biotech
The new documentary “Make People Better” leans toward a different narrative about gene-editing than we’ve heard before.
Only recently have scientists directly witnessed this most pivotal of events in biology.
It was a particularly good year for biotech and medical technology. There were also notable advances in energy.
What if you could just grow your own blood?
It will be able to produce 22 million pounds of cultivated meat annually.
Merely 256 genetically engineered mice could make an island’s pest population go extinct.
De-extinction, if it is ever possible, will not be simple.
In an animal study, it blocked the drug from crossing into the brain.
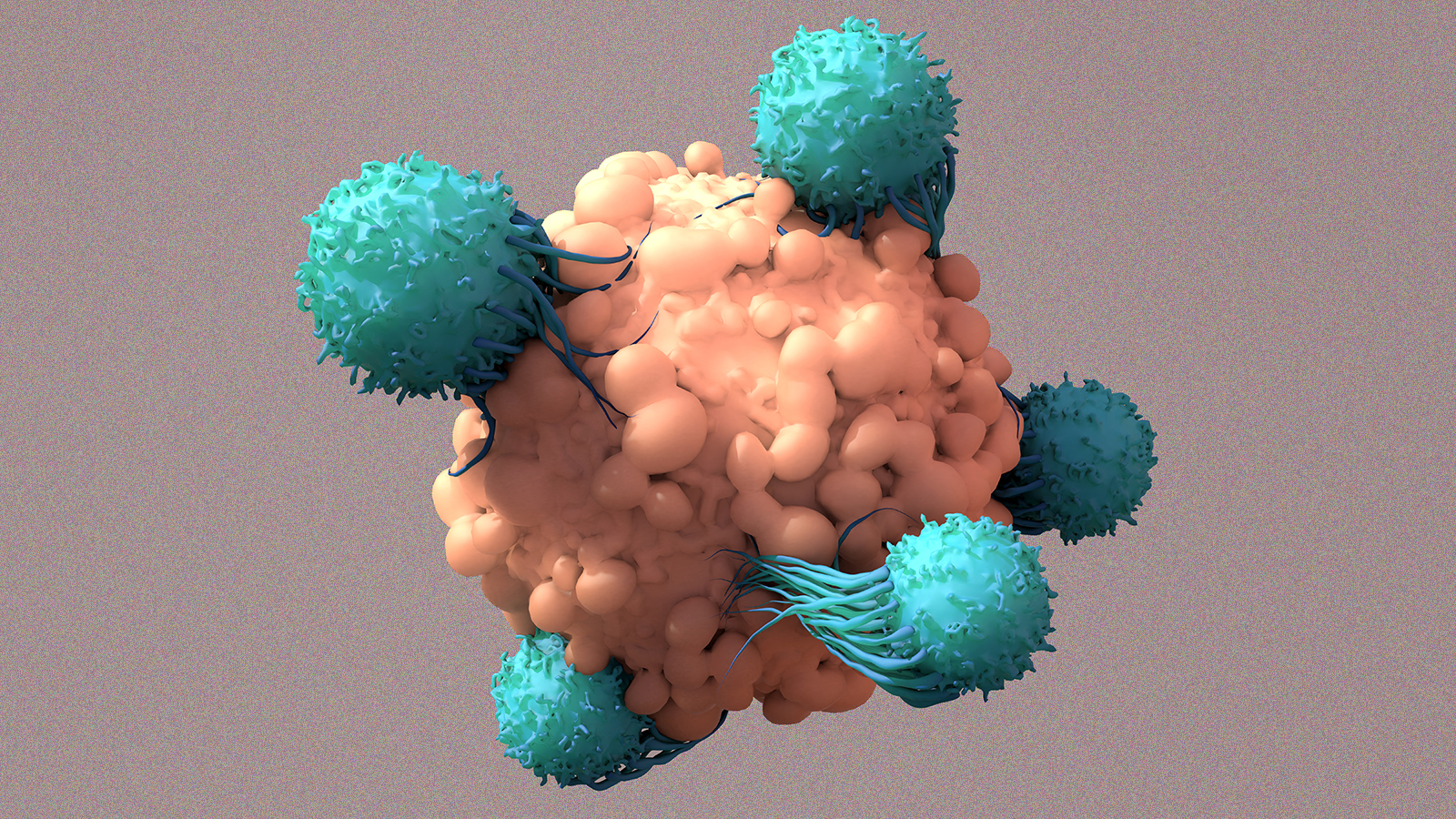
This small phase 1 study suggests that CRISPR-engineered T cells are safe and potentially effective, but there is a long way to go.
