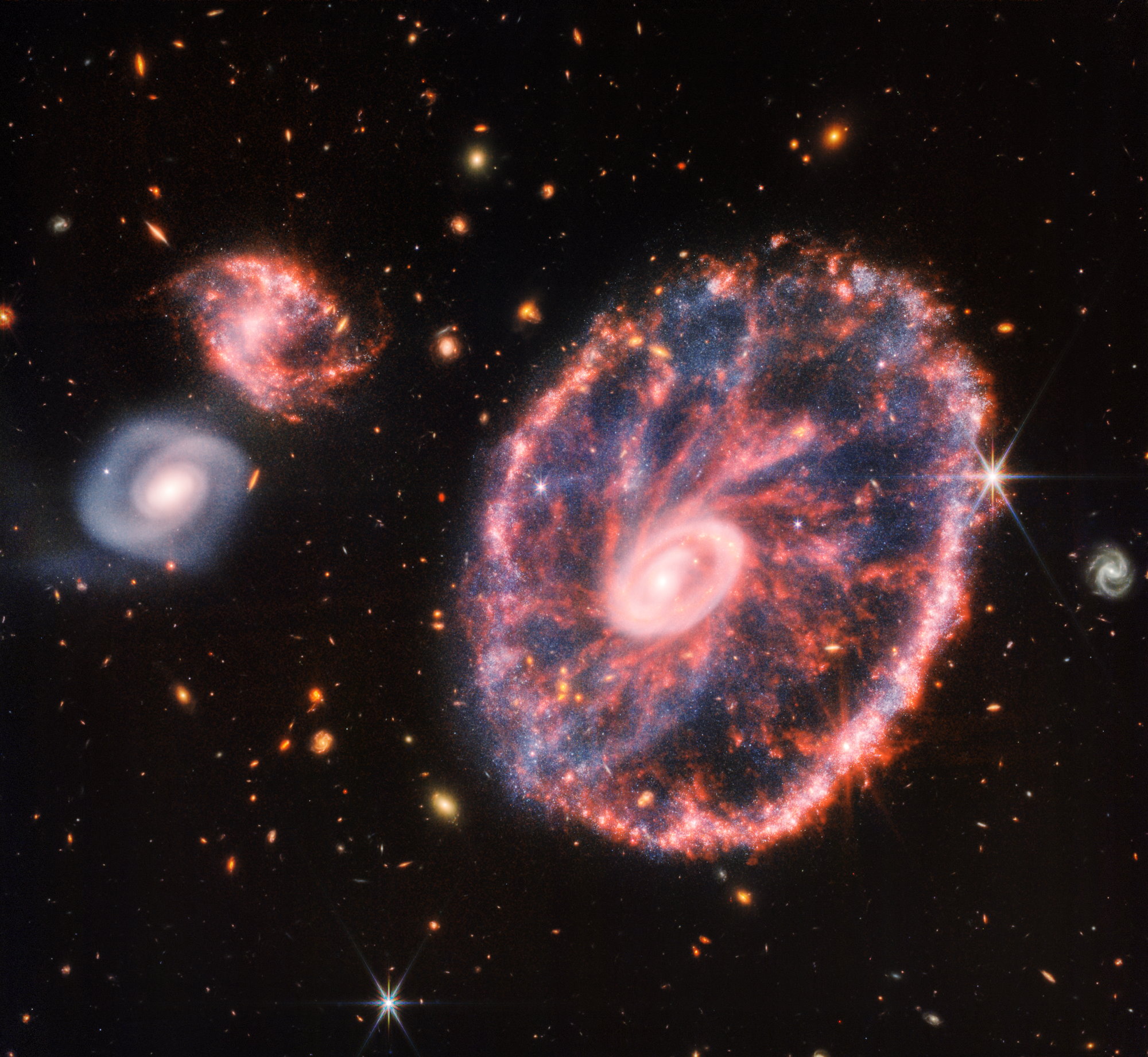
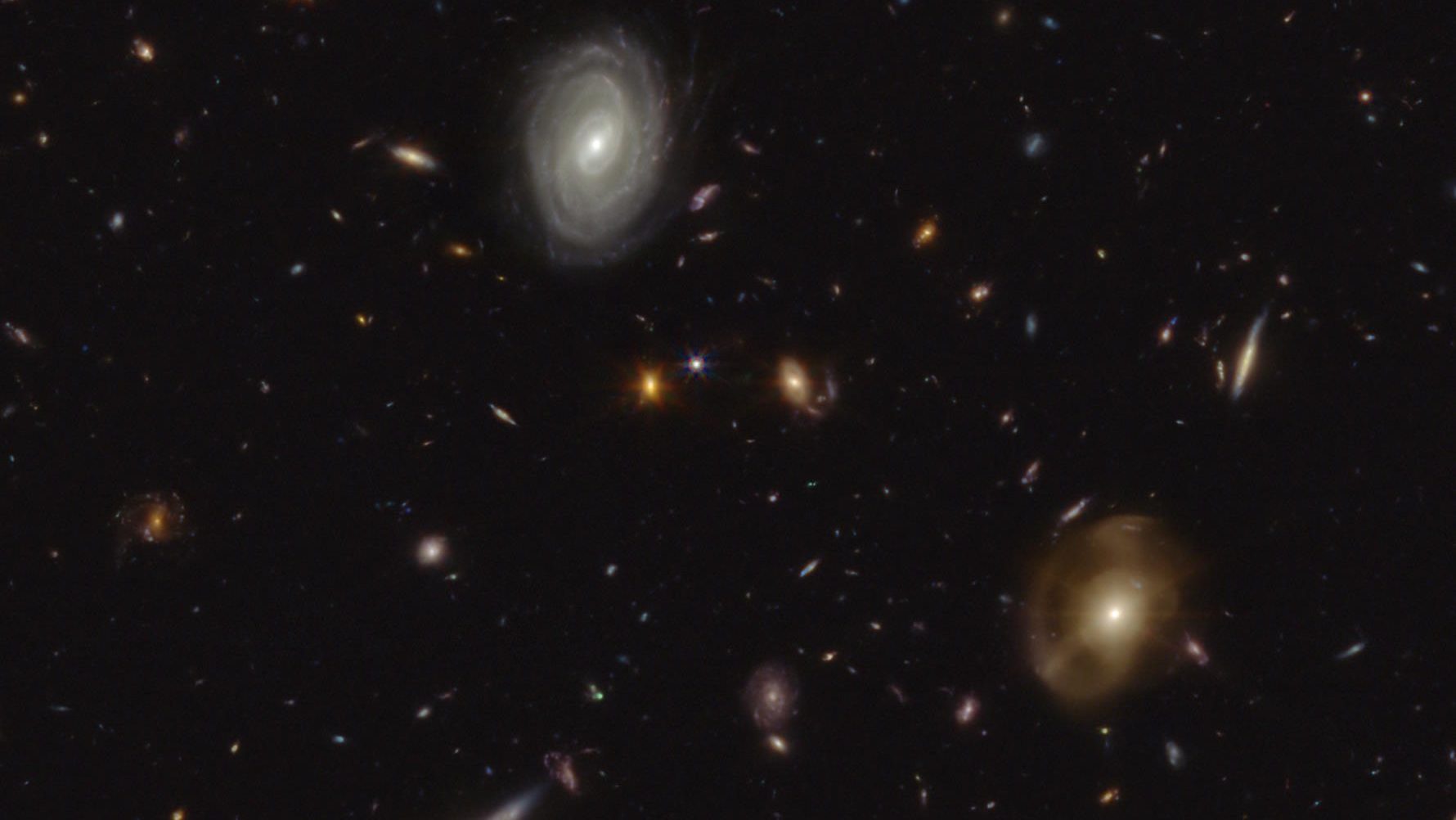
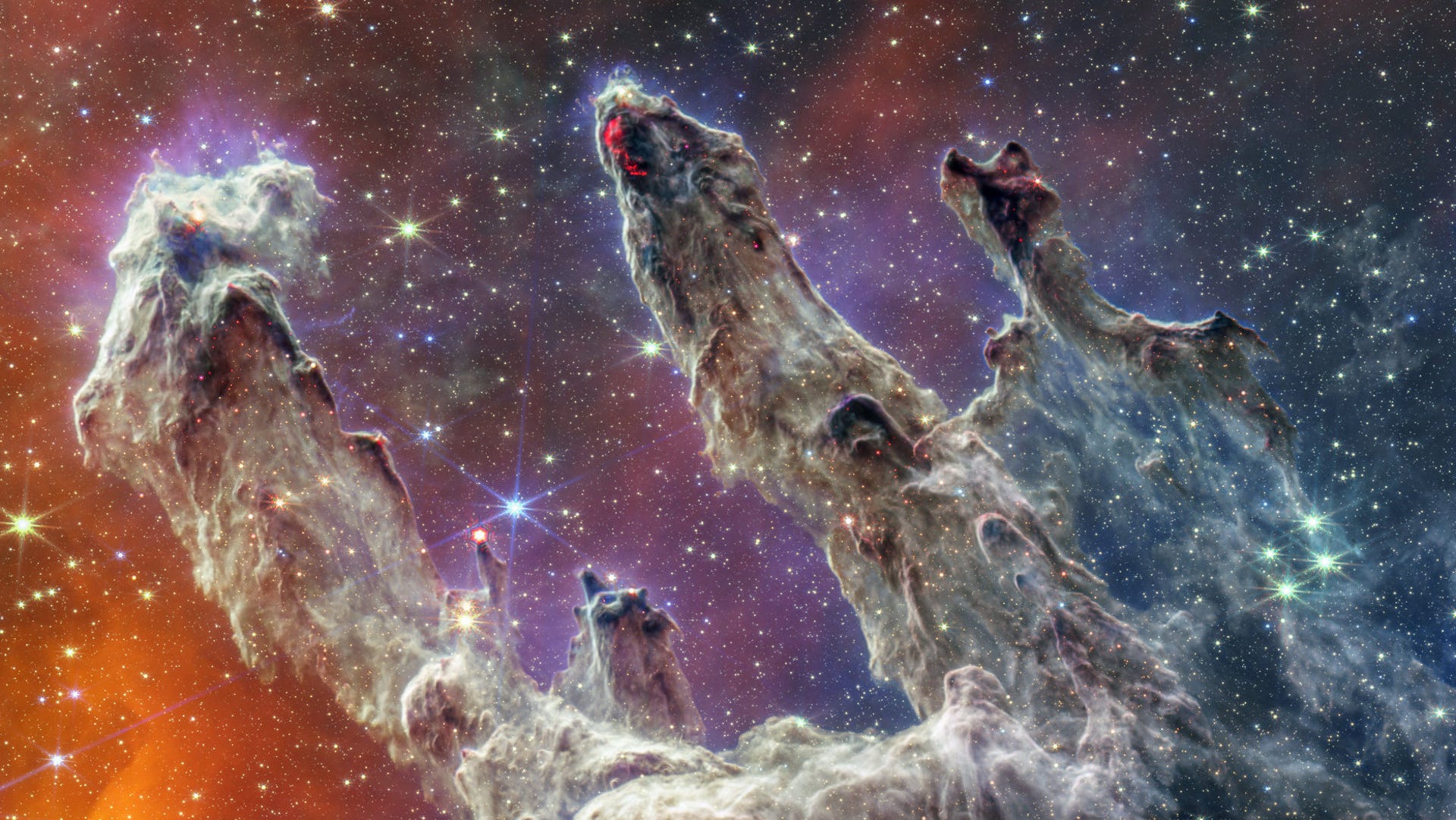
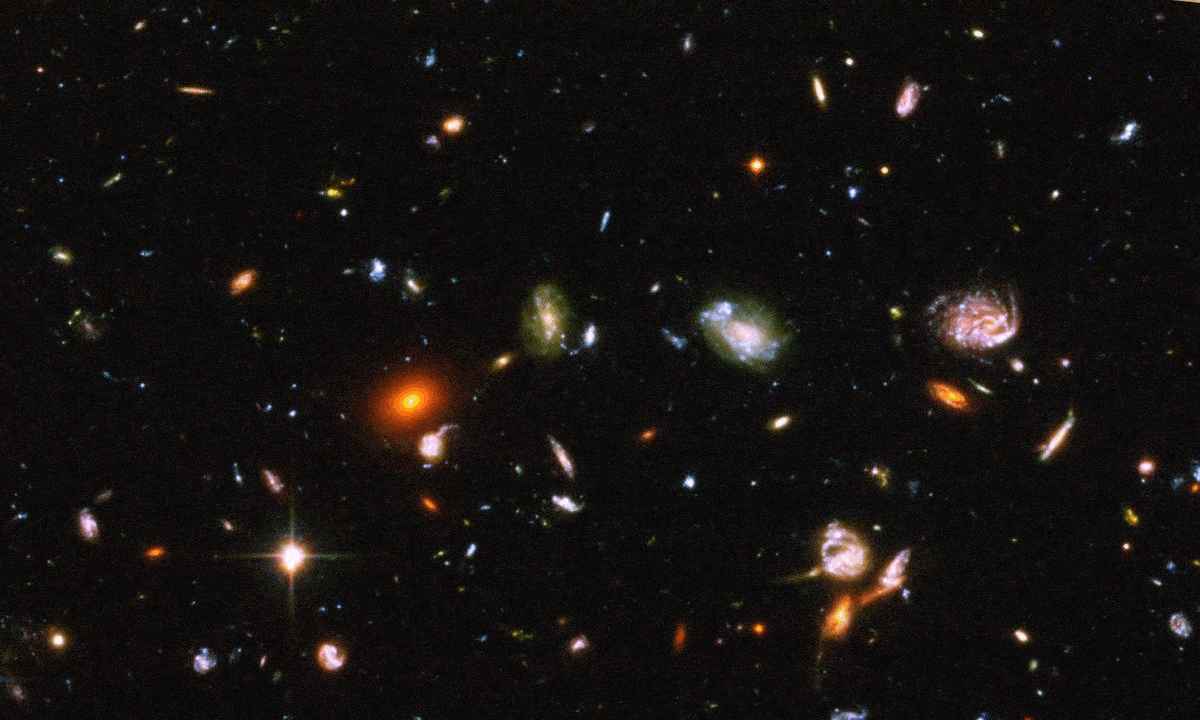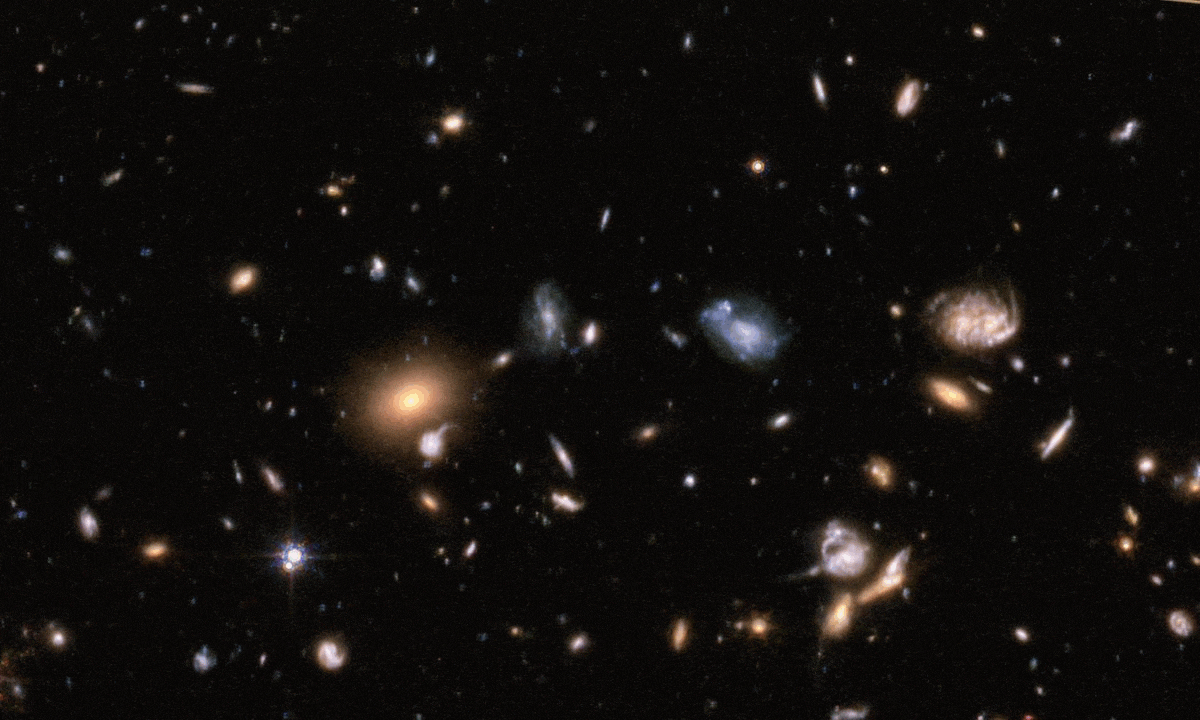