Culture & Religion
All Stories
In a 1977 interview with Glenn O’Brien for the marijuana lifestyle magazine High Times, O’Brien asked Andy Warhol if his teachers recognized his early “natural talent.” “Something like that,” Warhol responded with his characteristic unconventionality, “unnatural talent.” Warhol’s “unnatural talent” quip alluded not only to his mass-produced, machine-like paintings of soup cans and silk screen portraits, but also to his sexual orientation — the “unnatural” life of a homosexual. Just as Warhol turned that verbal double play, art scholar Michael Maizels tries to touch those two bases of Warhol’s art in “Doing It Yourself: Machines, Masturbation, and Andy Warhol” in the Fall 2014 issue of Art Journal. For Maizels, the way that Warhol made art reflected the way Warhol lived his life as a homosexual male in late 20th century America. When we look at Warhol’s art, Maizels suggests, we should see not just a critique of commercialized society and its art, but also a critique of that same society’s sexual tolerance.
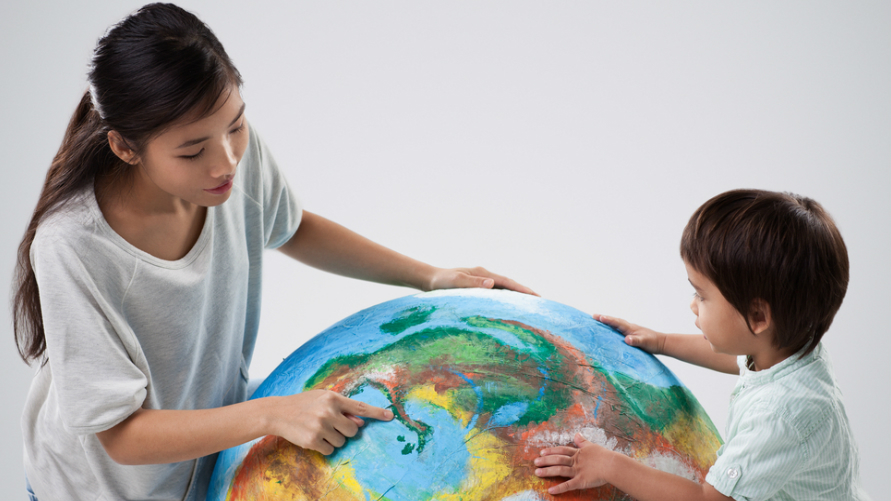
Perspective-taking describes the ability to see things from another’s point of view and it’s an important skill to teach children early on.
