neuroscience
Participants’ brains revealed they were doing a kind of “neural replay” of the game they had been manipulated to win.
“We do not experience primarily because we have brains; we experience because we are alive.”
When it comes to behavior, genetics may play a larger role than you think.
The findings suggest that biochemical and physical effects of exercise could help heal nerves.
The color of the shirt you’re wearing right now depends on many factors, from your eye shape to what language you speak.
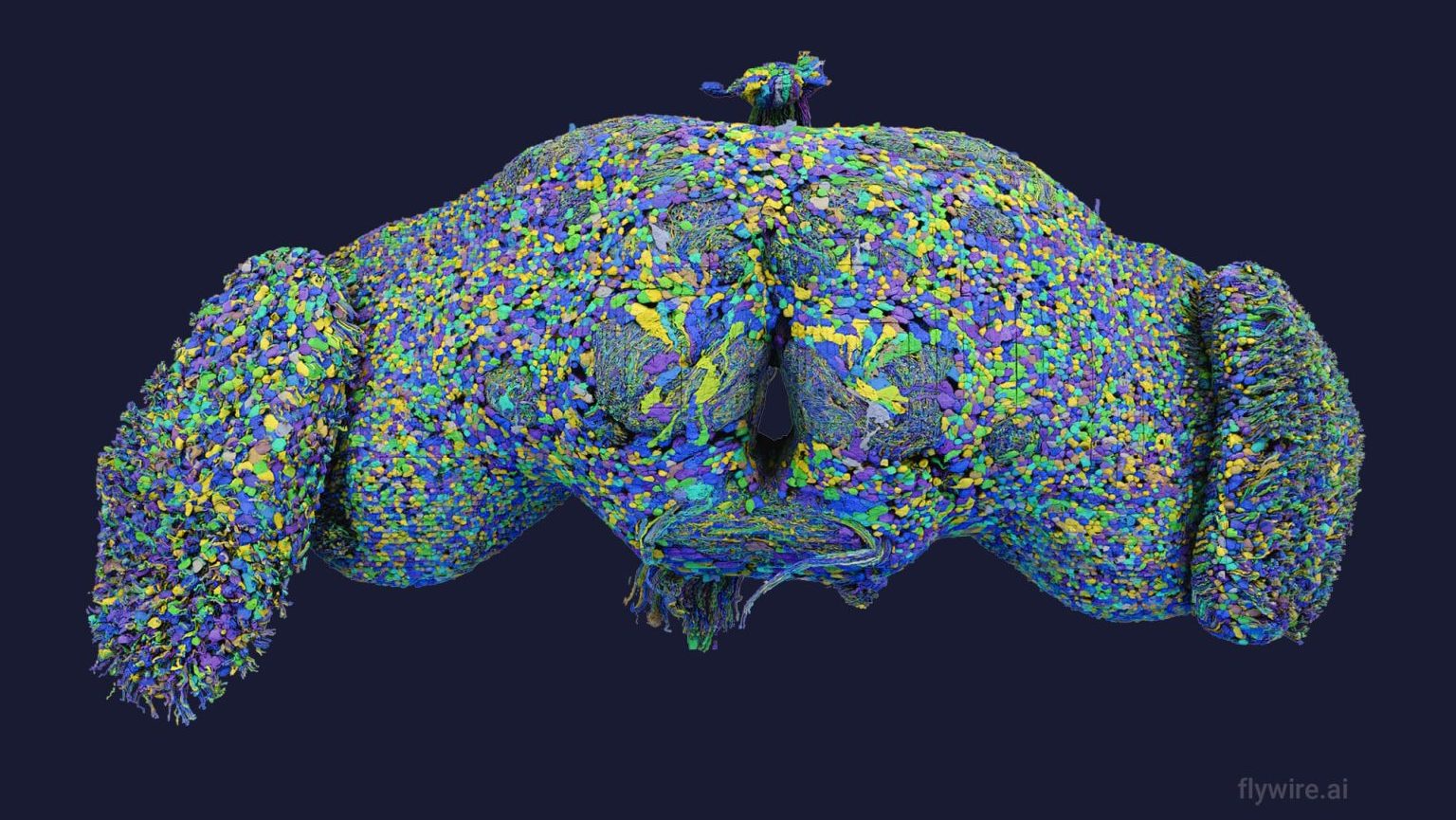
Scientists have created a magnificent portrait of every connection among neurons in a fruit fly’s brain.
The controversial theory about magic mushrooms and human evolution gets a much-needed update.
Changing the narrative on false memories might be surprisingly simple.
If you’re out on a walk, you will see a different world than your dog, a bee, or an ant. Here are three reasons why that matters.
Research suggests curiosity triggers parts of the brain associated with anticipation, making answers more rewarding once discovered.
