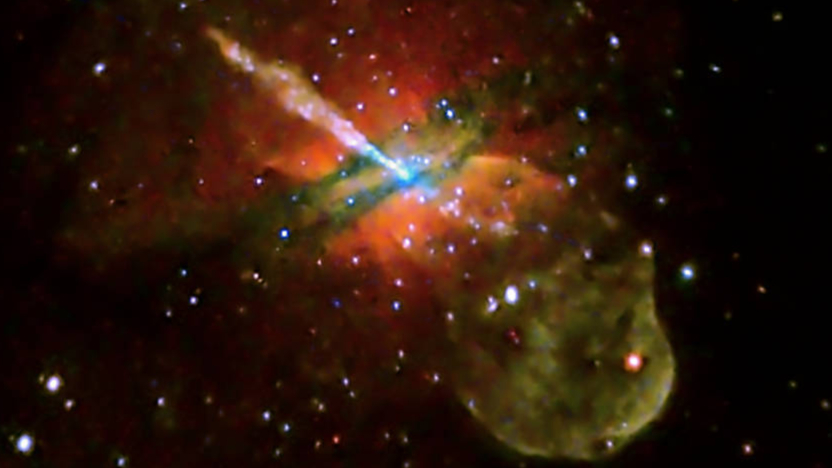
There are 5 eras in the universe’s lifecycle. Right now, we’re in the second era.

Image source: Pablo Carlos Budassi
- We’re in the middle, or thereabouts, of the universe’s Stelliferous era.
- If you think there’s a lot going on out there now, the first era’s drama makes things these days look pretty calm.
- Scientists attempt to understand the past and present by bringing together the last couple of centuries’ major schools of thought.
If you’re fortunate enough to get yourself beneath a clear sky in a dark place on a moonless night, a gorgeous space-scape of stars waits. If you have binoculars and point them upward, you’re treated to a mind-bogglingly dense backdrop of countless specks of light absolutely everywhere, stacked atop each other, burrowing outward and backward through space and time. Such is the universe of the cosmological era in which we live. It’s called the Stelliferous era, and there are four others.
Image based on logarithmic maps of the Universe put together by Princeton University researchers, and images produced by NASA based on observations made by their telescopes and roving spacecraftImage source: Pablo Carlos Budassi
There are many ways to consider and discuss the past, present, and future of the universe, but one in particular has caught the fancy of many astronomers. First published in 1999 in their book The Five Ages of the Universe: Inside the Physics of Eternity, Fred Adams and Gregory Laughlin divided the universe’s life story into five eras:
- Primordial era
- Stellferous era
- Degenerate era
- Black Hole Era
- Dark era
The book was last updated according to current scientific understandings in 2013.
It’s worth noting that not everyone is a subscriber to the book’s structure. Popular astrophysics writer Ethan C. Siegel, for example, published an article on Medium last June called “We Have Already Entered The Sixth And Final Era Of Our Universe.” Nonetheless, many astronomers find the quintet a useful way of discuss such an extraordinarily vast amount of time.

Image source: Sagittarius Production/Shutterstock
This is where the universe begins, though what came before it and where it came from are certainly still up for discussion. It begins at the Big Bang about 13.8 billion years ago.
For the first little, and we mean very little, bit of time, spacetime and the laws of physics are thought not yet to have existed. That weird, unknowable interval is the Planck Epoch that lasted for 10-44 seconds, or 10 million of a trillion of a trillion of a trillionth of a second. Much of what we currently believe about the Planck Epoch eras is theoretical, based largely on a hybrid of general-relativity and quantum theories called quantum gravity. And it’s all subject to revision.
That having been said, within a second after the Big Bang finished Big Banging, inflation began, a sudden ballooning of the universe into 100 trillion trillion times its original size.
Within minutes, the plasma began cooling, and subatomic particles began to form and stick together. In the 20 minutes after the Big Bang, atoms started forming in the super-hot, fusion-fired universe. Cooling proceeded apace, leaving us with a universe containing mostly 75% hydrogen and 25% helium, similar to that we see in the Sun today. Electrons gobbled up photons, leaving the universe opaque.
About 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe had cooled enough that the first stable atoms capable of surviving began forming. With electrons thus occupied in atoms, photons were released as the background glow that astronomers detect today as cosmic background radiation.
Inflation is believed to have happened due to the remarkable overall consistency astronomers measure in cosmic background radiation. Astronomer Phil Plait suggests that inflation was like pulling on a bedsheet, suddenly pulling the universe’s energy smooth. The smaller irregularities that survived eventually enlarged, pooling in denser areas of energy that served as seeds for star formation—their gravity pulled in dark matter and matter that eventually coalesced into the first stars.

