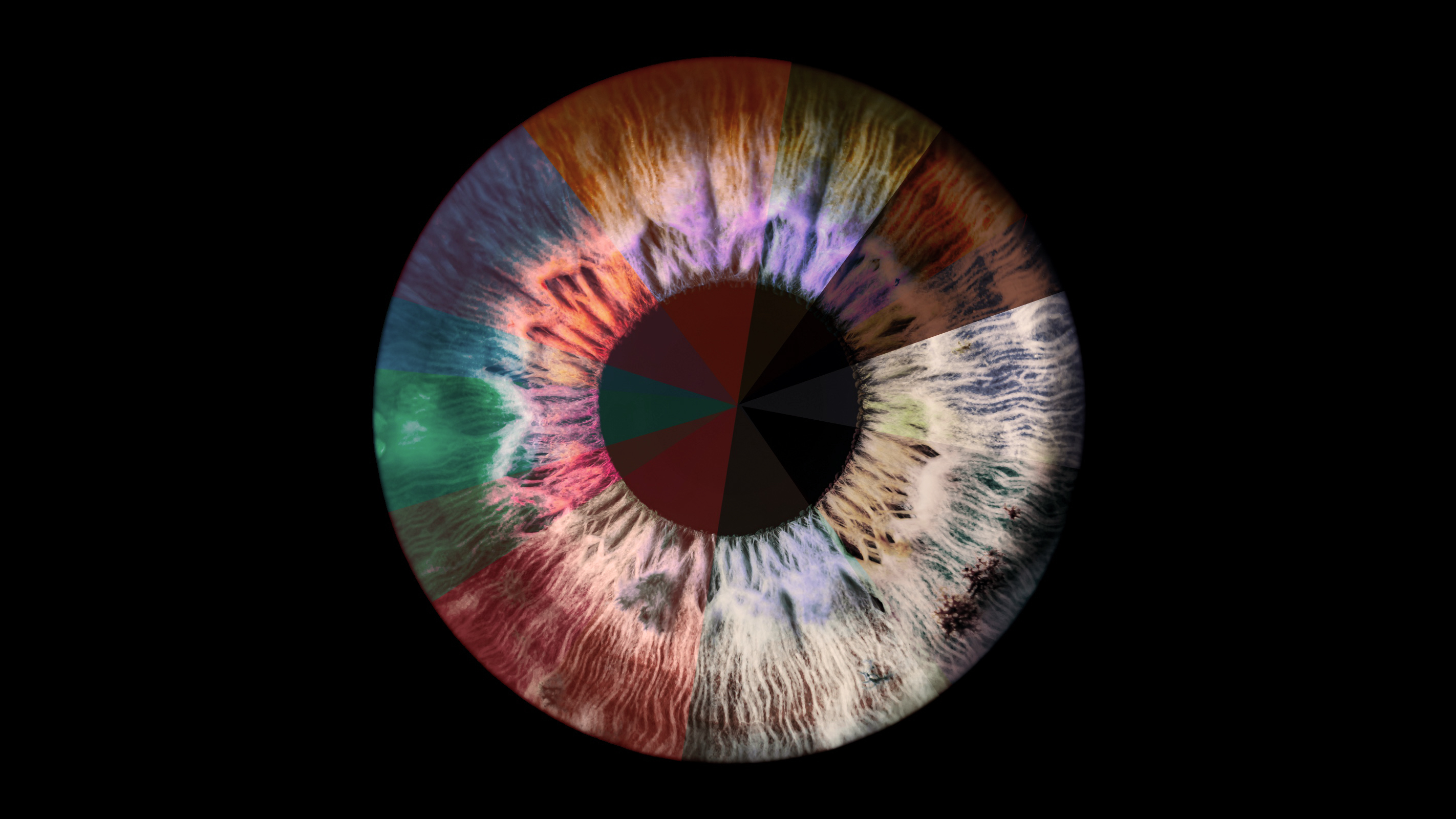
Eyes with lower pigment (blue or grey eyes) don’t need to absorb as much light as brown or dark eyes before this information reaches the retinal cells. This might provide light-eyed people with some resilience to SAD.
Search Results
You searched for: light
Some constants, like the speed of light, exist with no underlying explanation. How many “fundamental constants” does our Universe require?
Some say that the Sun is a green-yellow color, but our human eyes see it as white, or yellow-to-red during sunset. What color is it really?
For many years, cosmologists have claimed the Universe is 13.8 billion years old. A new paper says no, it’s 26.7 billion. How do we decide?
Physicists have yet to pinpoint the hypothetical matter that keeps galaxies from flying apart. Now they have a new focus.
If light can’t be bent by electric or magnetic fields (and it can’t), then how do the Zeeman and Stark effects split atomic energy levels?