Brown noise, the better-known white noise, and even pink noise are all sonic hues.
Giving speech to the speechless.
This opens the door to manipulating networks of specific neurons.
The researchers suggest that their results demonstrate intelligence in silico.
Biotechnology can convert enemy viruses into anti-cancer mercenaries.
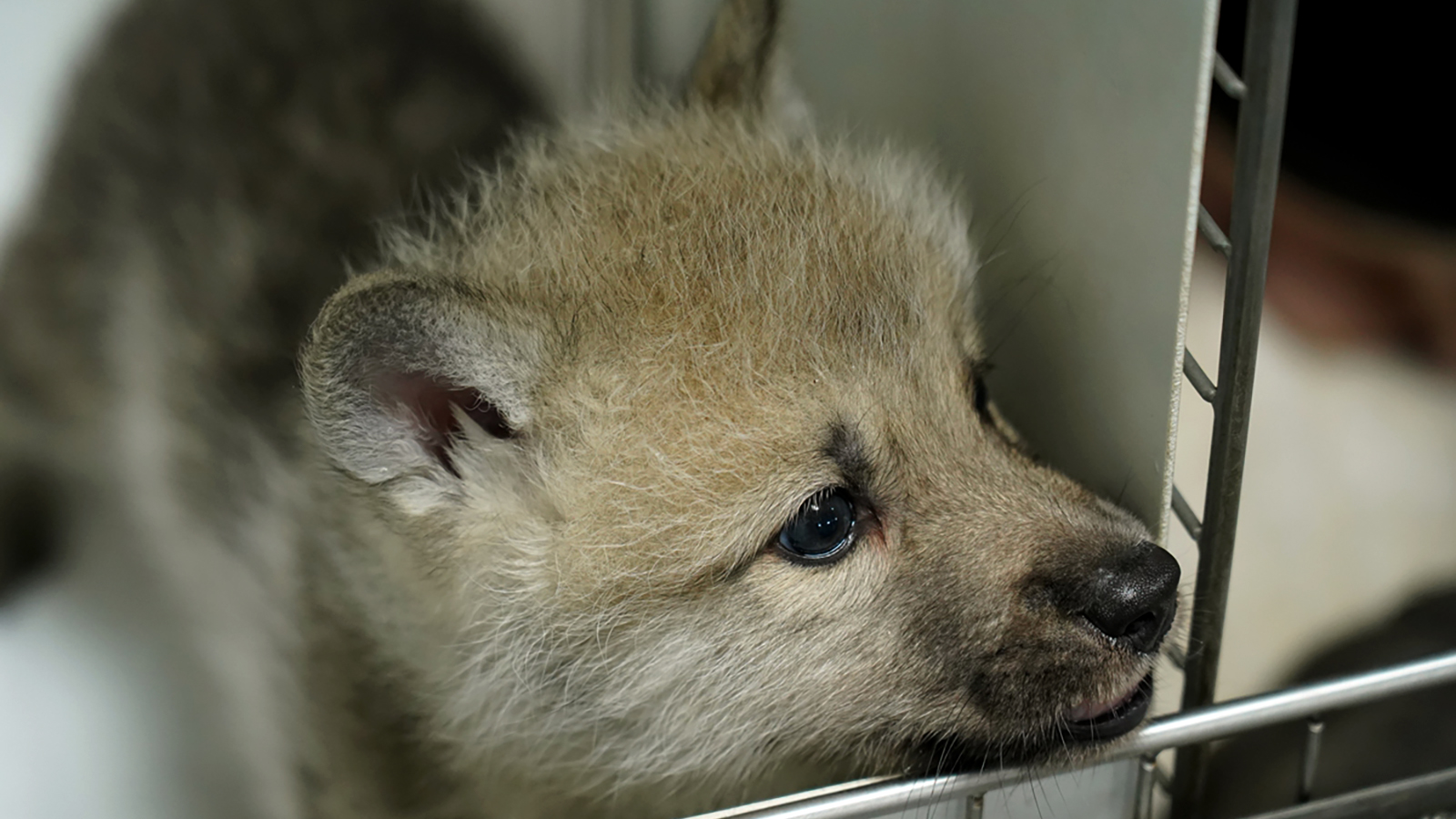
This pup puts us one step closer to resurrecting extinct species.
