biotech
The scientists are headed “straight to the FDA” to begin human trials.
The paper-thin device may also someday be used to stimulate bone growth.
The cause of Alzheimer’s is still not fully understood, but we might be able to vaccinate against it anyway.
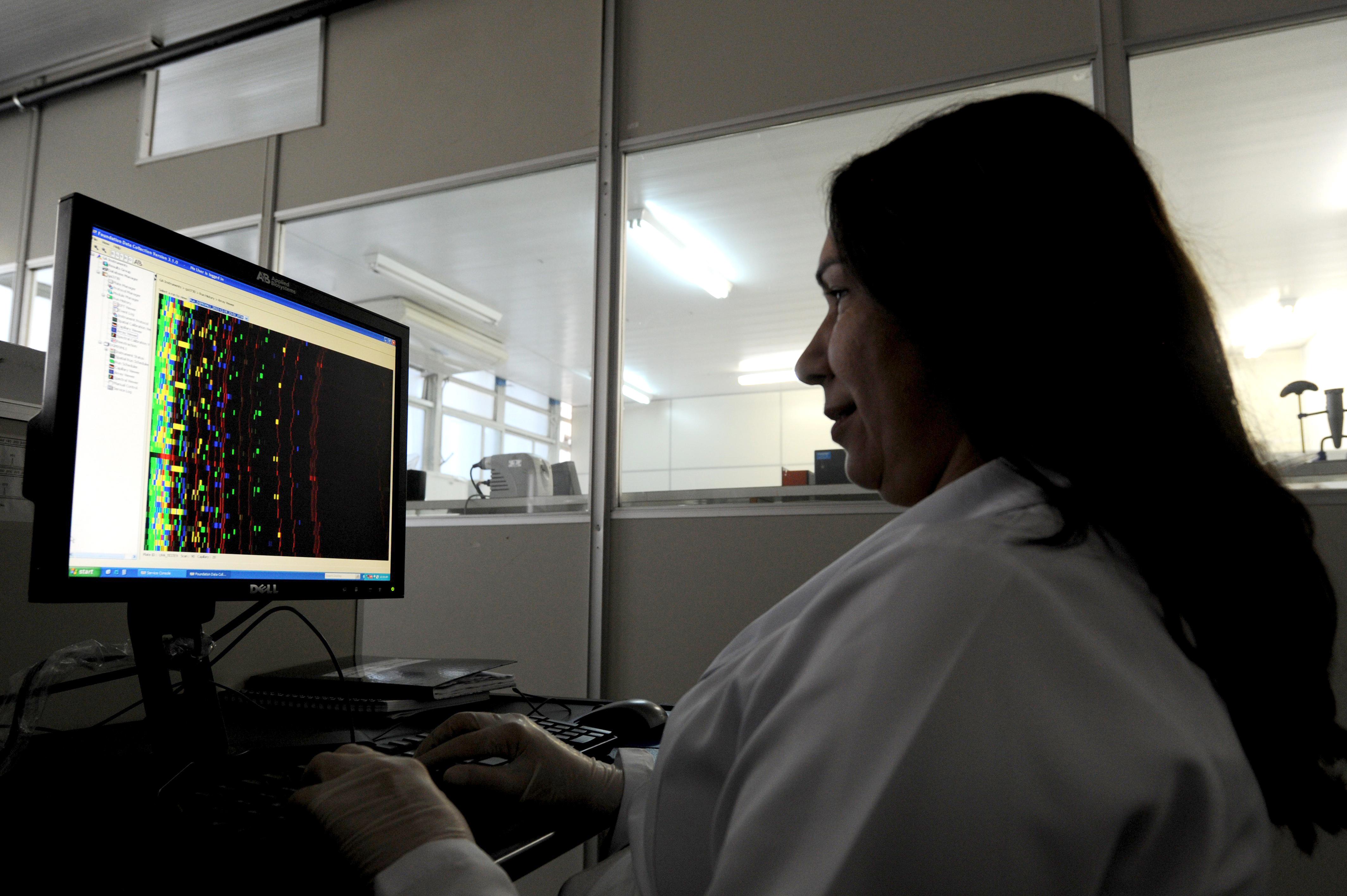
“This will be one of the most important datasets since the mapping of the Human Genome.”
Using DNA from samples of extinct flowers, synthetic biologists managed to approximate long-lost floral scents.
An evolutionary biologist explains why you probably won’t grow a tail.
Prozac is a widely used antidepressant. Data indicates that the drug could be used to prevent blindness due to macular degeneration.
