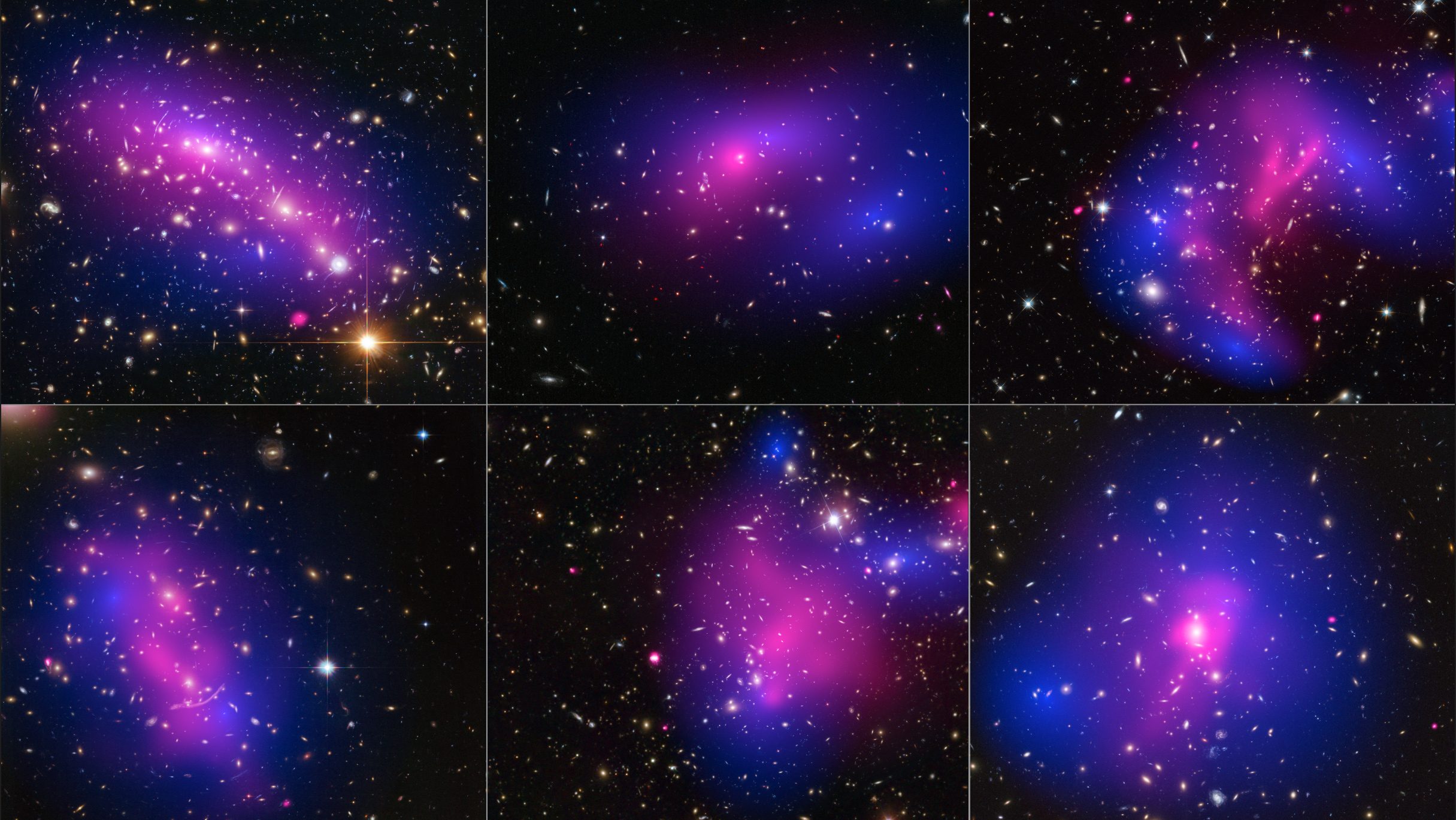
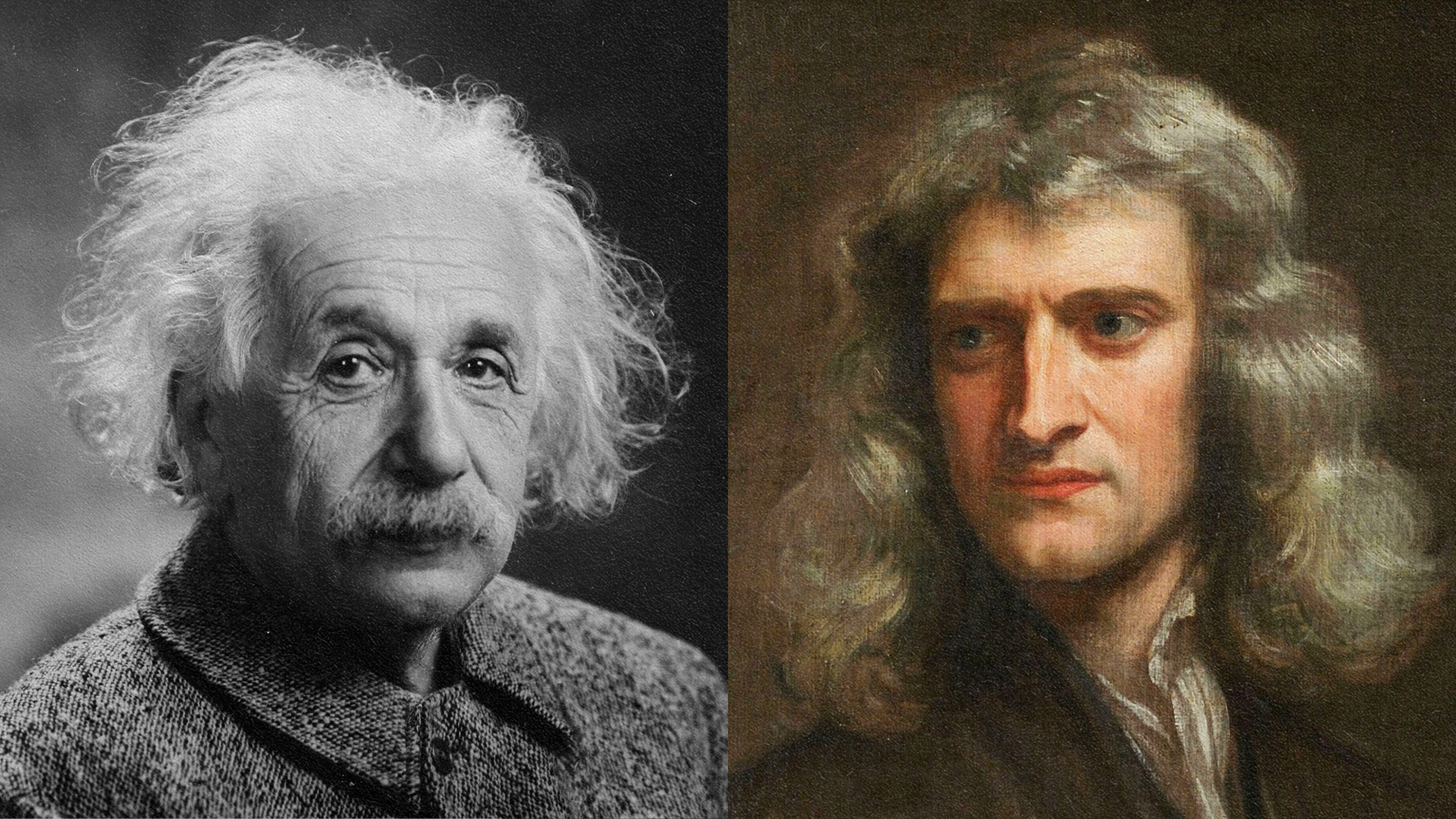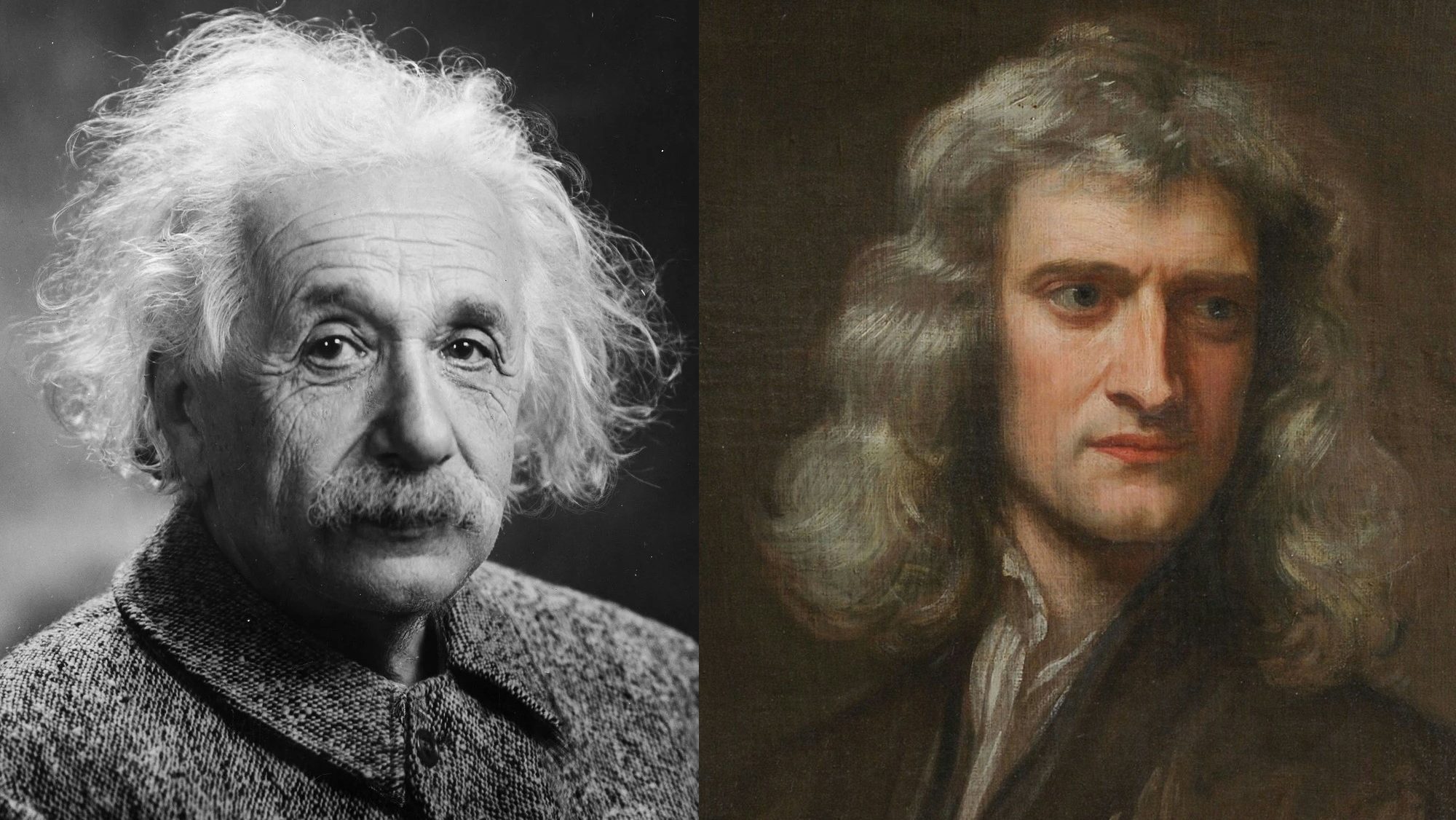Is gravity weaker over distances of billions of light-years?
Search Results
You searched for: gravity
For generations, physicists have been searching for a quantum