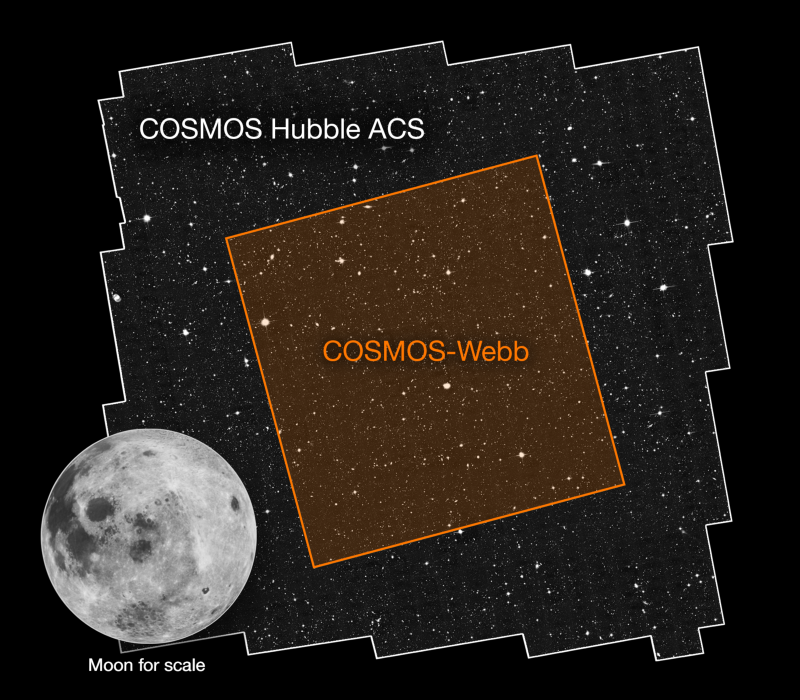
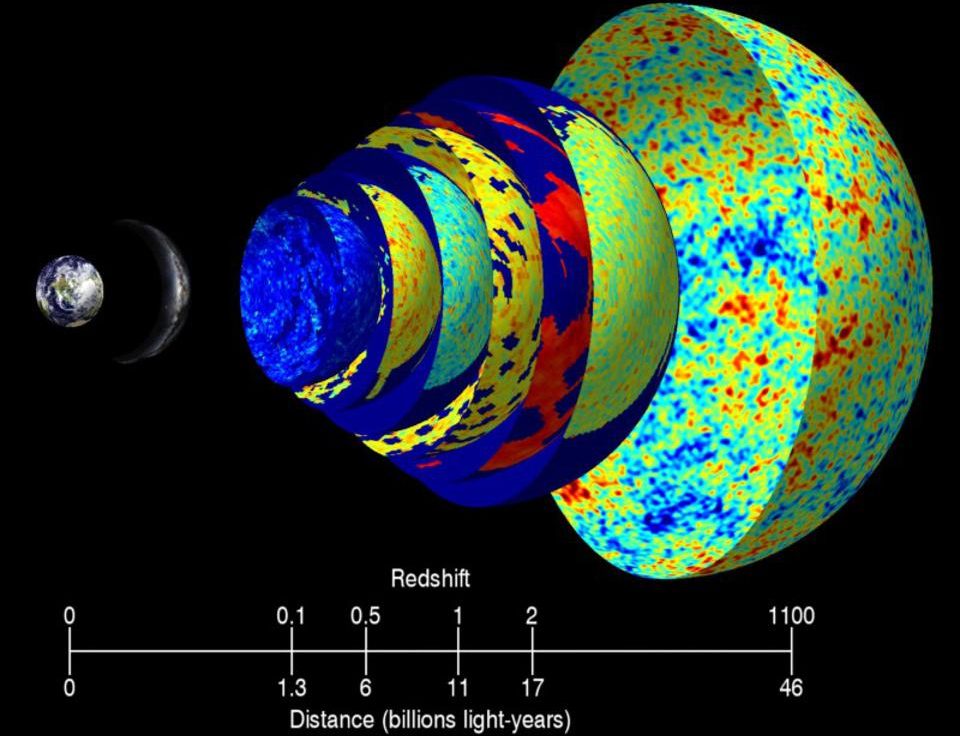
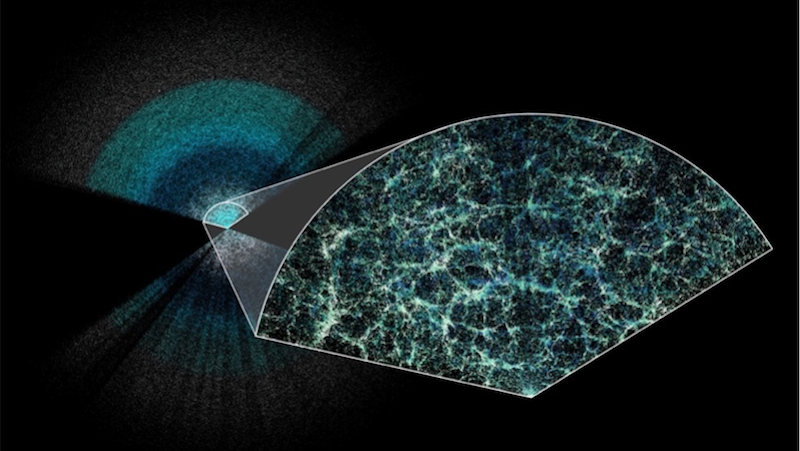
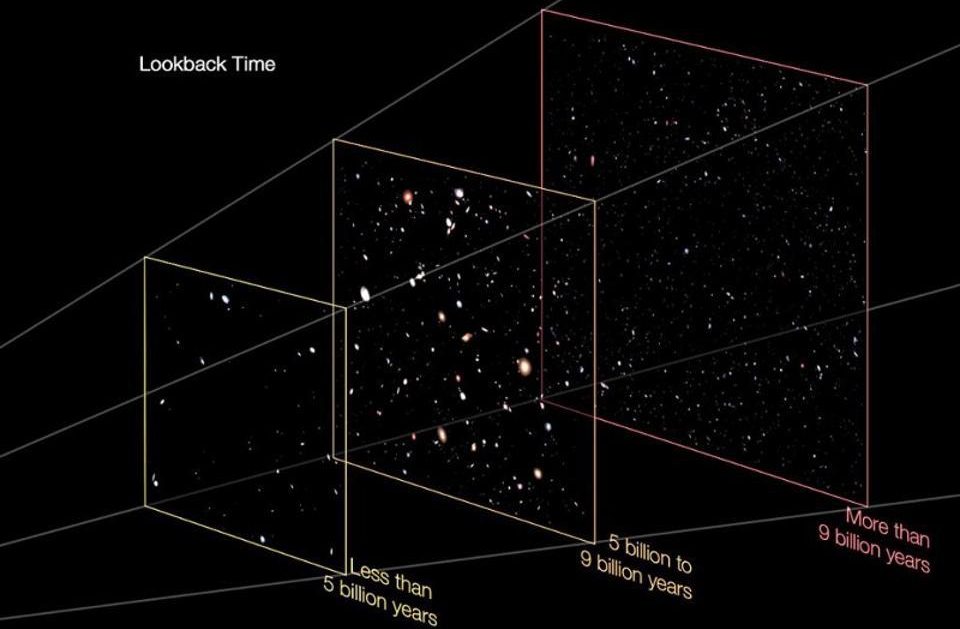
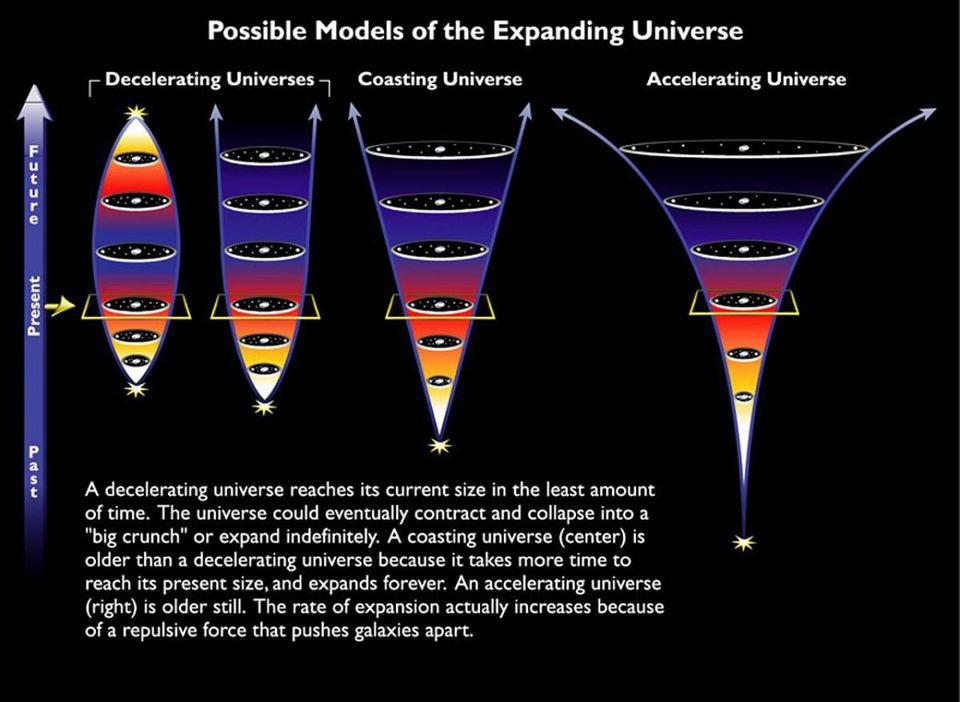
In the 20th century, many options abounded as to our cosmic origins. Today, only the Big Bang survives, thanks to this critical evidence.
Search Results
You searched for: Telescope
From exoplanets to supermassive black holes to the first stars and galaxies, Webb will show us the Universe as we’ve never seen it before.
Our Universe isn’t just expanding, the expansion is accelerating. Instead of dark energy, could a “lumpy” Universe be at fault?
Straddling the bounds of science and religion, Newton wondered who set the planets in motion. Astrophysics reveals the answer.
There are so many problems, all across planet Earth, that harm and threaten humanity. Why invest in researching the Universe?
Cosmologists are largely still in the dark about the forces that drive the Universe.
How scientists found out that we live in a cosmic aquarium.
Some astrobiologists believe life is rare, while others believe it is common in the Universe. How can we find out which view is correct?
For nearly 60 years, the hot Big Bang has been accepted as the best story of our cosmic origin. Could the Steady-State theory be possible?
