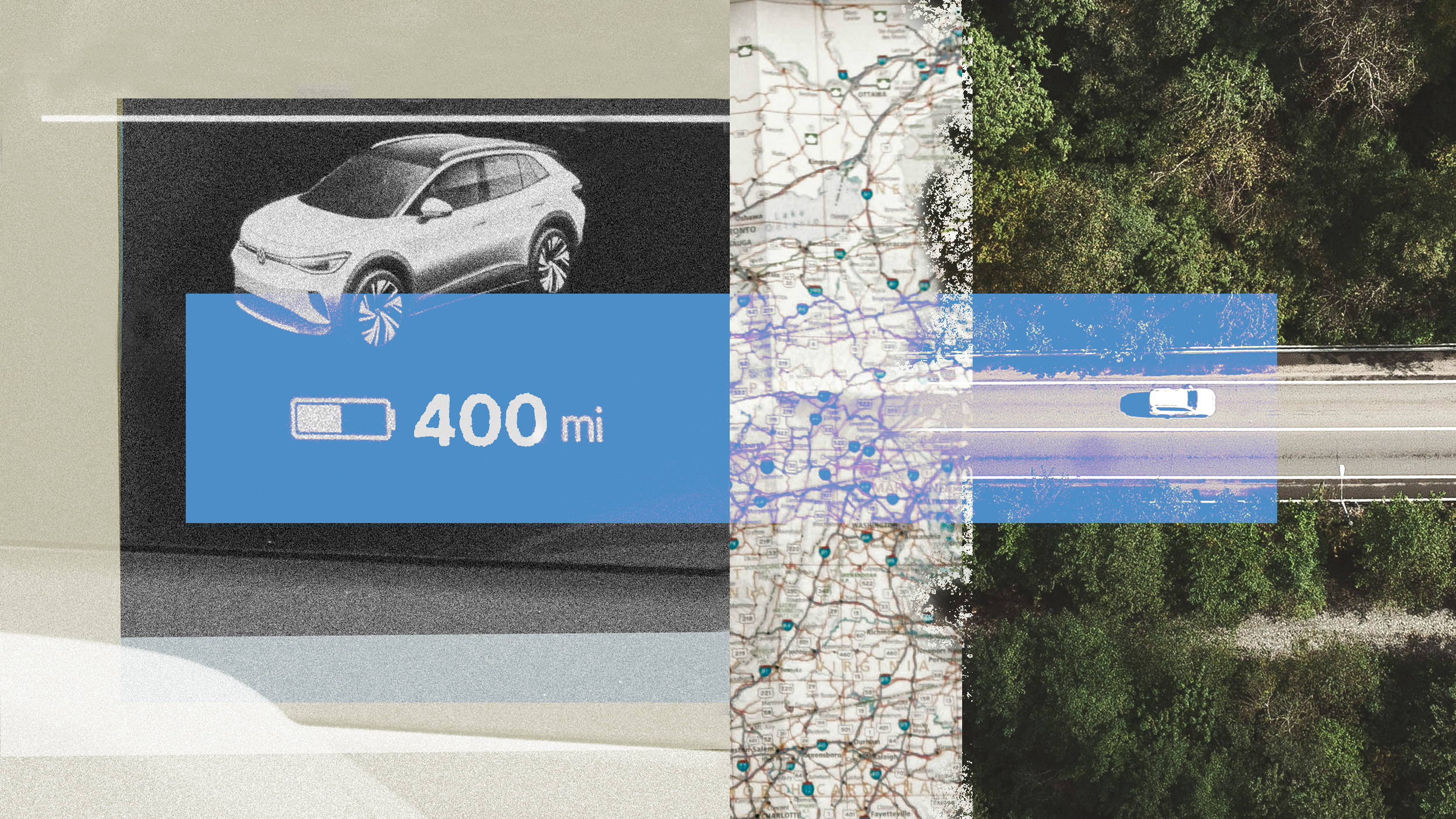
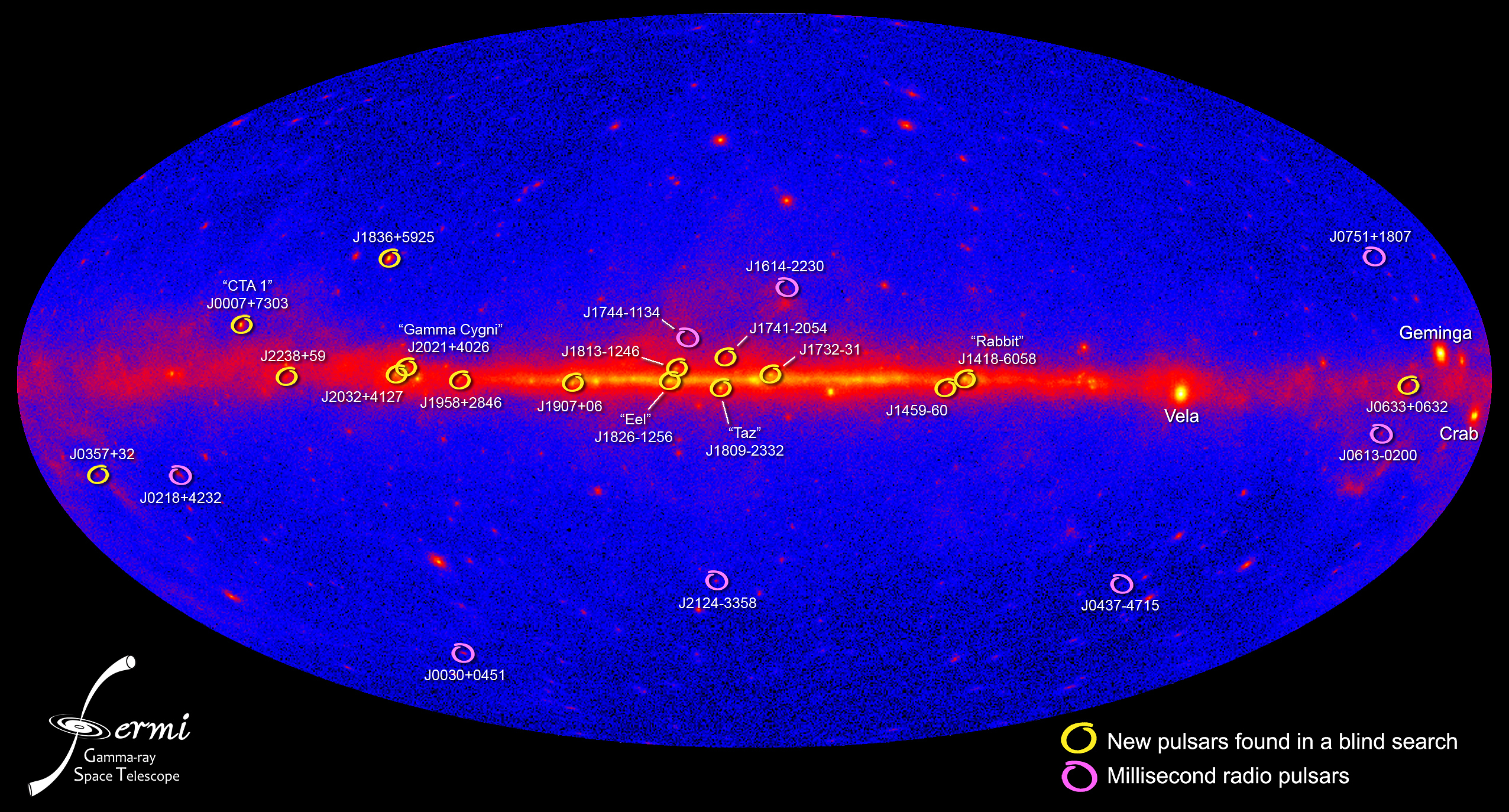
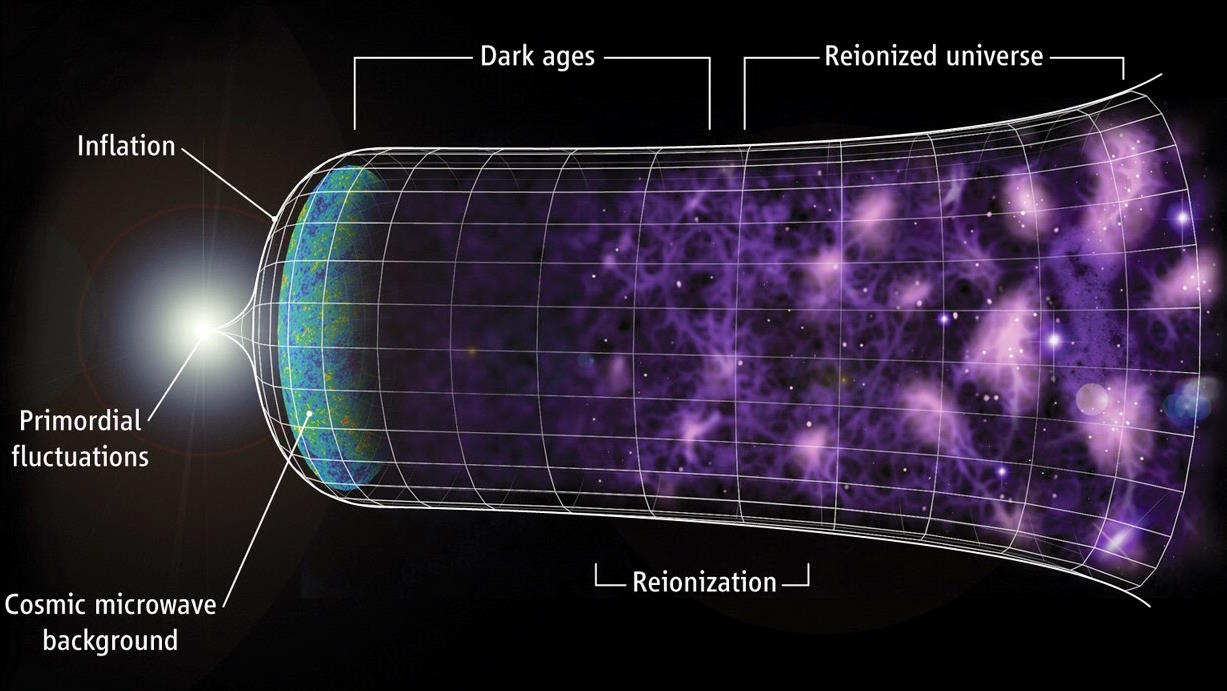
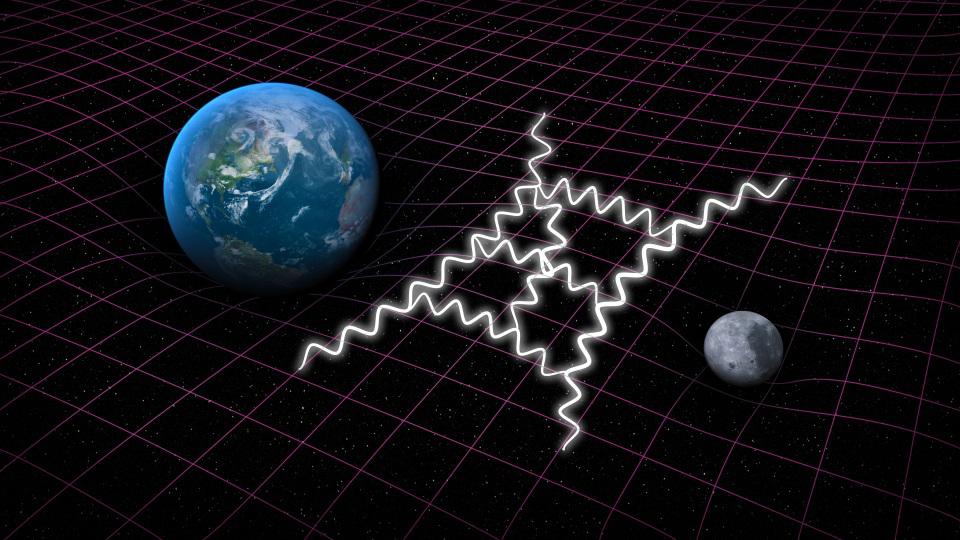
A $30,000 electric vehicle with 400 miles of range that charges in under 10 minutes remains a pipe dream over the near future.
Search Results
You searched for: energy
