NASA’s Dawn probe solves Ceres’ multiple mysteries

Those white spots are still salt, but there’s so much more there!
“Although impact processes dominate the surface geology on Ceres, we have identified specific color variations on the surface indicating material alterations that are due to a complex interaction of the impact process and the subsurface composition.” –Ralf Jaumann, Dawn scientist
Just a few years ago, the highest-resolution map of Ceres, ever, was taken from millions of miles away by the Hubble Space Telescope, and could only see features about 20 miles (32 km) in size. Today, NASA’s Dawn spacecraft has just released images it took orbiting just 240 miles (385 km) above the surface, where we can now resolve features as small as 115 feet (35 meters) across. What we found was a world that was not only full of small and mid-sized craters, somewhat resembling our Moon, but that held a number of mysteries, including a dearth of large craters, strange white spots at various locations along the surface, and a crust that varied wildly in its chemical makeup.
But the latest data release solves a number of mysteries, and does so spectacularly. In addition to cameras, you see, the Dawn spacecraft has a number of detailed instruments on board that are sensitive to color differences, the presence or absence of molecules, the emission of gamma rays and much, much more. Here are the three biggest pieces of knowledge we’ve just uncovered, each of which illustrates how science is a progressive process, and that new knowledge reveals new questions to answer.
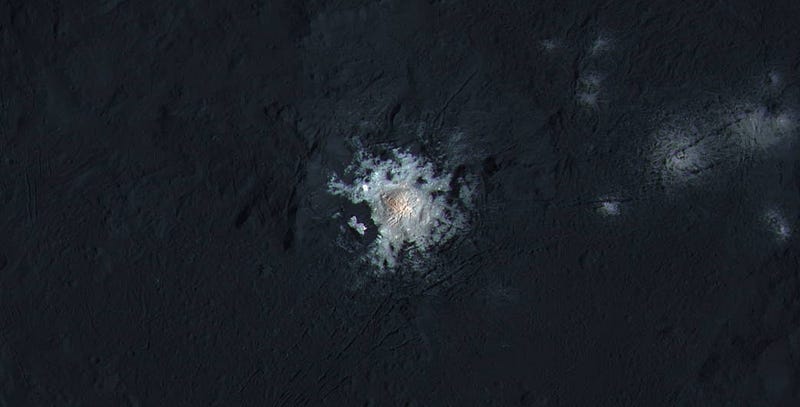

