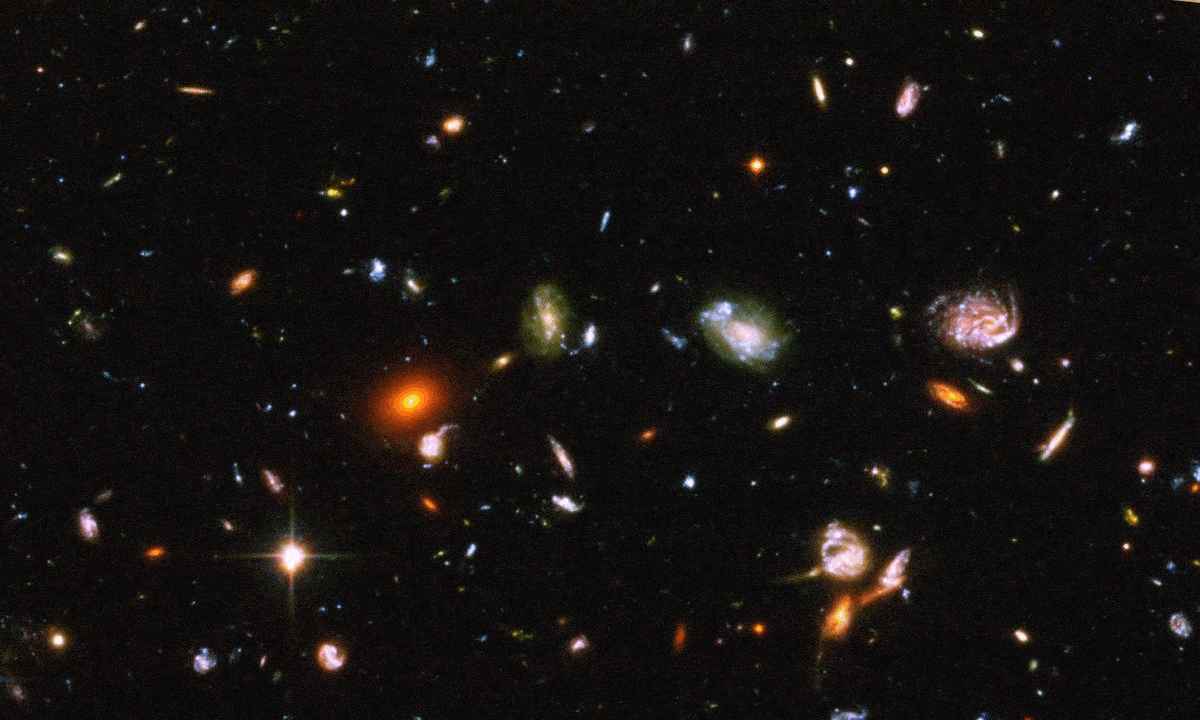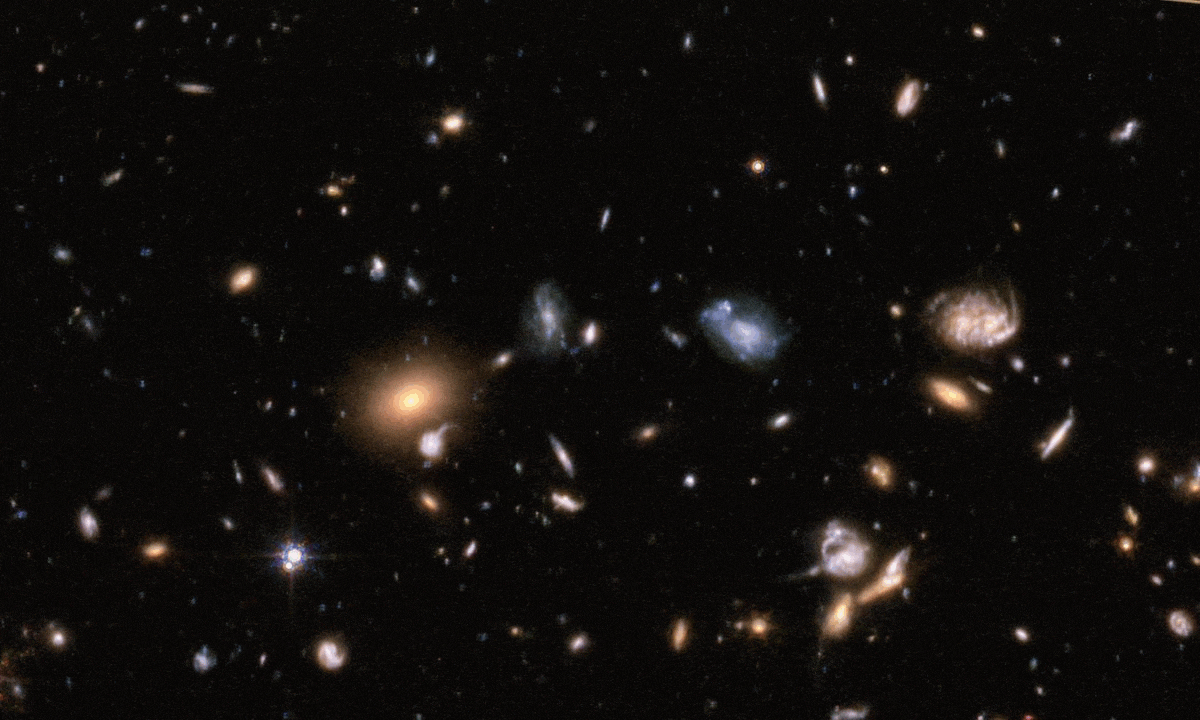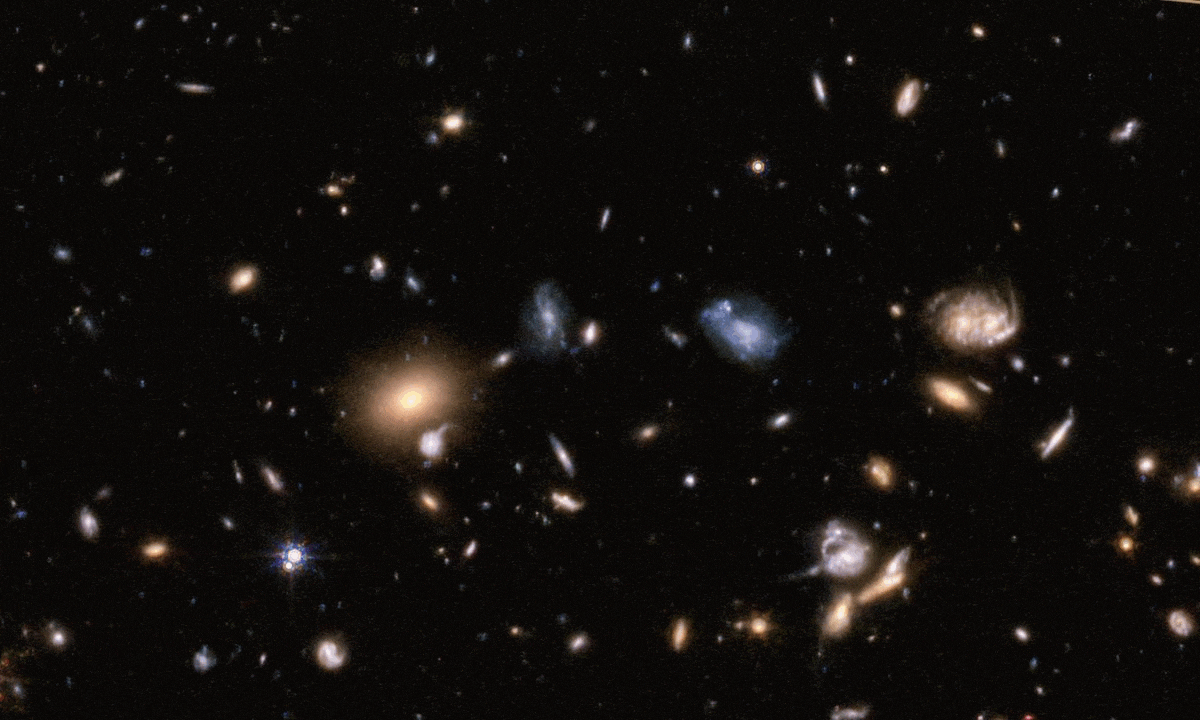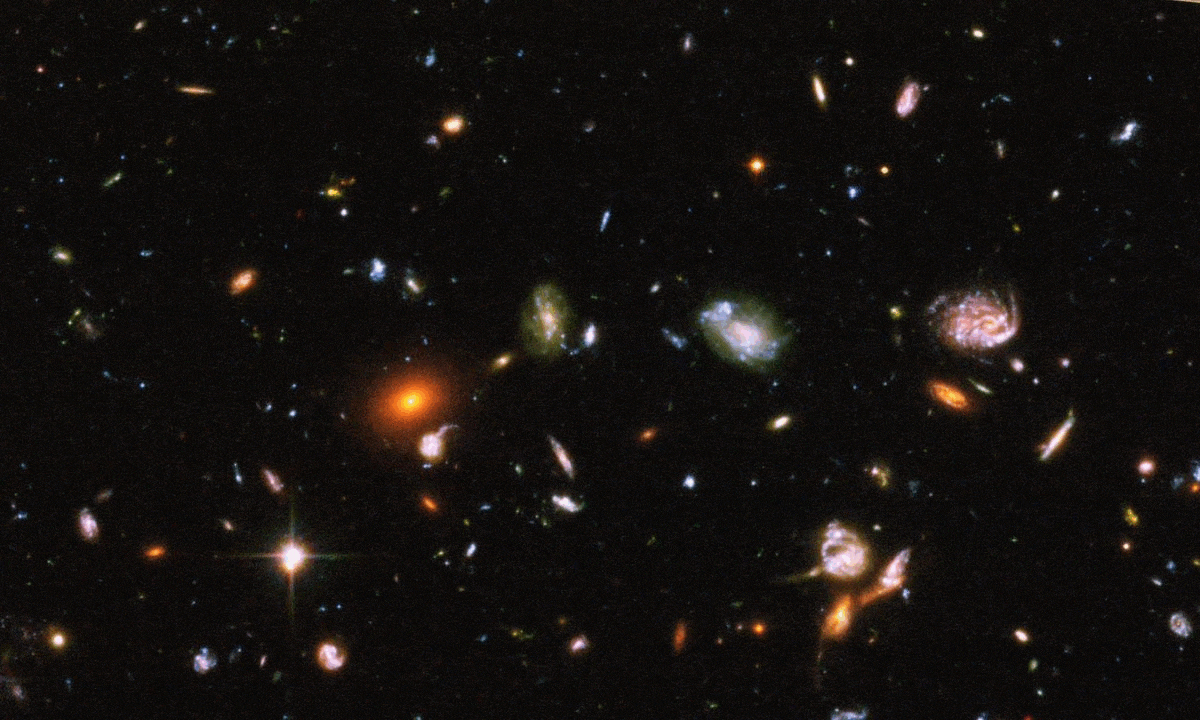“Nobody expects a computer simulation of a hurricane to generate real wind and real rain,” writes neuroscientist Anil Seth.
Search Results
You searched for: simulation
“When you feel the isolation setting in at times, you have to reframe your mindset.”