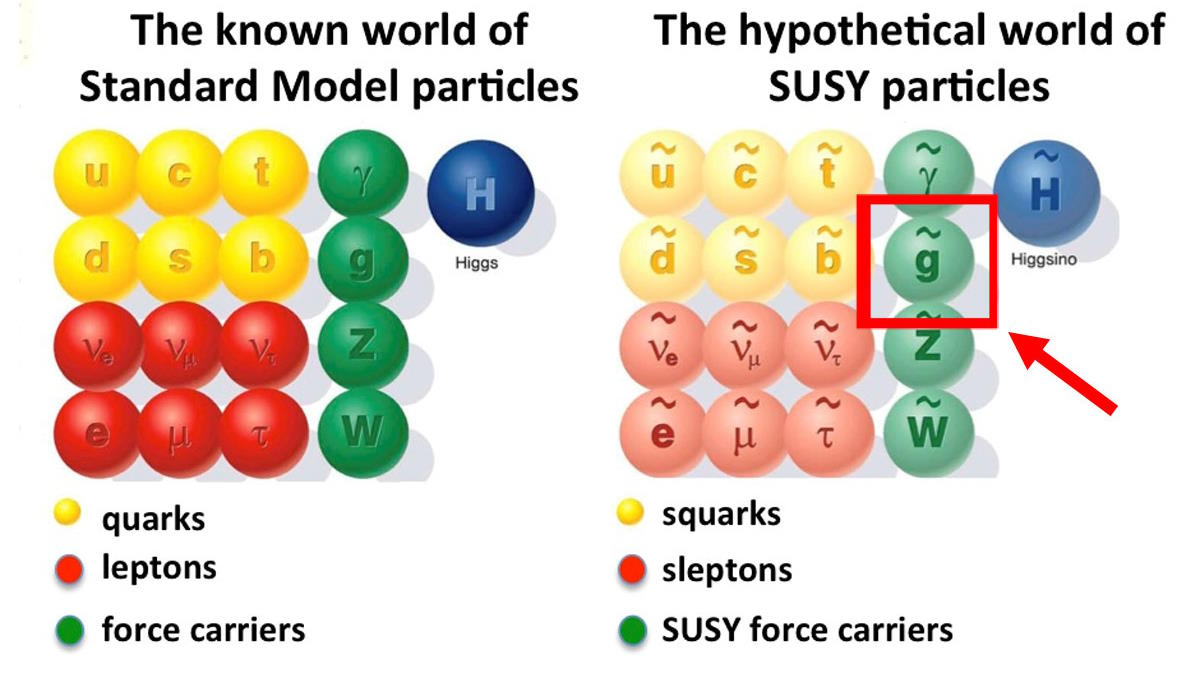
Almost 100 years ago, an asymmetric pathology led Dirac to postulate the positron. A similar pathology could lead us to supersymmetry.
From forming bound states to normal scattering, many possibilities abound for matter-antimatter interactions. So why do they annihilate?