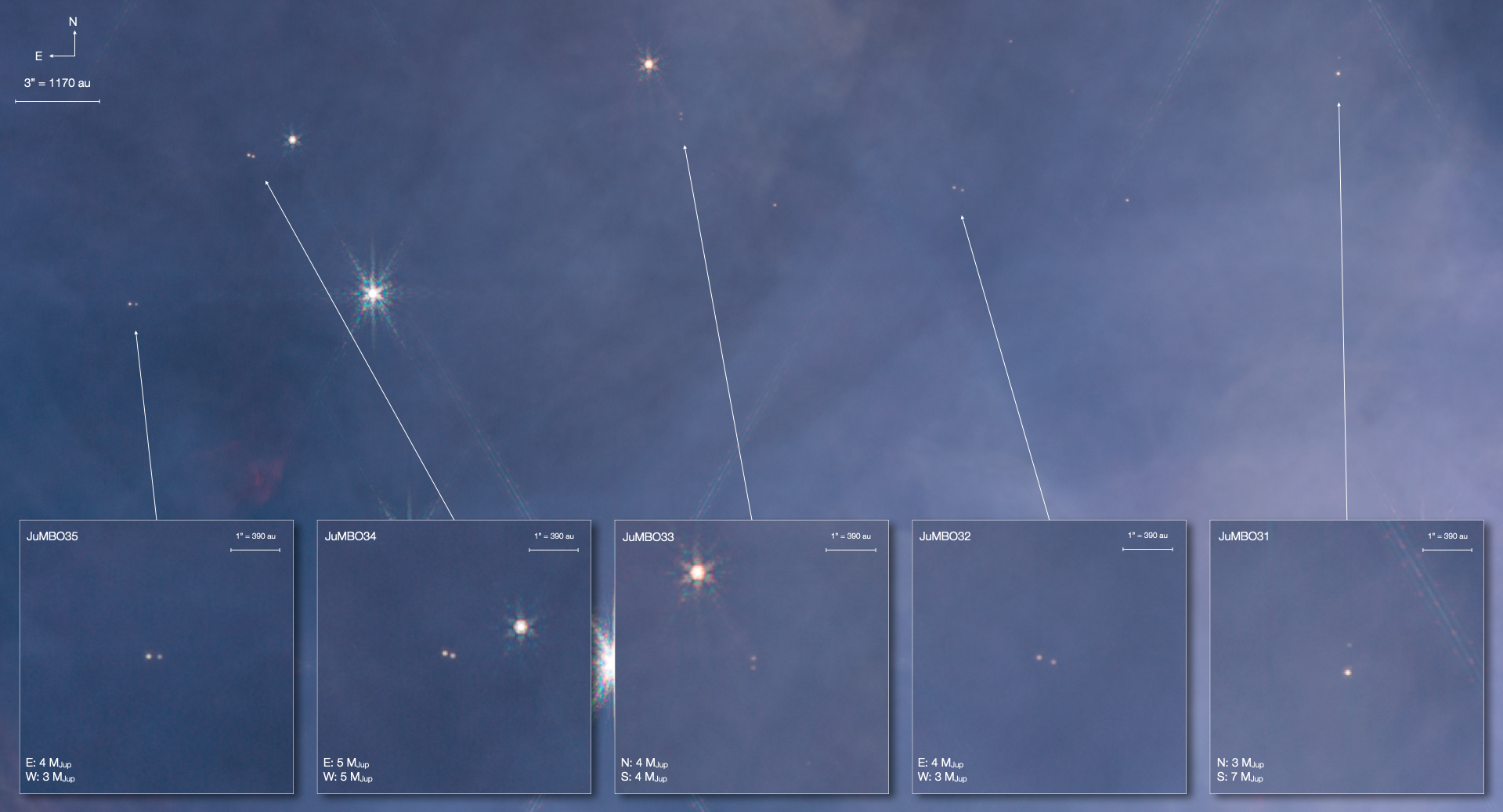
In the largest star-forming region close to Earth, JWST found hundreds of planetary-mass objects. How do these free-floating planets form?
