neuroscience
The plant-like sea creatures contain a molecule that improves memory, learning, and even hair quality, according to a new study in mice.
Easily distracted? Try a “distractibility delay.”
Willpower alone likely isn’t enough to replace a bad habit with a good one.
Screens were around in previous generations, but now they truly define childhood.
Signals from the environment, such as those detected by your sense organs, have no inherent psychological meaning. Your brain creates the meaning.
Understanding these links could bring us closer to a cure.
An experiment in rats suggests that gene editing may be a treatment for anxiety and alcoholism in adults who were exposed to binge-drinking in their adolescence.
Hoarders know their habits are abnormal, and yet they cannot help themselves. Maybe you can help them.
Are psychopaths cold-blooded murderers? Not usually.
Protein fibrils accumulate in the brain during neurodegeneration. Cryo-electron microscopy has now uncovered fibrils of an unexpected protein.
Learning another language might make you richer, sexier, and smarter. Why not try it?
Disulfiram is an FDA-approved drug for the treatment of chronic alcoholism. It might also serve as anti-anxiety medication.
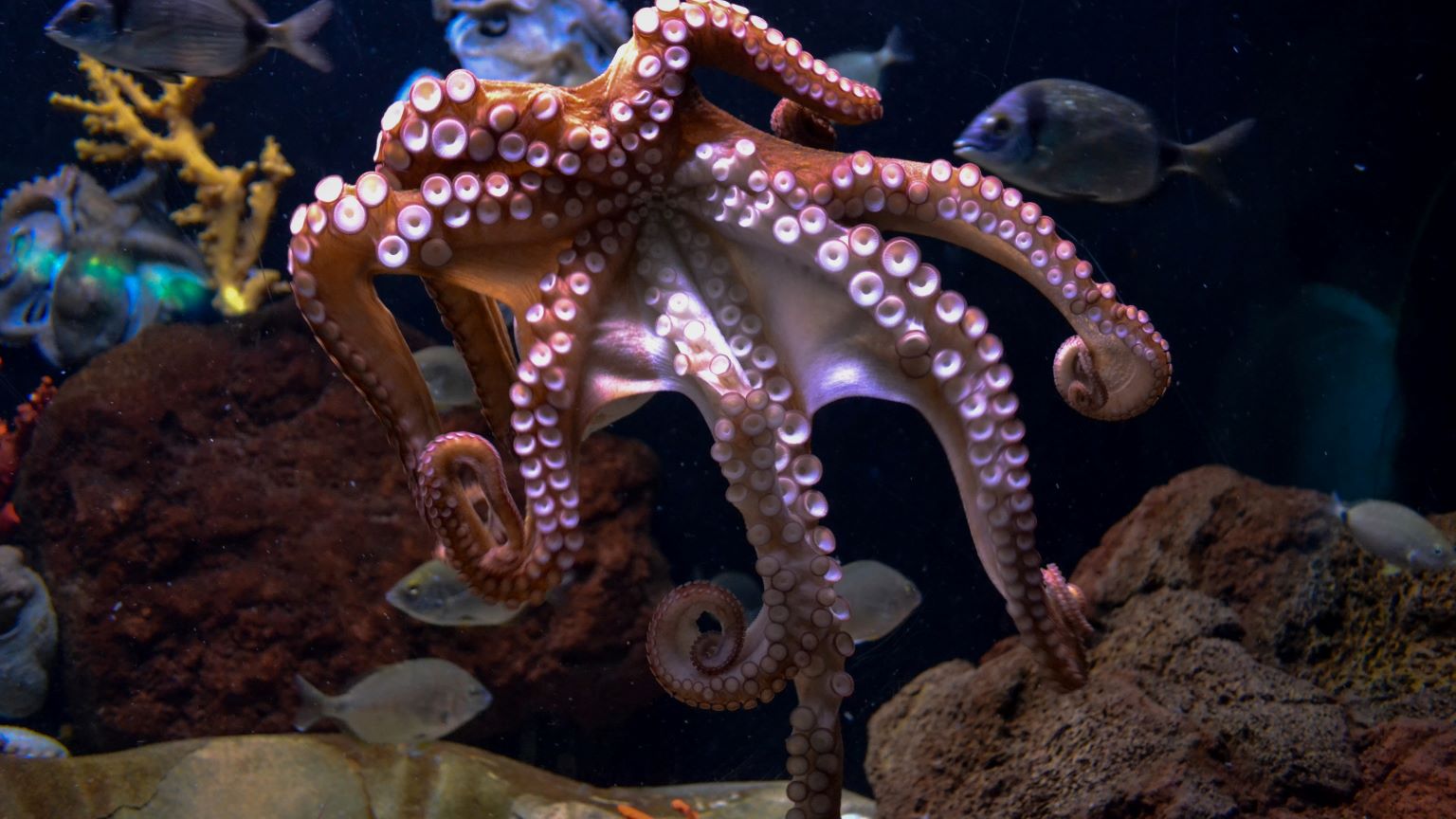
Research shows that octopuses are sentient, emotional creatures.
The ability is tied to mental health, consciousness, and memory in humans.