The new agency wants to push the boundaries of science and technology.
Synthetic biology has the power to cure and kill. Have we learned from our past mistakes?
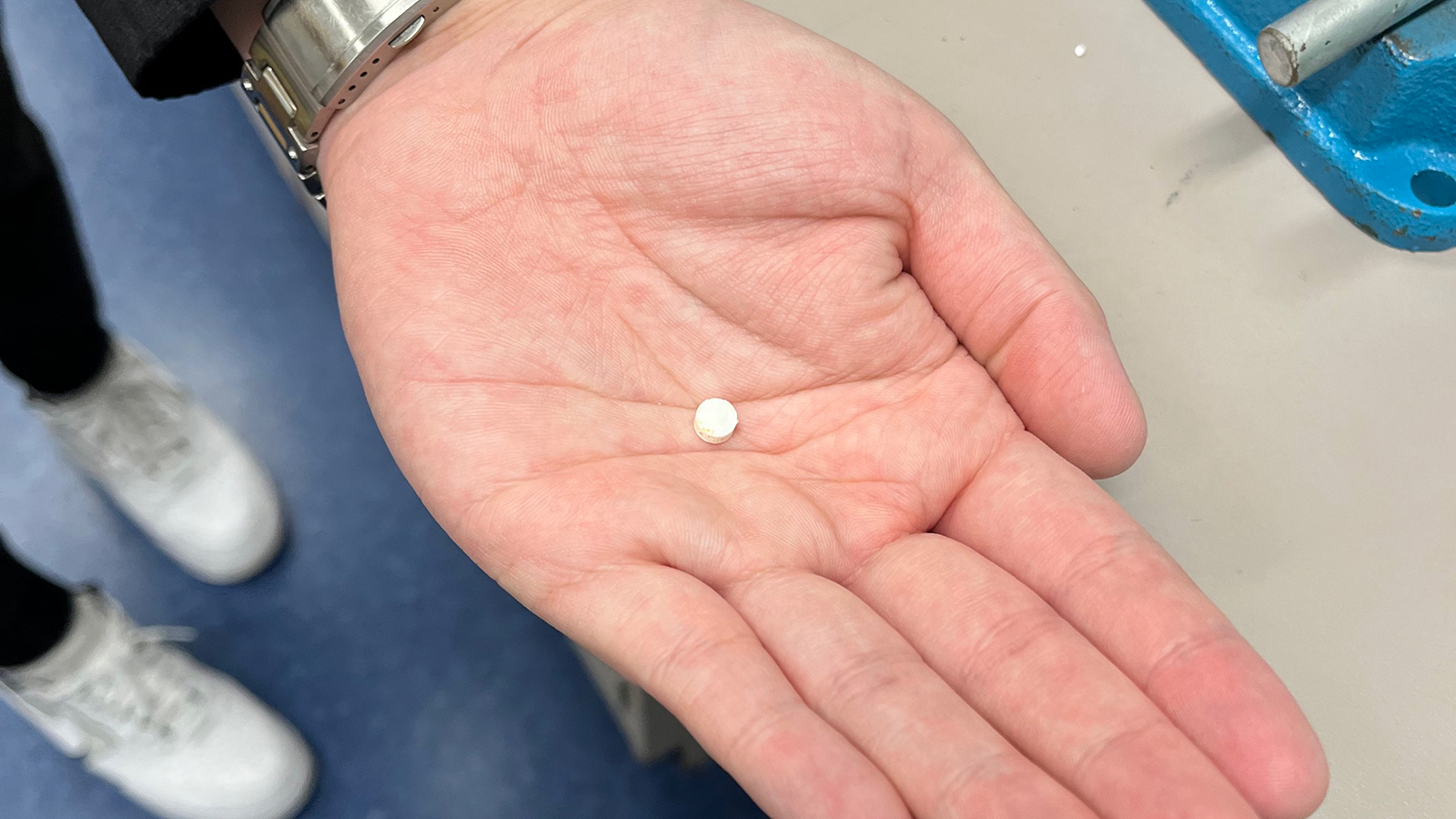
These dissolvable pills aren’t meant to be swallowed, though.
Advances in ancient DNA analysis gave researchers a new way to trace the movements of peoples across Eurasia.