Capacitors, acid batteries, and other methods of storing electric charges all lose energy over time. These gravity-fed batteries won’t.
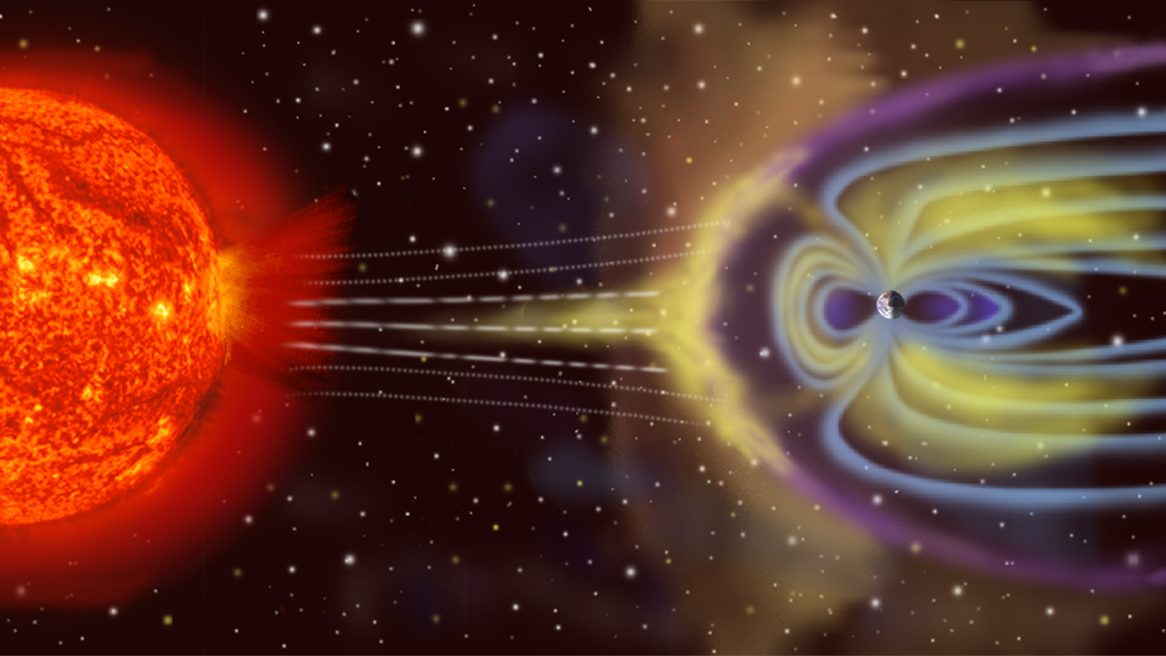
As the Sun ages, it loses mass, causing Earth to spiral outward in its orbit. Will that cool the Earth down, or will other effects win out?
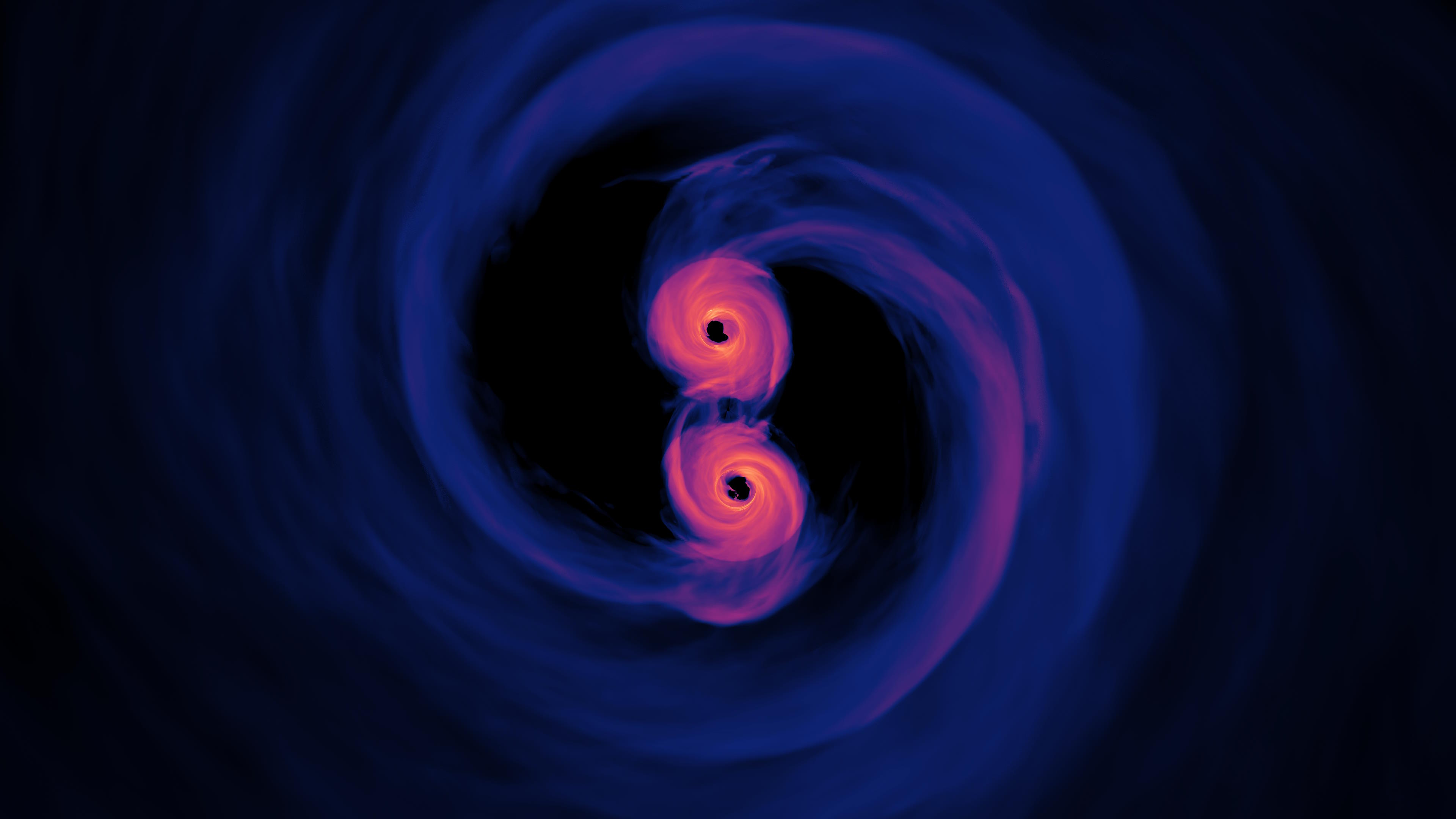
Gravitational waves carry enormous amounts of energy, but spread out quickly once they leave the source. Could they ever create black holes?
CERN’s NA64 experiment used a high-energy muon beam technique to advance the elusive search for dark matter, offering new hope for solving one of astronomy’s greatest mysteries.
If you bring too much mass or energy together in one location, you’ll inevitably create a black hole. So why didn’t the Big Bang become one?