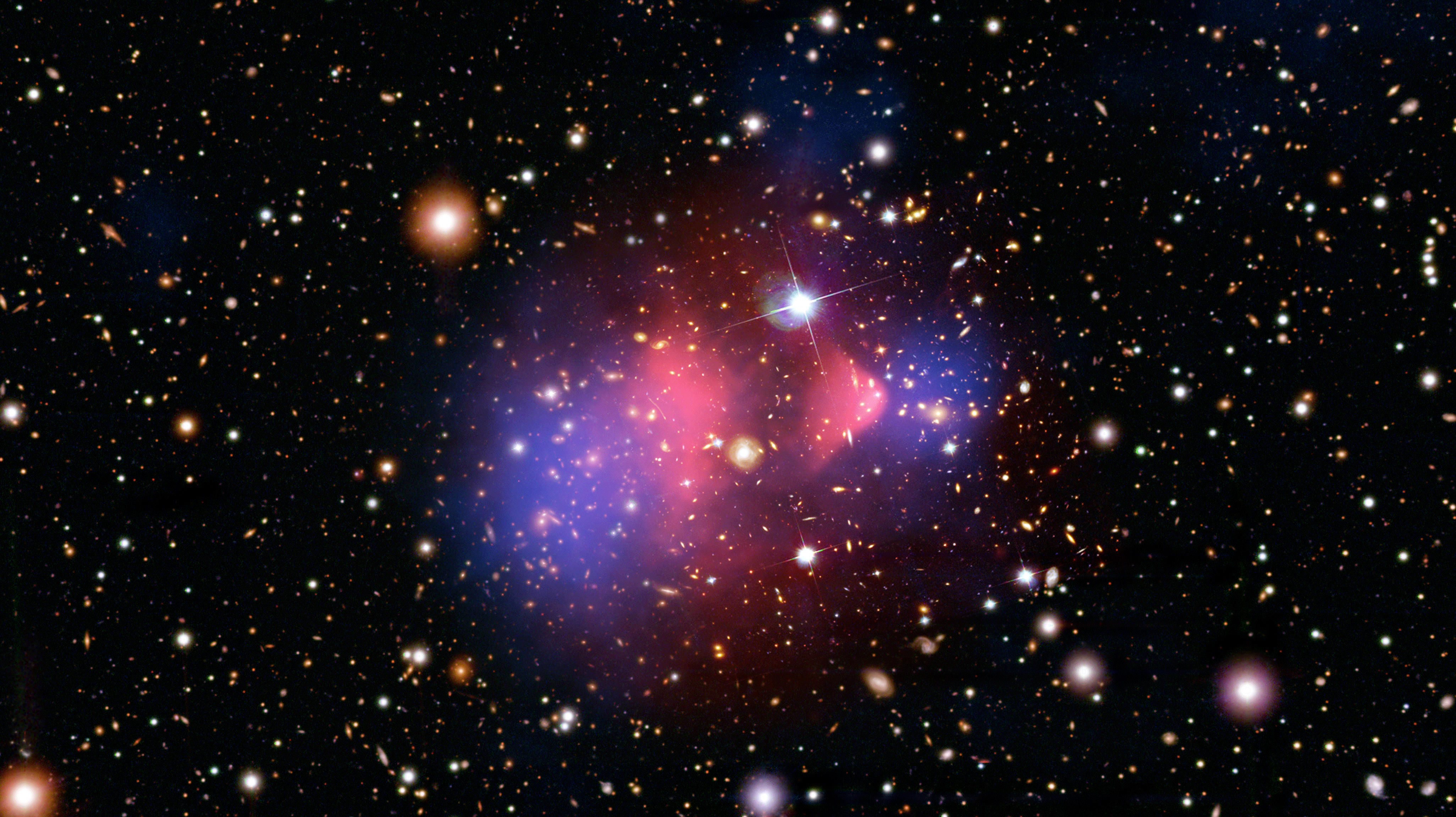
The Bullet Cluster has, for nearly 20 years, been hailed as an empirical “proof” of dark matter. Can their detractors explain it away?