Image source: Casey Horner/unsplash
The era we know, the age of stars, in which most matter existing in the universe takes the form of stars and galaxies during this active period.
A star is formed when a gas pocket becomes denser and denser until it, and matter nearby, collapse in on itself, producing enough heat to trigger nuclear fusion in its core, the source of most of the universe’s energy now. The first stars were immense, eventually exploding as supernovas, forming many more, smaller stars. These coalesced, thanks to gravity, into galaxies.
One axiom of the Stelliferous era is that the bigger the star, the more quickly it burns through its energy, and then dies, typically in just a couple of million years. Smaller stars that consume energy more slowly stay active longer. In any event, stars — and galaxies — are coming and going all the time in this era, burning out and colliding.
Scientists predict that our Milky Way galaxy, for example, will crash into and combine with the neighboring Andromeda galaxy in about 4 billion years to form a new one astronomers are calling the Milkomeda galaxy.
Our solar system may actually survive that merger, amazingly, but don’t get too complacent. About a billion years later, the Sun will start running out of hydrogen and begin enlarging into its red giant phase, eventually subsuming Earth and its companions, before shrining down to a white dwarf star.

Image source: Diego Barucco/Shutterstock/Big Think
Next up is the Degenerate era, which will begin about 1 quintillion years after the Big Bang, and last until 1 duodecillion after it. This is the period during which the remains of stars we see today will dominate the universe. Were we to look up — we’ll assuredly be outta here long before then — we’d see a much darker sky with just a handful of dim pinpoints of light remaining: white dwarfs, brown dwarfs, and neutron stars. These”degenerate stars” are much cooler and less light-emitting than what we see up there now. Occasionally, star corpses will pair off into orbital death spirals that result in a brief flash of energy as they collide, and their combined mass may become low-wattage stars that will last for a little while in cosmic-timescale terms. But mostly the skies will be be bereft of light in the visible spectrum.
During this era, small brown dwarfs will wind up holding most of the available hydrogen, and black holes will grow and grow and grow, fed on stellar remains. With so little hydrogen around for the formation of new stars, the universe will grow duller and duller, colder and colder.
And then the protons, having been around since the beginning of the universe will start dying off, dissolving matter, leaving behind a universe of subatomic particles, unclaimed radiation…and black holes.

Image source: Vadim Sadovski/Shutterstock/Big Think
For a considerable length of time, black holes will dominate the universe, pulling in what mass and energy still remain.
Eventually, though, black holes evaporate, albeit super-slowly, leaking small bits of their contents as they do. Plait estimates that a small black hole 50 times the mass of the sun would take about 1068 years to dissipate. A massive one? A 1 followed by 92 zeros.
When a black hole finally drips to its last drop, a small pop of light occurs letting out some of the only remaining energy in the universe. At that point, at 1092, the universe will be pretty much history, containing only low-energy, very weak subatomic particles and photons.

Image source: Big Think
We can sum this up pretty easily. Lights out. Forever.
Tonight, if it’s clear, maybe you want to step outside, take a nice deep breath, and look up, grateful that we are where we are, and when we are, in spite of all the day’s hardships. We’ve got a serious amount of temporal elbow room here, far more than we need, so not to worry, and those stars aren’t going anywhere for a long, long time.