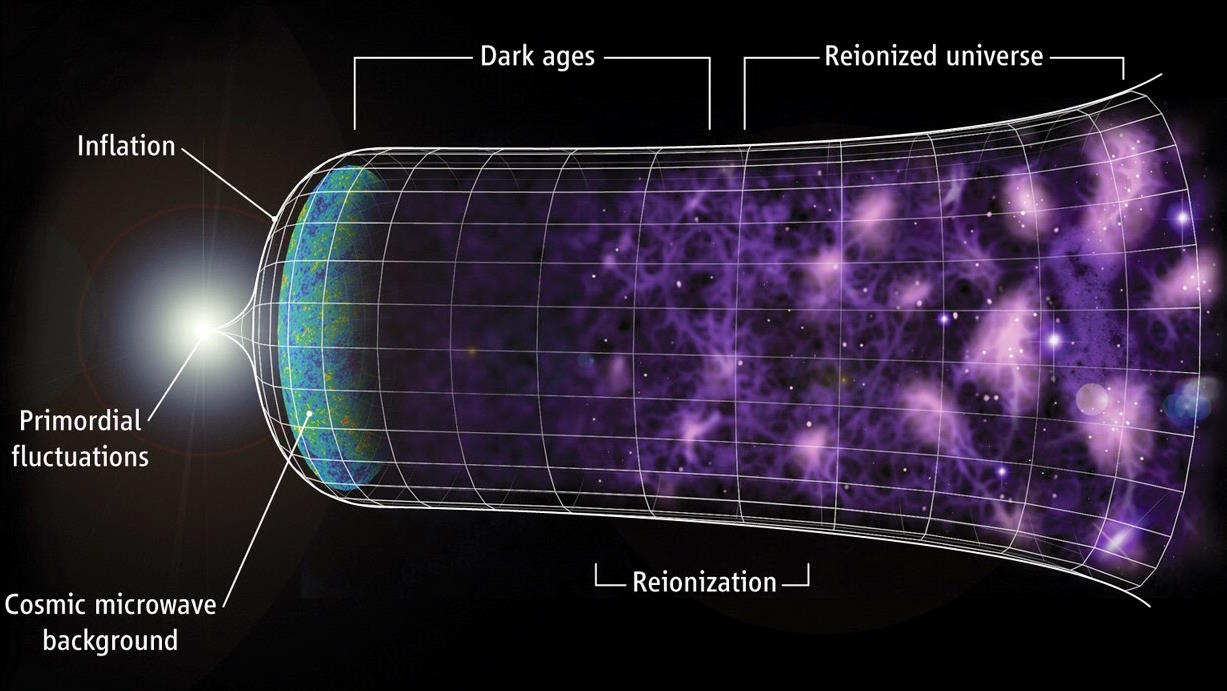
The hot Big Bang was an energetic, brilliantly luminous event. Today’s Universe is alight with stars. But in between, the dark ages ruled.
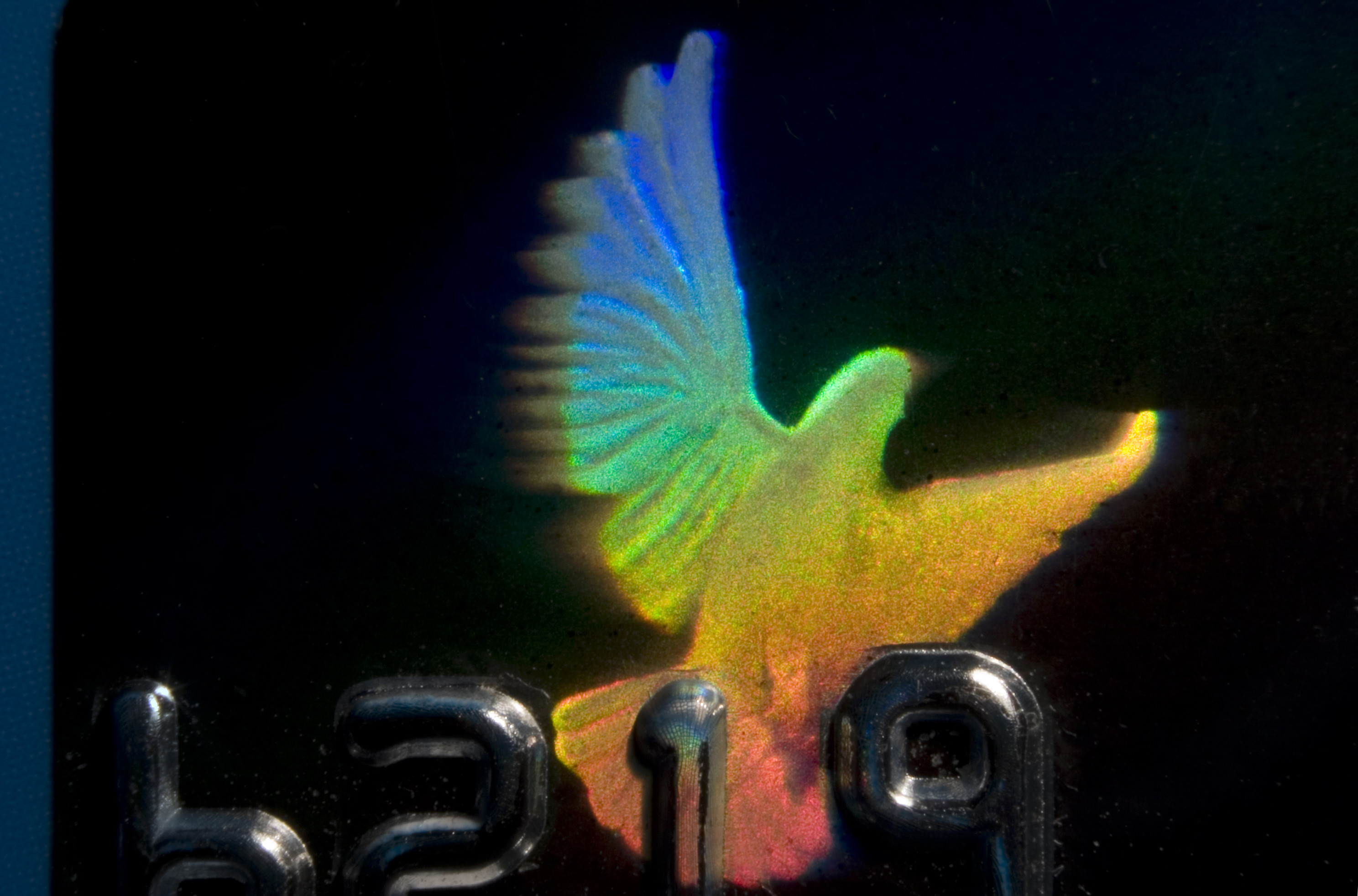