theory of gravity. But what if gravity isn’t actually quantum at all?
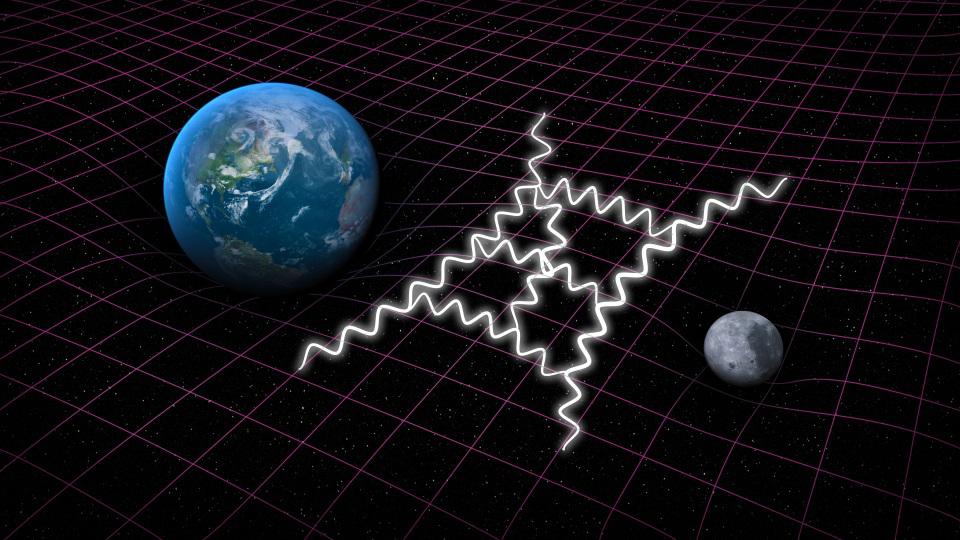
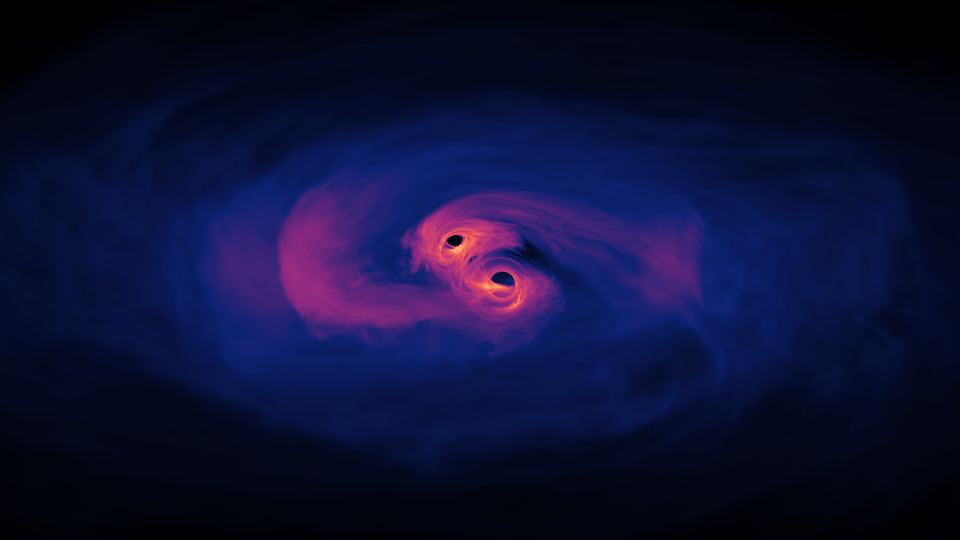
Thanks to observations of gravitational waves, scientists were able to settle a longstanding debate over the speed of gravity.
