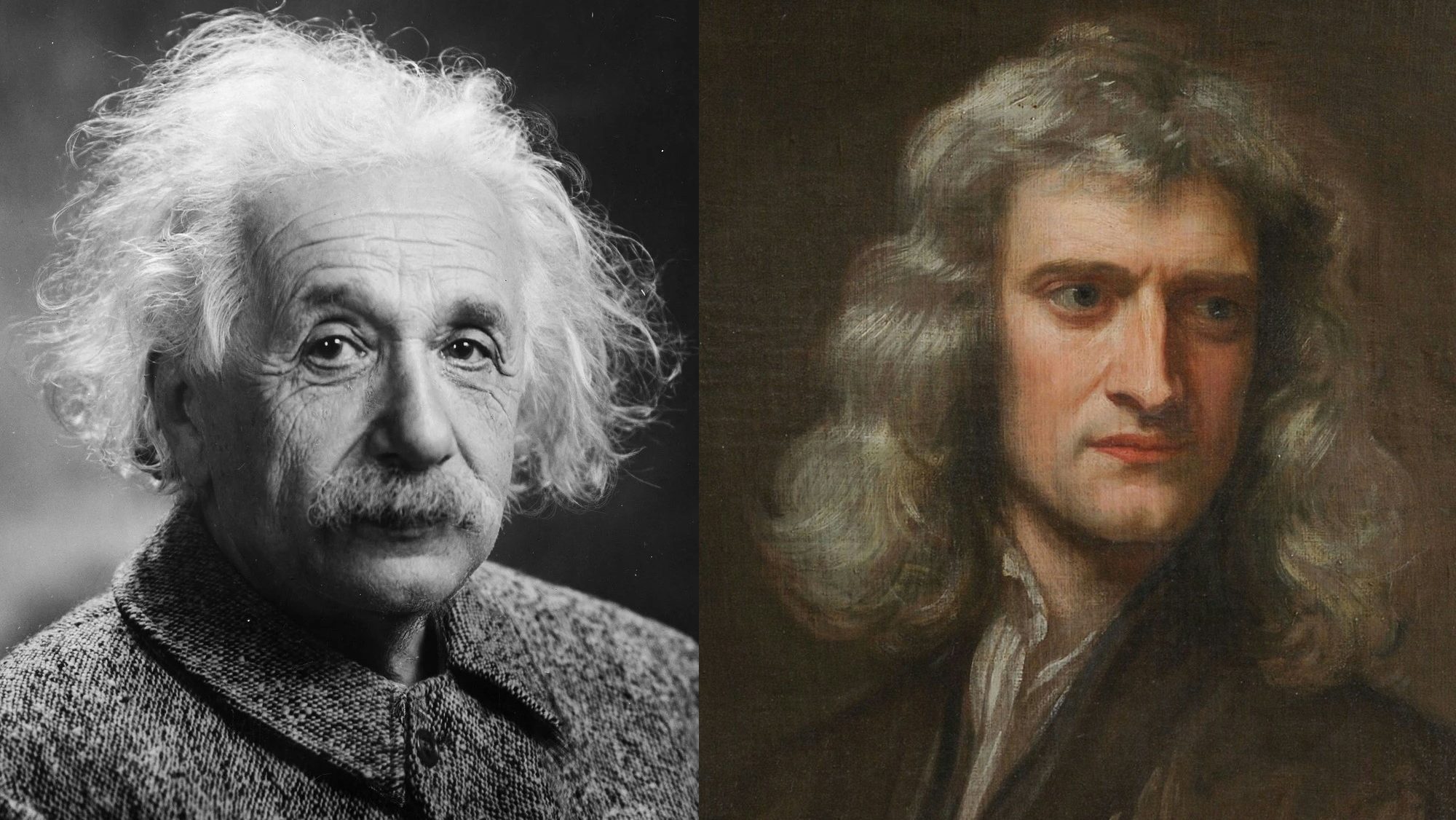The most iconic, longest-lived space telescope of all, NASA’s Hubble, is experiencing orbital decay as the solar cycle peaks. Here’s why.
Search Results
You searched for: light
The Michelson-Morley experiment of 1887, despite expectations, revealed a null result: no effect. The implications were revolutionary.
