Culture & Religion
All Stories
Conversations between mother and daughter contain more emotional content than conversations mothers have with their sons, according to a new study.
While our culture praises innovation and invention, we owe our greatest successes—including those of the innovator and inventor—to imitation and outright copying.
Should certain organizations be exempt from paying artists a minimum wage? This question becomes difficult to tackle when lines between ‘work’ and ‘play’ become blurred. At the same time, some of these institutions are able to get away with paying workers nothing.
Maintaining both a personal and professional presence online requires both a delicate touch and an understanding that lines are inevitably going to become blurred.
The United State owns the market on personal data with companies like Facebook and Google. This puts America in a position of power when talking about privacy rights. But that may mean being at odds with the international community.
When prison populations began to surge in the mid-20th century, it changed the entire social dynamic of incarceration. Prison gangs grew out of a need for inmates to organize and defend themselves.
What if money was like food? Life’s limits hold lessons for healthy self-interest (individual and collective).
Slow Down Your Brain to Get More Done, with Steven Kotler The best-selling author discusses hypofrontality — literally the slowing of the brain’s prefrontal cortex — and how it allows […]
A recent study out of Russia concludes there are two new sleep types: those who are most productive at the start and end of the day but feel sluggish during the middle hours, and the reverse.
While kind of discount airlines that Europe enjoys have not caught in the United States, an Icelandic carrier named WOW Air will soon offer inexpensive transatlantic flights.
What is Punk? Punk isn’t about mohawks or studded leather, says Henry Rollins – it’s about resistance to tyranny in any form. How Art Can Change Society, with Sarah Lewis Sarah […]
What would it take to create a system of principles that guide our behavior without a religious grounding?
Facebook is addicting — this idea is nothing new. But take away the numbers and suddenly the site becomes much less appealing.
Anyone who has seen James Cameron’s 1984 film The Terminator remembers “seeing” through the eyes of the killer android sent into the past as it scans its surroundings for clothes, weapons, and, eventually, its target. German filmmaker Harun Farocki would later call those pictures “operational images”—the machine-made and machine-used pictures of the world that threatened to supplant not just how people see, but people period.
Combining alcoholic drinks with caffeine causes people to drink more for a variety of reasons, say psychological researchers from several American universities.
Wouldn’t it be more fair if being elected to a federal office required a majority rather than plurality of votes? Perhaps it’s time to replace our current voting system with a ranked ballot.
Despite all those early quarrels, research suggests that having a sibling greatly improves your behavioral development and quality of life.
“Bürgerschreck!” rang the accusations in German at Austrian painter Egon Schiele in April 1912. This “shocker of the bourgeois” found his home rifled by local constables searching for evidence of the immorality locals suspected of a man who lived with a woman not his wife and invited local children to pose for him. The constables brought over one hundred drawings as well as Schiele himself to the local jail, where he sat for 24 days until a court trial during which the judge flamboyantly burned one of Schiele’s “pornographic” portraits in front of the chastised artist before releasing him. That experience changed the rest of Schiele’s life and art. Egon Schiele: Portraits at the Neue Galerie in New York City centers on this turning point in Schiele’s portraits, which remain some of the most psychologically penetrating and sexual explicit portraits of the modern age. Schiele’s capacity to shock today’s audience may have declined as modern mores finally catch up to him, but the power of his portraits to captivate through their unconventionality, sensitivity, and empathy never gets old.
If you’re a winter sports buff who’s always wanted a custom-built snowboard, perhaps look into a trip to Innsbruck. There, a company called Spurart will guide you in handcrafting your own board.
Author and academic Kenji Yoshino describes the difference between passing and covering, and how companies will sometimes employ a myopic form of diversity inclusion that necessitates the abandonment of one’s identity.
The so-called sharing economy rarely features actual instances of people sharing items with each other, or at least not without a price. Starting a neighborhood sharing network is a great way to unite a community beneath the banner of pooled resources.
Taking long walks, dimming the lights down low, mussing up your desk–we all have our tricks to get the creative juices flowing. But there’s another way to invigorate the right-side of your brain: a sense of entitlement.
Meat consumption is increasingly seen as a health risk, an environmental risk, and a misuse of precious land and water resources.
Besides the political fallout from yesterday’s midterm elections, America’s long war against recreational marijuana is slowly but steadily coming to an end.
Giving birth doesn’t seem likely to augment the finely tuned fitness of a professional athlete, but having a child may favorably change the physical and hormonal composition of mothers.
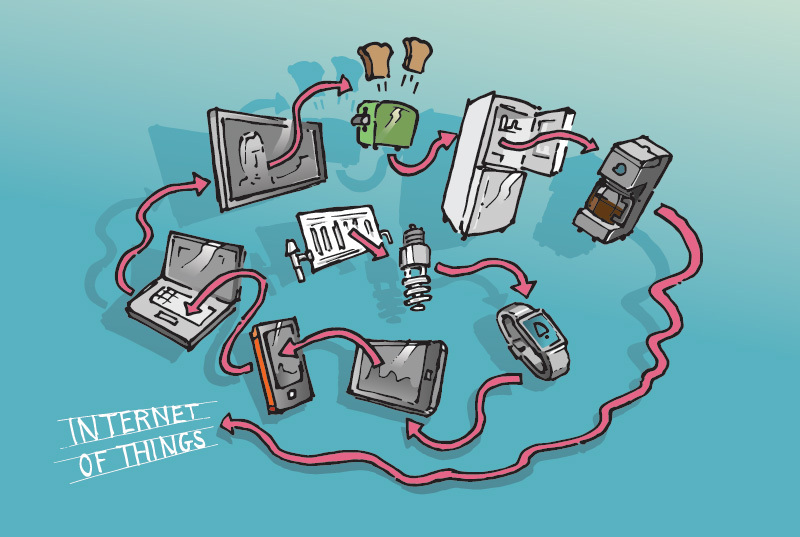
Futurists who believe endlessly in the miracle of technology are seizing on the approaching Internet of Things as the next harbinger of leisure, independence, and fun in the sun.
The extreme action dance pioneer takes us through the theory behind PopAction and how flying, falling dancers teach audiences about resilience and hope.
Biologist Edward O. Wilson tackles the meaning of life and existence. He argues that explaining why we’re here, what we are, and where we’re going is a task best suited to science, not philosophy. He identifies five major scientific branches that are currently making the most progress.
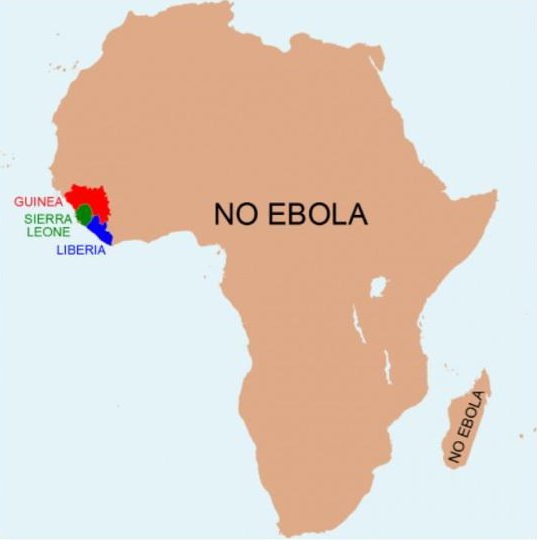
A map of Africa displaying Ebola’s limited geographical reach seeks to educate the internet about the ridiculousness of ostracizing people who have recently returned from Sub-Saharan Africa.
Numerous studies have identified a link connecting feelings of gratitude with happiness, good health, and generosity.