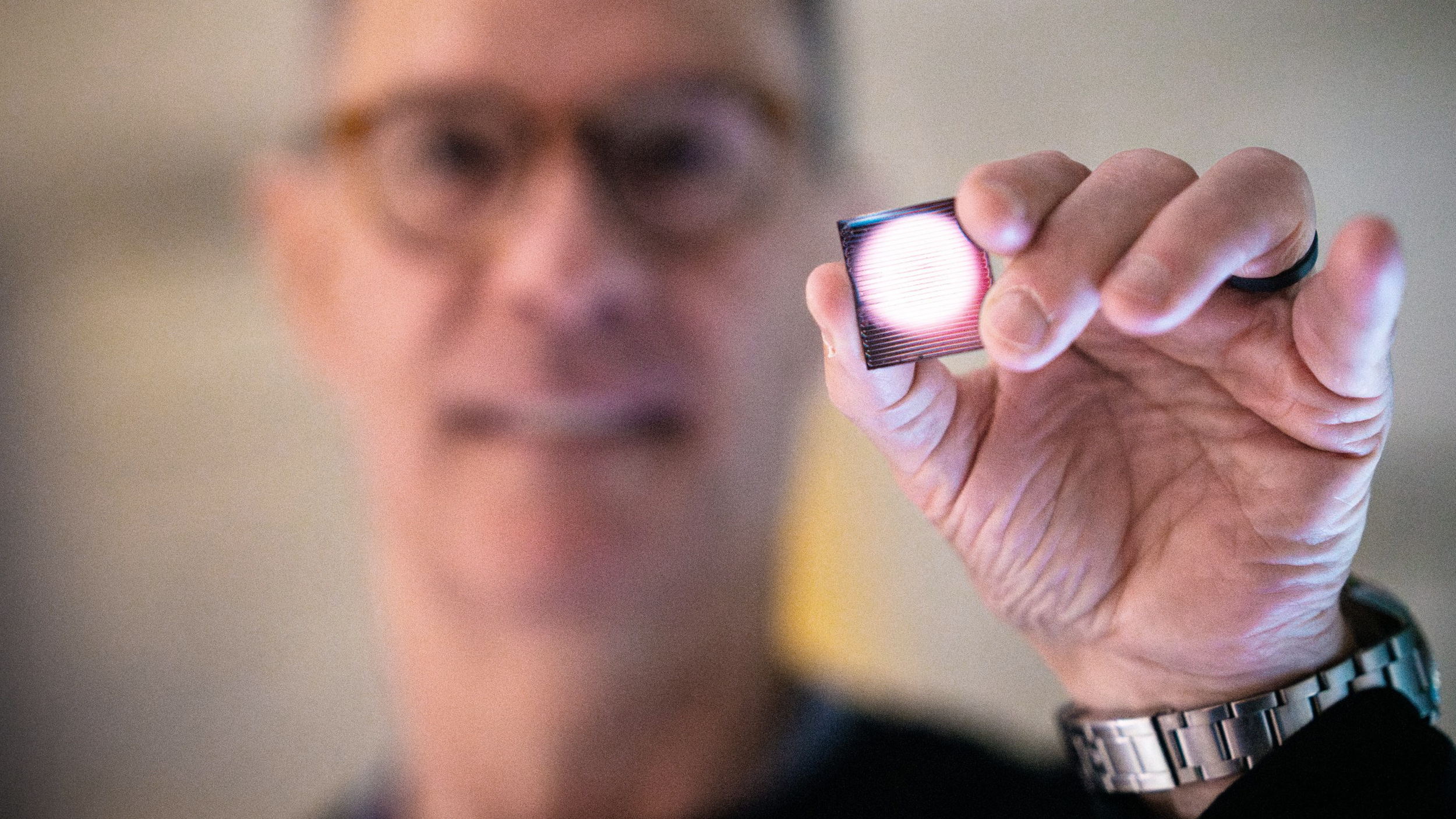
“I think it has a real chance to reverse motor symptoms, essentially replacing a missing part.”