Individuals who cheat in life quickly ignore the fact that their success is fraudulent, believing instead that their own abilities will carry them to even greater heights.
In this Big Think+ preview, Dr. Tony Coles introduces the concept of “service leadership” first developed in 1970 by Robert K. Greenleaf.
What does it mean to be confident? Author and broadcaster Claire Shipman explains what surprised her most when researching confidence in both professional and nonprofessional contexts.
Moral sciences are back. Natural laws of ethics, envisioned early in the Enlightenment, can now be objectively studied. Game Theory is reteaching scientists and “rationalists” old wisdoms, while suggesting a “Golden Punishment Rule,” and a Naturalistic Fallacy reform (via “negative telos”).
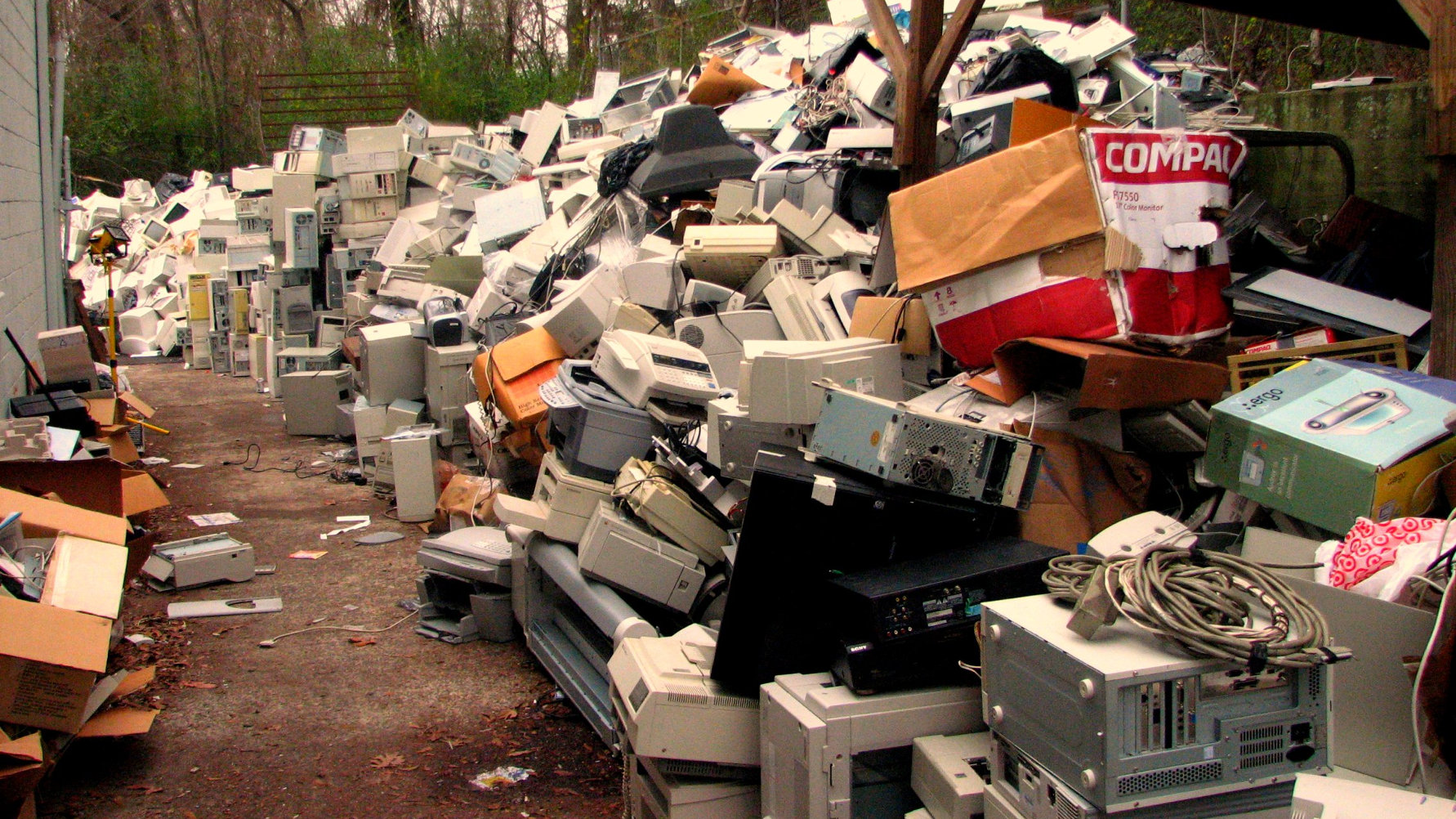
Product design might be one answer to the mounting e-waste dilemma Americans are facing.
One of the brightest minds in basketball walks through the theory and implementation of advanced analytics.
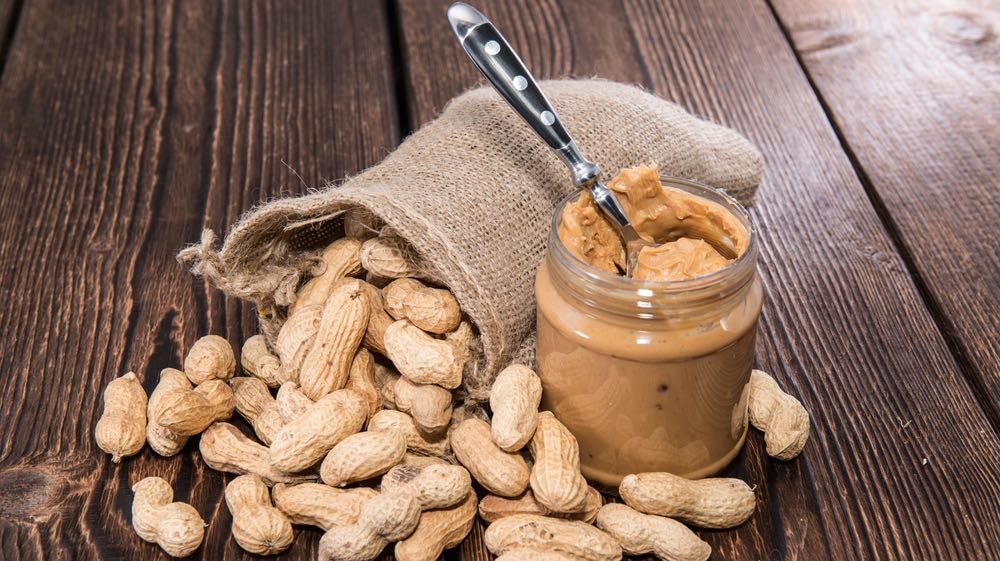
Peanut allergies can be severe, but preventing the sensitivity may be as simple as exposing your infant to peanuts while they are young.
