MICHELLE THALLER: Is time real or is it an illusion? Well, time is certainly real but the question is what do we mean by the word time? And it may surprise you that physicists don't have a simple answer for that.
JAMES GLEICK: Physicists argue about and physicists actually have symposia on the subject of is there such a thing as time. And it's also something that has a traditional in philosophy going back about a century. But, I think it's fair to say that in one sense it's a ridiculous idea. How can you say time doesn't exist when we have such a profound experience of it first of all. And second of all we're talking about it constantly. I mean we couldn't get, I can't get through this sentence with out referring to time. I was going to say we couldn't get through the day without discussing time. So, obviously when a physicist questions the existence of time they are trying to say something specialized, something technical.
BILL NYE: Notice that in English we don't have any other word for time except time. It's unique. It's this wild fourth dimension in nature. This is one dimension, this is one dimension, this is one dimension and time is the fourth dimension. And we call it the fourth dimension not just in theoretical physics but in engineering. I worked on four dimensional autopilots so you tell where you want to go and what altitude it is above sea level and then when you want to get there. Like you can't get there at any time.
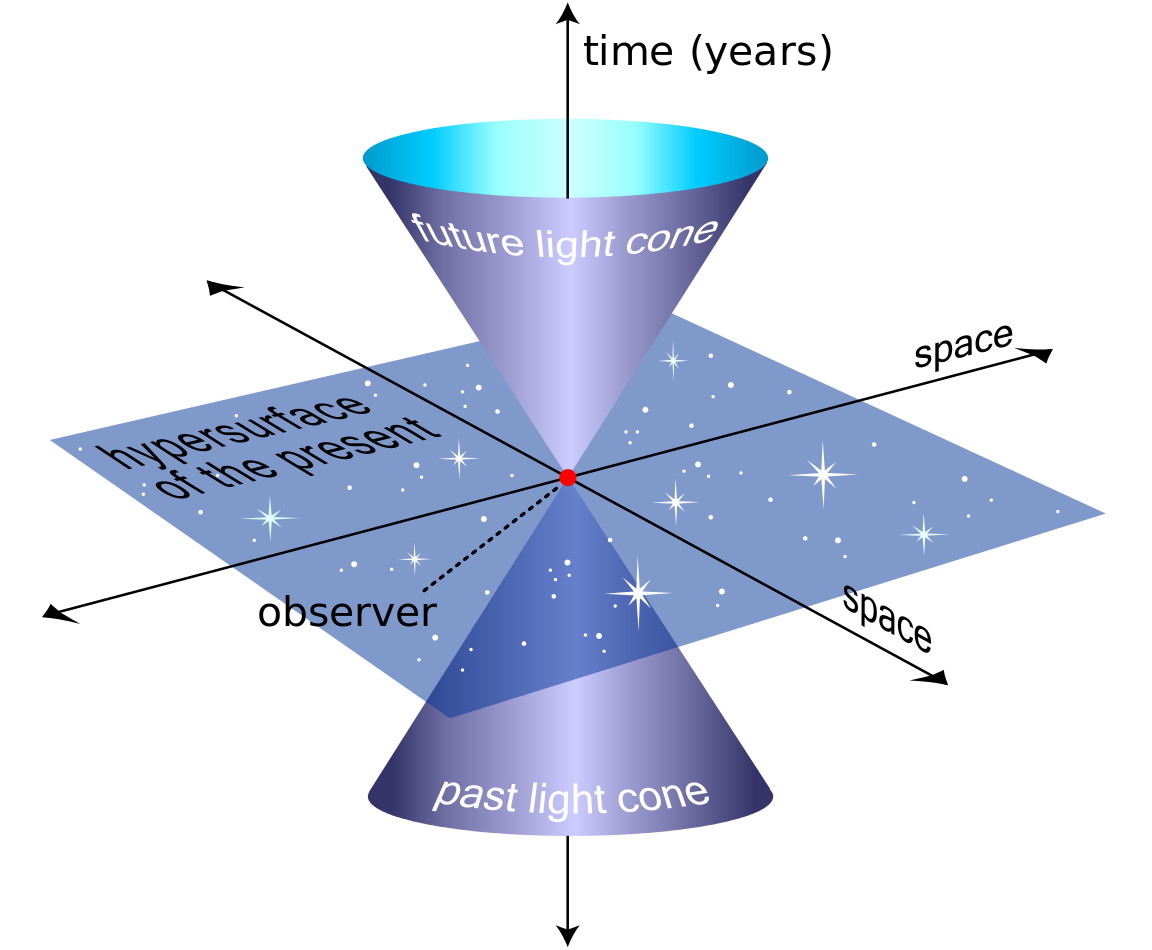
GLEICK: Einstein or maybe I should say more properly Minkowski, his teacher and contemporary, offers a vision of space-time as a single thing, as a four dimensional block in which the past and the future are just like spatial dimensions. They're just like north and south in the equations of physics. And so you can construct a view of the world in which the future is already there and you can say, and physicists do say something very much like this, that in the fundamental laws of physics there is no distinction between the past and the future. And so if you're playing that game you're essentially saying time as an independent thing doesn't exist. Time is just another dimension like space. Again, that is in obvious conflict with our intuitions about the world. We go through the day acting as though the past is over and the future has not yet happened and it might happen this way or it might happen that way. We could flip a coin and see. We tend to believe in our gut that the future is not fully determined and therefore is different from the past.
DEAN BUONOMANO: If the flow if time, if our subjective sense of the flow of time is an illusion we have this clash between physics and neuroscience because the dominant theory in physics is that we live in the block universe. And I should be clear. There's no consensus. There's no 100 percent agreement. But the standard view in physics is that, and this comes in large part from relativity, that we live in an eternalist universe, in a block universe in which the past, present and future is equally real. So, this raises the question of whether we can trust our brain to tell us that time is flowing.