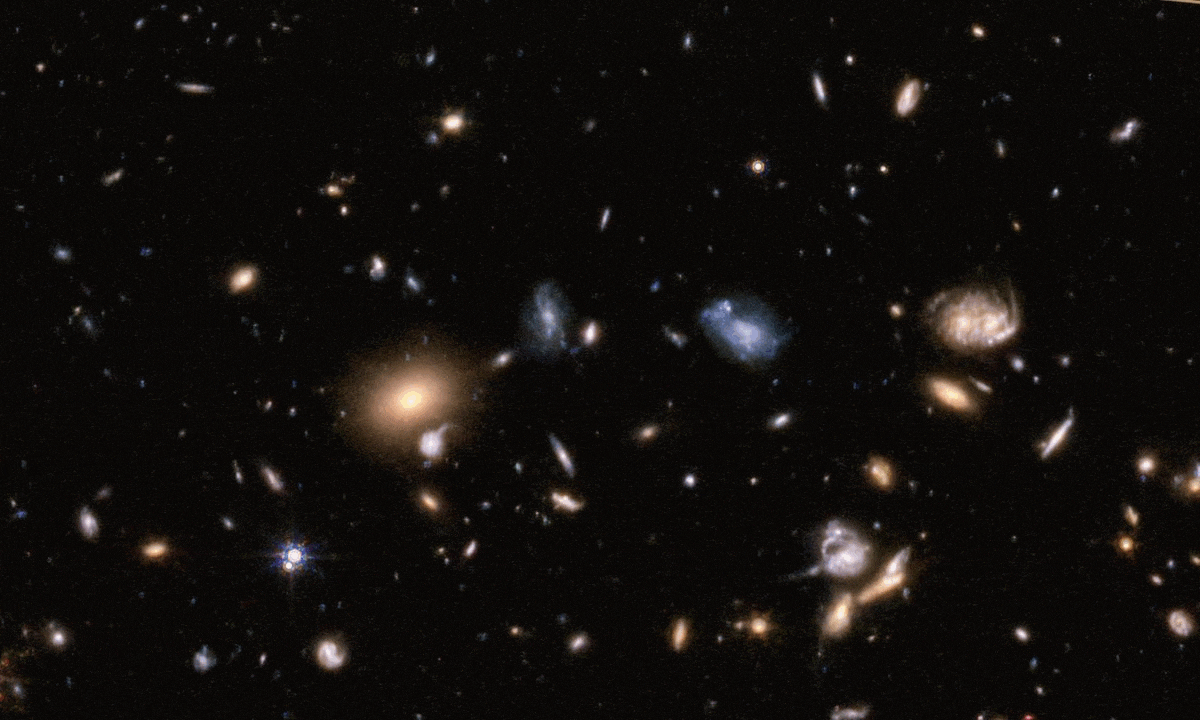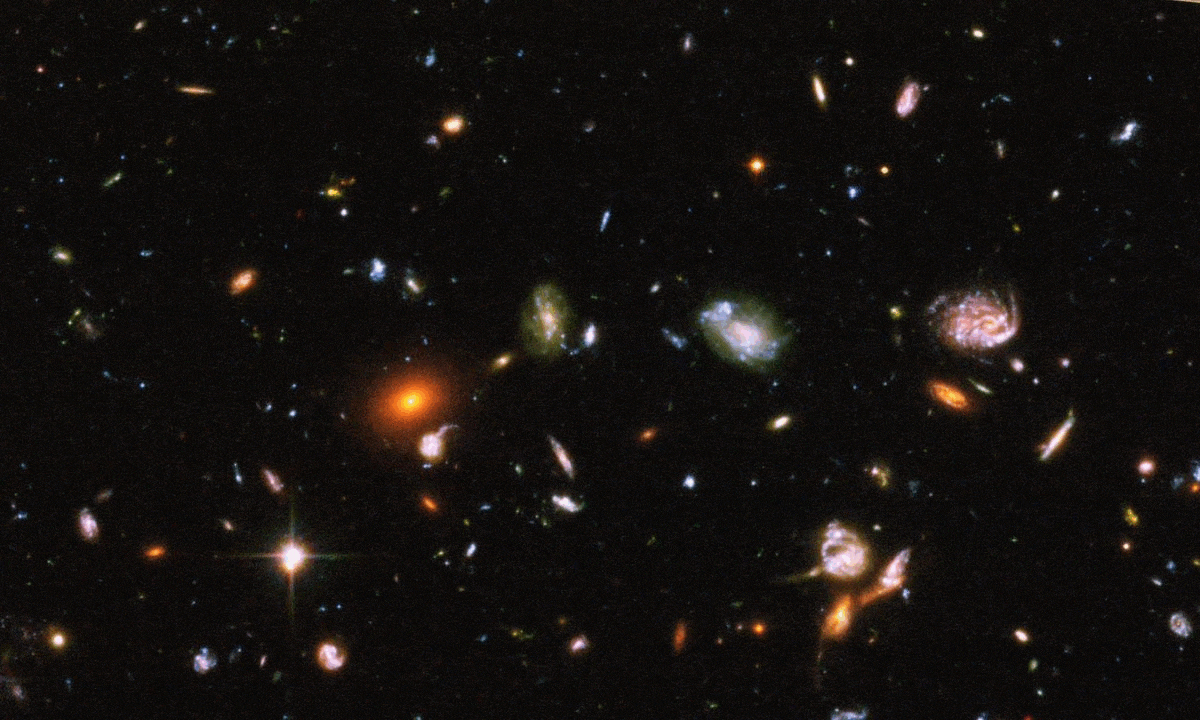Humanity’s newest, most powerful space telescope is performing even better than predicted. The reason why is unprecedented.
Search Results
