neuroscience
Michio Kaku predicts, among other things, how we’ll build cities on Mars and why cancer will one day be like the common cold.
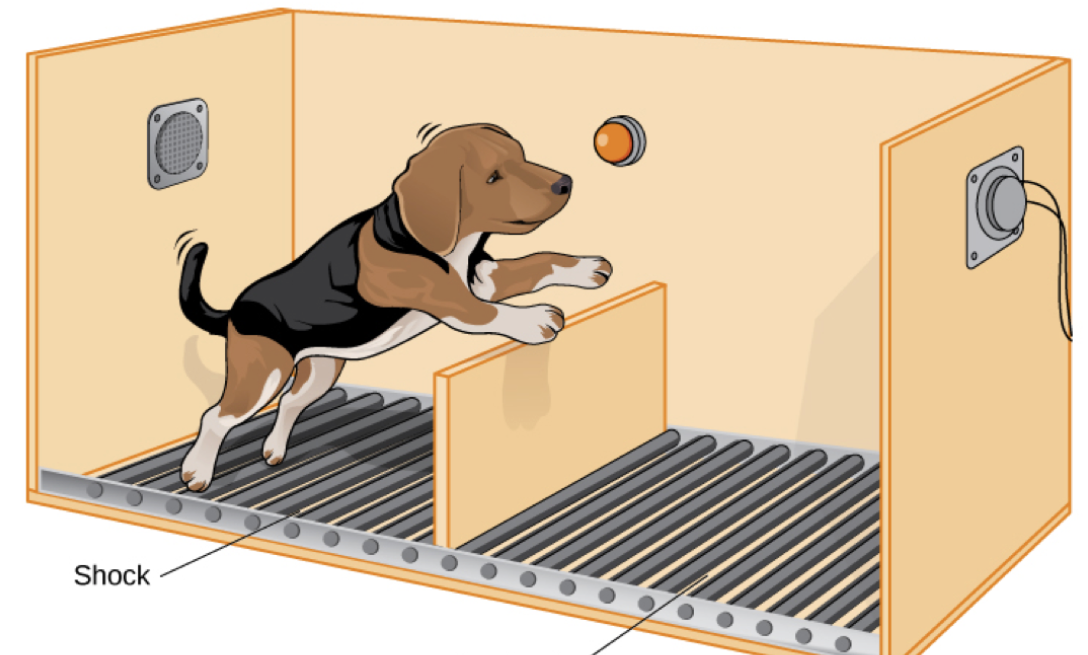
Helplessness isn’t learned — it’s an instinctual response that can be overcome.
About six minutes after the heart stops, the brain essentially dies.
Salk scientists studied complex decision-making capabilities in a worm with just 302 neurons and a mouth full of teeth. It’s smarter than you would think.
We imagine and debate the inner lives of literary characters, knowing there can be no truth about their real motives or beliefs. Could our own inner lives also be works of fiction?
Head direction cells act like internal compasses to help the birds navigate during long flights.
Discussions of human evolution are usually backward looking, as if the greatest triumphs and challenges were in the distant past.
“At that time, it was just a wild idea, […] that instead of just a loss of consciousness, anesthetics may do something to the brain that actually turns pain off.”
Two aspects of memory – fast updating and long lasting – are typically considered incompatible, yet the insects combined them.
Do the health risks outweigh the benefits?
MIT neuroscientists have identified a population of neurons in the human brain that respond to singing but not other types of music.
Researchers look to an FDA-approved drug ingredient that can “scoop-up” and store cholesterol and possibly stave off post-stroke dementia.
The first recorded brain activity of a person during their death suggests a biological trigger for near-death experiences.
Choking under pressure seems to have deep evolutionary roots.
Ingesting tiny doses of hallucinogens might not have the outsized benefits that some people claim it does.
Whenever you’re surprised, there’s a good chance that your brain is busy tweaking your memories.
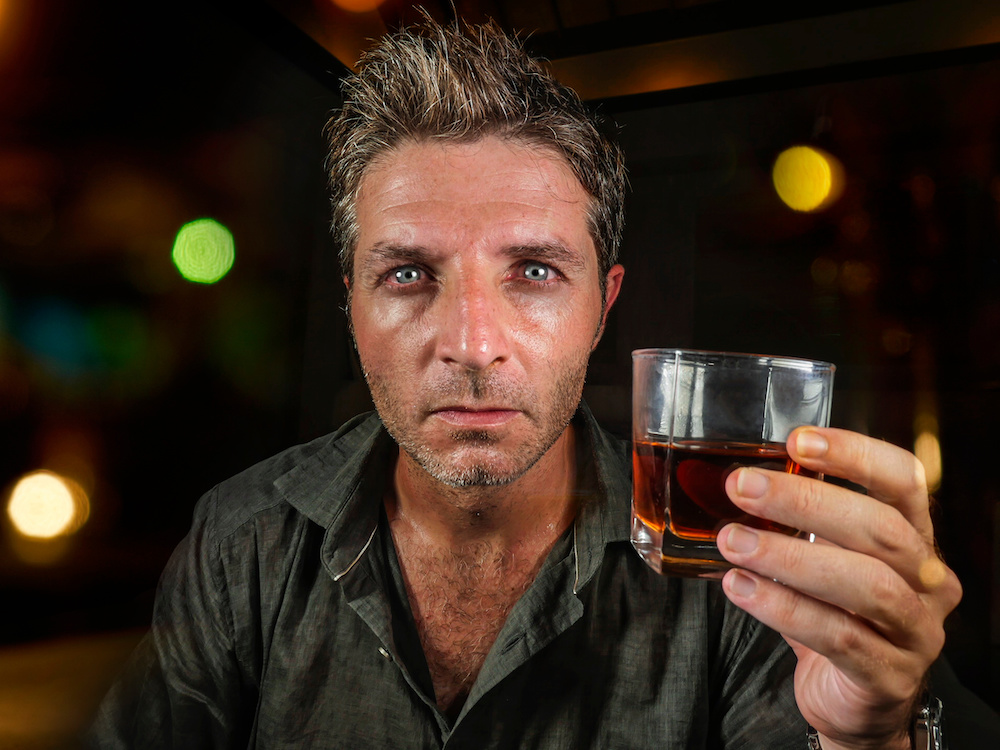
Should we take people’s drunken behavior as evidence of their true character?