Guided by ultrasound waves, swarms of microrobots could soon be used to deliver medicine to targeted sites in the body.
The development of the revolutionary gene-engineering tool CRISPR is a tale fit for the big screen.
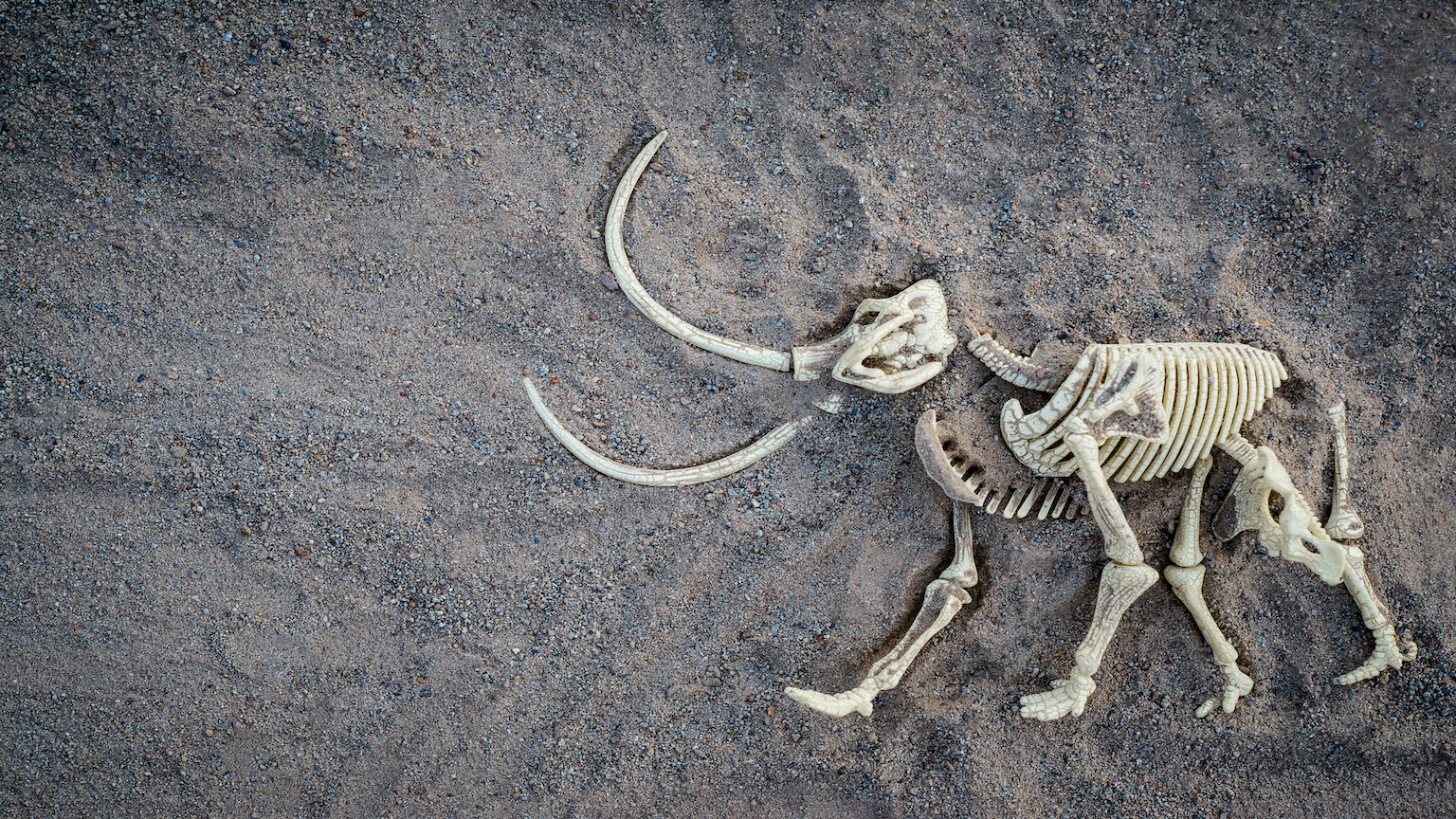
A biotech startup has received $15 million in funding to genetically recreate woolly mammoths and rewild them in Siberia.
One day, this powerful tool could be in millions of smartphones.
Smallpox, Ebola, HIV, influenza, the plague, malaria, and a whole host of terrible bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites were cooked up by Mother Nature, all on her own. Apparently, Mother Nature hasn’t banned gain-of-function research.