A small percentage of people who consume psychedelics experience strange lingering effects, sometimes years after they took the drug.
Can electrical stimulation meaningfully substitute for natural touch during a complex task in the real world? We think so.
Bruce Willis has announced he is stepping away from acting.
Studies show that feelings of ease and comfort in a given situation are tied to feelings of authenticity.
An emerging field studies parasites that take over the nervous system of a host.
Older adults who napped at least once or for more than an hour a day had a 40% higher chance of developing Alzheimer’s than those who napped less.
The results of a 2021 study suggest that the world’s most powerful psychedelic may be an underutilized peace-building tool.
Stress-busting soundtrack or placebo effect?
The study shows that it’s possible to map the wildly subjective psychedelic experiences to specific brain regions.
Revolutionary techniques for understanding brain functions in animals could soon help us understand how emotions guide our lives.
More than 200 years ago, scientists tried to figure out how bats navigate in the dark (or without eyes). This set in motion a series of events that led to the development of ultrasound as a form of psychotherapy.
Michio Kaku predicts, among other things, how we’ll build cities on Mars and why cancer will one day be like the common cold.
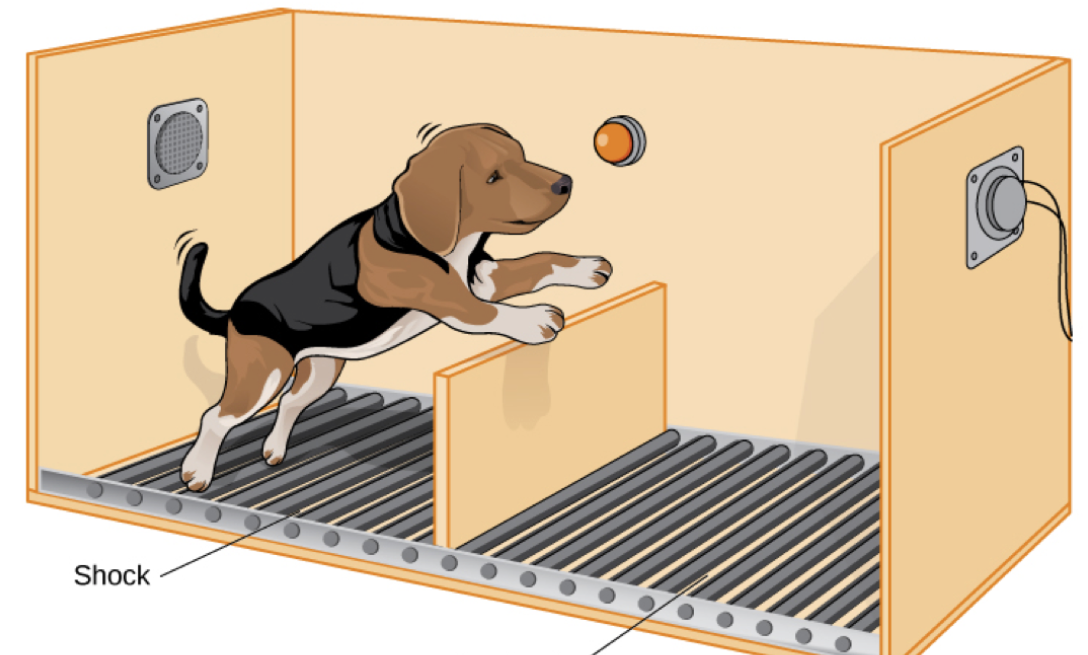
Helplessness isn’t learned — it’s an instinctual response that can be overcome.
About six minutes after the heart stops, the brain essentially dies.
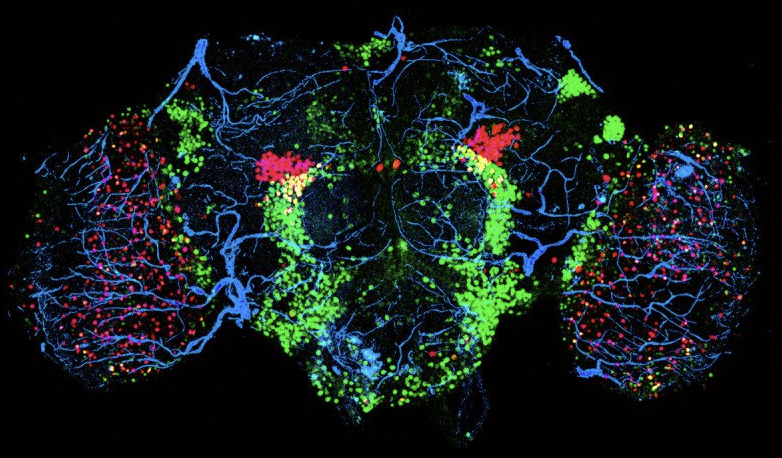
Salk scientists studied complex decision-making capabilities in a worm with just 302 neurons and a mouth full of teeth. It’s smarter than you would think.
We imagine and debate the inner lives of literary characters, knowing there can be no truth about their real motives or beliefs. Could our own inner lives also be works of fiction?