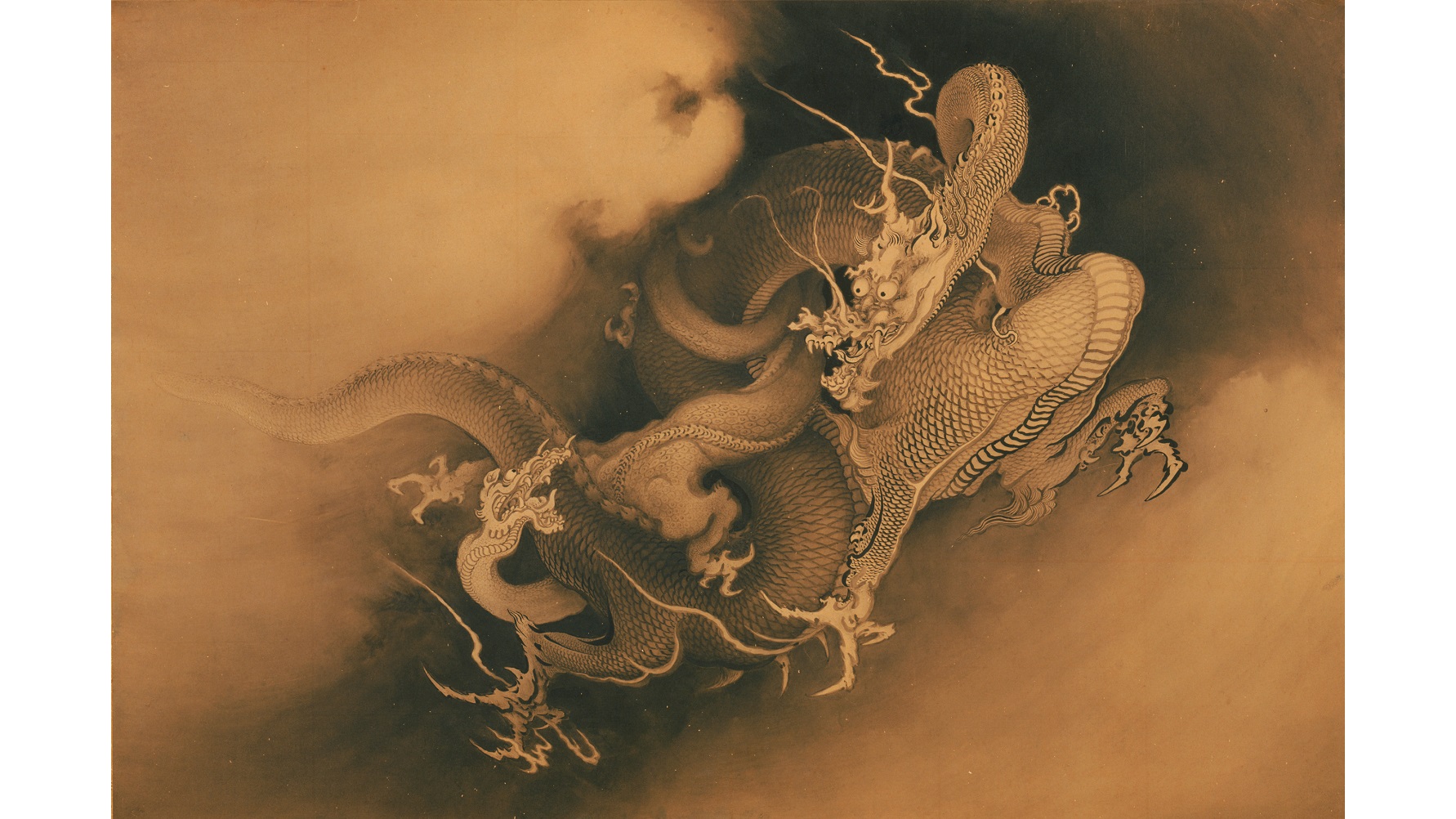
Ever since American Commodore Matthew C. Perry sailed into Uraga Harbor near Edo (the earlier name for Tokyo) on July 8, 1853, ending the isolationist policy of sakoku and “opening” (willingly or not) Japan to the West, “the Land of the Rising Sun” and its culture have fascinated Westerners. Yet, despite this fascination, true understanding of that history remains elusive. A new exhibition at the Philadelphia Museum of Art, Ink and Gold: Art of the Kano builds a cultural bridge for Westerners to Japan’s heritage through the art of the “Kano School,” a family of painters to the powerful who influenced all of Japanese art from the 15th to the late 19th century. Combining the sumptuousness of golden artworks with the compelling story of their makers, Ink and Gold: Art of the Kano offers the key to unlocking the mystery of Japan through the art of the Kano.