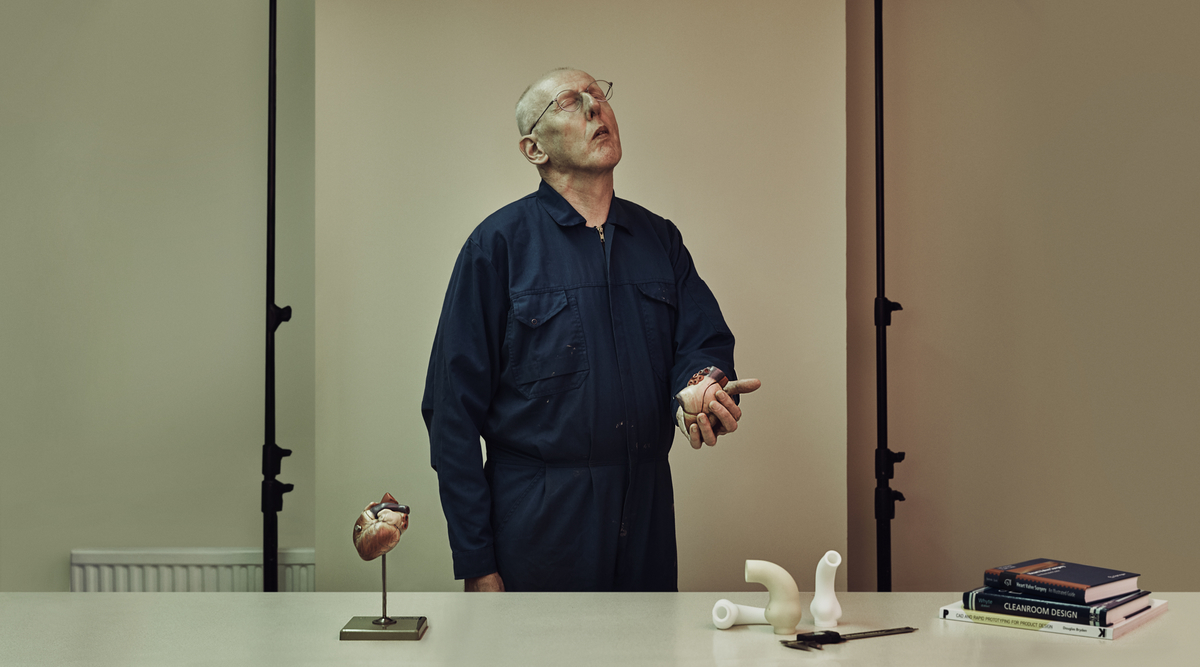
When Tal Golesworthy was told he was at risk of his aorta bursting, he wasn’t impressed with the surgery on offer – so he came up with his own idea.
Organ transplantation is in dire need of biotechnological advances. 3D bioprinting and genetic modification of pigs provide a path forward.
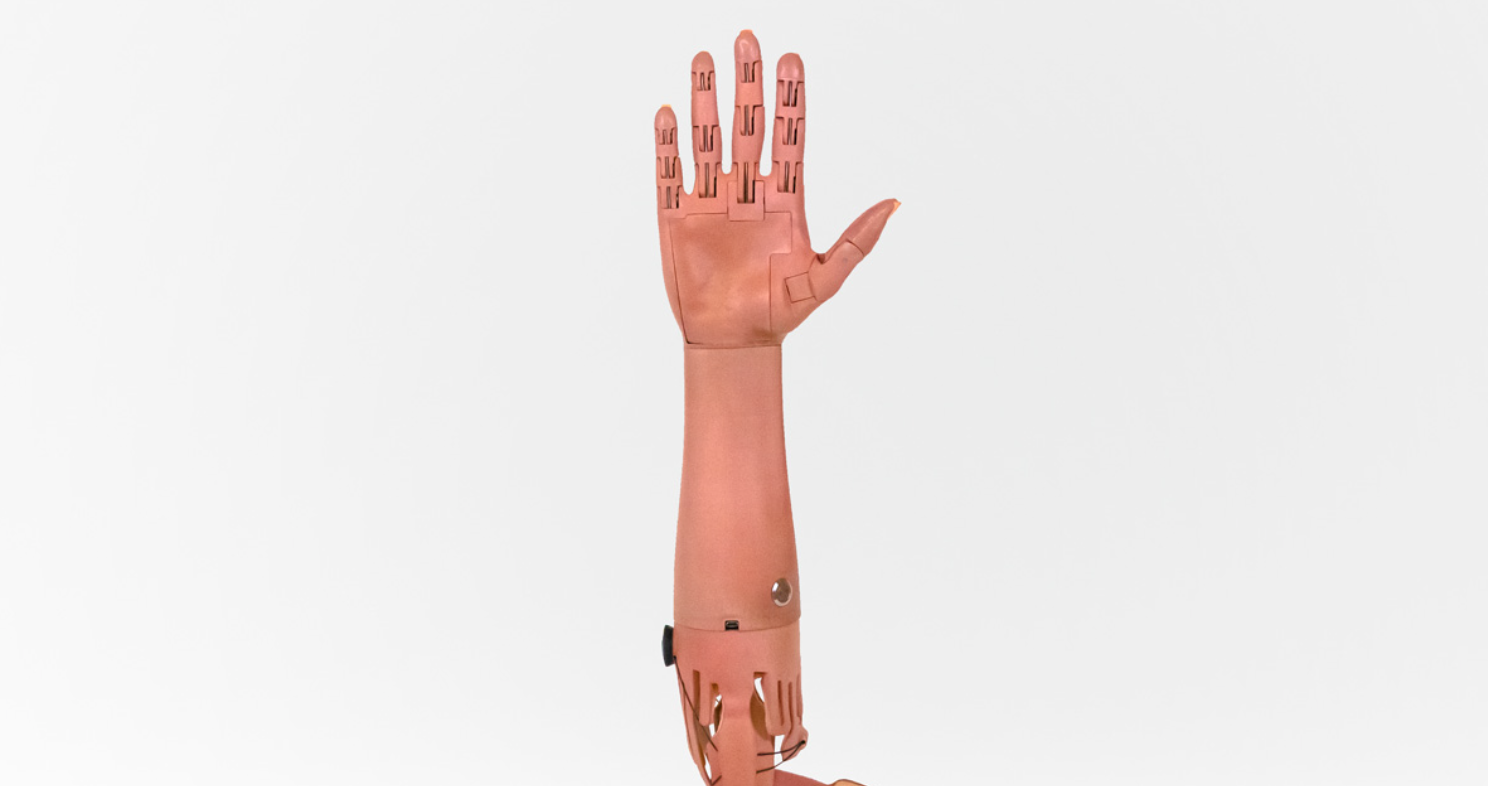
