Science won’t ever make philosophy or religion obsolete

- As we come to understand the Universe to better precision and more comprehensively, many questions which were previously pondered by philosophical and religious thought-leaders grow to have definitive answers.
- However, the information we possess within our observable Universe is now, and will always be, finite and limited, implying that there’s a fundamental limit to what’s knowable.
- As long as we remain curious about the unknown and the unknowable, there will always be a place for philosophy and religion both, independently of whatever becomes scientifically known. Here’s why.
For hundreds of thousands of years — nearly all of human history — we had no definitive answers to some of the biggest existential questions we could formulate. How did humans come into existence on planet Earth? What are we made of, at a fundamental level? How big is the Universe, and what is its origin? For countless generations, these were questions for theologians, philosophers, and poets.
But over the past few hundred years, humanity has discovered the most compelling and convincing answers we’ve ever had to those questions and many others. Through the process of performing experiments and making observations, we have increased our definitive, scientific knowledge tremendously, enabling us to draw conclusions rather than merely to engage in unprovable speculations. Yet even with as far as we’ve come from a scientific perspective, philosophy and religion will never become obsolete. Here’s why.

Science. When most people think about what science is, they only get it halfway right. Science is, simultaneously, both of the following:
- The entire body of definite knowledge that we have about the Universe. All of the cumulative results of every experiment, measurement, and observation that we have ever recorded makes up the body of scientific facts we have about the Universe. The theories, predictive models, frameworks, and equations that govern the Universe are all an essential and important part of science.
- The process by which we investigate and learn more about the Universe. Science is ongoing and constantly revealing new truths and facts about the Universe, and the entire process of scientific inquiry — hypothesizing, experimenting, drawing conclusions in the context of our full suite of knowledge, etc. — is indispensable to what we know of as science.

But for all of the questions that science has answered and all of the lessons it’s taught us, it does not teach us everything. Every scientific theory, no matter how robustly supported by the entire set of knowledge compiled by humanity over our history, only has a limited range over which it is demonstrably correct. Even our most vaunted ideas have their limitations.
- Evolution explains how traits are inherited and gives a mechanism for how populations of organisms change over time, but does not explain the origin of life.
- The Big Bang explains how the Universe arose from an early, hot, dense state, but doesn’t explain how it emerged with those conditions.
- General Relativity explains how matter and energy cause spacetime to curve and gravitation to occur, but does not explain what occurs at the singularity inside a black hole.

In other words, no matter how far we’ve come in our scientific understanding of the world and the Universe, there is always a place where our established scientific understanding ends. Once we have definite knowledge of a phenomenon and a detailed understanding of the processes that underpin it, we can securely place that phenomenon within the realm of science.
But there are many questions that we can pose that do not — at least not yet — fall within the scientist’s purview. Sure, we can speculate as to what scientific ideas might eventually wind up solving these puzzles, but this is predicated on extending our current scientific knowledge into a realm where it has not yet arrived. Many of today’s most exciting mysteries, from the origin of life to extraterrestrial intelligence to quantum gravity to the puzzles of dark matter and dark energy, currently lie beyond the realm of what’s scientifically well-understood.

Theology. There are religious and ethical conceptions that we have about the Universe, which is typically what we understand as the realm of theology. Whatever your personal religious views may be, theology in general deals with questions such as purpose, right and wrong, and an authoritative source that sets forth some tenets that must be accepted as incontrovertibly true.
Science attempts to answer questions that start with “how,” venturing to explain and predict what the outcome (or sets of possible outcomes) of a physical system, initially set up with certain conditions, will be. On the other hand, theology attempts to answer questions that ask “why,” pondering questions that surpass definitive knowledge and offering confident — albeit controversial to many — answers to those inquiries.