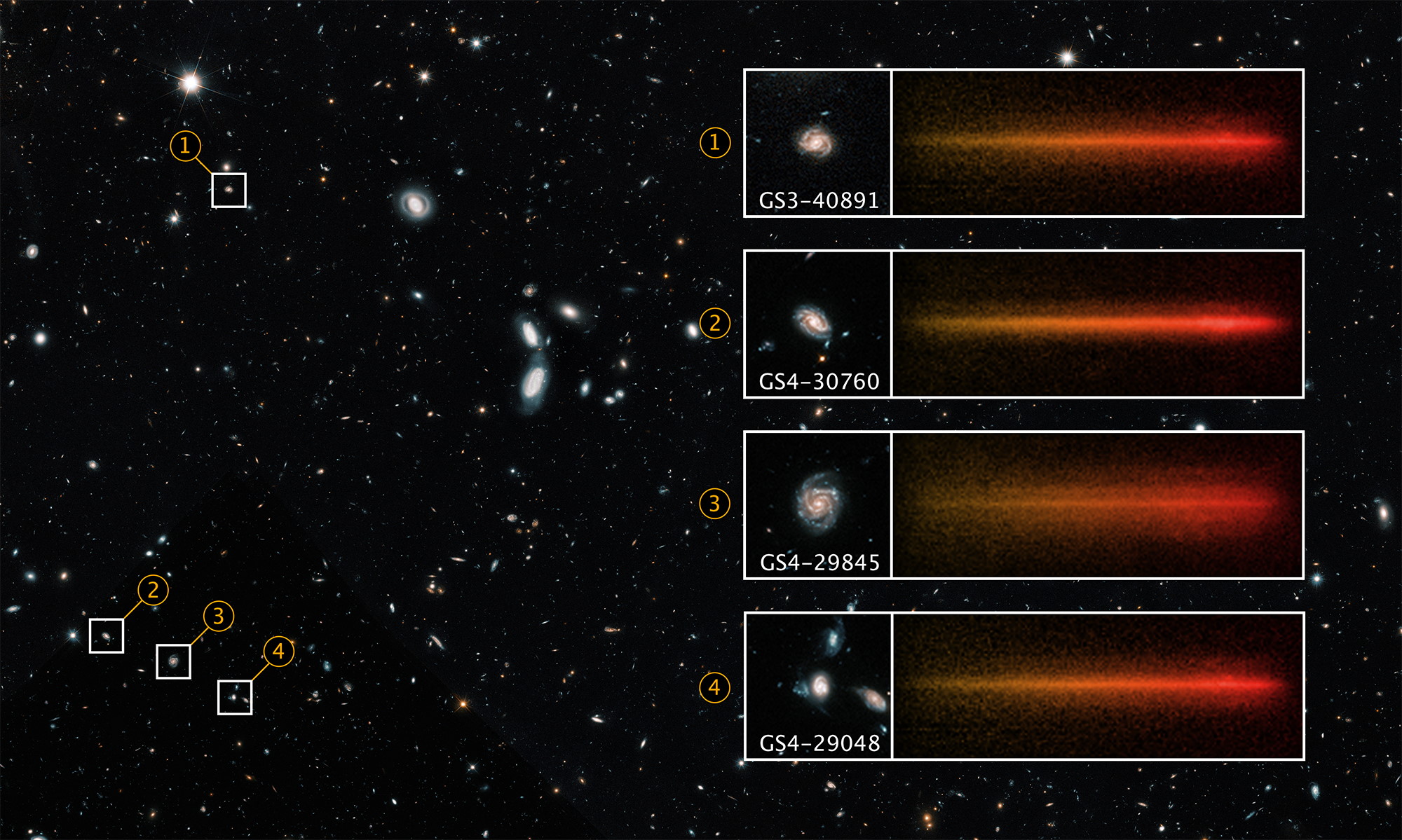
All telescopes are fundamentally limited in what they can see. JWST reveals more distant galaxies than Hubble, but still can’t see them all.
The Universe, although violent, is filled with creation events following destructive ones. 1850 light-years away, both types are unfolding.
Recent research sheds light on how the brain overgeneralizes fear, causing people to be afraid of harmless situations.
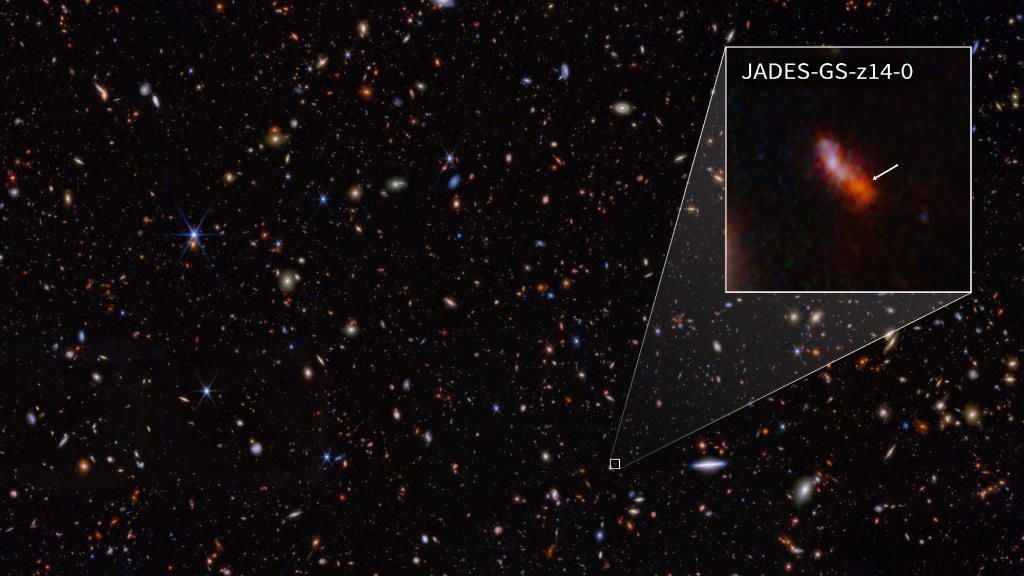
For 550 million years, neutral atoms blocked the light made in stars from traveling freely through the Universe. Here’s how it then changed.
The concept of ‘relativistic mass’ has been around almost as long as relativity has. But is it a reasonable way to make sense of things?
Finding a tiny planet around bright stars dozens or hundreds of light-years from Earth is extremely difficult.