The spray uses snippets of DNA to gum up virus replication.
HIV mutates rapidly, which has made the development of a vaccine an enormous challenge for decades. Finally, we might have one.
The AI test can be done every night at home while the person is asleep, without even touching their body.
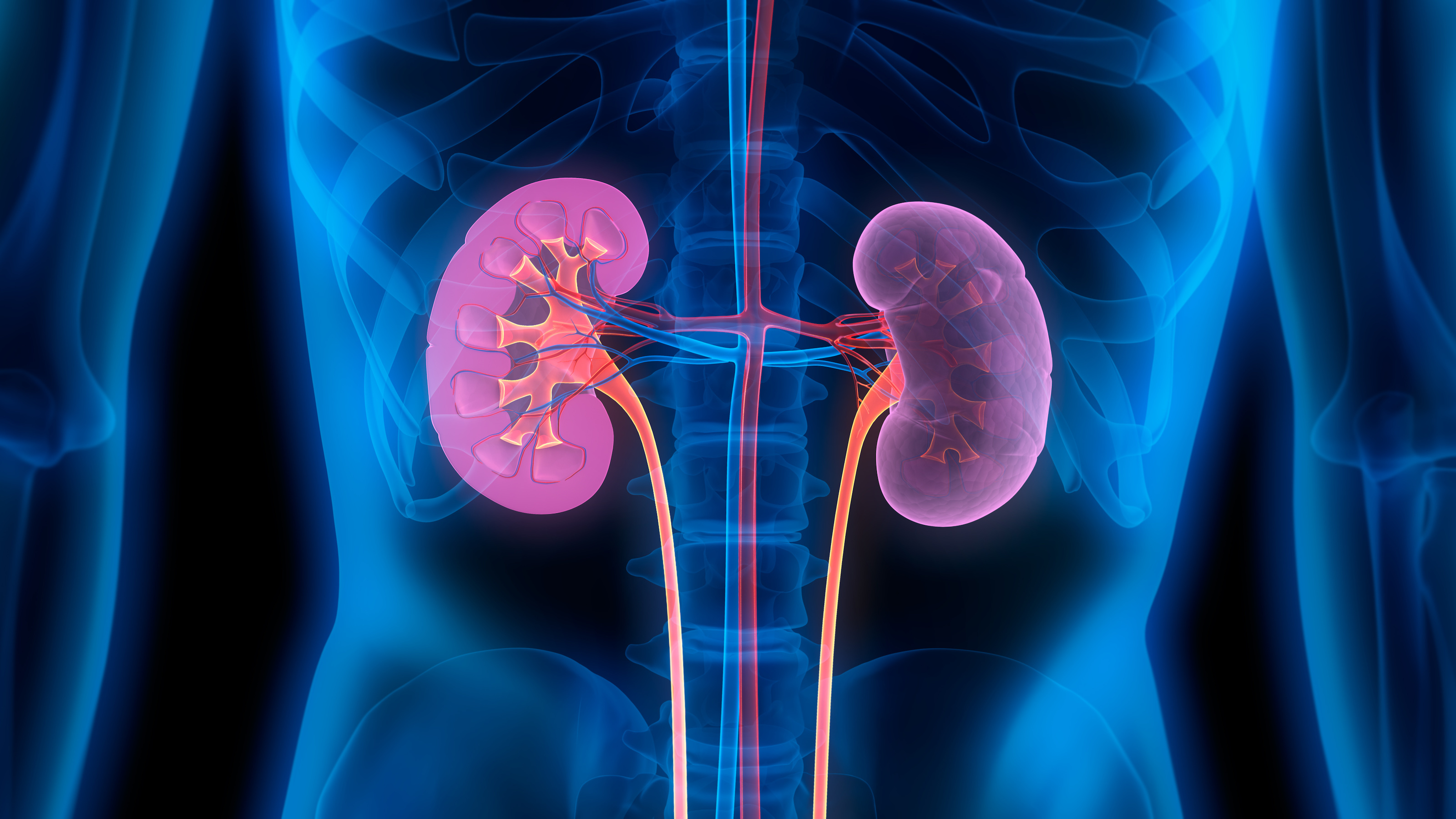