“We do not experience primarily because we have brains; we experience because we are alive.”
Neuroscientist Christof Koch on human minds, AI, and bacteria.
We may be on the brink of finally seeing human-level intelligence in an AI — thanks to robots.
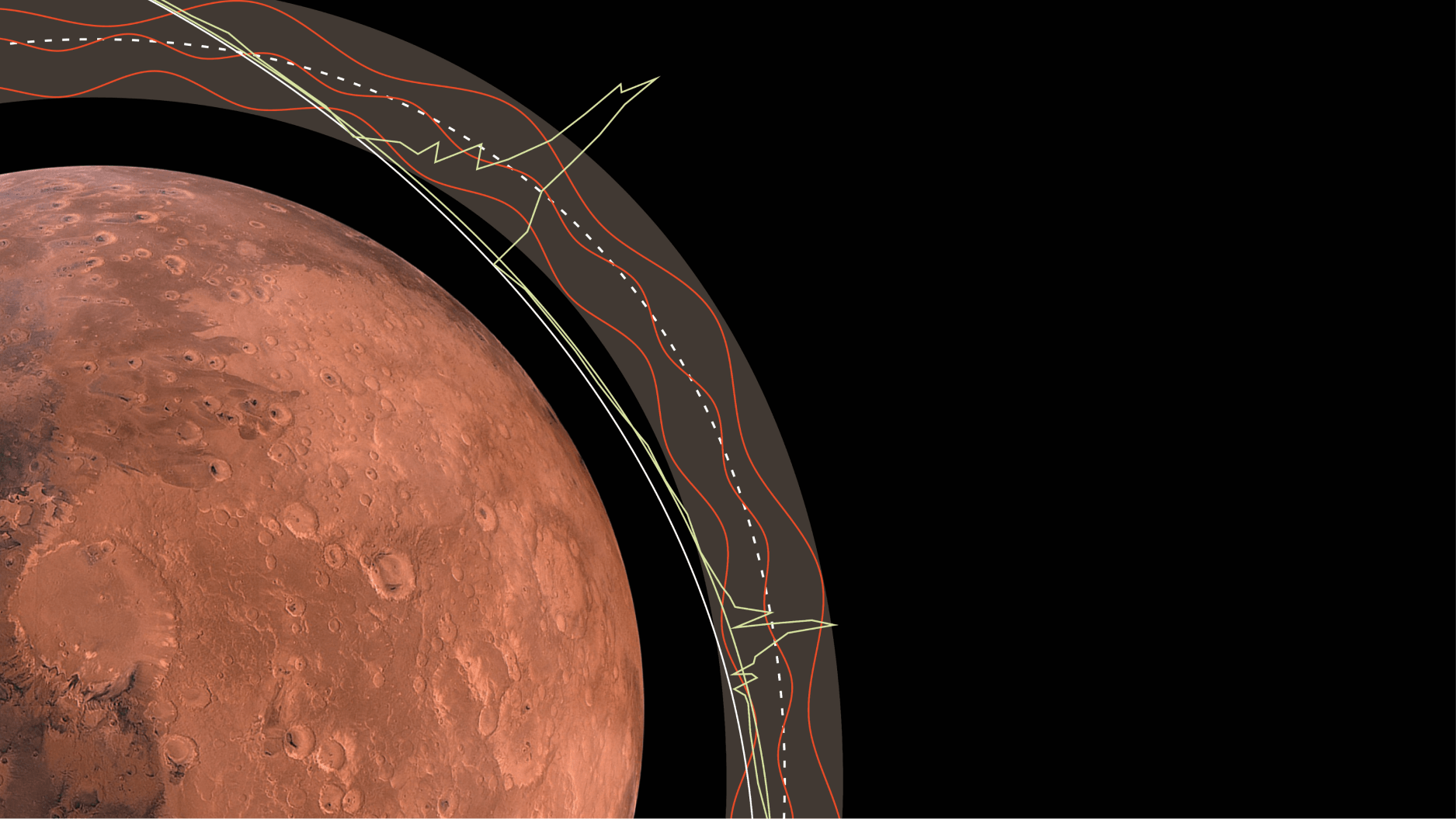
Watching for changes in the Red Planet’s orbit over time could be new way to detect passing dark matter.
