These Two Galaxies Can’t Both Exist Without Dark Matter

From galaxies with no dark matter to ones with hundreds of times more dark matter than normal, our Universe needs it more than ever.
One of the most mysterious substances in the entire Universe is dark matter. Gravitationally, there’s much more mass in large structures than normal matter alone — even including the normal matter that doesn’t emit light — can explain. From individually rotating galaxies to groups and clusters of galaxies to the large-scale structure of the Universe to even the imperfections in the Cosmic Microwave Background, the same 5-to-1 ratio of dark matter to normal matter is required to make the Universe add up.
But when we look at small, low-mass galaxies, the story must change dramatically if dark matter is real. Some galaxies collide and interact, expelling large amounts of normal matter in the process; that normal matter should then gravitationally contract to form small galaxies with hardly any dark matter at all. Similarly, small galaxies that form lots of new stars will generate radiation, capable of ejecting the normal matter but leaving all the dark matter intact. If both galaxy types are found, with widely mismatched ratios, dark matter must be real. The evidence is in, and what we’ve learned is remarkable.
The way that theoretical cosmology — a branch of theoretical astrophysics — works is generally straightforward, but hard to visualize. What we do is:
- try, from our observations, to understand what the Universe is made of today,
- learn, from our experiments, what the laws and rules are that govern it,
- to measure certain properties like how quickly it’s expanding, how old it is,
and then to simulate what the Universe ought to look like based on our understanding.
Those simulations then start from some early time, when the Universe was simpler, more uniform, hotter, and denser. As it expands and cools, the different forms of energy — including normal matter, radiation, neutrinos, and (if it’s present) dark matter — interact according the the laws that govern them. These simulations can tell us what types of structures are expected to form in the Universe, giving us a set of predictions under various scenarios and circumstances, to compare our observations to.