It’s true that many questions that were once considered to fall into the realm of theology, where we lacked definitive knowledge, have now become scientific questions that have definitive answers. Scientifically, we now know:
- how planet Earth emerged during the formation of our Solar System some 4.5 billion years ago,
- how life evolved and various plants and animals emerged throughout the ages on planet Earth,
- how recent and ancient events shaped our planet’s geological, atmospheric, and hydrological history,
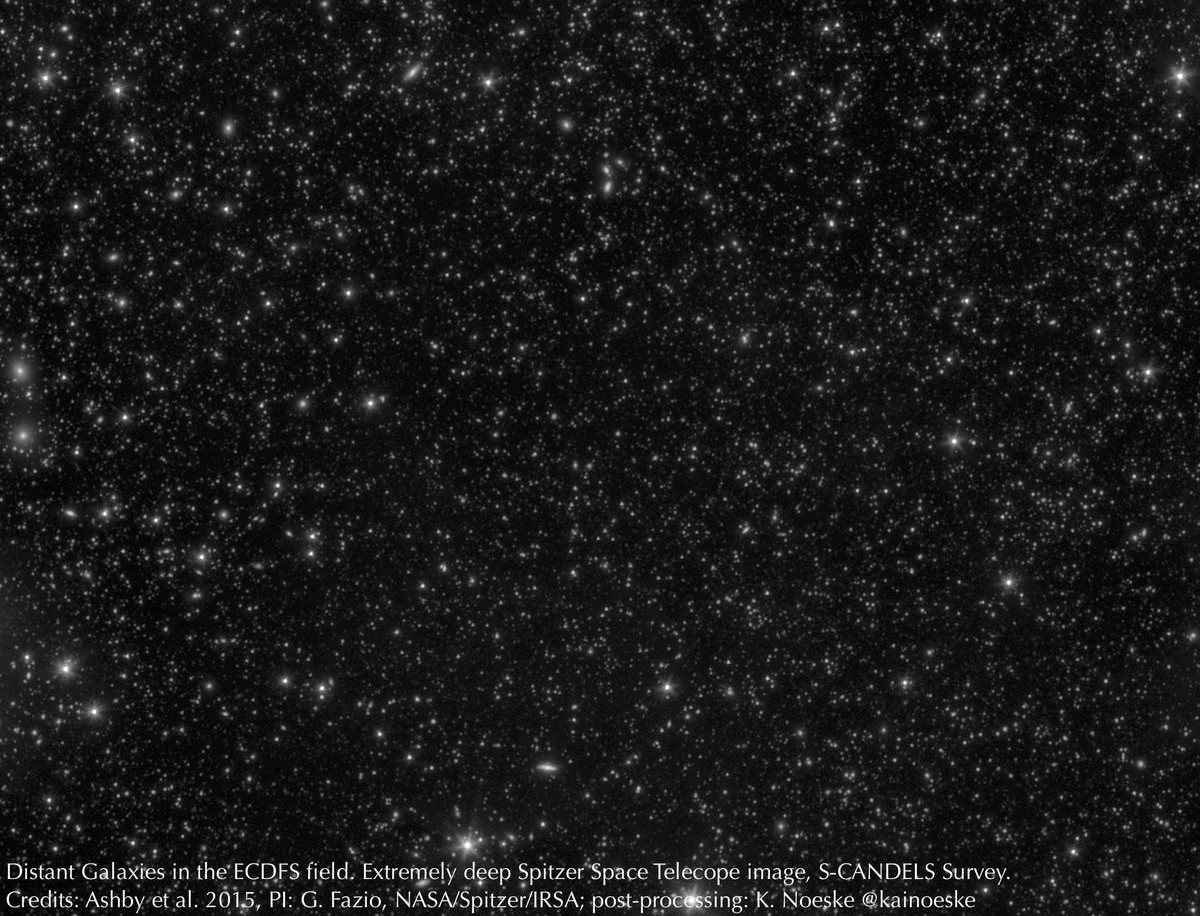
- and how the stars, galaxies, and larger structures in our Universe formed and grew up from a more uniform, smaller, denser, hotter past.
Yet in between the interface of these two fields, science and theology, beyond our definite knowledge but without an appeal to an authoritative source, lies philosophy.

Philosophy. This is, in some sense, the ultimate warzone. Encroaching on the interface — and the limits — of both science and religion, philosophy seeks to probe questions that science cannot (yet) answer. However, unlike religion, philosophy approaches these questions with appeals to reason and logic, and attempts to use these tools to explore questions whose answers are not yet known, but may someday be knowable.
Where our scientific knowledge is insufficient and where theological answers fail to compel and convince us, philosophy remains a useful endeavor. Questions concerning consciousness, the purpose of the Universe, whether reality is objective or is observer-dependent, of whether the laws of nature and the physical constants of the Universe are unchanging with time or whether they are mutable, etc., are all realms where philosophy may be of use to the intellectually curious.