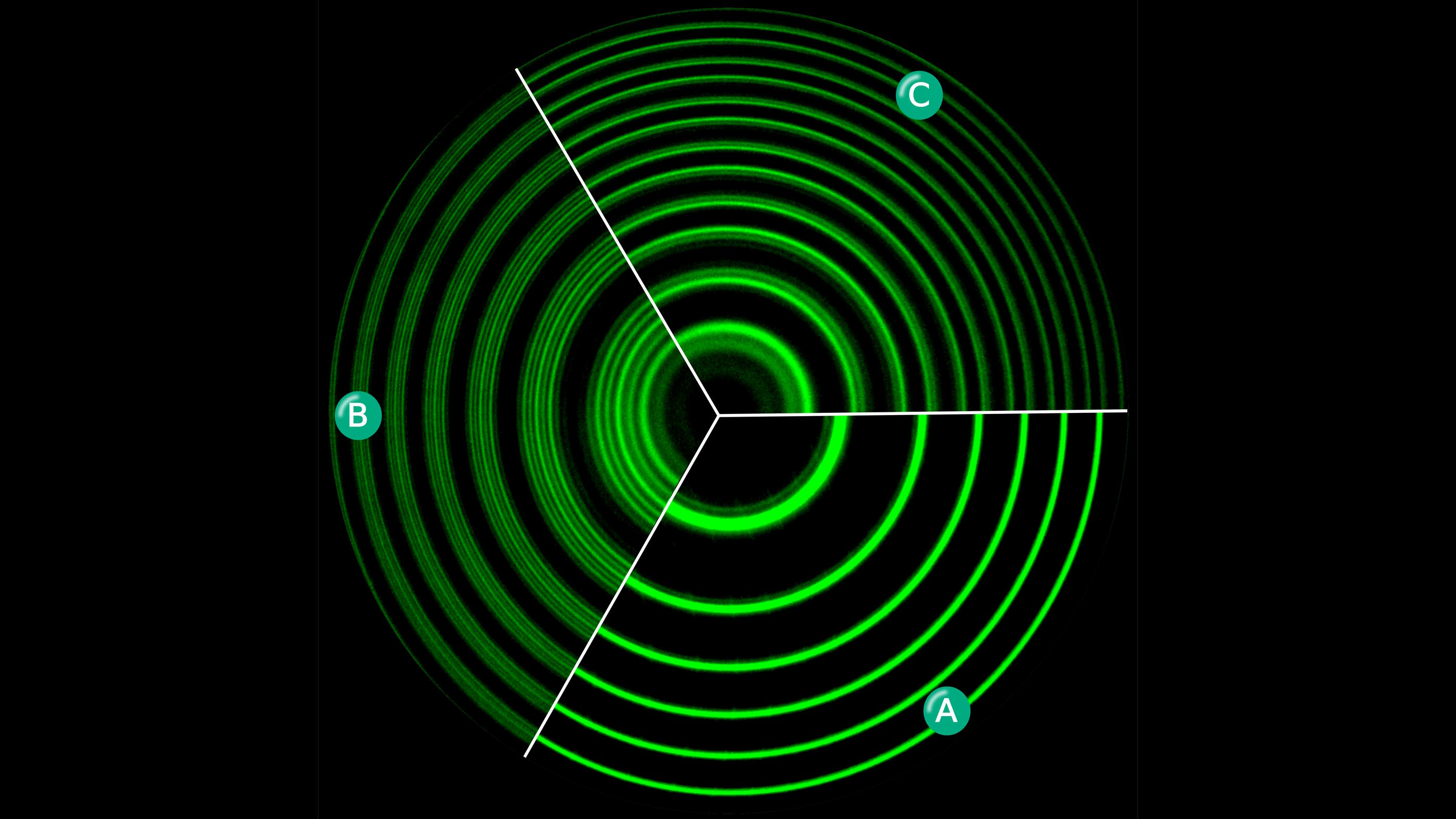
Holograms preserve all of an object’s 3D information, but on a 2D surface. Could the holographic Universe idea lead us to higher dimensions?