You searched for: Telescope
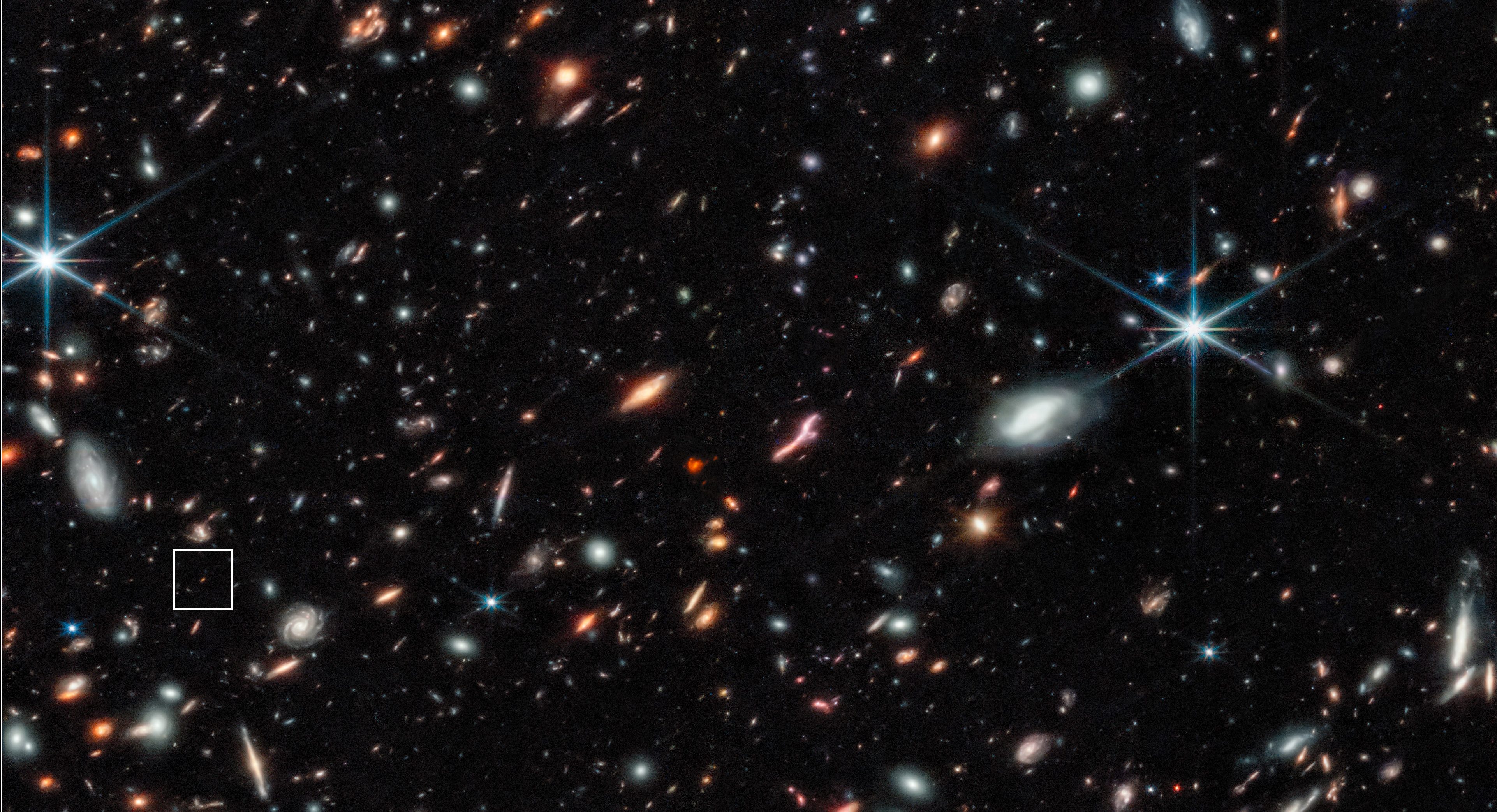
In 2022, Hubble owned the record for most distant galaxy. Today, that galaxy is down to the 9th most distant object. Thanks, JWST.