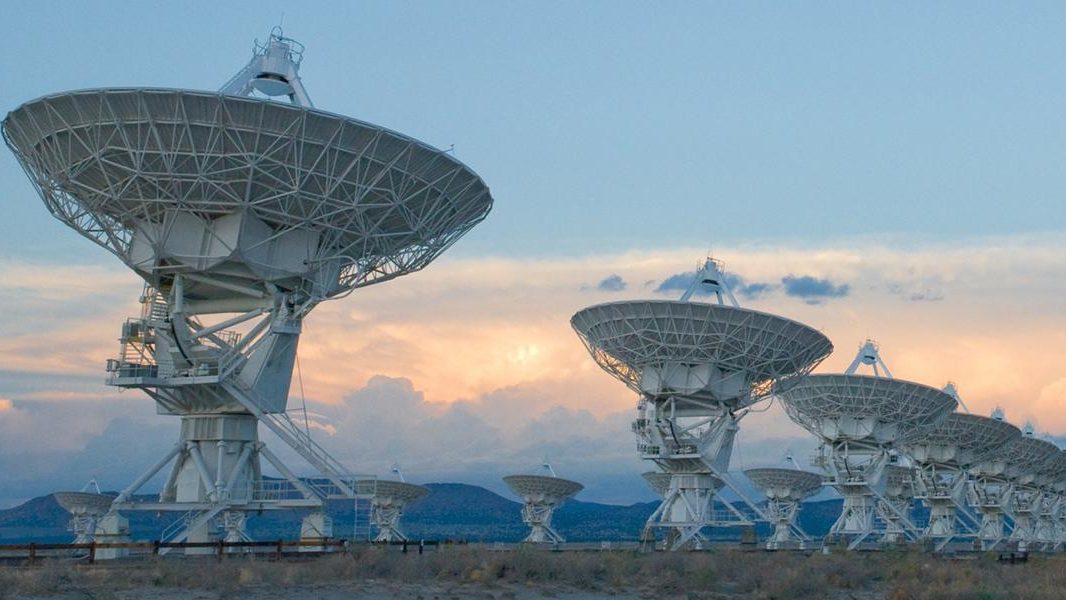
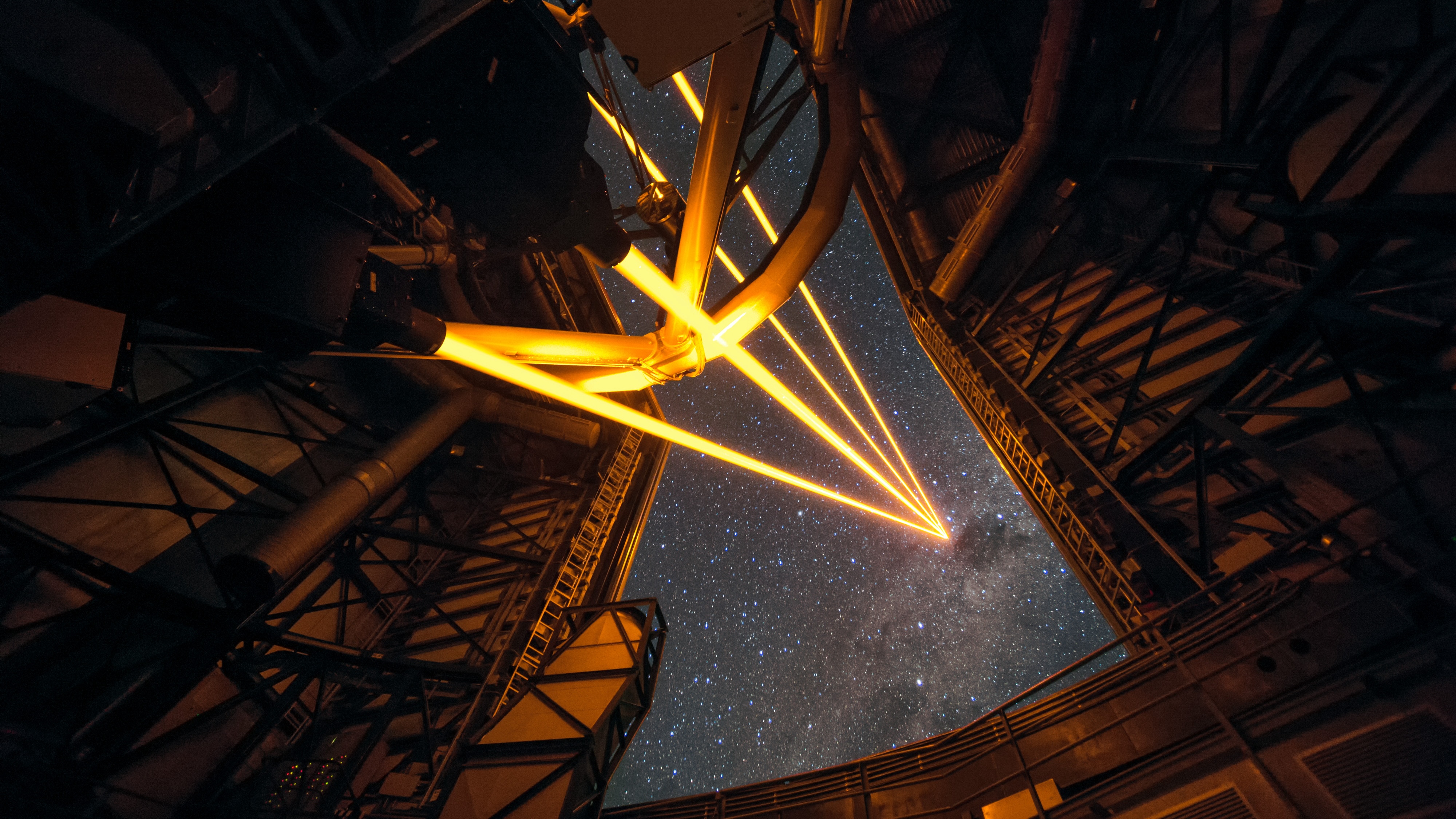
The sharpest optical images, for now, come from the Hubble Space Telescope. A ground-based technique can make images over 100 times sharper.
Everything acts like a wave while it propagates, but behaves like a particle whenever it interacts. The origins of this duality go way back.
National Geographic’s first James Webb Space Telescope book shows us the cosmos like never before.
For centuries, Newton’s inverse square law of gravity worked beautifully, but no one knew why. Here’s how Einstein finally explained it.
Our Universe requires dark matter in order to make sense of things, astrophysically. Could massive photons do the trick?
