Neuropsych
All Stories
Only humans can voluntarily conjure new objects and events in our minds.
A healthy endocannabinoid system is critical to the human body’s immune functions.
Studies show talk therapy works, but experts disagree about how it does so. Finding the answer could help professionals and patients.
While ticker tape synesthesia was first identified in the 1880s, new research looks at this unique phenomenon — and what it means for language comprehension.
There’s a link between dark personality traits and breaches of battlefield ethics.
It may be an advantage in some contexts.
Research shows how “dark” Brett Martinpersonality traits affect Bitcoin enthusiasm.
Anyone can have a bad day at work, but not everyone scores this high on narcissism, psychopathy and Machiavellianism.
If a court needs to know if two trademarks look too similar to each other, perhaps the jury should be given a brain scan.
Human thinking is antiquated.
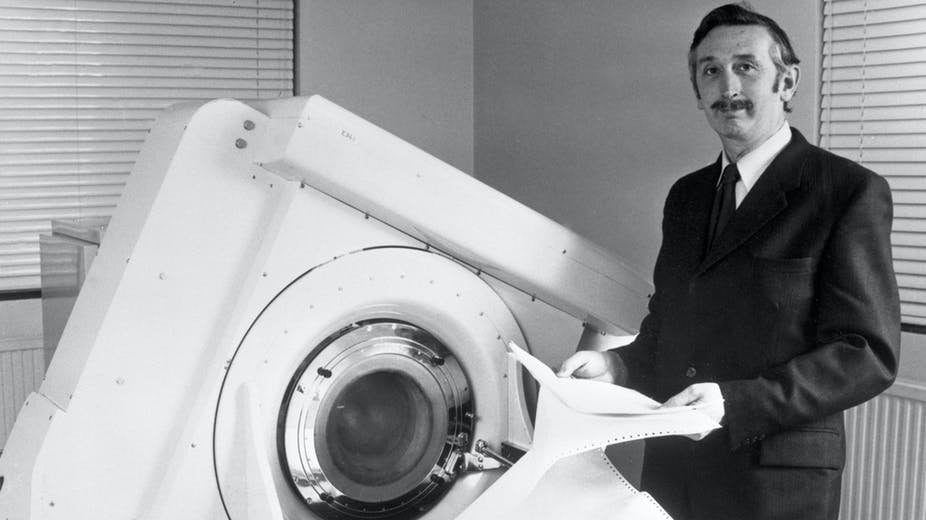
Godfrey Hounsfield’s early life did not suggest that he would accomplish much at all.
When migraine and tension-headache patients overuse their medications, they can actually trigger more headaches.
Your brain may notice fearful faces, even if you don’t consciously realize it.
Instead of walking a mile in someone’s shoes, try reading a chapter in their book.
Sex, it turns out, isn’t as easy or simple as popular culture might lead us to believe.
“Language is the most distinctively human talent.”
Without the time to mentally disengage from work, people can slip into burnout.
The rewards price to get a free cup of hot coffee at Starbucks is going up.
In a citizen science project, thousands of pet dogs are helping scientists to understand what happens to memory and cognition in old age.
A new 20-year analysis of over 14,000 psychology studies finds that a study’s media coverage is negatively linked to its replicability.
Forgetfulness isn’t always a “glitch” in our memories; it can be a tool to help us make sense of the present and plan for the future.
In a study involving mice, scientists used two different techniques — one optogenetic and one pharmacologic — to recover “lost” memories.
Your breathing rhythm influences a wide range of behaviors, cognition, and emotion.
Compared to people who took a placebo, the brains of those who took caffeine pills had a temporarily smaller gray matter volume.
Sniffing out a deal.
When we don’t find ways to relieve chronic stress, personal burnout is the likely consequence.
Has the “age of psychopharmacology” shrunk society’s sense of responsibility for mental health?
It may be possible to give people the tools to withstand difficulty before it attaches to them.