The first observational evidence showing the Universe is expanding is 100 years old now: in 2023. Here’s the story of its 100th anniversary.
NASA has finally chosen which flagship mission, like Hubble and JWST, will launch in ~2040. Detecting alien life is now a reachable goal.
Viewing Uranus’s largest moons with Hubble, astronomers hoped to find darkening on the trailing side. They found the exact opposite instead.
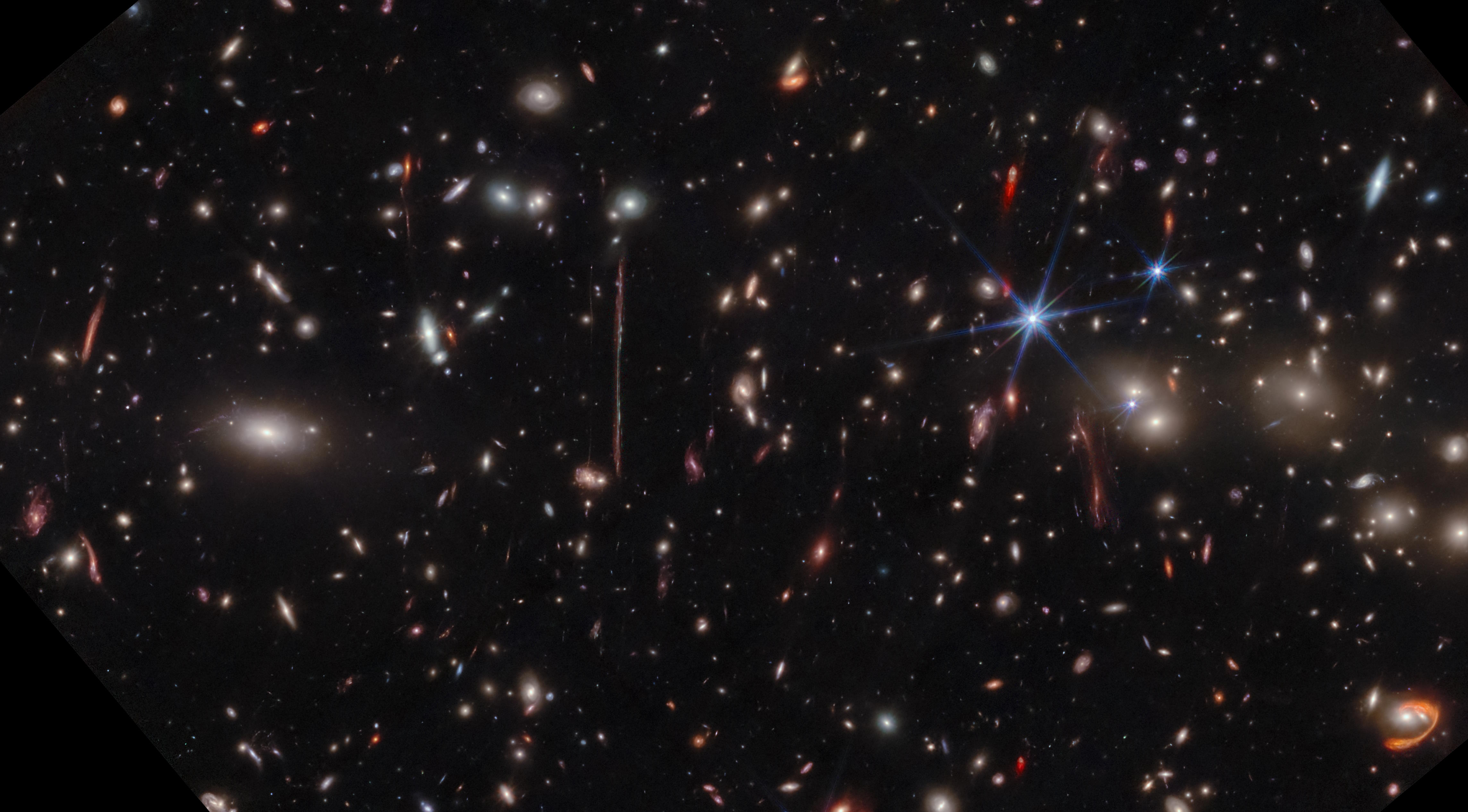
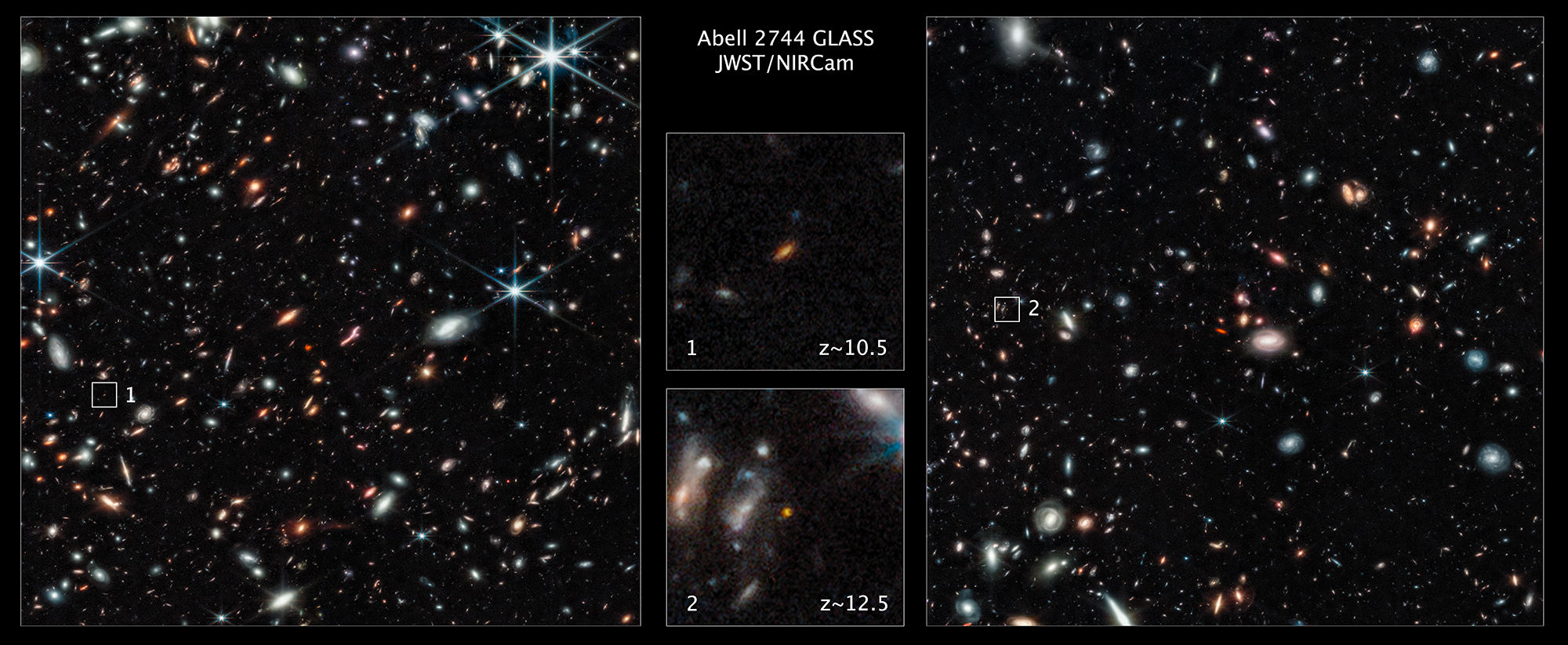
The COSMOS-Web has just finalized their release of their full field: larger and deeper than any other JWST program. Here’s what’s inside.
With stars, gas, and dark matter, galaxies come in a great array of sizes. This new one, Ursa Major III/UNIONS 1, is the smallest by far.
As democracy recedes and fascism rises in the USA and around the world in 2025, history provides a lesson in how science can fight fascism.