When we look at the large-scale structures in the Universe, these simulations do a remarkable job of aligning with what our observations reveal. Simulations and observations both yield an intricate cosmic web, consistent even in the specific details of how galaxies clump and cluster. The features in the cosmic microwave background require a five-to-one ratio of dark matter to normal matter. In galaxy groups and clusters, dark matter is required to explain how the cluster members remain bound, to account for the gravitational lensing effects observed, and to explain why X-rays are emitted in a location offset from the total mass when these groups or clusters collide.
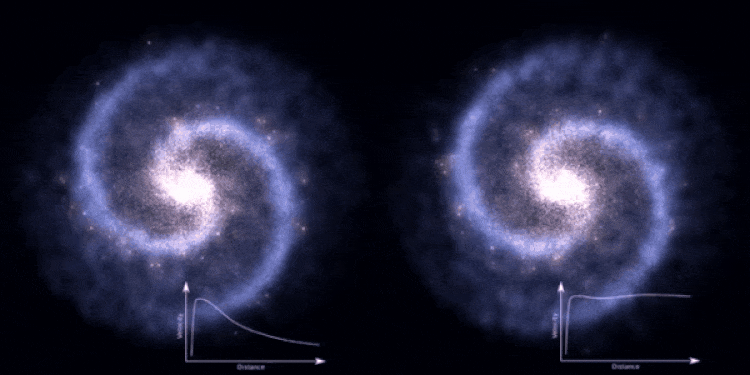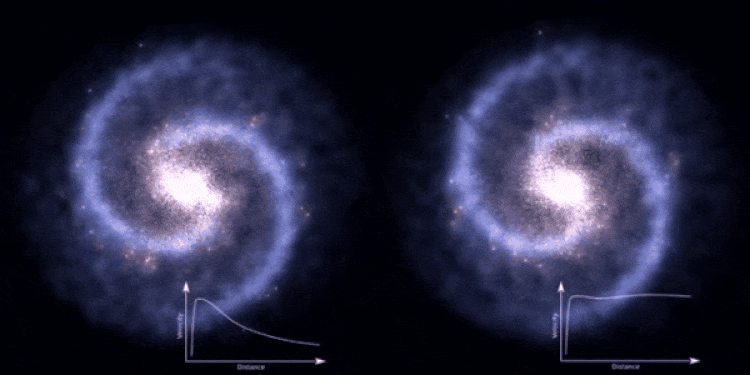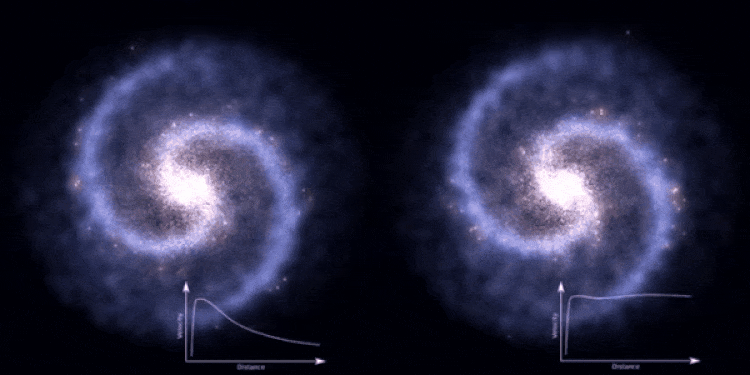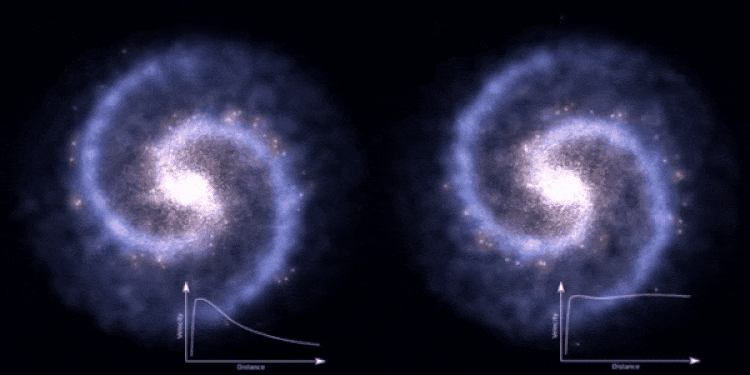
On the scales of large, individual galaxies, the inner regions appear to be dominated by normal matter, while the regions closer to the outskirts are influenced by some addition, invisible mass: dark matter. Whereas the normal matter not only gravitates but also collides, interacts, sticks together, and emits or absorbs radiation, the dark matter only interacts gravitationally. The normal matter sinks towards the center of each galaxy, while the dark matter remains distributed in a diffuse, large-volume halo.

In each one of these cases, you can put in the same ratio of dark matter to normal matter: five-to-one. For every proton in the Universe — an example of normal matter — there must exist five times as much mass in the form of invisible dark matter. This holds true for the fluctuations in the cosmic microwave background, the features found throughout the cosmic web, galaxy clusters and groups, and even large, individual, isolated galaxies.
But when galaxies interact, merge, or form large bursts of new stars, those ratios can change significantly. Remember: dark matter only interacts gravitationally, while normal matter can also:
- collide with normal matter particles,
- experience pressure from radiation,
- absorb energy, exciting atoms or ionizing them entirely,
- radiate energy away,
- and stick together, dissipate energy, and shed angular momentum from interactions.
It’s why, when we see a galaxy speeding through a matter-rich environment, like the space between galaxies within a massive cluster, the normal matter within it can get stripped out entirely.
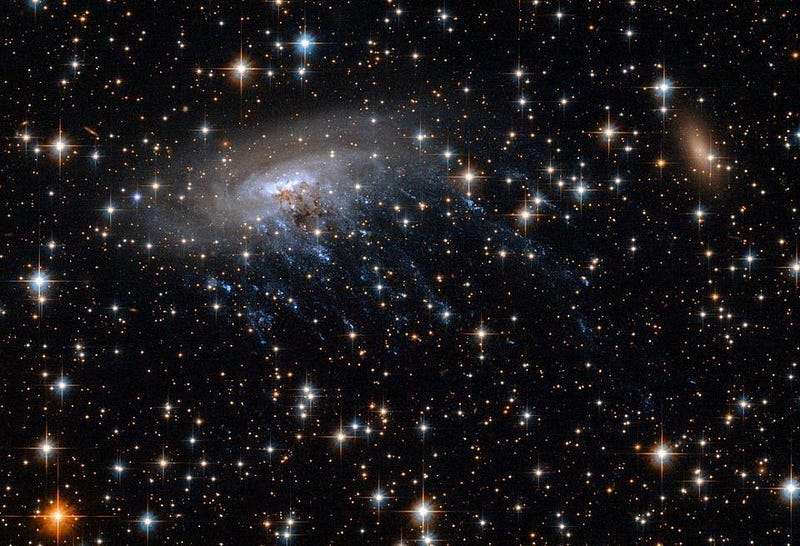

That stripping is due to collisions between normal matter within the galaxy and normal matter in the external environment through which it moves, but there are other mechanisms that can also successfully separate dark matter from normal matter.