NYE: In my opinion time is both subjective and objective. What we do in science and engineering and in life, astronomy, is measure time as carefully as we can because it's so important to our everyday world. You go to plant crops you want to know when to plant them. You want to know when to harvest them. If you want to have a global positioning system that enables you to determine which side of the street you're on, from your phone you need to take into account both the traditional passage of time that you might be familiar with watching a clock here on the Earth's surface, and the passage of time as it's affected by the speed of the spacecraft, and the passage of time as it's affected by the gravity of the Earth itself, both special and general relativities. It's astonishing. We work very hard to measure time with all sorts of extraordinary clocks, but there is no question with our brains which are wet chemical computers we lose track of time. We don't know if sometimes it feels short, sometimes it feels long and it's just the nature I think of being constrained by measuring time with our brains. This is why we build instruments to measure time outside of ourselves externally.
BUONOMANO: The brain has been telling time since the dawn of animal species. So even plants have the ability to tell time in terms of Circadian clock. So it's reasonable to ask so is that how the brain tells time? Does the brain have some oscillator that's ticking away and some circuit that's counting those ticks and tocks. The answer is no. The brain seems to have fundamentally different ways of telling time. So the first thing to notice is that while the mechanical clocks that we make, even your quartz watch, can tell time across a vast range of scales from tens of milliseconds to hours, minutes and days and months and years. So, the brain has many different clocks in order to tell the milliseconds and seconds and to tell the time of day. So one way to think about it is the Circadian clock, the clock that tells you what time of day it is and when to rise and when to go to sleep. That doesn't have a minute hand, much less a second hand. In contrast, the clock that tells you, the timing device in your brain that tells you hmm, this red light is taking a bit too long to turn. This traffic light is taking a bit long to turn or I think the waiter forgot my coffee. That clock doesn't have an hour hand, much less a number of days that have gone by. So the brain has different areas, different mechanisms in order to tell time. We don't understand, fully understand how the brain tells you what the tempo is a song is or when the red light is going to change. But it doesn't seem to have to do with any oscillator counter mechanisms. It seems to do with neural dynamics which is the fact that patterns of neurons, neurons are coupled to each other, neurons are connected to each other. And when you activate some neurons that group of neurons can activate another group of neurons which can activate another group of neurons. So you can have these evolving patterns of neural activity. So, this is consistent with what we call the multiple clock principle which is the brain doesn't have any master clock. It has many different circuits, each specialized or that focuses on processing time on one scale or another.