Prosthetic arms can cost amputees $80,000. A startup called Unlimited Tomorrow is aiming to change that by making customized 3D-printed bionic arms for just $8,000.
The new brain tumor treatment targets a cancer that kills 75% of patients within a year.
Some neurology experiments — such as growing miniature human brains and reanimating the brains of dead pigs — are getting weird. It’s time to discuss ethics.
It marks a breakthrough in using gene editing to treat diseases.
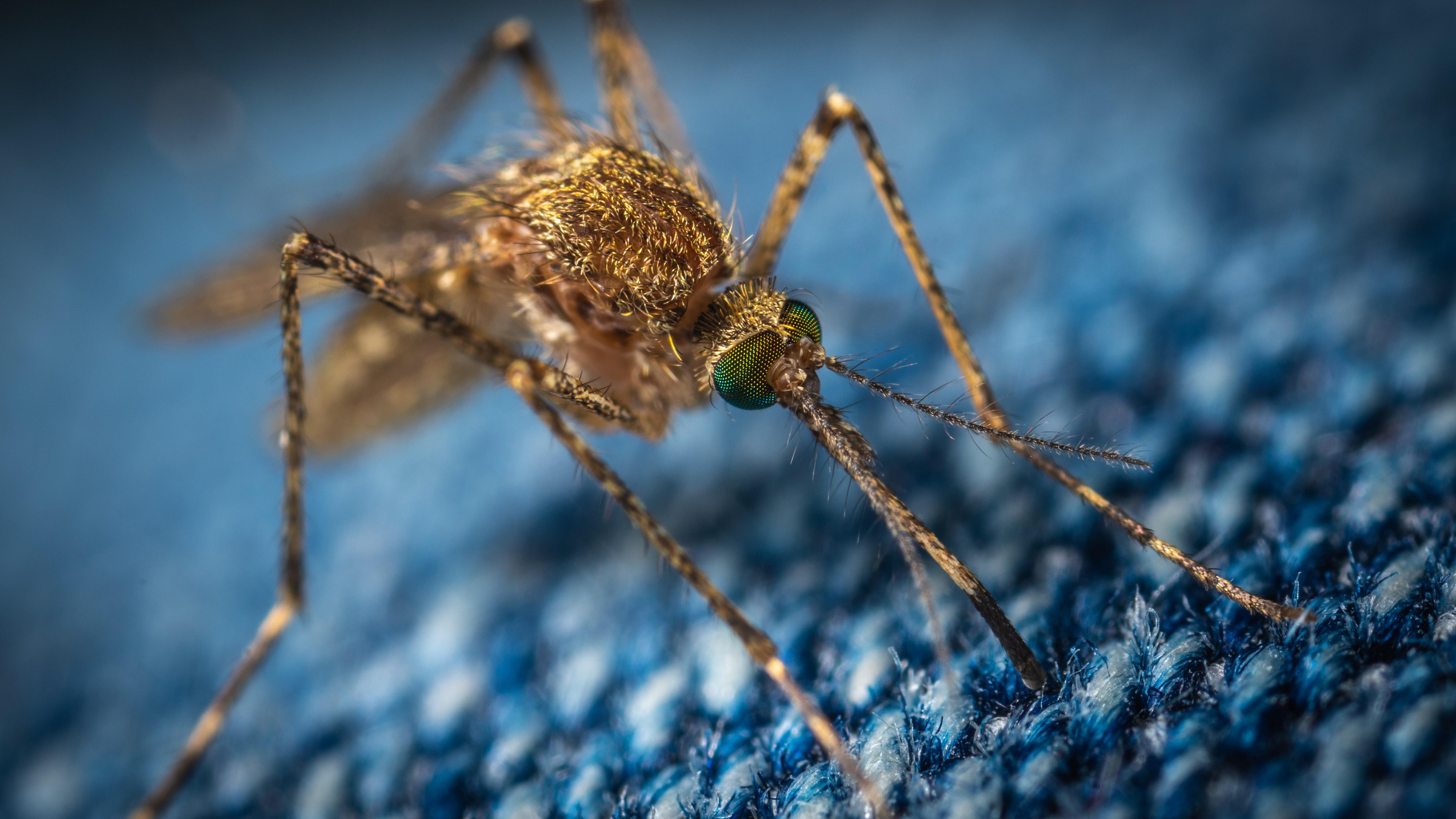
Gain-of-function mutation research may help predict the next pandemic — or, critics argue, cause one.
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy uses small molecules to alter RNA. Researchers have now used those molecules to alleviate a genetic form of blindness.
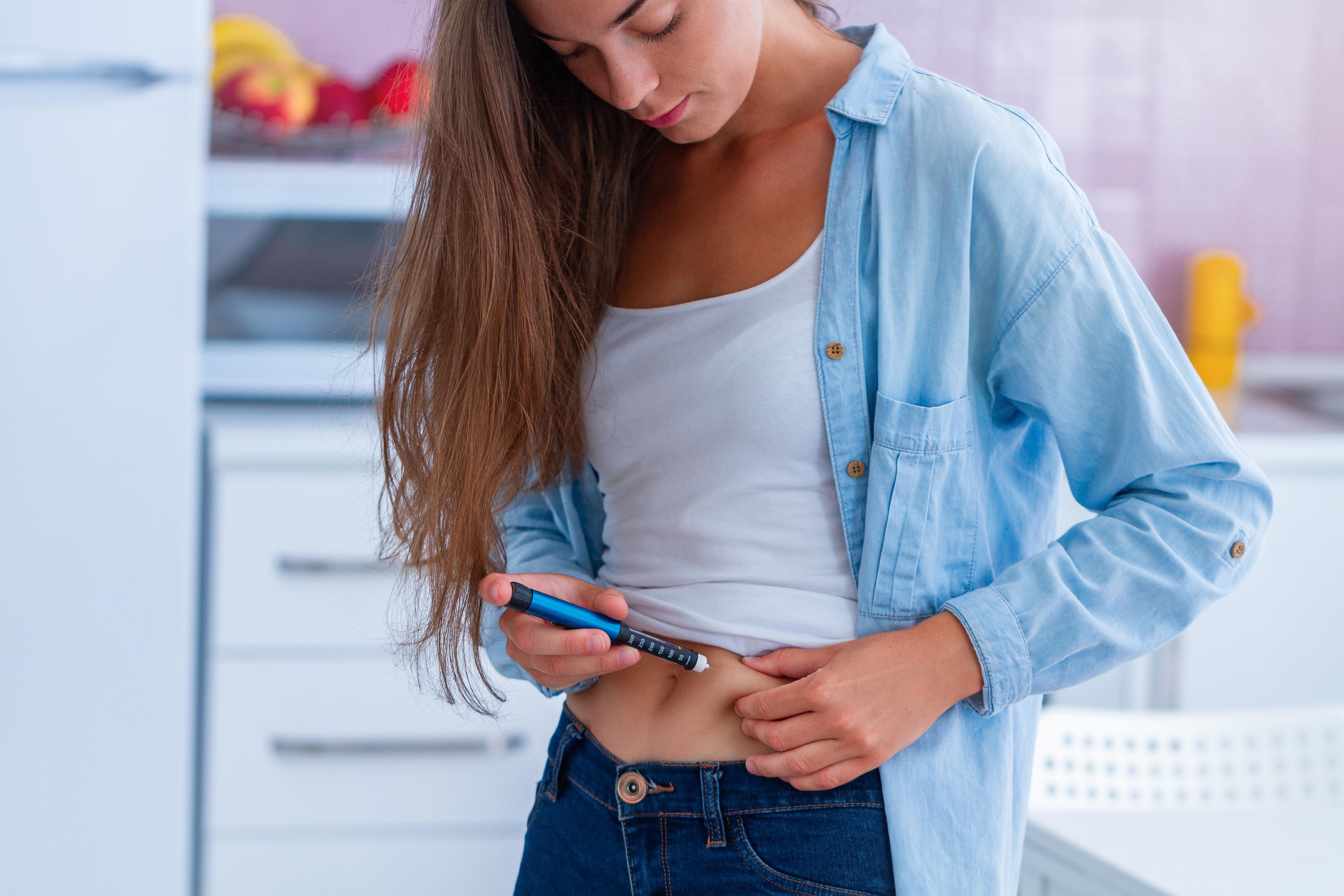
A team of biohackers is on a David-versus-Goliath mission to make insulin affordable to an increasing number of diabetics.