Isaac Newton and Albert Einstein are locked in an eternal battle over the nature of gravity. Whose side are you on?
How are we to deal with the quantization of spacetime and gravity?
Gravity defies quantum mechanics. What does that mean for a theory of everything?
▸
6 min
—
with
This measurement is crucial to confirm that one of the assumptions of Einstein’s theory of gravity is valid.
Roger Babson wanted a “partial insulator, reflector, or absorber of gravity” — something, anything, that would stop or dampen it.
There are many theories of gravity out there, and many interpretations of wide binary star data. What have we really learned from it all?
Newton thought that gravitation would happen instantly, propagating at infinite speeds. Einstein showed otherwise; gravity isn’t instant.
Forensics has reached the final frontier, and could be used to solve future space accidents—or crimes.
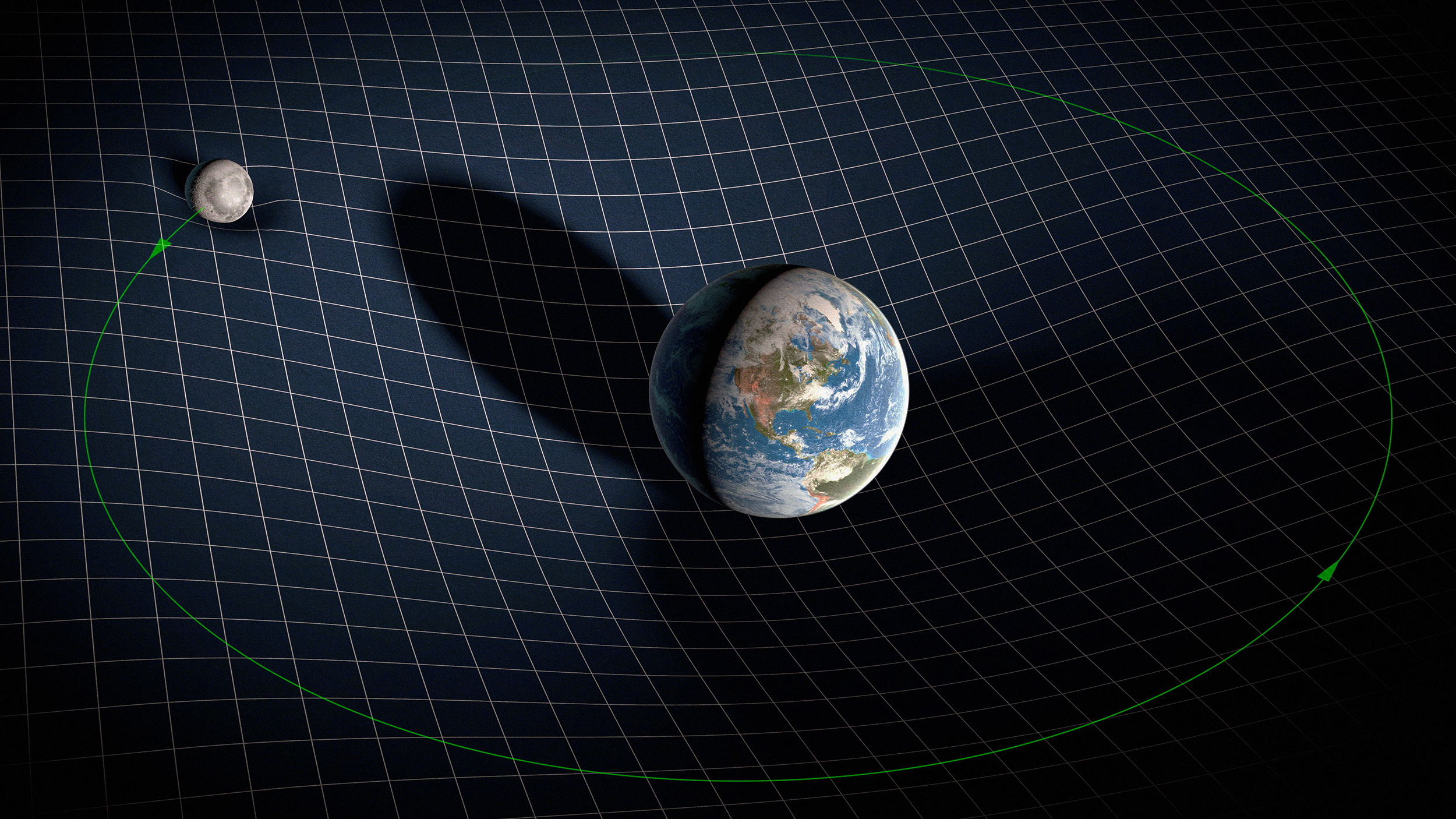
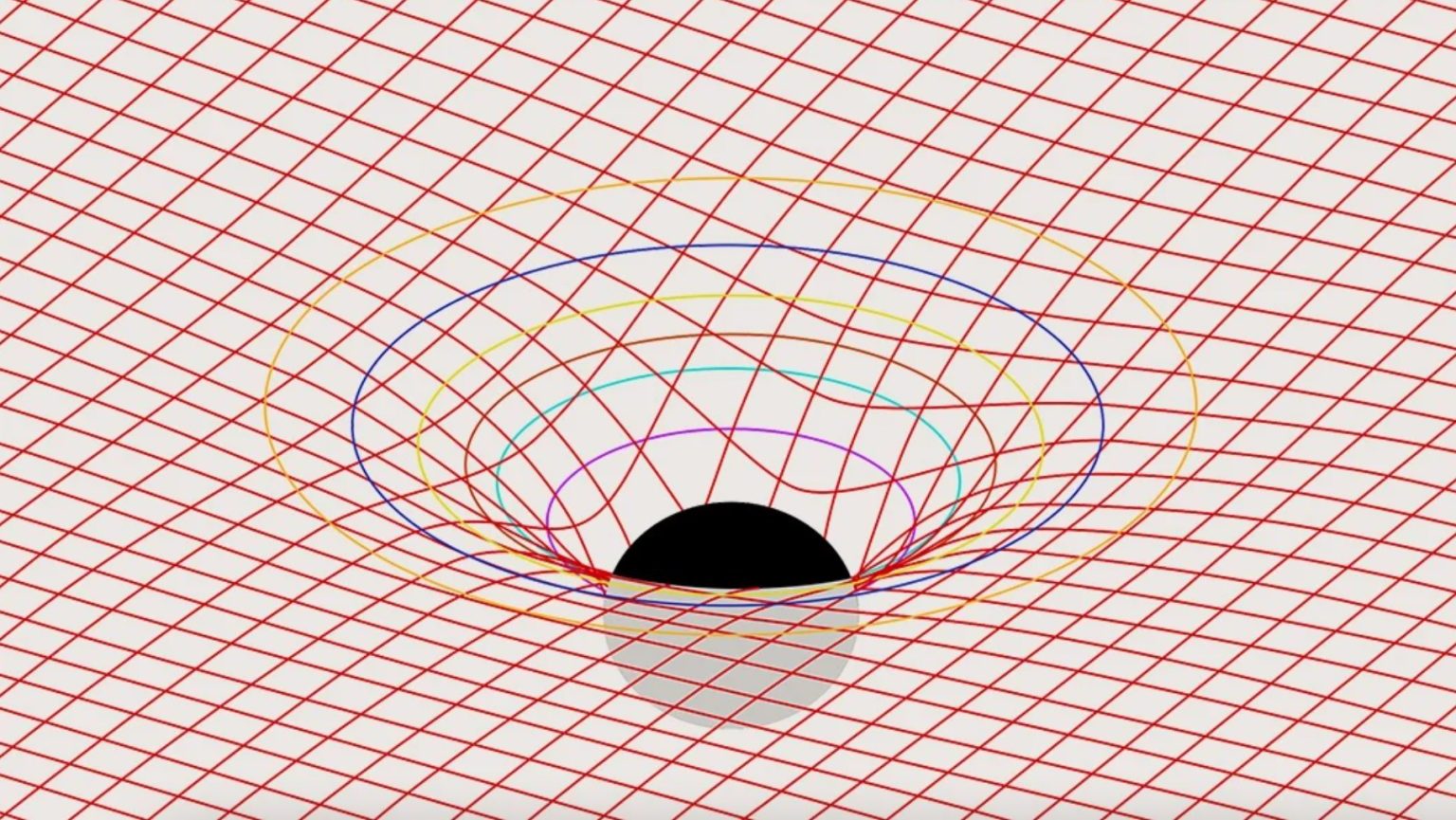
For centuries, Newton’s inverse square law of gravity worked beautifully, but no one knew why. Here’s how Einstein finally explained it.
In general relativity, matter and energy curve spacetime, which we experience as gravity. Why can’t there be an “antigravity” force?
Want to avoid getting “spaghettified” by a black hole? Steer clear of the smaller ones.
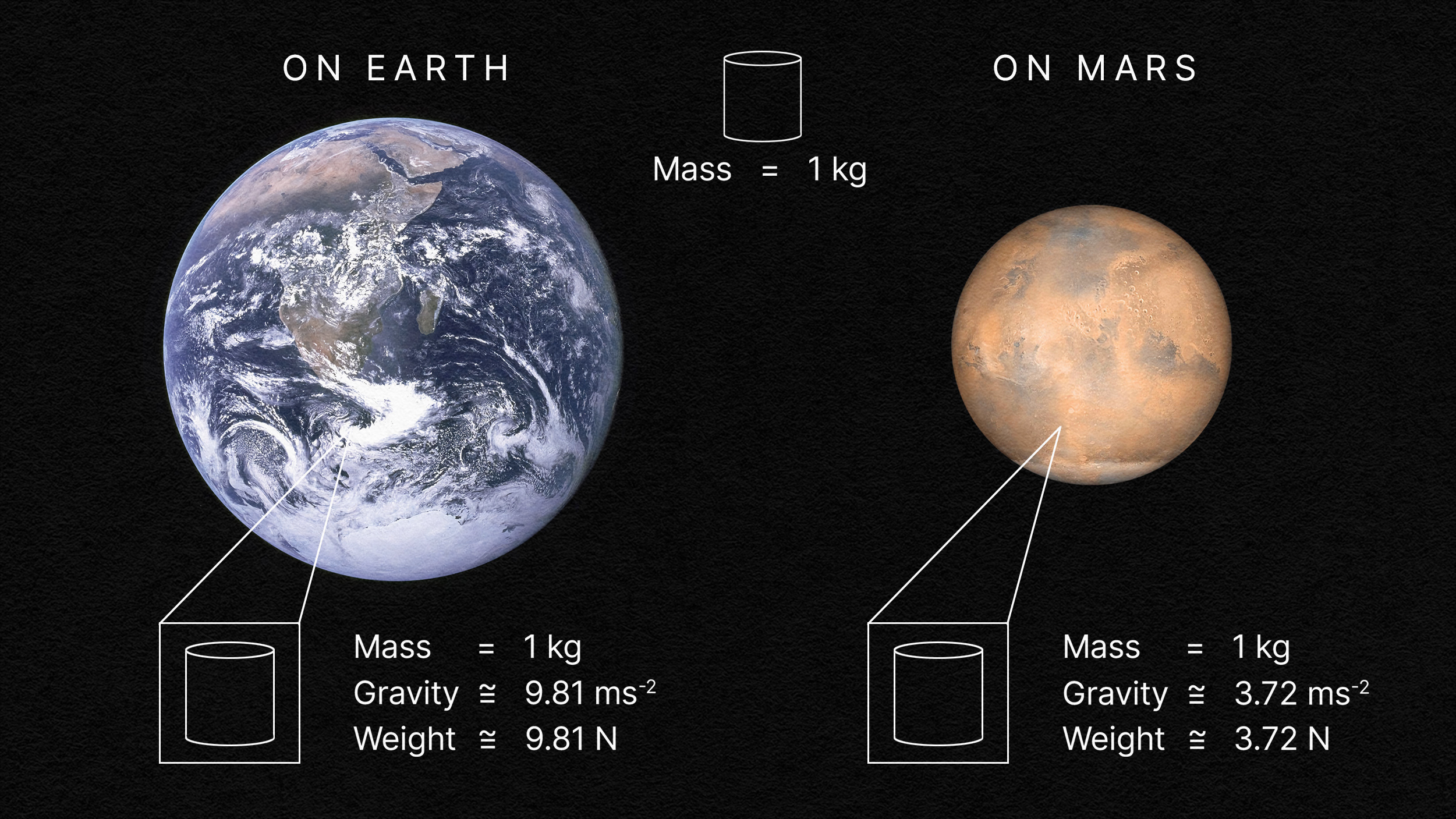
Here on Earth, we commonly use terms like weight (in pounds) and mass (in kilograms) as though they’re interchangeable. They’re not.