When galaxies collide and merge, or when they have a near-miss encounter, both galaxies will experience what’s known as tidal disruption: where the gravitational force on the side of the galaxy “closer to” its neighbor is greater than the force “farther from” its neighbor. This differential force causes the galaxy to elongate, and can strip matter out of both galaxies if the configuration is right.
Additionally, where you have large enough amounts of normal matter to trigger a burst of star-formation, the radiation and winds from those new stars — particularly if some of them are high-mass stars that produce large amounts of ultraviolet light — can expel the normal matter that hasn’t already formed stars, while leaving the dark matter untouched.
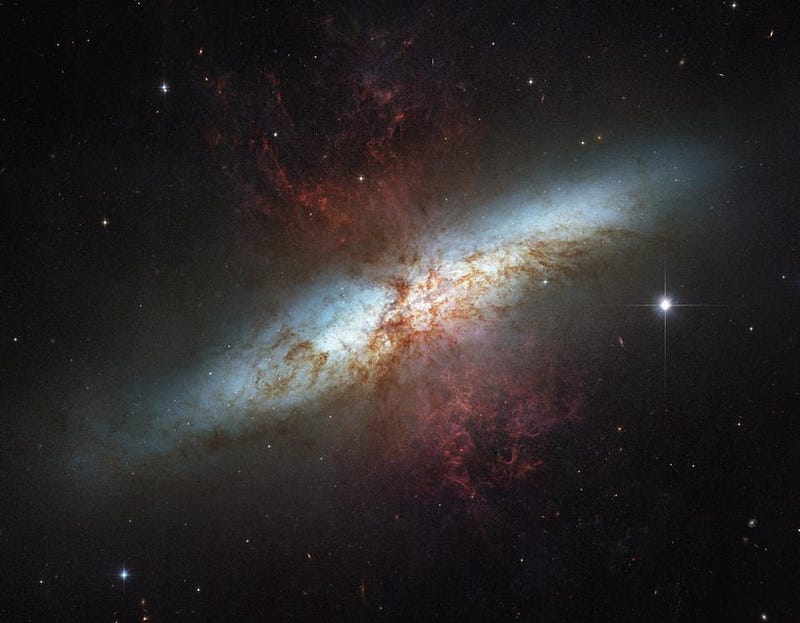

In other words, every structure that forms in the Universe should initially form with that same universal dark matter-to-normal matter ratio: 5-to-1. But when stars form, when galaxies interact or merge, and when galaxies speed through matter-rich regions, normal matter can find itself purged from these structures, with more severe effects occurring for lower-mass galaxies. In particular, this should result in two types of low-mass galaxies that don’t have the same dark matter-to-normal matter ratios as everything else.
- There should be galaxies that have lost most of their normal matter, either through interactions or through expulsion from star formation, but still have all of their dark matter intact. Except for a small population of stars, their dark matter-to-normal matter ratios can be much greater than 5-to-1, particularly for extremely low-mass galaxies.
- There should be galaxies that form from the normal matter that gets pulled out of these galaxies and recollapses over cosmic times. These galaxies should be physically small, low in mass, and either dark matter-poor or dark matter-free, with a composition of up to 100% normal matter alone.