How were mRNA vaccines developed? Pfizer’s Dr Bill Gruber explains the science behind this record-breaking achievement and how it was developed without compromising safety.
▸
7 min
—
with
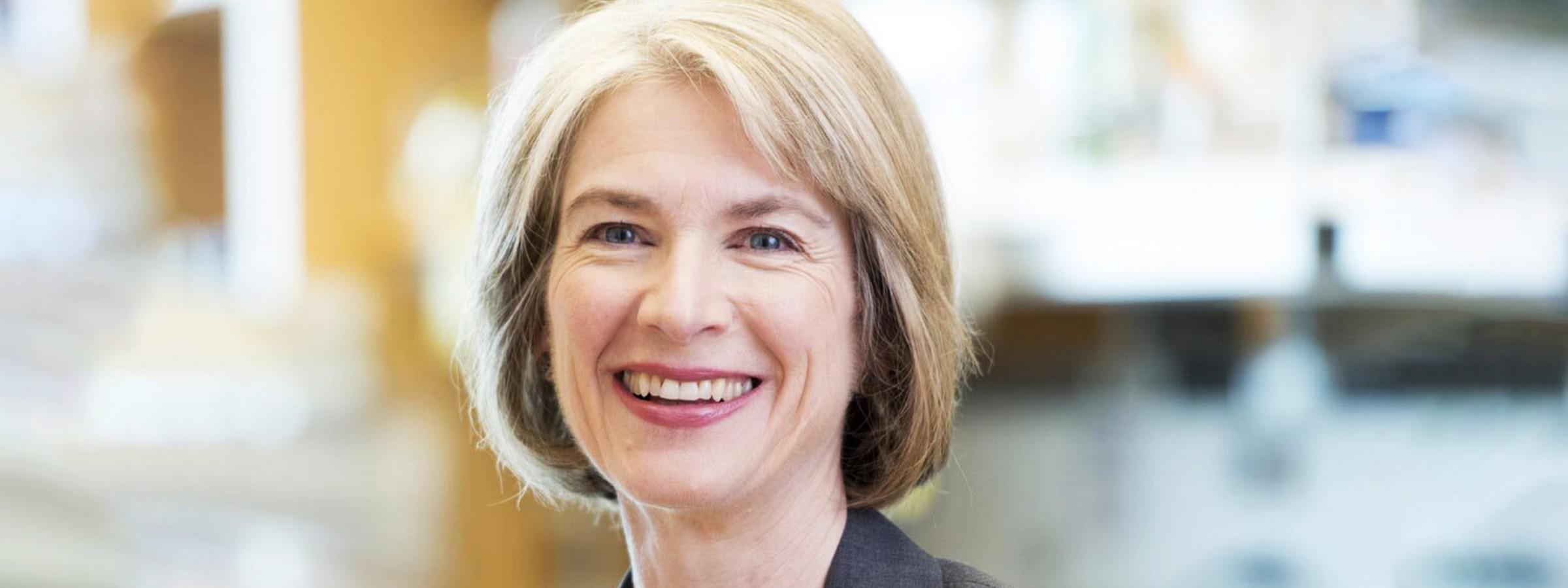
She helped create CRISPR, a gene-editing technology that is changing the way we treat genetic diseases and even how we produce food.