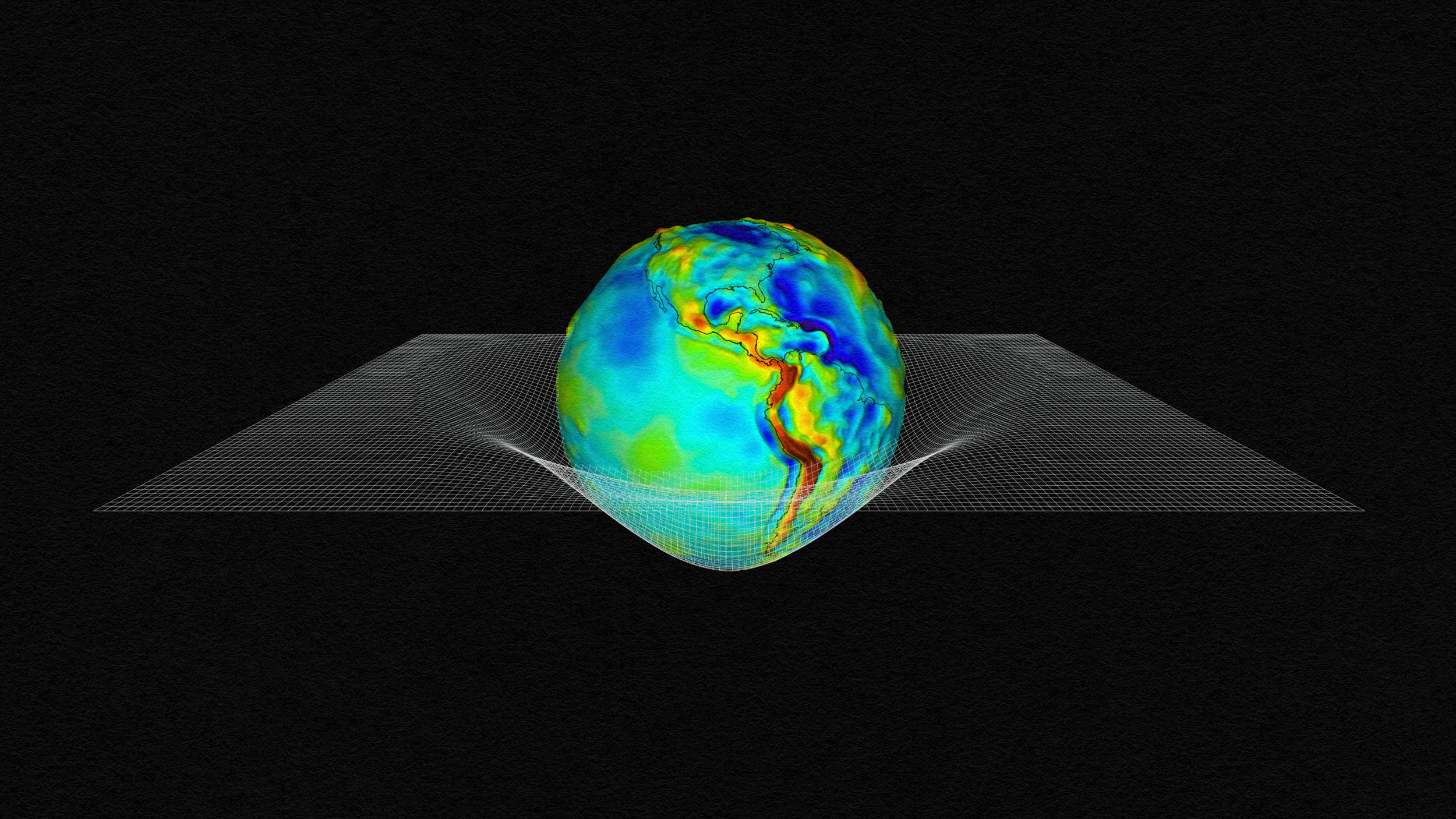
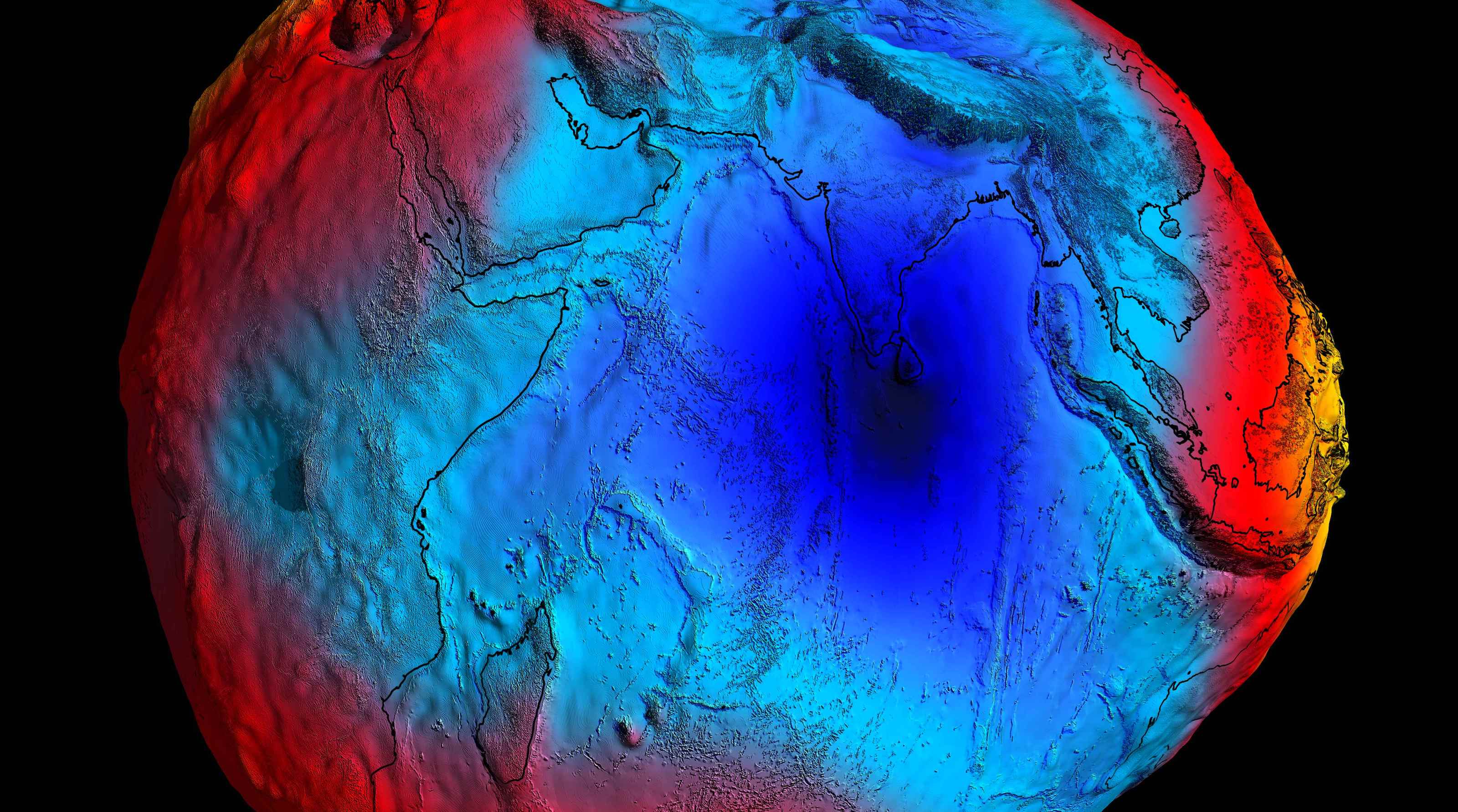
Seventy-five years after the anomaly’s discovery, scientists have finally figured out why sea levels are so much lower here.