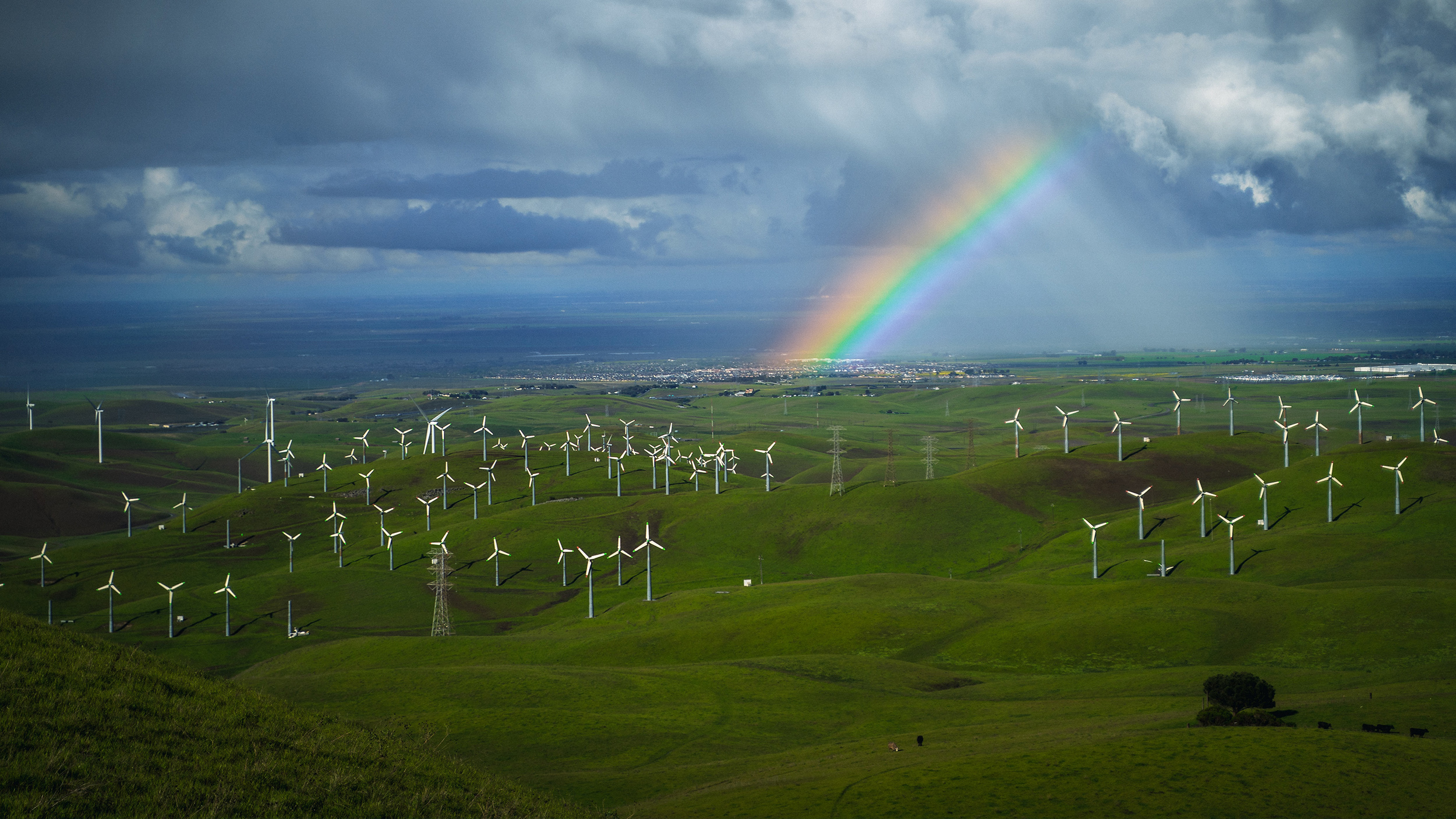
As wind power grows around the world, so does the threat the turbines pose to wildlife. From simple fixes to high-tech solutions, new approaches can help.
McDermitt Caldera, the site of an ancient volcanic eruption, straddles the border of Oregon and Nevada.
Energy balance is the greatest arbiter of weight gain. Embrace the “oinker diet.”
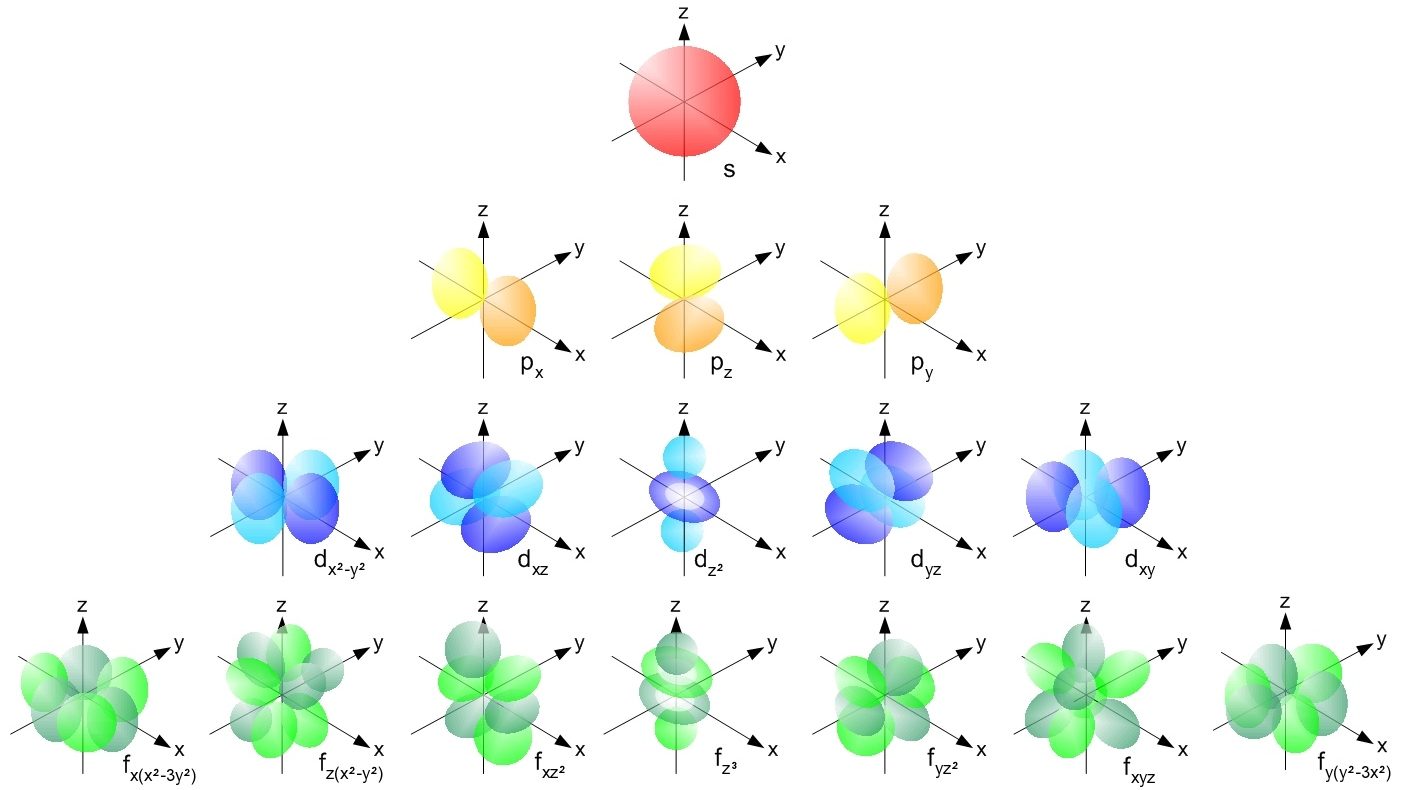
One of the fundamental constants of nature, the fine-structure constant, determines so much about our Universe. Here’s why it matters.