For every well-posed question that we can ask, the ultimate goal should be to eventually find a scientific answer: to bring an investigation whose outcome is unknown to a satisfying conclusion based in definitive knowledge. If we could create life from non-life in a laboratory setting, discover a way to test various interpretations of quantum mechanics against one another, or measure the physical constants across cosmic distances and times, we would be well-justified in drawing scientific conclusions.
But until we do, we must admit our own ignorance. Our best scientific theories are only well-established over a certain range of validity; outside of that range, we do not know with any certainty where and how those rules break down. We can explore scenarios, run simulations, and model the behavior of systems based on certain assumptions. Without enough relevant data to learn the definite answer, however, we can only employ the tools at our disposal.
This is where philosophy has its real opportunity to shine. By coming up to the scientific frontiers — and by understanding what the current body of scientific knowledge is and how we obtained it — we can peer over the edge and explore a variety of speculative ideas. The ones that lead to logical inconsistencies or impossible conclusions can be ruled out, enabling us to favor or disfavor ideas even without definitive, scientific knowledge.
However, this is by no means an easy task. It requires the philosopher to understand the relevant science as well as a scientist does, including its limitations. It requires that we understand the logical rules the Universe plays by, which can run counter to our common experience. Notions like cause-and-effect, the idea that a × b = b × a, or that particles that are placed in an unopened box remain in the box are ubiquitous, but are not true in all circumstances.