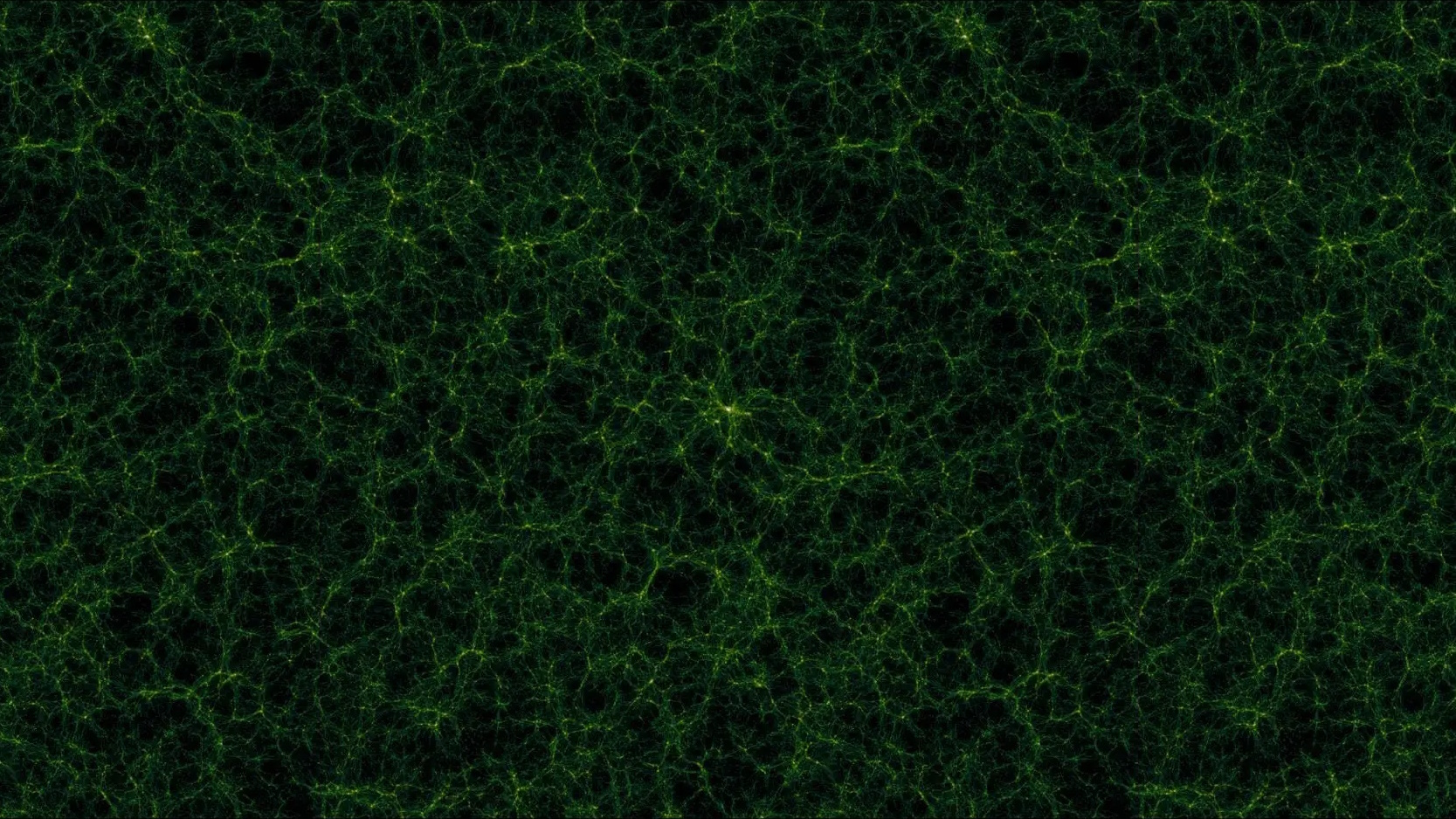
On larger and larger scales, many of the same structures we see at small ones repeat themselves. Do we live in a fractal Universe?
One of the most promising dark matter candidates is light particles, like axions. With JWST, we can rule out many of those options already.
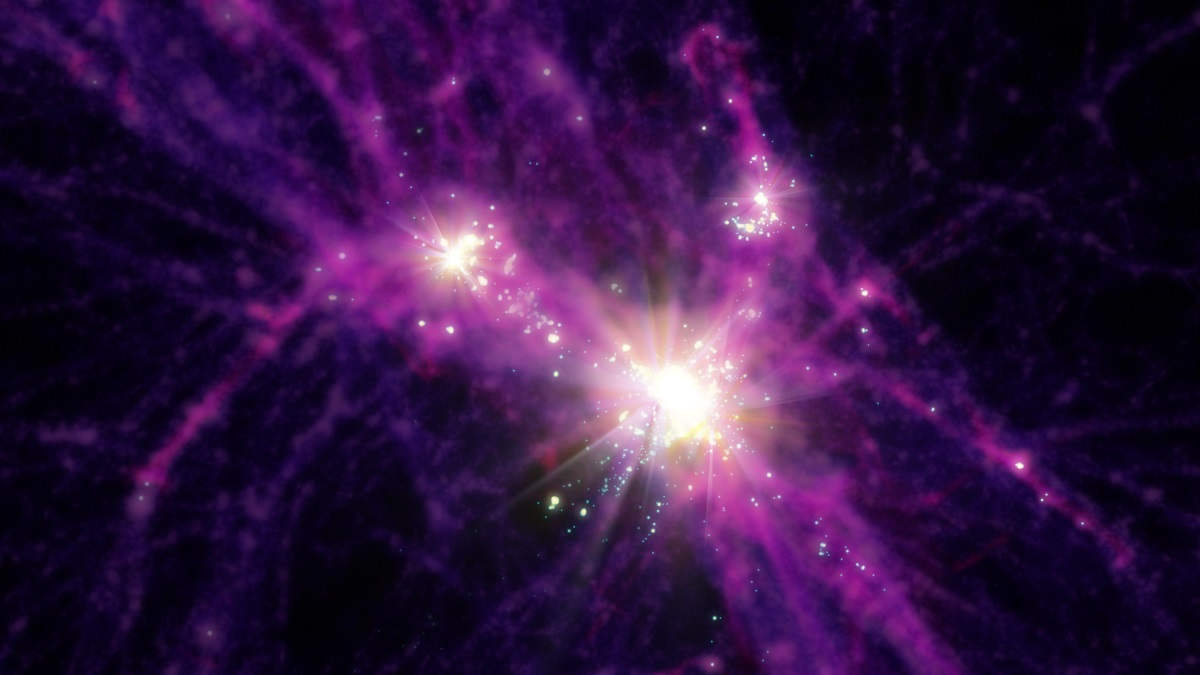
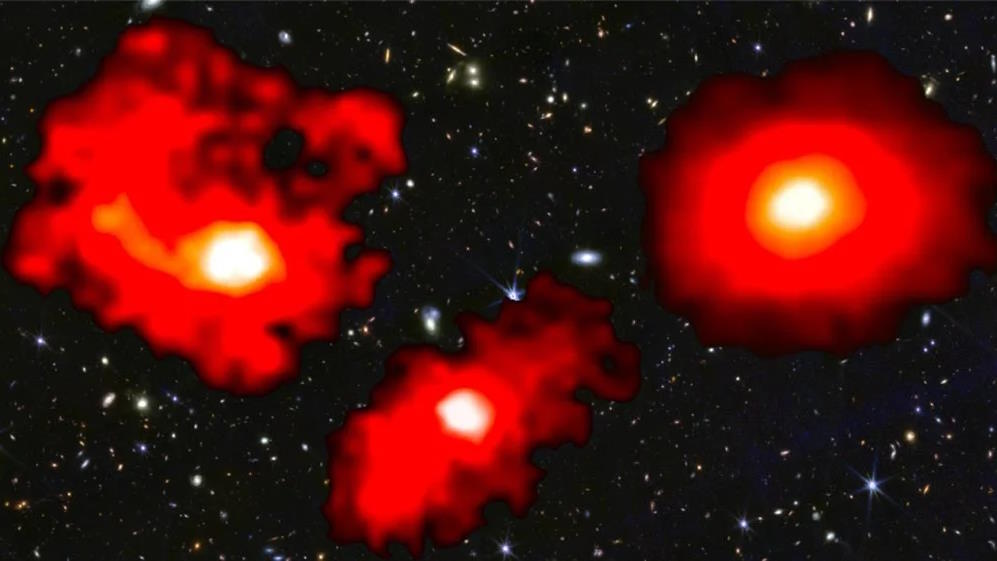
The “little red dots” were touted as being too massive, too early, for cosmology to explain. With new knowledge, everything adds up.
In theory, dark matter is cold, collisionless, and only interacts via gravity. What we see in ultra-diffuse galaxies indicates otherwise.
The simulation hypothesis is fun to talk about, but believing it requires an act of faith.