THALLER: One thing we are absolutely sure of is that the rate of time does change. Time is not just simply a progression like a river that keeps flowing. It can change depending on how fast you're moving through space and this is Einstein's special Theory of Relativity. The idea is that the faster you go, the slower time appears to be moving for you if other observers look at you going by. As you go faster and faster and approach the speed of light your time slows down more and more. And the amazing thing is that at the speed of light time does not progress at all. There are more everyday applications to this too. For example, the global positioning satellites that allow you to take your location from your smartphone. Those satellites are going overhead very, very fast. They're going nearly 20,000 miles an hour. And it turns out that that's fast enough that their time is slowed down. They're actually in a slightly different timeframe than we are. And we have to account for that. We have to correct for that mathematically. Otherwise, you would not get the right location. So, we know that time slows down. We observe this happening all around us. It was a really hard thing in modern physics about a hundred years ago for people to let go of the idea that time just has a rate that it flows. That, in fact, it can flow at different rates for different observers. Then there's the question of what is time related to space. And you may have heard that Einstein talked about a concept called space-time. He didn't believe that space and time were separate things. We certainly perceive them differently in our human brains. We can move through space, but time always seems to go just in one rate and in one direction. But Einstein thought they were part of a fabric, they were woven together. And one of the ways he illustrated this was that you have to adjust space and time so they always kind of balance out. If I am not moving through space, I'm sitting here still in this chair, then time just seems to go forward at a natural rate and time just flows. But if I start going faster and faster, my time slows down. So, in a sense I'm moving through space very fast so I can't move through time as fast as I might have. The two balance each other, space-time. If you move through space very fast time begins to slow down. And now something gets even stranger and that is that Einstein thought that the beginning of the universe, the Big Bang, created all of space and all of time at once in a big whole something. So every point in the past and every point in the future are just as real as the point of time you feel yourself in right now. Einstein believed that literally. One of his best friends died and he wrote a letter to this person's wife talking about how his friend still exists. Time is a landscape and if you had the right perspective on the universe you would see all of it laid out in front of you. All past, present, and future as a whole thing. And he said, you know, your husband, my friend, is just over the next hill. He's still there. We can't see him where we are now, but we are on this landscape with him and he still exists just as much as he ever has. Einstein believed that you right now had been dead for trillions of years, but you haven't been born yet. That everything that's happened to you if you could get the right perspective on the universe you could see all at once.
BUONOMANO: The present is the notion is that only the present is real. The past was real, the future some configuration of the future universe will be real, but for now only the present is real. In contrast the opposing view is called eternalism. Eternalism you have the past, present and future are all equally real. So, that makes the present just an arbitrary point in time or an arbitrary moment in time. So one way to think about this is now is to time as here is to space. So in the same sense that I happen to be here and some viewers are out at some other point in space and we're all comfortable with that notion that other points in space are equally real, in eternalism you have to be comfortable with the notion that other moments in time are as equally real as this moment in time and this is just an arbitrary moment.
GLEICK: And so if a physicist comes to me and says do some readjustment. Face it, the future looks different from the past to you, but actually physics tells us it's the same. I at least acknowledge that I have an obligation to take that seriously, to listen to it. And physicists do argue about these things and it's fair to argue about it.
THALLER: So modern physics has required us to really let go of the idea of time as something that just flows. We can measure that it's changing around us all over the place – satellites, particle accelerators, anything going fast. And it may be that space and time are the same thing all wrapped up together and it all exists all at once.