Our intuitive understanding of time is very different from a physicist’s understanding of time. How do we reconcile these views?
Search Results
You searched for: gravity
It would get rid of our hazardous, radioactive, and pollutive waste for good, but physics tells us it’s a losing strategy for elimination.
A deep dive into the chaotic journey of star formation.
Inflation, dark matter, and string theory are all proposed extensions to the prior consensus picture. But what does the evidence say?
The mass that gravitates and the mass that resists motion are, somehow, the same mass. But even Einstein didn’t know why this is so.
Quantum wormholes are mathematically possible — but might also be physically impossible. Physicist Janna Levin explains Hawking’s famous information paradox.
▸
12 min
—
with
“Is it possible that consciousness is a much more basic phenomenon in nature and is essentially pervading everything?”
▸
10 min
—
with
Particles behave differently when freed from the force of gravity. A new space factory aims to use this to synthesize pharmaceuticals.
Even after the first stars form, those overdense regions gravitationally attract matter and also merge. Here’s how they grow into galaxies.
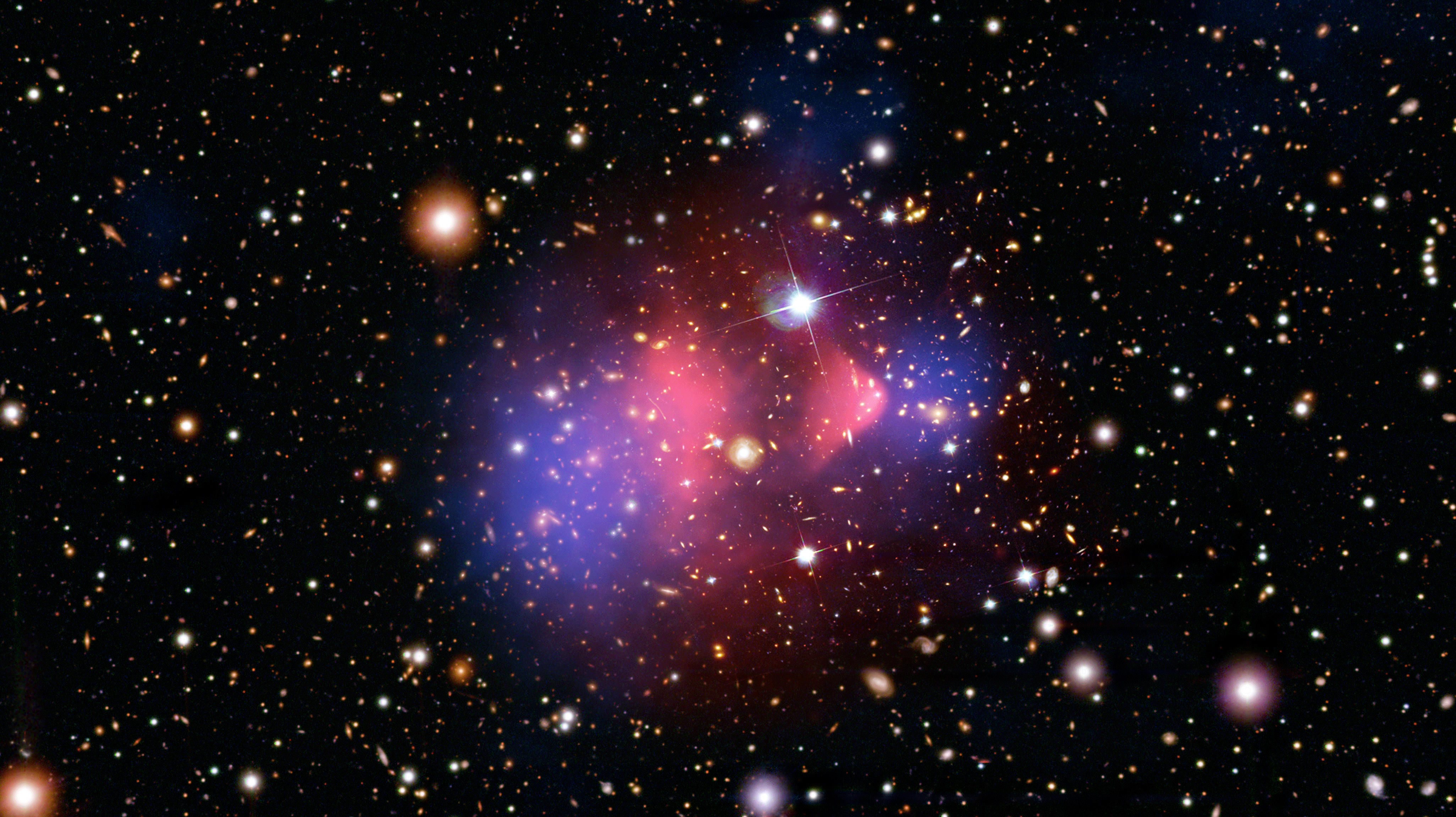
19 years ago, the Bullet Cluster provided an empirical proof for dark matter. Even today, modified gravity still can’t explain it.