The standard picture of our Universe is that it’s dominated by dark matter and dark energy. But this alternative is also worth considering.
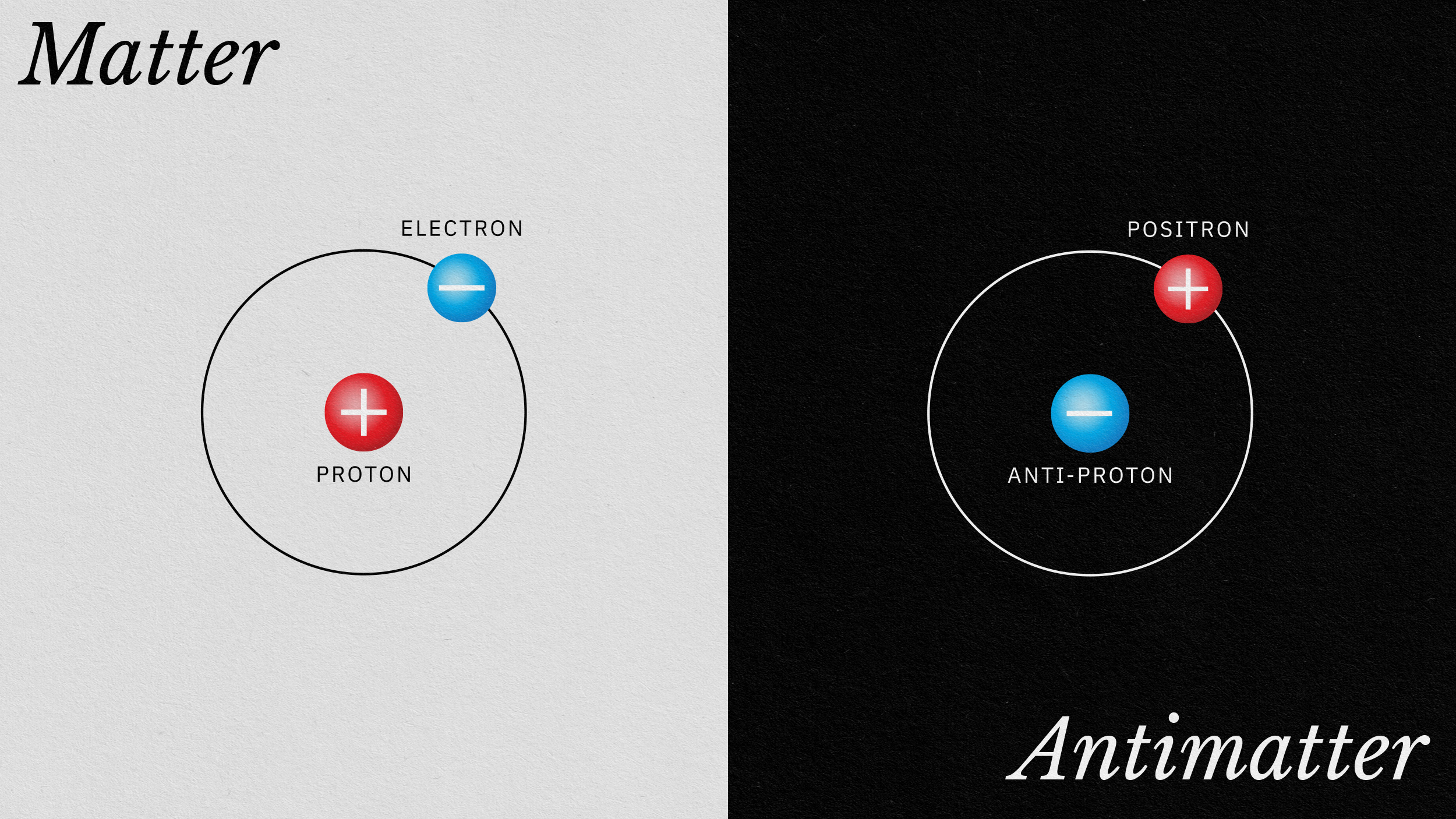
Sci-fi enthusiasts have long hoped that a substance called antimatter might experience gravity opposite that of ordinary matter. It doesn’t.
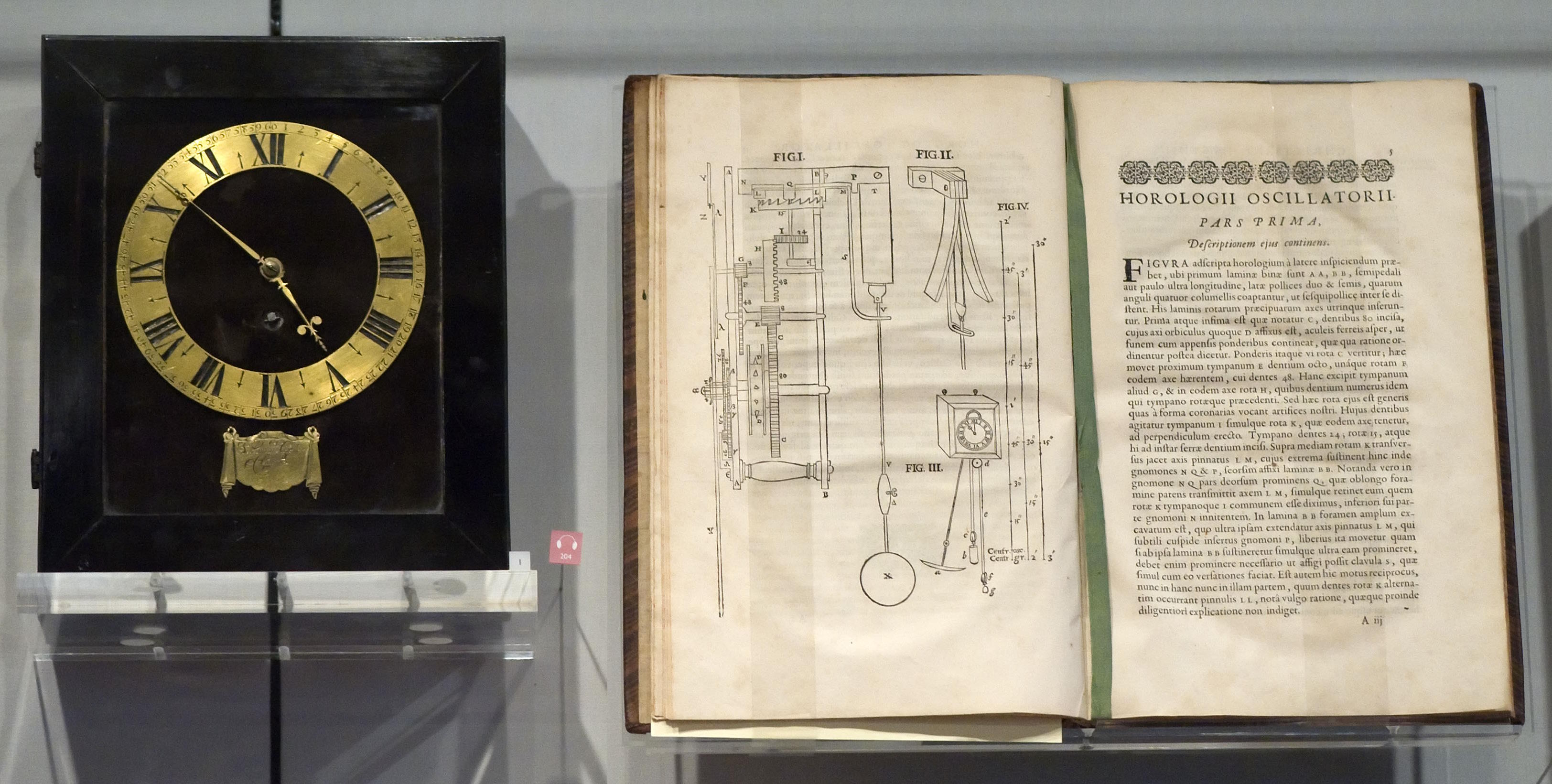
A clock, designed and built in Europe, ran hopelessly at the wrong rate when brought to America. The physics of gravity explains why.
