Now that the Higgs has been discovered, the Standard Model is complete. But are there any other new particles? “The particle and the planet are subject to the same laws […]
Search Results
You searched for: Telescope
Inflation tells us that it’s likely real, but can it be the answer to any of our scientific questions? Probably not. “Physical reality does not require that we be pleased with […]
How many times would you have to fold a piece of paper in half for it to reach the Moon? “Only on paper has humanity yet achieved glory, beauty, truth, knowledge, […]
The speed of light in a vacuum is the limit for massless particles, but massive ones are limited even further! “All our sweetest hours fly the fastest.” -Virgil If you’ve been […]
Bill Nye: Our intellect and treasure is really best used in exploring space.
Does space stretch or does new space get created, and what does that mean for the conservation of energy? “If you put yourself in a position where you have to stretch […]
The brightest galaxy in a spectacular close grouping of three provides a beacon of insight into our far future. “Three can keep a secret, if two of them are dead.” -Benjamin […]
Capitalism, the dominant secular faith of our times, risks a reformation.
The greatest Messier object of them all, a treat all winter long. “What caused me to undertake the catalog was the nebula I discovered above the southern horn of Taurus on […]
Two new studies agree that Kepler-78b is about the same size and composition as Earth, but because it orbits its star at one-tenth the distance of our orbit, it’s way too hot to support life.
They’re the densest objects in the Universe, but even they won’t live forever. Here’s why not. “It’s like, how much more black could this be? And the answer is none. None […]
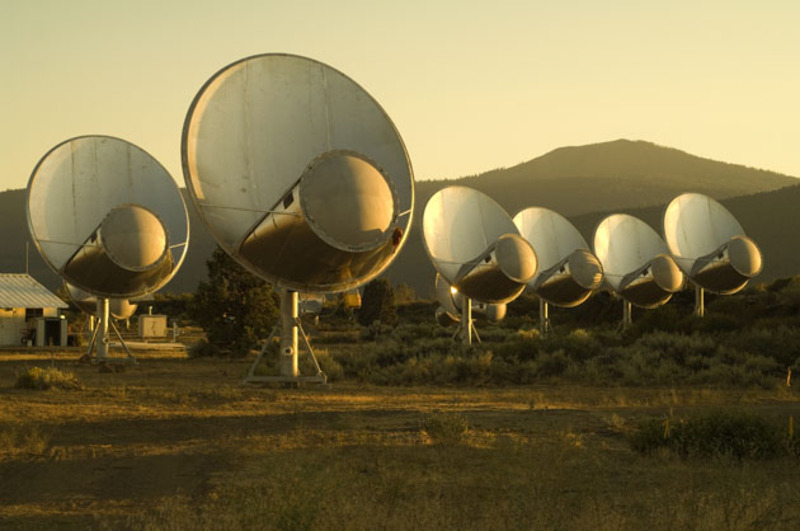
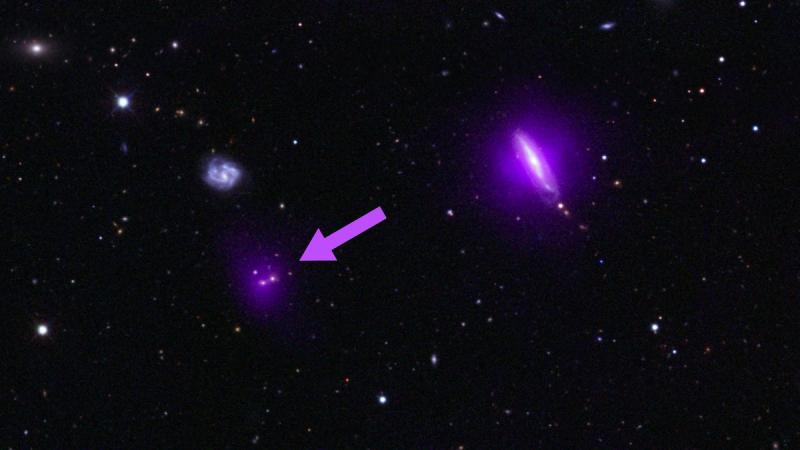
NASA’s “black-hole-hunter” spacecraft, the Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, has serendipitously discovered its first 10 supermassive black holes.