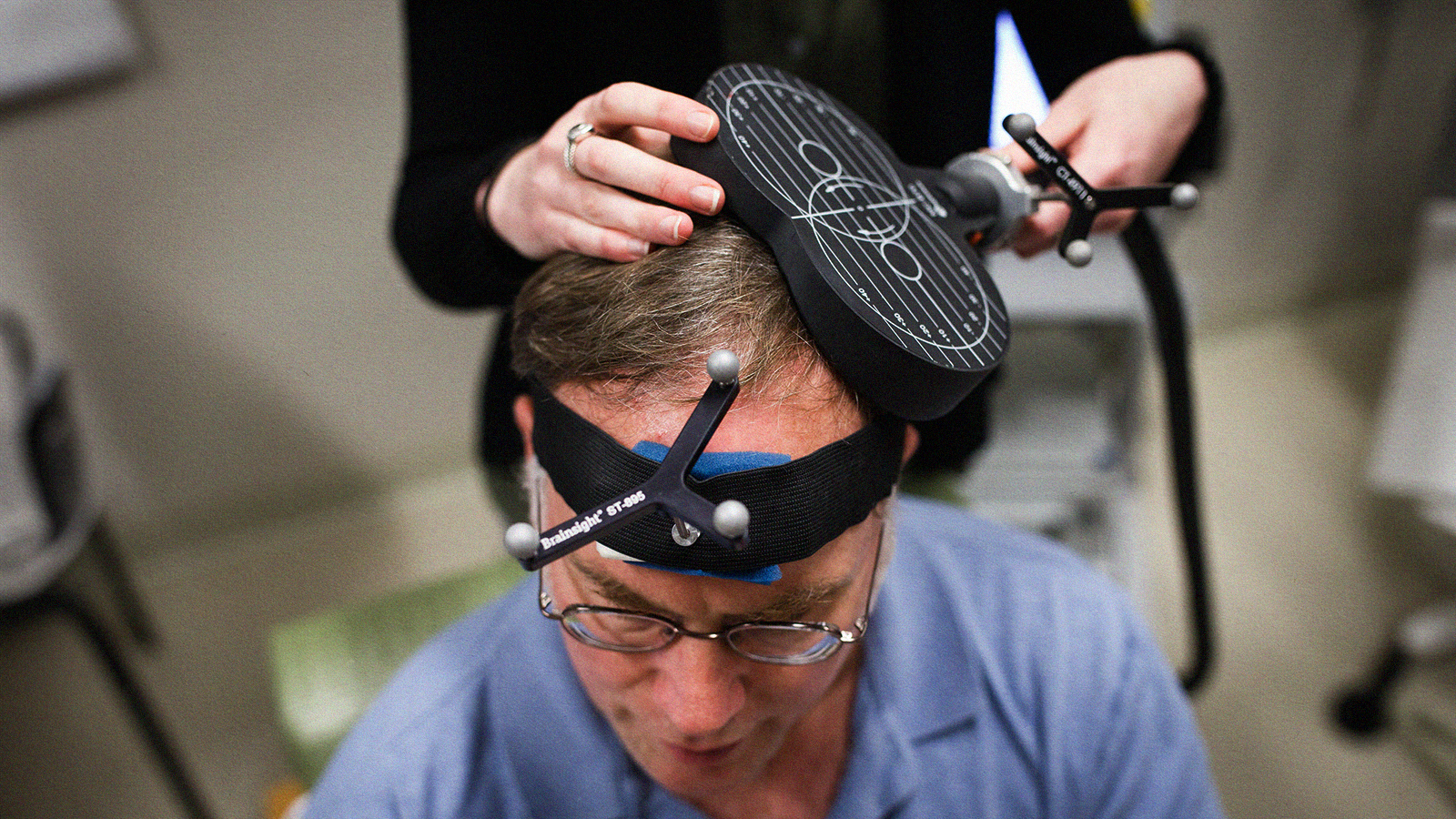
For people with hard-to-treat depression, a non-invasive technique called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) can provide relief.
The amygdala can hijack your brain’s response if it recognizes past trauma in a current situation. To regain control, simply press pause.
