To the brain, reading computer code is not the same as reading language

Photo by ThisisEngineering RAEng on Unsplash
In some ways, learning to program a computer is similar to learning a new language.
It requires learning new symbols and terms, which must be organized correctly to instruct the computer what to do. The computer code must also be clear enough that other programmers can read and understand it.
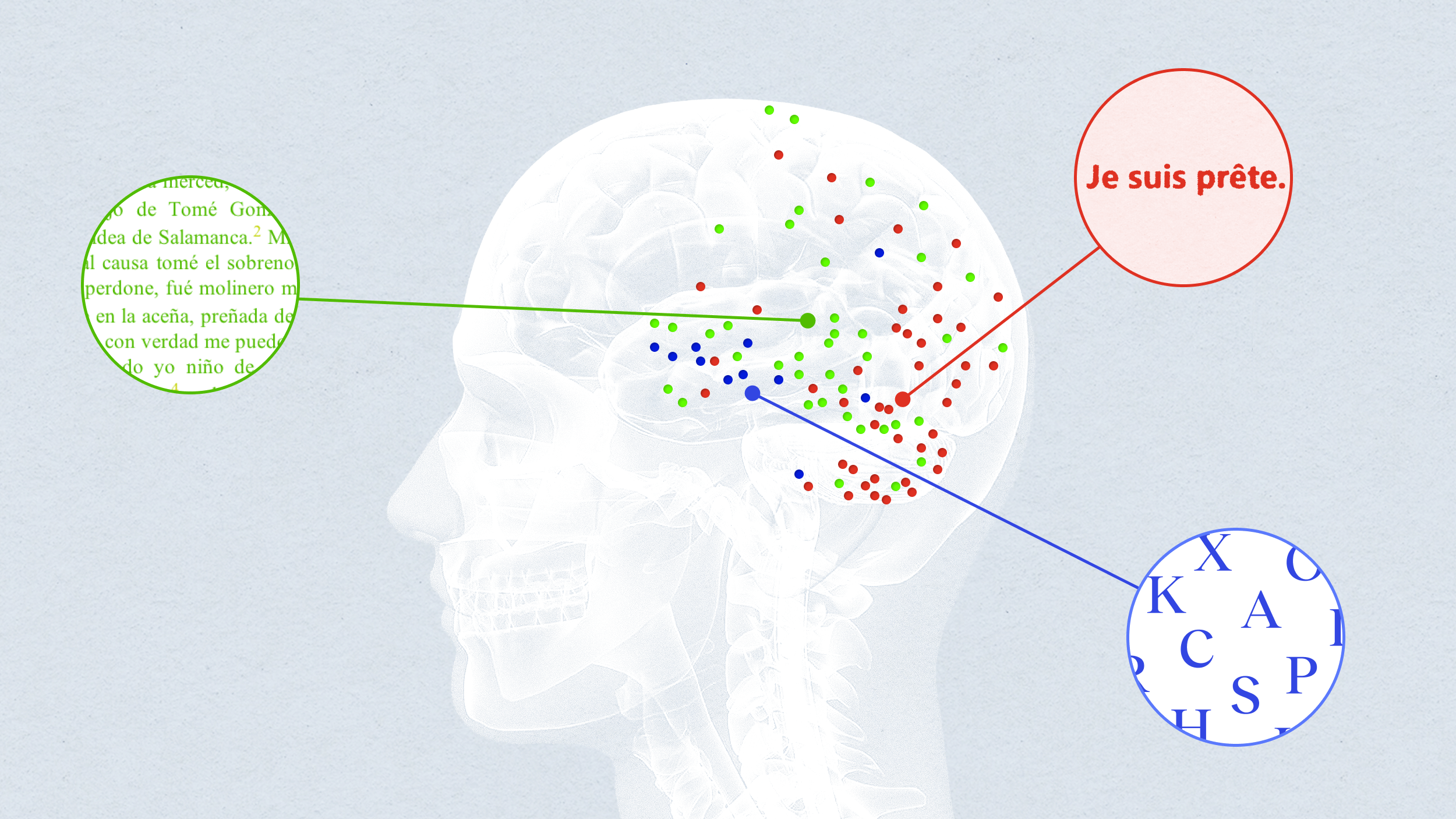
In spite of those similarities, MIT neuroscientists have found that reading computer code does not activate the regions of the brain that are involved in language processing. Instead, it activates a distributed network called the multiple demand network, which is also recruited for complex cognitive tasks such as solving math problems or crossword puzzles.