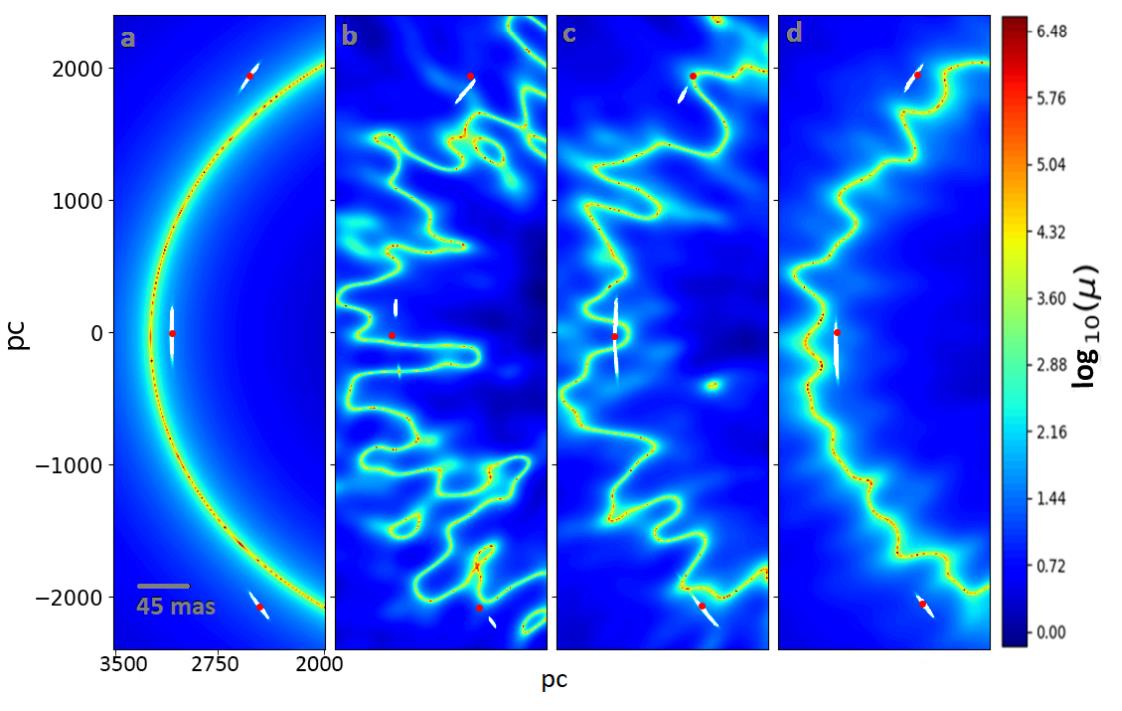
The best evidence for dark matter is astrophysical and indirect. Do new lensing observations point to ultra-light, wave-like dark matter?
Lord Kelvin is thought to have said there was nothing new to discover in physics. His real view was the opposite.
The JWST’s observations of well-developed galaxies early in universal history may coincide with accepted astronomical theory after all.
A Fermilab study confirms decades-old measurements regarding the size and structure of protons.
In July of 2022, the first science images from JWST were unveiled. Two years later, it’s changed our view of the Universe.
Within the next few decades, we may well have hard evidence for the existence of alien life on worlds light-years distant from Earth.
What do the dark recesses of the early Universe and Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom have in common? More than you could have ever hoped for.
Nothing lives forever, at least, not in the physical Universe. But relativity allows us to get closer than ever, from one perspective.
All stars, eventually, run out of fuel and die. Given all the stars we can see and the vast distance to them, are any of them already dead?
Here’s why the answer may forever elude scientists.