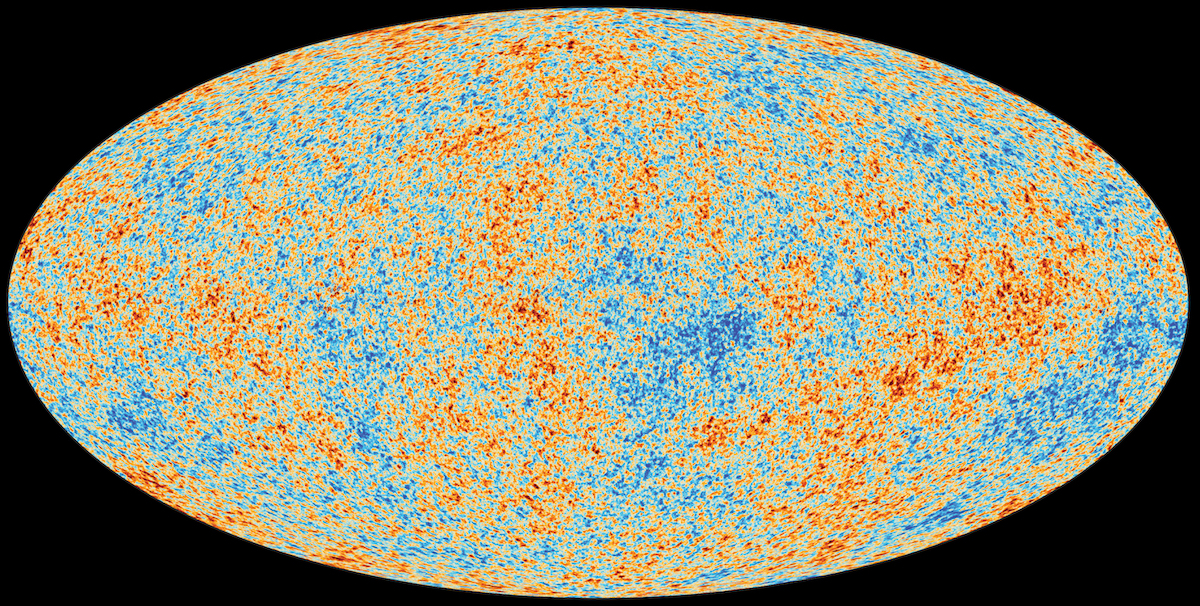
Today, the deepest depths of intergalactic space aren’t at absolute zero, but at a chill 2.73 K. How does that temperature change over time?
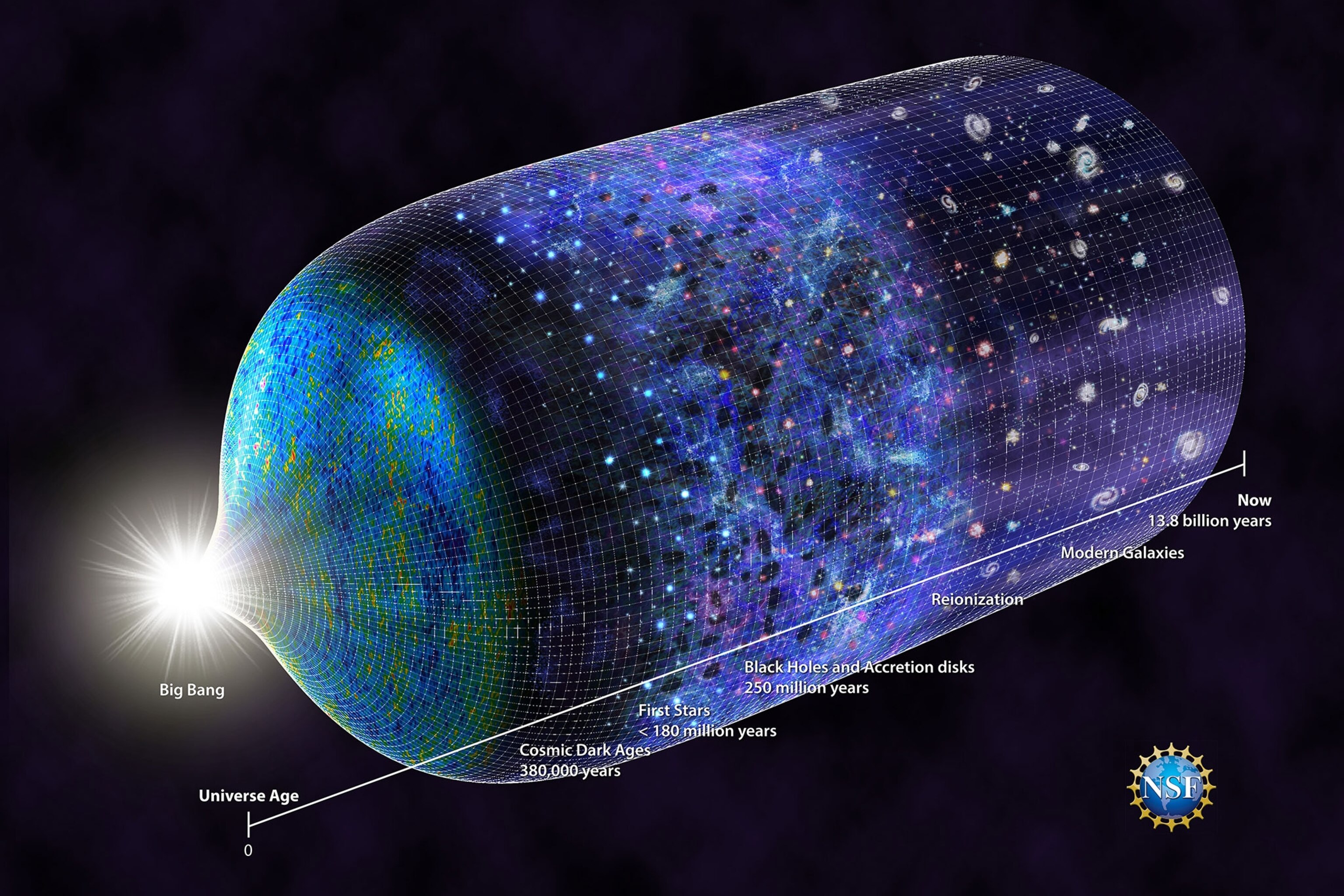
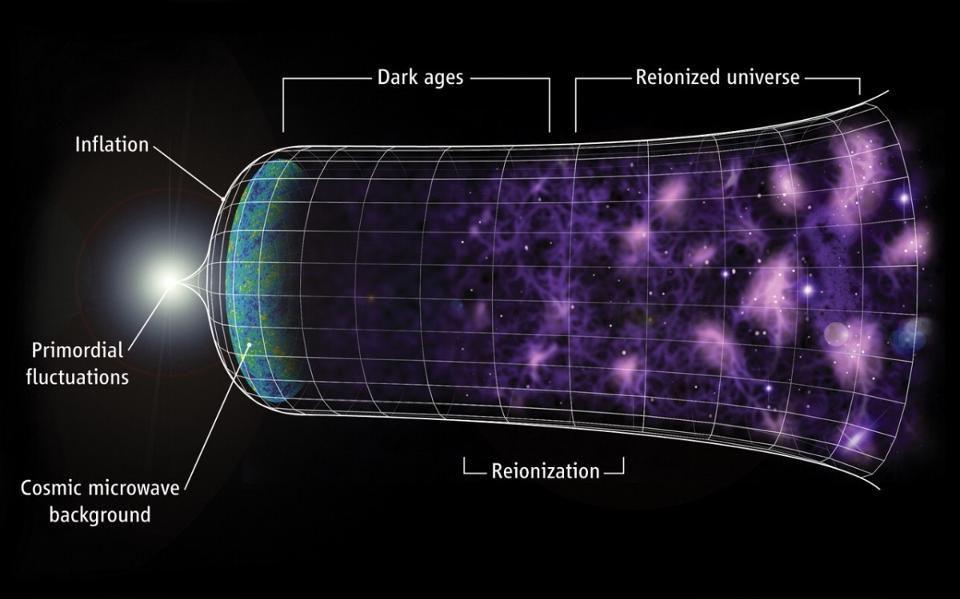
From the earliest stages of the hot Big Bang (and even before) to our dark energy-dominated present, how and when did the Universe grow up?