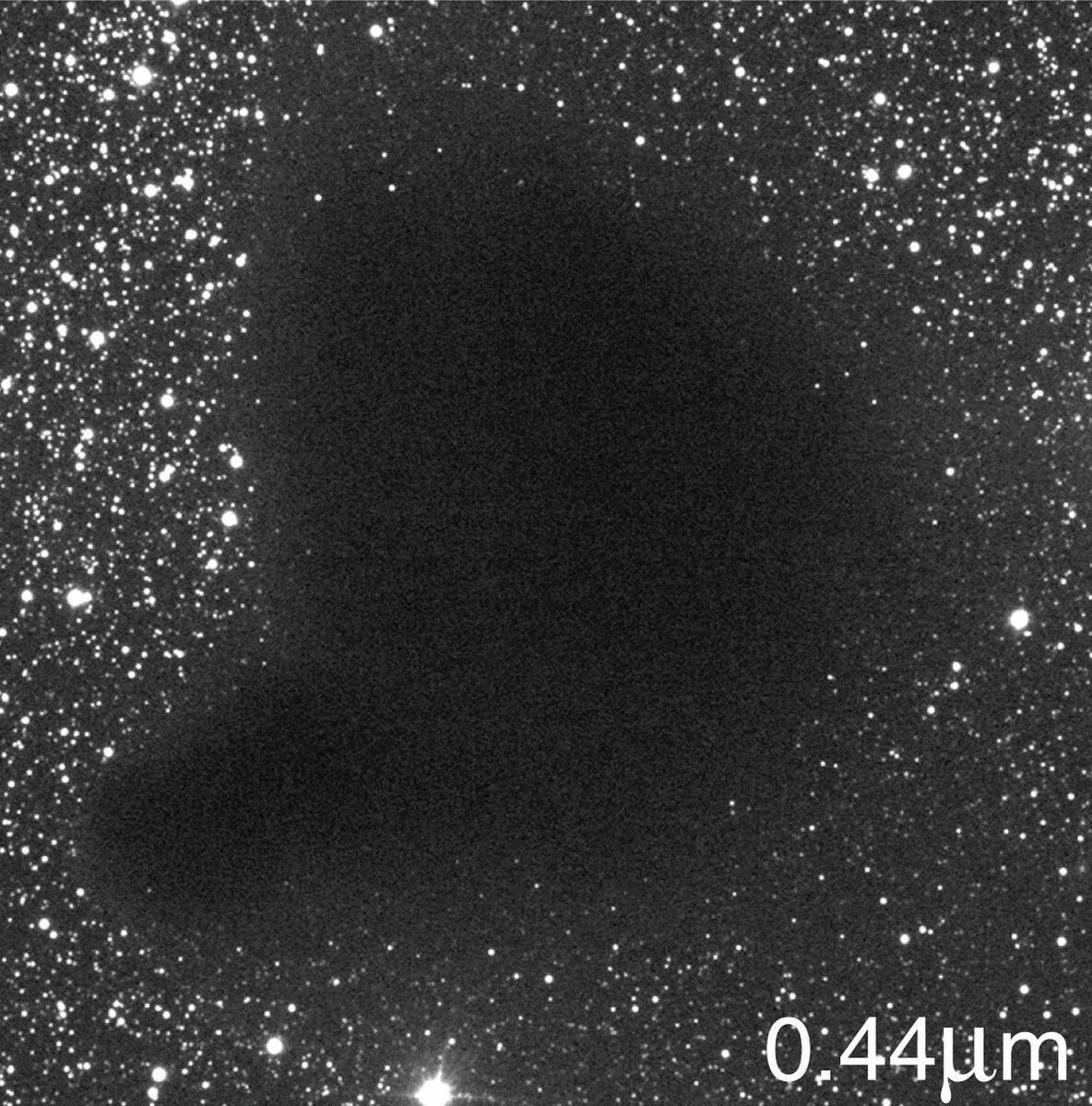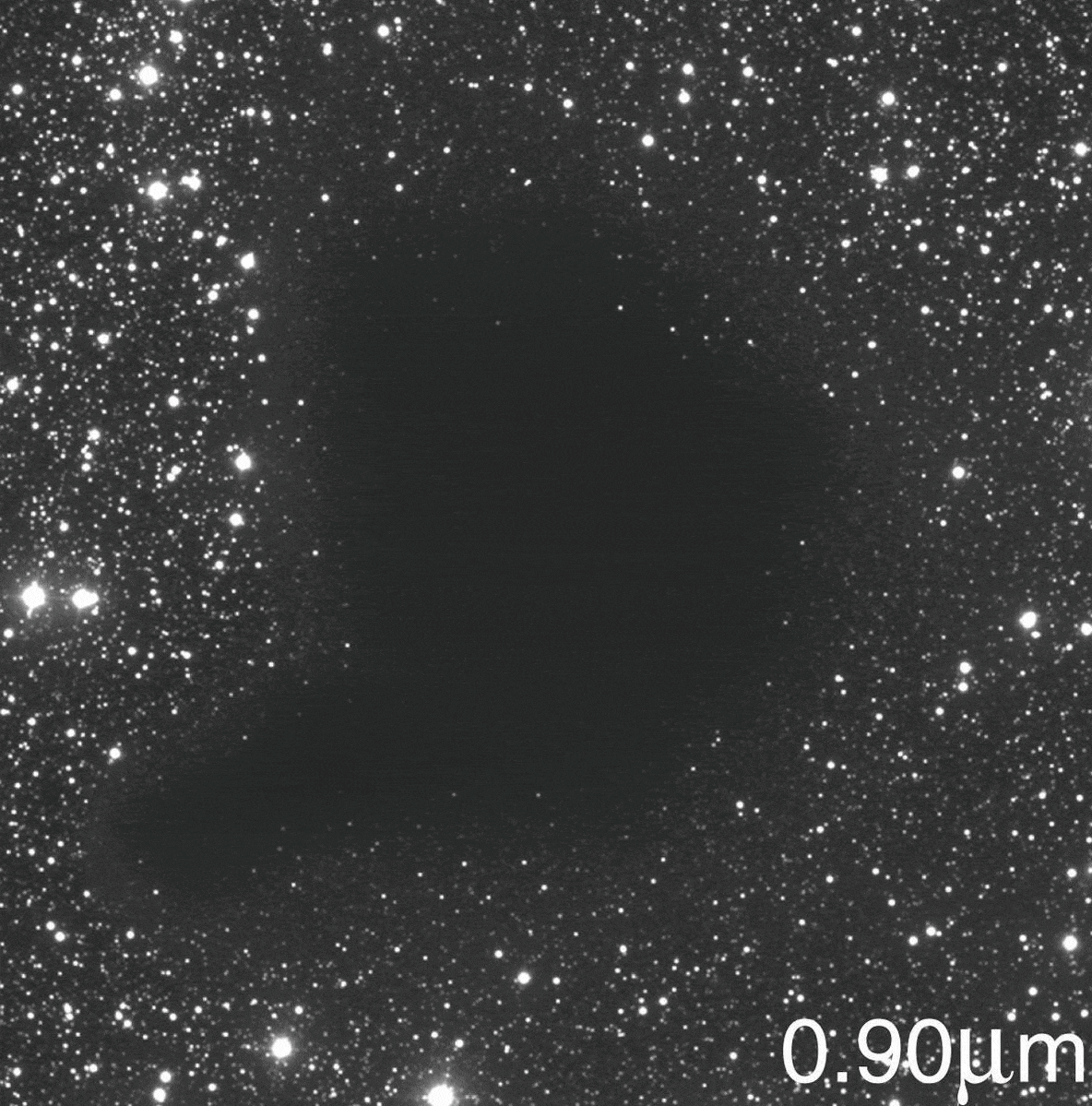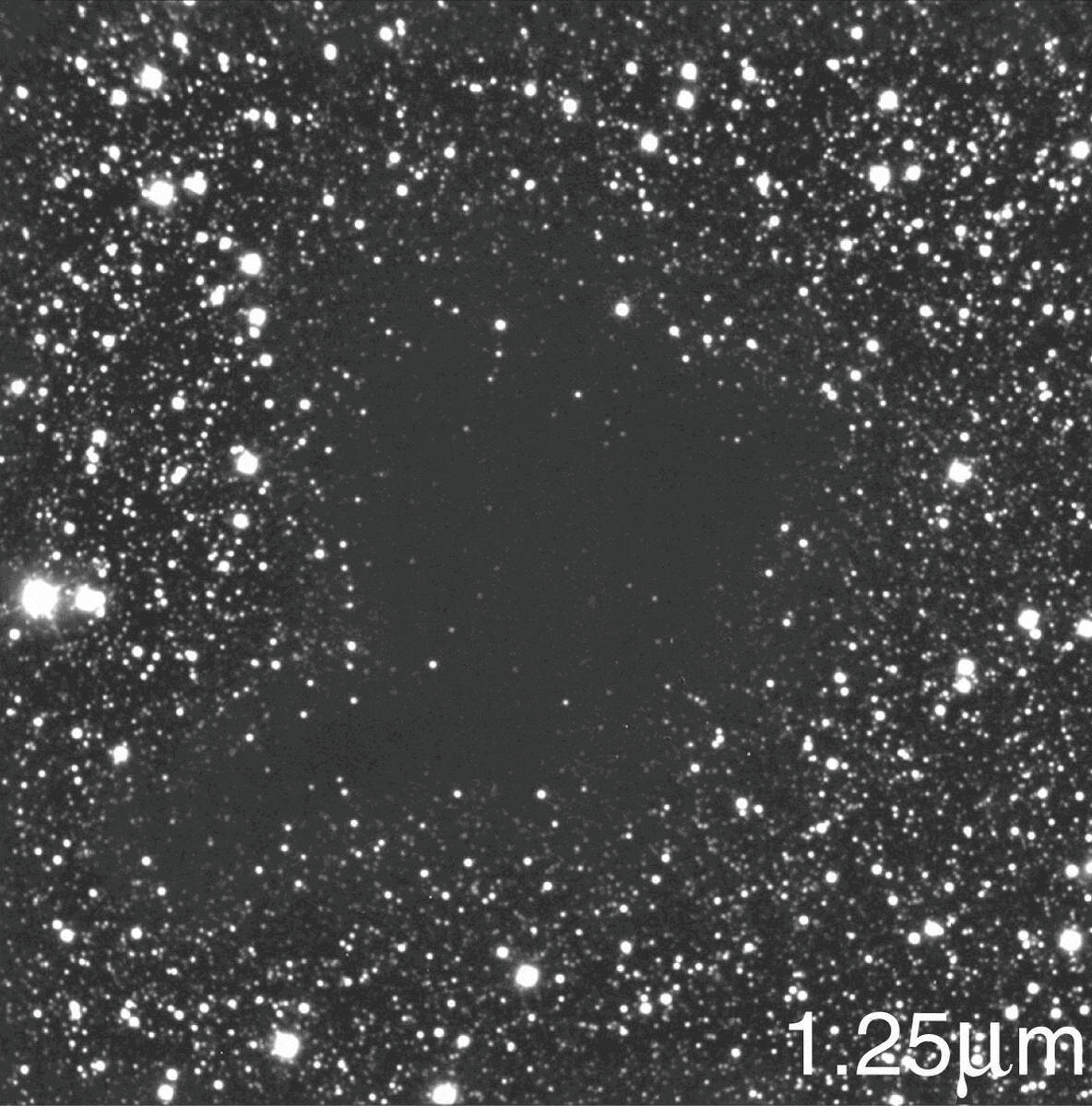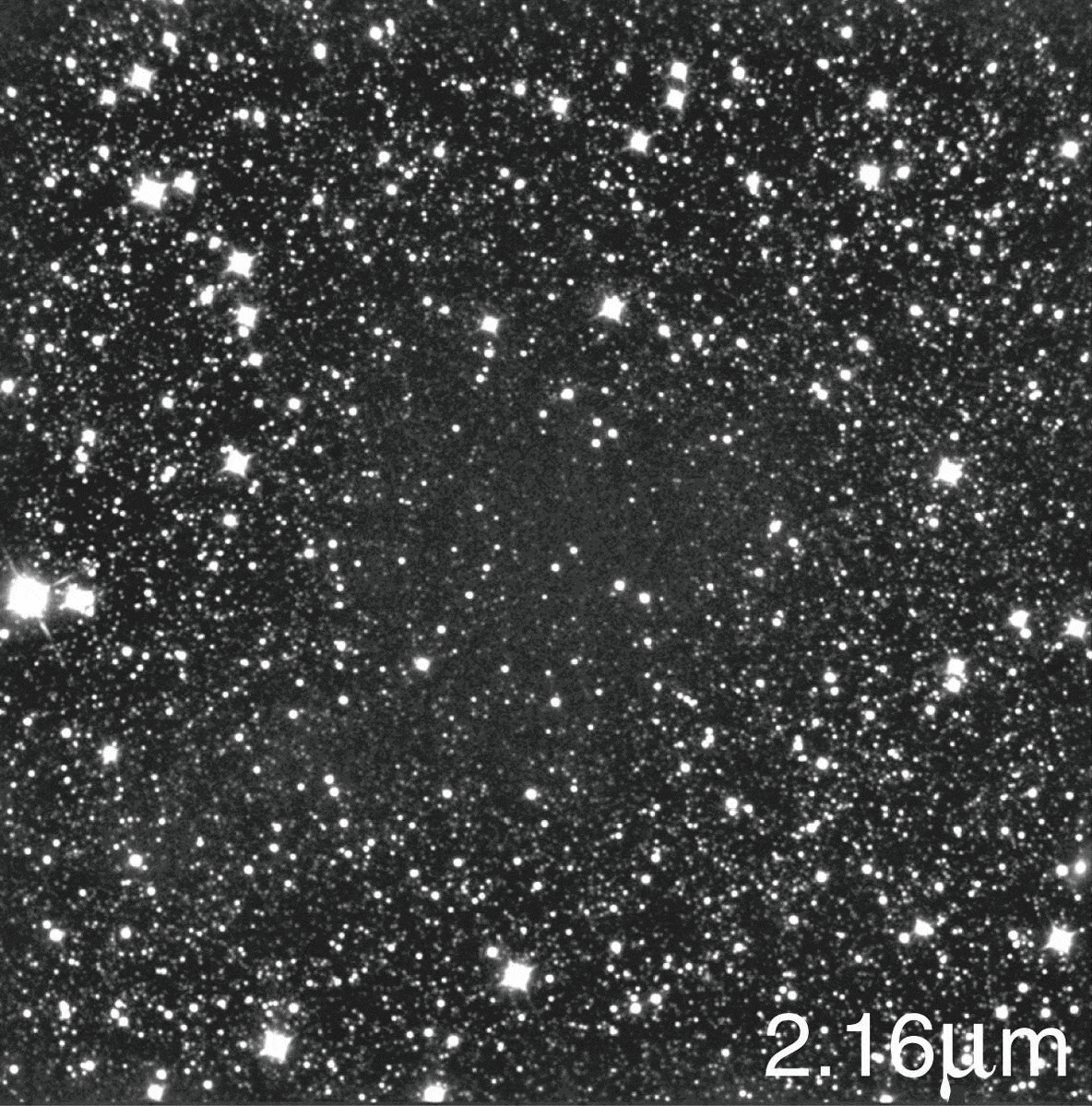
The image you’re seeing isn’t a hole in the Universe, and the cosmic voids that do exist aren’t hole-like at all.
In 1990, we only knew of the planets in our own Solar System. Today, the exoplanet count is more than 5000. Here’s what we’ve learned.
There really might be extraterrestrials out there, attempting to make contact. Here’s how science, not fiction, is attempting to find them.
But the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope compels us to add, “so far.” Beginning with its 1990 launch, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope revolutionized our conception of the Universe. This photo of […]
From the Big Bang to dark energy, knowledge of the cosmos has sped up in the past century — but big questions linger.
In our Universe, dark matter outmasses normal matter by a 5-to-1 ratio, shaping the Universe as we know it. What if it simply weren’t there?
If it weren’t for the intricate rules of quantum physics, we wouldn’t have formed neutral atoms “only” ~380,000 years after the Big Bang.
We understand many things about our Universe, and our home within it, extremely well. The number of stars in the Milky Way isn’t among them.