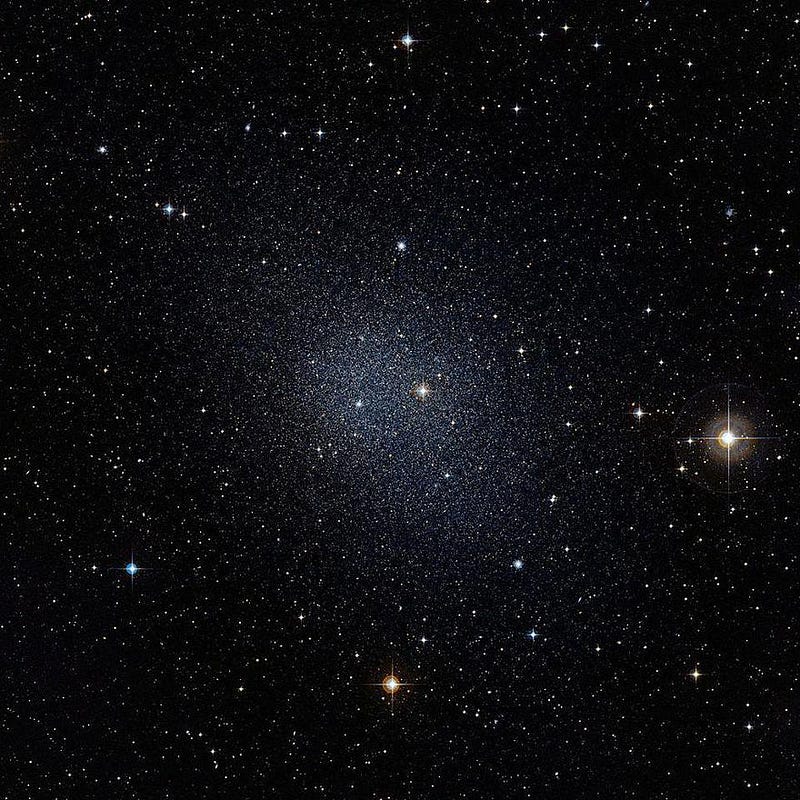

When we measure most small, low-mass galaxies, we find that the majority of them have stars that not only move move quickly than the normal matter alone can account for, but that the amount of dark matter required for most of them significantly exceeds the typical dark matter-to-normal matter ratio.
One class of galaxy — known as UDGs (ultra diffuse galaxies) — are naturally low in luminosity, but still have large gravitational masses. Typically, their mass-to-light ratios are around 30-to-1, about a factor of six greater than normal, non-ultra-diffuse galaxies. They exist, they’re abundant, and they provide evidence that dark matter behaves differently from normal matter that’s just non-luminous.
But the most severe galaxies of all are known as Segue 1 and Segue 3: dwarf galaxies that are right here in our own cosmic backyard. Segue 1, in particular, is one of the smallest and faintest satellite galaxies known: it only gives off 300 times the light of our Sun, consisting of around 1000 stars total to create that light. But based on the motions of its stars inside, it has a total mass of around 600,000 Suns, giving it a mass-to-light ratio of ~3400. It is the most dark matter-dominated object presently known.

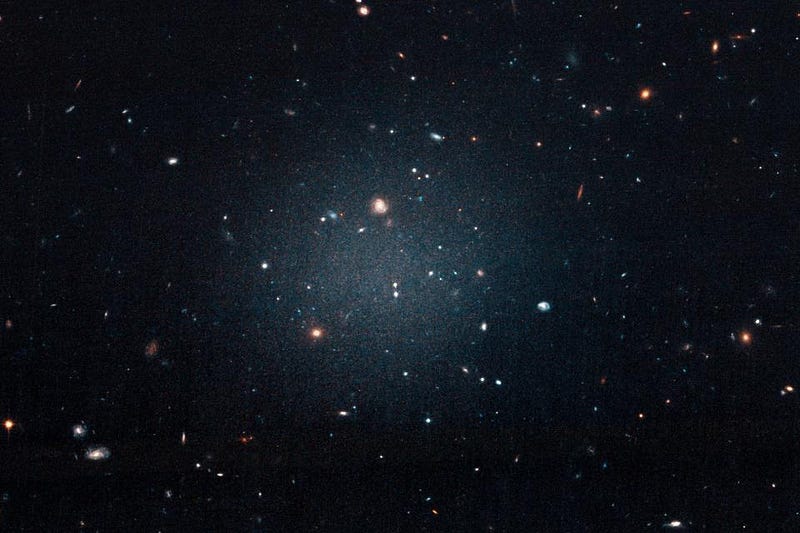
For a long time, many of these galaxies with higher-than-normal ratios of dark matter-to-normal matter were known, but there were none on the other side: no galaxies that appeared to have a dearth of dark matter in them. That all changed with the discovery of two dwarf galaxies that appear to be satellite members of a group dominated by the large elliptical galaxy NGC 1052. These two satellites, NGC 1052-DF2 and NGC 1052-DF4 — called DF2 and DF4 for short — have significant luminosities, but the stars within them appear to be moving very slowly: as though there were no dark matter at all.