The Utah Women and Leadership Project is helping the state overcome its ranking as one of the nation’s serious underachievers when it comes to gender equality in the workplace.
The futurist and entrepreneur takes an analytic approach to assessing the existential risks inherent in pursuing artificial intelligence.
The first woman to head a major North American pro sports union has made several major splashes in her first seven months on the job while exuding confidence every step of the way.
Homo sapiens aren’t alone in their division of chores by sex; our Neanderthal cousins also delegated a few tasks according to gender.
What happens when you let a computer determine each child’s personalized curriculum? Math teachers in several schools across America are seeing results through a growing brand of “blended learning.”
A long-lost, completed manuscript belonging to famous children’s author Ted Geisel — better known as Dr. Seuss — is scheduled for release in July 2015.
Strong psychological reactions — call it the yuck factor — could prevent innovative ideas from maturing and therefore from reaching populations in need.
Silicon Valley should be alarmed by a new report on the NSA’s international spying programs, says The Week’s Ryan Cooper. He calls the NSA “the kind of parasite that eventually kills its host.”
Female social entrepreneurs pay themselves an average of 29 percent less than their male colleagues, according to new research conducted at the London Business School.
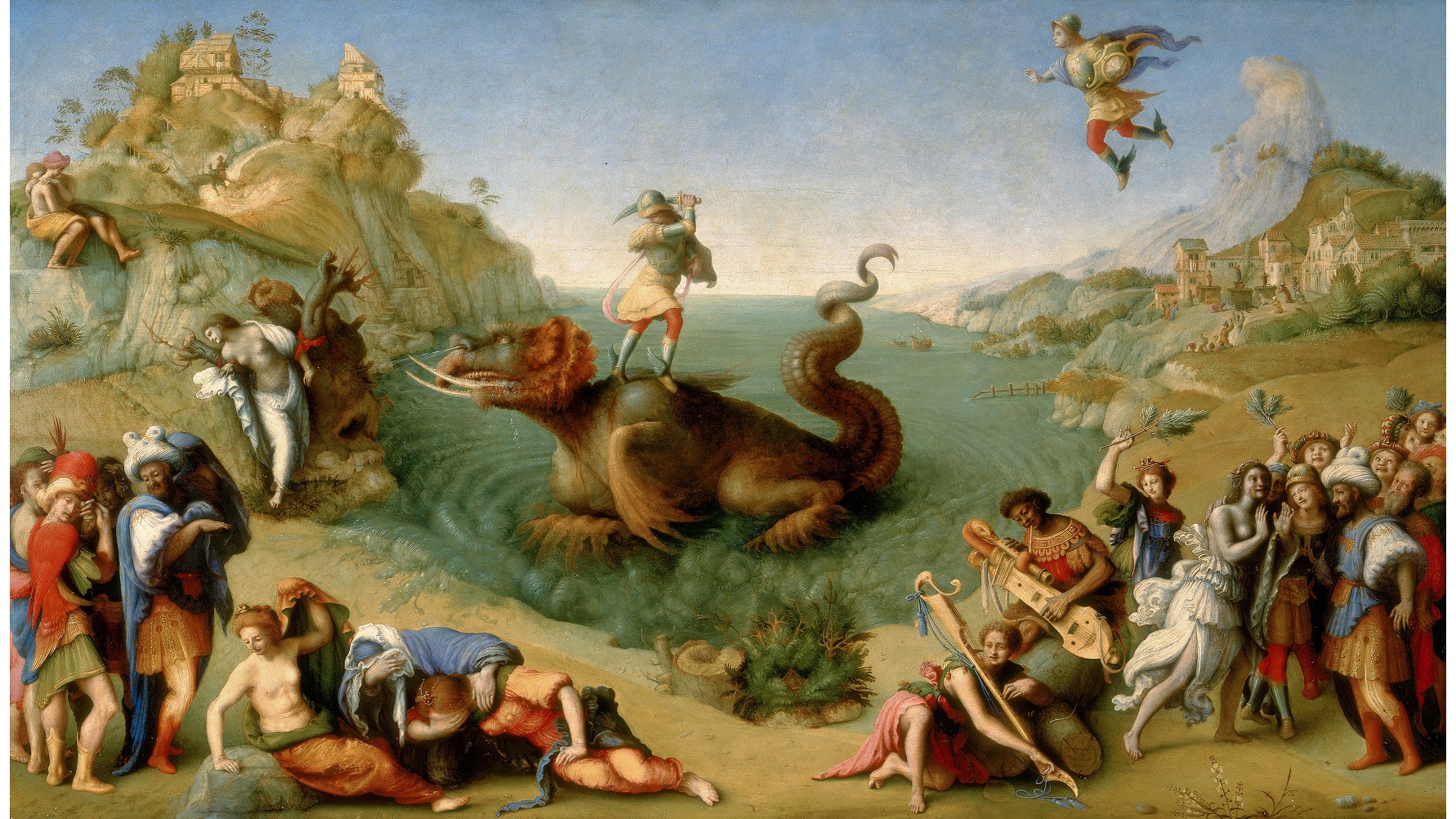
Half a millennium later, you would think the Italian Renaissance could hold no more secrets from us, no “codes” to decipher. And, yet, secrets hiding in plain sight continue to startle modern audiences with the depth and breadth of that amazing era. One of the well-kept secrets, at least until now, was the work of Piero di Cosimo, subject of his first major retrospective, Piero di Cosimo: The Poetry of Painting in Renaissance Florence at the National Gallery of Art, Washington, DC. Called “a madman” for his personal