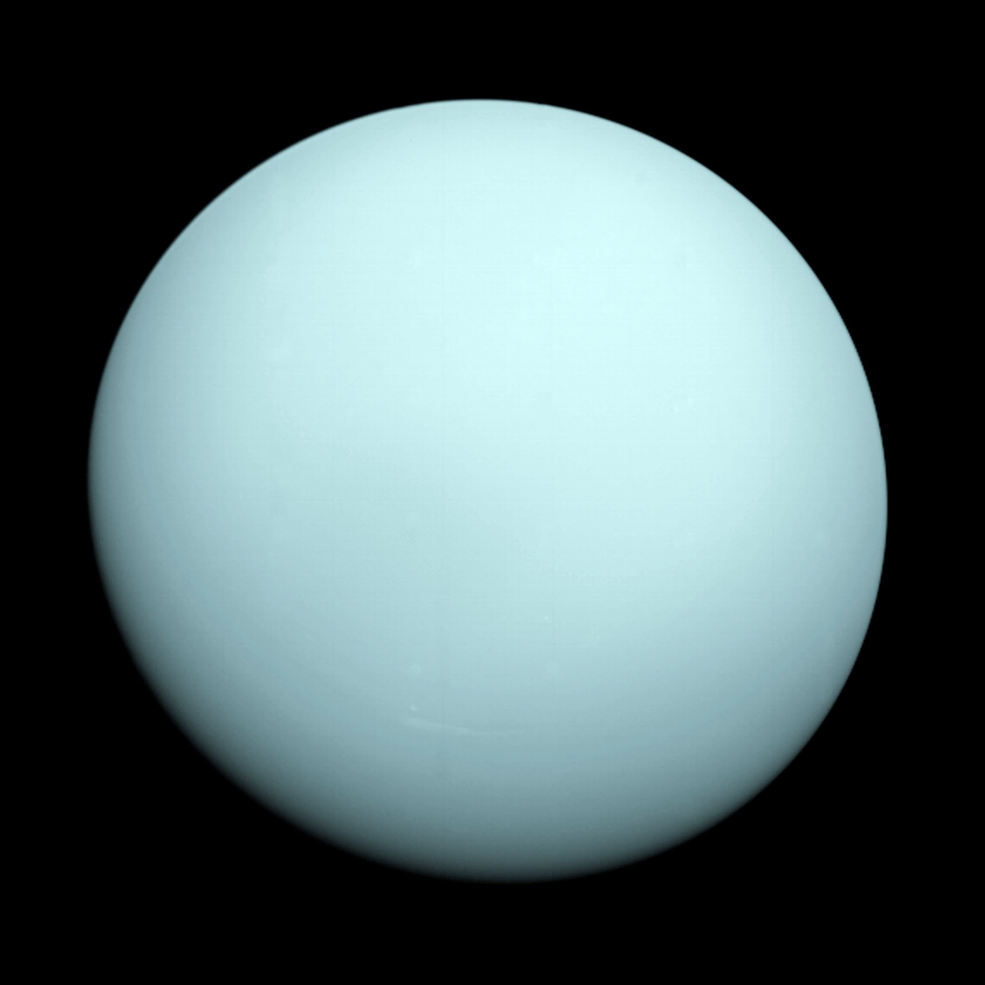
We’ve only seen Uranus up close once: from Voyager 2, back in 1986. The next time we do it, its features will look entirely different.
Hubble, our greatest space-based observatory today, is just the beginning. The Hubble Space Telescope has been astronomy’s most revolutionary observatory in history. The stars and galaxies we see today didn’t […]
In all the Universe, only a few particles are eternally stable. The photon, the quantum of light, has an infinite lifetime. Or does it?
Dark energy is one of the biggest mysteries in all the Universe. Is there any way to avoid “having to live with it?”
Finding out we’re not alone in the Universe would fundamentally change everything. Here’s how we could do it.
Our understanding always will remain incomplete.
Earth, the only rocky planet with a large, massive satellite, is greatly affected by the Moon. Destroying it would cause 7 major changes.
Science has come a long way since Mary Shelley penned “Frankenstein.” But we still grapple with the same questions.
The Universe is expanding, and the Hubble constant tells us how fast. But how can it be a constant if the expansion is accelerating?
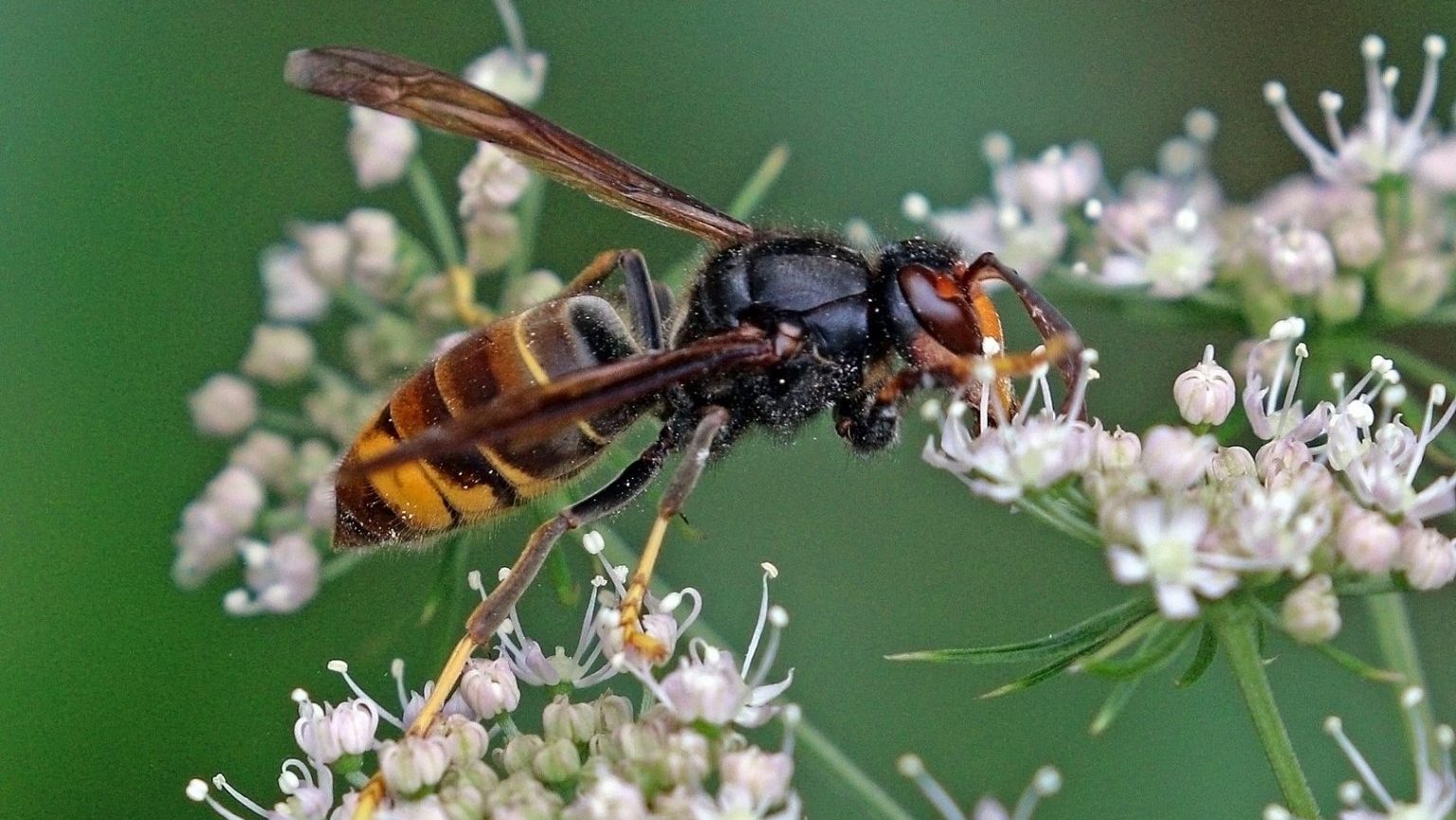
Researchers are working nest by nest to limit the threat while developing better eradication methods.