By creating a type O kidney, they hope to make more organs available for transplant.
The synthetic cartilage was made from cellulose fibers — the stuff found in wood — mixed with a goo called polyvinyl alcohol.
The antibodies elicited by the “S2 vaccine” not only neutralize COVID’s multiple strains but also coronaviruses that cause the common cold.
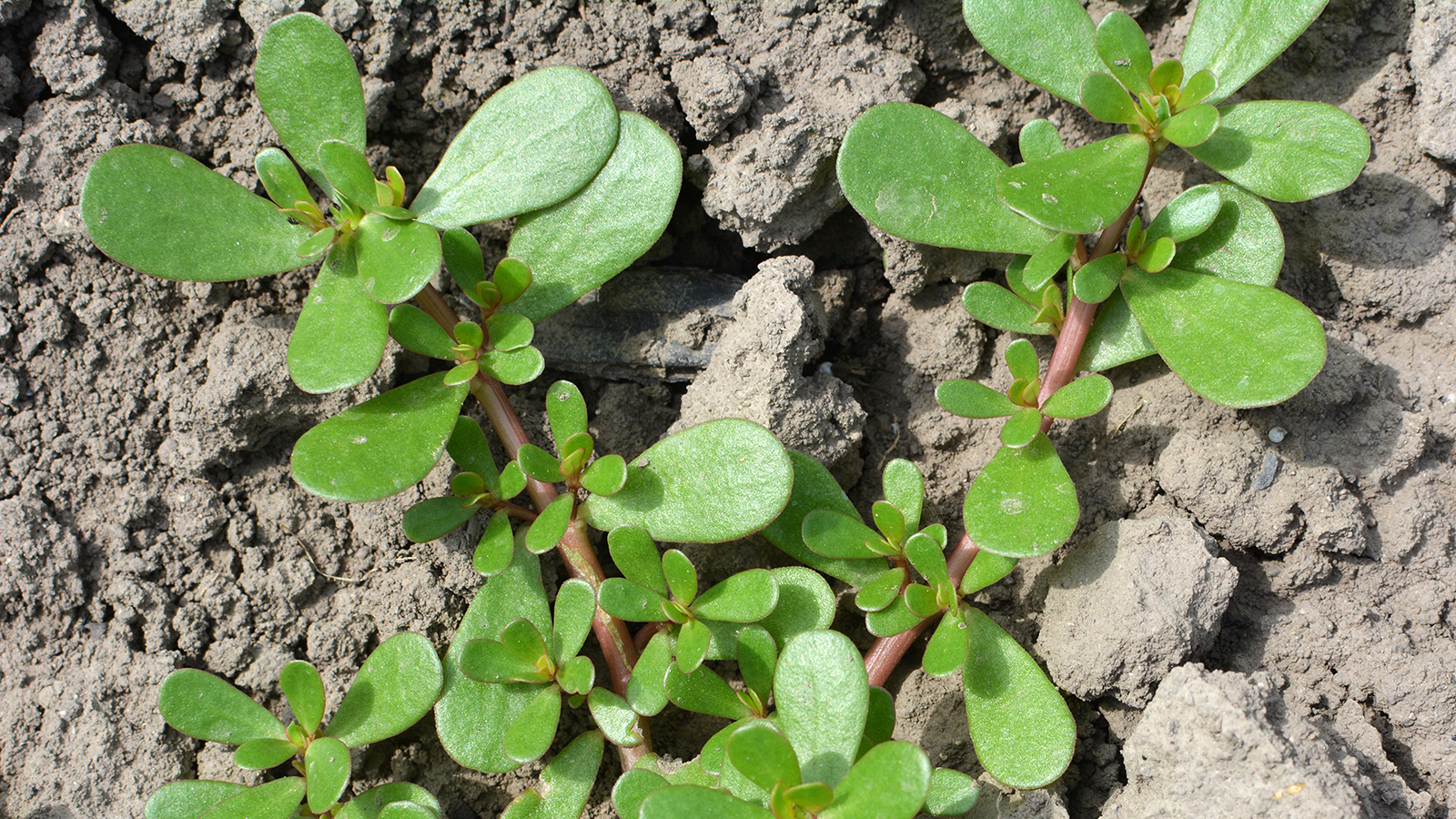
A common weed uses uncommon types of photosynthesis.
An interview with CRISPR co-discoverer and Nobel Prize-winner Dr. Jennifer Doudna.
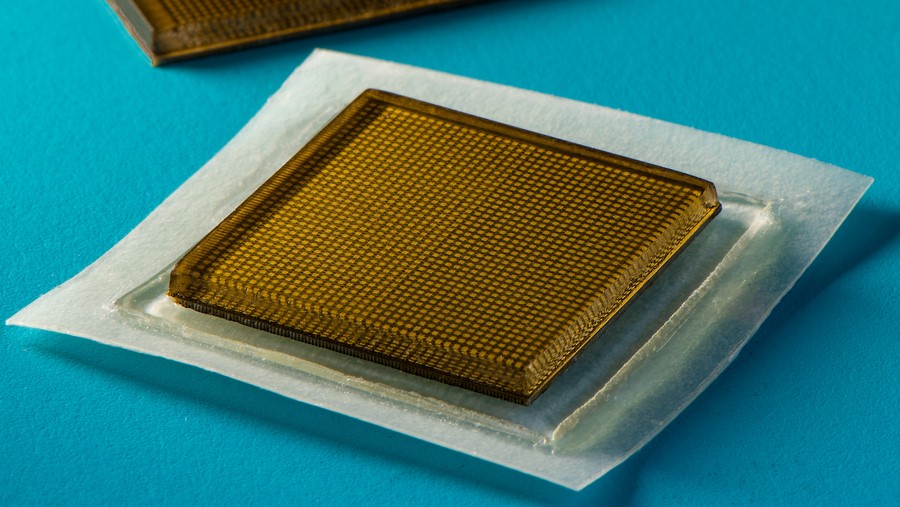
New stamp-sized ultrasound adhesives produce clear images of heart, lungs, and other internal organs.
While one may be helpful, the other may be harmful.