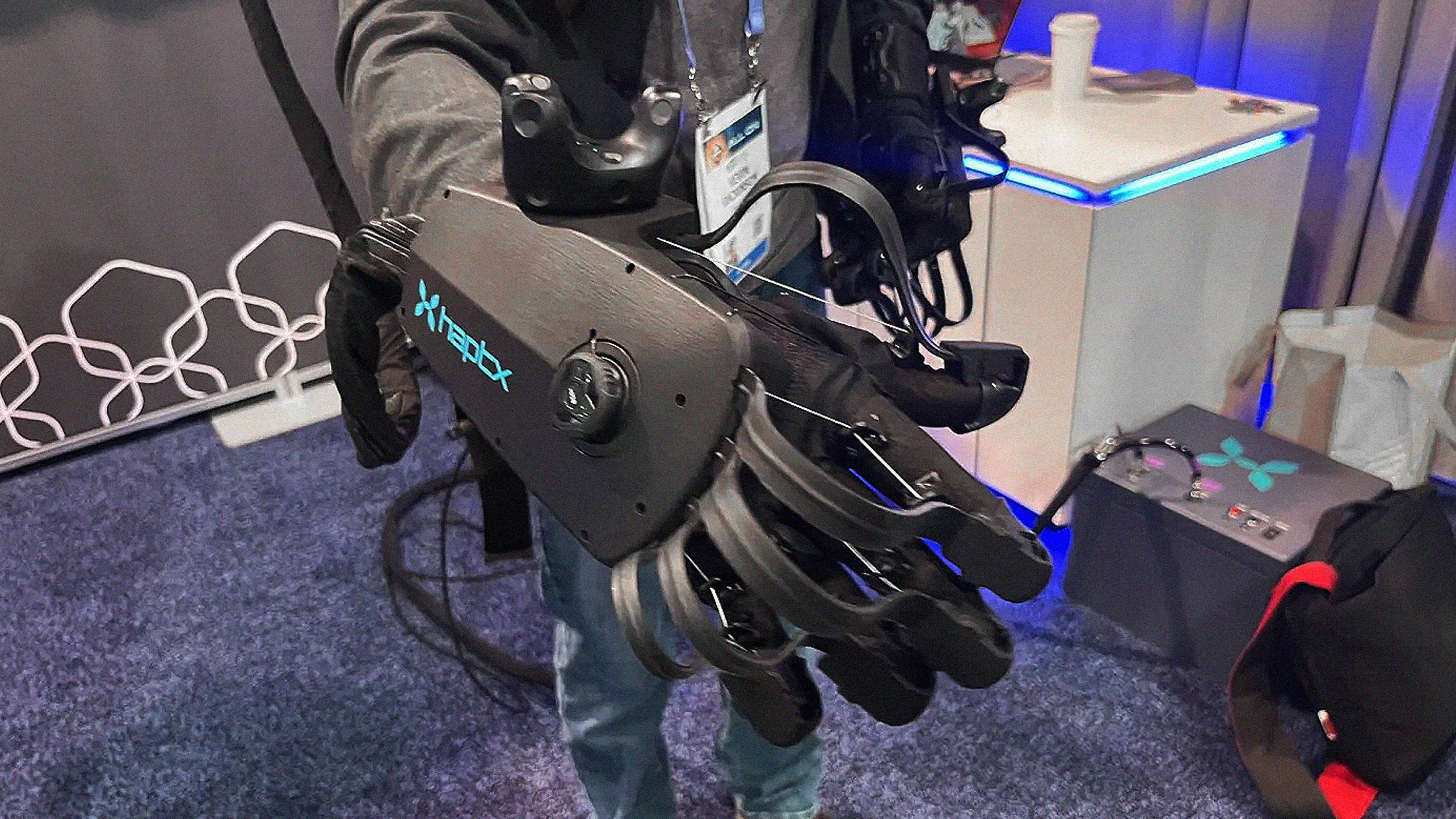
HaptX gloves provide high-fidelity touch feedback of virtual spaces (and they look cool, too).
Locked inside their minds, thousands await a cure. Neuroscientist Daniel Toker is racing to find it.
Here in our Solar System, terrestrial bodies get moons from gravitational capture or collisions. The Pluto-Charon system? It was both.
Frontier, the ORNL supercomputer, used machine learning to perform 9.95 quintillion calculations per second.
Your life’s memories could, in principle, be stored in the universe’s structure.
With so many early galaxies of unexpectedly large brightnesses, JWST surprised us all. Here’s how scientists made sense of what we see.