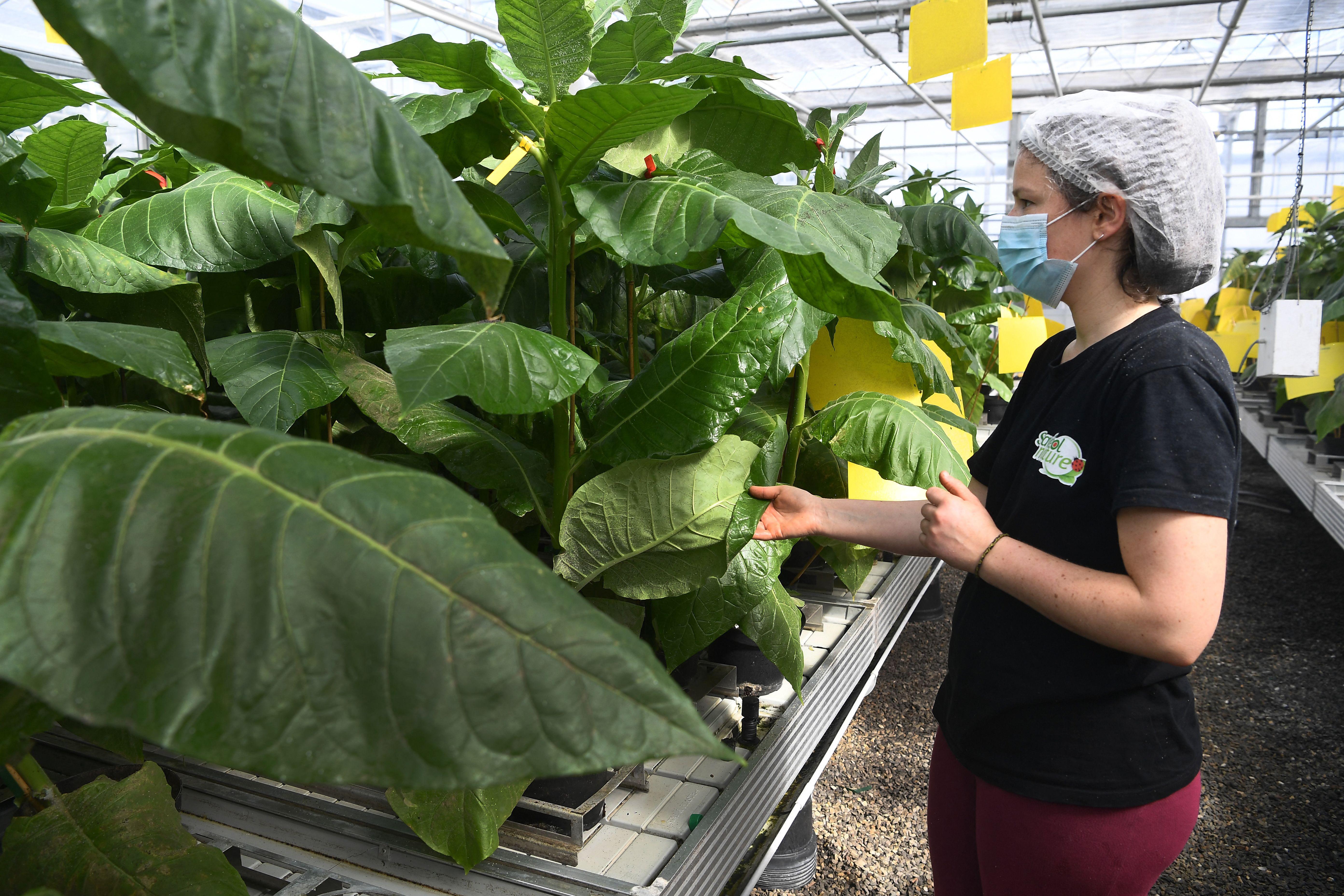
Vaccines can be grown in and extracted from the leaves of plants.