1.) The ultra-bright spots inside Occator crater. Back in December, we learned that Ceres’ white spots in Occator crater are salt, but just why these white spots were so bright and isolated remained a puzzle. These salt flats outshine every other location on Ceres’ surface, even the other white spots, as they reflect a far greater percentage of sunlight than anywhere else, and are only found at the bottom of this crater.
This new suite of data revealed a fantastic explanation: the bright, salty regions we see? They are atop a dome-like region at a lower elevation than any other location on the world measured thus far. Occator crater is four kilometers (2.5 miles) deep, and the dome at the center is an extremely suggestive feature for the origin of these salts, which appear in only a few isolated, deposited locations.
- An impactor — the one that caused the crater — kicked up sub-surface volatiles and water. Minerals dissolved inside the water, and when the water evaporated/sublimated, the salts were left behind.
- The crater-causing impact phenomenon created a weakness in the crater’s bottom, and a geological feature, an eruption of some sort, deposited the salts.
- Or, the fissures, cracks and streaks on the dome wall point to recent geologic activity, where perhaps subsurface ice/water came upwards and left a trail of salty deposits behind.
Geologic dating of this crater, which requires better mapping and improved geometric analysis of the walls, floor and dome, should help us determine which explanation is the best.
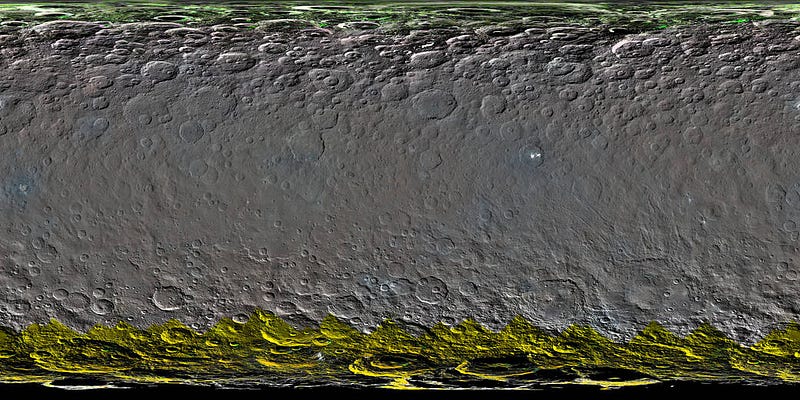
2.) The likely presence of sub-surface ice, but only at the poles. There’s an instrument aboard Dawn — the Gamma Ray and Neutron Detector (GRaND) — which began acquiring data from Ceres in December. Gamma rays and neutron are emitted where cosmic rays interact with the minerals all over Ceres. Over much of the surface, it points to the existence of carbon-based and silicon-based minerals, with roughly uniform amounts of neutrons giving evidence to that. But the polar regions (both north and south poles) are sparserin neutrons than all the other locations, indicating that there’s more hydrogen at these high latitudes.
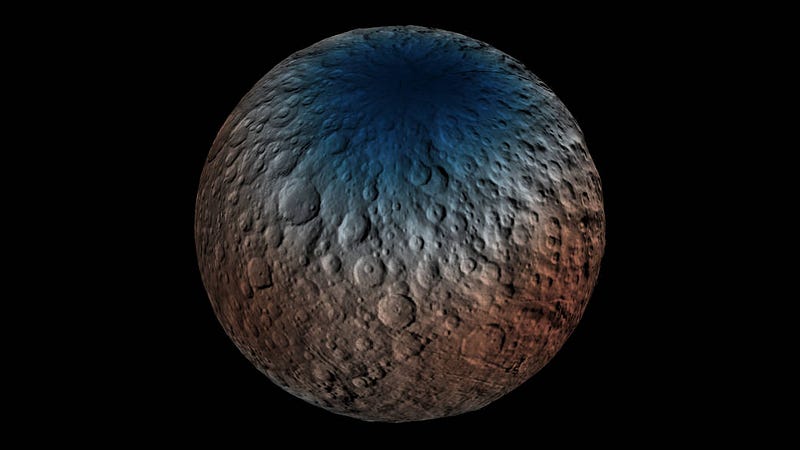

Hydrogen, of course, is a key ingredient in water. But there’s no water visible at the poles anywhere, indicating that it’s probably sub-surface water, likely within the top meter (3 feet) of Ceres’ top layer of material. As future data comes in from GRaND, we should be able to determine both the presence and abundances of water at these locations. “Our analyses will test a longstanding prediction that water ice can survive just beneath Ceres’ cold, high-latitude surface for billions of years,” according to Tom Pettyman, the leader of the GRaND instrument.
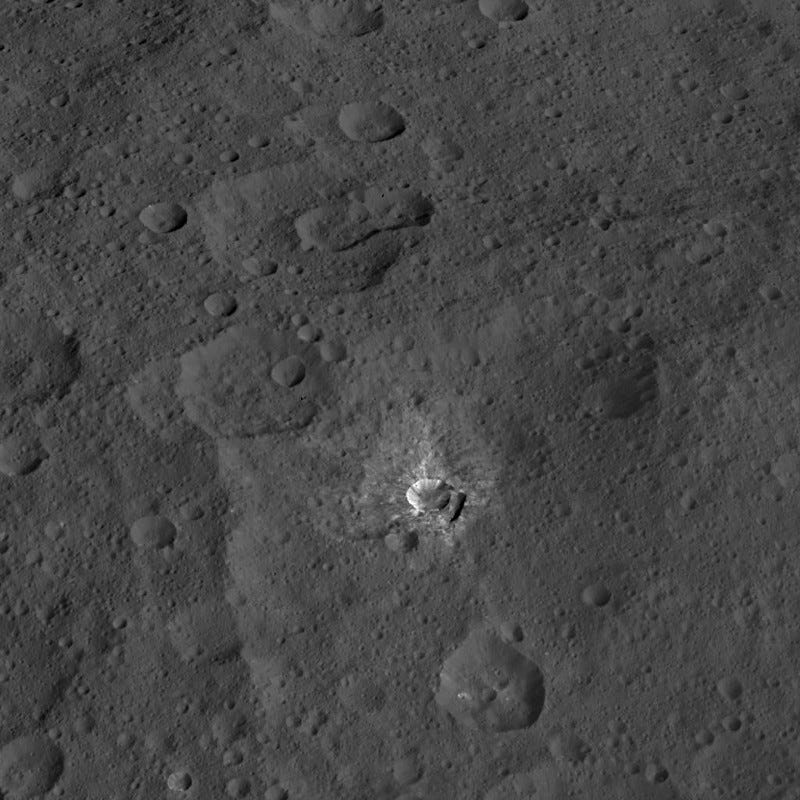