Why “audio gaps” in video meetings wear us out — and why we need the meaningful relationships forged in communal workspaces.
New evidence suggests the corvid family has surprising mental abilities.
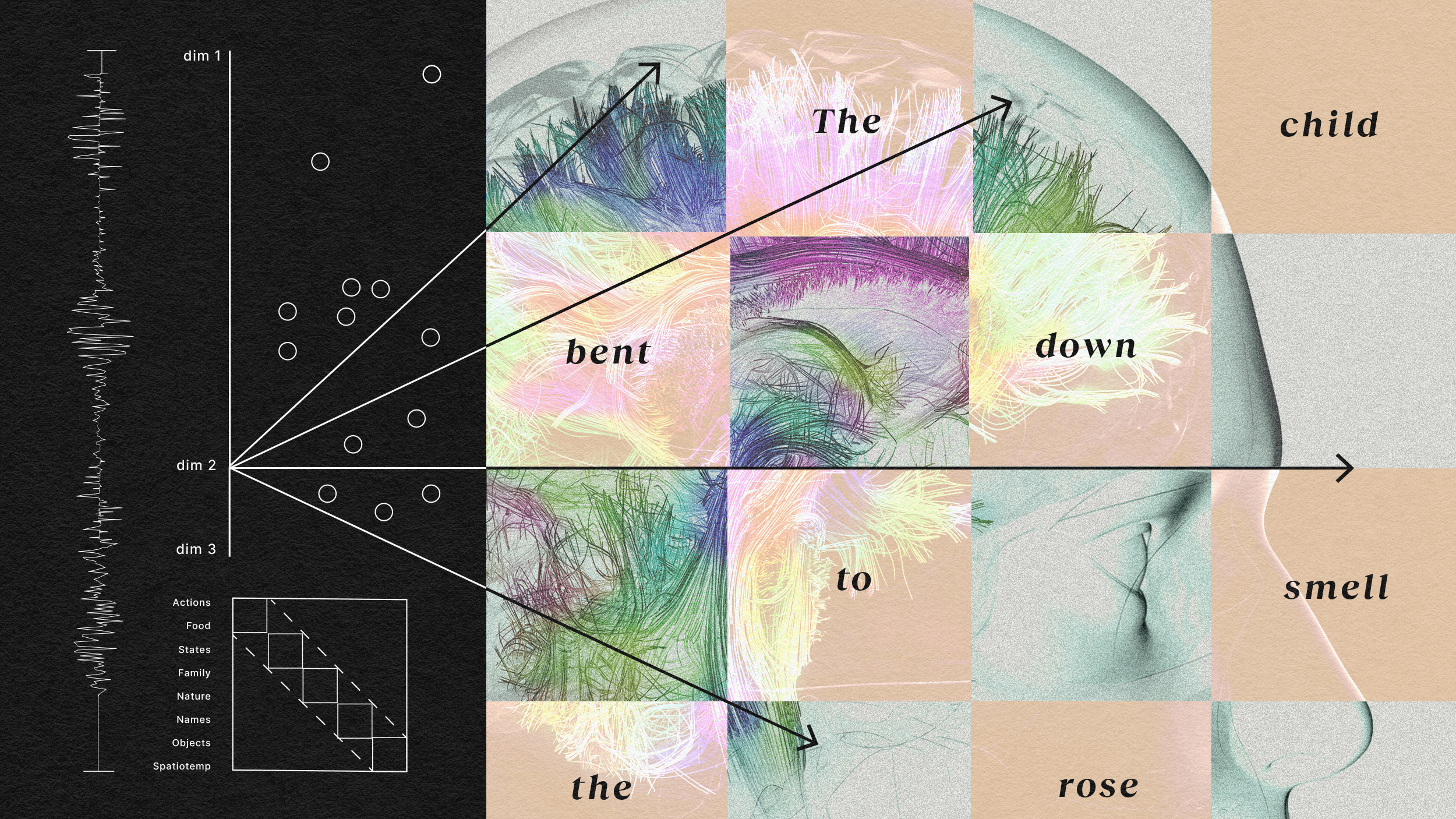
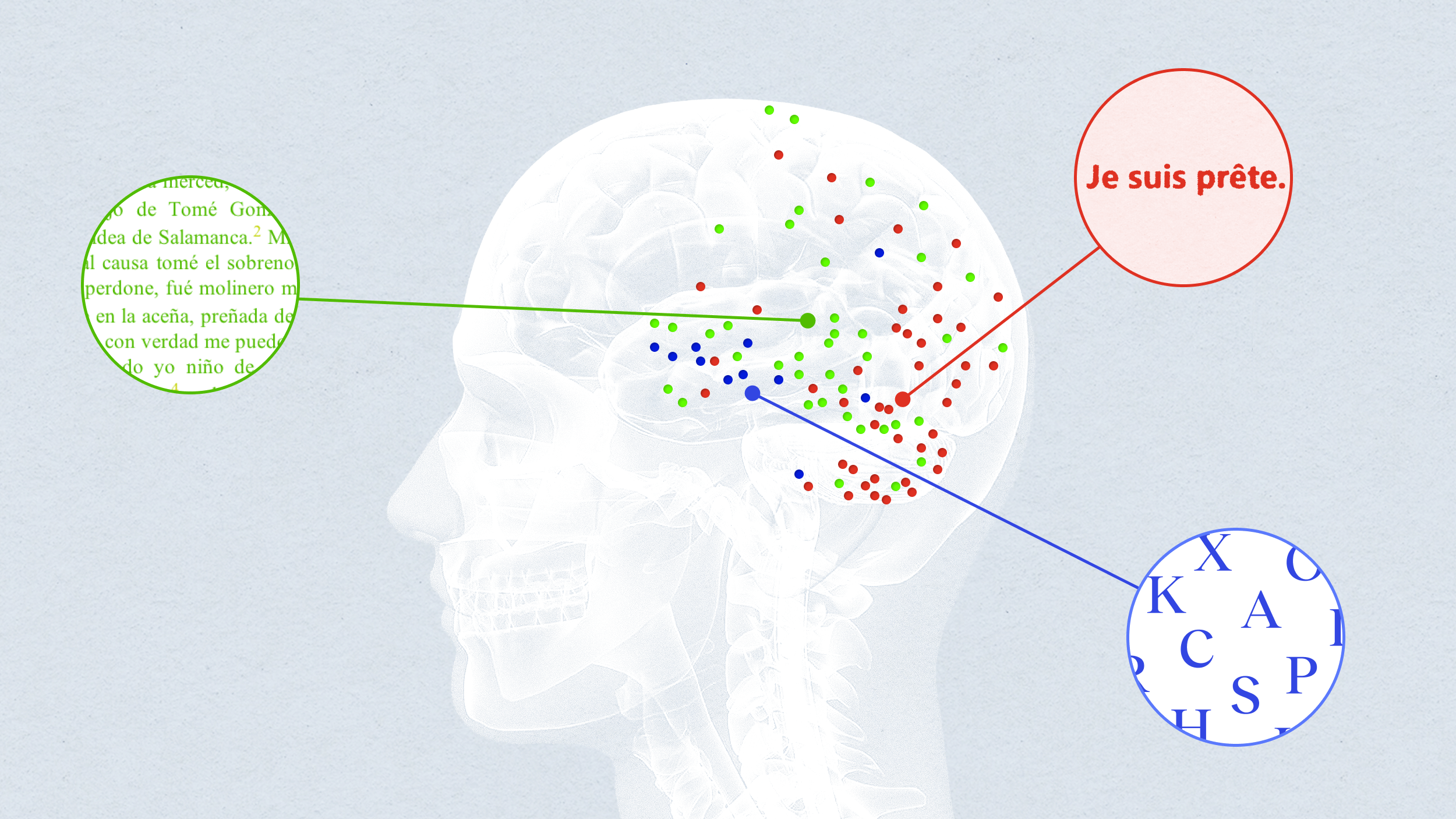
The findings show that even small areas in the brain may have the potential to represent complex meanings.
In the brain’s language-processing centers, some cells respond to one word, while others respond to strings of words together.
From hunter-gathers to desk jockeys, we work best when short, intense sessions are followed by lighter fare.
Thinking of a number between one and ten? Here’s how predictable human responses create the illusion of telepathy.
Manipulating a signaling pathway in mice reversed their anxiety — and offers hope for a new class of anti-anxiety medications for humans.
“I know what you’re thinking” can sound kind or creepy — depending on who’s saying it.
“The brain is never the same from one moment to the next throughout life. Never ever.”
“Upon emergence, these patients are sincerely unsure what was reality and what was a ‘dream.'”
The evidence is far less clear than popular media might lead you to believe.
A researcher weighs in on who’s accountable, when and why, in the eyes of the law — and whether the measures work as intended.
Neuroscientist Christof Koch on human minds, AI, and bacteria.
Sound may be an overlooked tool for boosting well-being.
An excerpt from renowned neuropsychologist Nicholas Humphrey’s book “Sentience: The Invention of Consciousness.”
Depression can cause you to think too much — and physically sense too little.
Fixing chronic pain in the body may sometimes require a treatment focused on the brain.
Recent research sheds light on how the brain overgeneralizes fear, causing people to be afraid of harmless situations.
An argument for emphasis on subjective experience.
A new framework describes how thought arises from the coordination of neural activity driven by oscillating electric fields — a.k.a. brain “waves” or “rhythms.”