Some processes, like quantum tunneling, have been shown to occur instantaneously. But the ultimate cosmic speed limit remains unavoidable.
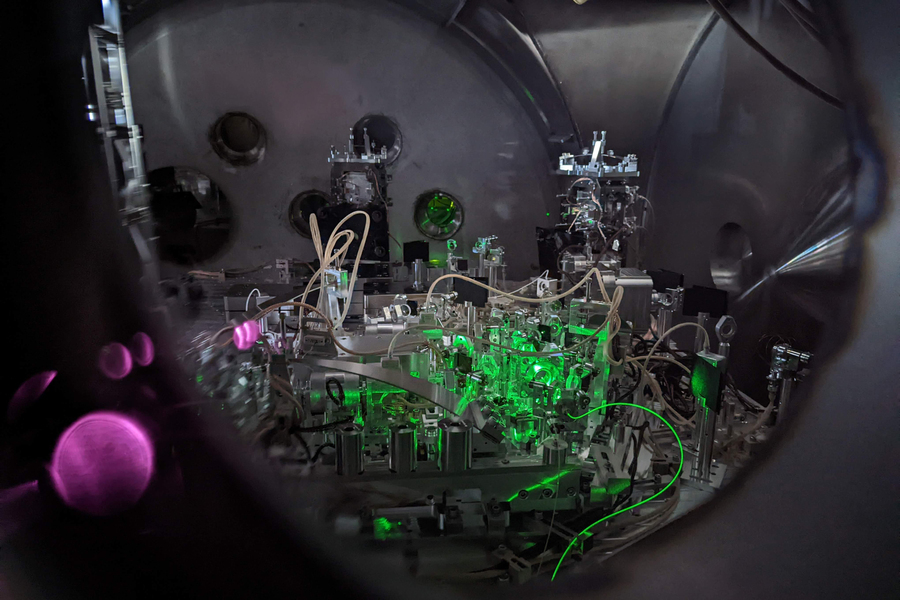