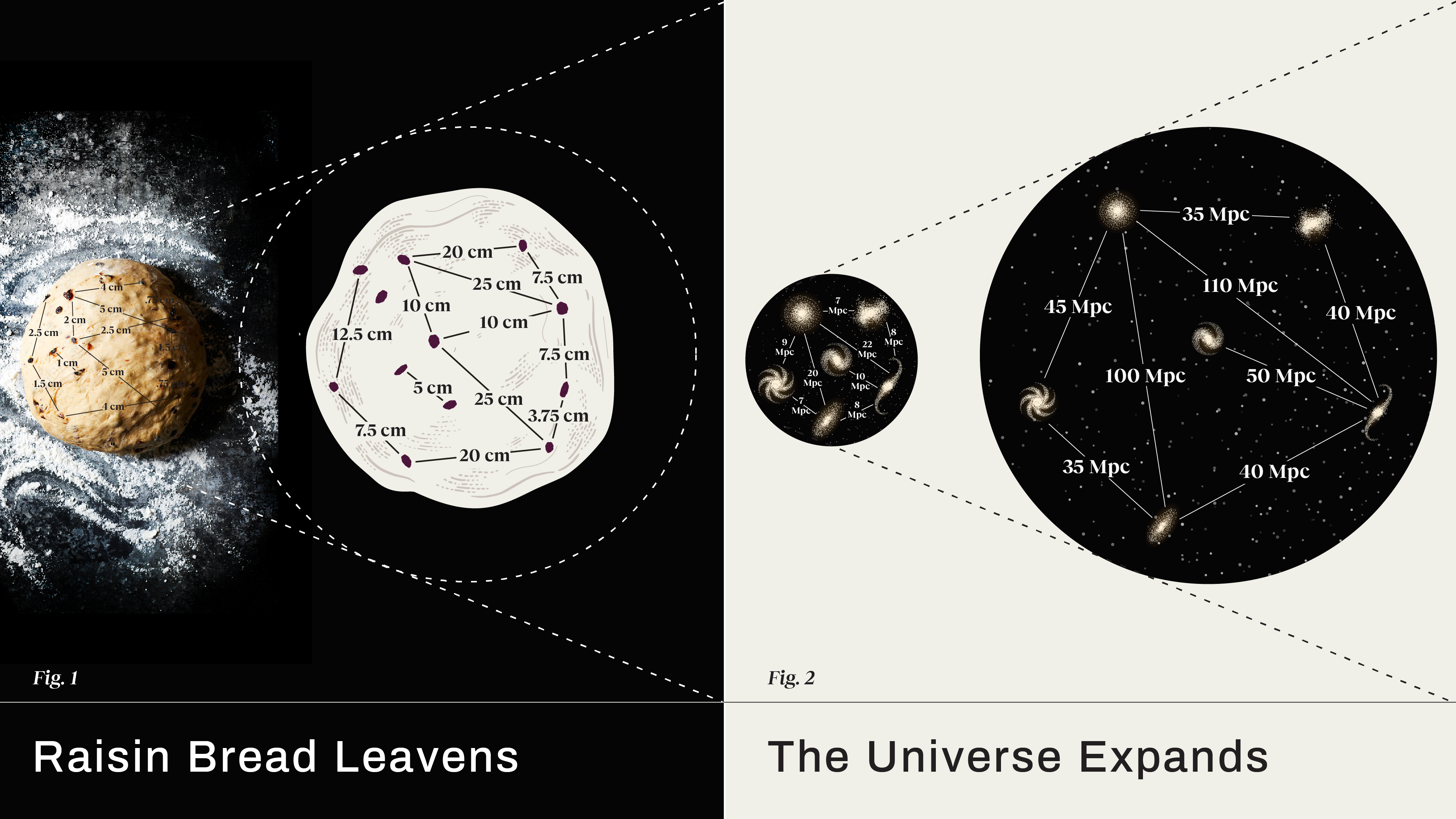
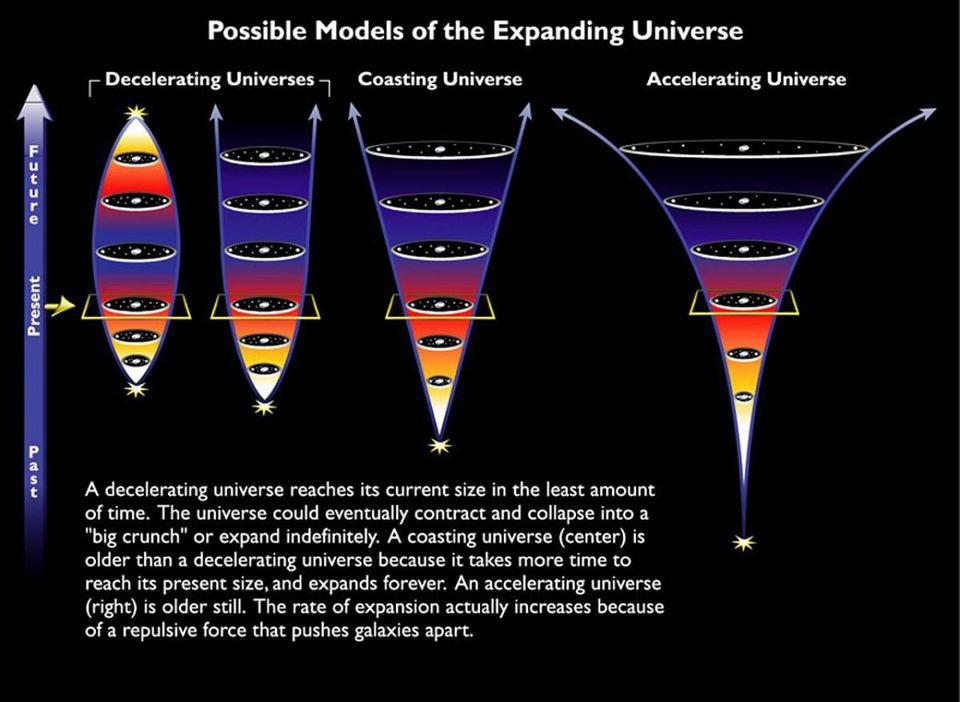
The evidence that the Universe is expanding is overwhelming. But how? By stretching the existing space, or by creating new space itself?