Three fundamental forces matter inside an atom, but gravity is mind-bogglingly weak on those scales. Could extra dimensions explain why?
Here’s why the answer may forever elude scientists.
Our intuitive understanding of time is very different from a physicist’s understanding of time. How do we reconcile these views?
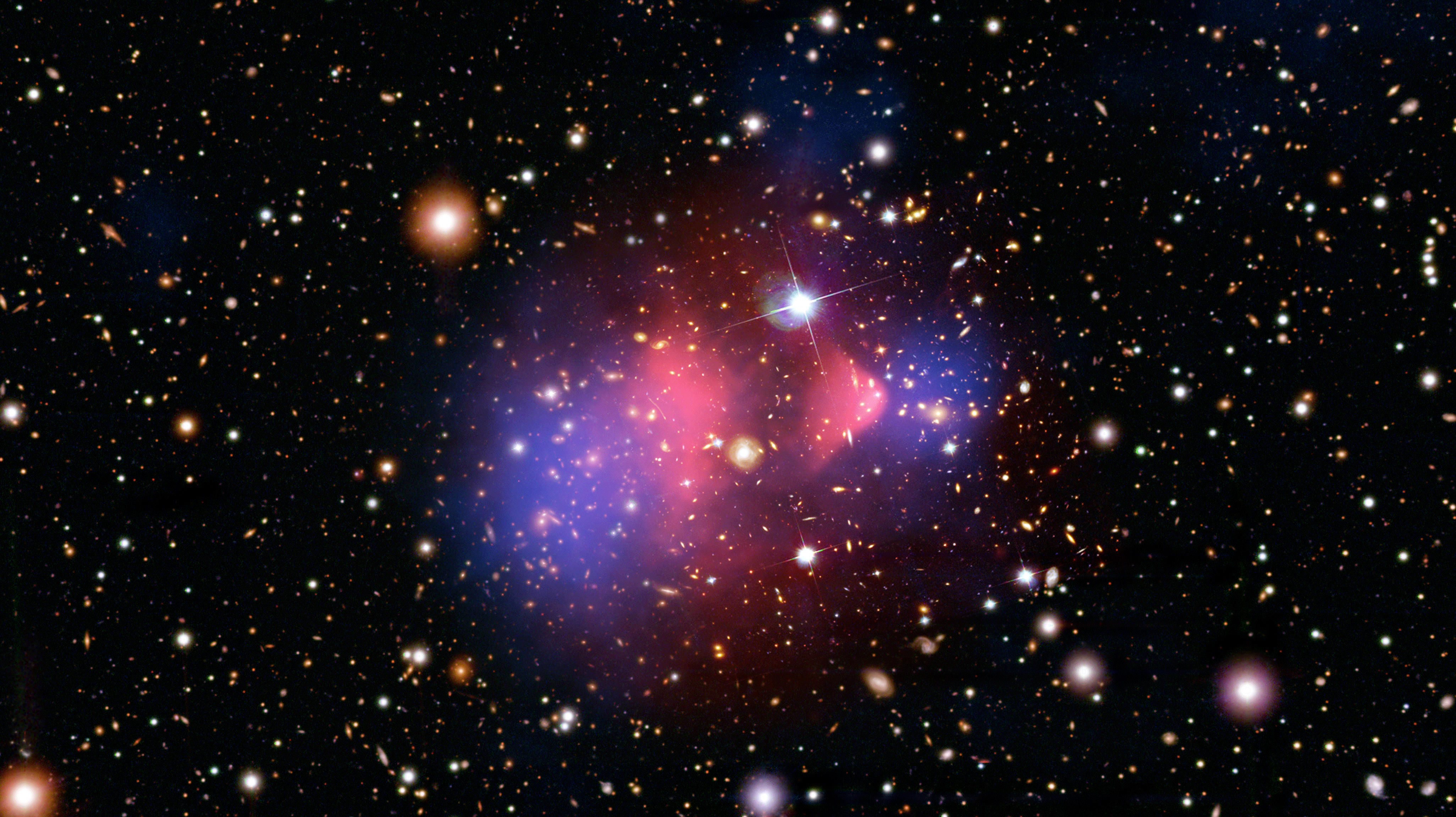
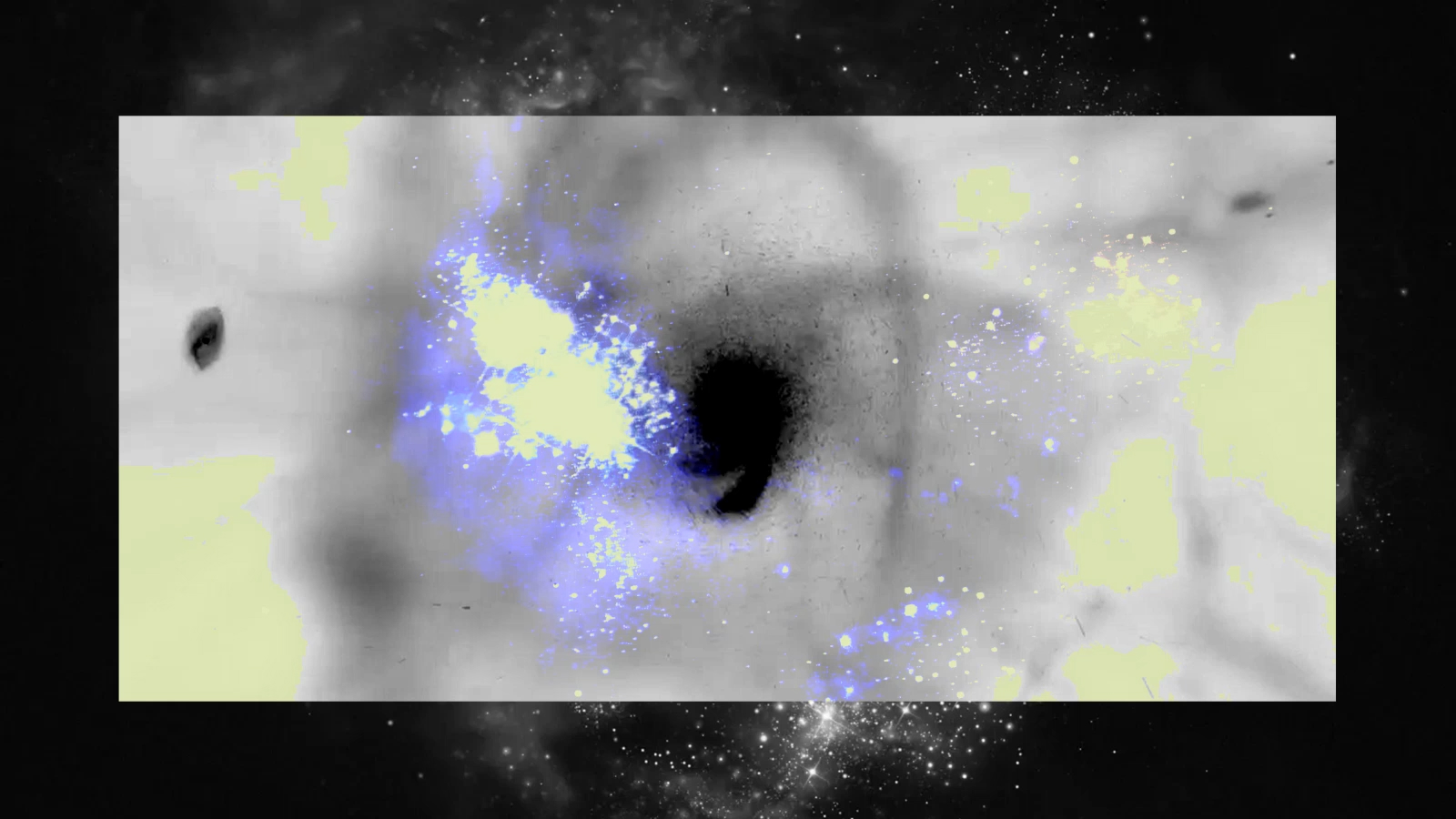
19 years ago, the Bullet Cluster provided an empirical proof for dark matter. Even today, modified gravity still can’t explain it.
Particles behave differently when freed from the force of gravity. A new space factory aims to use this to synthesize pharmaceuticals.