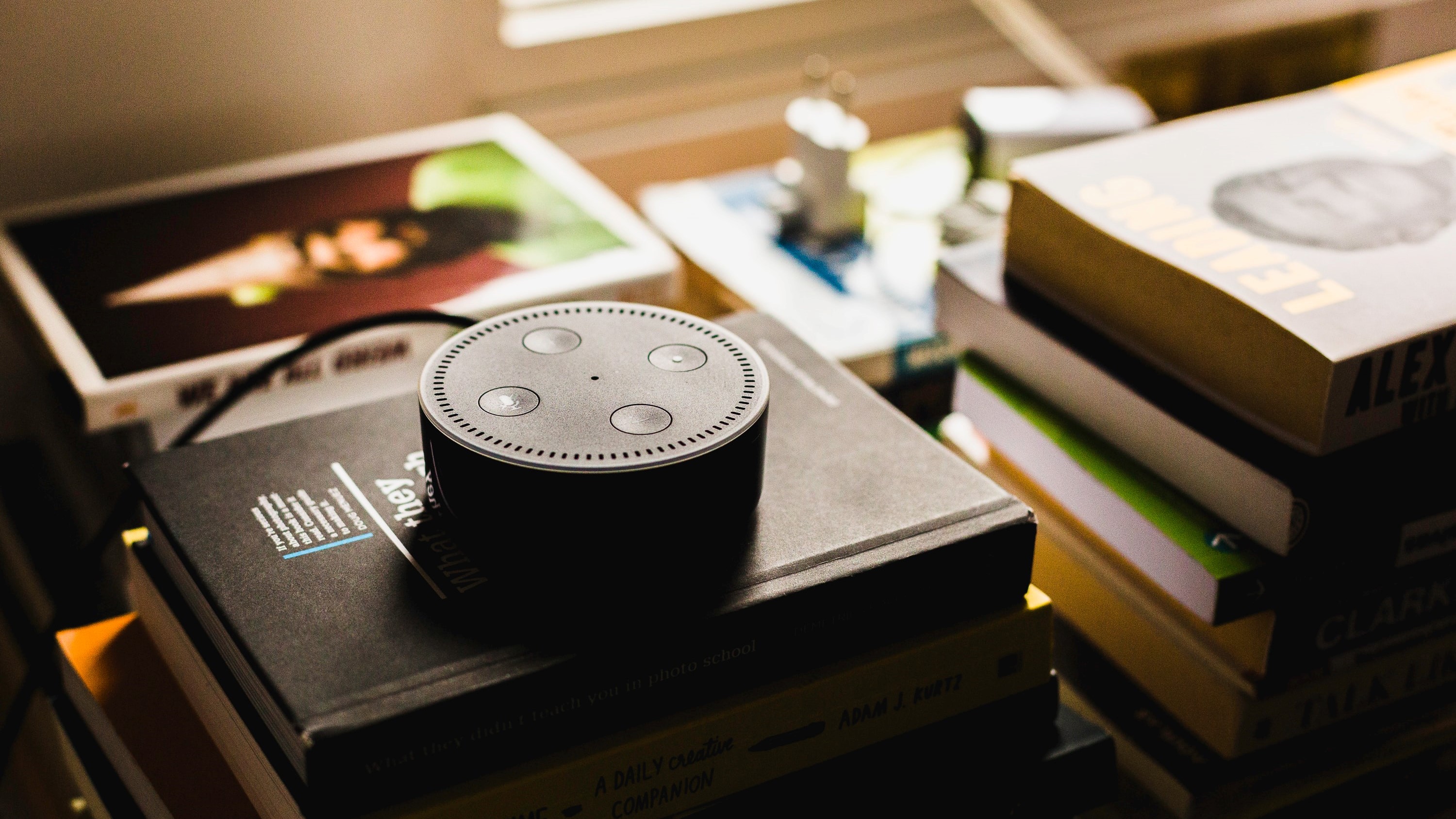
The more social behaviors a voice-user interface exhibits, the more likely people are to trust it, engage with it, and consider it to be competent.