In the quest to measure how antimatter falls, the possibility that it fell “up” provided hope for warp drive. Here’s how it all fell apart.
Einstein’s laws of gravity have been challenged many times, but have always emerged victorious. Could wide binary stars change all that?
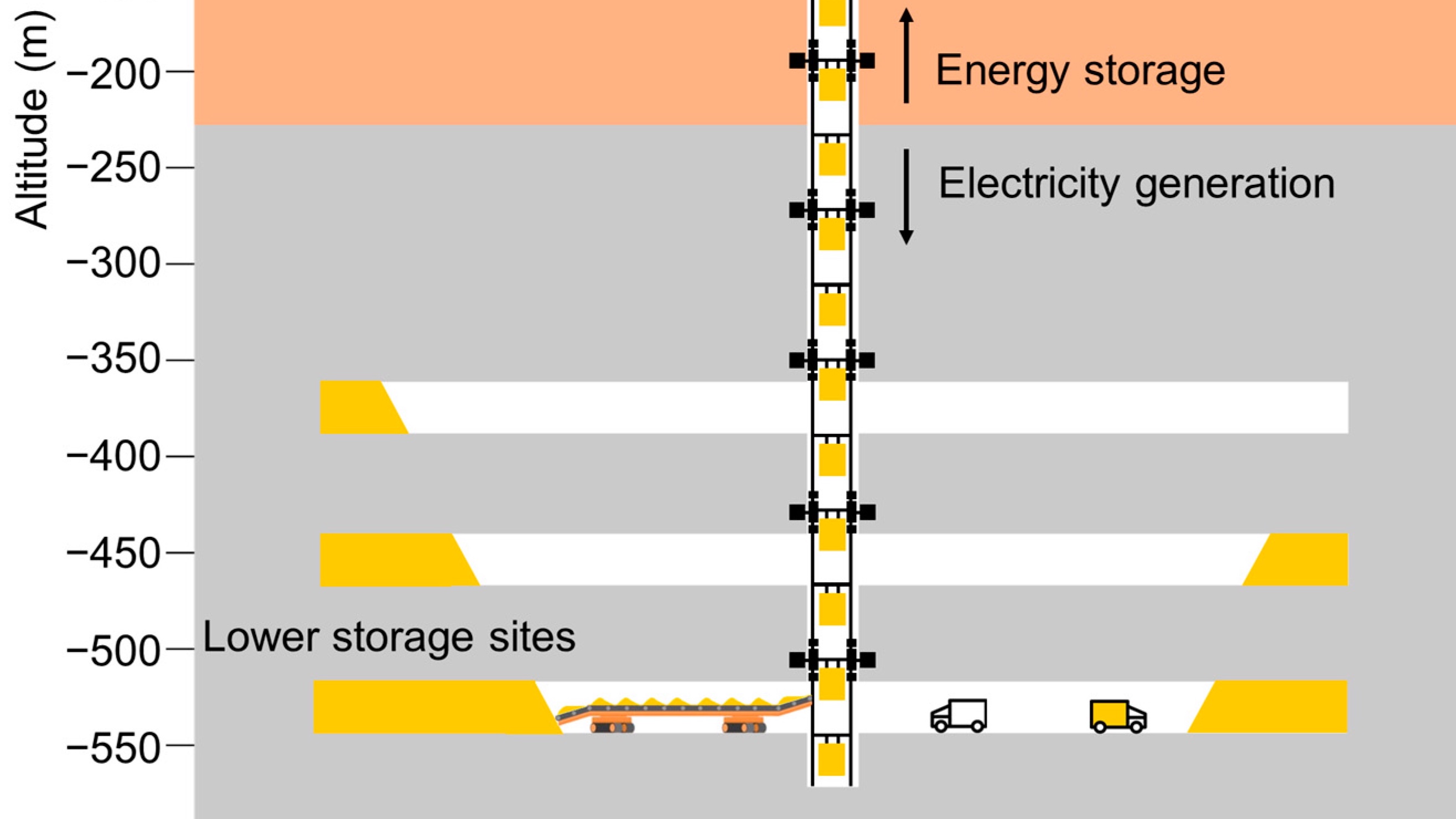
Old coal mines can be converted into “gravity batteries” by retrofitting them with equipment that raises and lowers giant piles of sand.