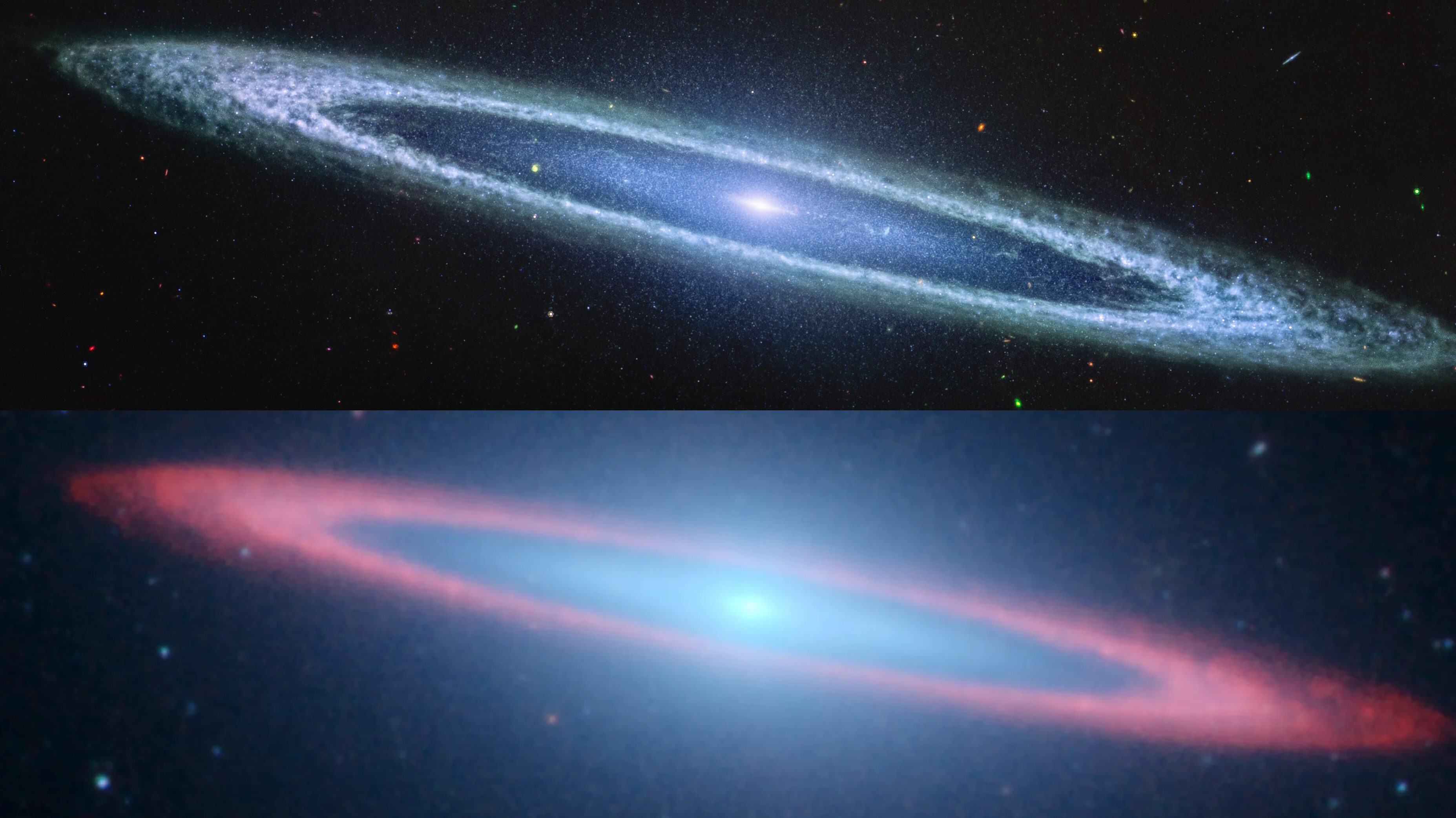
The COSMOS-Web survey is now complete, combining JWST and Hubble infrared data. Its spectacular views show us the Universe as never before.
The most massive early galaxies grew up faster, and have more stars, than astronomers expected, according to JWST. What does it all mean?
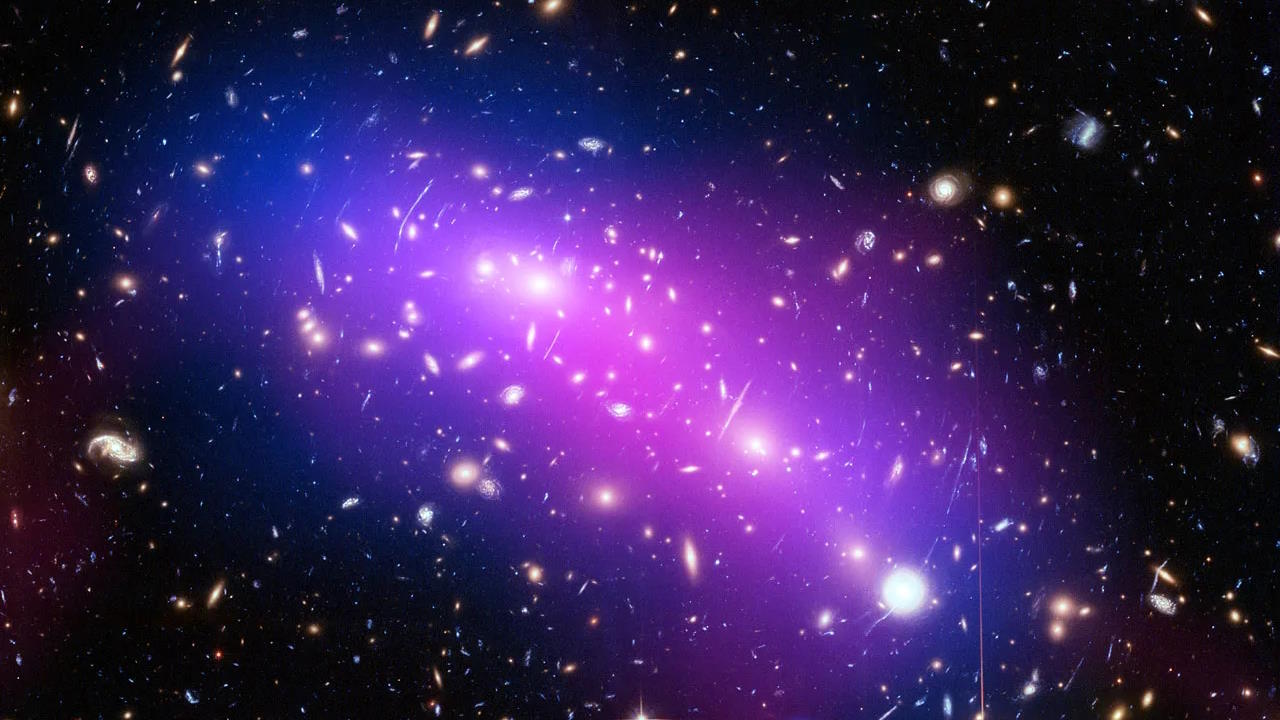
How do normal matter and dark matter separate by so much when galaxy clusters collide? Astronomers find the surprising, unexpected answer.
There was a time where no starlight was visible throughout the entire cosmos. That time was short-lived: shorter than astronomers imagined.
Want to know how to handle work-life pressure? Big Think asked Warfare co-directors Alex Garland and Ray Mendoza.
Whether it’s LeBron’s shooting patterns or your corporate AI strategy, actionable insights are the key to turning data into meaningful results.