What everyone should know about where our matter-and-radiation-filled Universe came from. “I don’t think at this point we have any way of knowing where the laws of physics came from. We […]
Scientists can be harsh film critics, as evidenced by Neil deGrasse Tyson’s recent evisceration of the film Gravity on Twitter.
Using data from space telescopes, including the now-sidelined Kepler, astronomers have identified cloud structures on Kepler-7b, a “hot Jupiter” exoplanet that was one of the first discovered.
It’s a scientific truth of the Universe, one that many people — children especially — have trouble coming to terms with. But it doesn’t have to be a tragedy. “Through that last dark cloud is […]
One of the only members of the Virgo Cluster… that isn’t located in Virgo! “[L]ife is a luminous halo, a semi-transparent envelope surrounding us from the beginning of consciousness to the […]
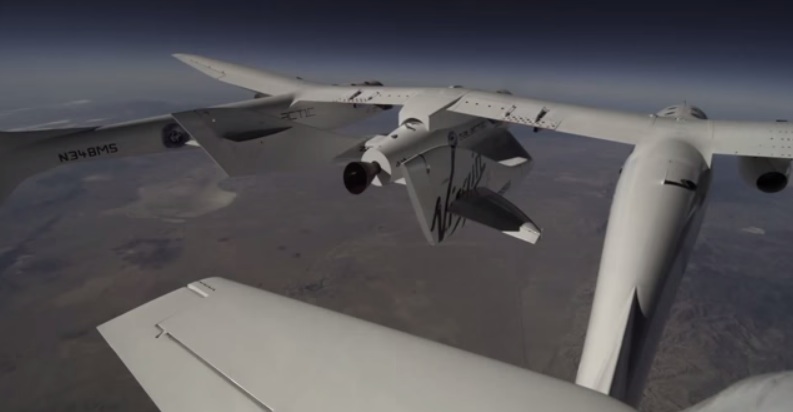
SpaceShipTwo’s second rocket powered test flight reached supersonic speeds of over 1,000 mph.
When we look across the Universe, we find that things used to be closer together in the past. So how large do things appear when they’re very far away? “Life is […]
Given all the stars, galaxies and what we know about the laws governing reality, how many planets are there in our observable Universe? “Stuff your eyes with wonder, live as […]
It’s easier than you might think, and we’ve been doing it for over a century. “The doctors realized in retrospect that even though most of these dead had also suffered from […]
They’re the first major finds by NASA’s X-ray space observatory, which went into orbit last year. Scientists expect it to find many more in the near future.
Discovered in the constellation of Capricornus with the help of the Very Large Telescope (VLT), HIP 102152’s characteristics confirm longstanding scientific speculation about how stars like ours age.
How the closest supernova in a generation — soon to be visible to skywatchers almost everywhere — is about to help us better understand the entire Universe. “I saw a star explode and send […]
As part of this week’s Festival of the Planets celebration, University College London has made available to the public a selection of historic images from its archive. Included are glimpses of the surface of Venus.
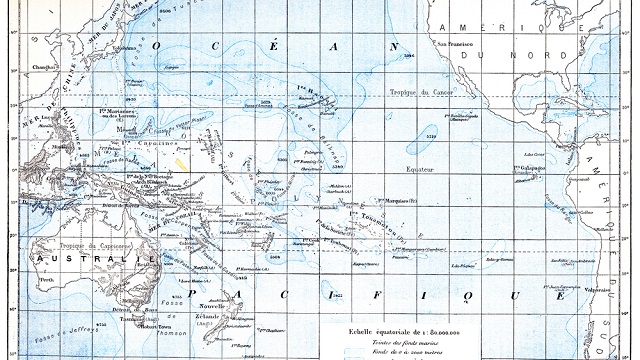
Researchers have confirmed that Tamu Massif, located in the northern Pacific, is a single volcano rather than a composite of different eruption points. At 120,000 square miles in size, it’s about as big as the entire state of New Mexico.
More than 400 years after Galileo’s first telescopic observations, we’re more certain than ever that the Earth is moving through space. How do we know? “Nature is relentless and unchangeable, and […]
How the Universe tells us its age, size, and properties, and leads us inescapably to the conclusion that it’s billions, not merely thousands, of years old. Today, we’re lucky enough to […]
The 23-year-old space telescope may be a few years away from retirement, but its eye is still good: The newly discovered 14th moon is only 12 miles in diameter.
Galileo must have developed “a new theory of optics as revolutionary as the device itself.” This theory he kept secret.