Elephants mourn the dead, dolphins give names to each other, and insects can recognize faces. The animal world is much smarter than we think.
Neuroscience research suggests it might be time to rethink our ideas about when exactly a child becomes an adult.
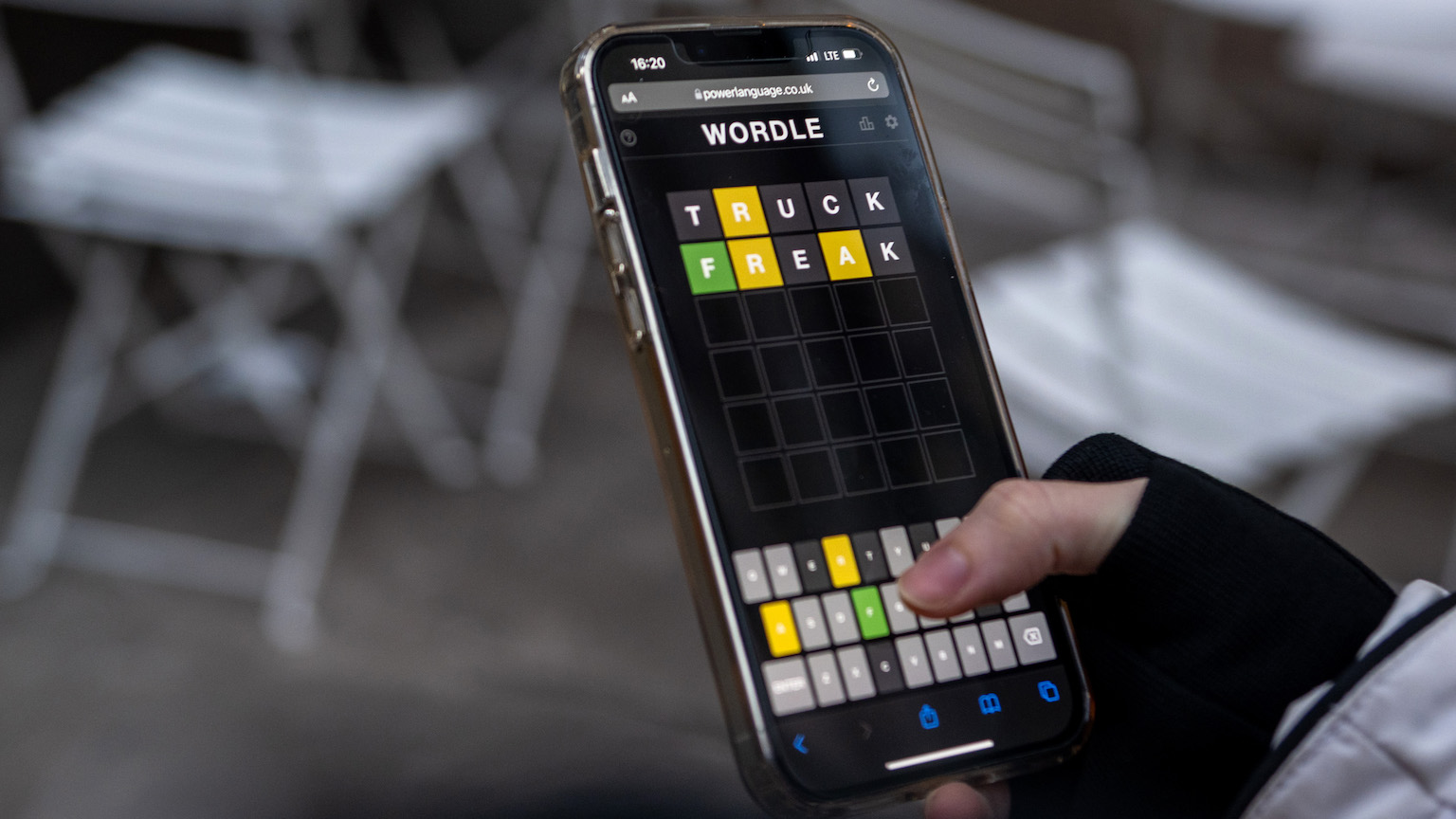
Wordle activates both the language and logic parts of our brain and give us a nice boost of dopamine, whether we win or lose.
OCD and addiction may result in part from improper “reward” pathways in the brain. Ultrasound can disrupt those pathways.
Your brain is remarkably good at mapping out physical spaces — even if it’s an imaginary space like Hogwarts. But how does the brain do it?
The first personality tests revolved around assessing people’s reactions to ambiguous and often unsettling images. Today, the gold standard is a barrage of questions.
Regret isn’t just unpleasant, it’s unhealthy.
Temporal lobe epilepsy seems to rewire a part of the brain that’s key to storing memories.
Certain types of dogs seem to be more discerning than others, however.
New research suggests they may be in the connections between your brain cells.
The Virtual Metaverse will be for gaming and other short duration uses, while the Augmented Metaverse will revolutionize society.
The use of AI within mental health services could be a game-changer.