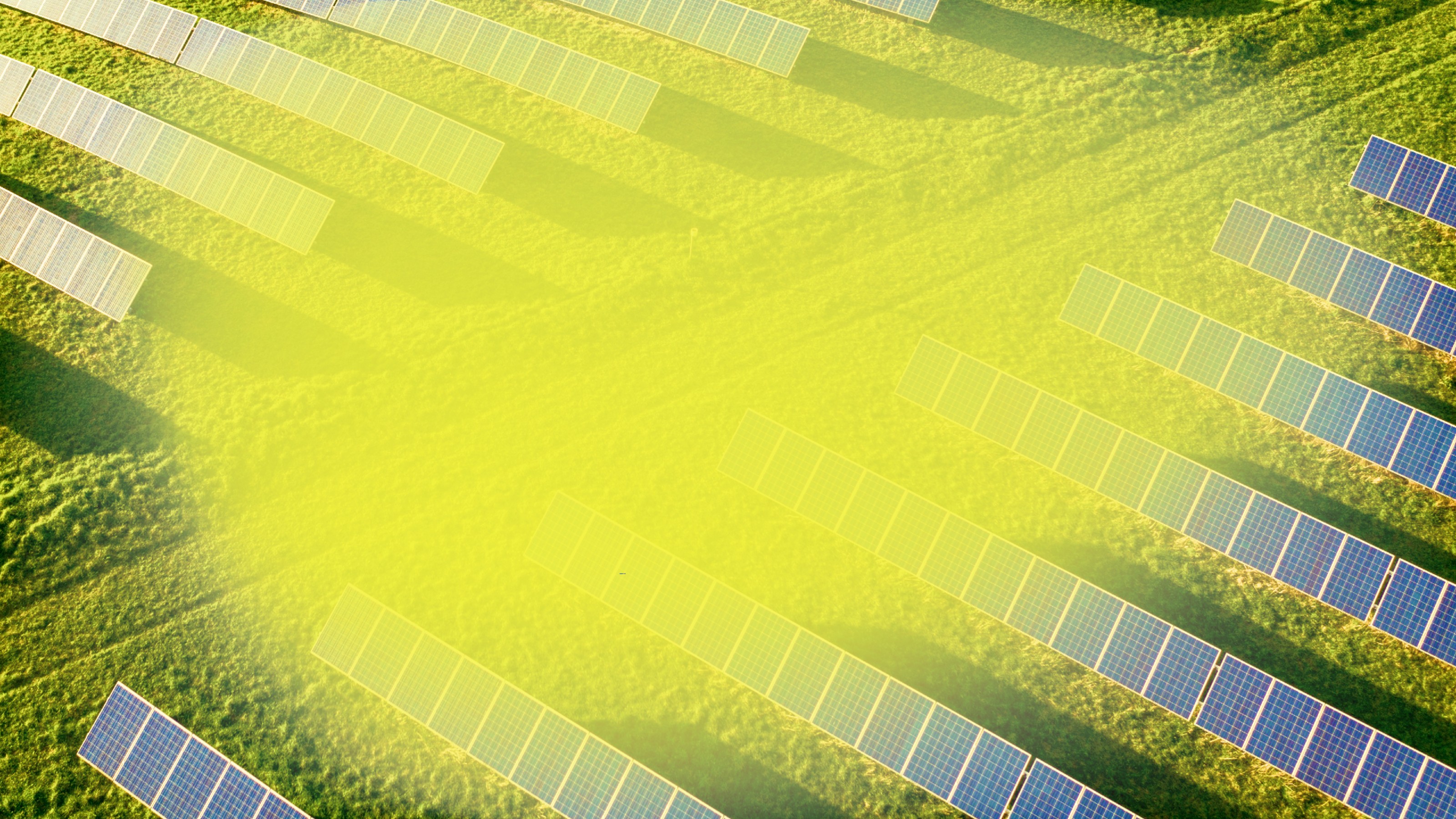
A look back at the rise of solar power in the US and what’s next.
We need more data centers for AI. Developers are getting creative about where to build them.
The Universe is expanding, and the Hubble constant tells us how fast. But how can it be a constant if the expansion is accelerating?
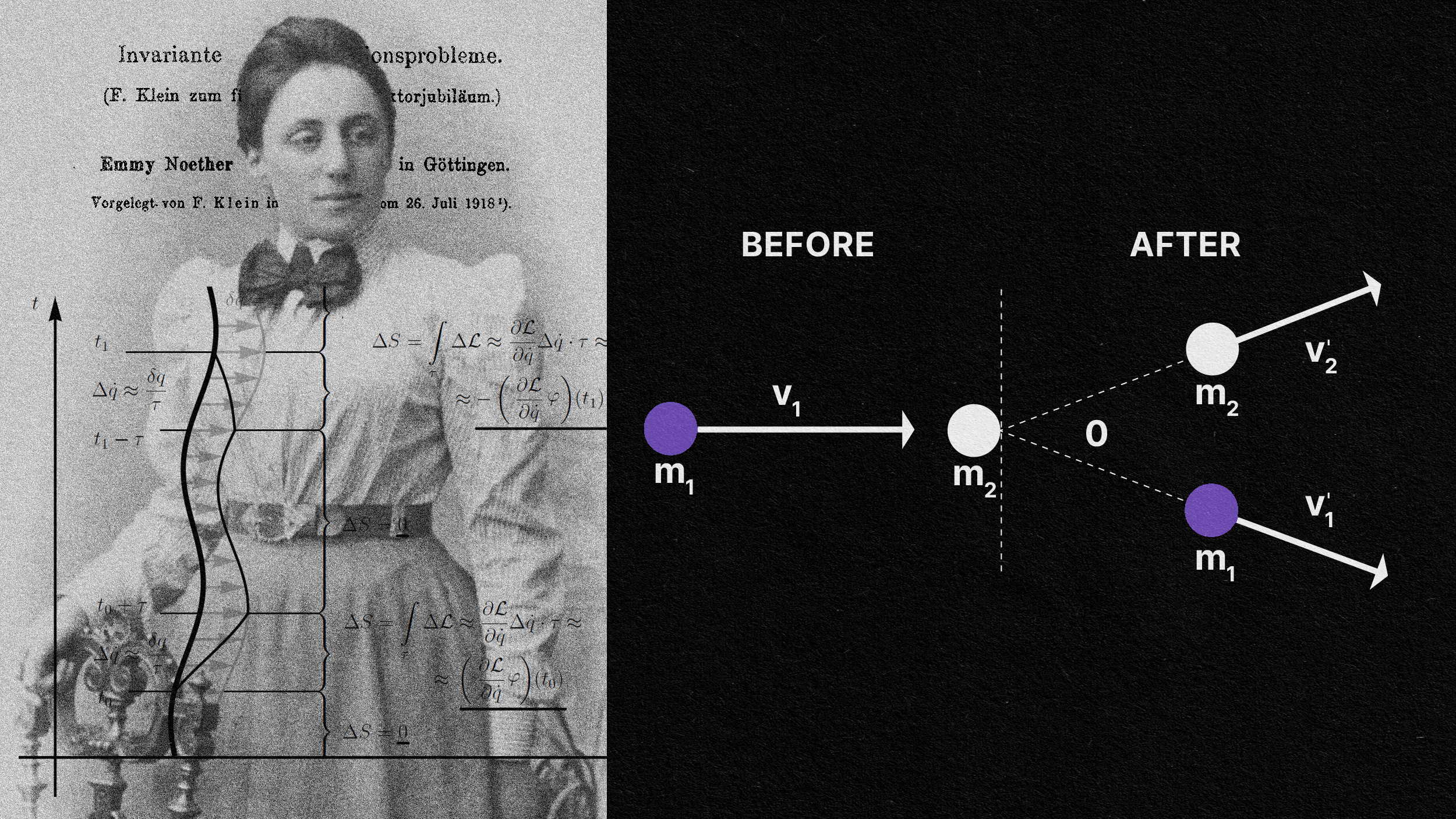
First derived by Emmy Noether, for every symmetry a theory possesses, there’s an associated conserved quantity. Here’s the profound link.