There’s a quantum limit to how precisely anything can be measured. By squeezing light, LIGO has now surpassed all previous limitations.
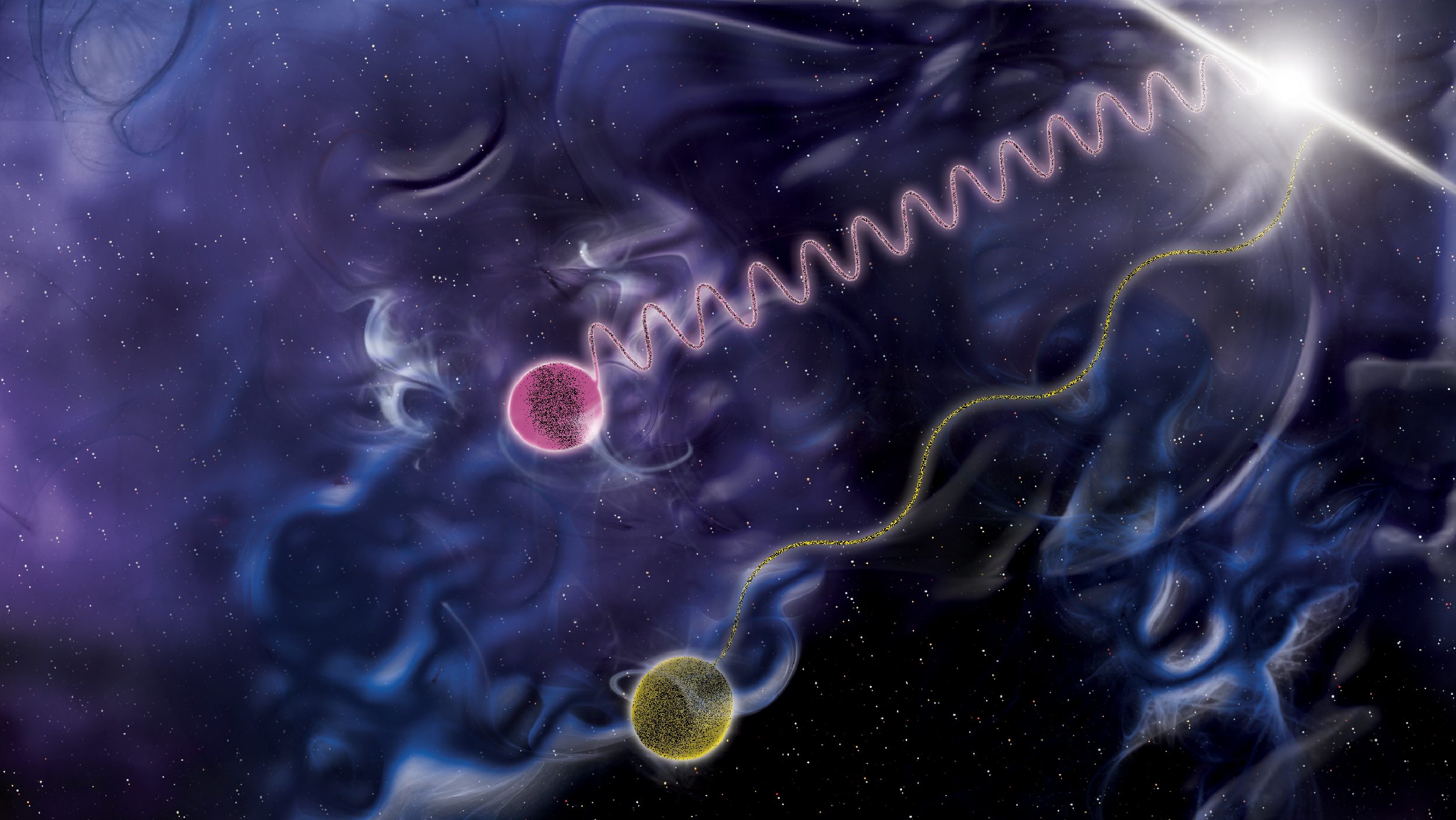
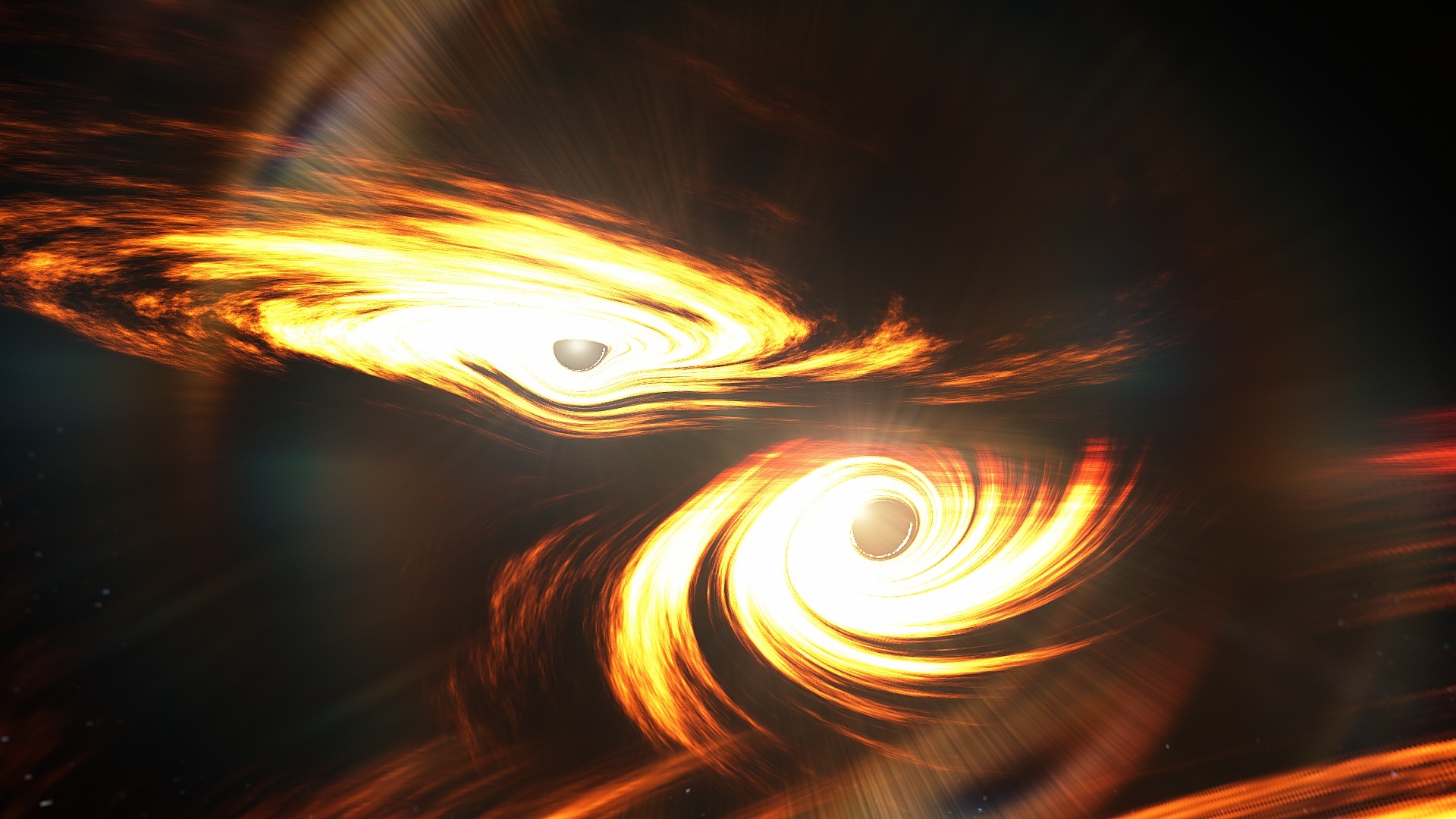