Quantum wormholes are mathematically possible — but might also be physically impossible. Physicist Janna Levin explains Hawking’s famous information paradox.
▸
12 min
—
with
A deep dive into the chaotic journey of star formation.
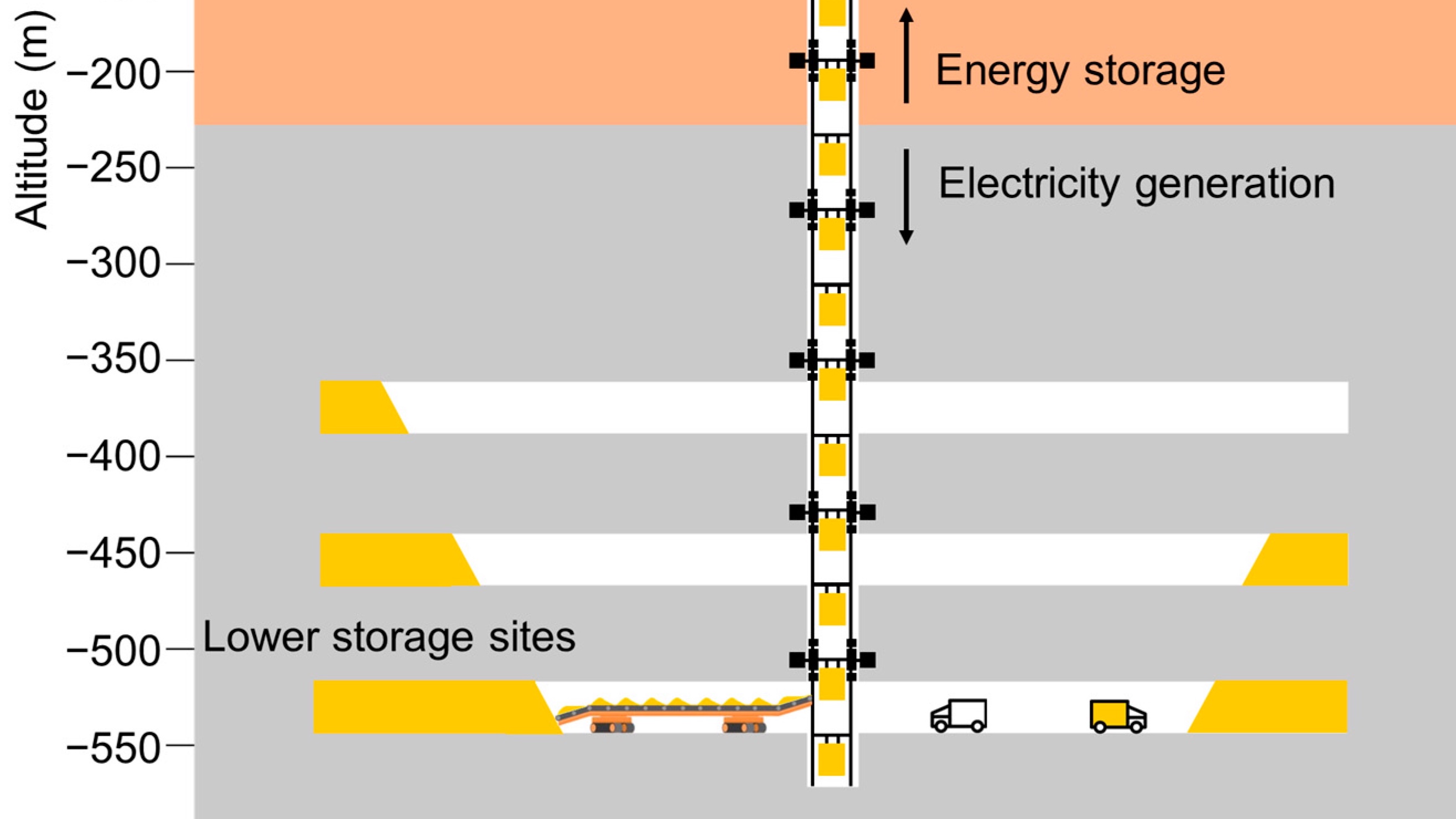
Old coal mines can be converted into “gravity batteries” by retrofitting them with equipment that raises and lowers giant piles of sand.
In the quest to measure how antimatter falls, the possibility that it fell “up” provided hope for warp drive. Here’s how it all fell apart.
Einstein’s laws of gravity have been challenged many times, but have always emerged victorious. Could wide binary stars change all that?
Even after the first stars form, those overdense regions gravitationally attract matter and also merge. Here’s how they grow into galaxies.