3.) The second brightest crater on Ceres, Oxo, is the only location that exhibits surface water. This small, 9 kilometer (6 mile) wide crater is most likely very young, as water ice should sublimate in the sunlight on timescales of a few million years at most: much shorter than the lifetime of this world. Either it’s one of the most recent impact craters, and practically allimpact craters dredge up subsurface water, or there’s been recent landslide that exposed this water. Future analyses should be able to reveal whether there’s other water-ice on the surface (at lower density than what’s found here), as well as determining whether this is pure water-ice, or whether this is frozen water that’s bound into minerals, making them more stable against sublimation than water-ice on its own.
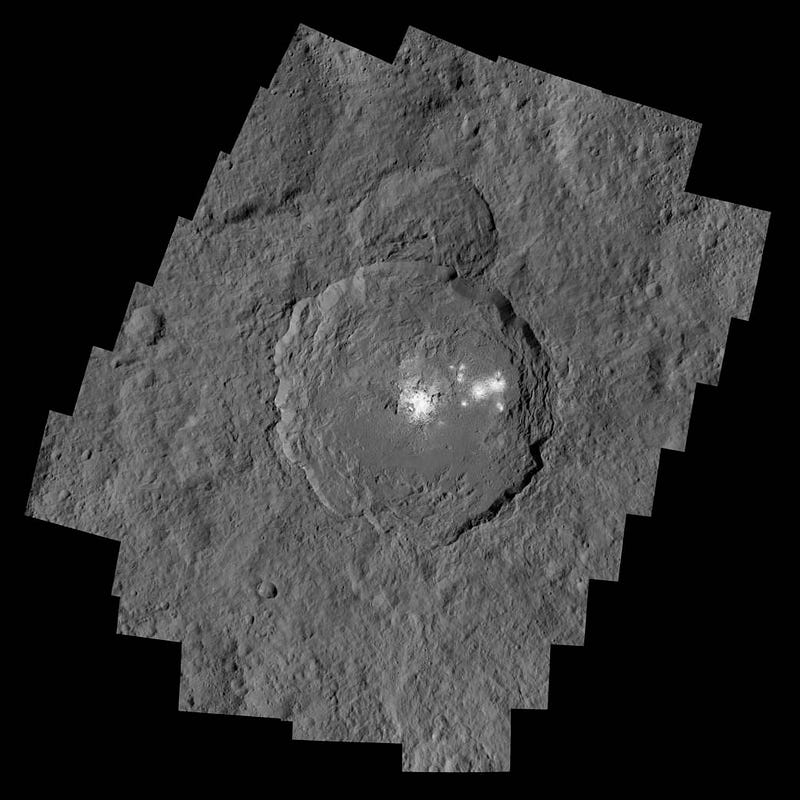

Ceres is the largest object in the asteroid belt, and as Dawn is showing us, is quite different from the other asteroid it observed and mapped: Vesta. As Carol Raymond, deputy-PI of Dawn, related: “We’re excited to unveil these beautiful new images, especially Occator, which illustrate the complexity of the processes shaping Ceres’ surface. Now that we can see Ceres’ enigmatic bright spots, surface minerals and morphology in high resolution, we’re busy working to figure out what processes shaped this unique dwarf planet. By comparing Ceres with Vesta, we’ll glean new insights about the early solar system.” Perhaps there are even greater mysteries still to be solved by this mission.
This post first appeared at Forbes. Leave your comments on our forum, check out our first book: Beyond The Galaxy, and support our Patreon campaign!