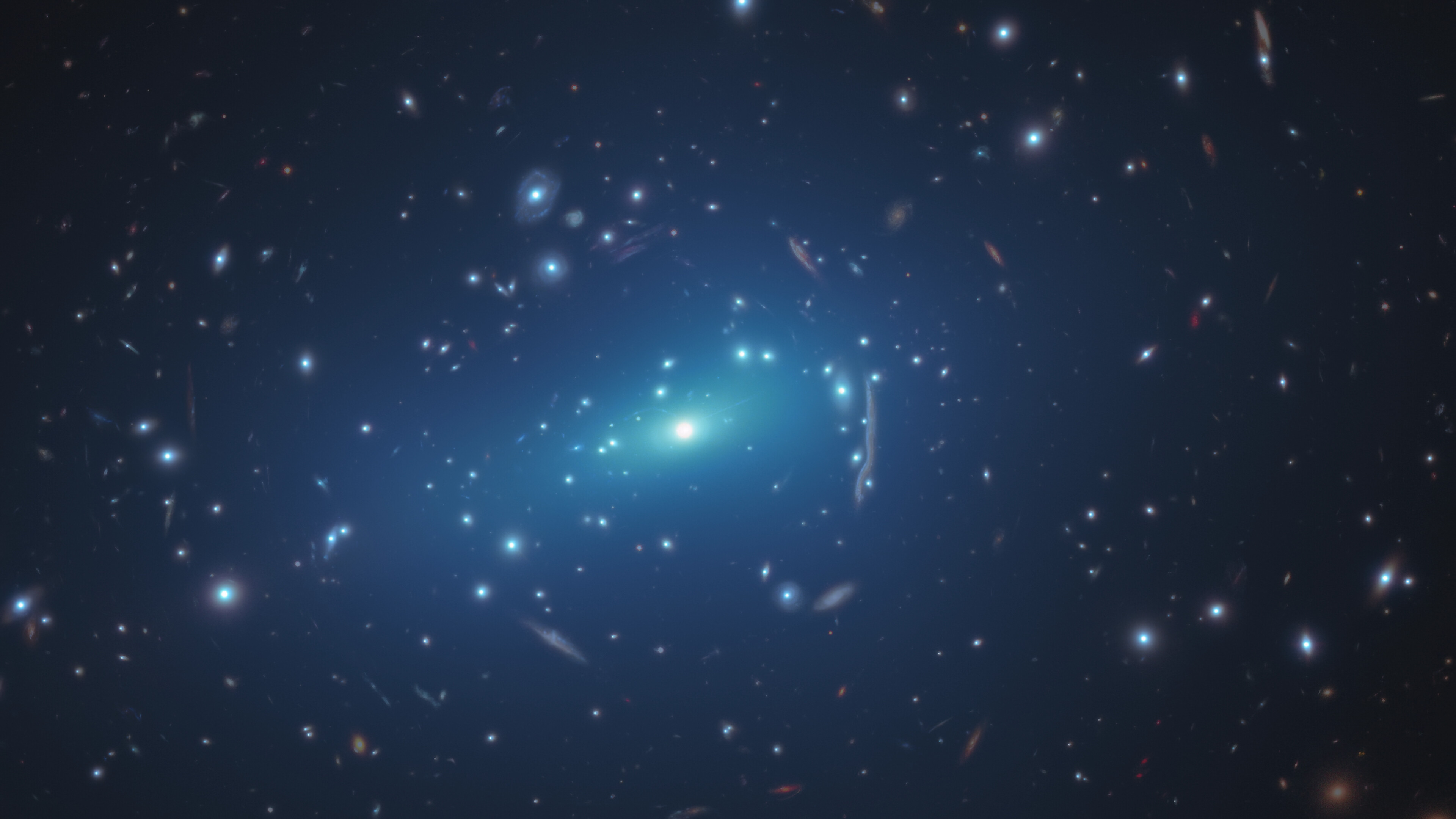
These high-mass, rapidly star-forming galaxies have called modern cosmology into question. But hi-res simulations show no tension at all.
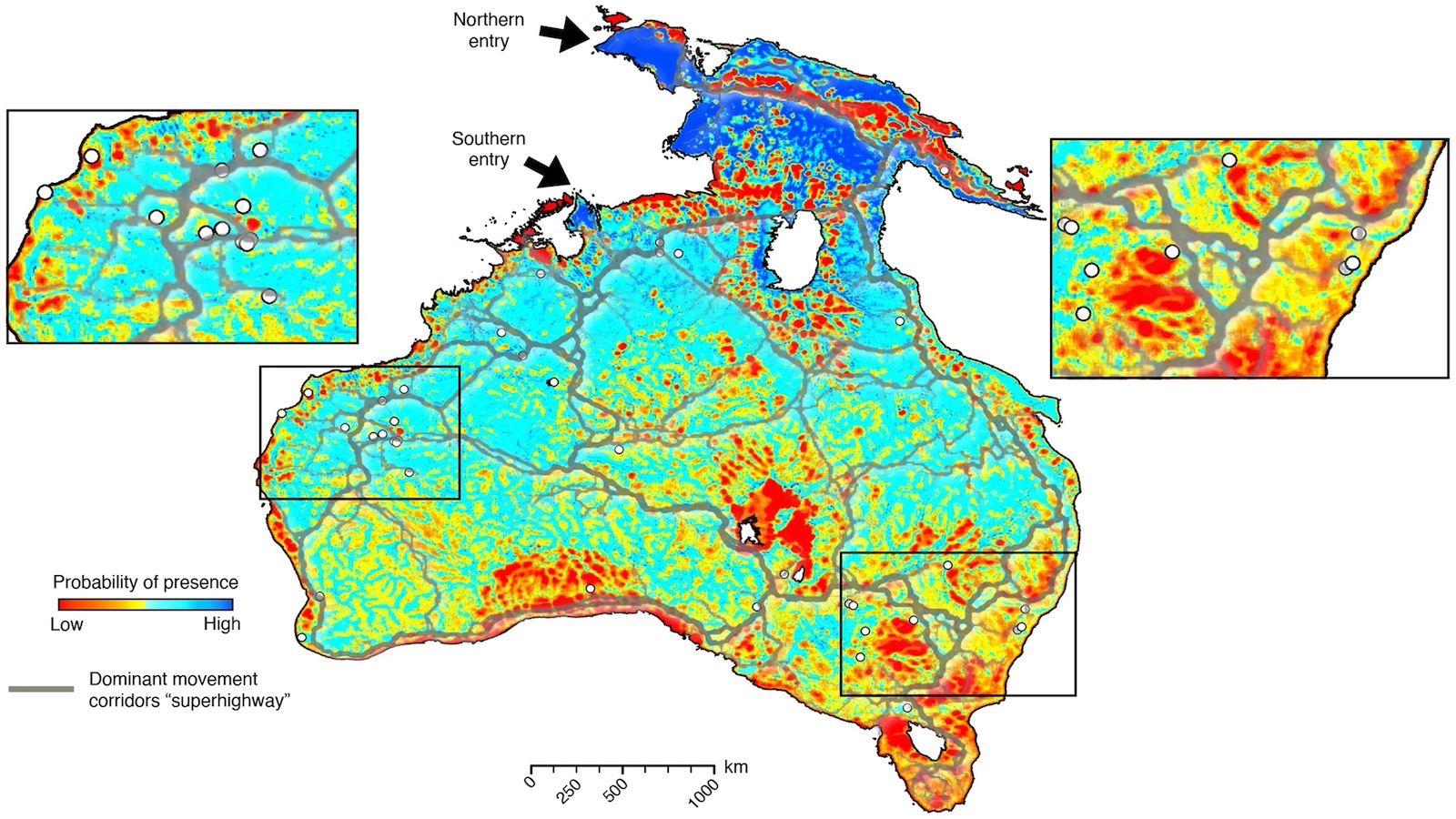
A new method of mapping migration factors in erratic movements and changing climate.