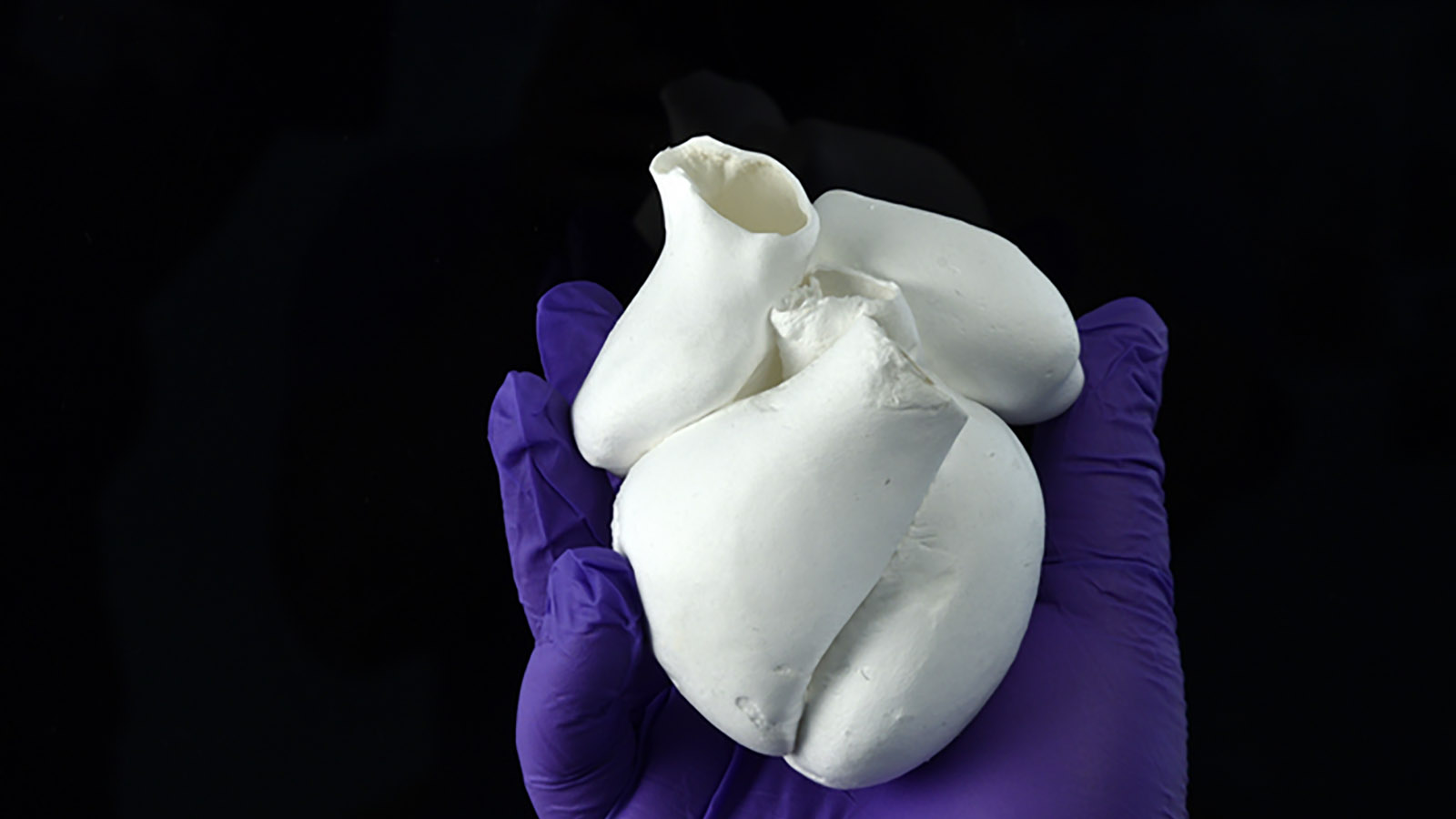
Heart muscle is shaped like a spiral, a mystery that has eluded scientists since 1669. New research has recreated the structure.