Engineered immune cells have prevented Type 1 diabetes in mice.
Many thousands of different genetic variants are responsible for complex behavior.
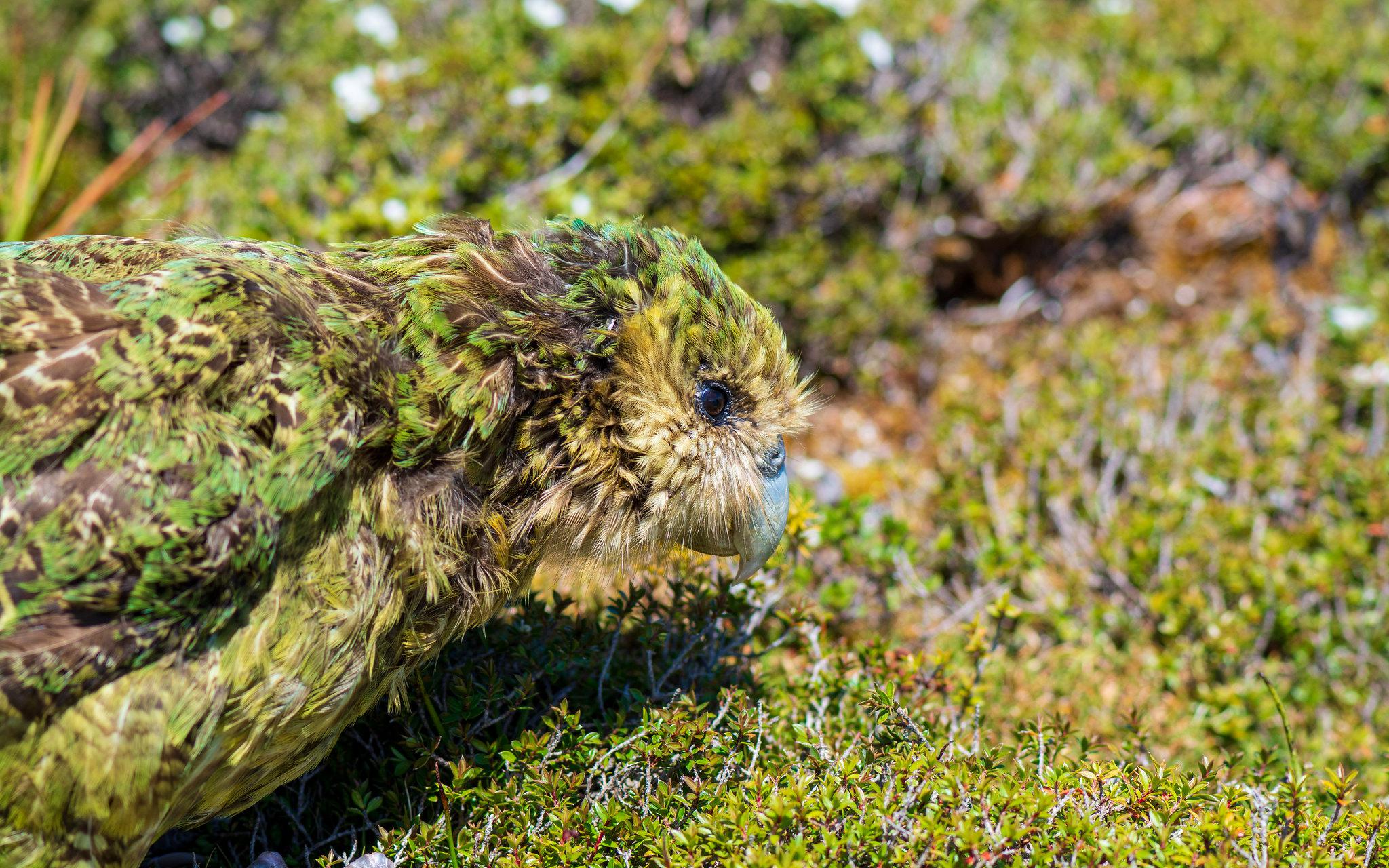
The Vertebrate Genomes Project may spell good news for the kakapo and the vaquita.
“The question is which are okay, which are not okay.”
▸
14 min
—
with