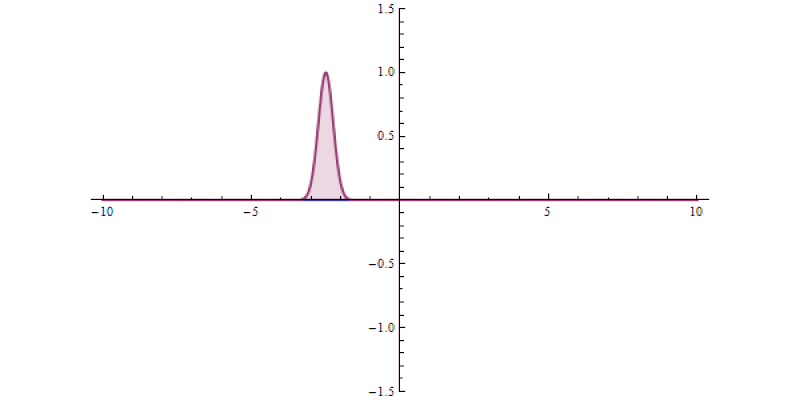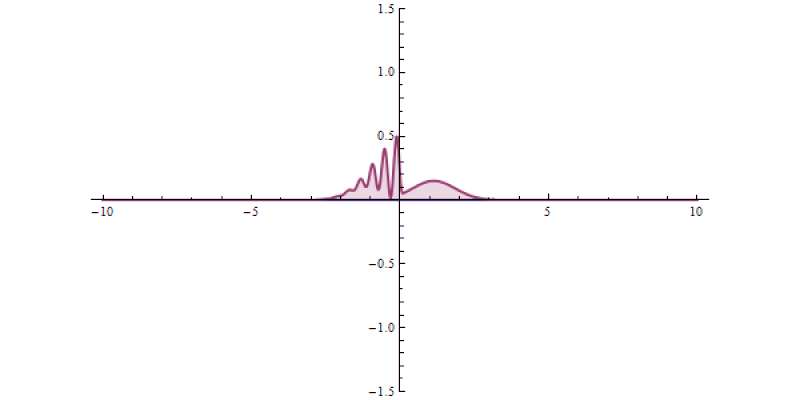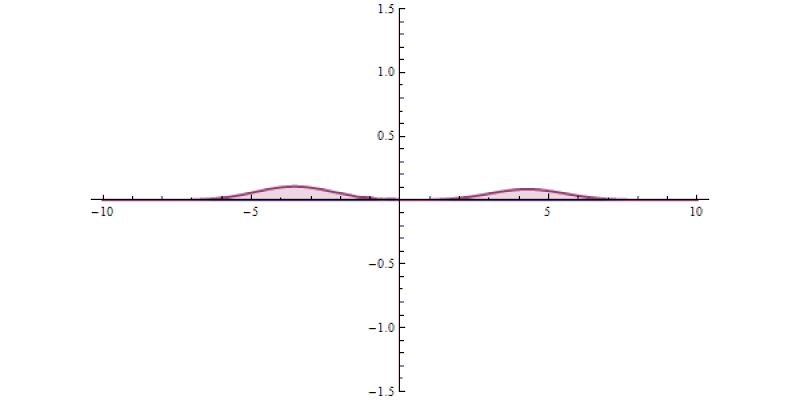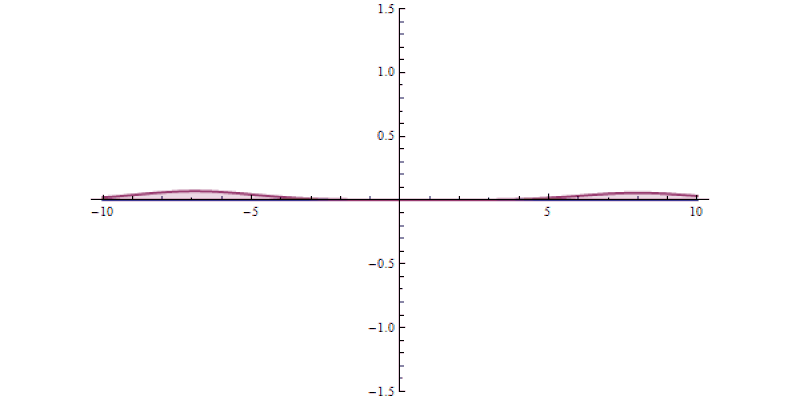
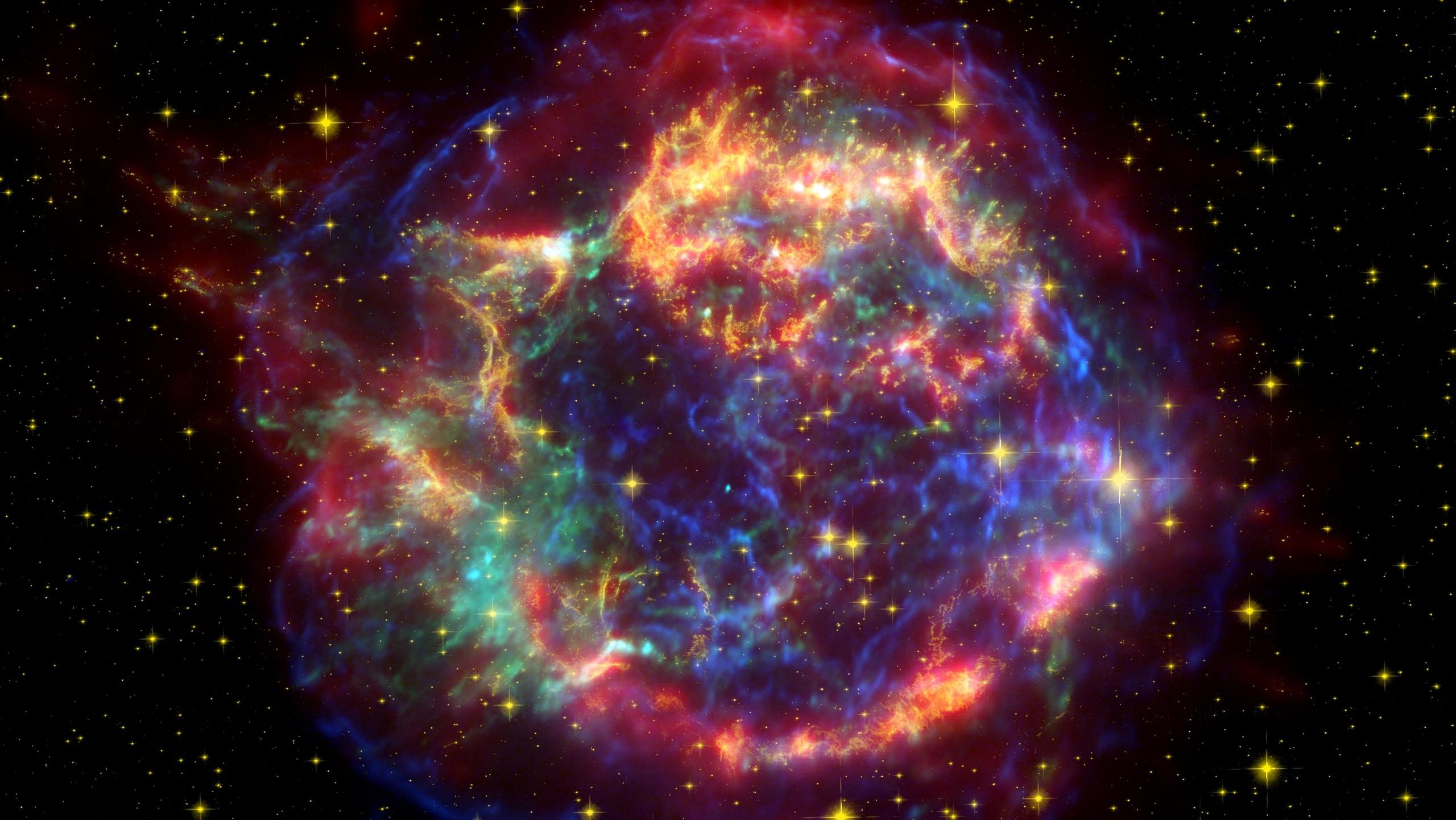
No matter how large our body of scientific knowledge grows, there will always be questions that are beyond the realm of science to adequately answer. The number of particles contained within the observable Universe is finite; the amount of information encoded in all the Universe is finite; no matter how much we learn, the amount that we know will always be finite. Beyond all definite knowledge, there will always be room for philosophy. And when it comes to questions of purpose, meaning, or ideas that are in principle unable to be physically investigated, religion will always have a place as well.
This doesn’t necessarily imply that all philosophizing done at the frontier is useful, interesting, or worth listening to, however. Philosophy that is ignorant of science, or of the bizarre and arcane logical rules that science actually follows, will lead even the most brilliant of thinkers astray. To the speculative, curious mind, however, what is known today will never be satisfactory. Until science makes those critical advances, philosophizing will be a necessary tool for gazing beyond today’s frontier, while there will always be room for religion to play a role in people finding their personal meanings to existence. Science is remarkable, but far from all there is.