and artistic quirks by Renaissance chronicler Giorgio Vasari, Piero’s ability to paint in multiple genres all with a dizzying amount of detail may have seemed madness to contemporaries, but appeals to modern audiences conditioned for such visual assaults. There may have been a method to Piero di Cosimo’s madness after all.
An international achievement report ranks American millennials—those between the ages of sixteen and thirty-four—far behind their European and Asian counterparts.
How do recent weather patterns influence our overall perceptions? Researchers seem to think, “Rain or shine, our minds tend to prize their freshest impressions.”
If you want to build a strong brand, you need to have loyal consumers. In order to get that, you’ll need to create something meaningful for people to associate with your logo.
Data just released by the VoIP app Viber indicates that the Spanish exchanged more love-related stickers in 2014 than any other nationality.
Not all bad bosses are mean, says The Seattle Times’ Lisa Quast. Most are simply not invested in their work. Employees who want to extract value from the relationship need to adopt strategies for communication.
Winning a competition or completing a challenge causes your brain to release dopamine. Game makers can elicit more positive reactions from players by designing toward this end.
In the age of Tinder, it can be deceptively easy to spend a boatload on going on dates. Instead, try the more casual route. It doesn’t need to be expensive; just well thought-out.
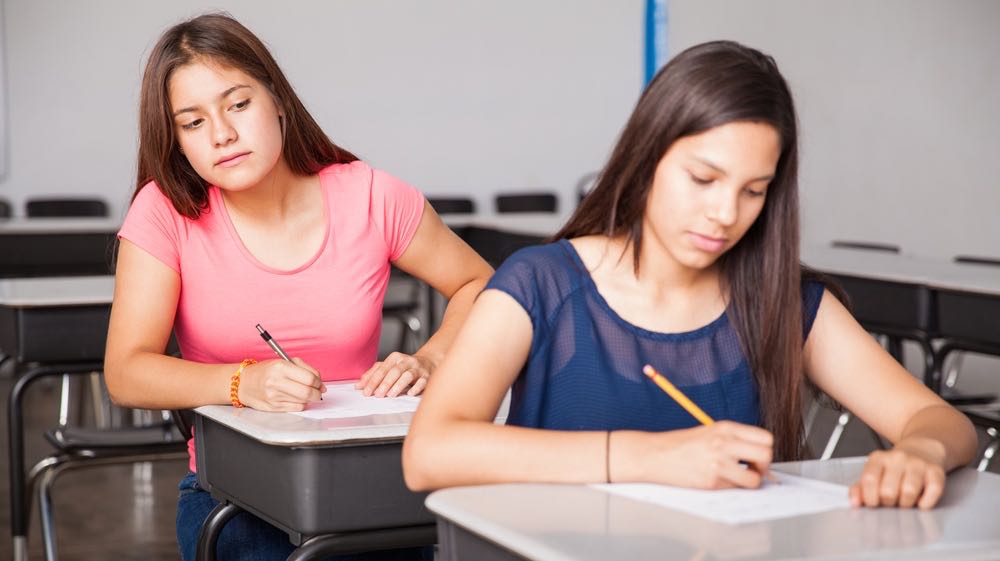
Managing a classroom is an underrated skill that can be honed with strategies that encourage participation without intimidating students.
Folks in the American Northeast need to monitor their behavior and emotions to avoid suffering from seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
All long-term relationships take commitment and work. New York Mag’s Ann Friedman points out that the relationship you have with yourself is by far the longest you’ll ever have. So work on it.