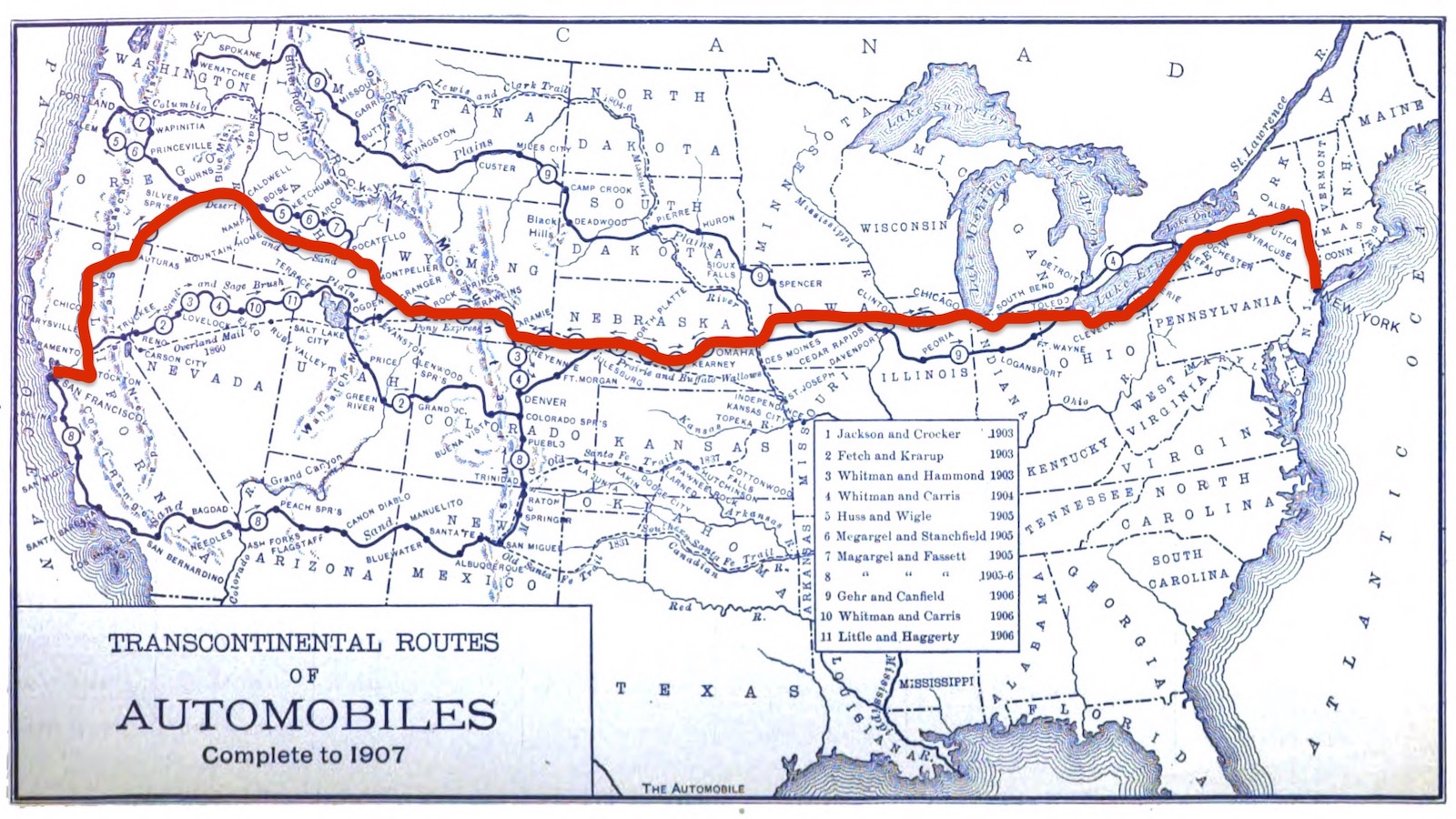
In 1903, a Vermont doctor bet $50 that he could cross America by car. It took him 63 days, $8,000, and 600 gallons of gas.