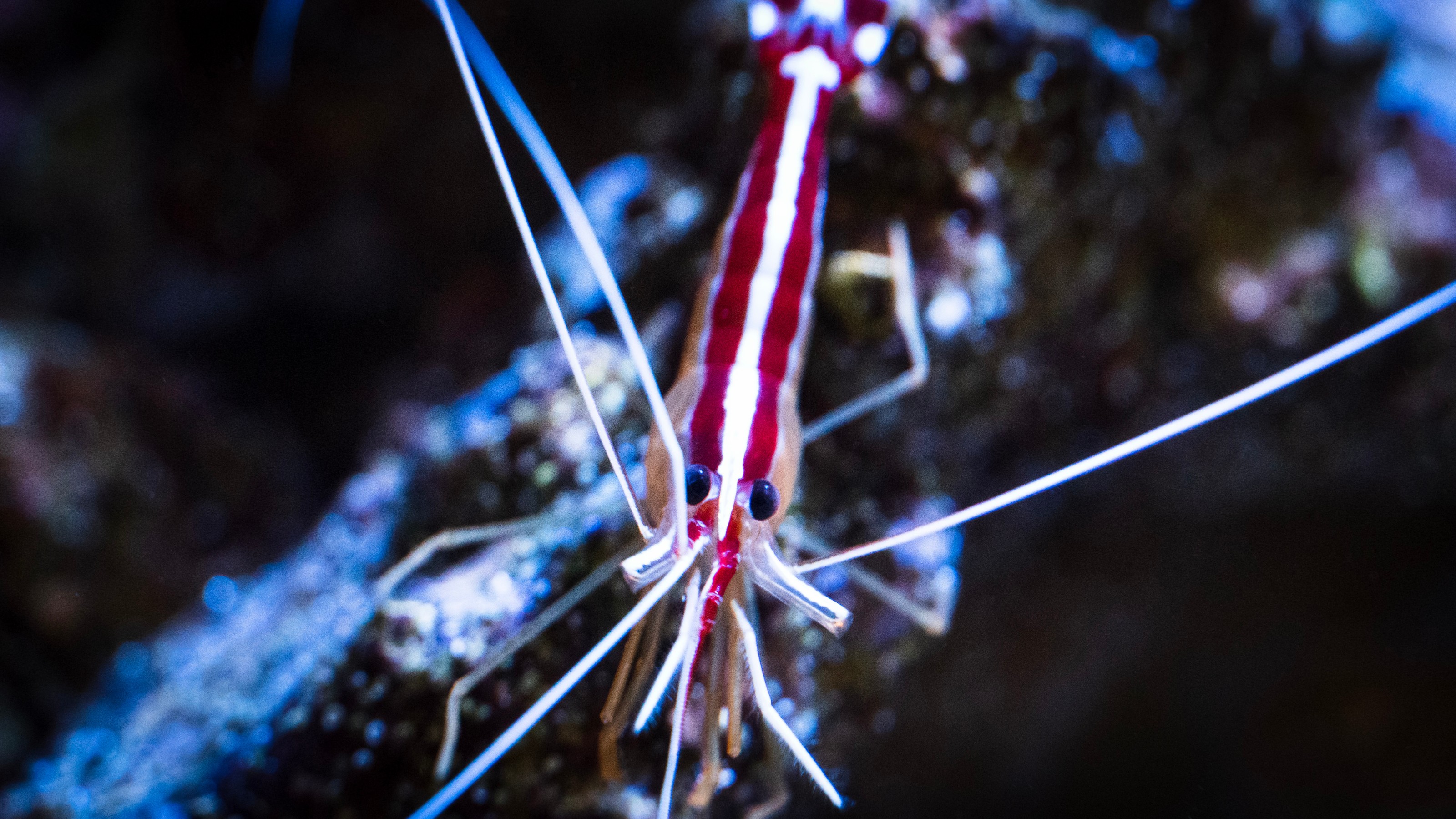
The intensely white coloration of the shrimp is a remarkable feat of bioengineering.