Although many have disputed the observations, these conclusions appear to be robust. If we look at the inner ~18,000 light-years around the galaxy DF2, for example, we can infer that there are approximately 100 million solar masses worth of material in there, due to stars alone. When we use the best measurements we have to infer the total mass of the galaxy out to the same distance, it indicates a nearly identical total mass of just ~130 million solar masses, albeit with substantial uncertainties.

The expectation is that the coming years will reveal a great variety of these small, low-mass galaxies, particularly as deeper, high-resolution, wide-field instruments come online. We fully anticipate that the number of dwarf galaxies with extremely large dark matter-to-normal matter ratios will be uncovered, with potentially many more in the hundreds-to-one or even thousands-to-one range. Additionally, it’s reasonable to speculate that galaxies such as DF2 and DF4 are actually commonplace, and our observational capabilities are only beginning to probe what’s actually out there.
In astronomy, what we observe is always biased. The brightest, closest objects to us always are the easiest ones to find, while the fainter, more distant ones actually represent the majority of what’s out there in the Universe. Segue 1 and Segue 3, the objects with the most severe dark matter enhancements, are located within the halo of the Milky Way (very close), while DF2 and DF4 are among the brightest dwarf satellite galaxies in their field-of-view.
When we look at all the low-mass dwarf galaxies together, we see that they really do exhibit an enormous variety of mass-to-light ratios.
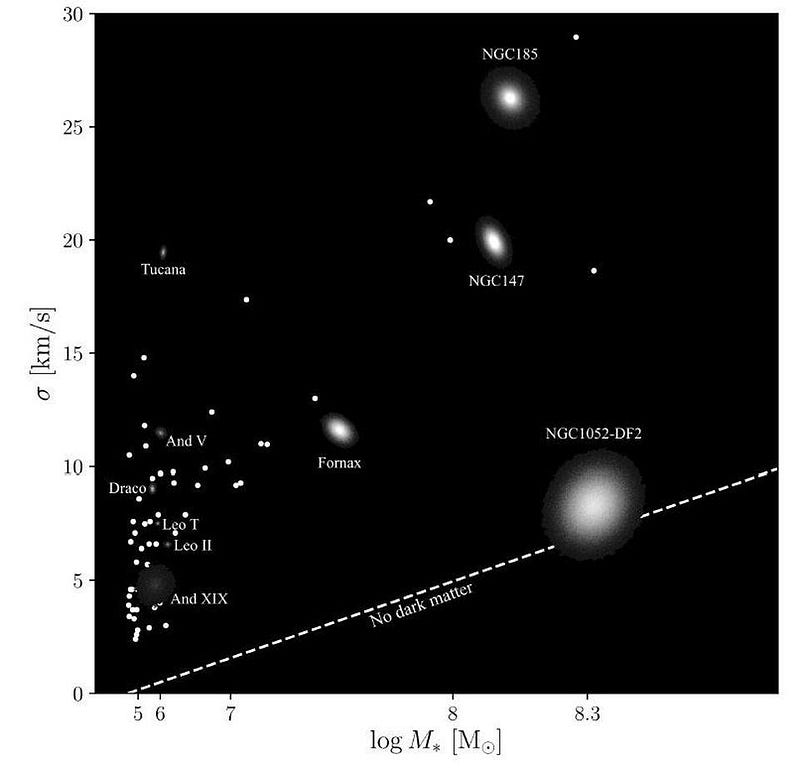
On the one hand, the total amount of starlight we can measure from galaxies tells us information about the masses and populations of the stars inside: if we measure starlight, we know enough about astronomy to draw conclusions about how much mass the stellar population contributes to the galaxy. On the other hand, by measuring how the stars in the galaxy move around, either from velocity dispersions, bulk rotation, or individual stellar motions, tells us how much total mass is inside.
Only if dark matter exists and doesn’t possess the standard interactions possessed by normal matter would we expect to have some dwarf galaxies displaying no evidence for dark matter, while others give indications that they have much more dark matter than otherwise typical regions. The fact that galaxies like Segue 1 exist in the same Universe where galaxies like DF2 exist not only shows us that dark matter is necessary, but showcases the variety of ways that structures arise and evolve in our Universe. Our astrophysical understanding of dark matter and the structures it forms is primed to grow extraordinarily as the flagship telescopes of the 2020s come online. It’s a great time to be alive.
Starts With A Bang is written by Ethan Siegel, Ph.D., author of Beyond The Galaxy, and Treknology: The Science of Star Trek from Tricorders to Warp Drive.