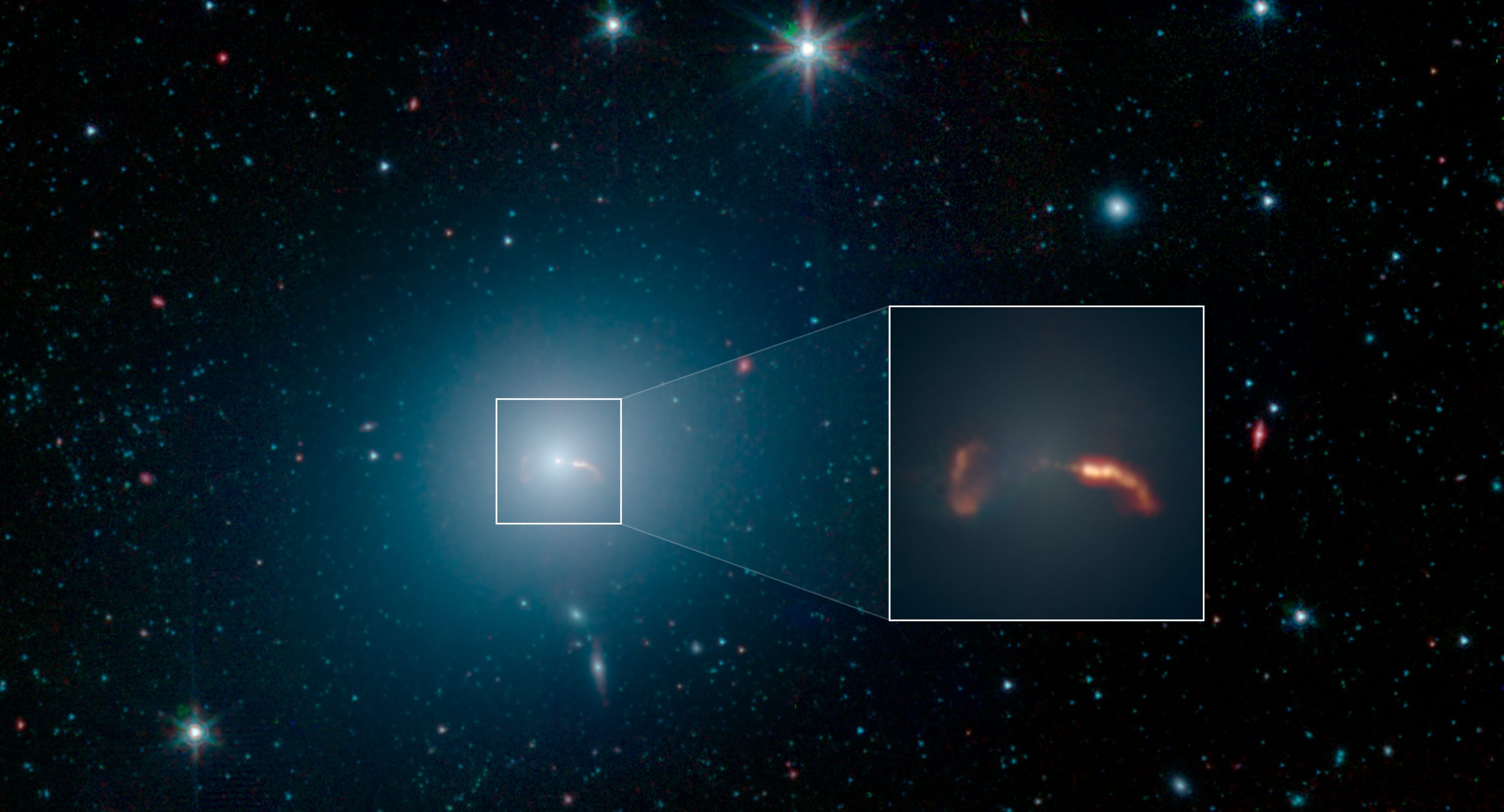
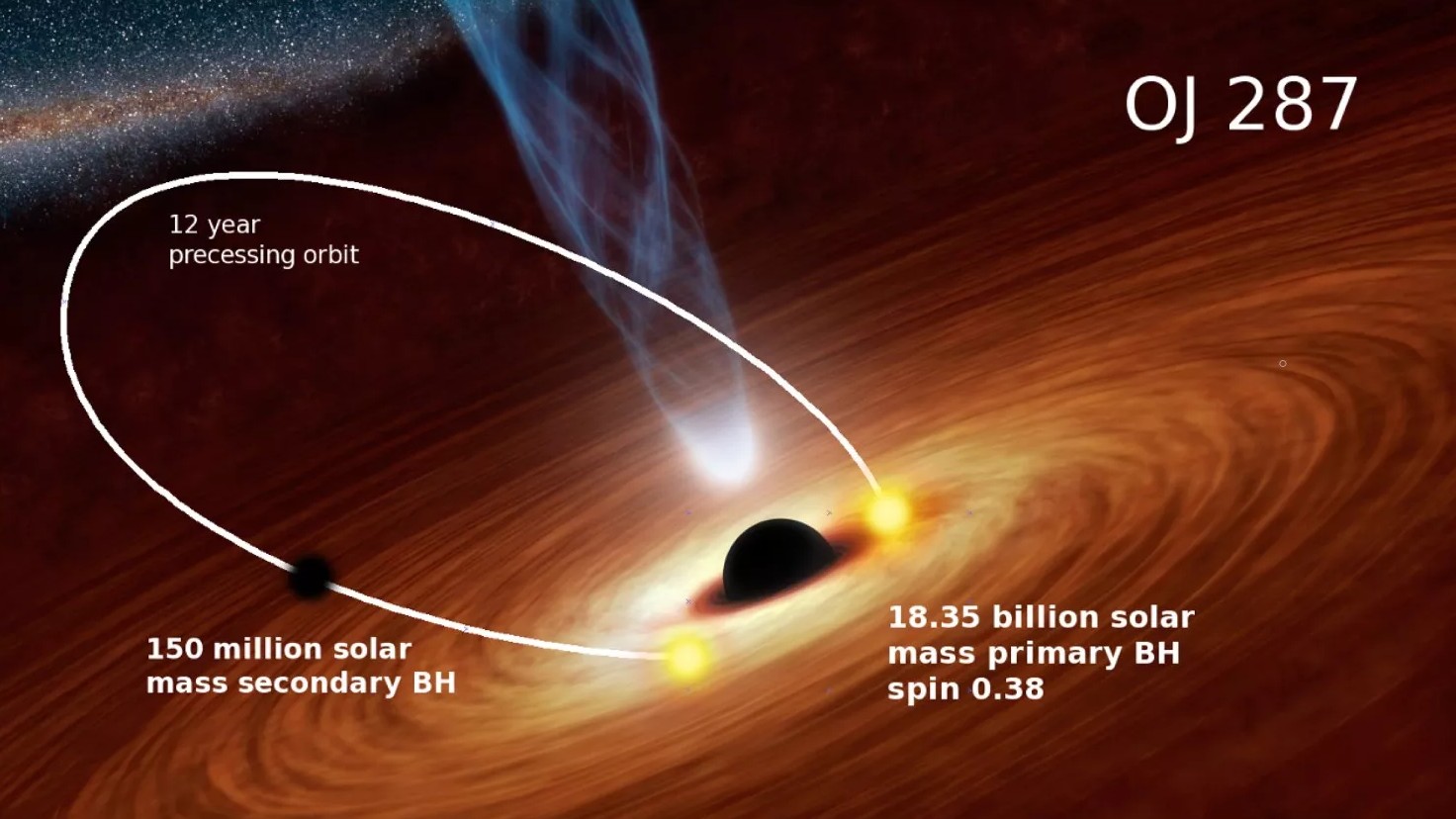
In a distant galaxy, a cosmic dance between two supermassive black holes emits periodic flashes of light.