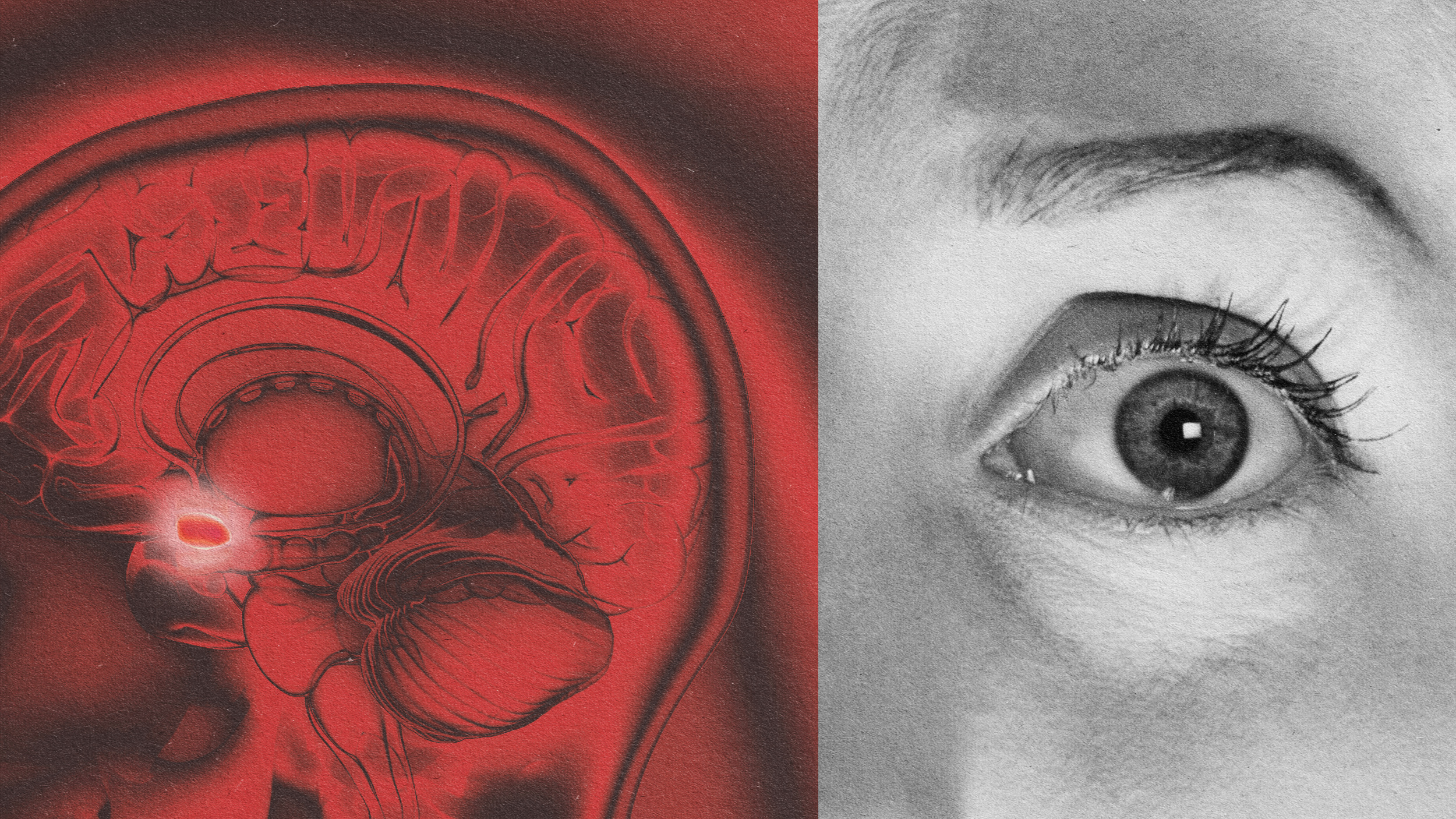
There are hints that it could lead to new treatments for Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and other brain disorders.
In a psychedelic state, the relationship between your “narrative” and “minimal” selves seems to transform in unique ways.
Exercise neuroscientist Wendy Suzuki explains how your brain can age gracefully and optimally — and it starts with just a 10-minute walk.
▸
4 min
—
with
Football is a risky sport, but bicycling to work is far more dangerous.
Subtle clues emerge ahead of the attack via changes in scent.
Interventions can make the most difference when Alzheimer’s is detected early.
Language influences how you visually process the world, which in turn influences your memory of it.