However, although reading computer code activates the multiple demand network, it appears to rely more on different parts of the network than math or logic problems do, suggesting that coding does not precisely replicate the cognitive demands of mathematics either.
“Understanding computer code seems to be its own thing. It’s not the same as language, and it’s not the same as math and logic,” says Anna Ivanova, an MIT graduate student and the lead author of the study.
Evelina Fedorenko, the Frederick A. and Carole J. Middleton Career Development Associate Professor of Neuroscience and a member of the McGovern Institute for Brain Research, is the senior author of the paper, which appears today in eLife. Researchers from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and Tufts University were also involved in the study.
Language and cognition
A major focus of Fedorenko’s research is the relationship between language and other cognitive functions. In particular, she has been studying the question of whether other functions rely on the brain’s language network, which includes Broca’s area and other regions in the left hemisphere of the brain. In previous work, her lab has shown that music and math do not appear to activate this language network.
“Here, we were interested in exploring the relationship between language and computer programming, partially because computer programming is such a new invention that we know that there couldn’t be any hardwired mechanisms that make us good programmers,” Ivanova says.
There are two schools of thought regarding how the brain learns to code, she says. One holds that in order to be good at programming, you must be good at math. The other suggests that because of the parallels between coding and language, language skills might be more relevant. To shed light on this issue, the researchers set out to study whether brain activity patterns while reading computer code would overlap with language-related brain activity.
The two programming languages that the researchers focused on in this study are known for their readability — Python and ScratchJr, a visual programming language designed for children age 5 and older. The subjects in the study were all young adults proficient in the language they were being tested on. While the programmers lay in a functional magnetic resonance (fMRI) scanner, the researchers showed them snippets of code and asked them to predict what action the code would produce.
The researchers saw little to no response to code in the language regions of the brain. Instead, they found that the coding task mainly activated the so-called multiple demand network. This network, whose activity is spread throughout the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain, is typically recruited for tasks that require holding many pieces of information in mind at once, and is responsible for our ability to perform a wide variety of mental tasks.
“It does pretty much anything that’s cognitively challenging, that makes you think hard,” Ivanova says.
Previous studies have shown that math and logic problems seem to rely mainly on the multiple demand regions in the left hemisphere, while tasks that involve spatial navigation activate the right hemisphere more than the left. The MIT team found that reading computer code appears to activate both the left and right sides of the multiple demand network, and ScratchJr activated the right side slightly more than the left. This finding goes against the hypothesis that math and coding rely on the same brain mechanisms.
Effects of experience
The researchers say that while they didn’t identify any regions that appear to be exclusively devoted to programming, such specialized brain activity might develop in people who have much more coding experience.
“It’s possible that if you take people who are professional programmers, who have spent 30 or 40 years coding in a particular language, you may start seeing some specialization, or some crystallization of parts of the multiple demand system,” Fedorenko says. “In people who are familiar with coding and can efficiently do these tasks, but have had relatively limited experience, it just doesn’t seem like you see any specialization yet.”
In a companion paper appearing in the same issue of eLife, a team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University also reported that solving code problems activates the multiple demand network rather than the language regions.
The findings suggest there isn’t a definitive answer to whether coding should be taught as a math-based skill or a language-based skill. In part, that’s because learning to program may draw on both language and multiple demand systems, even if — once learned — programming doesn’t rely on the language regions, the researchers say.
“There have been claims from both camps — it has to be together with math, it has to be together with language,” Ivanova says. “But it looks like computer science educators will have to develop their own approaches for teaching code most effectively.”
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, the Department of the Brain and Cognitive Sciences at MIT, and the McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
Reprinted with permission of MIT News. Read the original article.