medicine
The integration of artificial intelligence into public health could have revolutionary implications for the global south—if only it can get online.
Could studying the Oriental hornet lead to a treatment for people with alcohol use disorder?
Can laboratories become more humane, or is it time to end animal research altogether?
“The field is endless, but my life is limited, as are all of ours. But you do what you can with your time,” says CSO Mart Saarma.
Some go gently into the night. Others die less prettily in freak accidents or deadly invasions, or after a showy display.
Manipulating a signaling pathway in mice reversed their anxiety — and offers hope for a new class of anti-anxiety medications for humans.
Hospice nurse Julie McFadden shares three examples where people hold off death, just for a bit.
Could exercise be more effective than recently approved drugs?
Propofol, a drug commonly used for general anesthesia, derails the brain’s normal balance between stability and excitability.
Kurzweil predicts that AI will combine with biotechnology to defeat degenerative diseases this decade. Then things will get really interesting.
“By 2040, we hope to see a number of new drugs that have been designed with AI reaching patients.”
Female physicians tend to practice medicine as it should be practiced: with care and compassion.
While GLP-1 agonists help people lose weight, different drugs could help them retain muscle at the same time.
The hangover “cures” on the market don’t work. A new hydrogel does.
GLP-1 agonists may be able to treat addiction, prevent Alzheimer’s, and more.
A new family of drugs is changing the way scientists are thinking about obesity.
Joe Betts-LaCroix — co-founder and CEO of Retro Biosciences — talks to Big Think about invention, authenticity, and Sam Altman’s “art of the startup.”
Cancers can’t develop without genetic mutations — or can they?
Vaccines targeting some of our deadliest cancers are showing promise in early trials.
Forensics has reached the final frontier, and could be used to solve future space accidents—or crimes.
More than 90% of sexually active men will be infected with human papillomavirus in their lifetime. The virus may reduce fertility.
Susannah Fox, former chief technology officer for the HHS, explains how technology has empowered us to help fill in the cracks of the healthcare system.
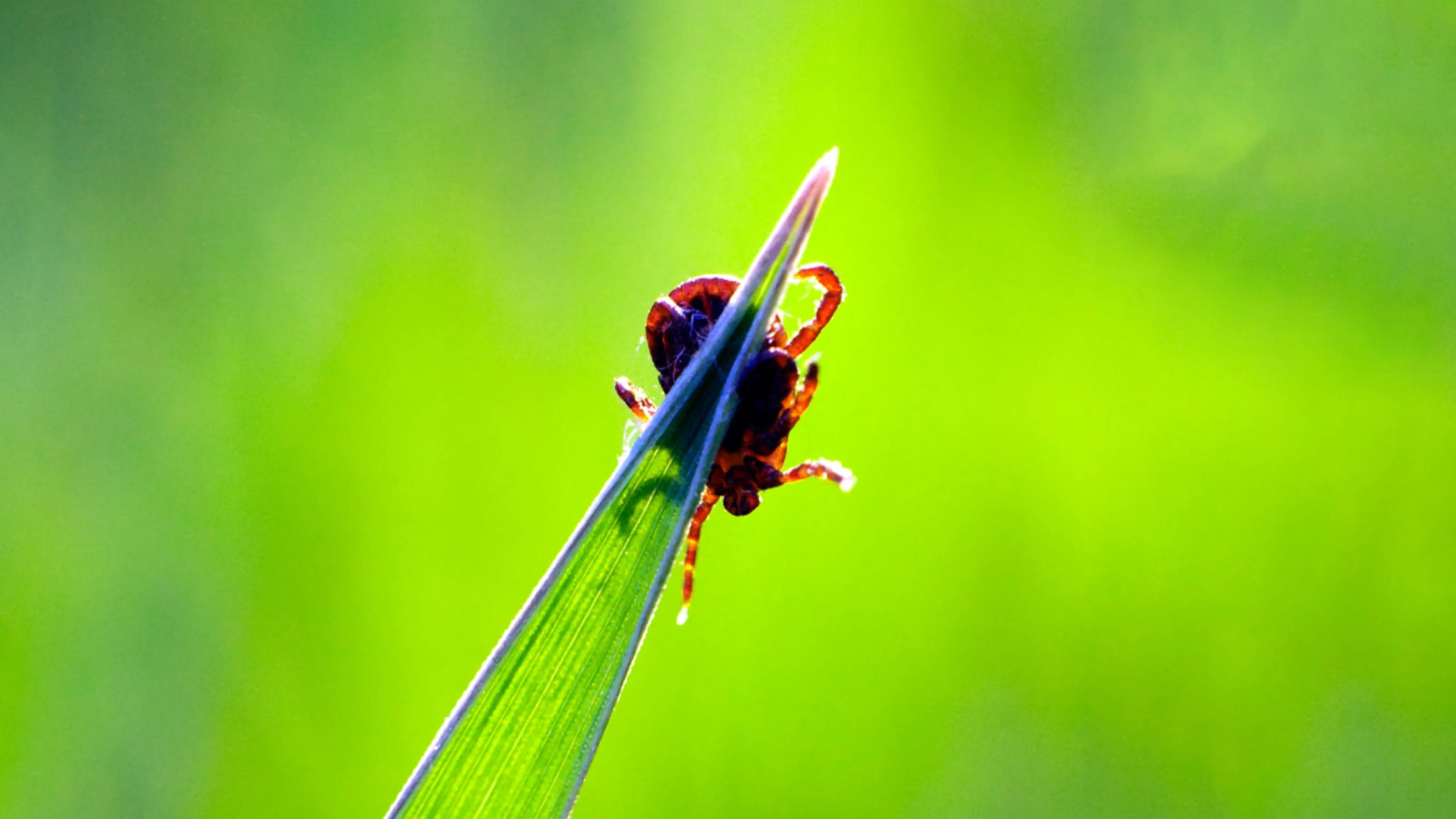
More than 90% of ticks that bit treated volunteers were dead within 24 hours.
The sober reality behind the effectiveness of two new drugs touted as Alzheimer’s breakthroughs: lecanemab and donanemab.
Long overlooked, menstrual stem cells could have important medical applications, including diagnosing endometriosis
They call it “Judo T-cell therapy,” and it’s 100 times more potent than regular CAR-T cells.
Placebo treatments don’t always need to be given deceptively to have positive effects.
Growing evidence suggests a link between the debilitating neurological illness and the microbes that live in our intestines. The vagus nerve may be a pathway.
The FDA approved a single-dose, long-acting injection to protect babies and toddlers from RSV over the fall and winter.
With any occupation comes a risk of health and safety hazards. When it comes to being Santa Claus, the challenges are unique.