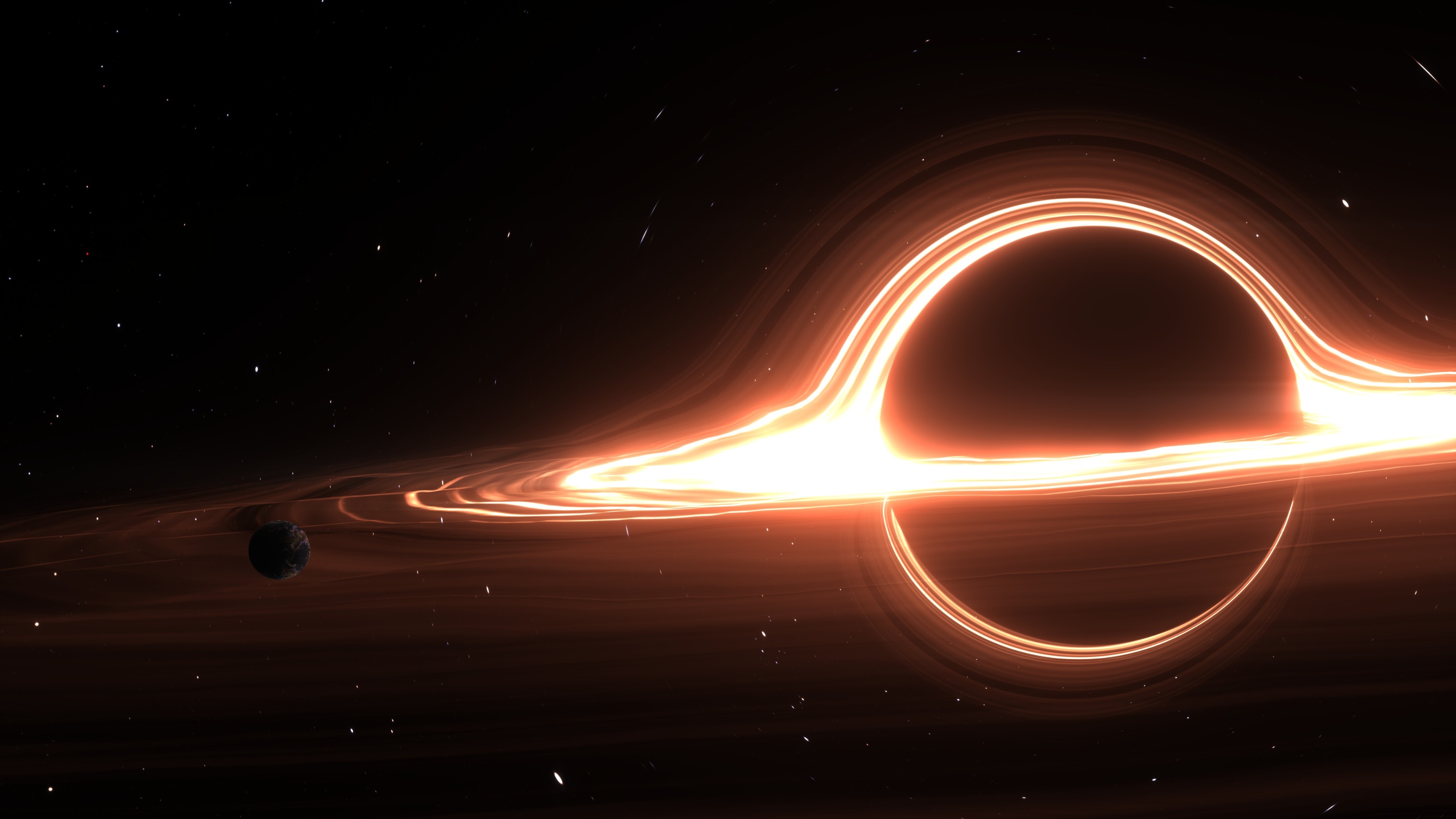
At 1,600 light years away, the black hole is practically in our cosmic backyard.
Dark energy is one of the biggest mysteries in all the Universe. Is there any way to avoid “having to live with it?”
An interview with Lisa Kaltenegger, the founding director of the Carl Sagan Institute, about the modern quest to answer an age-old question: “Are we alone in the cosmos?”
Explanations for the cosmic speed limit often conflate mass with inertia.
Most fundamental constants could be a little larger or smaller, and our Universe would still be similar. But not the mass of the electron.
The Universe is expanding, and the Hubble constant tells us how fast. But how can it be a constant if the expansion is accelerating?
The Universe is an amazing place. Under the incredible, infrared gaze of JWST, it’s coming into focus better than ever before.
The evolution of quantum technology is far from over.
Einstein’s theory of general relativity introduced the concept of space having a shape. So, what is the shape of space?