Our one-size-fits-all approach to sex education hasn’t worked for a long time. Sex educator Emily Nagoski explains what we know (and don’t know) about the role neurodiversity plays in intimacy.
▸
6 min
—
with
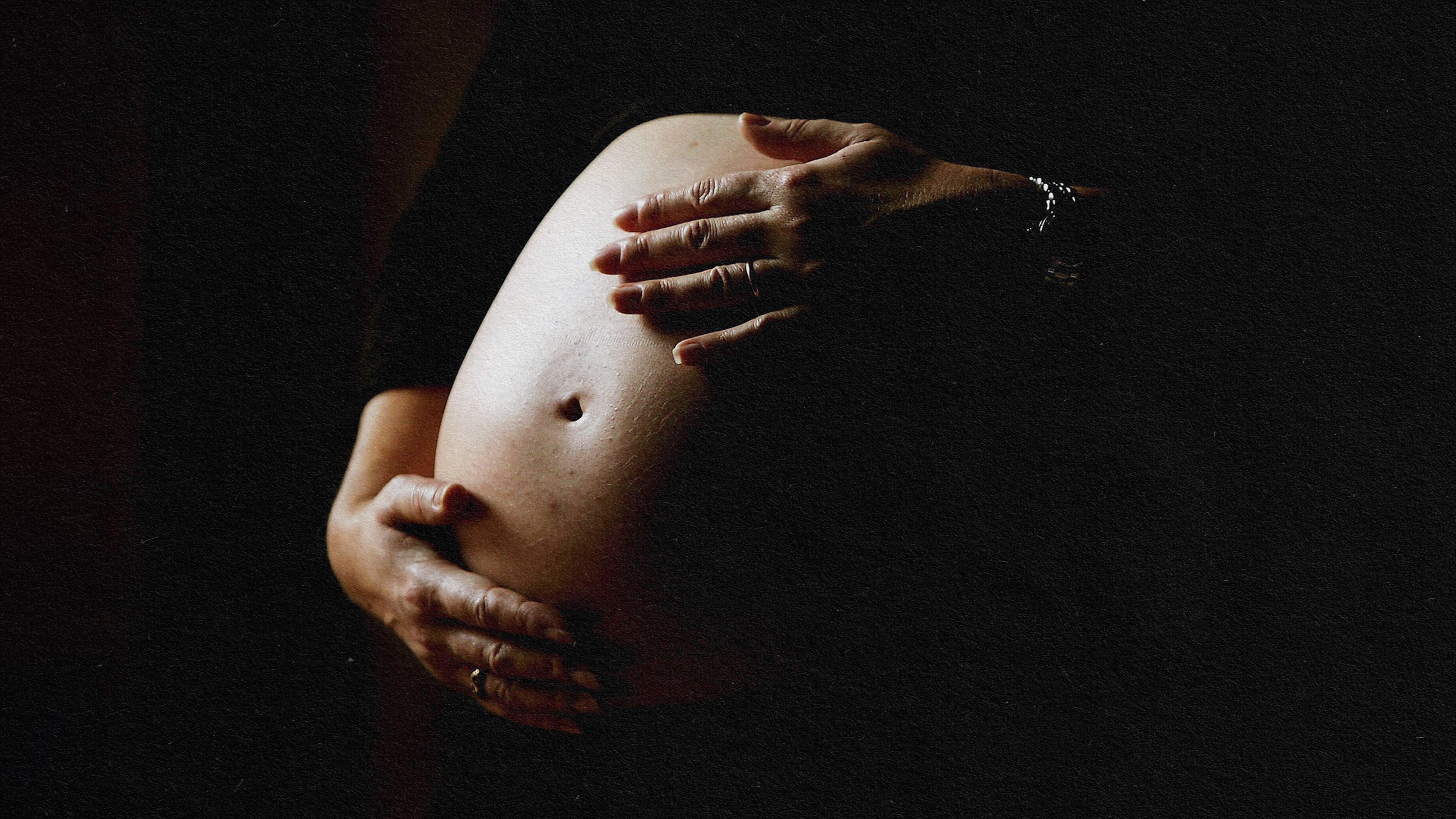
Medical psychologist Catherine Monk explains how prenatal mental care benefits both mothers and babies.
“They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.”