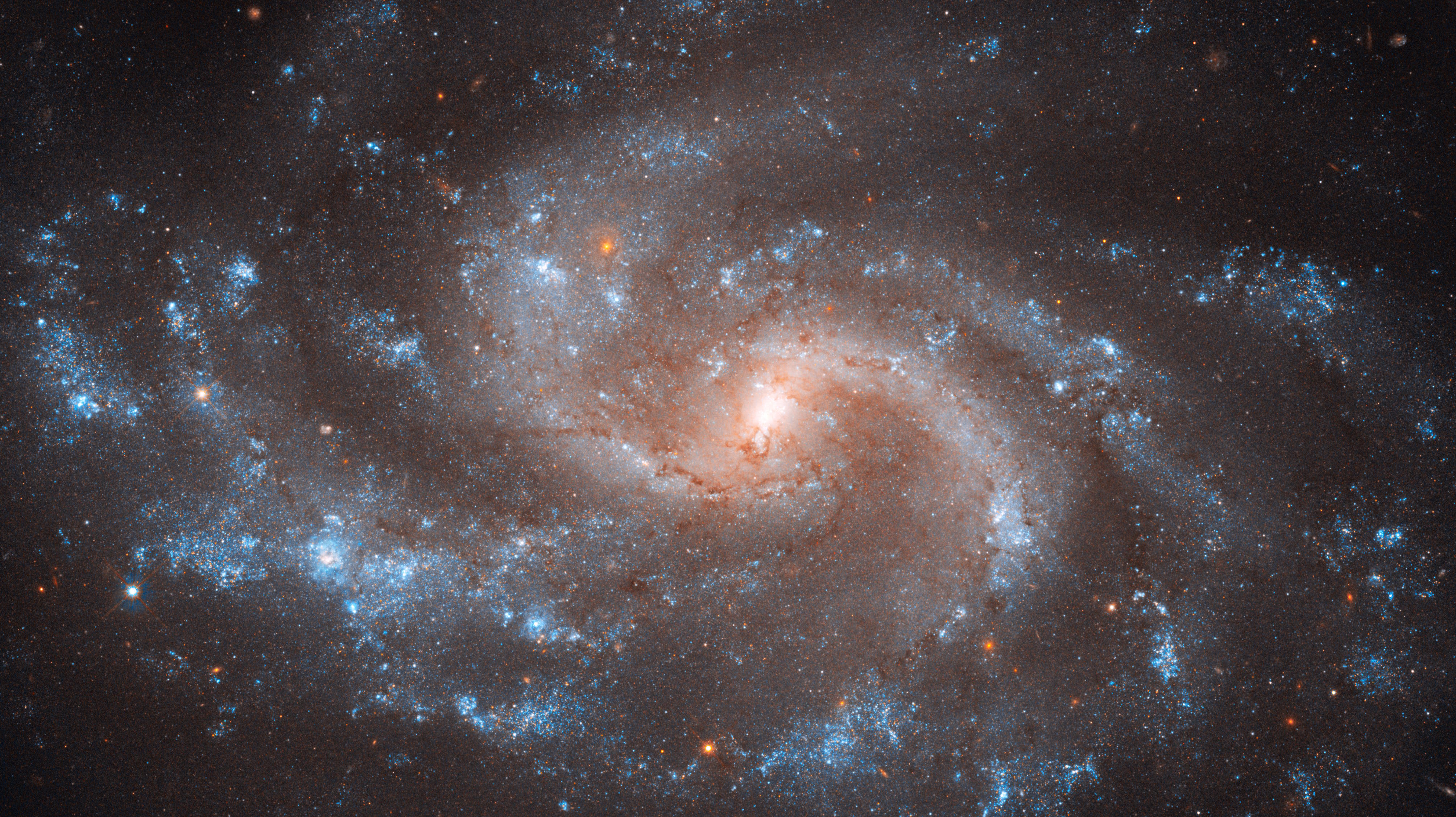
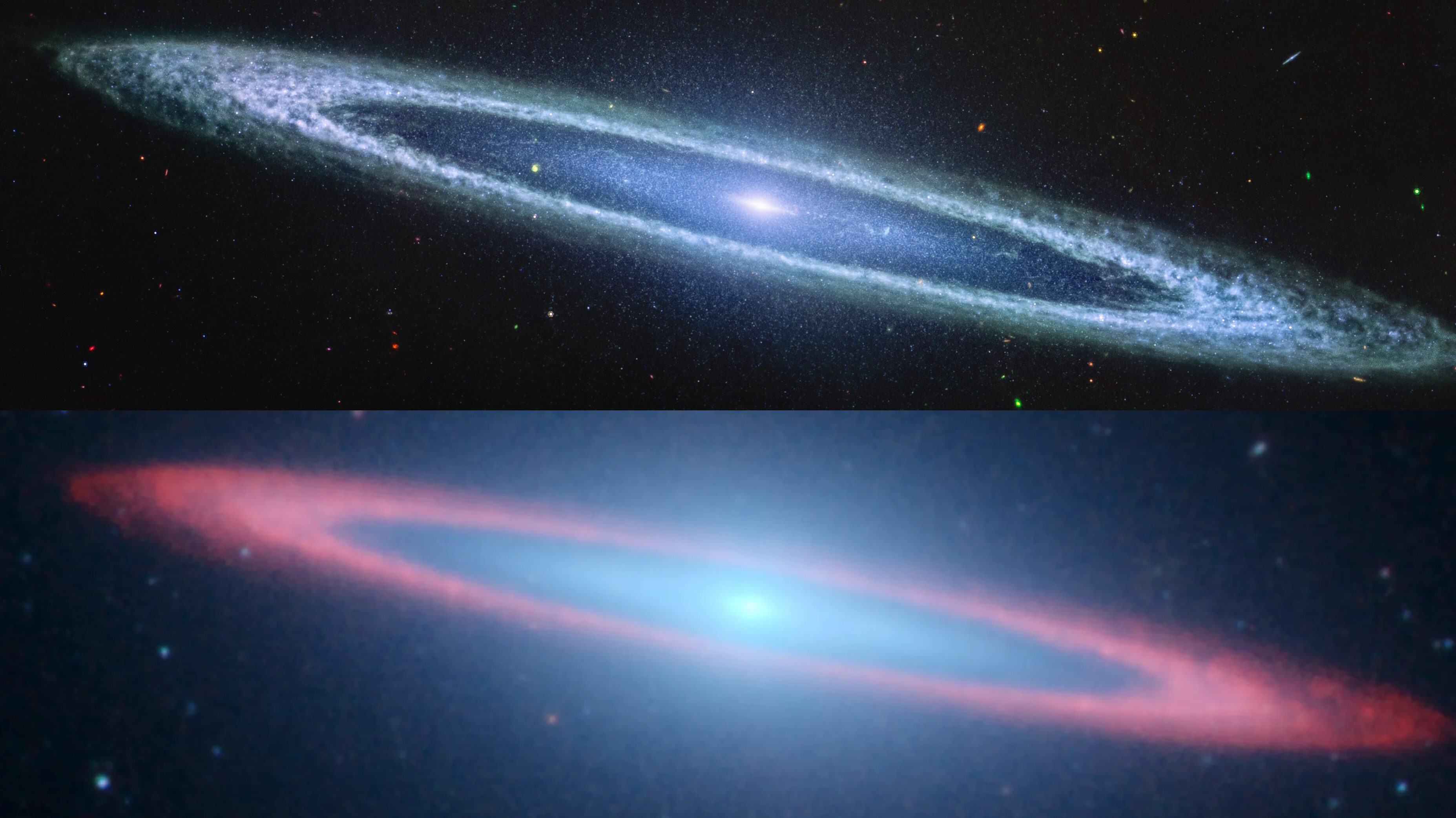
When we see spiral galaxies, some are face-on, others are edge-on, but most are tipped at an angle. But which side is closest to us?
A deep dive into the chaotic journey of star formation.
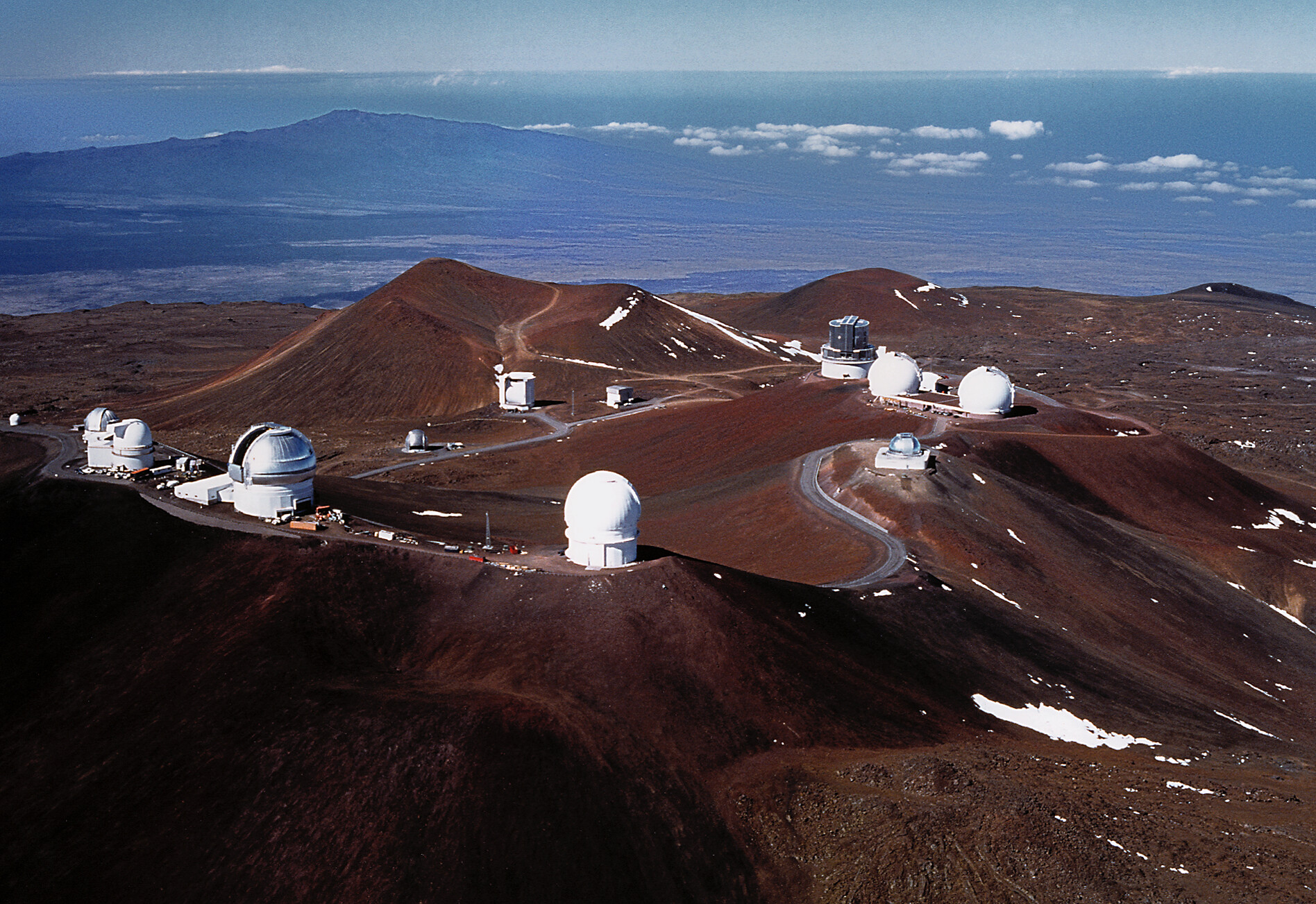
A history of injustice and the greatest natural location for ground-based telescopes have long been at odds. Here’s how the healing begins.