Welcome to The Nightcrawler — a weekly newsletter from Eric Markowitz covering tech, innovation, and long-term thinking.
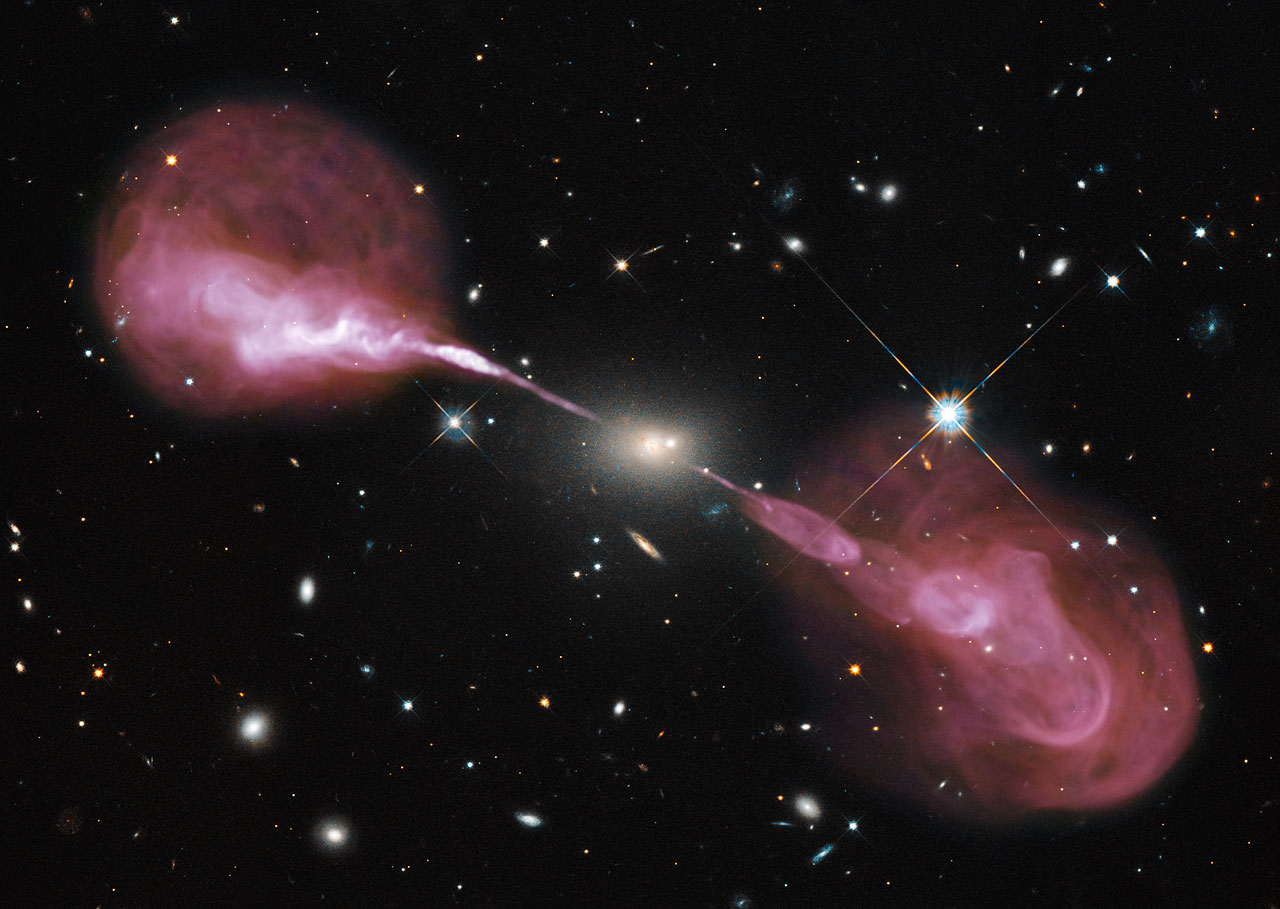
Galaxies don’t simply feed their central supermassive black holes, but the activity generated inside affects the entire galaxy and more.
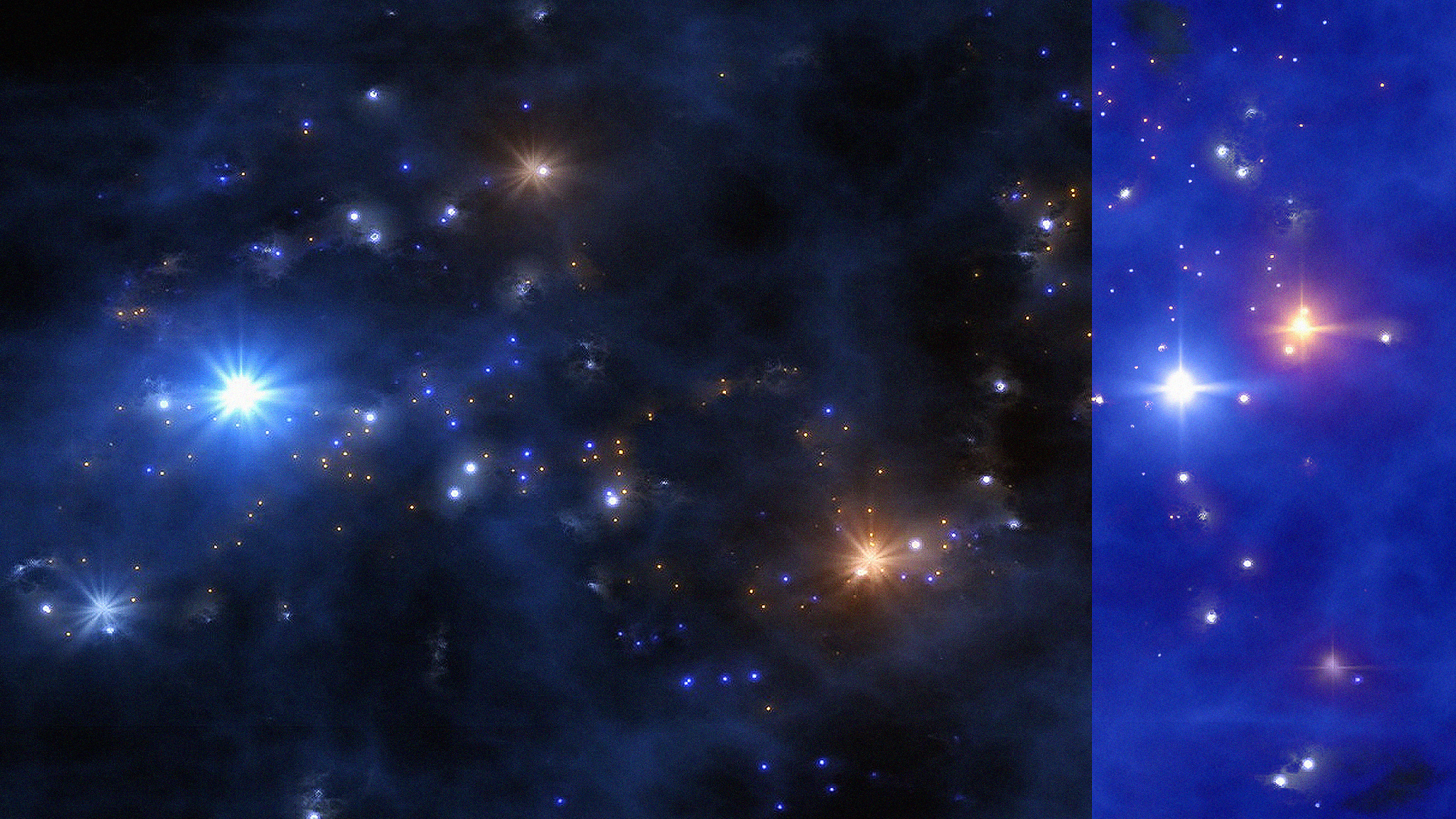
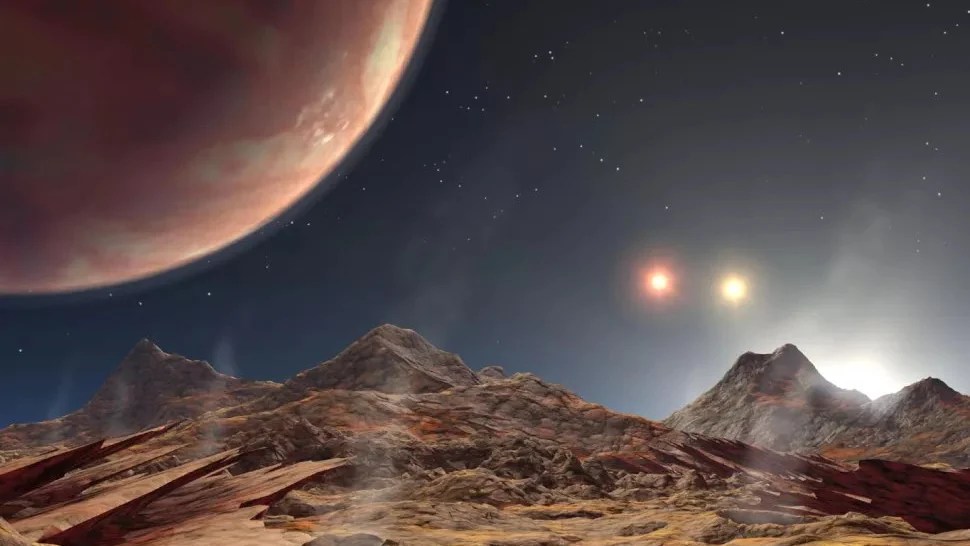