Lasers, mirrors, and computational advances can all work together to push ground-based astronomy past the limits of our atmosphere.
How the simple act of watching twilight can radically transform our perception of the world and our role within it.
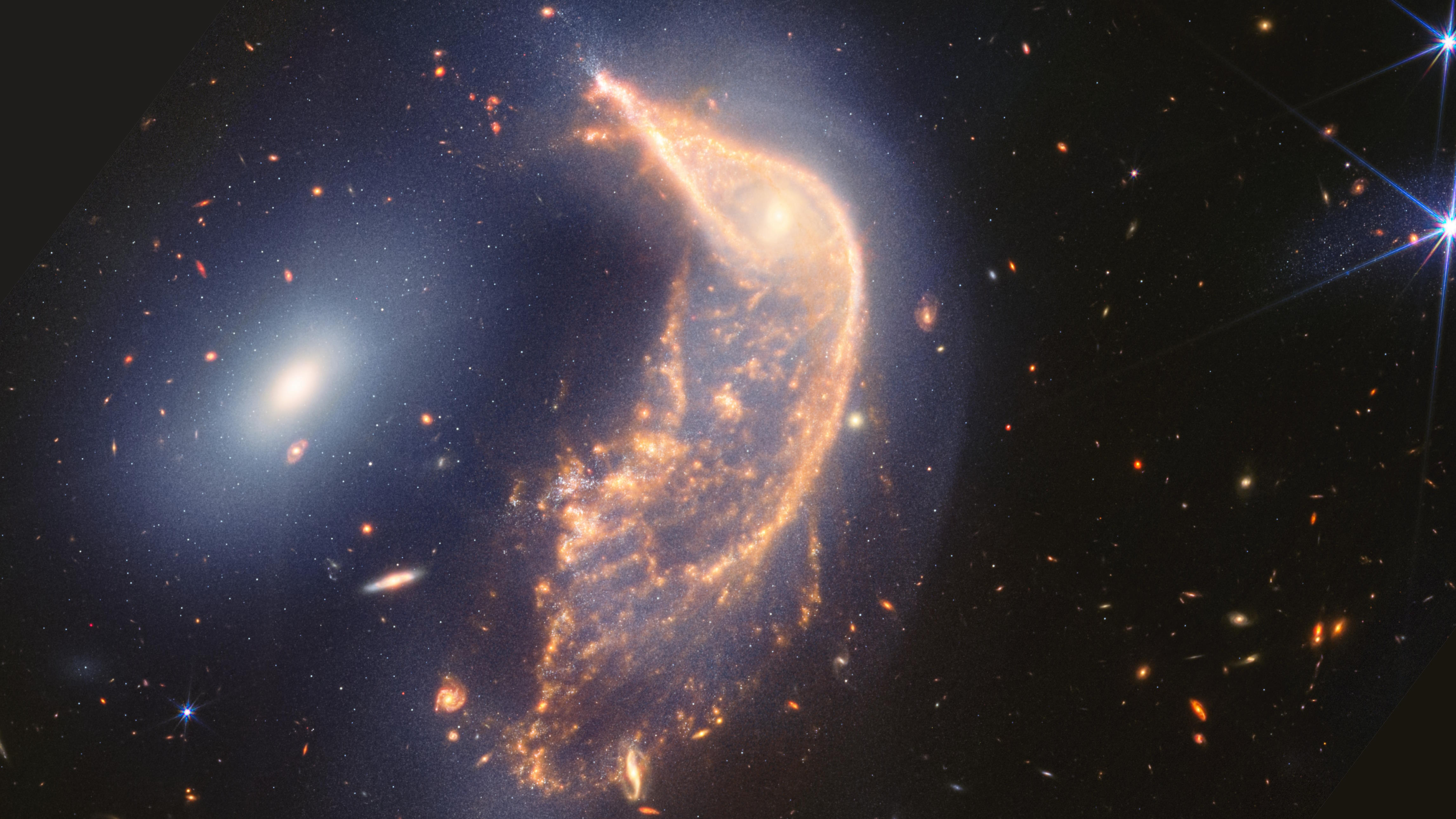
For its 2-year science anniversary, JWST has revealed unprecedented details in “the Penguin and the Egg.” Here are the surprises inside.
All matter particles can act as waves, and massless light waves show particle-like behavior. Can gravitational waves also be particle-like?