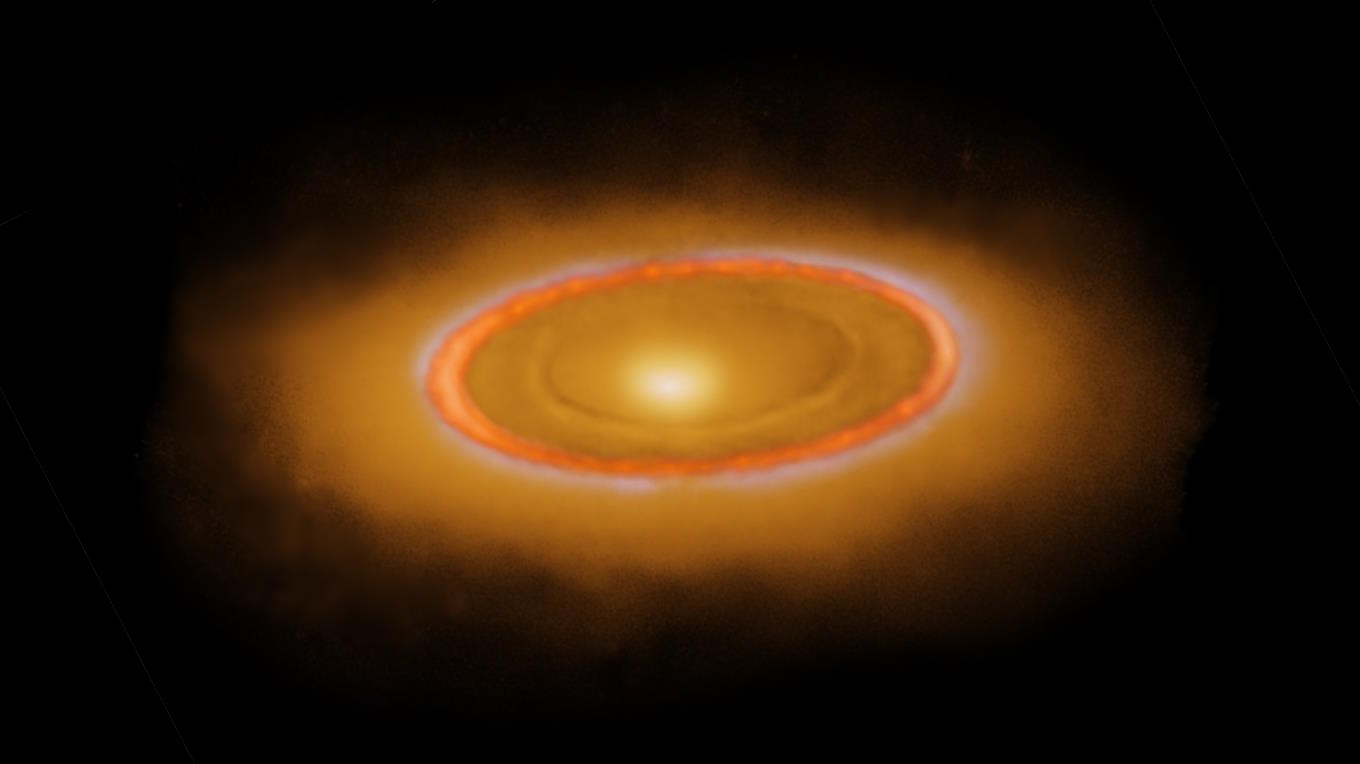
The nearby, bright star Fomalhaut had the first optically imaged planetary candidate. Using JWST’s eyes, astronomers found so much more.
On Earth, our particle accelerators can reach tera-electron-volt (TeV) energies. Particles from space are thousands of times as energetic.
In the expanding Universe, different ways of measuring its rate give incompatible answers. Nobel Laureate Adam Riess explains what it means.
How fast is the Universe expanding? Two major methods disagree. New JWST data, just released, strengthens this Hubble tension even further.
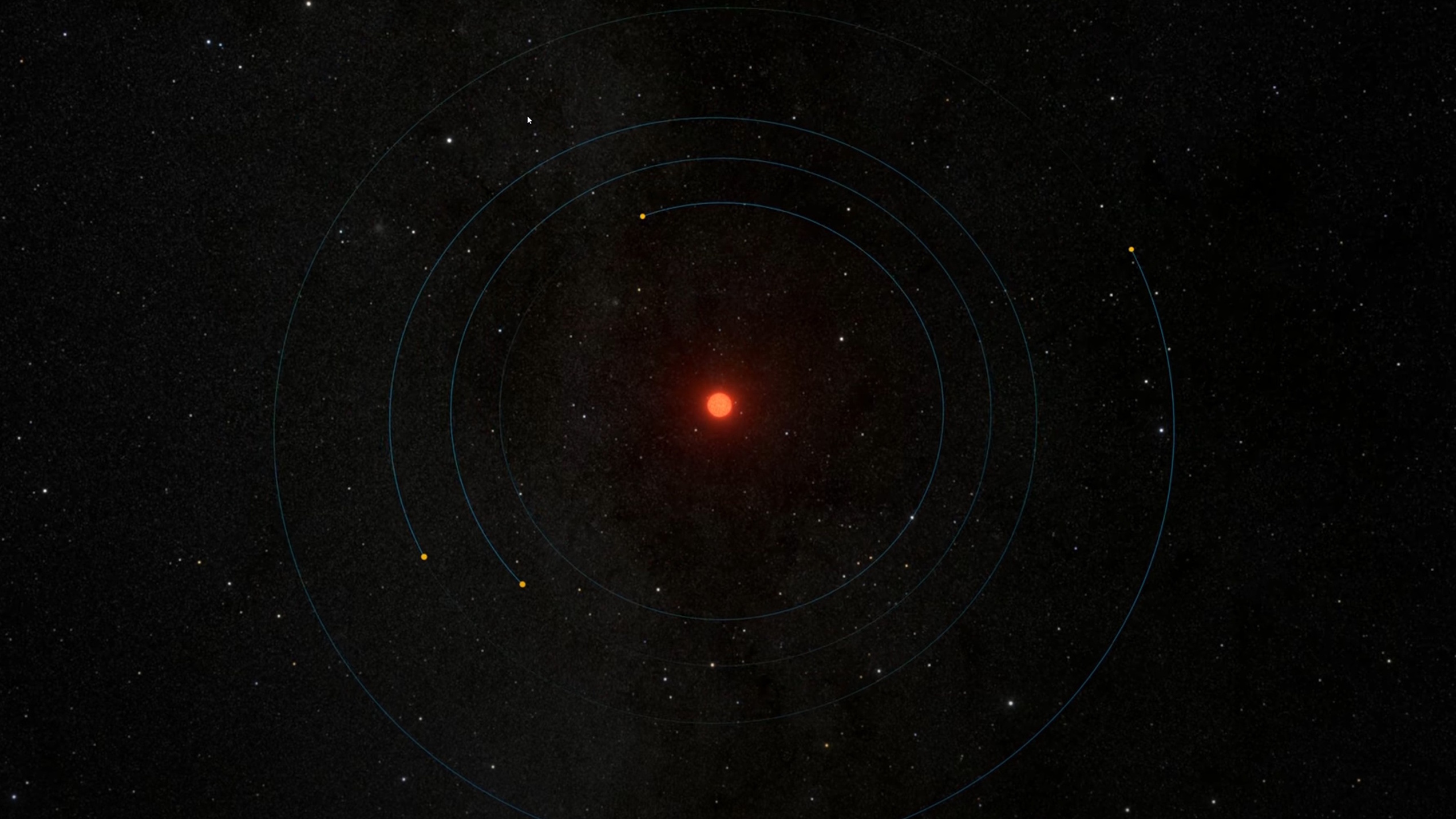
Barnard’s star, the closest singlet star system to ours, has long been a target for planet-hunters. We’ve finally confirmed it: they exist!