Due to chaos, it was long thought that planets couldn’t stably orbit systems containing three stars. GW Orionis is the first counterexample.
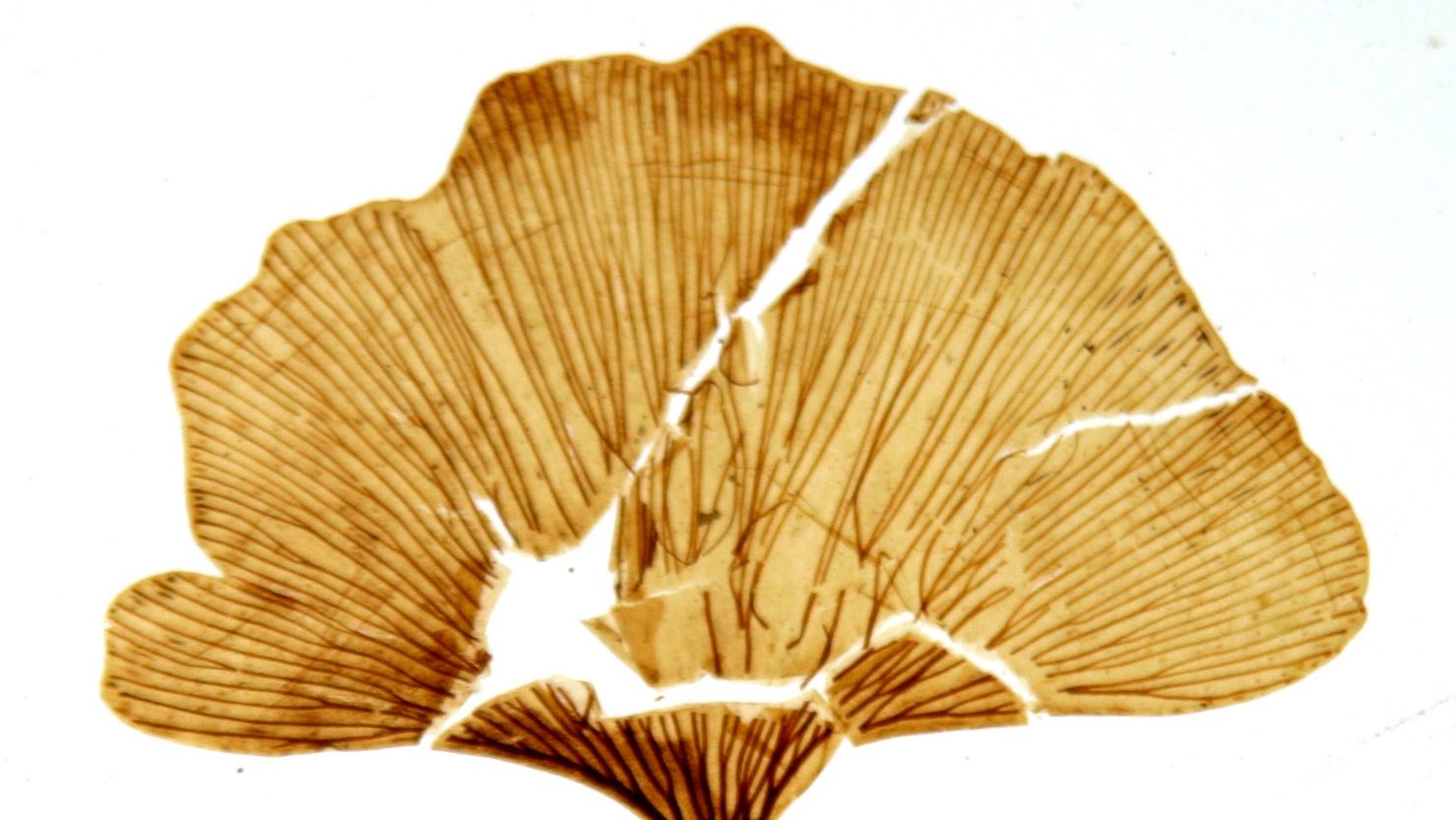
Well-preserved ancient plants and other finds at the Clarkia fossil beds hint at what kind of evidence any Martian life may have left behind.
Coming from just 280 million years after the Big Bang, or 98% of cosmic history ago, this new, massive galaxy is a puzzle, but not a mirage.