Neuroscientist Wendy Suzuki explains why zero anxiety isn’t the goal.
▸
8 min
—
with
A high-fat diet might trigger inflammation of the hypothalamus.
Bad news: Sleeping in on the weekends probably won’t cut it.
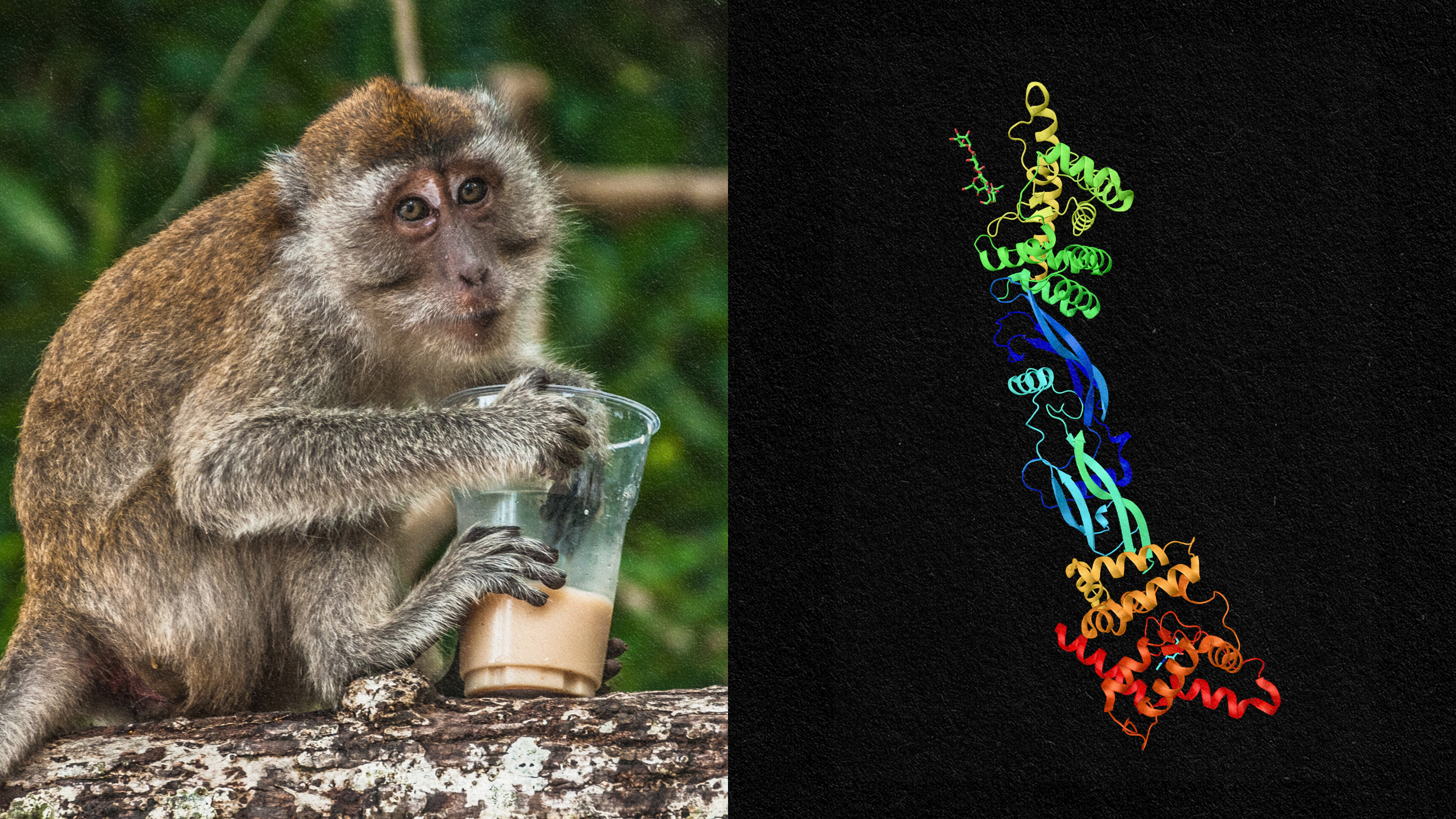
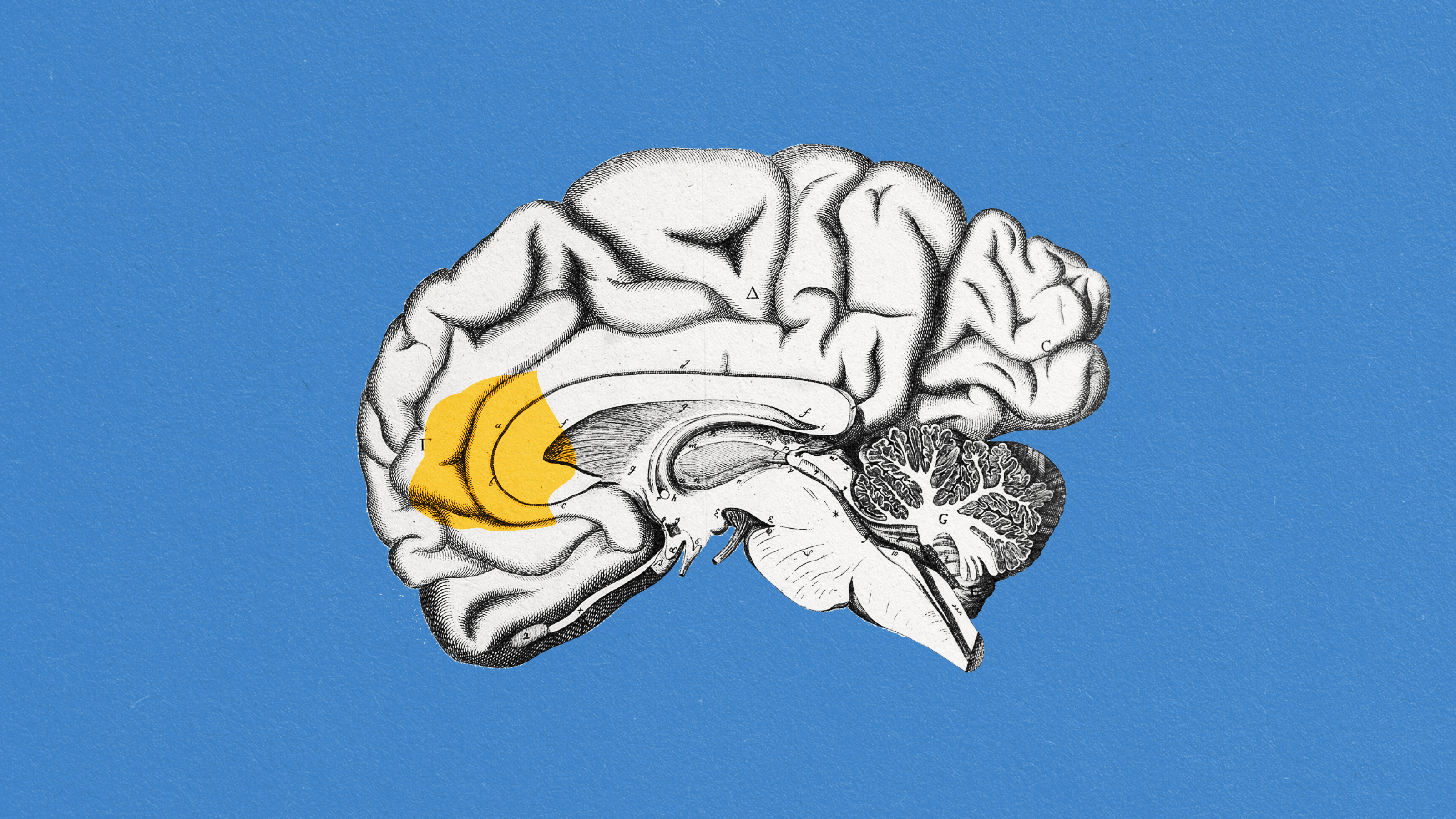
The structure is fully developed in humans, partially developed in chimps, and completely absent in Old World monkeys.
Decades of Alzheimer’s research might have missed a cellular culprit hiding in plain sight.
Your heart rate reveals your brain activity, which in turn can predict hit songs — and maybe stock performance, as well.
Why does the DMT experience feel so familiar to some people — even those who are trying the psychedelic for the first time?