One of the most promising dark matter candidates is light particles, like axions. With JWST, we can rule out many of those options already.
From when its light was emitted, the El Gordo galaxy cluster might be the most massive object in all of existence. Here’s how JWST sees it.
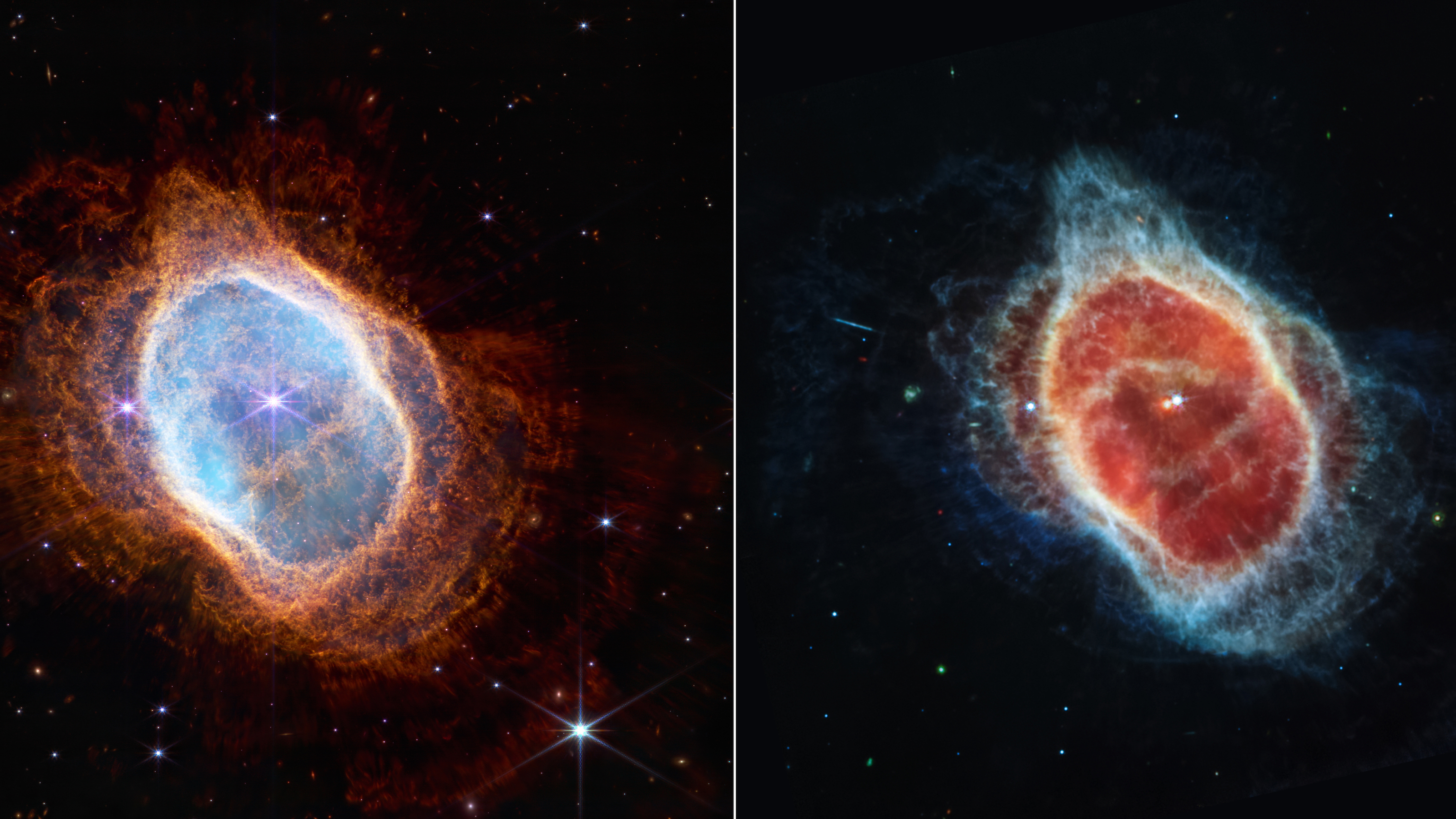
Like humans, stars die. The James Webb Space Telescope’s early images already give us a lot of information about how this happens.
Temperatures in the Sun’s core exceed 10 million degrees Celsius. But how on Earth did we actually come to know that?
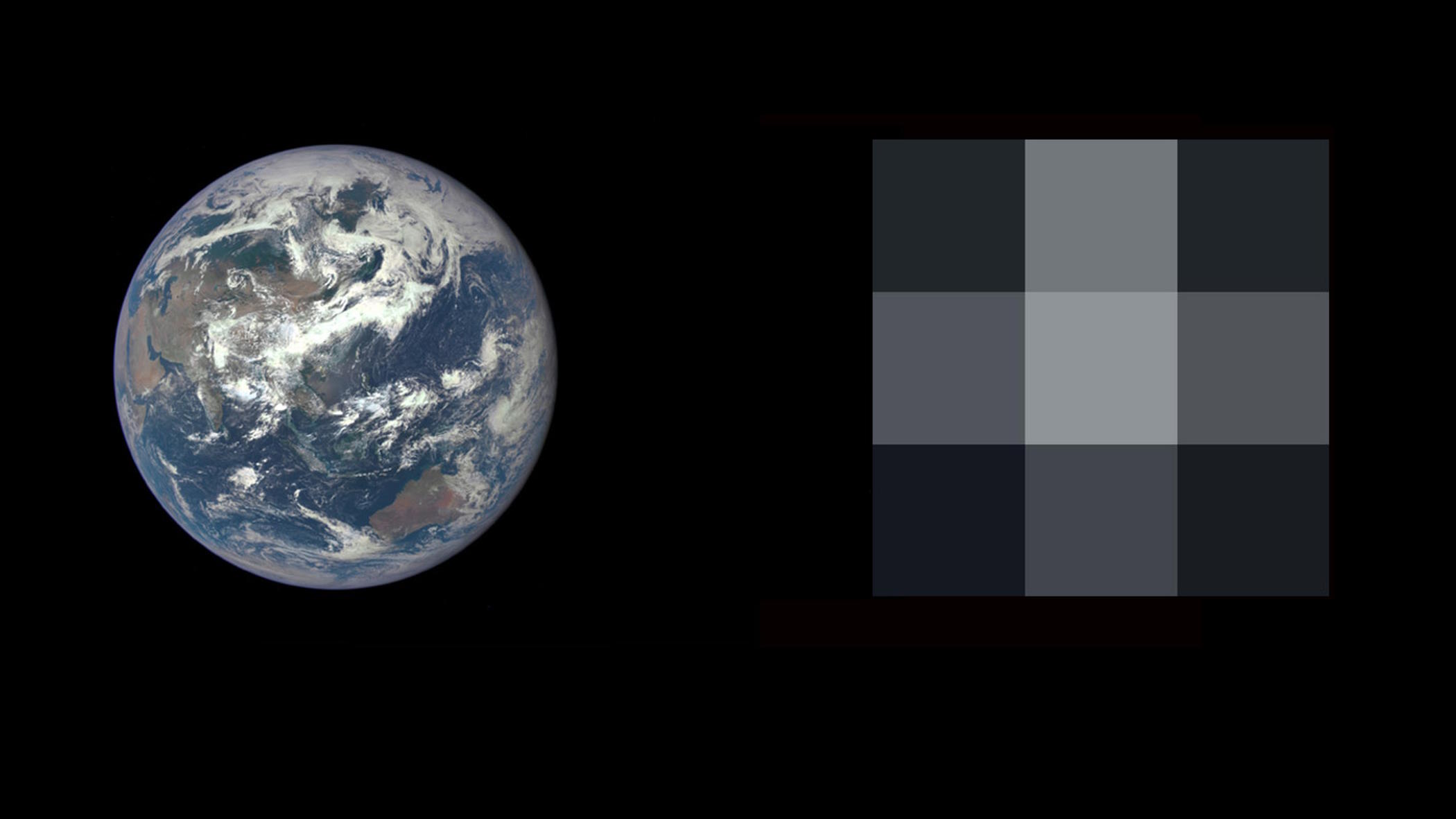
When we see pictures from Hubble or JWST, they show the Universe in a series of brilliant colors. But what do those colors really tell us?