Bang bang all over the Universe.
The mutual distance between well-separated galaxies increases with time as the Universe expands. What else expands, and what doesn’t?
What do ghosts and anomalous galaxy rotation rates have in common? Some sci-fi enthusiasts believe the answer involves “parallel universes.”
When it comes to predicting the energy of empty space, the two leading theories disagree by a factor of 100 googol quintillion.
Physicists just can’t leave an incomplete theory alone; they try to repair it. When nature is kind, it can lead to a major breakthrough.
Most waves need a medium to travel through. But the way that light and gravitational waves travel shows that space can’t be a medium at all.
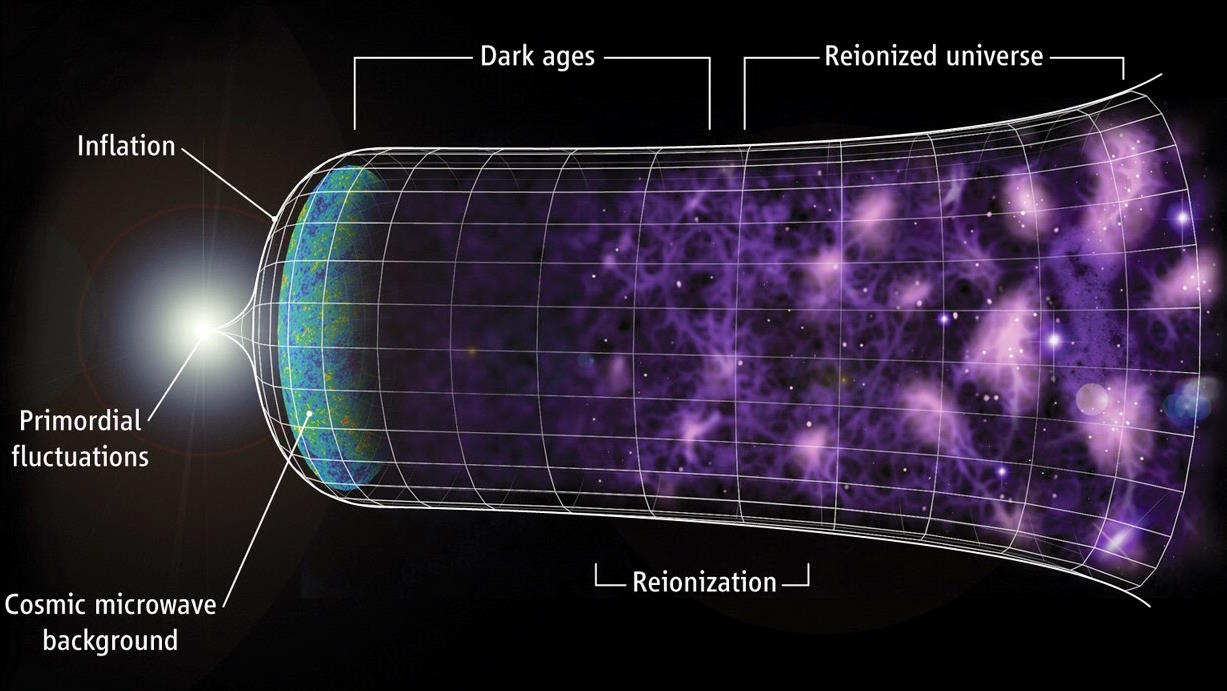
Atomic nuclei form in minutes. Atoms form in hundreds of thousands of years. But the “dark ages” rule thereafter, until stars finally form.