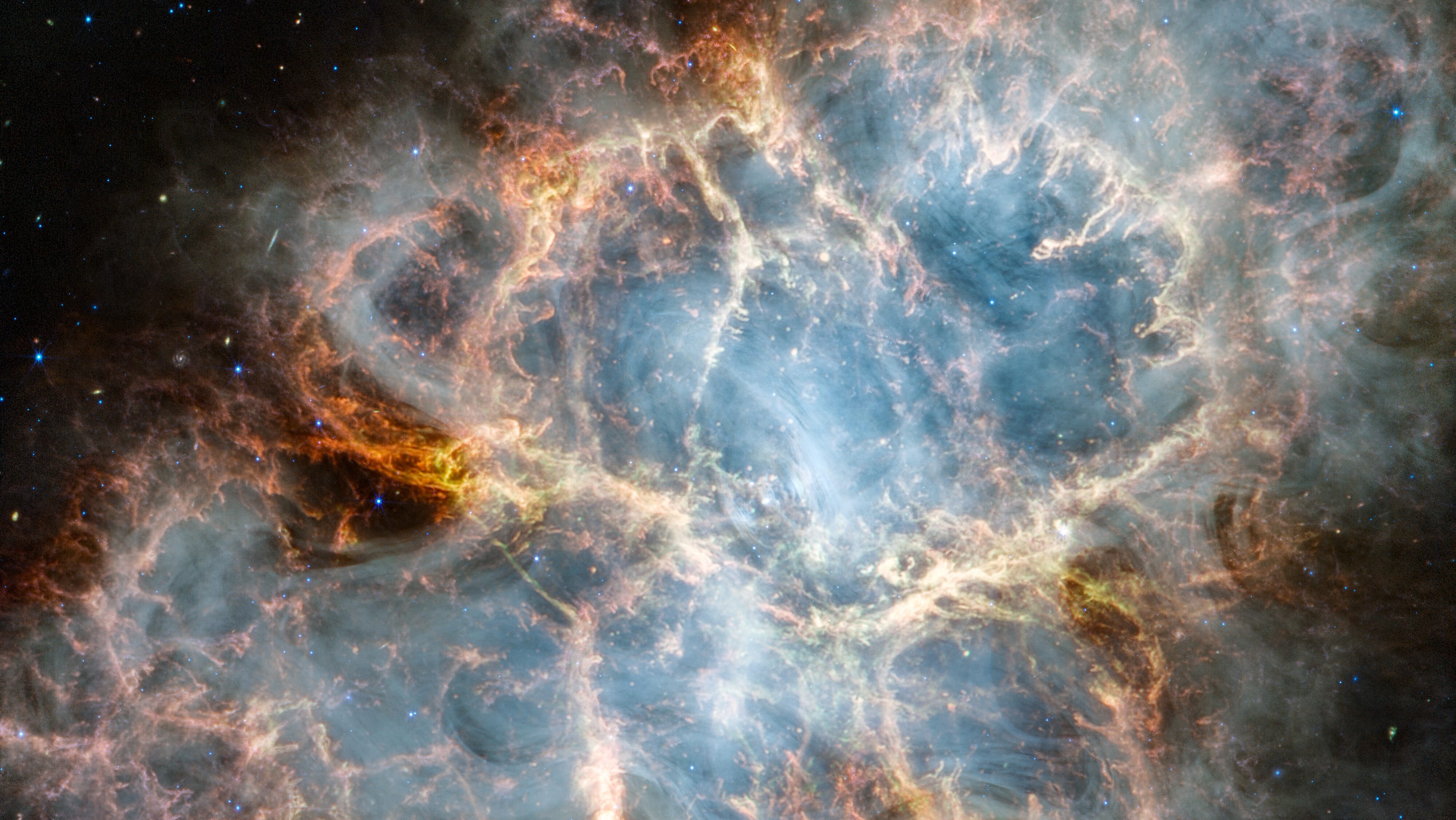
In 1054, a core-collapse supernova occurred 6500 light-years away. In 2023, JWST imaged the remnant, and might solve a massive mystery.
If you think of the Big Bang as an explosion, we can trace it back to a single point-of-origin. But what if it happened everywhere at once?
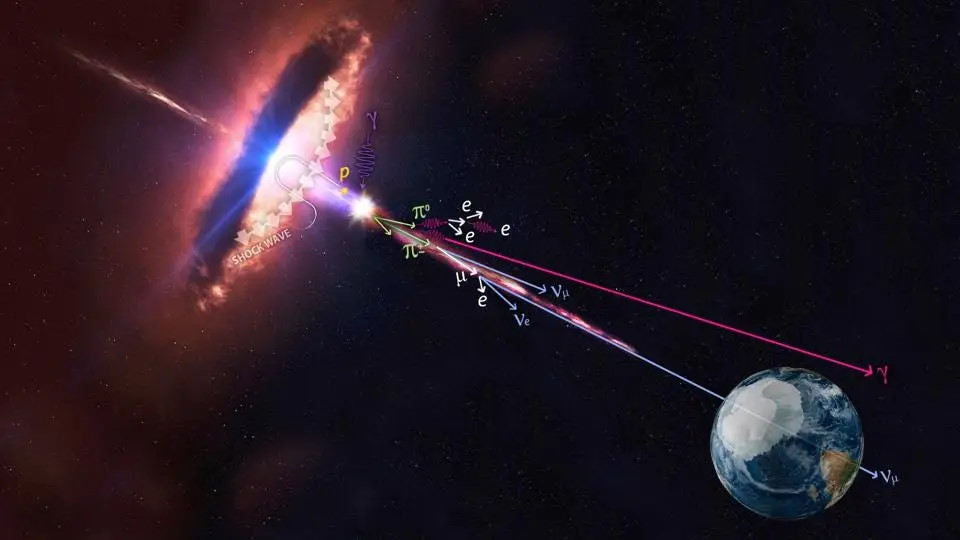
Nothing can escape from a black hole. So where do Hawking radiation, relativistic jets, and X-ray emissions around black holes come from?
The first-of-its-kind approval could change how we think about gene-edited foods.
Light carries with it the secrets of reality in ways we cannot completely understand.
Because of dark energy, distant objects speed away from us faster and faster as time goes on. How long before every galaxy is out of reach?
In logic, ‘reductio ad absurdum’ shows how flawed arguments fall apart. Our absurd Universe, however, often defies our intuitive reasoning.
A concept known as “wave-particle duality” famously applies to light. But it also applies to all matter — including you.
Figuring out the answer involved a prism, a pail of water, and a 50 year effort by the most famous father-son astronomer duo ever.
You are trapped in time. You never live in the world as it is but only as you experience it as it was.