And can we run the grid of the future without AI?
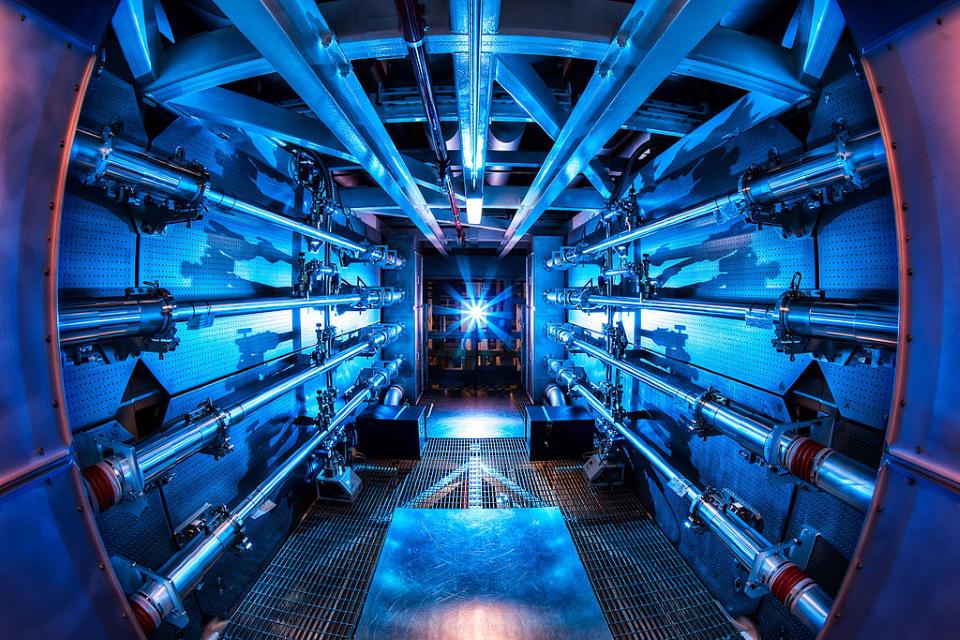
Nuclear fusion has long been seen as the future of energy. As the NIF now passes the breakeven point, how close are we to our ultimate goal?
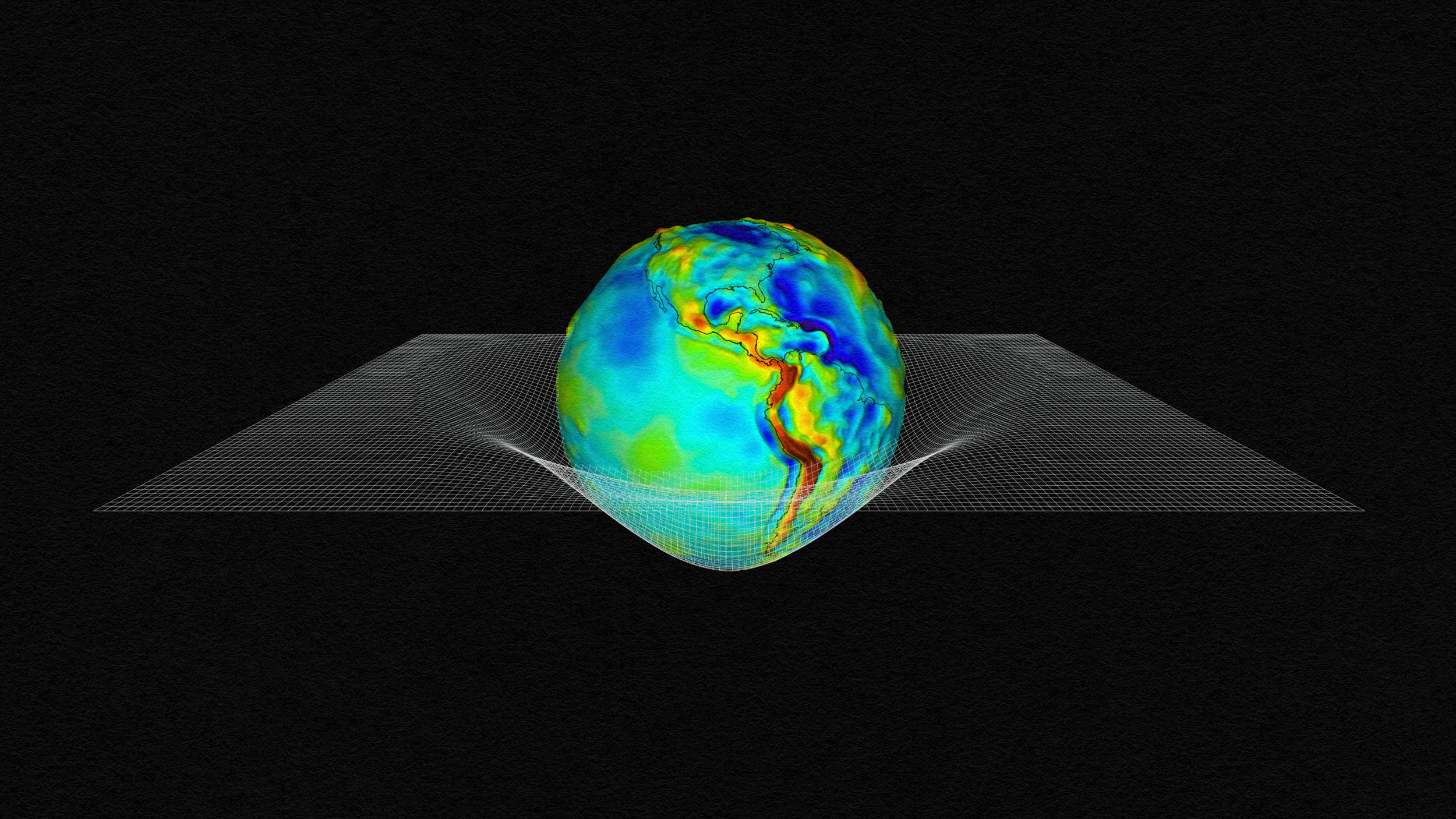
In general relativity, matter and energy curve spacetime, which we experience as gravity. Why can’t there be an “antigravity” force?
The Universe isn’t just expansion, but the expansion itself is accelerating. So why can’t we feel it in any measurable way?
The evolution of quantum technology is far from over.
It’s not about particle-antiparticle pairs falling into or escaping from a black hole. A deeper explanation alters our view of reality.