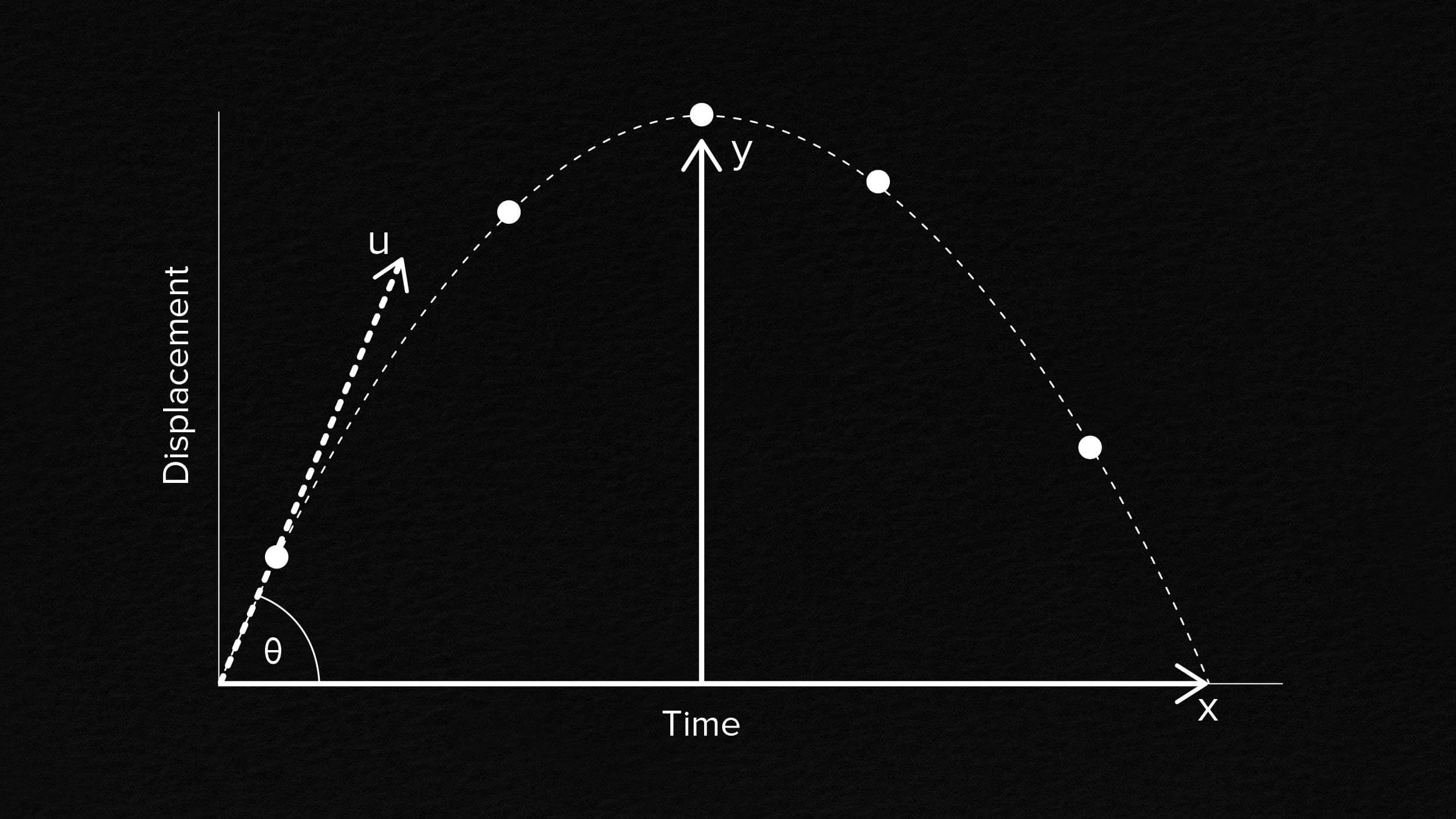
Taught in every introductory physics class for centuries, the parabola is only an imperfect approximation for the true path of a projectile.
In 2017, a kilonova sent light and gravitational waves across the Universe. Here on Earth, there was a 1.7 second signal arrival delay. Why?
The paper does not prove the existence of dark matter, but it mostly eliminates a rival theory called Modified Newtonian Dynamics.
Although many of Einstein’s papers revolutionized physics, there’s one Einsteinian advance, generally, that towers over all the rest.
The Bullet Cluster has, for nearly 20 years, been hailed as an empirical “proof” of dark matter. Can their detractors explain it away?
Though he renounced philosophy, Stephen Hawking’s final theory of the universe redraws the basic foundations of cosmology.
When black holes disappear, what happens to the stuff that fell in? Physicist Brian Cox explains.
▸
13 min
—
with
“I was stunned. Here in front of me was the original apparatus through which a new vision of the world was slowly and painfully brought to light.”
The “first cause” problem may forever remain unsolved, as it doesn’t fit with the way we do science.
If Einstein couldn’t solve the theory of everything, could anyone? Physicist Michio Kaku explains what it would take.
▸
6 min
—
with