Along with gravitational lensing and ALMA’s incredible long-wavelength spectroscopy, JWST is reshaping our view of the early Universe.
25 years ago, our concordance picture of cosmology, also known as ΛCDM, came into focus. 25 years later, are we about to break that model?
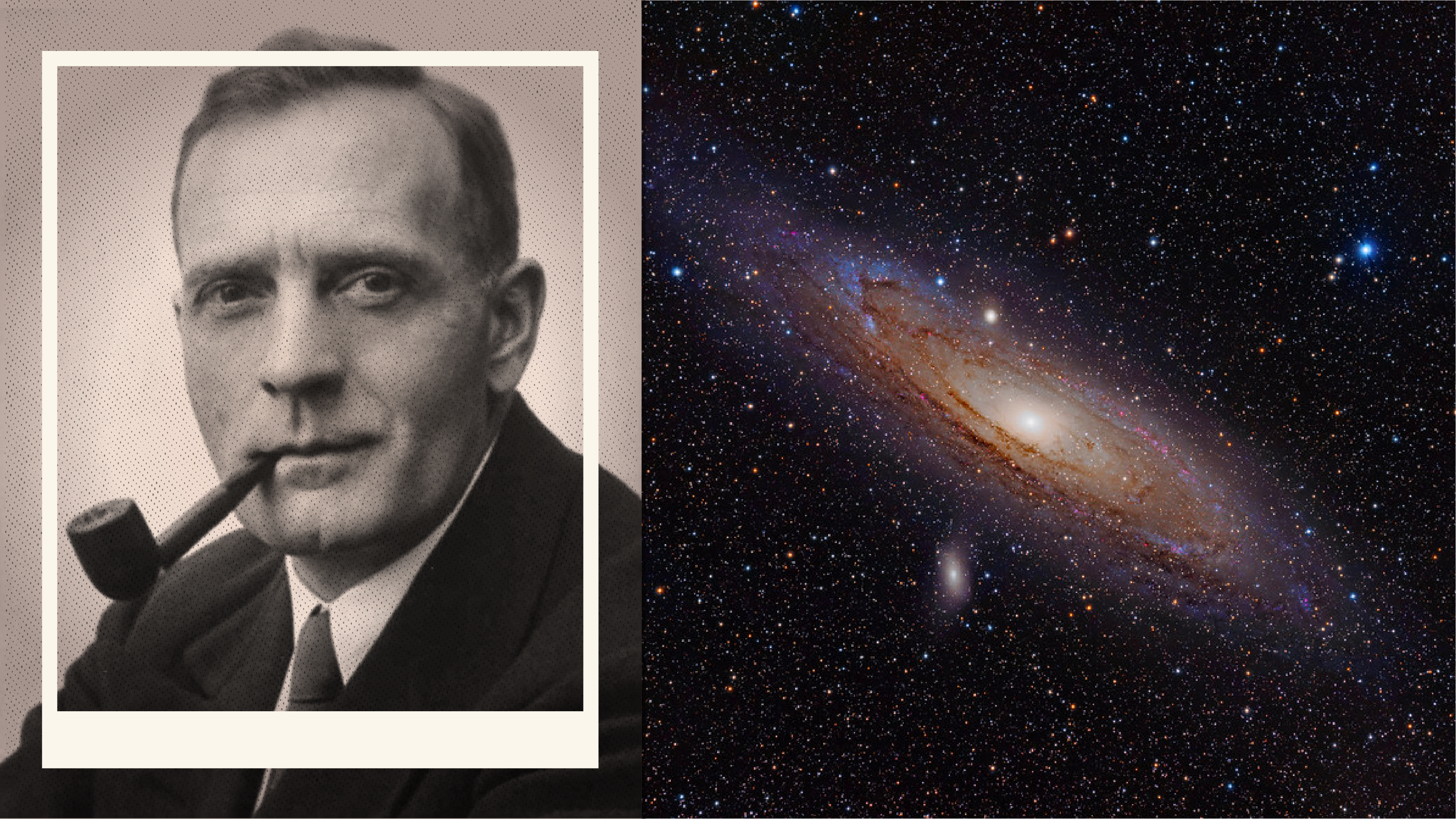
In 1924, Edwin Hubble found proof that the Milky Way isn’t the only galaxy in the Universe.
From inside our Solar System, zodiacal light prevents us from seeing true darkness. From billions of miles away, New Horizons finally can.
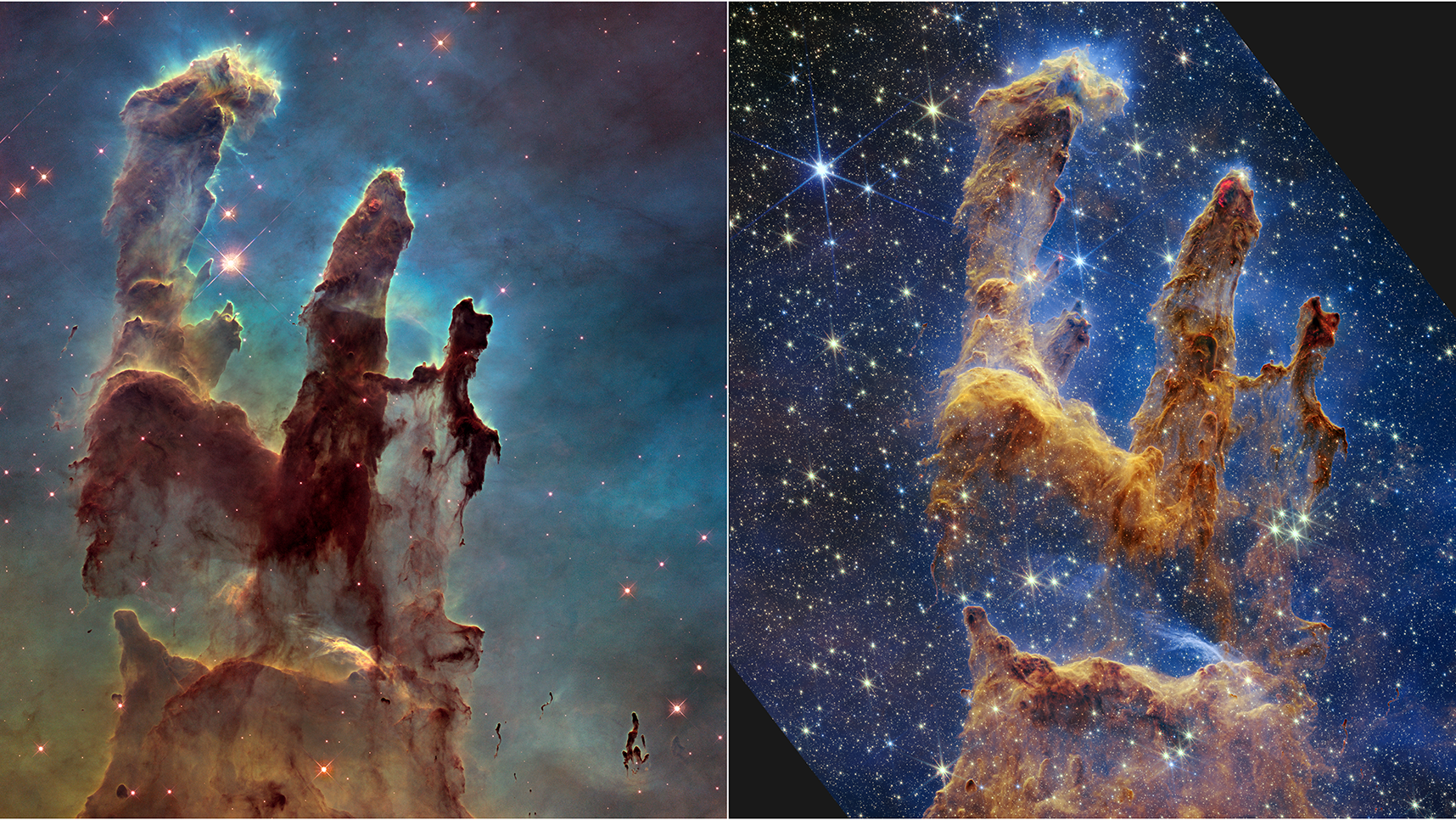
If you can identify a foreground star, the spike patterns are a dead giveaway as to whether it’s a JWST image or any other observatory.
The structure of our Solar System has been known for centuries. When we finally started finding exoplanets, they surprised everyone.
DESI has allowed astronomers to create an unprecedented 3D map of the Universe representing 20% of the entire sky.
There’s no upper limit to how massive galaxies or black holes can be, but the most massive known star is only ~260 solar masses. Here’s why.
A true scientific view of if, where, and when extraterrestrial life exists is within our grasp thanks to biosignatures and technosignatures.