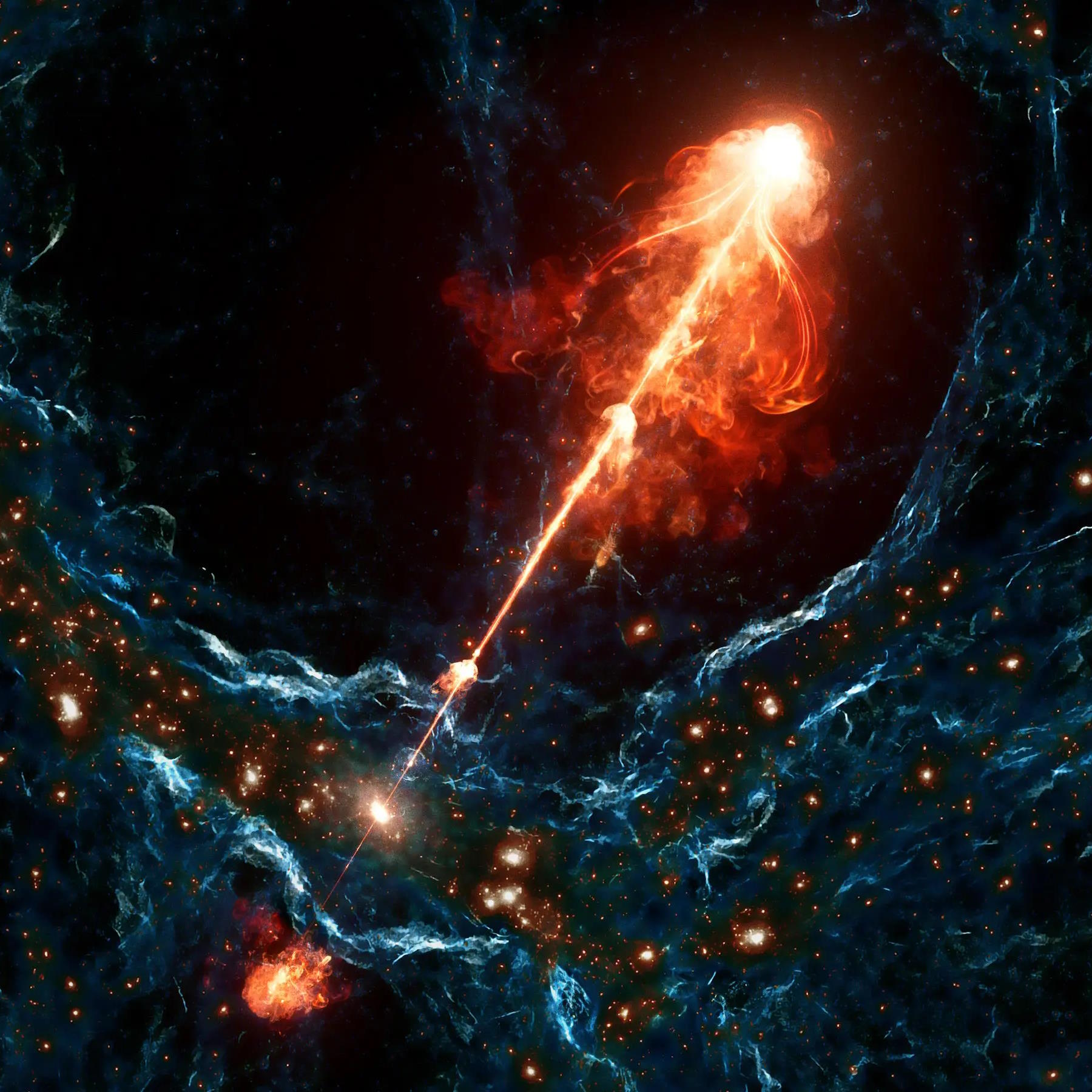
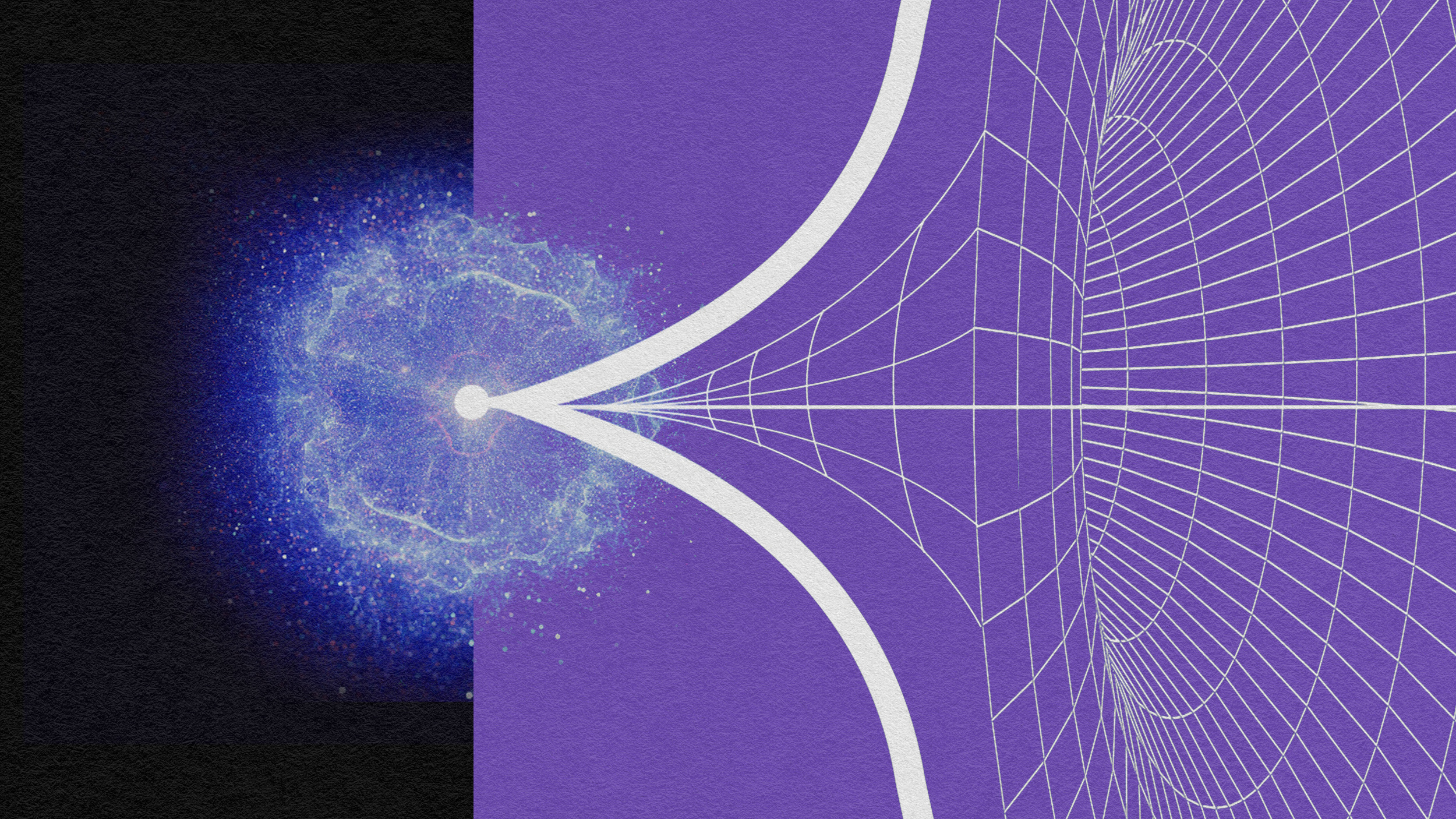
Black holes are the most massive individual objects, spanning up to a light-day across. So how do they make jets that affect the cosmic web?
An enormous amount of antimatter is coming from our galactic center. But the culprit probably isn’t dark matter, but merely neutron stars.
Inflation, dark matter, and string theory are all proposed extensions to the prior consensus picture. But what does the evidence say?
Bang bang all over the Universe.
Electromagnetism, both nuclear forces, and even the Higgs force are mediated by known bosons. What about gravity? Does it require gravitons?
Across all wavelengths of light, the Sun is brighter than the Moon. Until we went to the highest energies and saw a gamma-ray surprise.